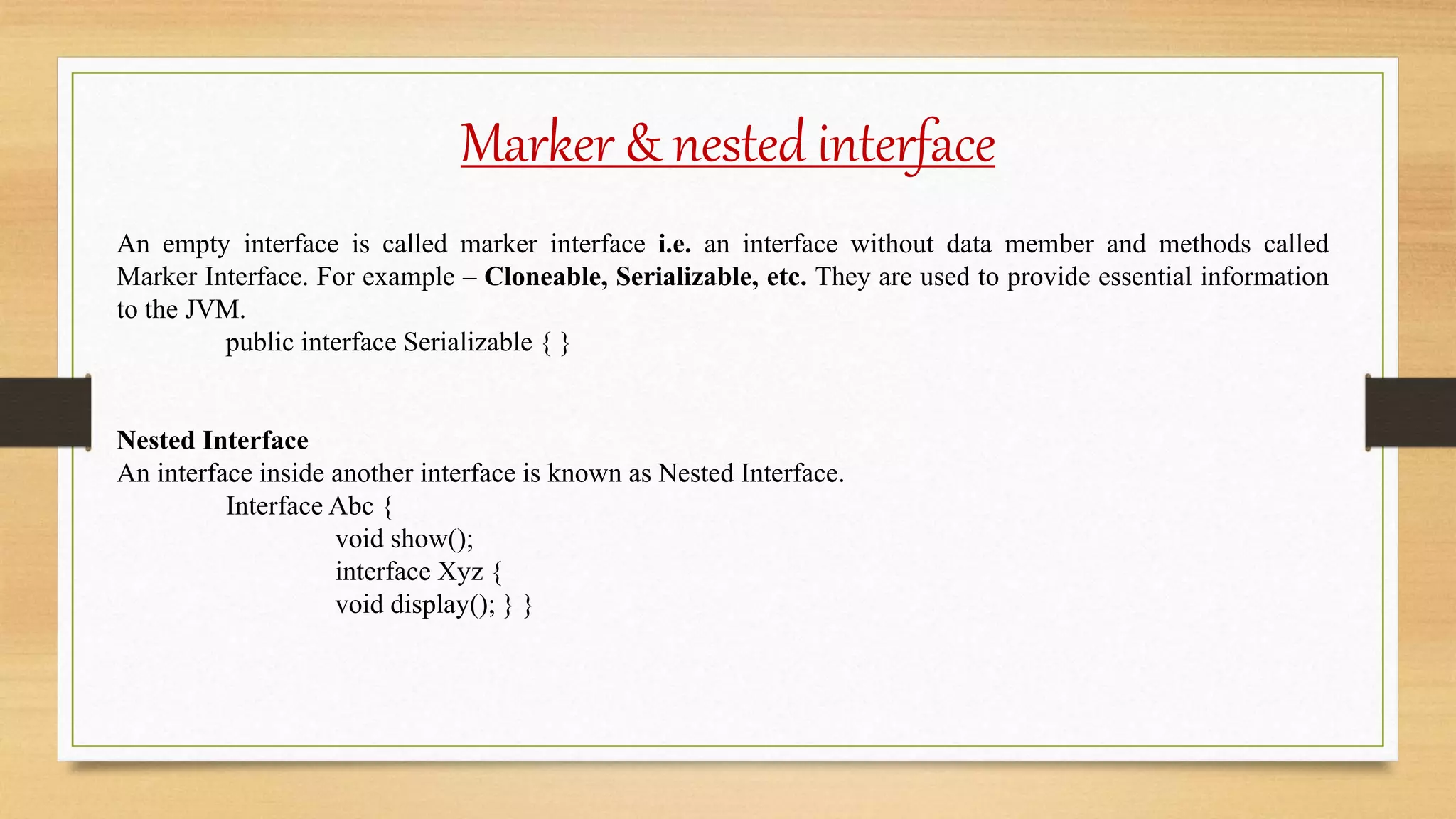
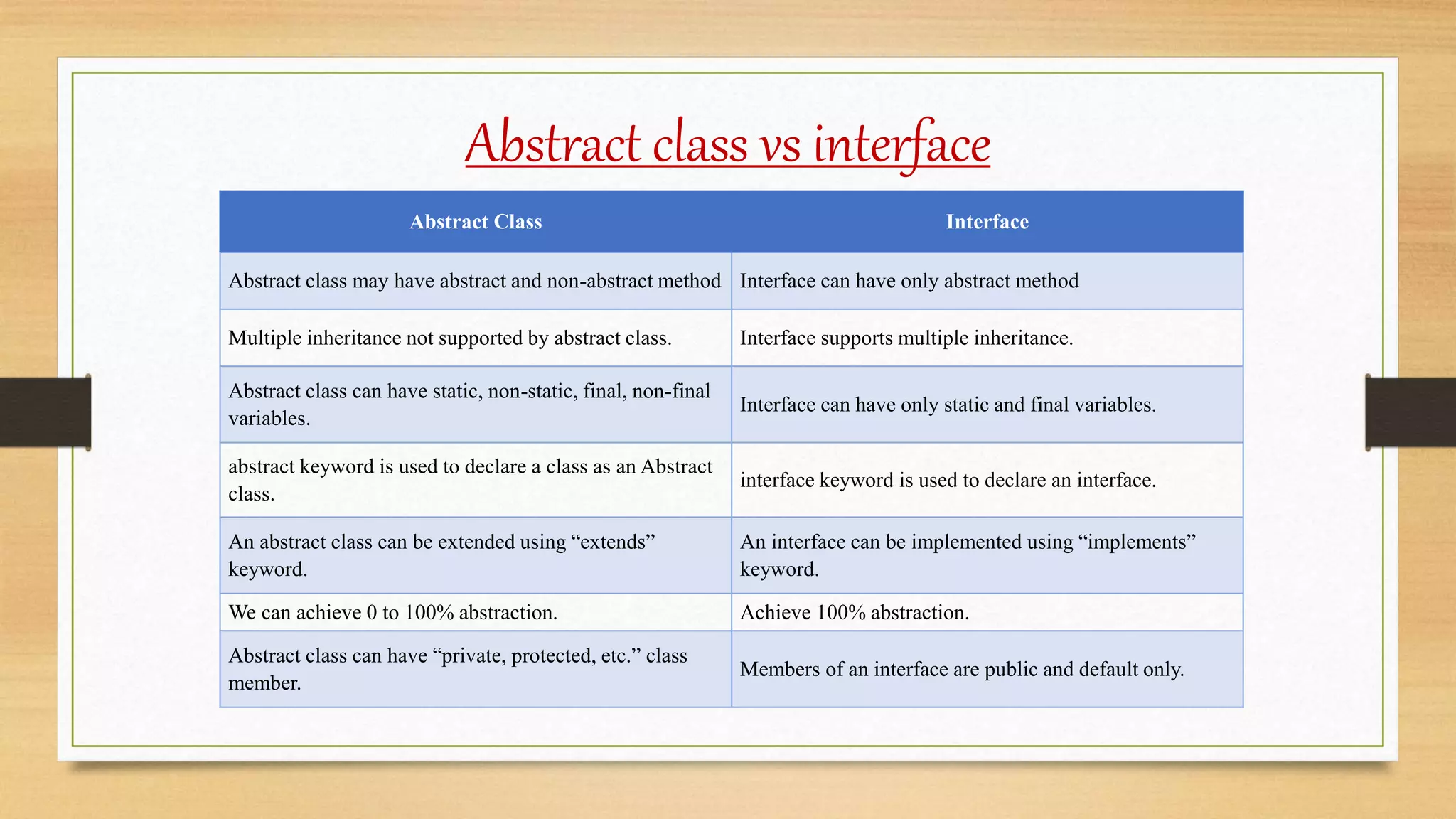
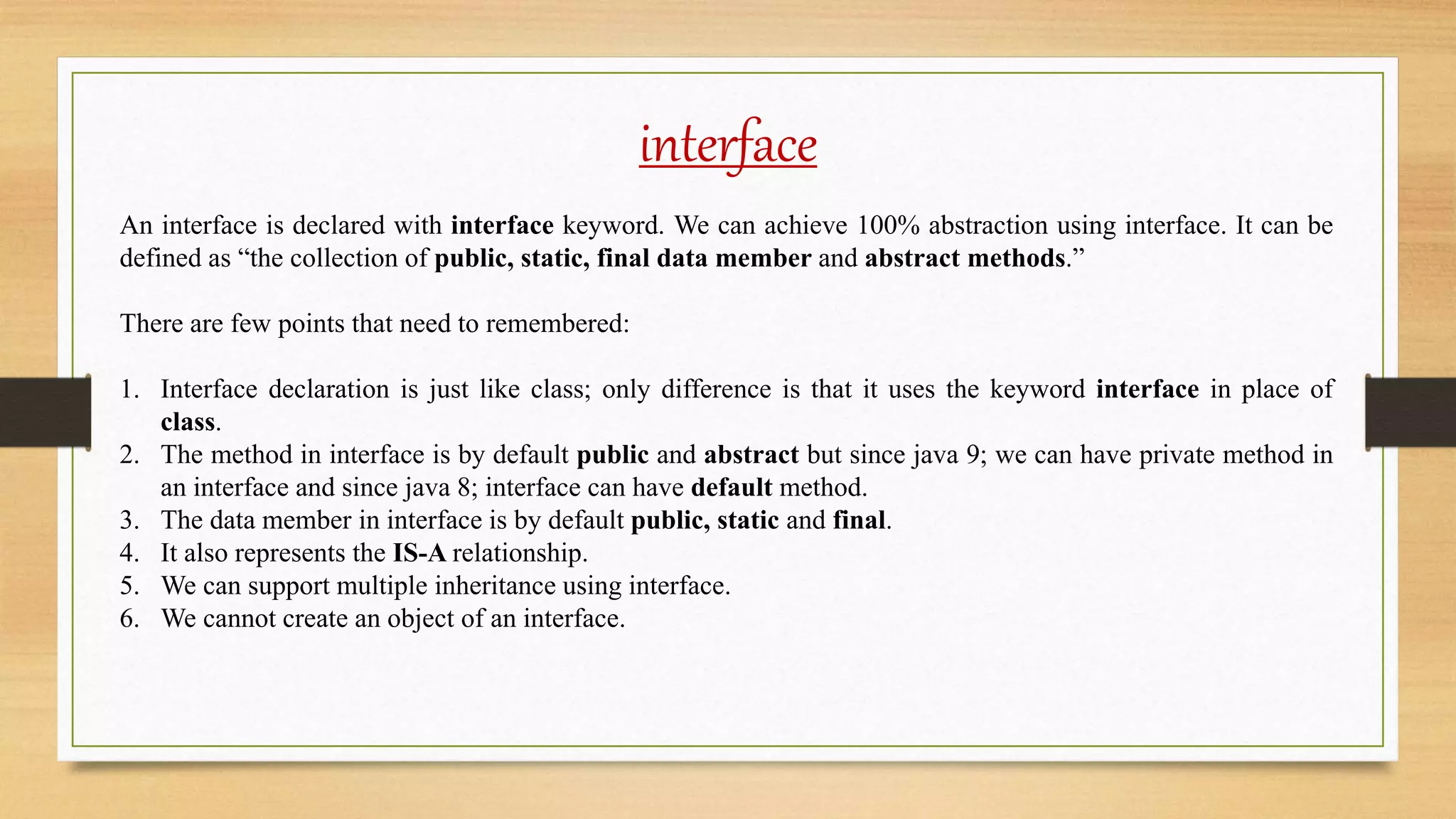
The document discusses abstract classes and interfaces in Java. It provides examples of abstract classes with abstract and non-abstract methods, and how abstract classes can be extended. It also discusses interfaces and how they can be implemented, allow for multiple inheritance, and define marker interfaces. The key differences between abstract classes and interfaces are that abstract classes can include non-abstract methods while interfaces contain only abstract methods, and abstract classes allow single inheritance while interfaces allow multiple inheritance.



![Example-1 abstract class Polygon { abstract void area(); } class Tringle extends Polygon { void area() { int r=10; double pi=3.14; double ar = pi *r*r; System.out.println("Area of tringle = "+ar); } public static void main(String args[]) { Polygon p = new Tringle(); p.area(); } } Tringle.java Output – Area of tringle = 314.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-4-2048.jpg)
![Example-2 Note: - When an abstract class is inherited, then derived class must provide the implementations for all the abstract method declared in base class otherwise it gives an error at compile time. Tringle.java abstract class Polygon { abstract void area(); abstract void display(); } class Tringle extends Polygon { void area() { int r=10; double pi=3.14; double ar = pi *r*r; System.out.println("Area of tringle = "+ar); } public static void main(String args[]) { Polygon p = new Tringle(); // Upcasting p.area(); } } Output- error: Tringle is not abstract and does not override abstract method display() in Polygon class Tringle extends Polygon { ^ 1 error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-5-2048.jpg)

![Importance of abstract class //Bank.java abstract class RBI { abstract int getROI(); } class SBI extends RBI { int getROI() { return 7; }} class PNB extends RBI { int getROI() { return 8; }} class Bank { public static void main(String args[]) { RBI rb; rb = new SBI(); System.out.println("ROI of SBI(%) = "+rb.getROI()); rb = new PNB(); System.out.println("ROI of PNB(%) = "+rb.getROI()); } } Output – ROI of SBI(%) = 7 ROI of PNB(%) = 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-7-2048.jpg)
![example AbstractClassExample.java (constructor, variables and methods): abstract class Polygon{ Polygon() { System.out.println("Polygon created."); } abstract void area(); void display() { System.out.println("This is non-abstract method"); }} class Rectangle extends Polygon { void area() { int l=10,w=7, area; area = l*w; System.out.println("Area of Rectangle = "+area); } } class AbstractClassExample { public static void main(String args[]) { Polygon p =new Rectangle(); p.area(); p.display(); } } Output – Polygon created. Area of Rectangle = 70 This is non-abstract method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-8-2048.jpg)

![Example - 1 interface Animal { void livingPlace(); } class Lion implements Animal { public void livingPlace() { System.out.println("The living place of Lion is Forest."); } public static void main(String args[]) { Animal an = new Lion(); an.livingPlace(); } } Output- The living place of Lion is Forest. Lion.java A class can implements an interface.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-11-2048.jpg)
![Example-2 Lion.java interface Animal { void livingPlace(); } interface Birds { void live(); } class Lion implements Animal, Birds { public void livingPlace() { System.out.println("The living place of Lion is Forest."); } public void live() { System.out.println("The living place of birds in Nest."); } public static void main(String args[]) { Animal an= new Lion(); an.livingPlace(); Birds b = new Lion(); b.live(); } } Output- The living place of Lion is Forest. The living place of birds in Nest. A class can implements an interface or more than one interface.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-12-2048.jpg)
![Example-3 interface Animal { void livingPlace(); } interface Birds extends Animal { void live(); } class Lion implements Birds { public void livingPlace() { System.out.println("The living place of Lion is Forest."); } public void live() { System.out.println("The living place of birds in Nest."); } public static void main(String args[]) { Birds b = new Lion(); b.livingPlace(); b.live(); } } Lion.java Output- The living place of Lion is Forest. The living place of birds in Nest. An interface can extends another interface.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-13-2048.jpg)
![Example-4 interface Polygon { int a = 10; void area(int x); } class Tringle implements Polygon { public void area(int x) { double pi = 3.14; double area = pi*x*x; System.out.println("Area of tringle = "+area); } public static void main(String args[]) { Polygon p = new Tringle(); p.area(10); } } Output- Area of tringle = 314.0 When you override the abstract method declared in interface it should be noted that overridden method must be public because the method in interface is by default public. When you declare a variable in interface then it is mandatory to initialize because it is by default; public, static and final.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-8abstractclassandinterface-201018124519/75/Lecture-8-abstract-class-and-interface-14-2048.jpg)