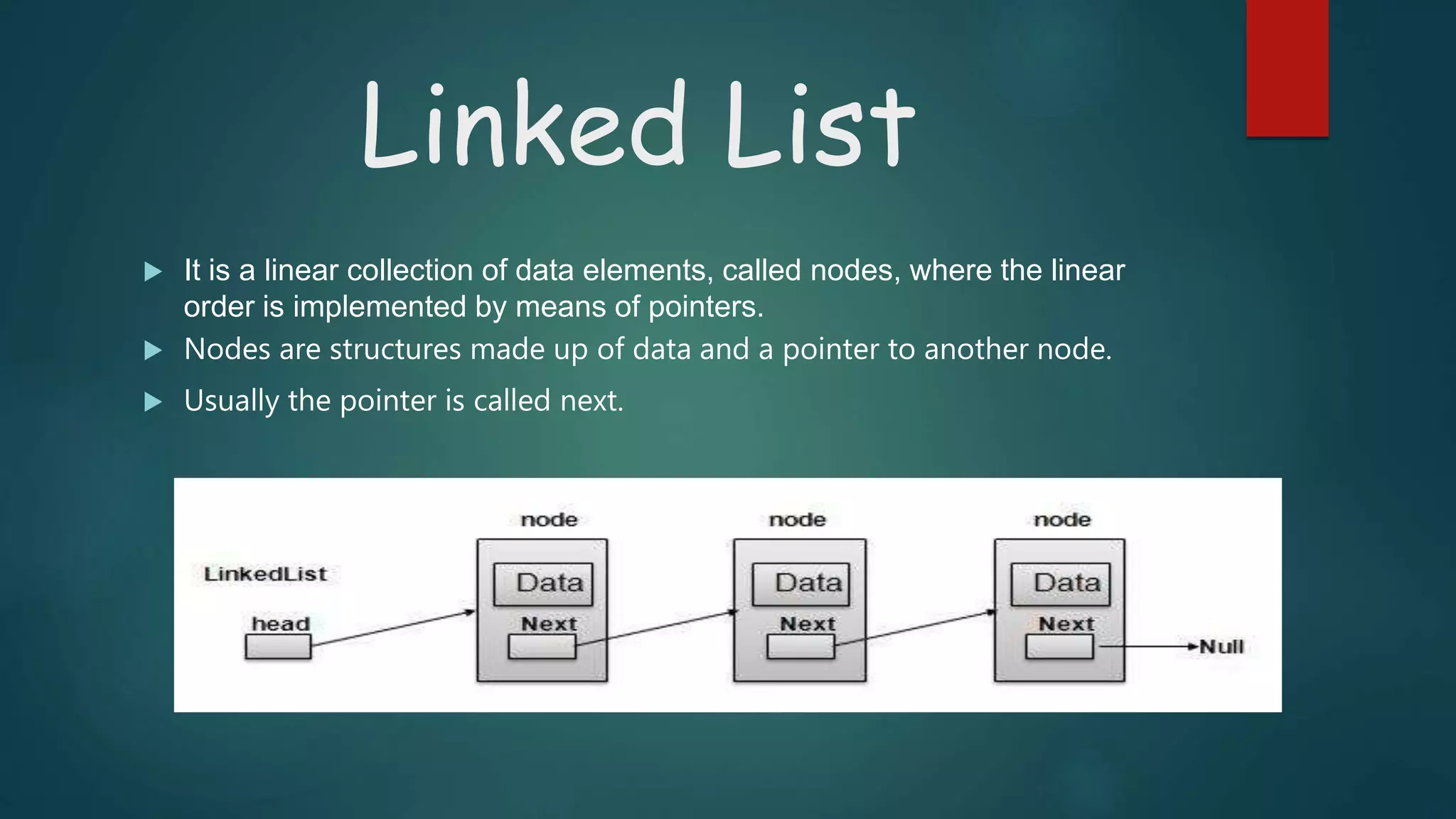
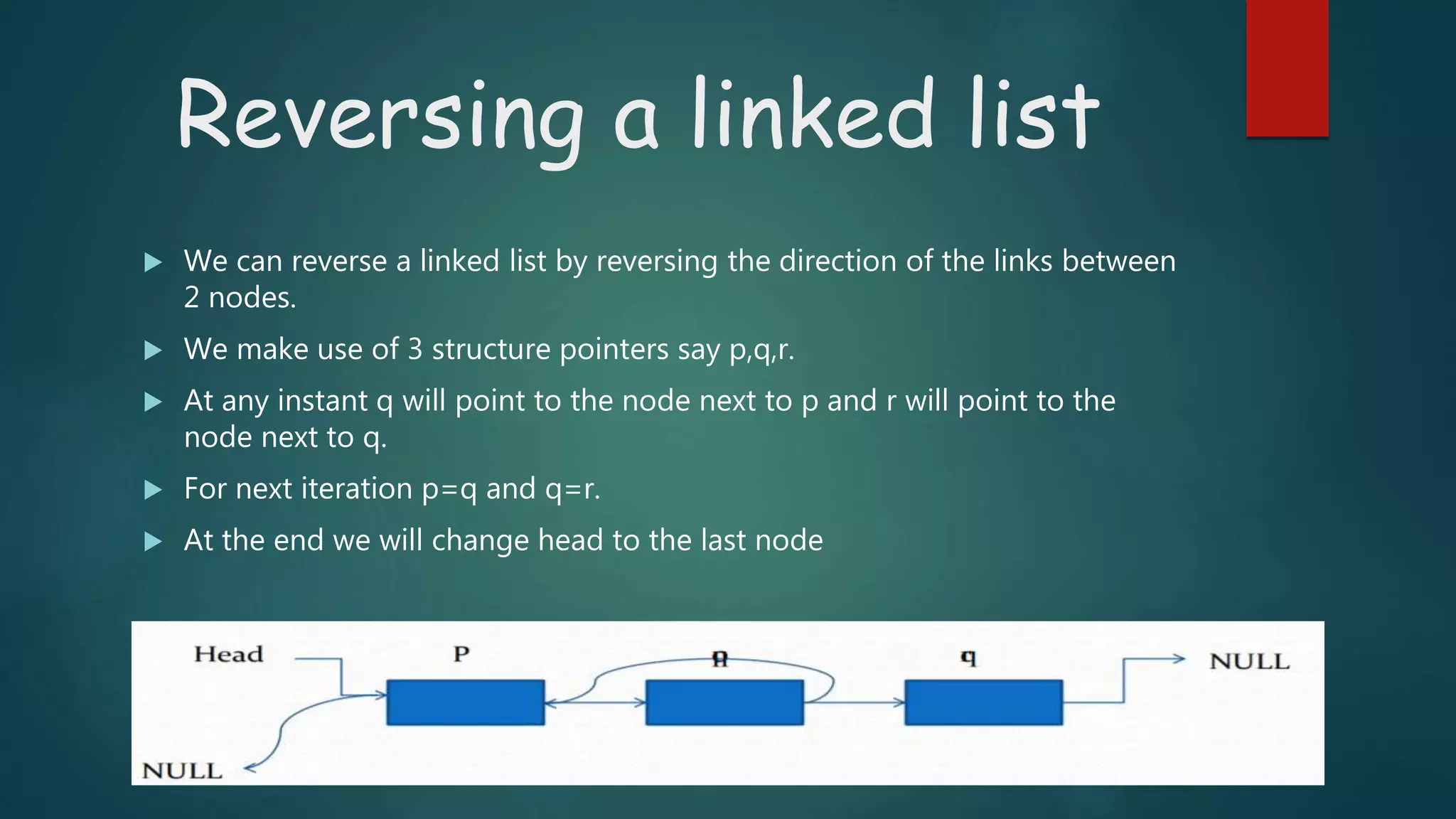
Linked lists are linear data structures where each element (called nodes) consists of data and a pointer to the next node. Nodes are dynamically allocated in memory. There are three types of linked lists: singly linked, doubly linked, and circular linked. Singly linked lists contain nodes with a data field and next pointer, with the last node pointing to null. Basic operations on linked lists include creating, inserting, deleting, searching, and reversing nodes. Doubly linked lists add a previous pointer to each node for bidirectional traversal. Circular linked lists connect the last and first nodes to form a loop.