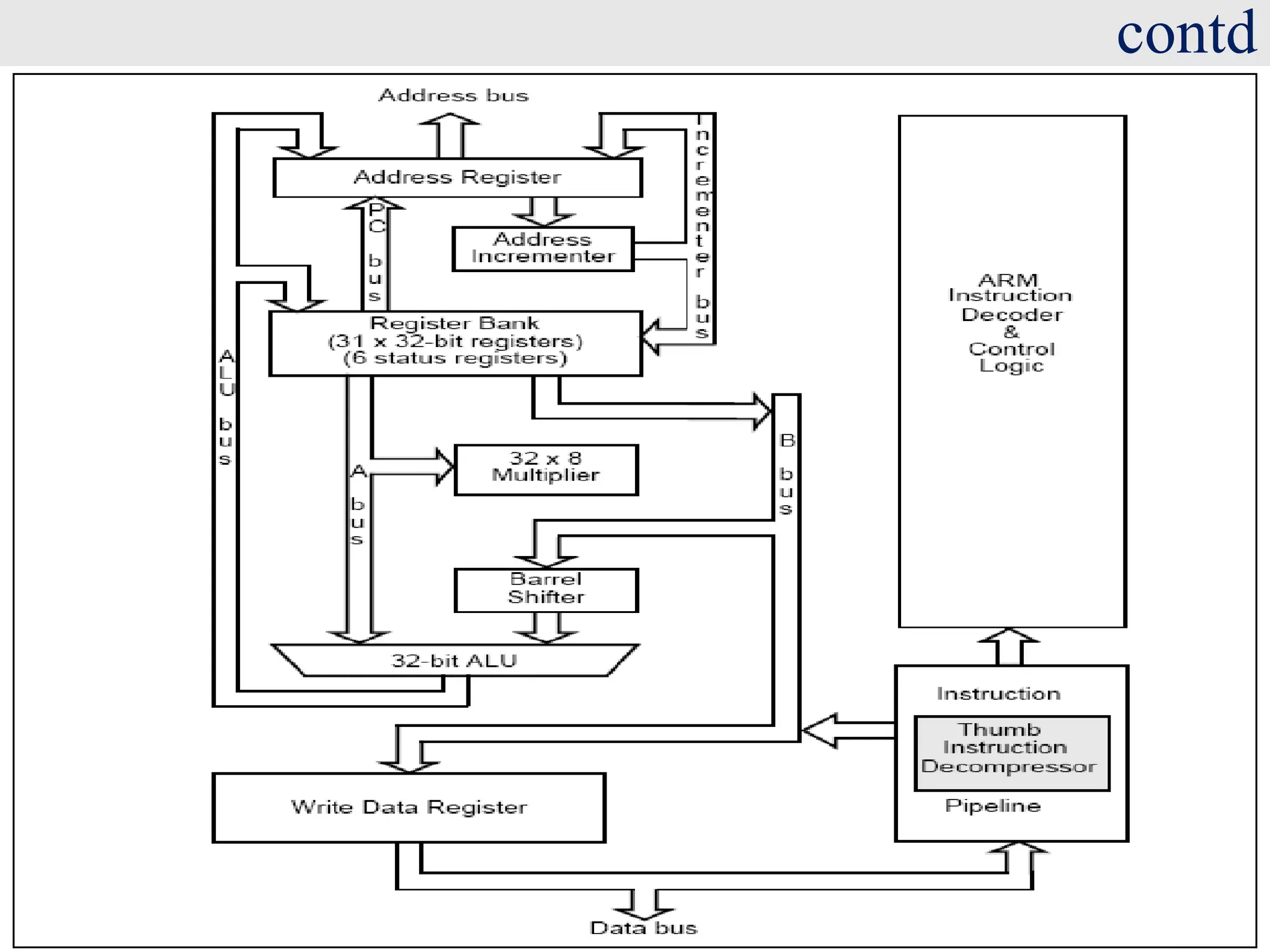
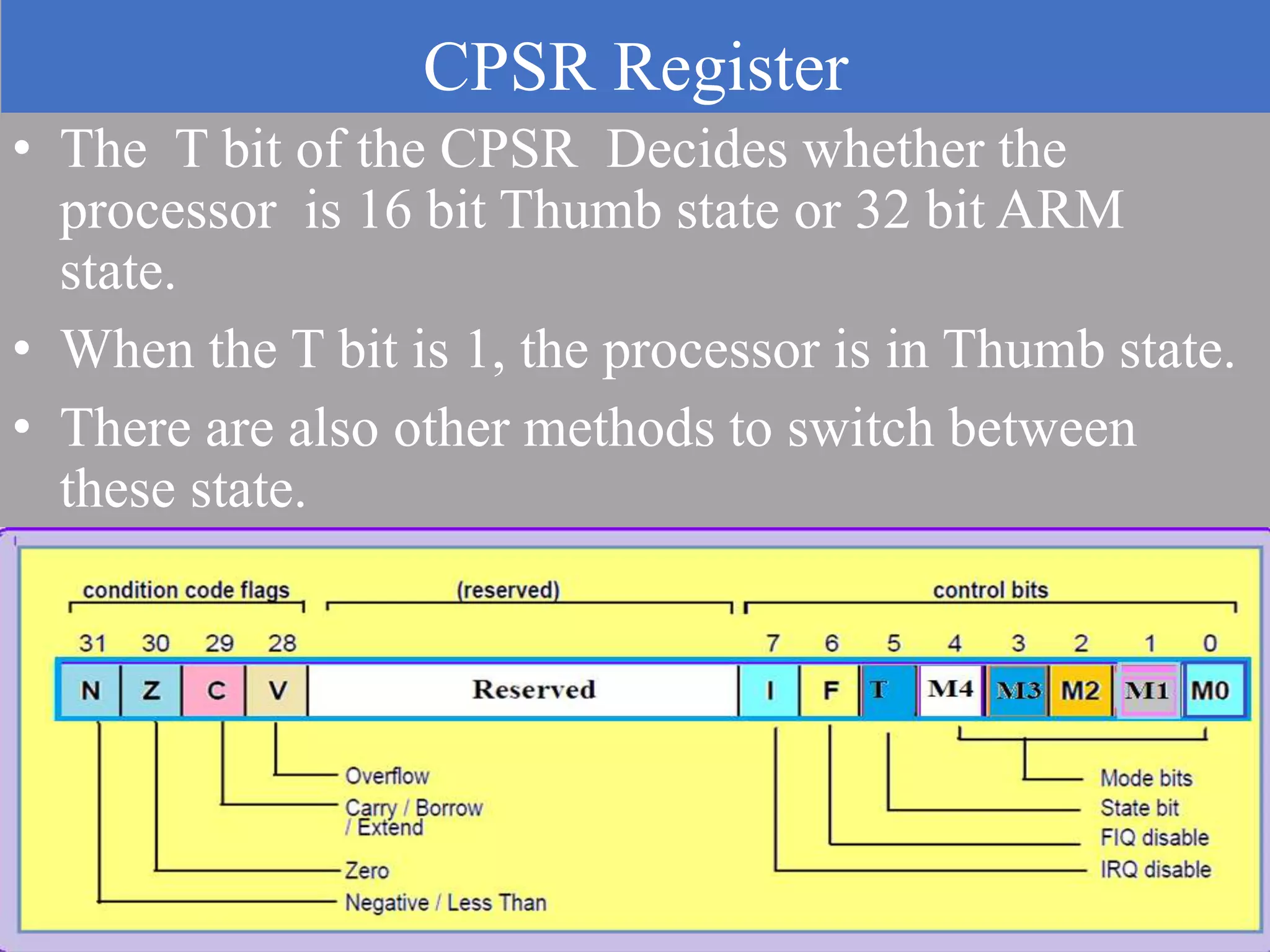
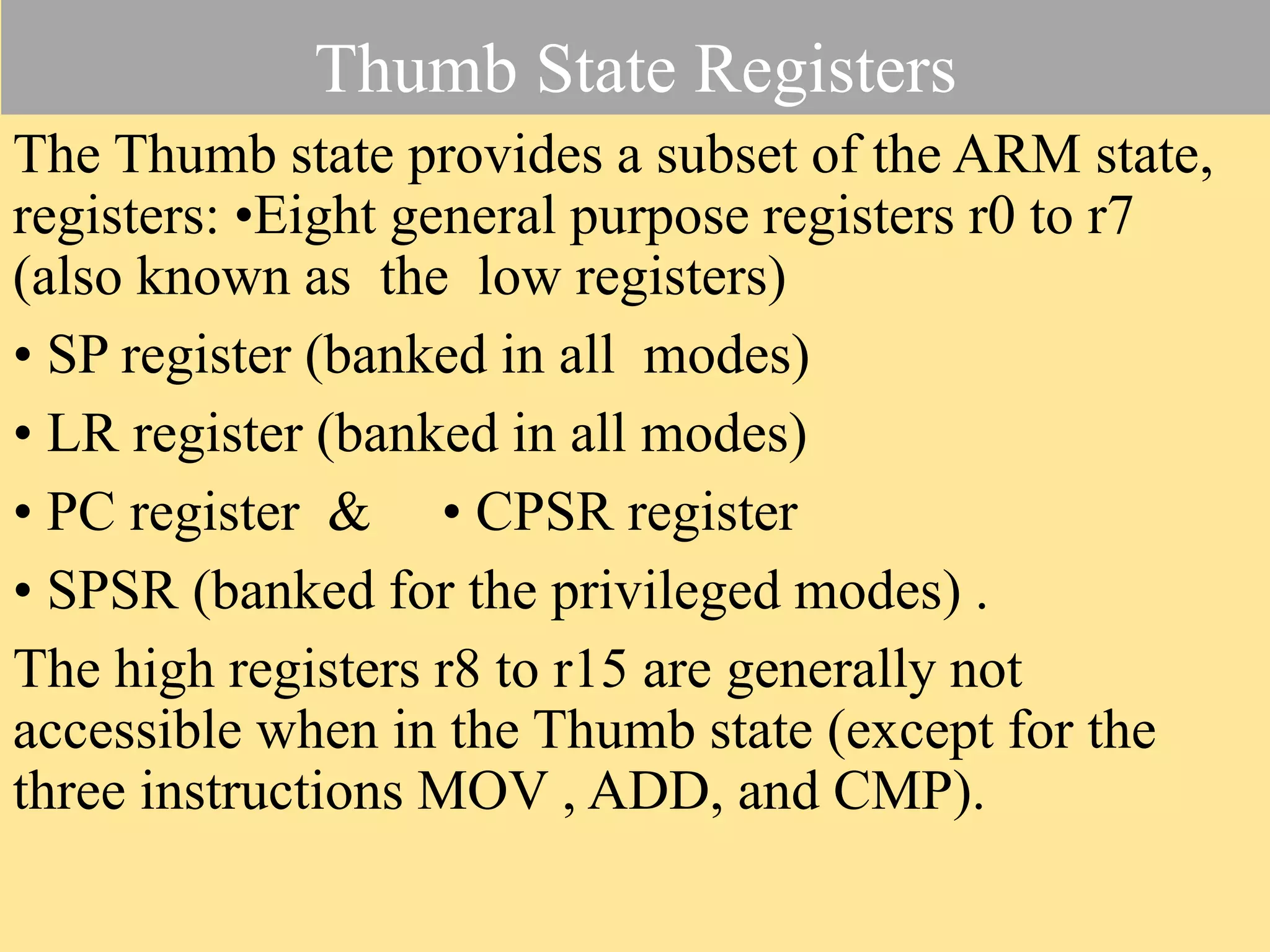
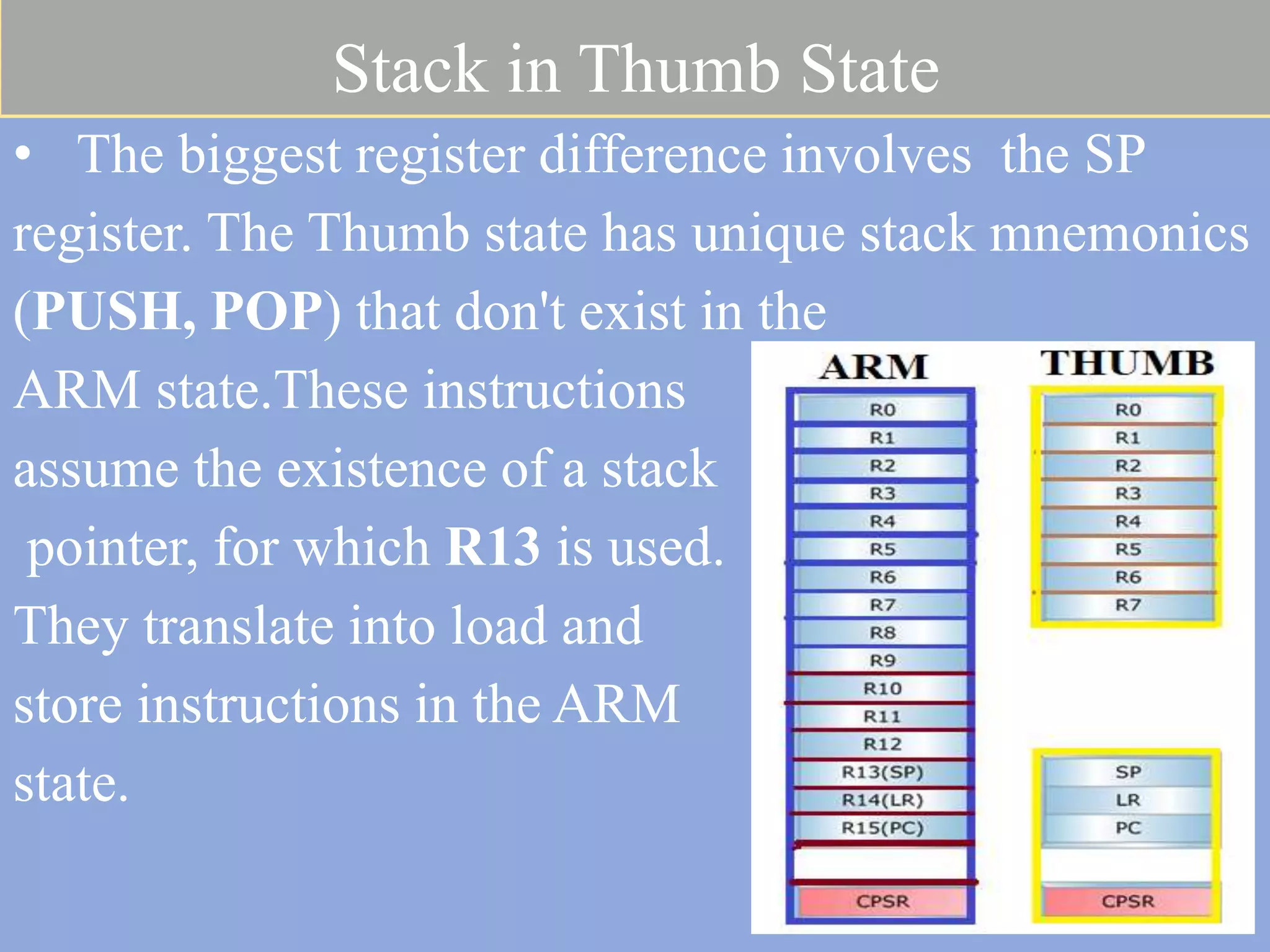
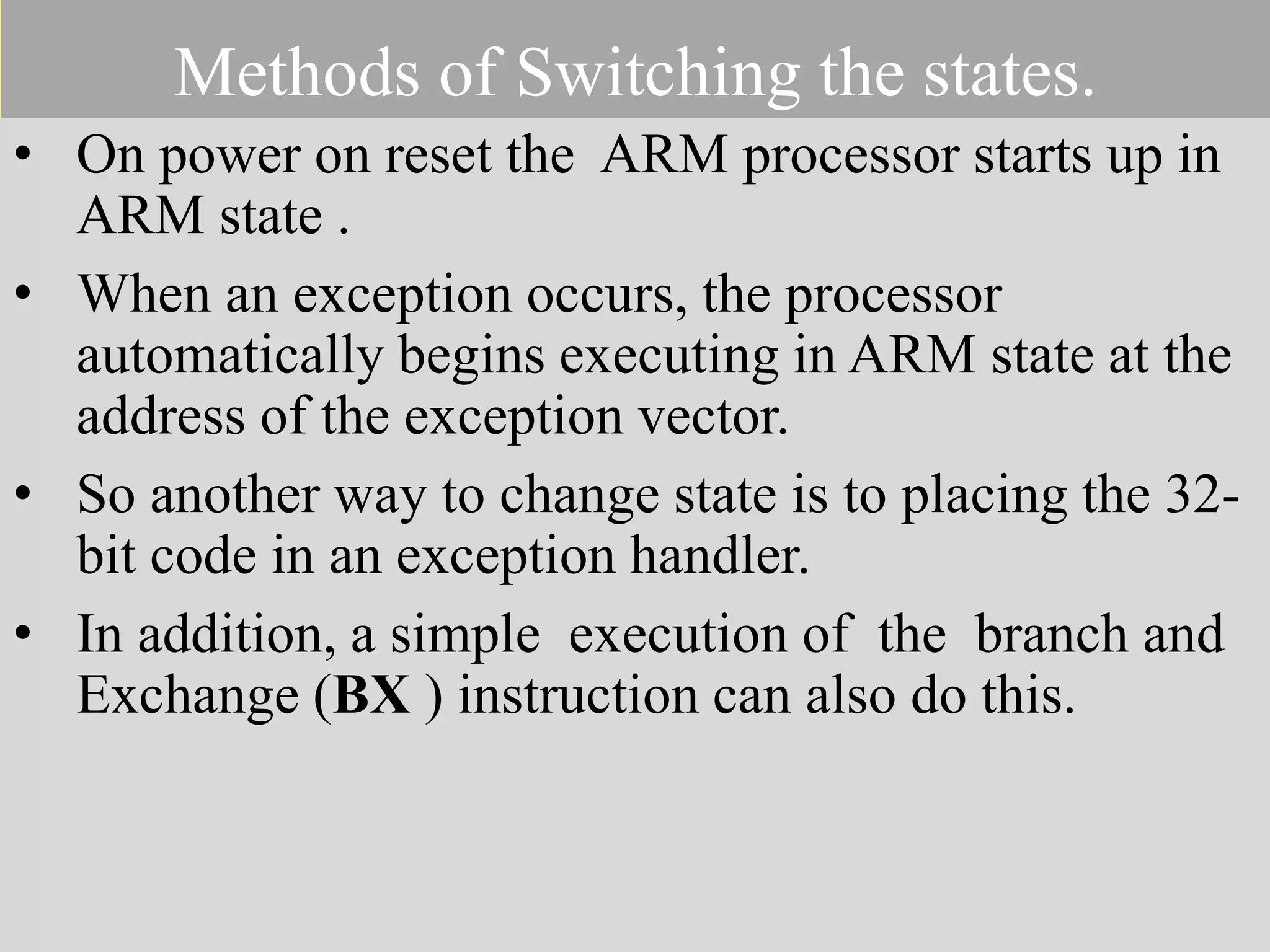
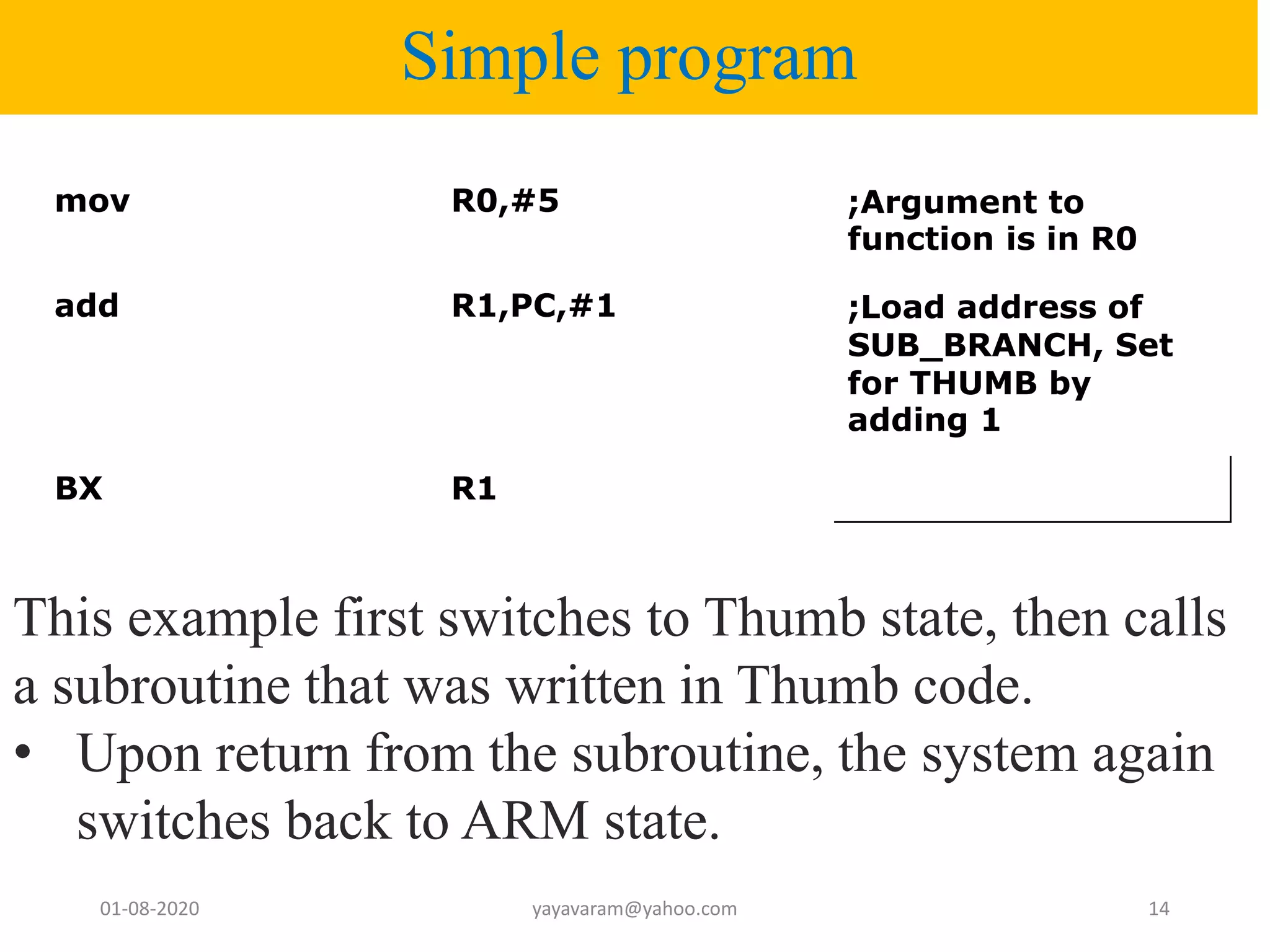
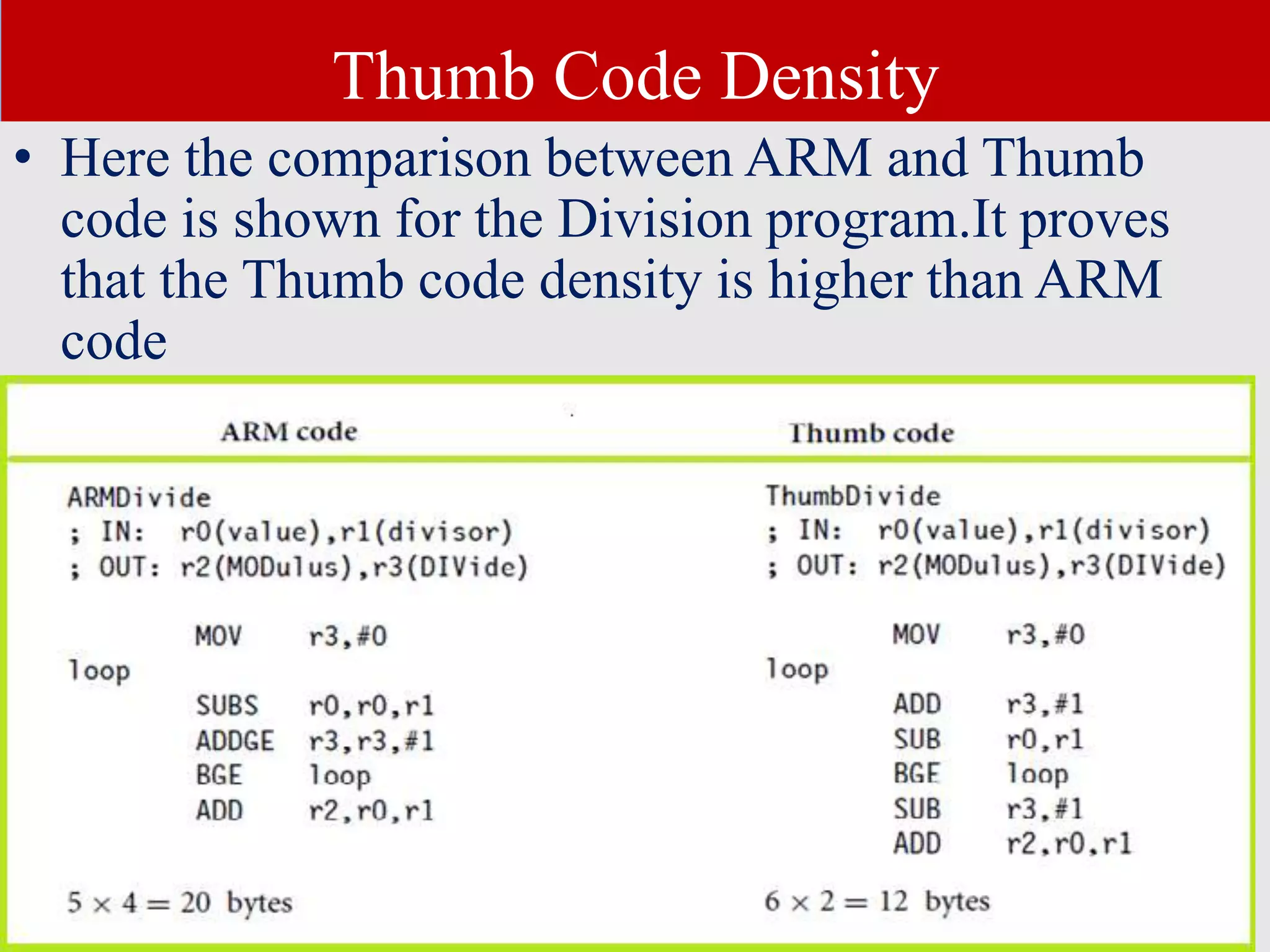
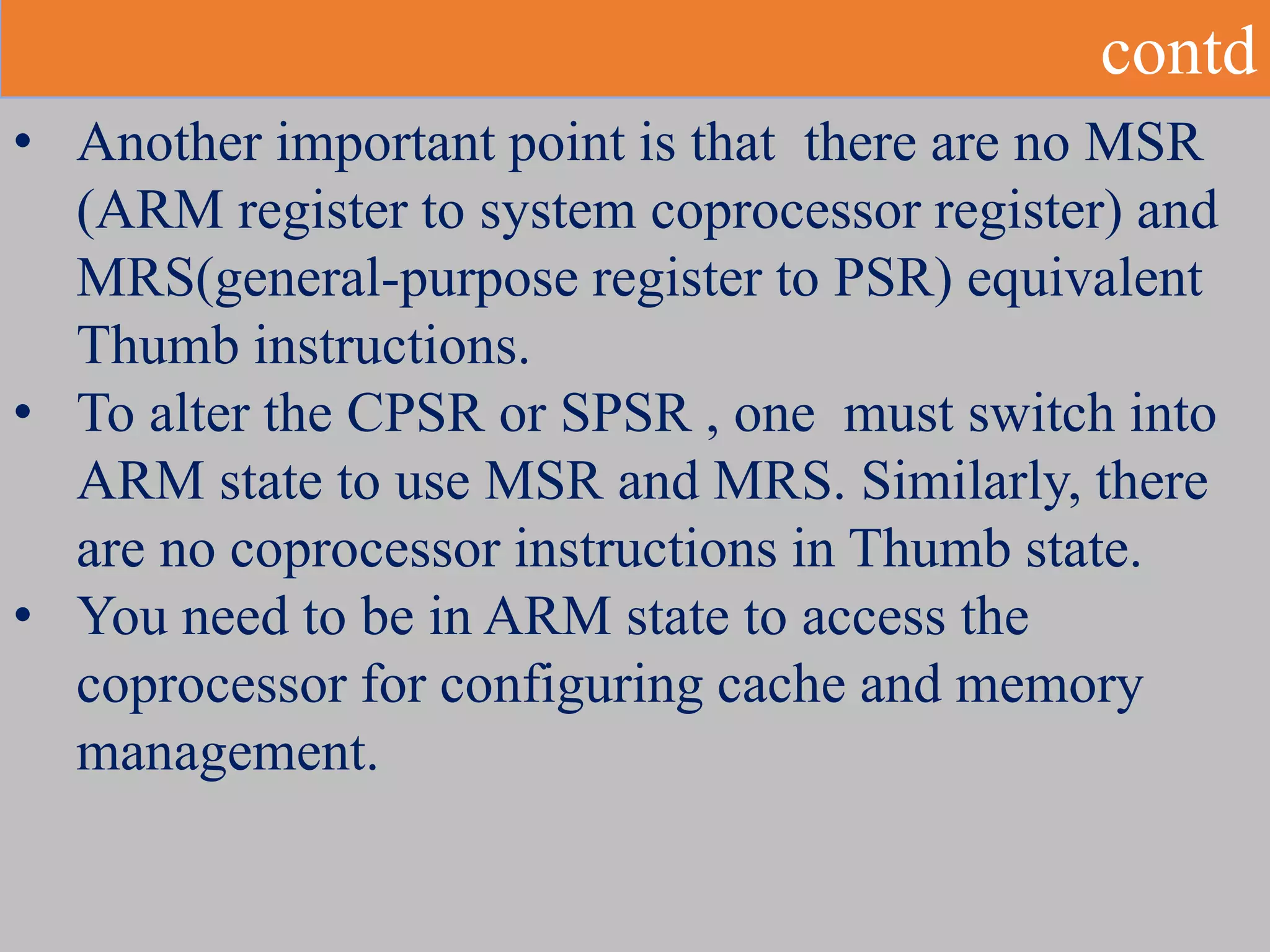
The document discusses the ARM7TDMI processor architecture, specifically its dual operating states: ARM and Thumb. The Thumb state employs 16-bit instructions to reduce memory requirements while allowing execution of a subset of 32-bit ARM instructions, making it suitable for applications with limited memory. It details the methods for switching between states, the differences in registers, and the implications for instruction execution.