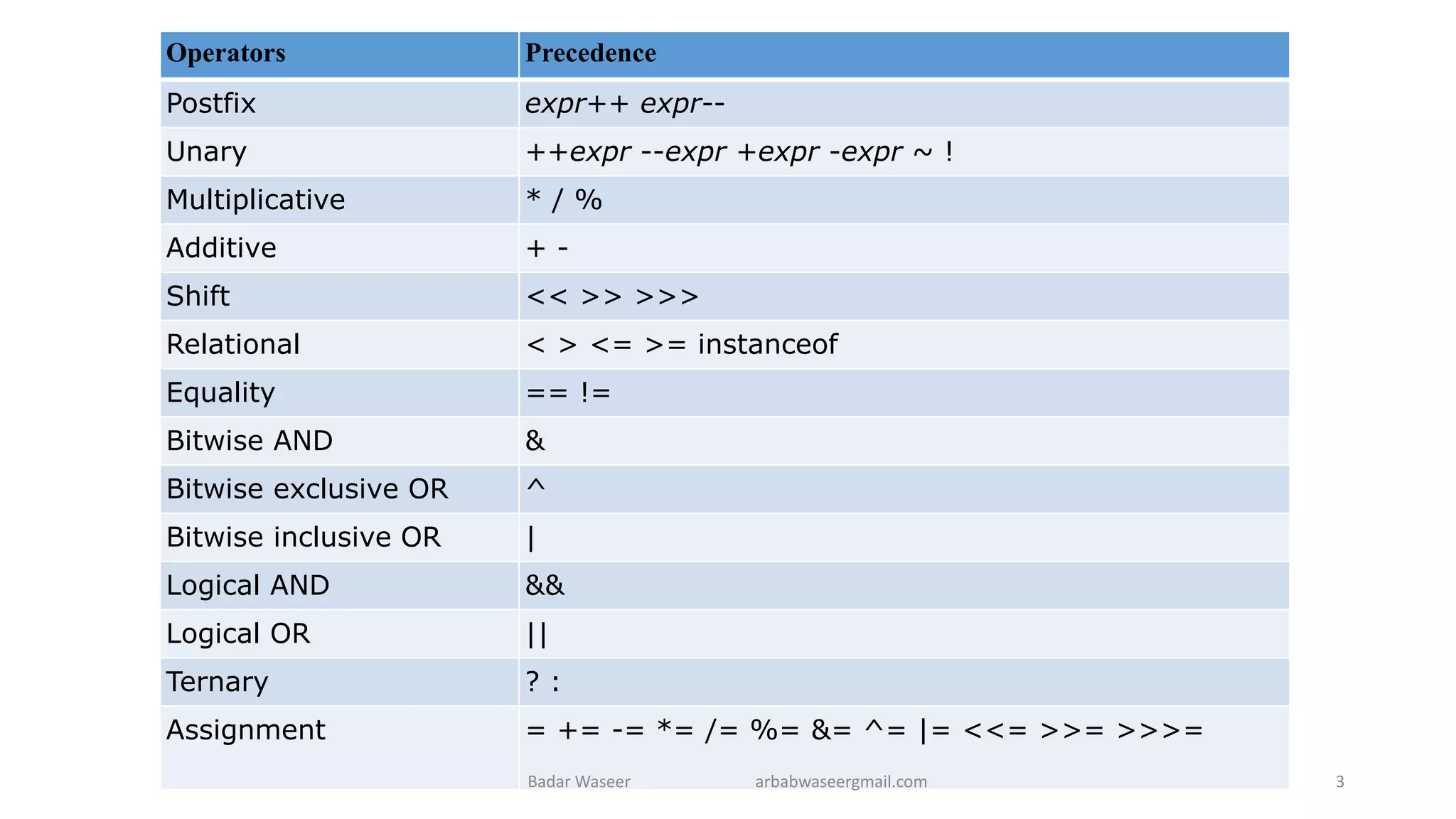
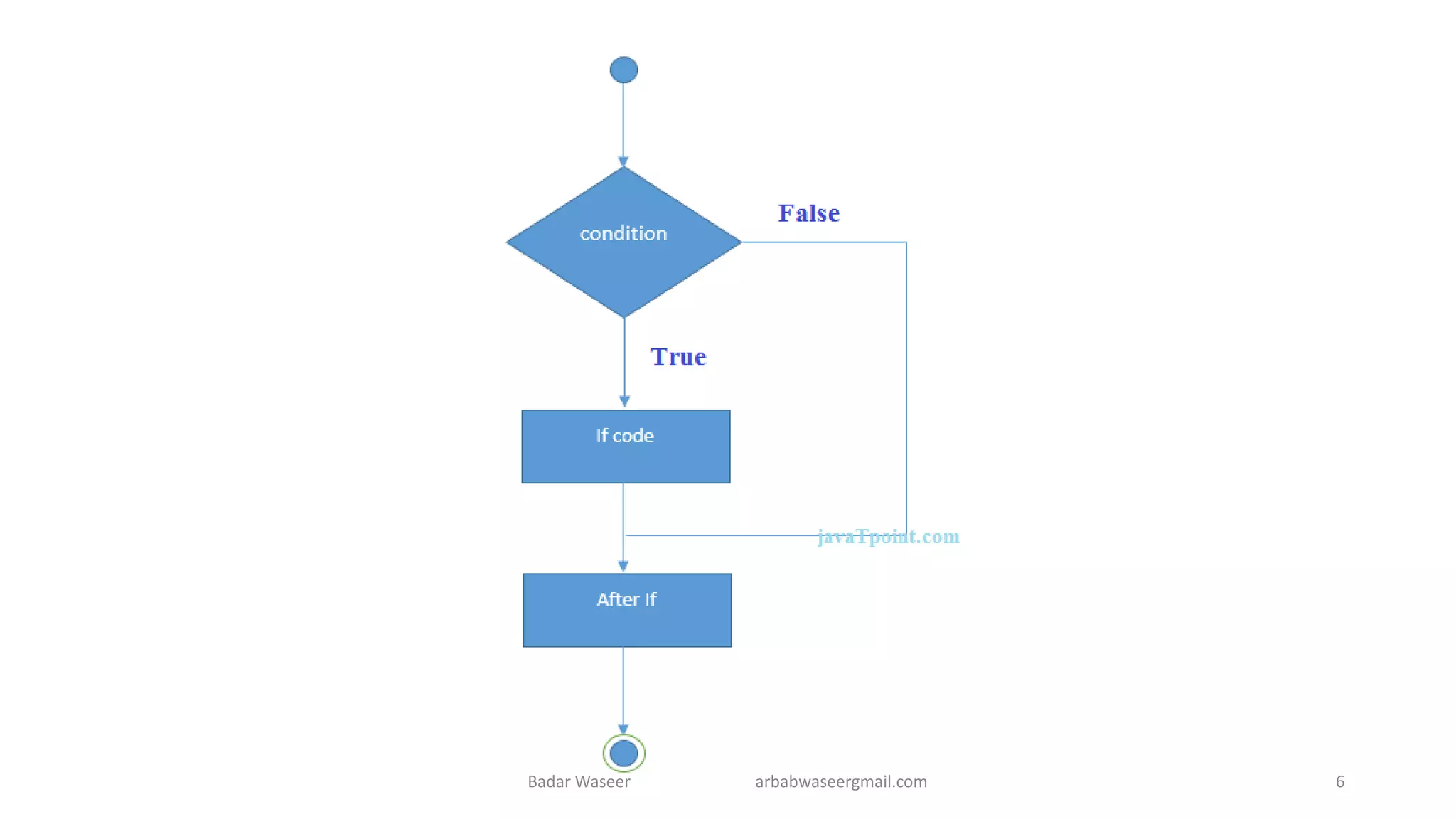
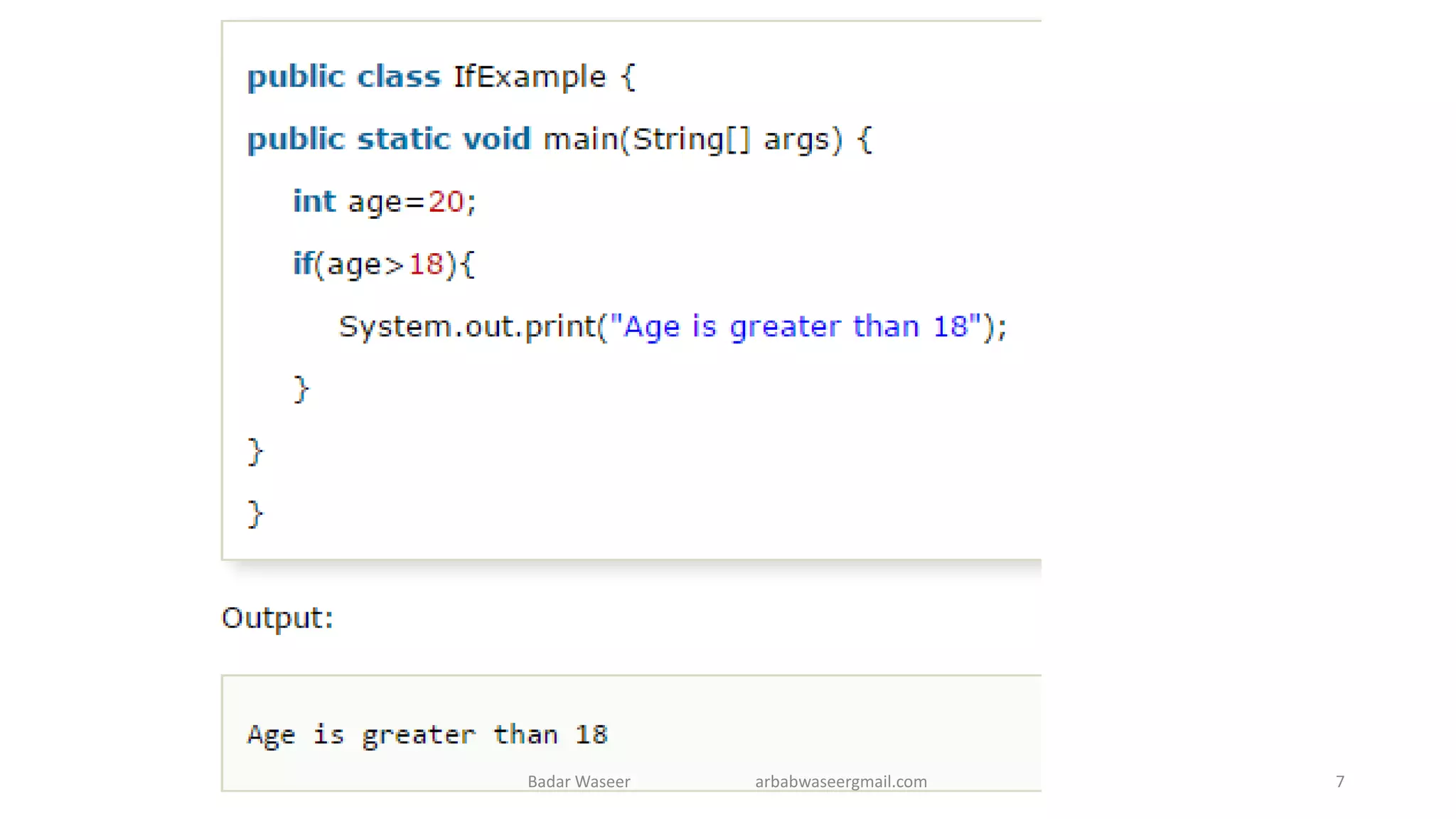
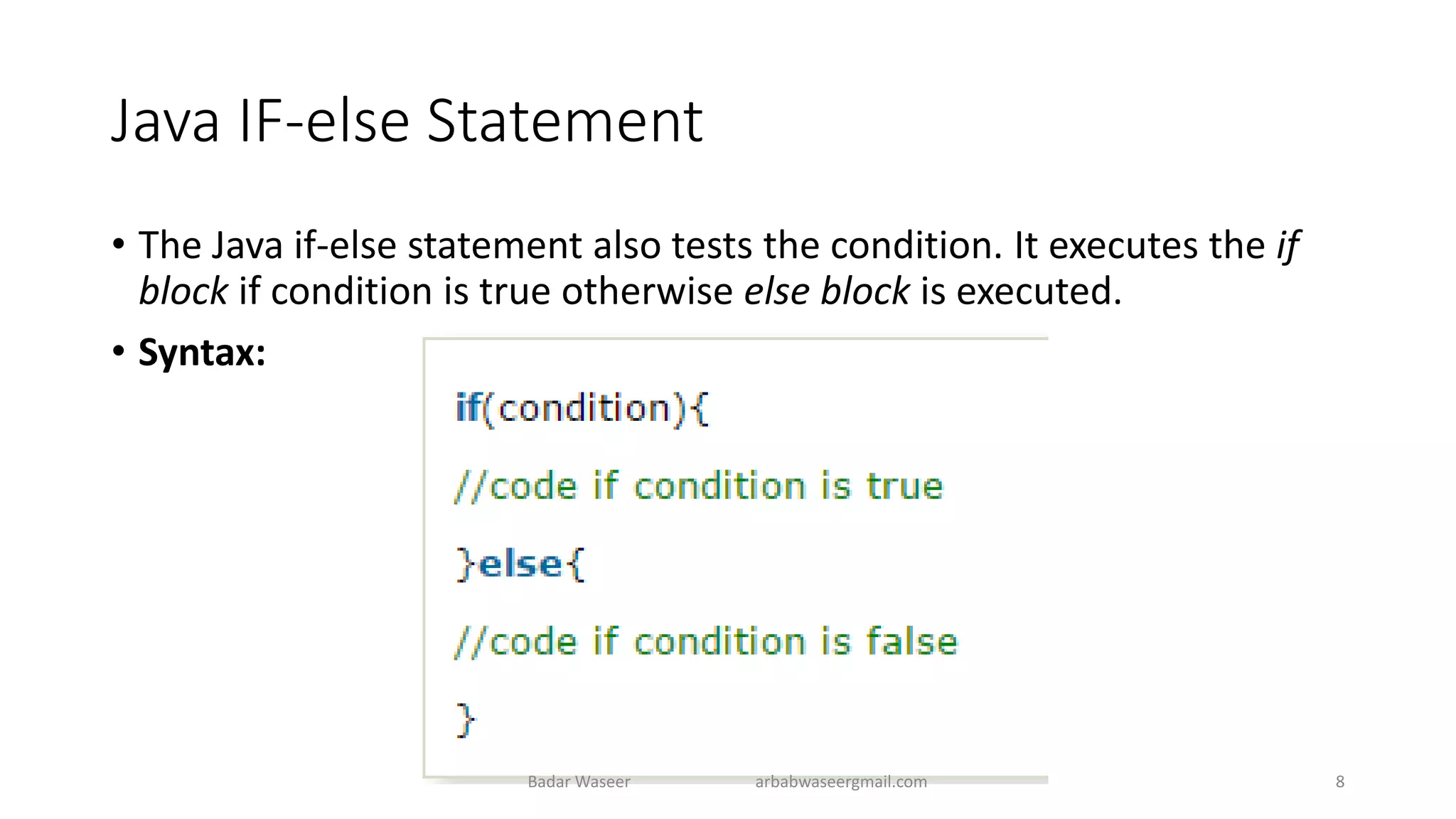
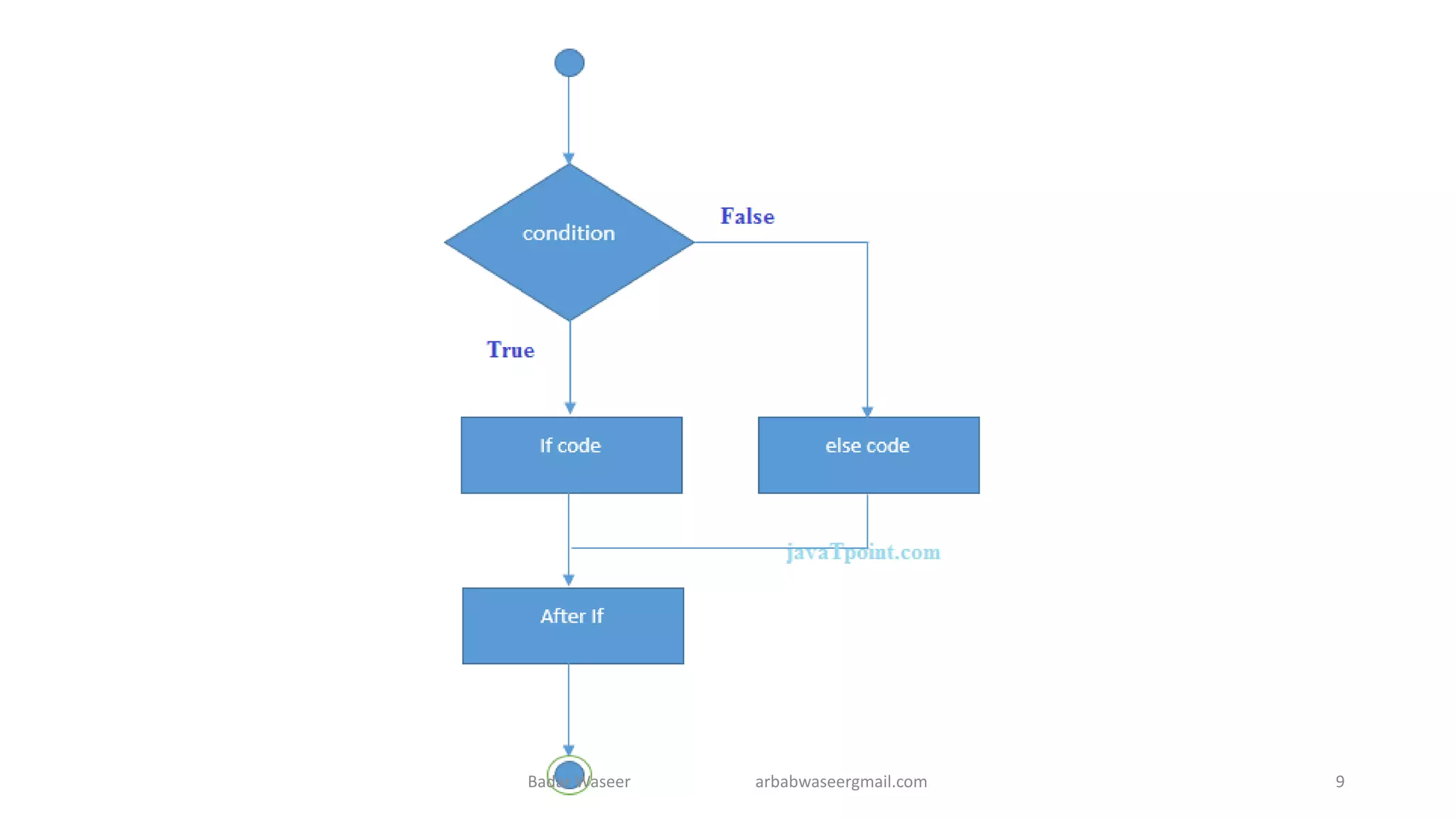
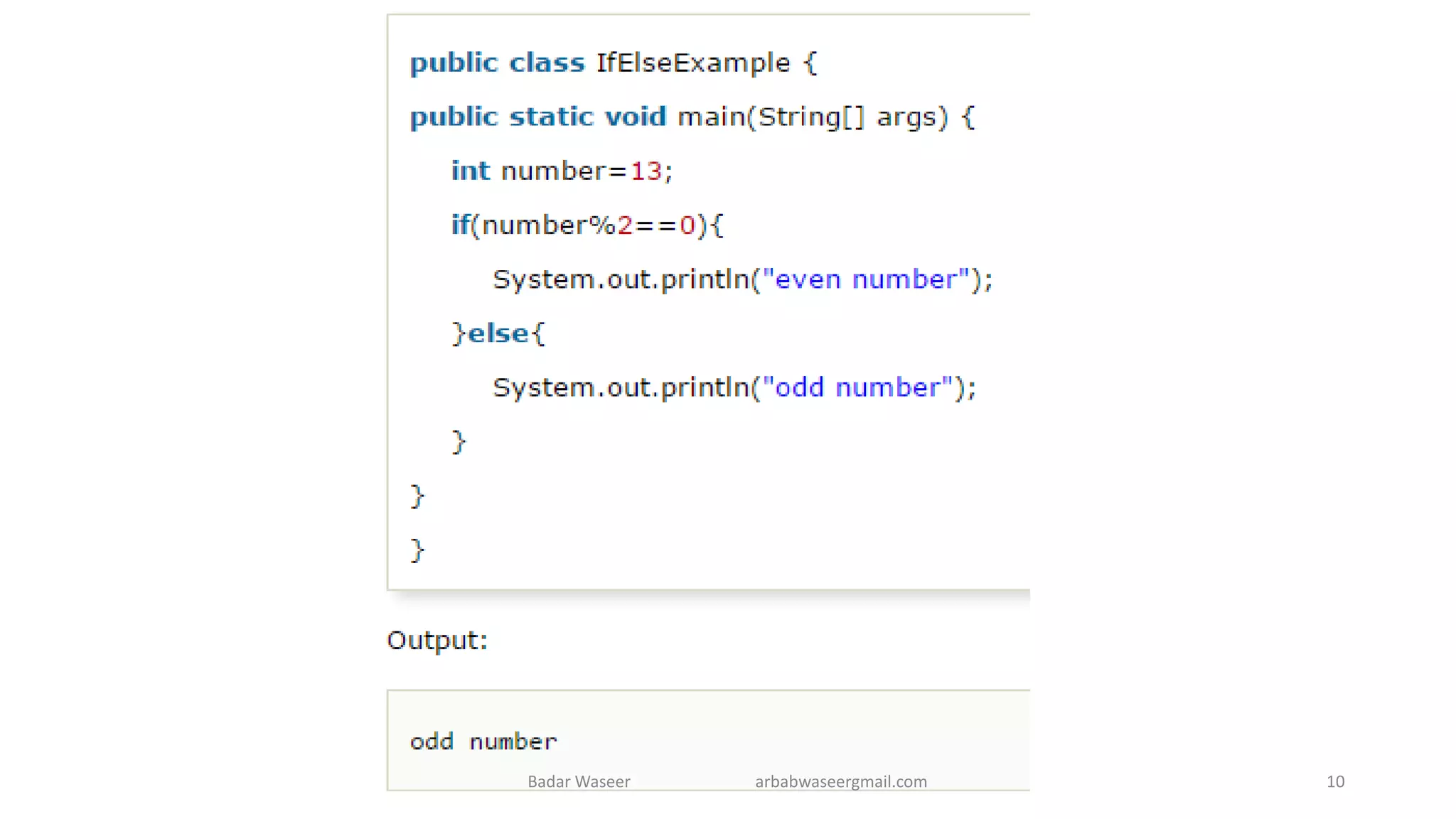
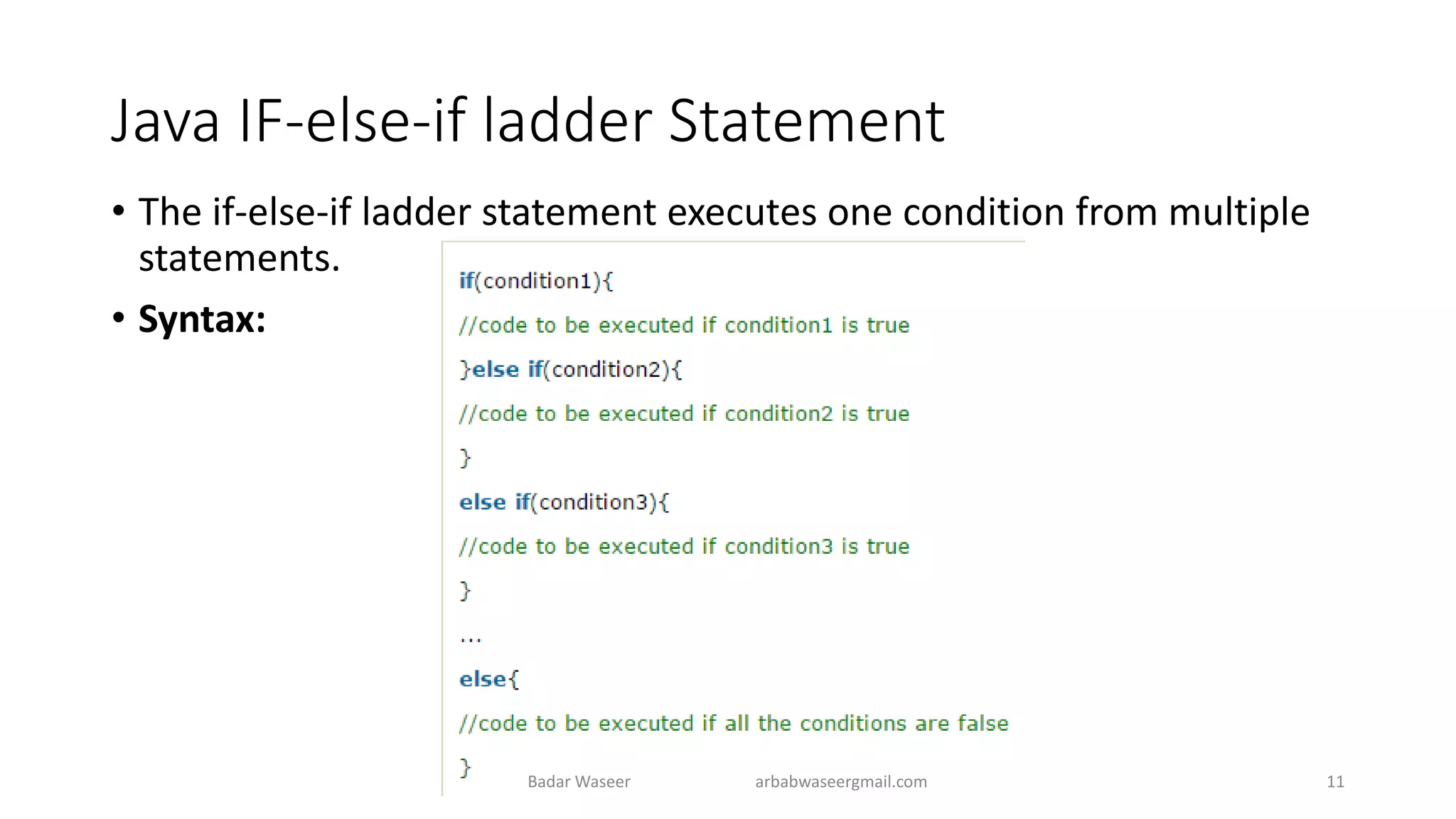
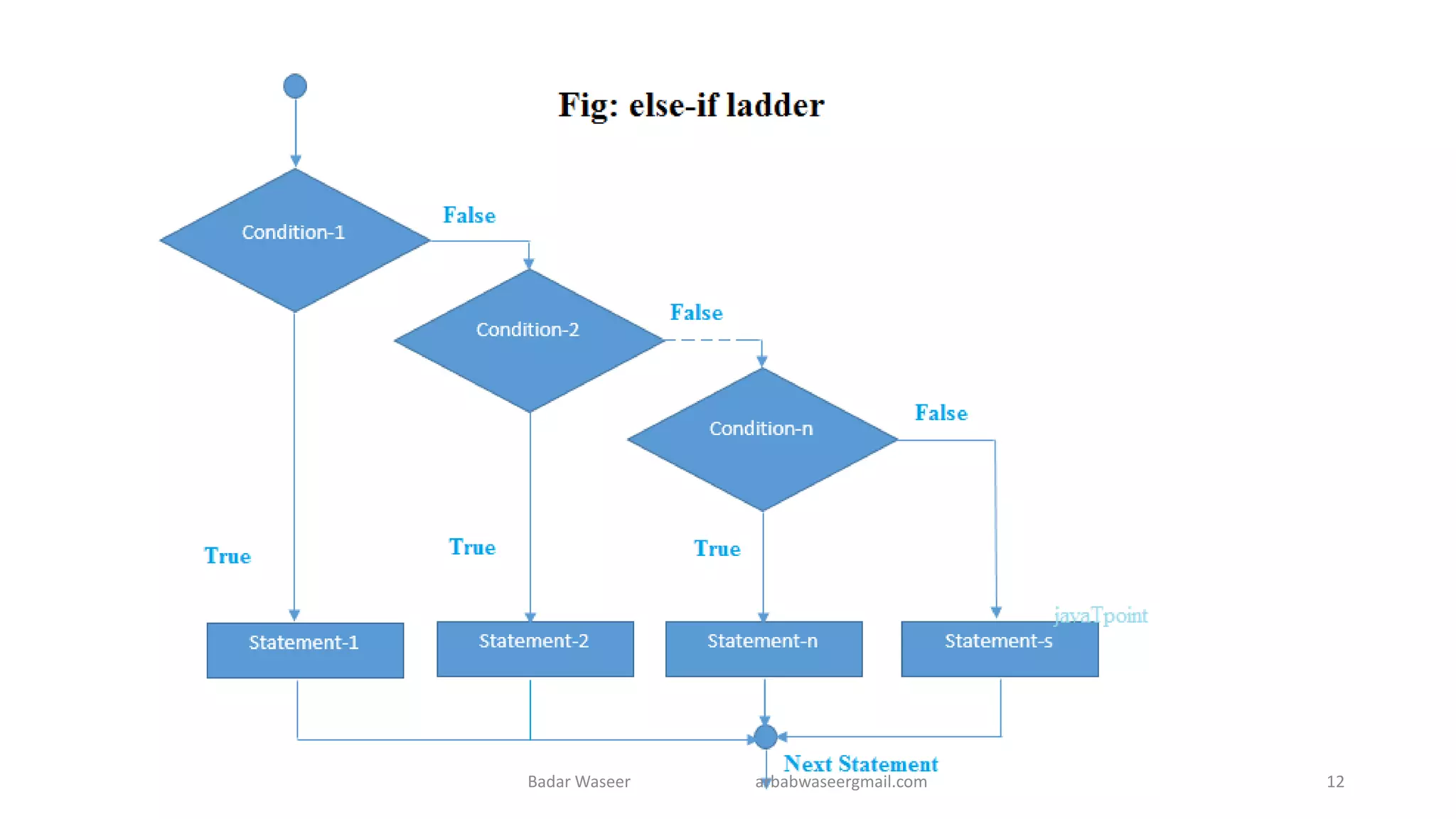
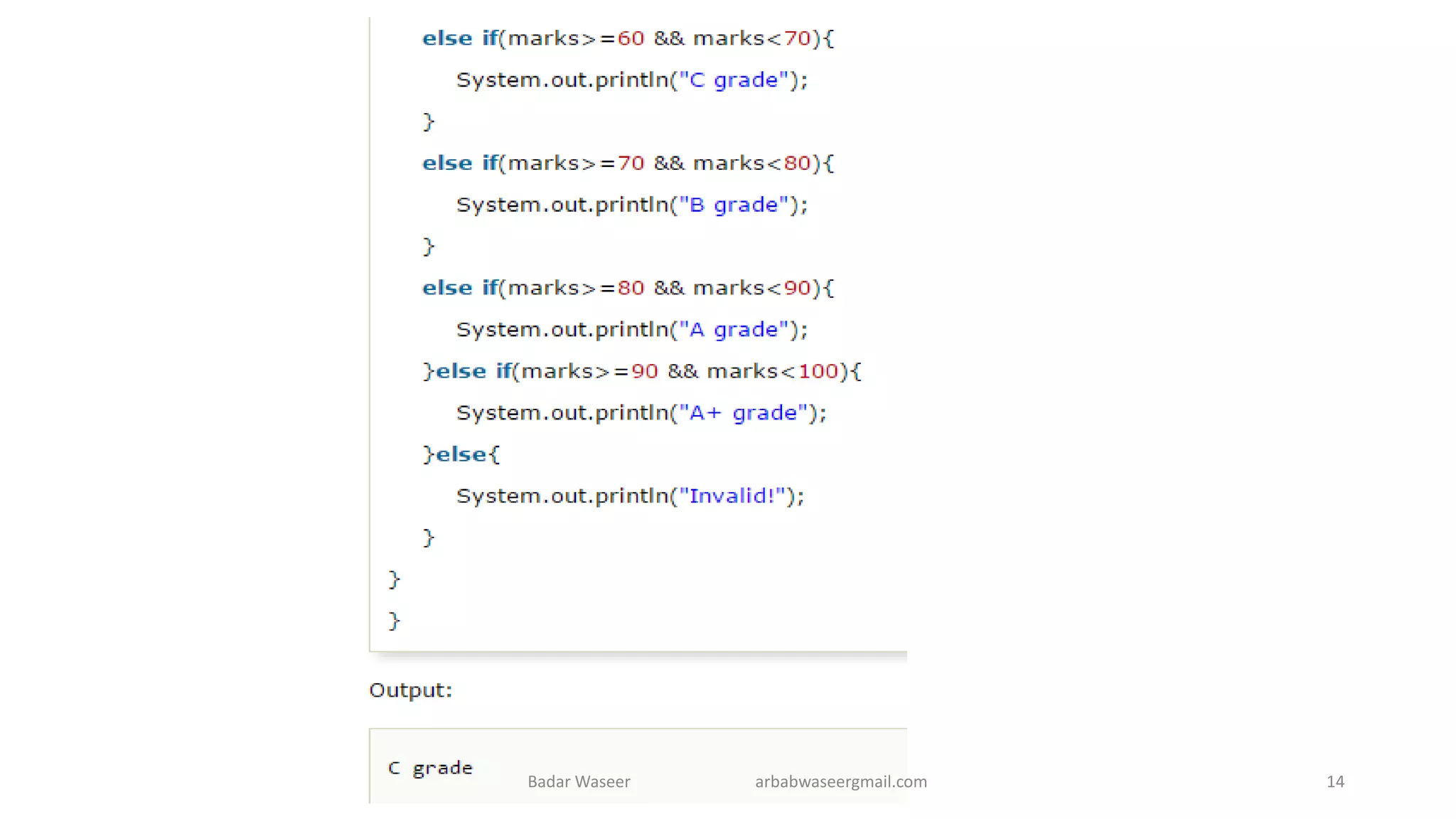
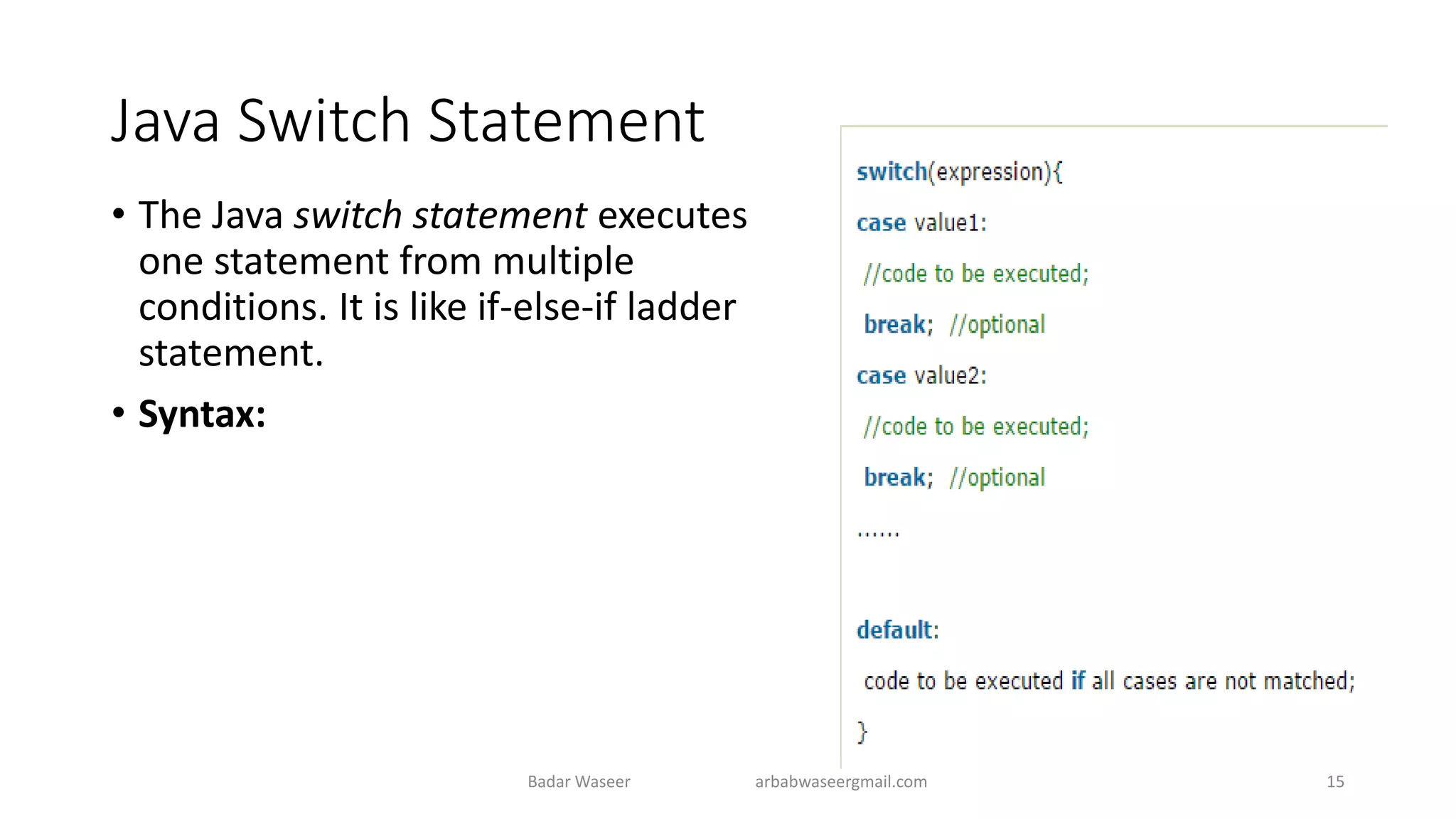
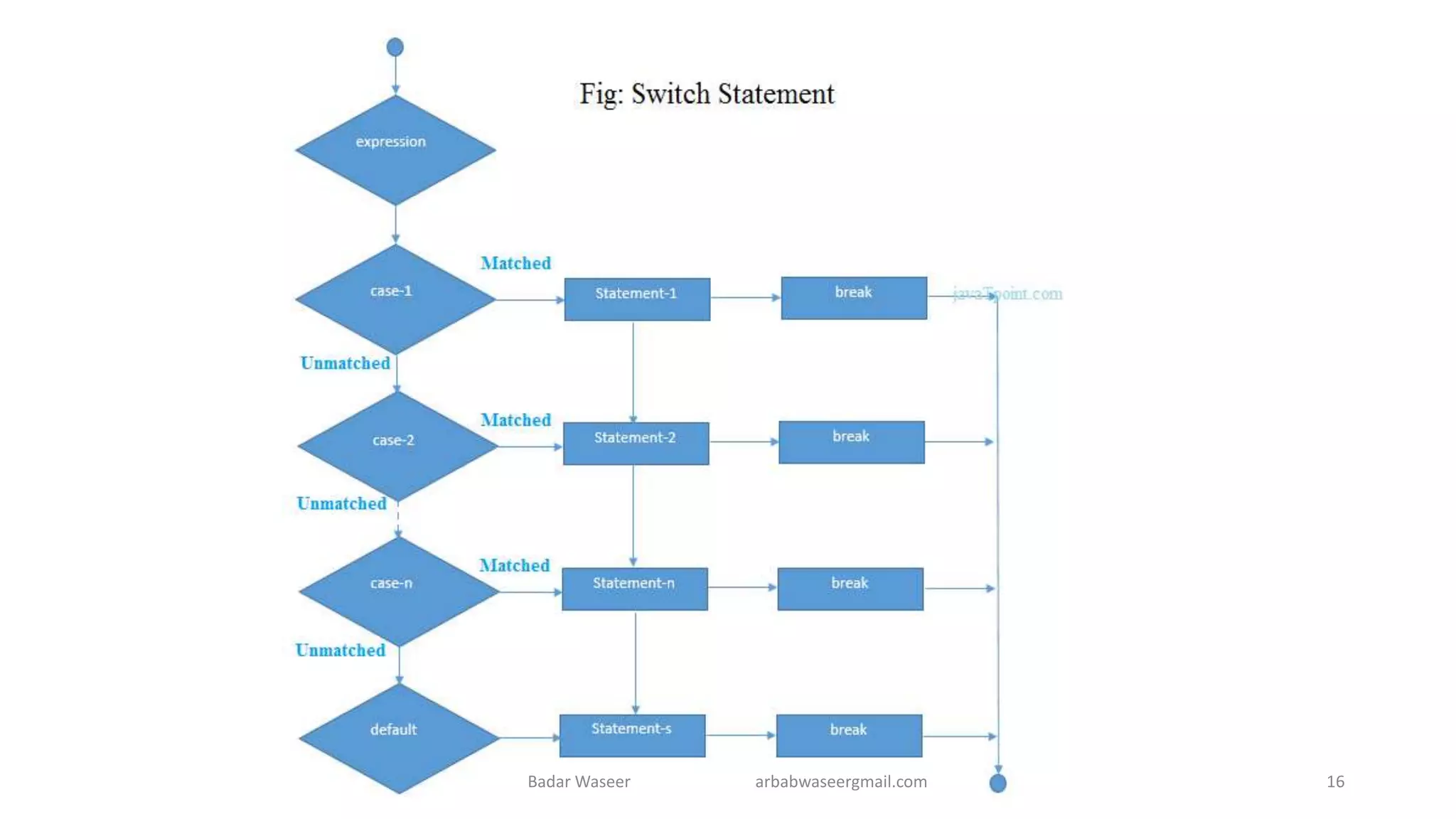
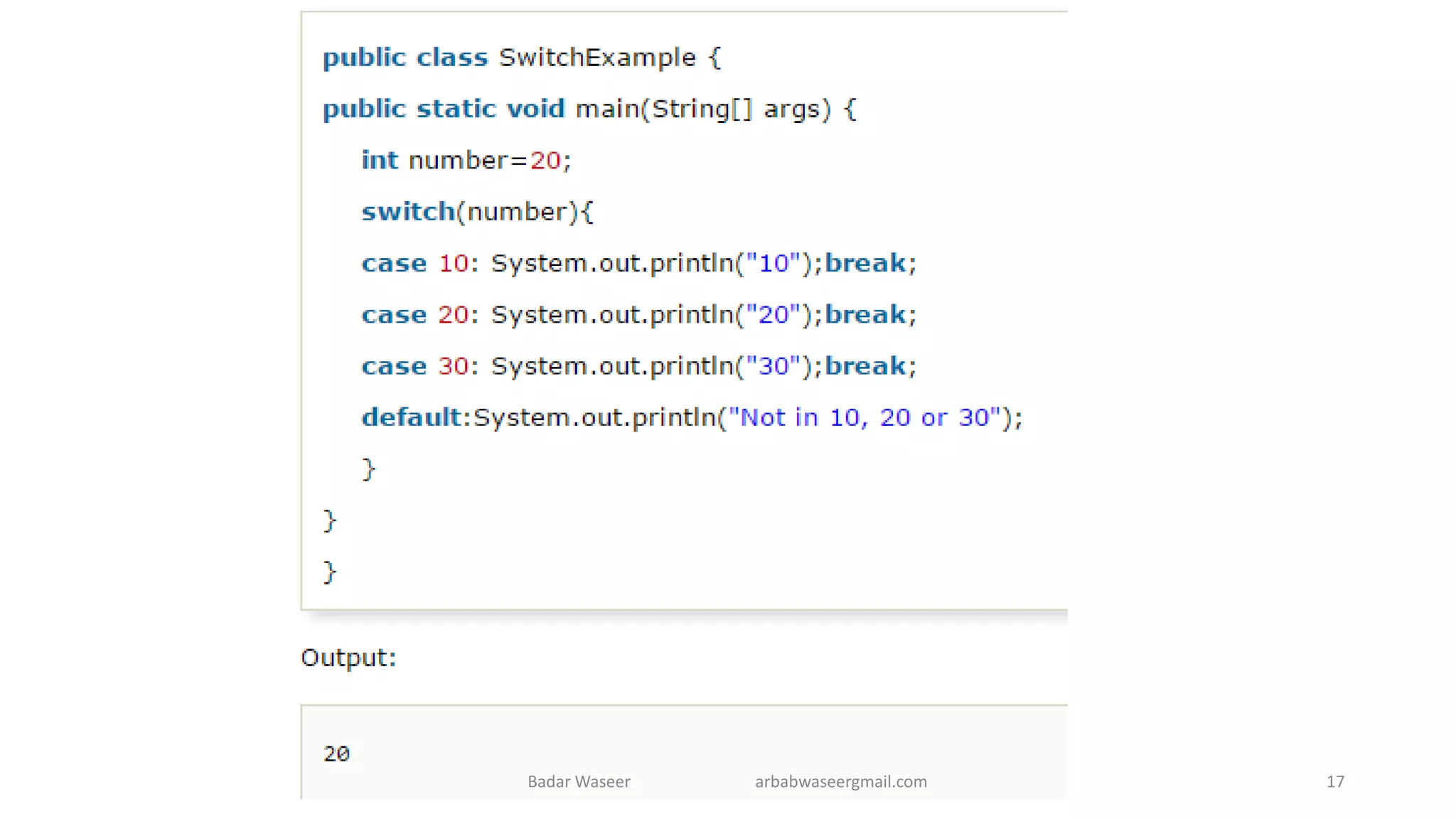
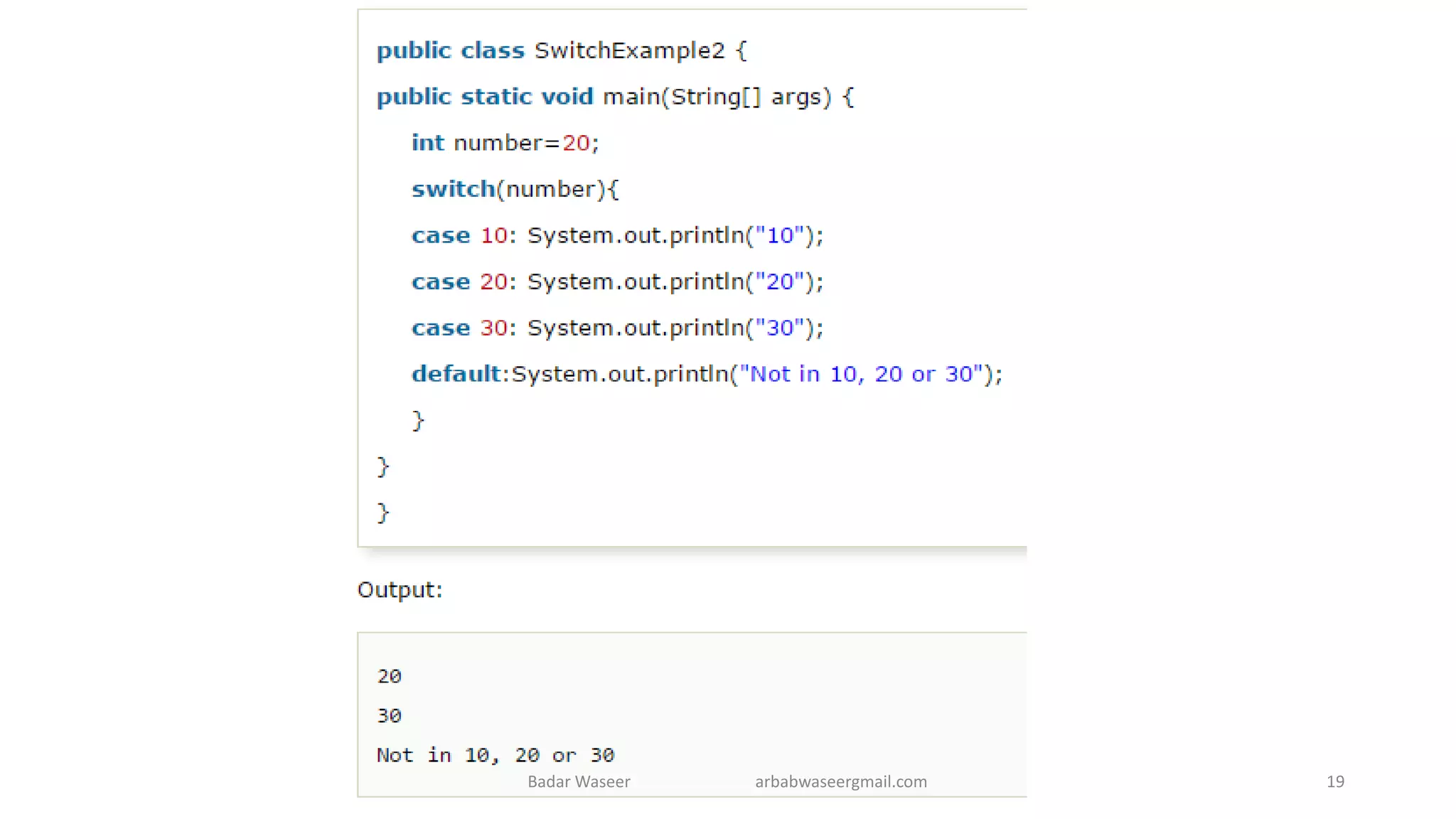
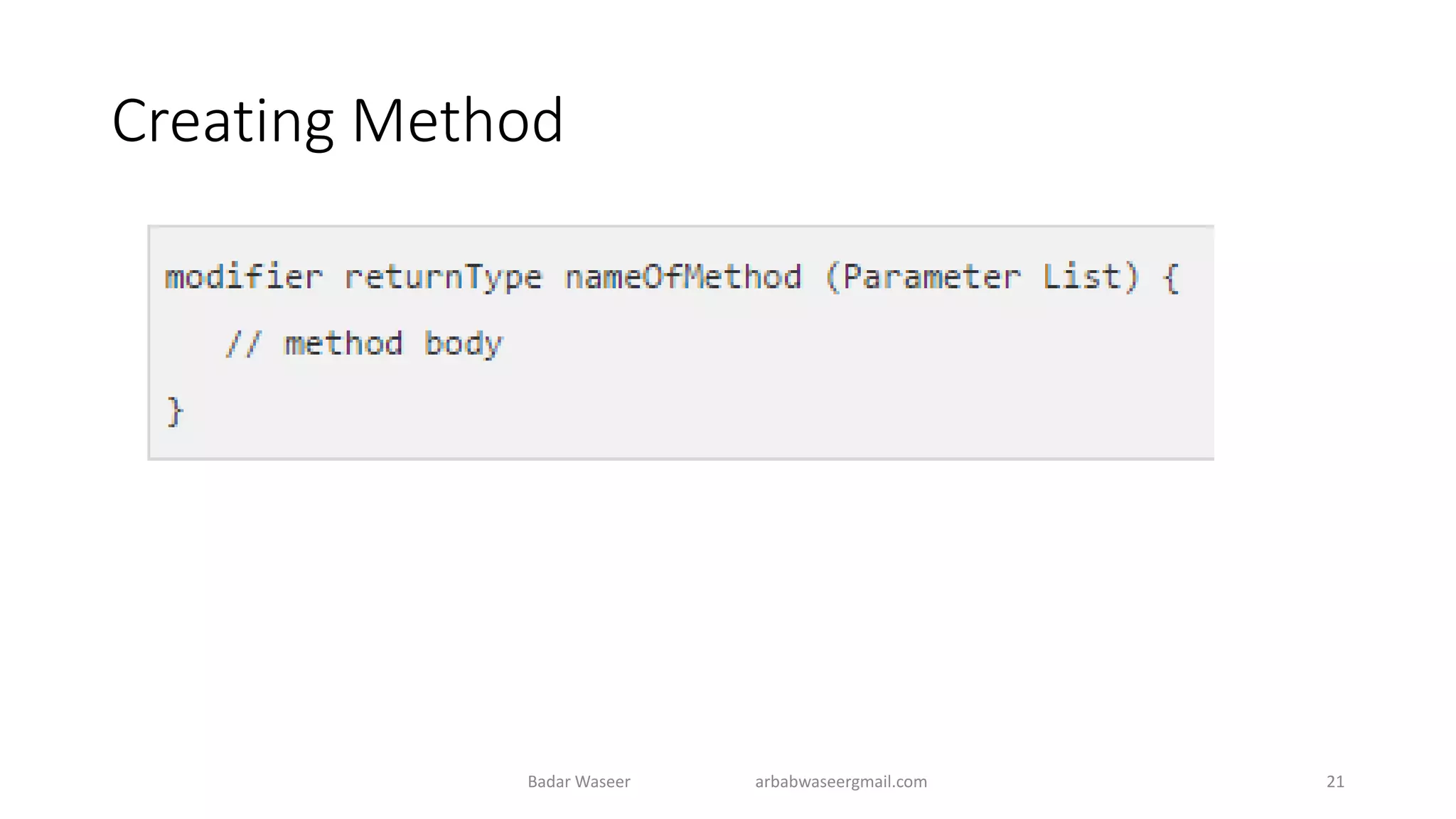
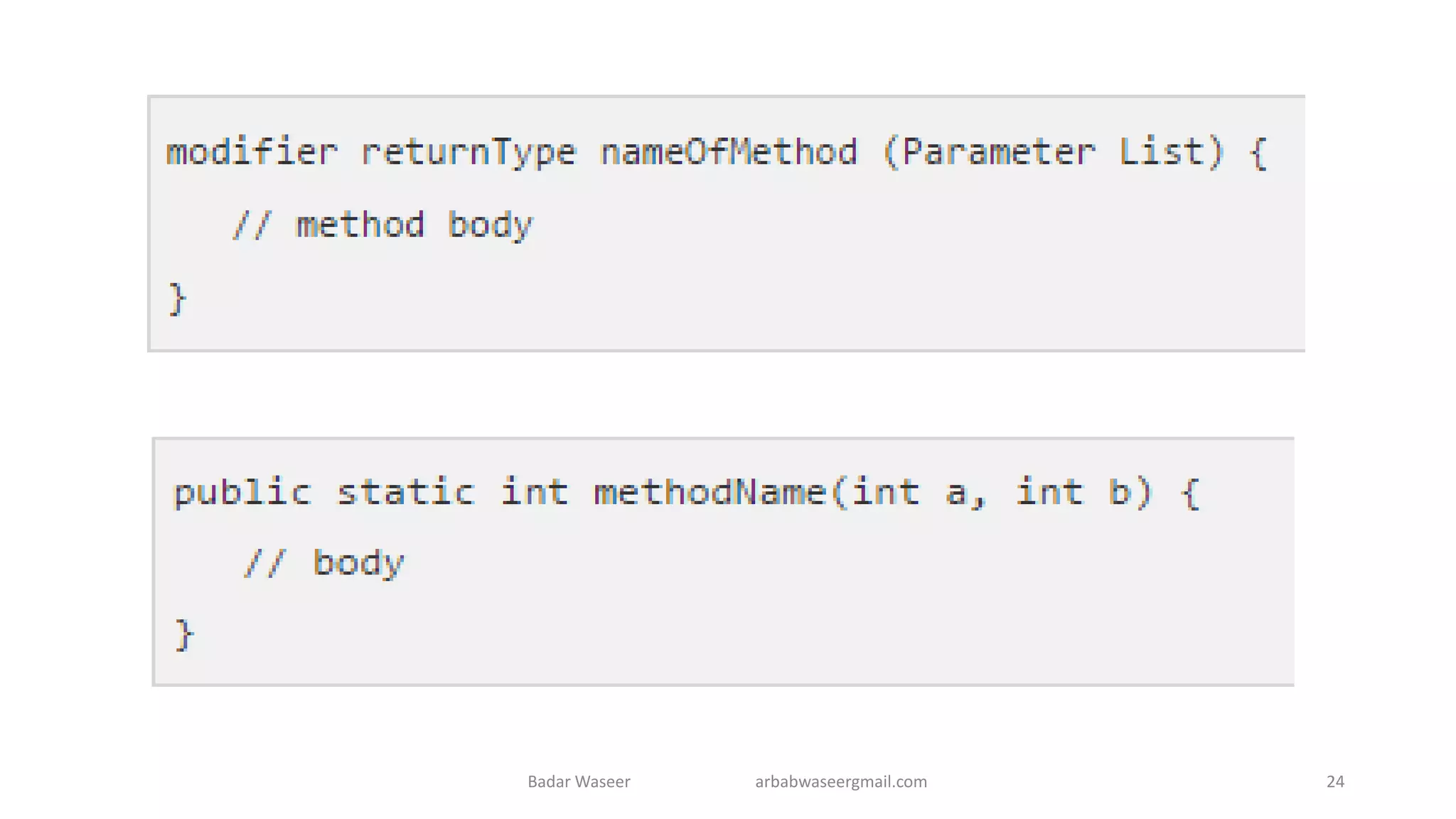
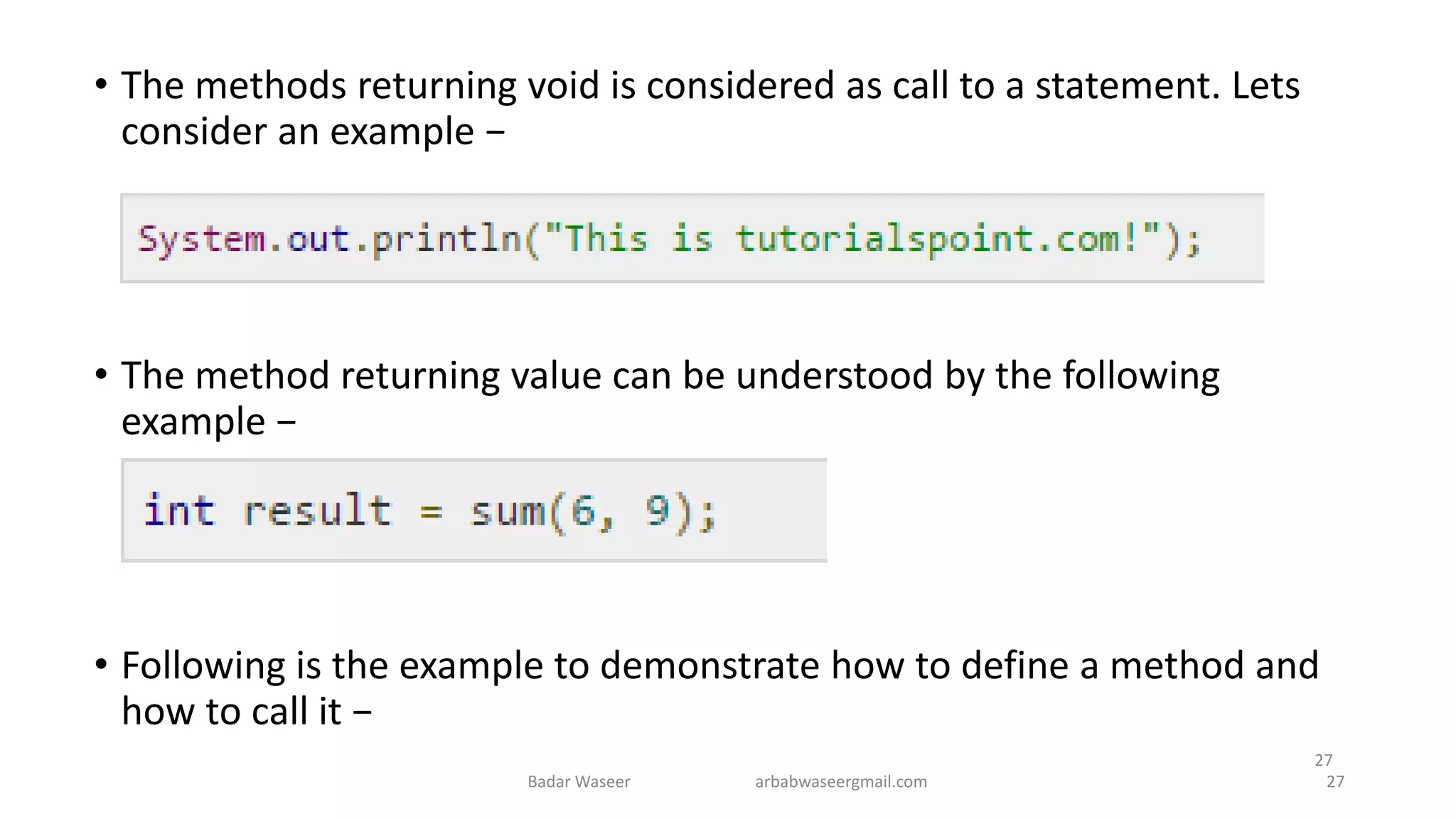
Operators in Java include unary, arithmetic, relational, shift, bitwise, ternary, and assignment operators. Operator precedence determines the order that operations are performed. Java supports if, if-else, nested if, and if-else-if statements to test conditions, as well as switch statements. Methods are blocks of code that perform operations. Methods can take parameters, return values, and be invoked from within a class.