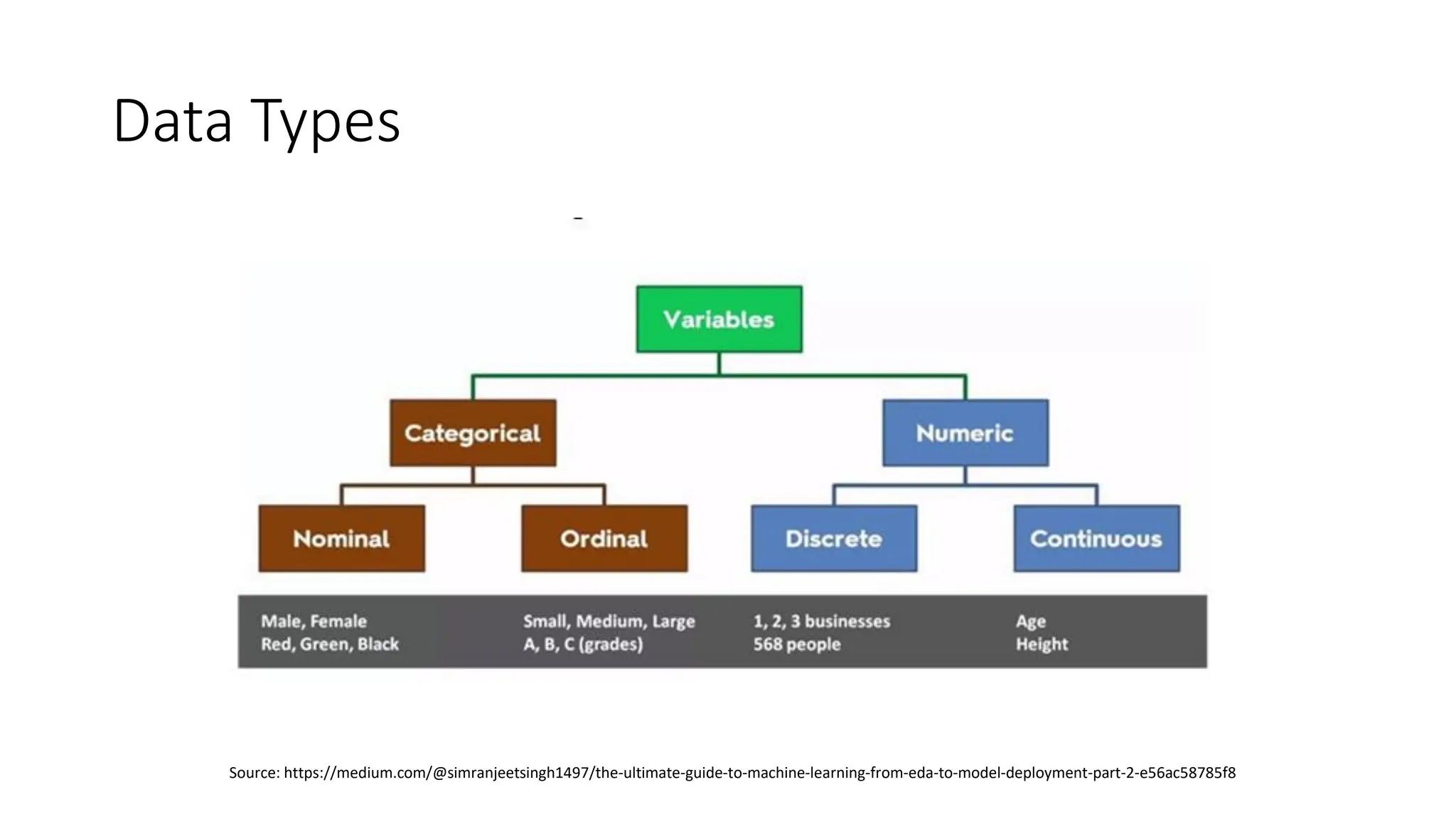
The document discusses Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA), emphasizing its importance in understanding, identifying patterns, cleaning, and preparing data for further analysis using libraries like Pandas and NumPy in Python. It outlines when to perform EDA based on dataset size and structure, and distinguishes between structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. Additionally, it encourages self-learning through hands-on homework with Pandas to reinforce concepts critical for machine learning.