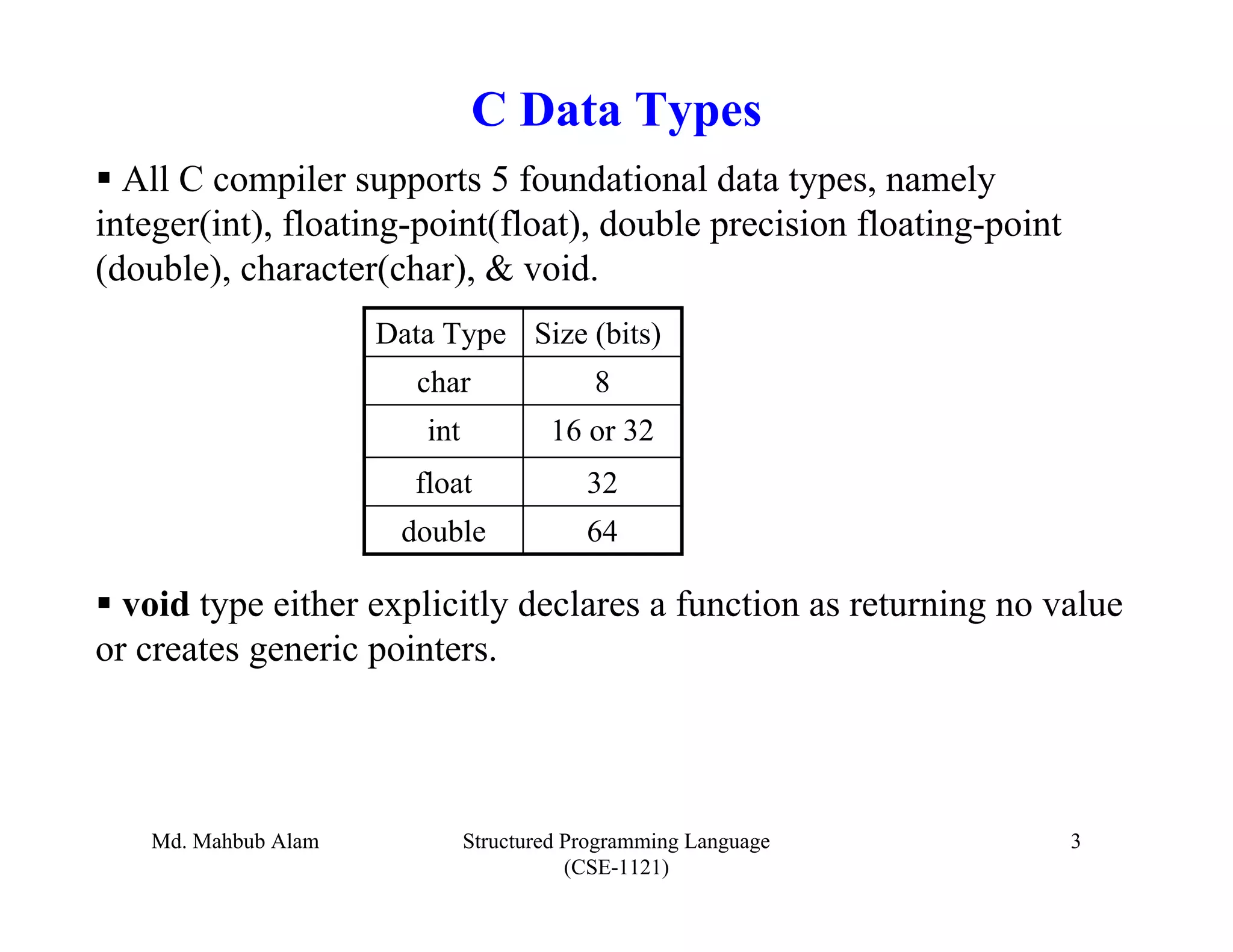
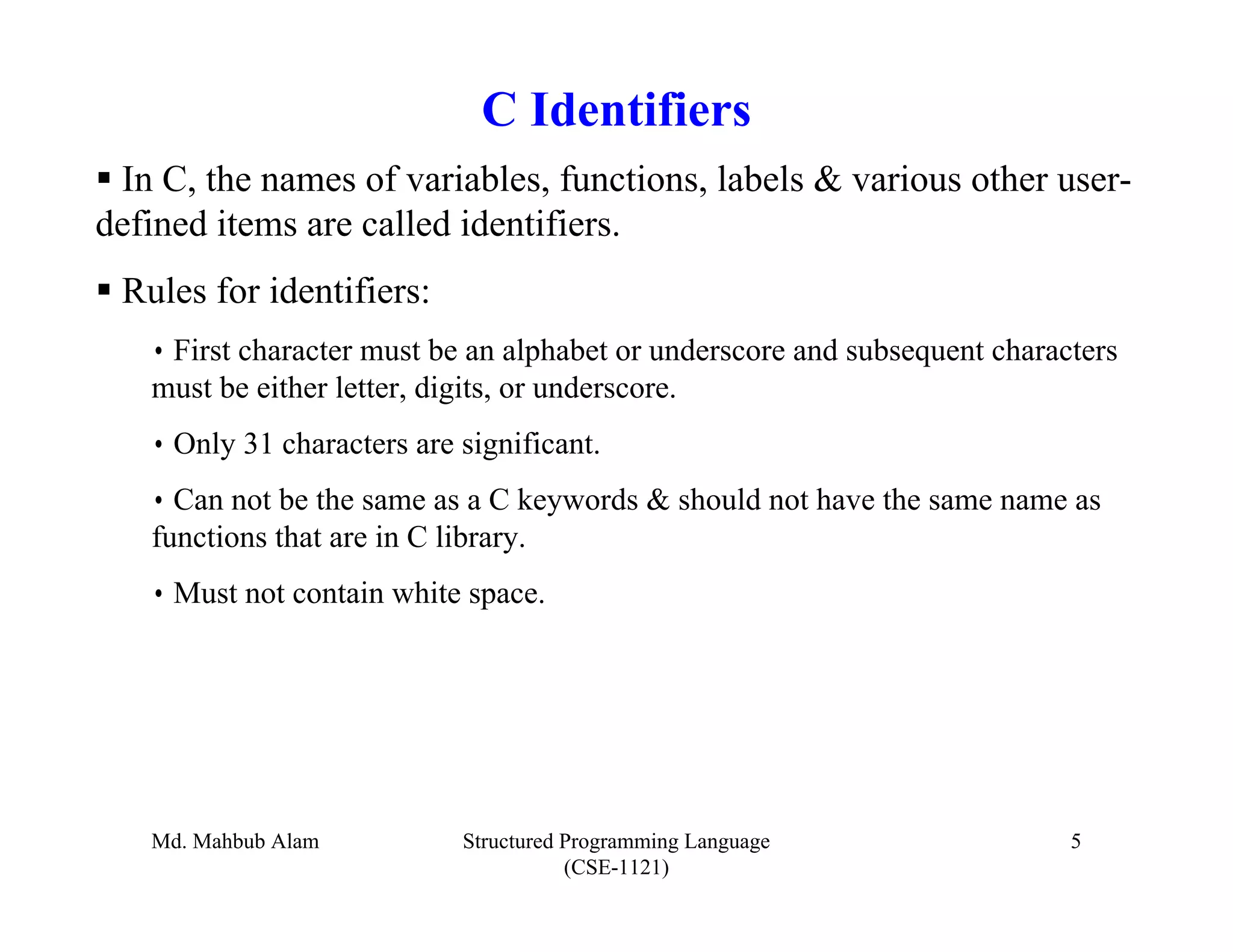
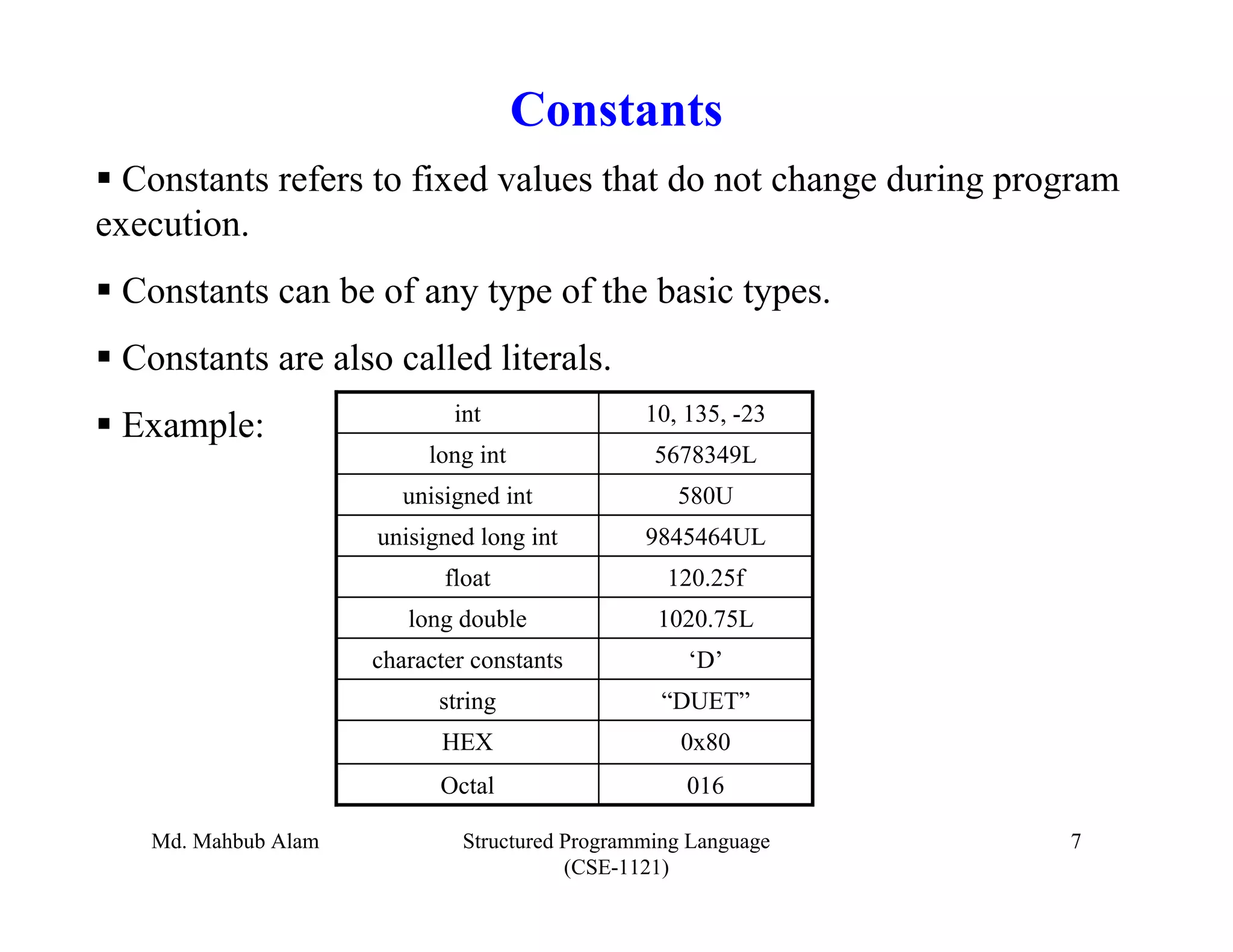
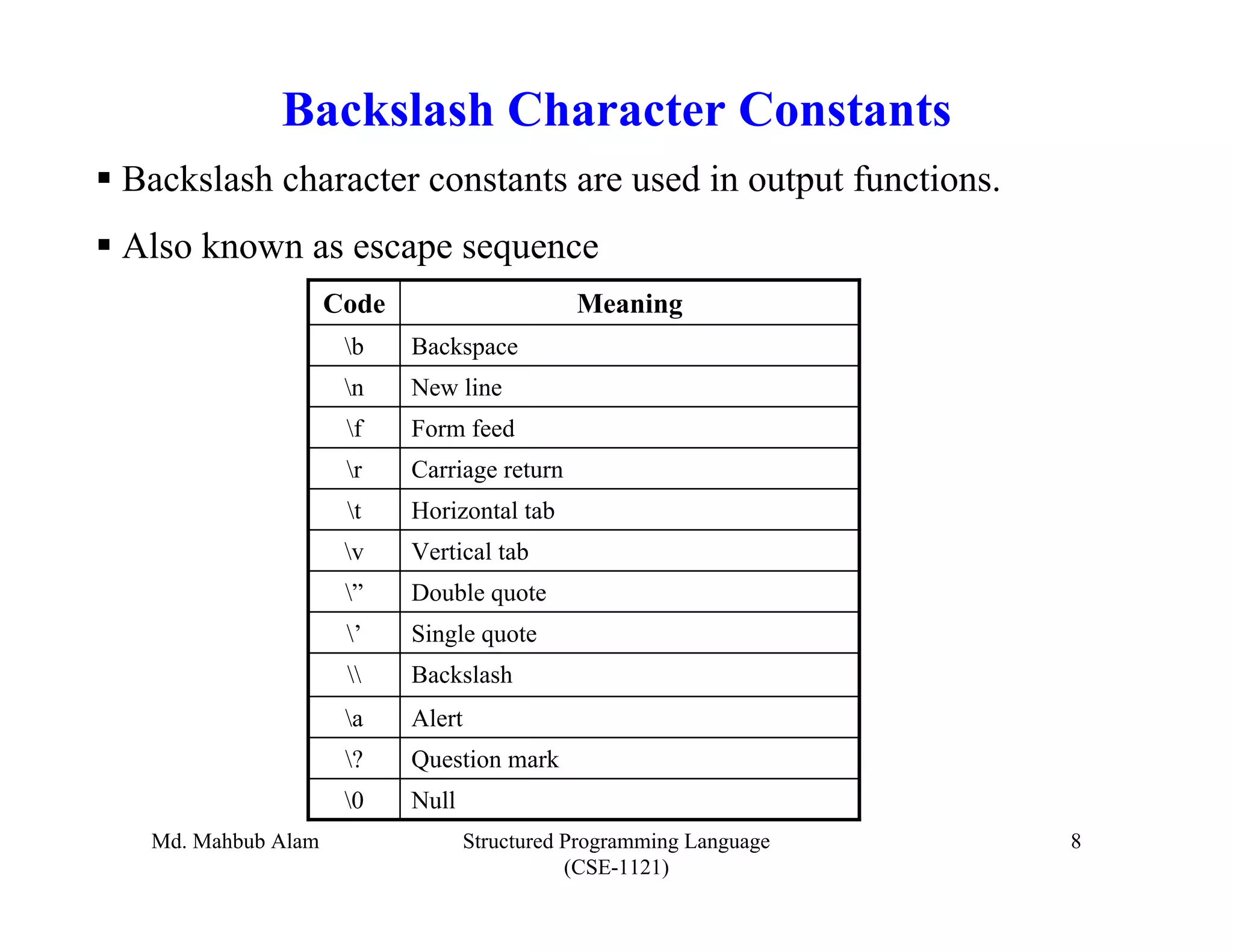
The document outlines key concepts in C programming including data types, tokens, keywords, identifiers, constants, variables, and scopes. It discusses the five fundamental data types in C (integer, floating-point, double, character, void), tokens like keywords and identifiers, common keywords and their meanings, rules for identifiers, how variables are declared and initialized, what constants are (fixed values that don't change), and the four scopes in C.
![C Tokens Token: Smallest individual units in C program are known as token. e.g. Keywords - int, break, for, struct etc Identifiers - count, amount etc Constants - 10, 5.5, -7.5 etc Strings - “DUET”, “1st Year” etc Operators - +, -, *, / Special Symbols - [] {} etc Md. Mahbub Alam Structured Programming Language 2 (CSE-1121)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture02constantsvariabledatatypes-101216005027-phpapp02/75/Lecture02-constants-variable-data-types-2-2048.jpg)