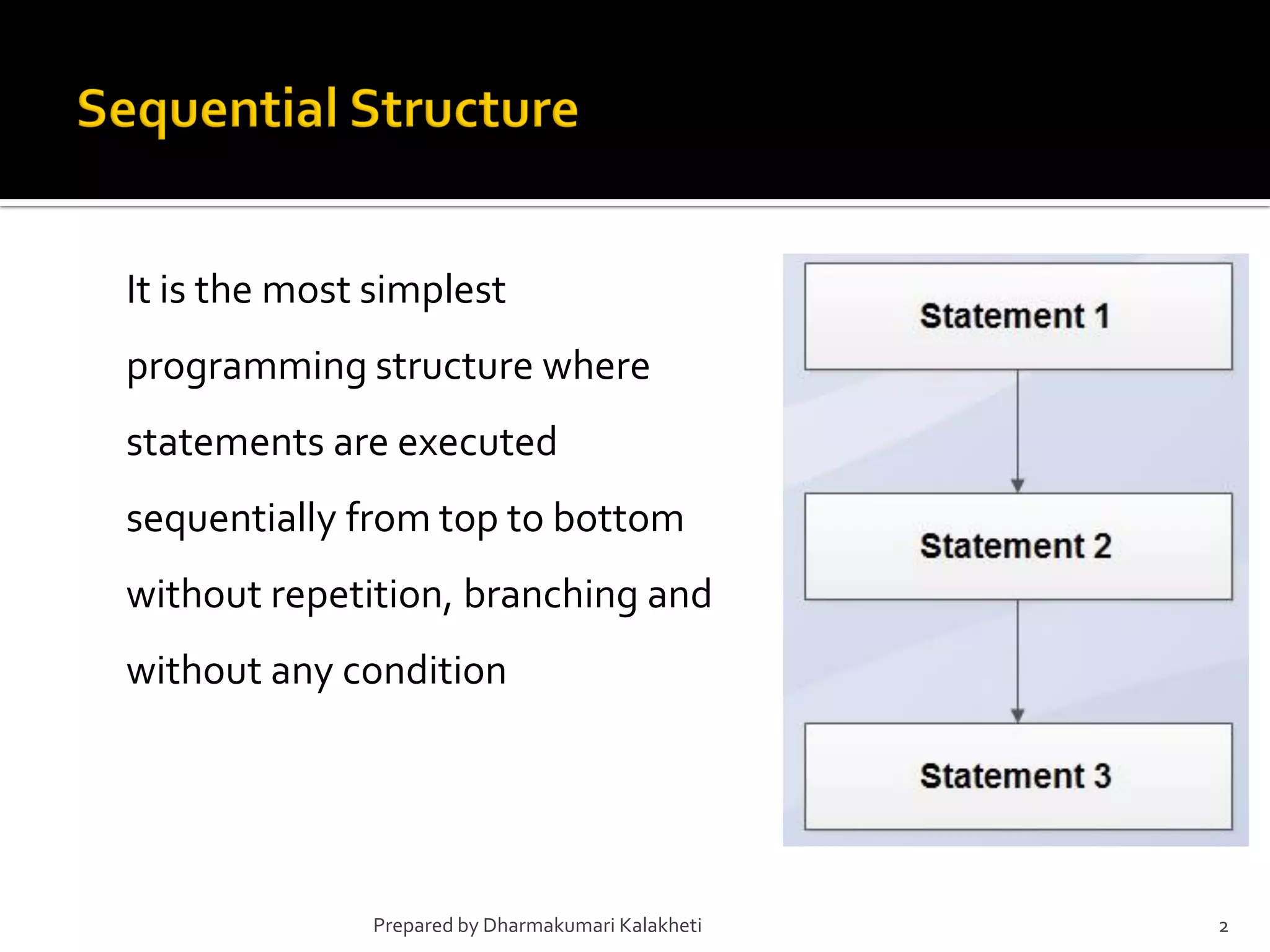
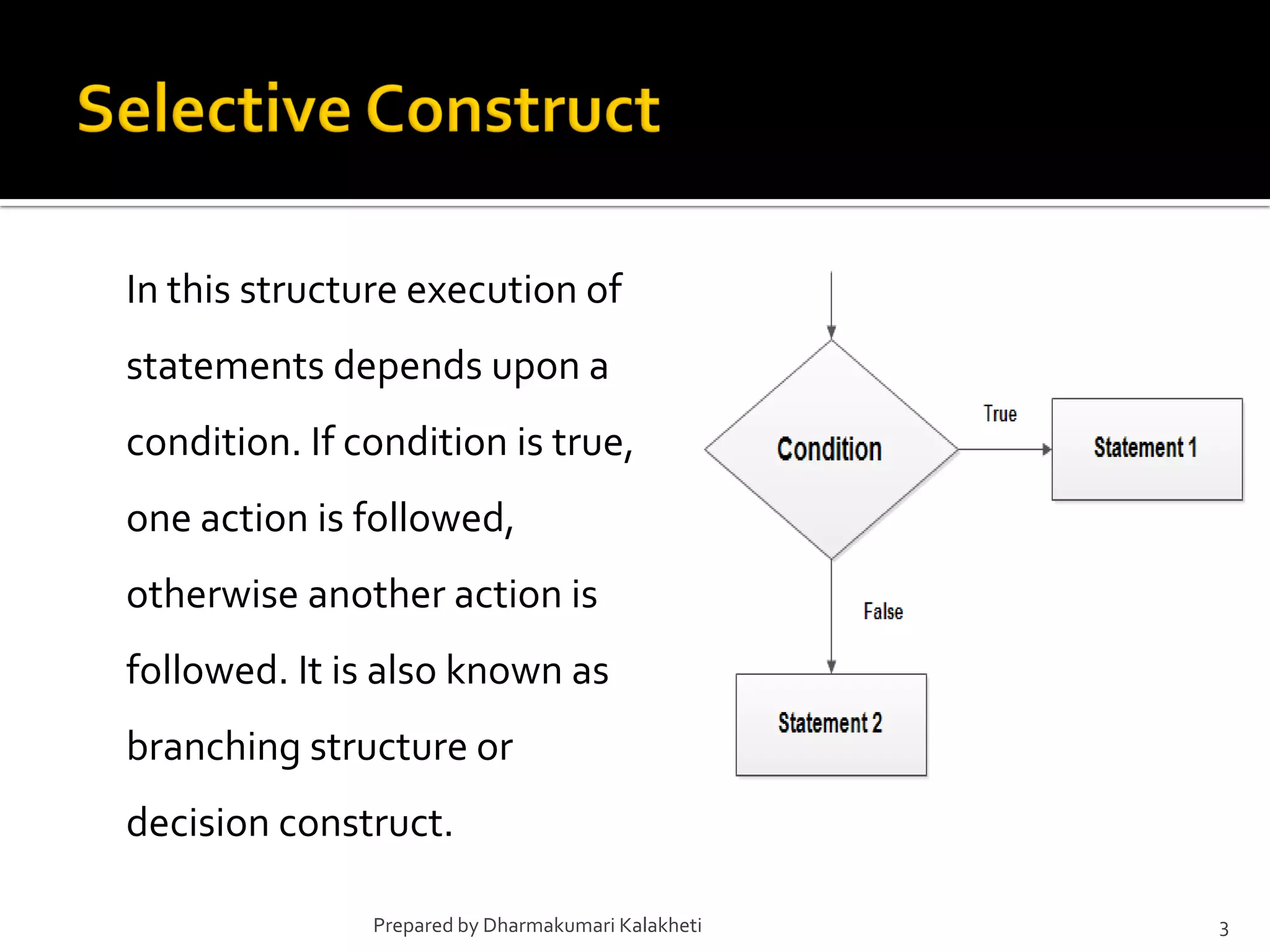
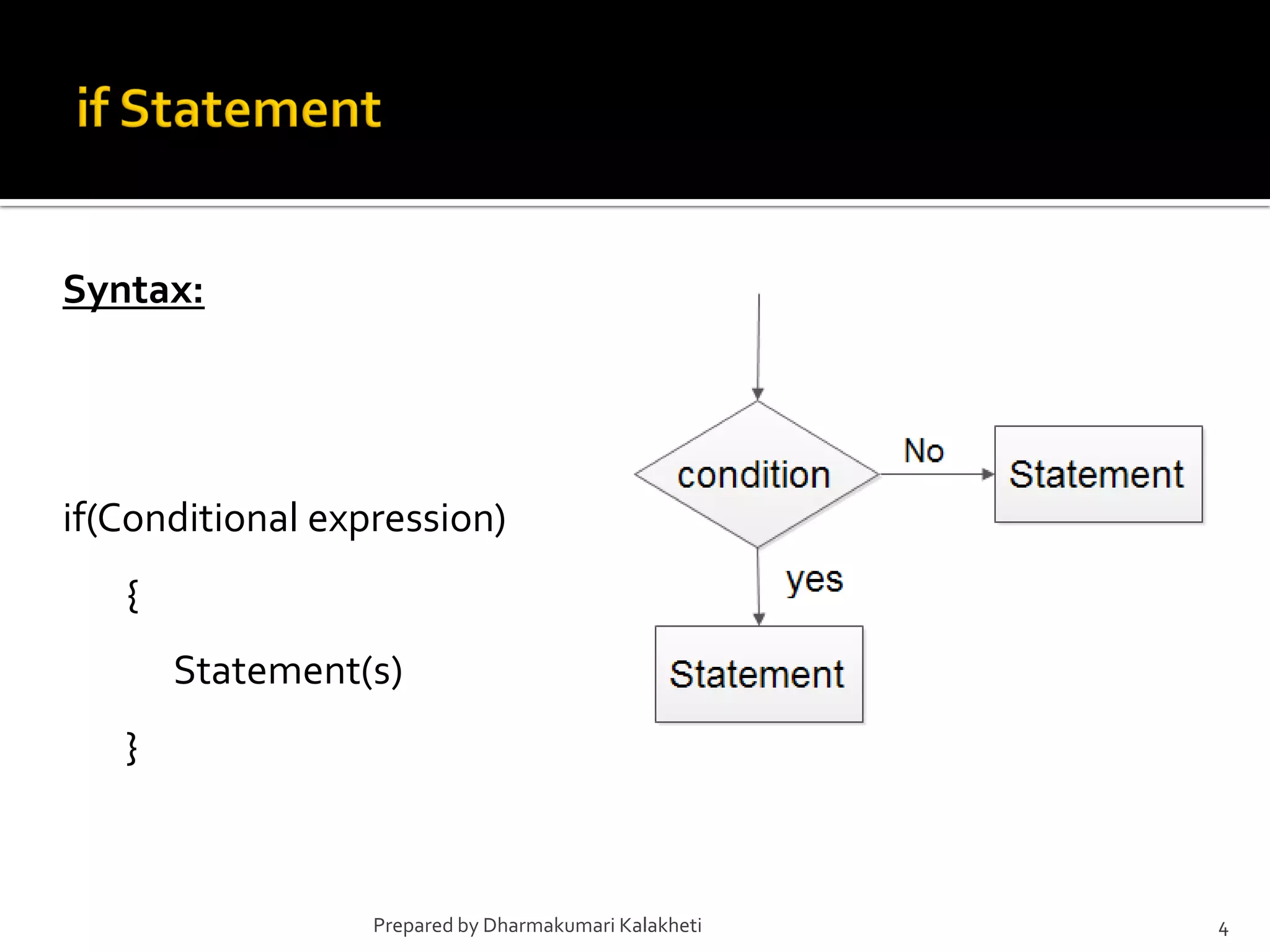
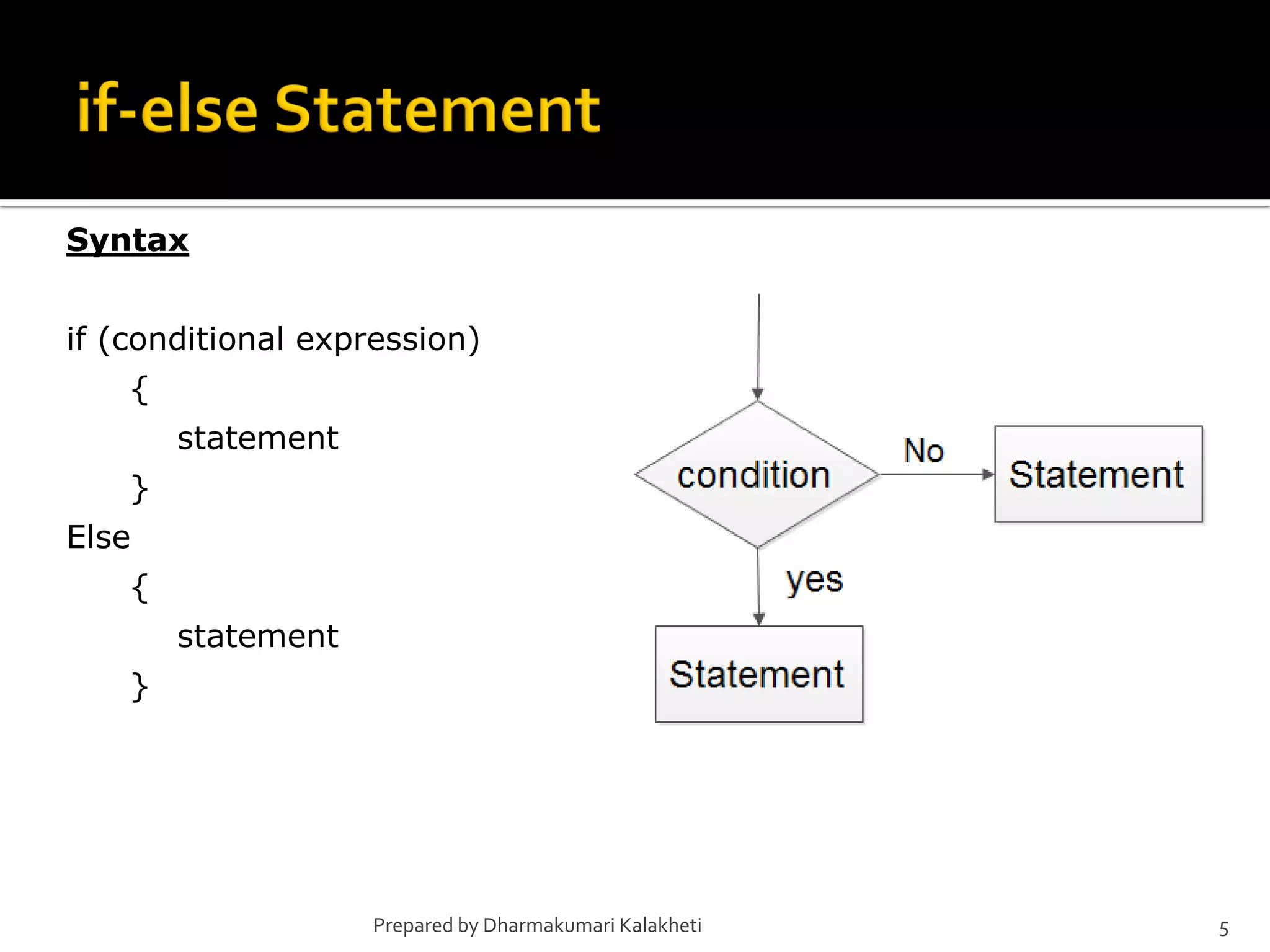
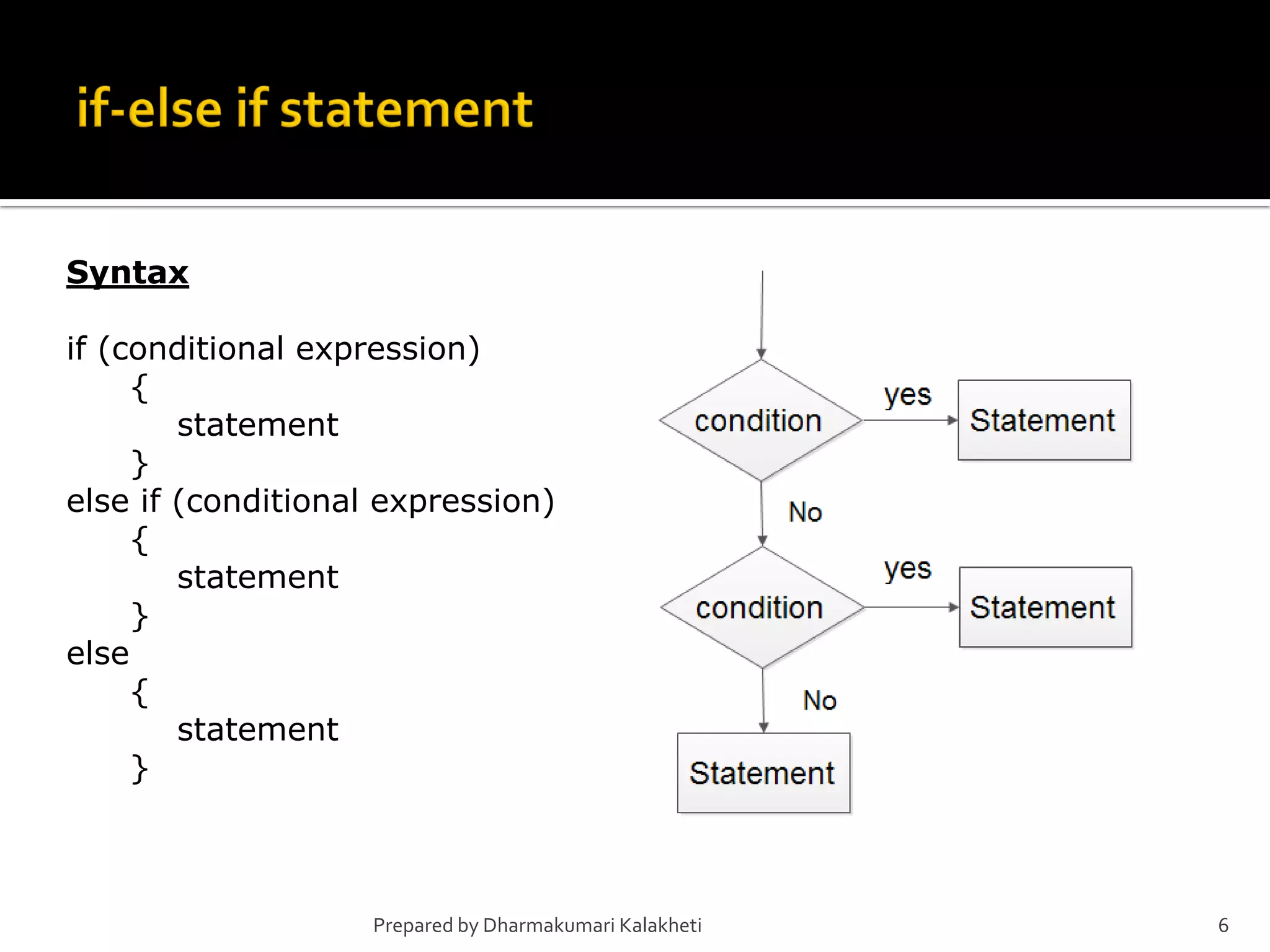
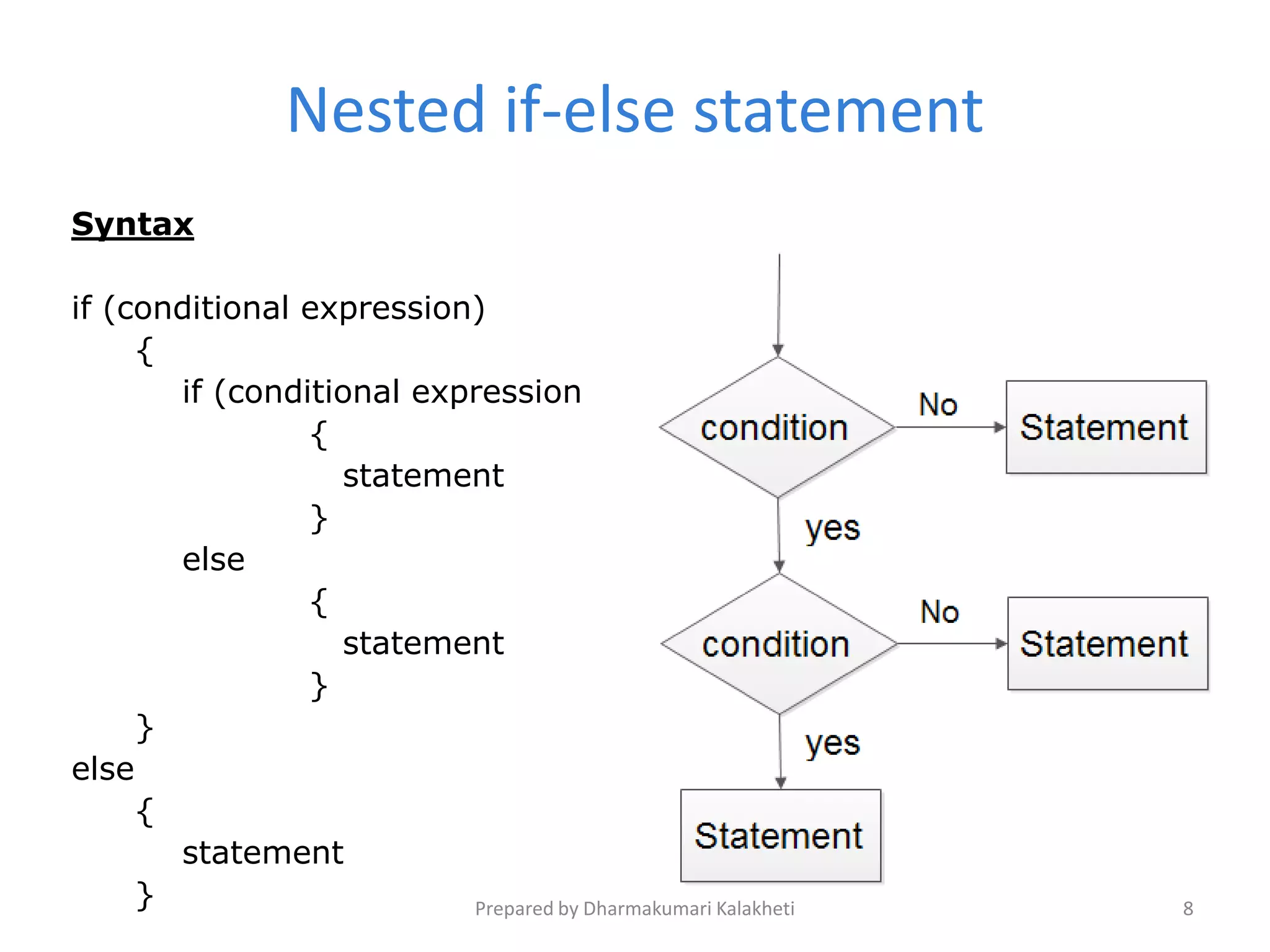
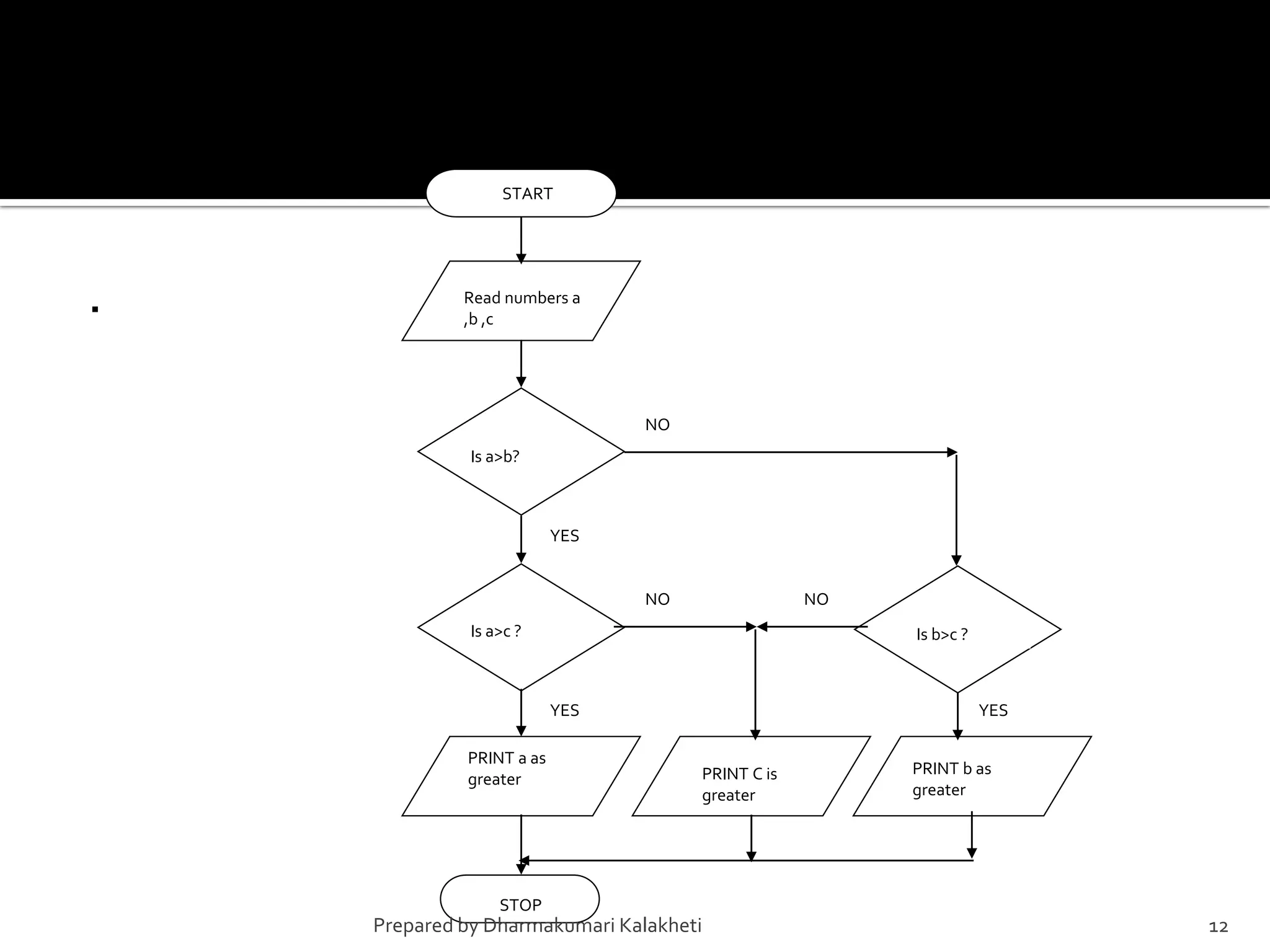
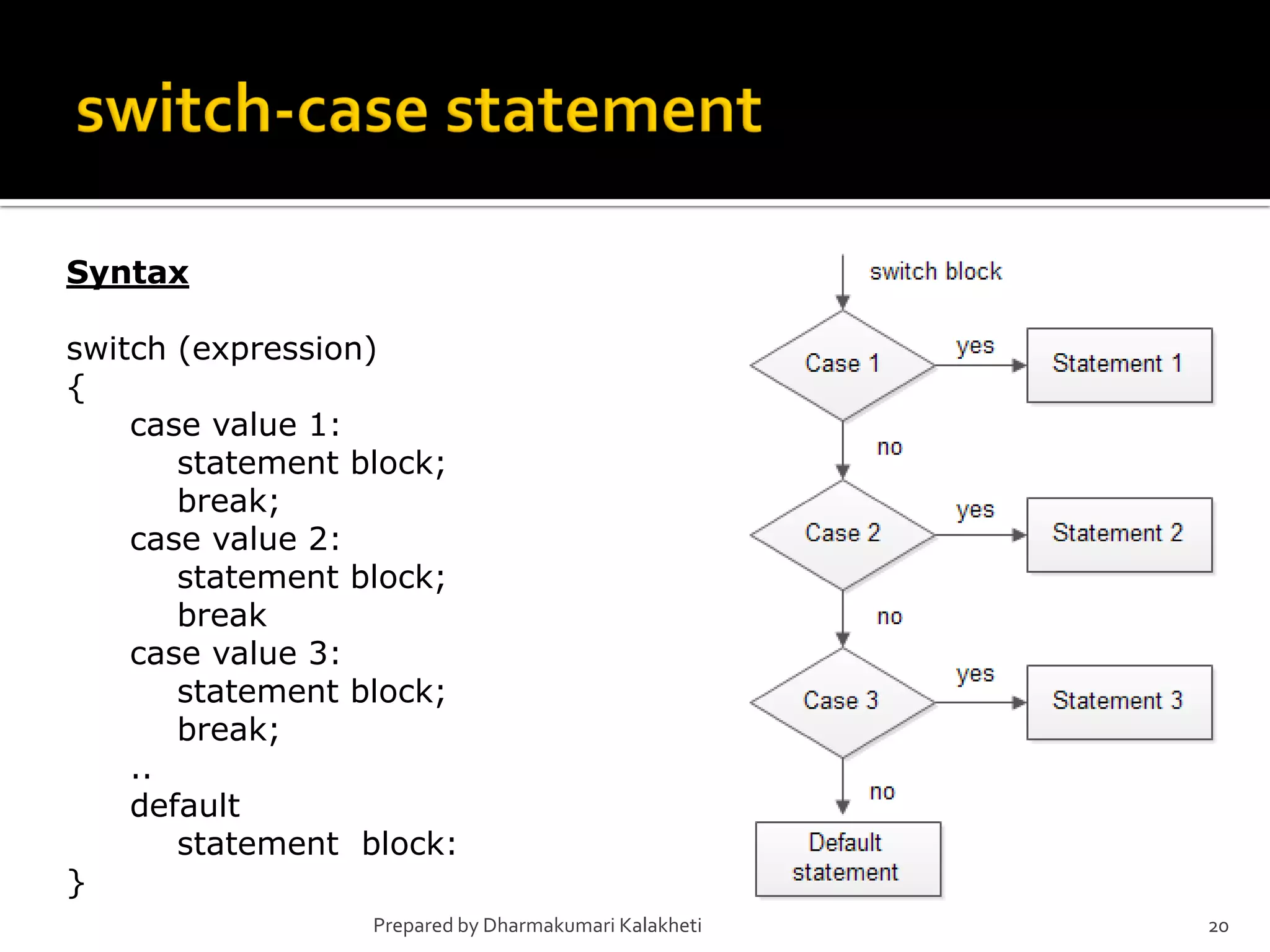
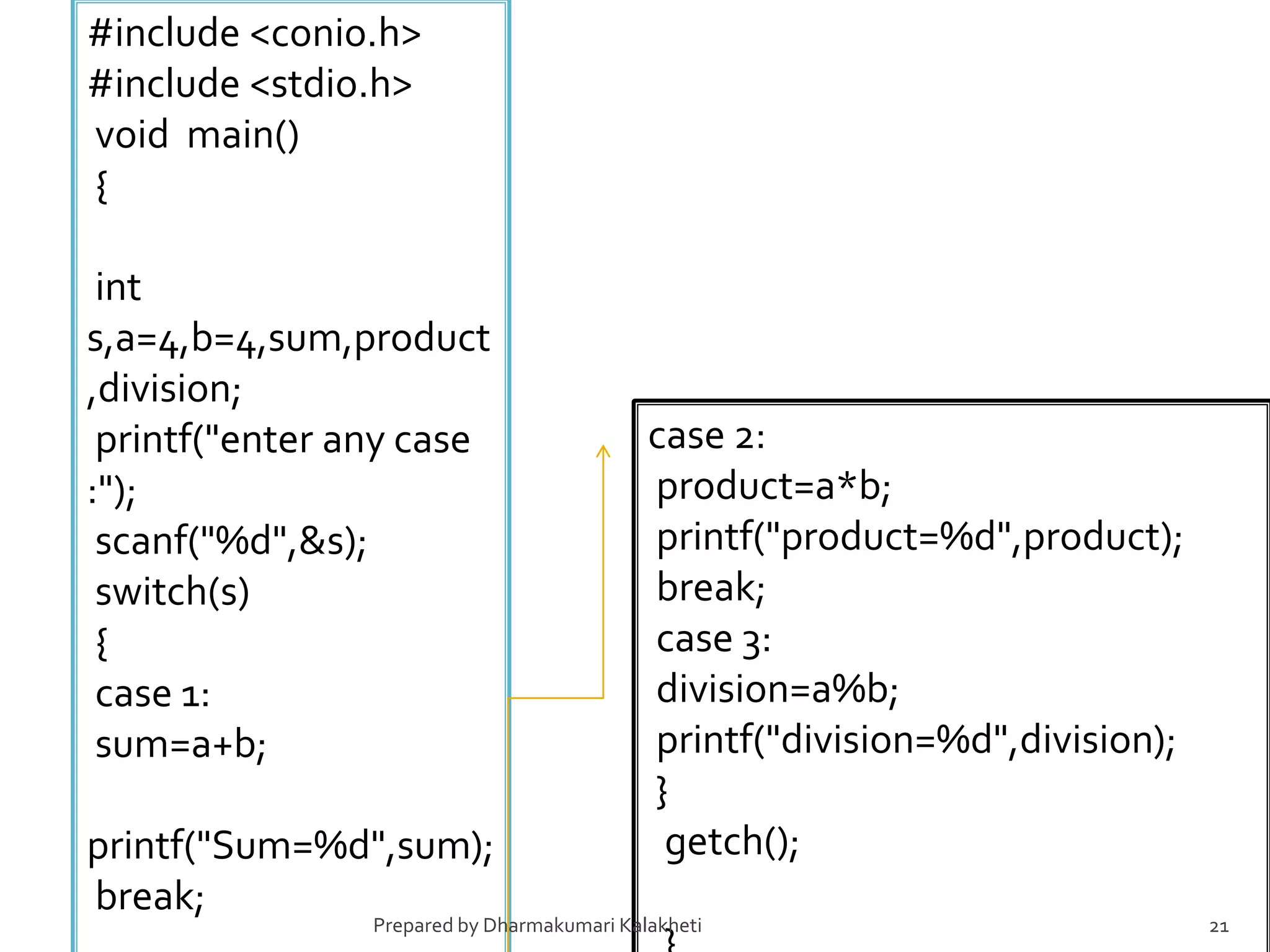
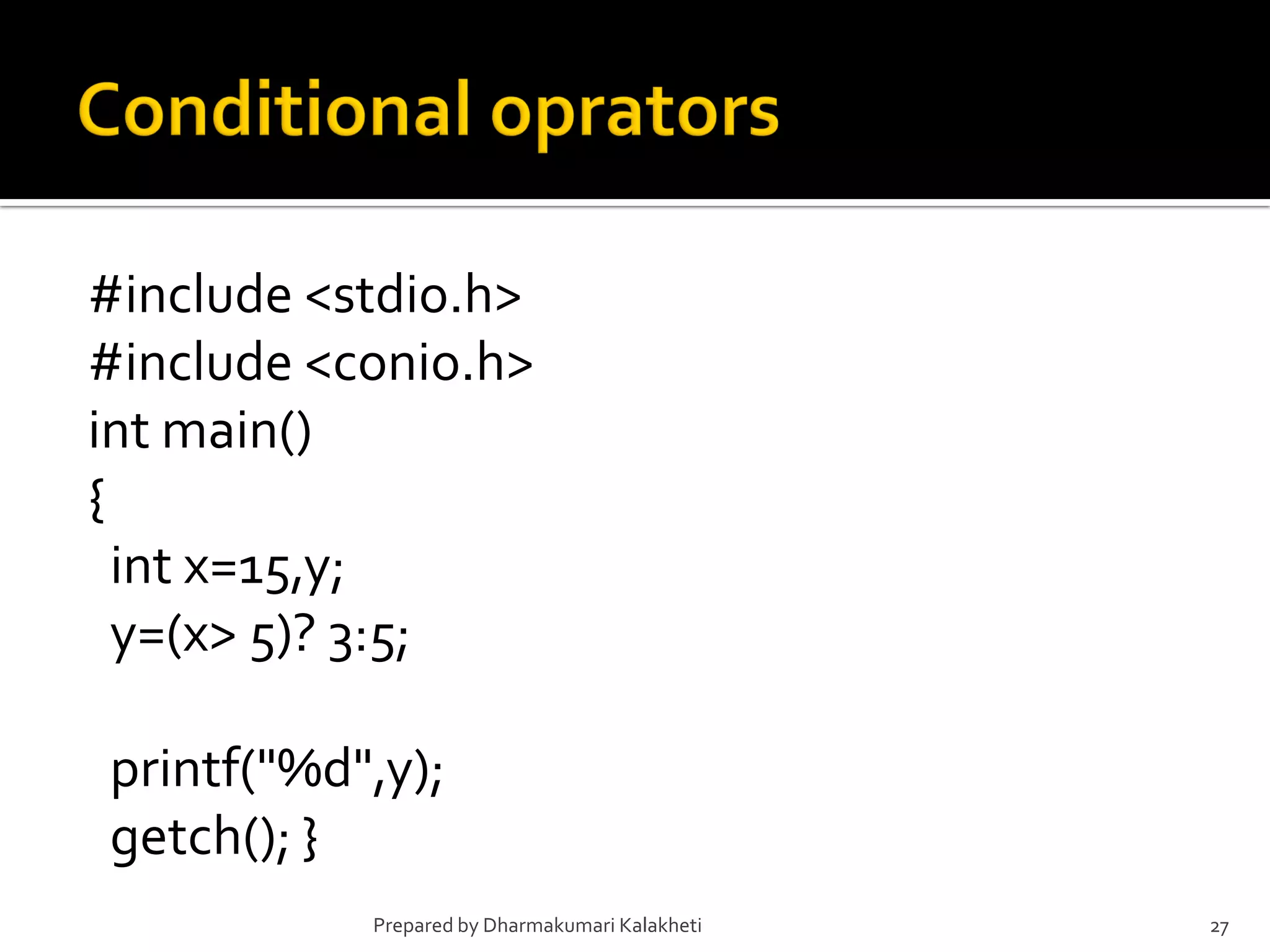
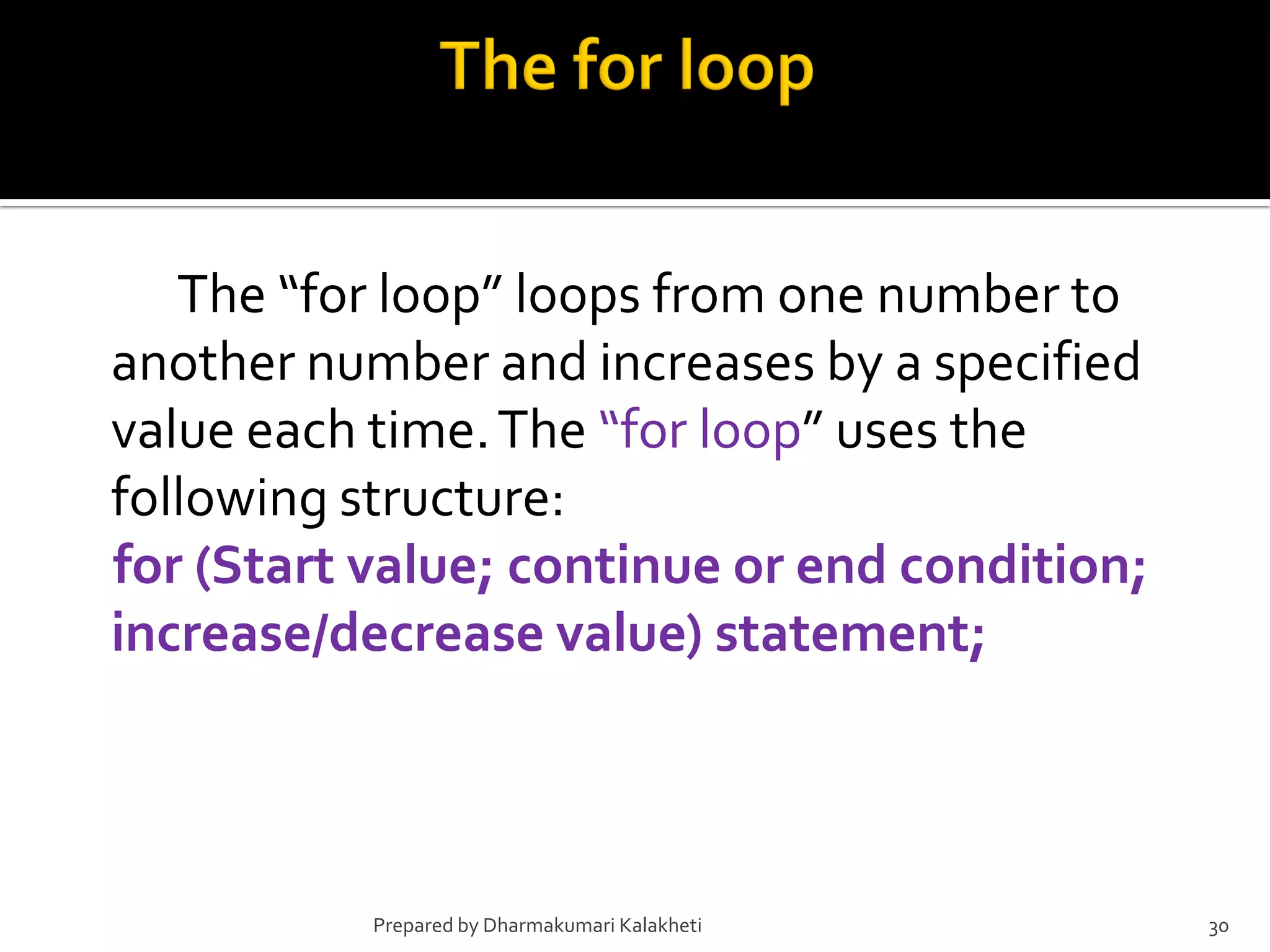
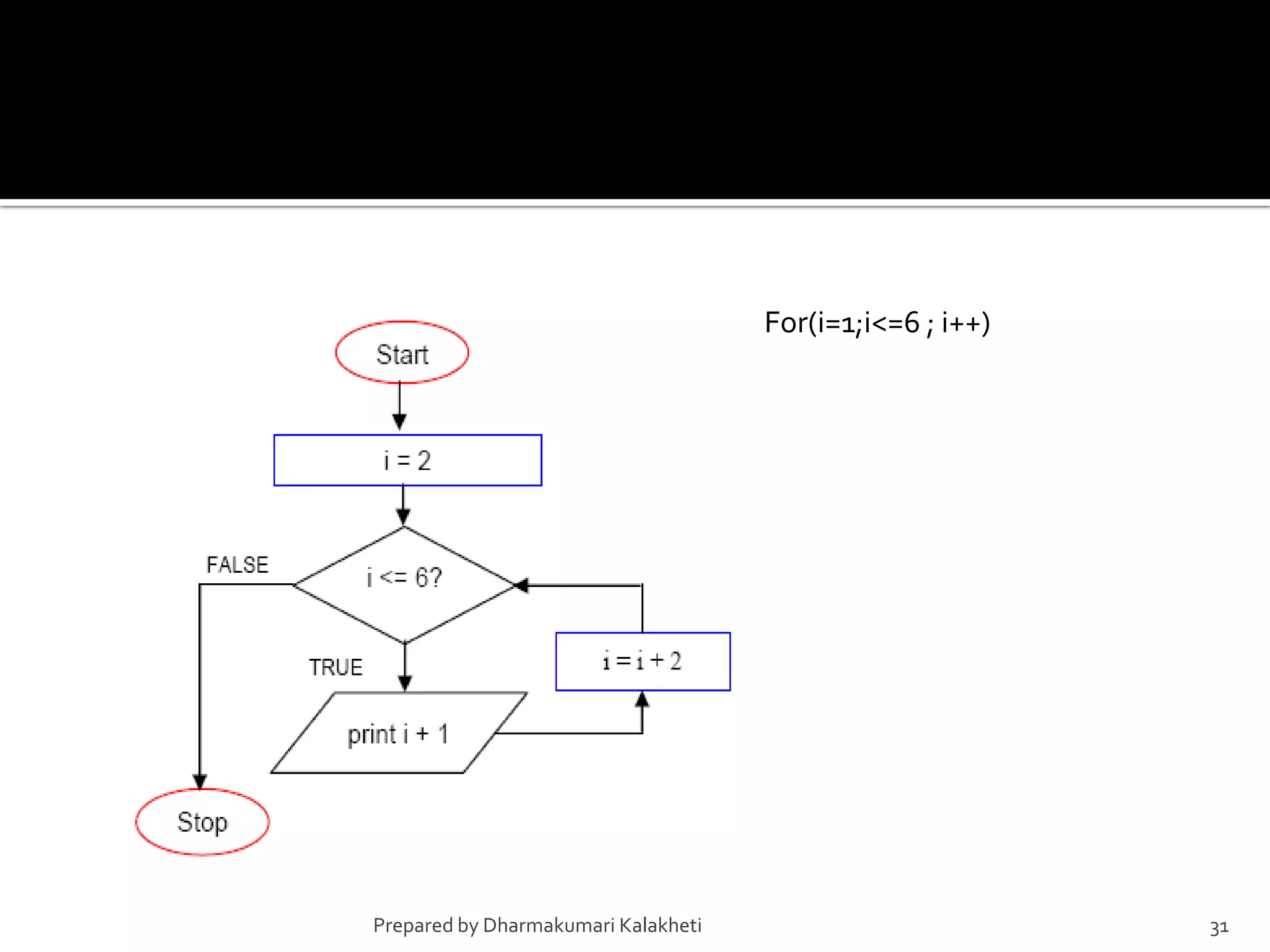
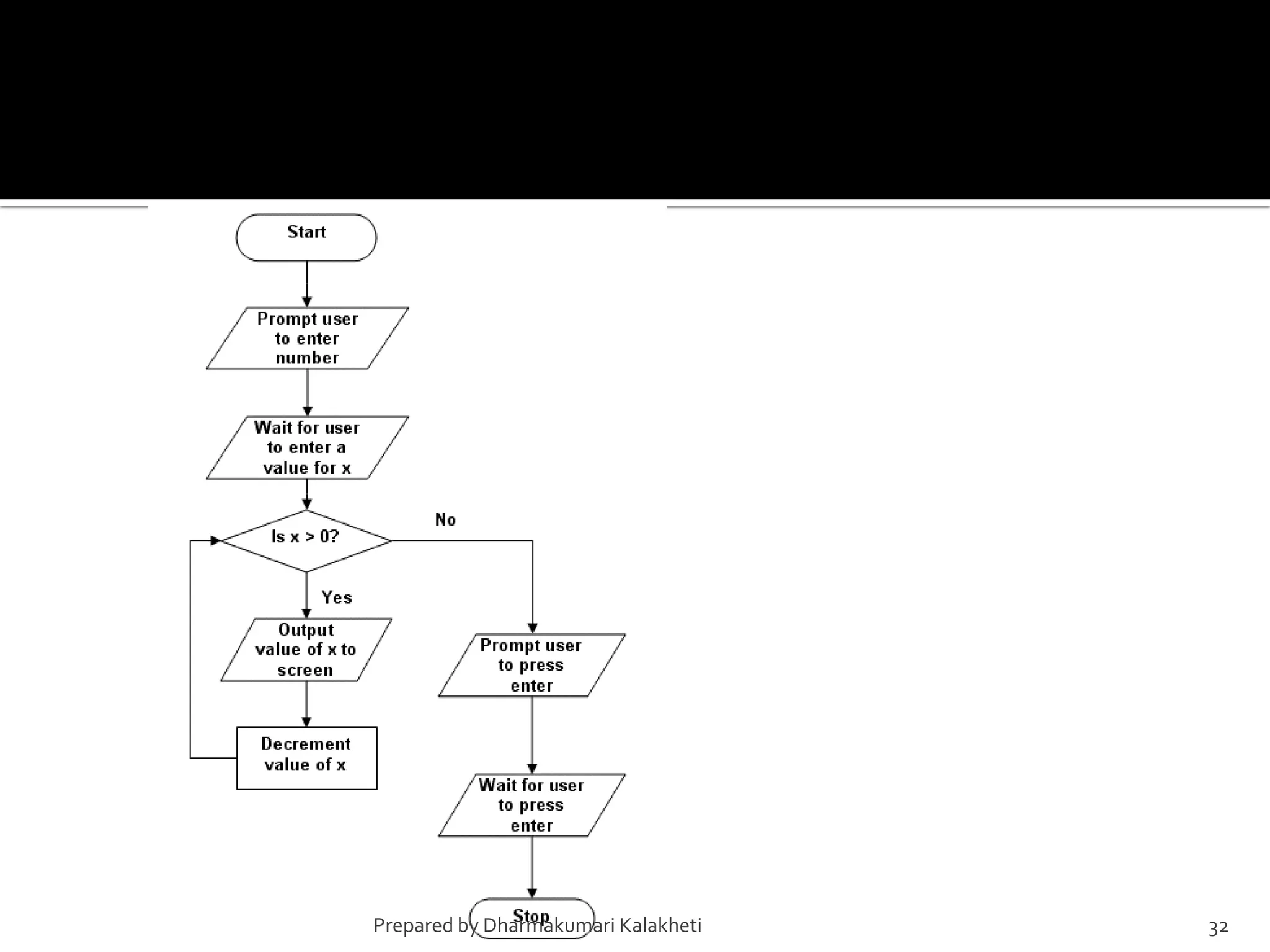
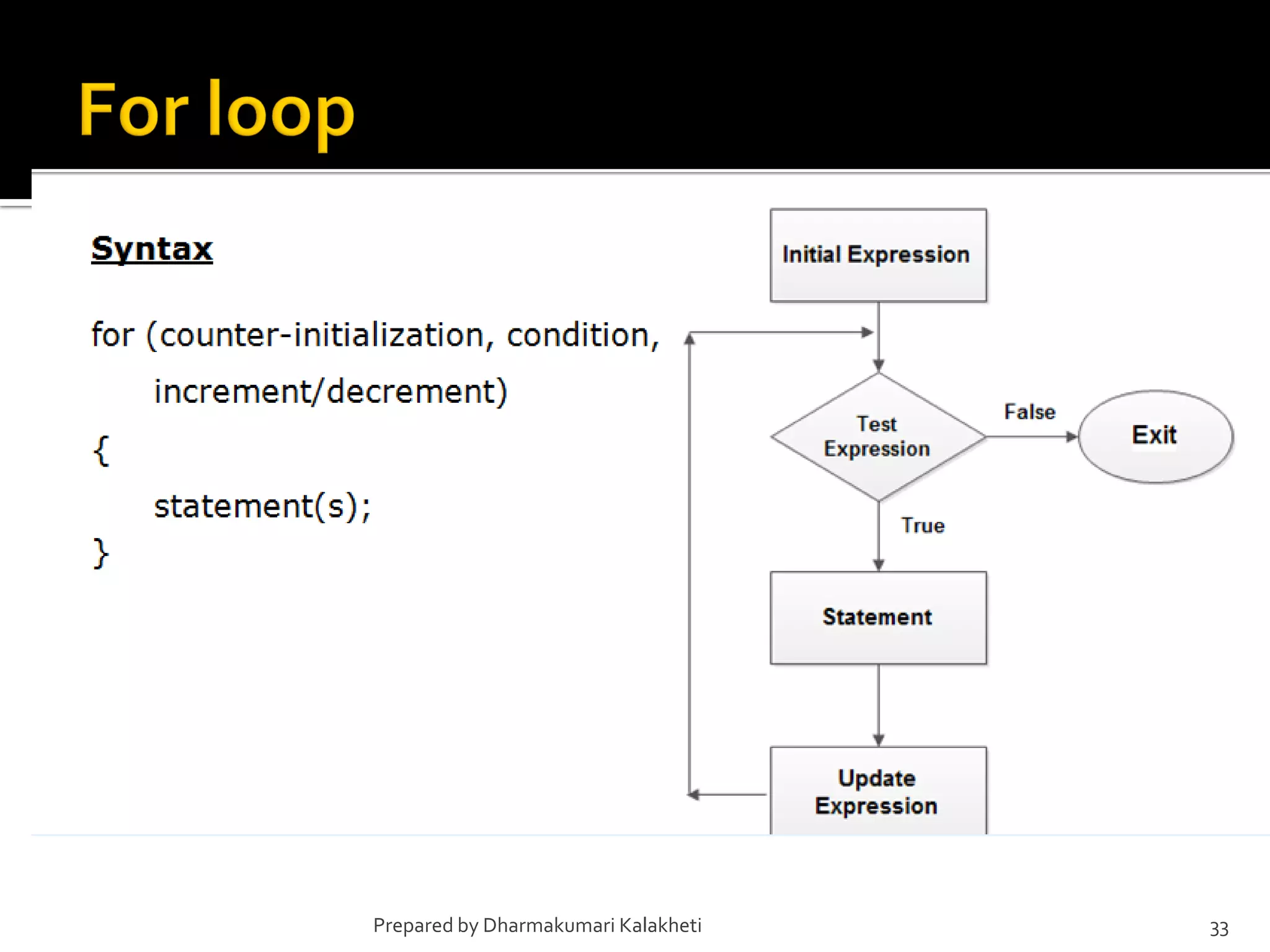
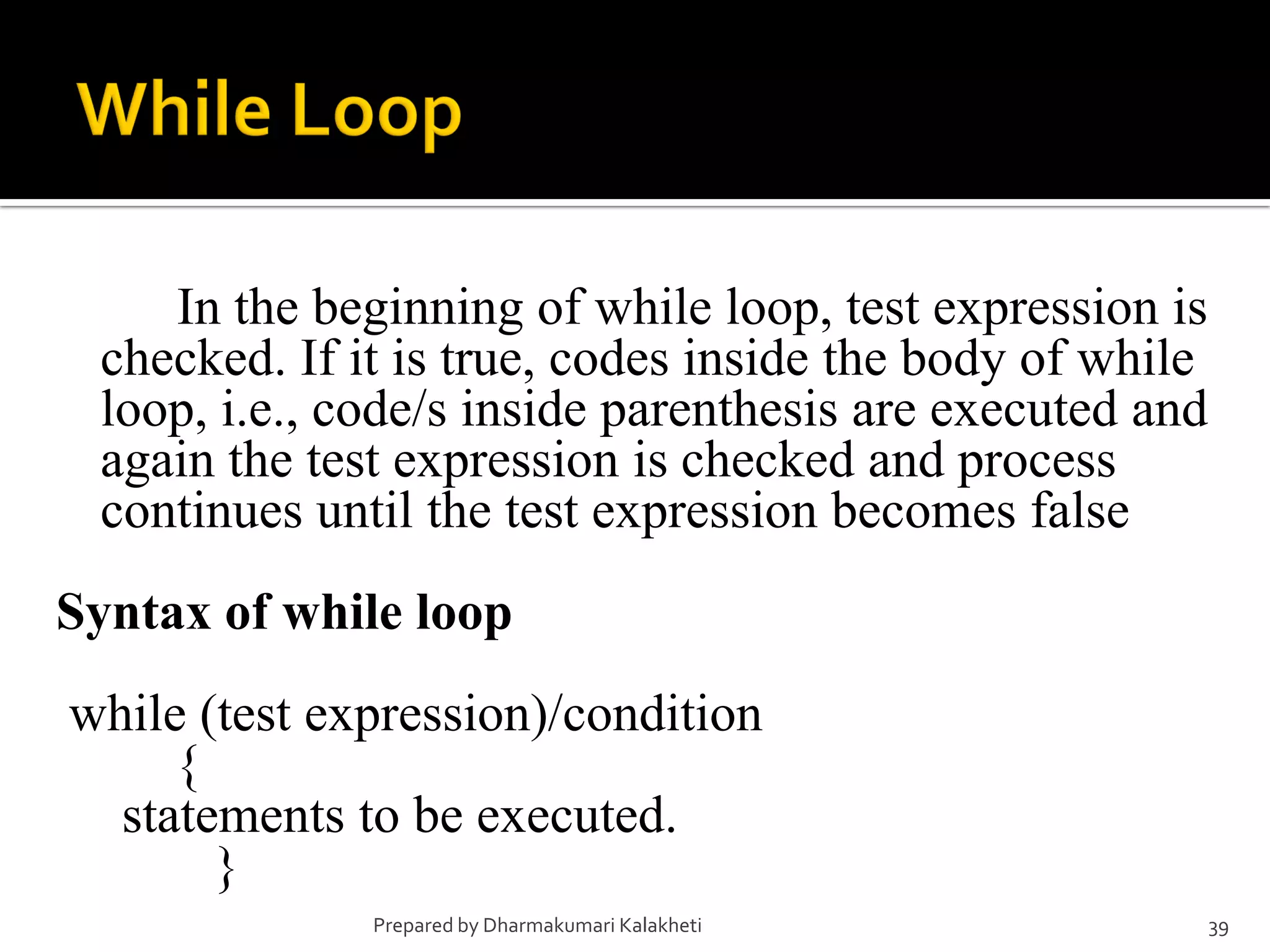
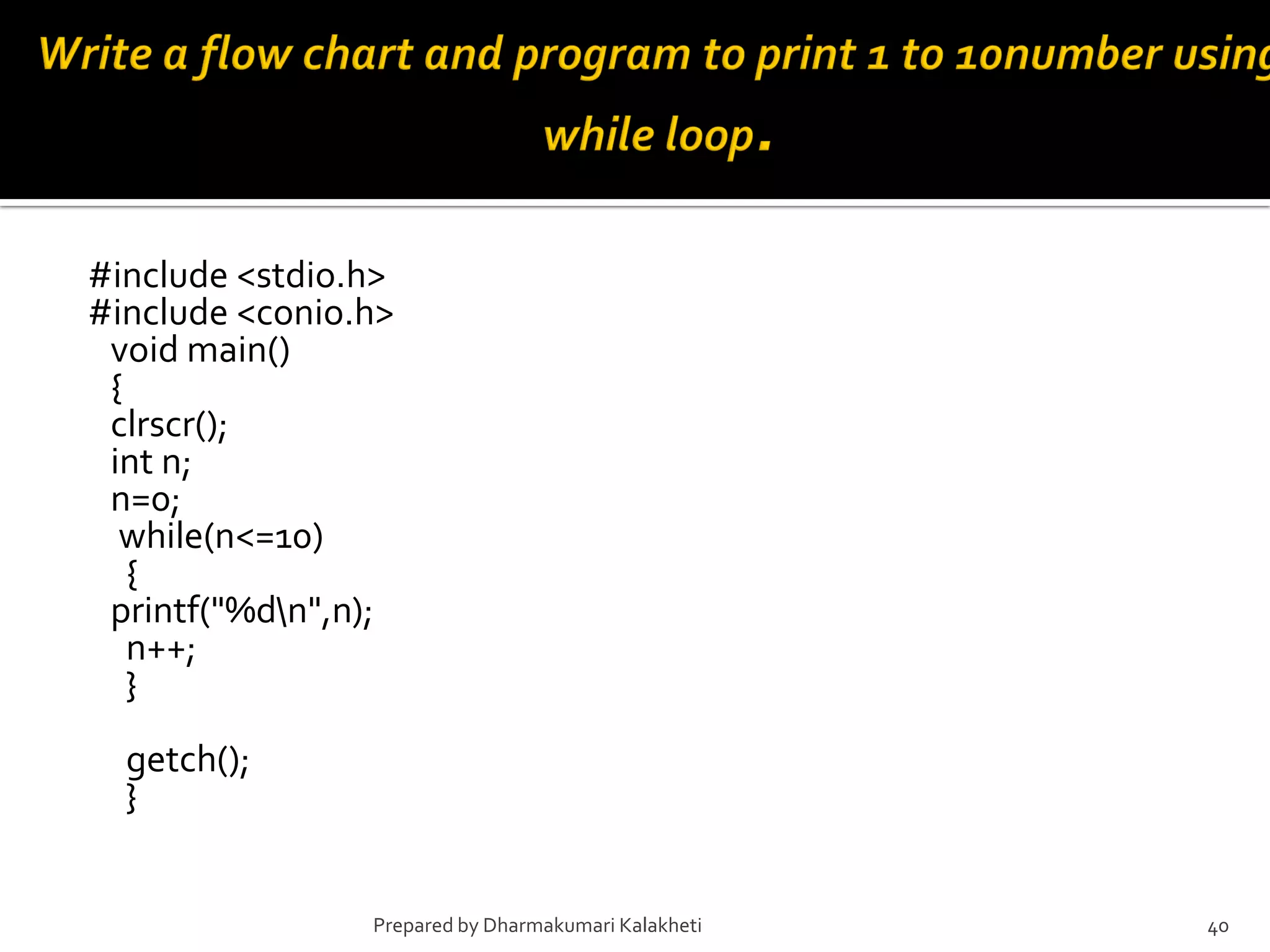
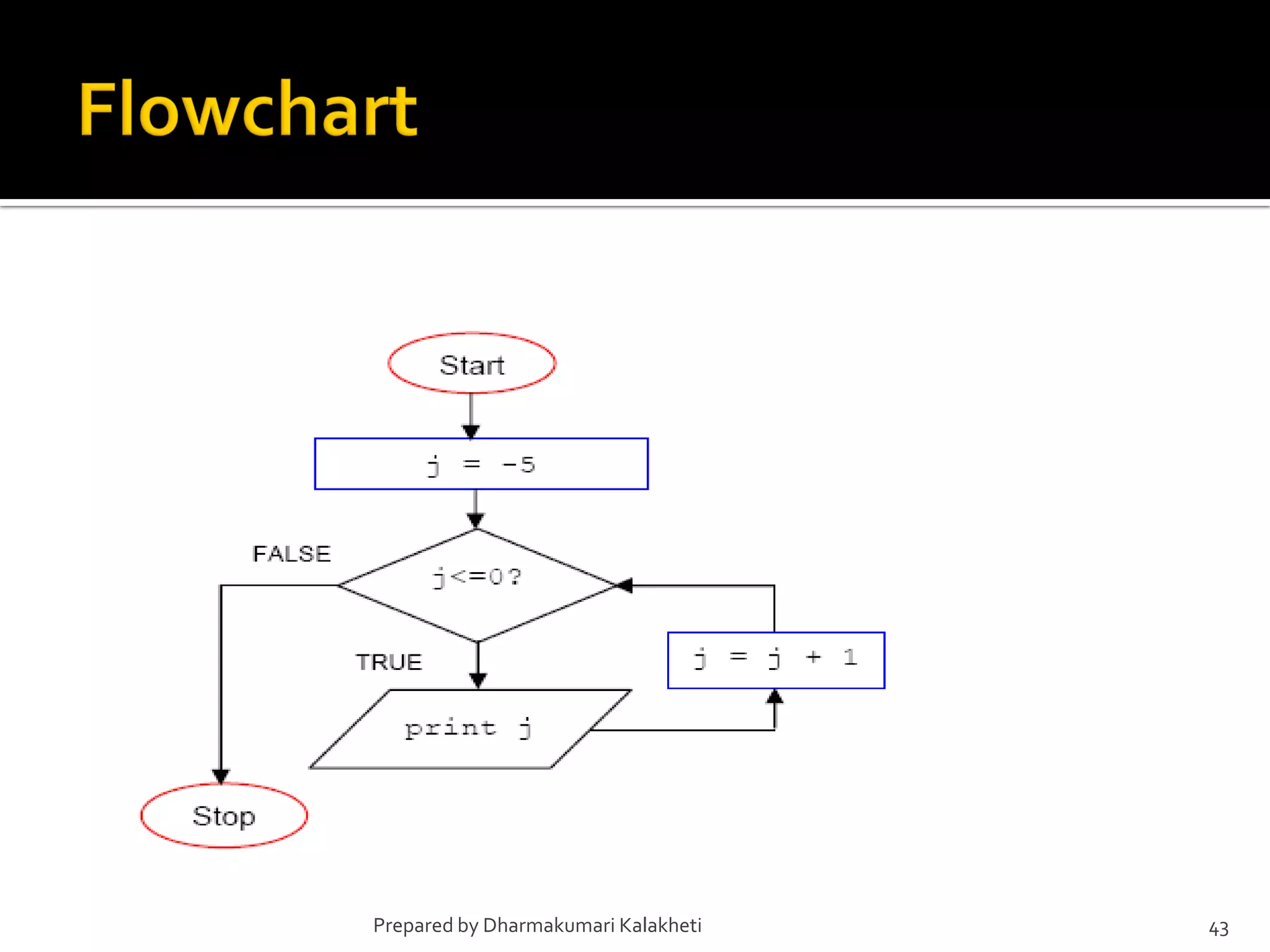
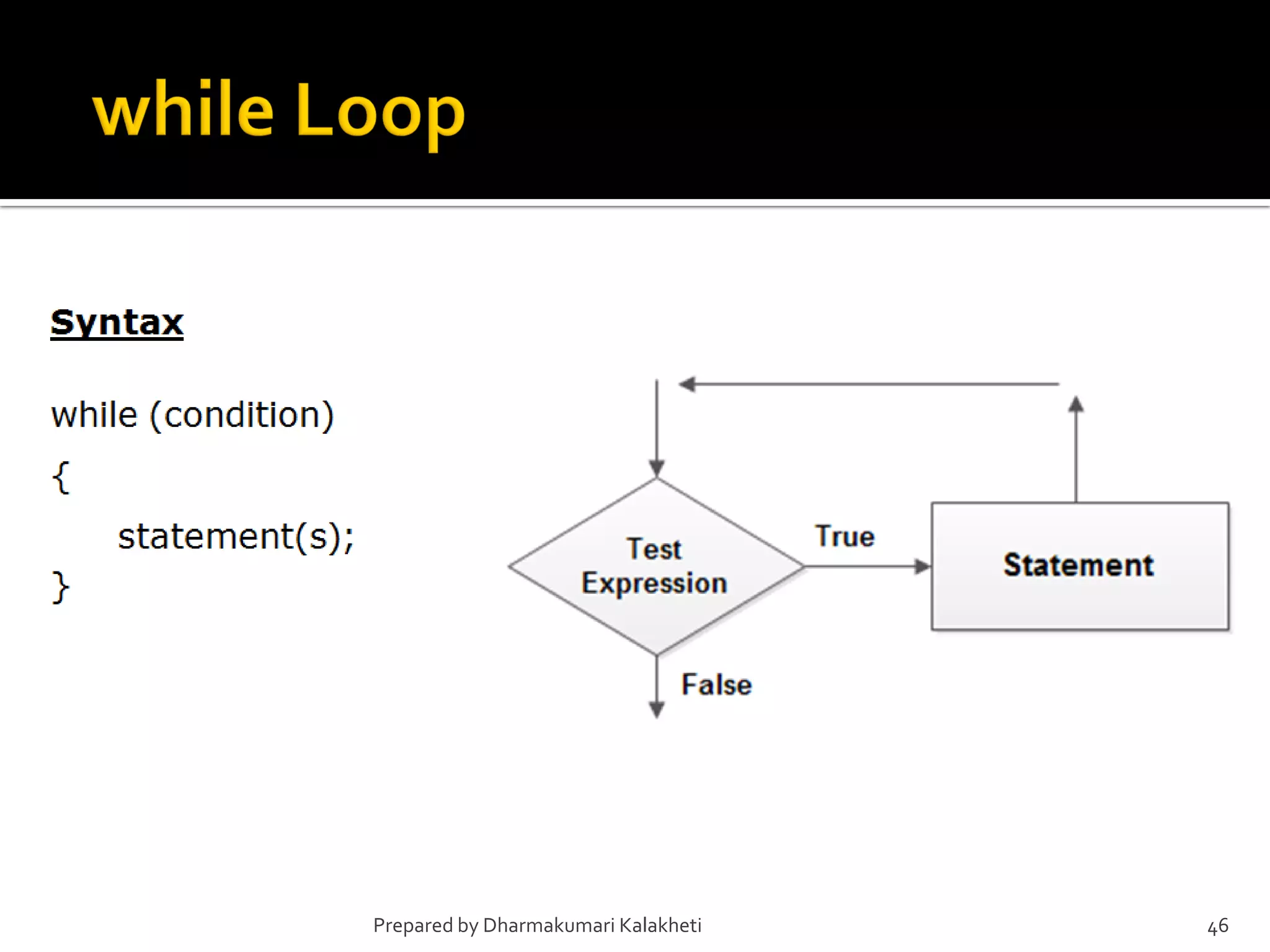
The document outlines various control structures in programming, including sequential, selection, and loop structures. It provides syntax examples and practical applications for conditional statements like if-else, switch-case, and loops such as for, while, and do-while. Additionally, it lists algorithms and sample programs to demonstrate concepts like finding maximum numbers, identifying even or odd numbers, and calculating conditions based on user input.