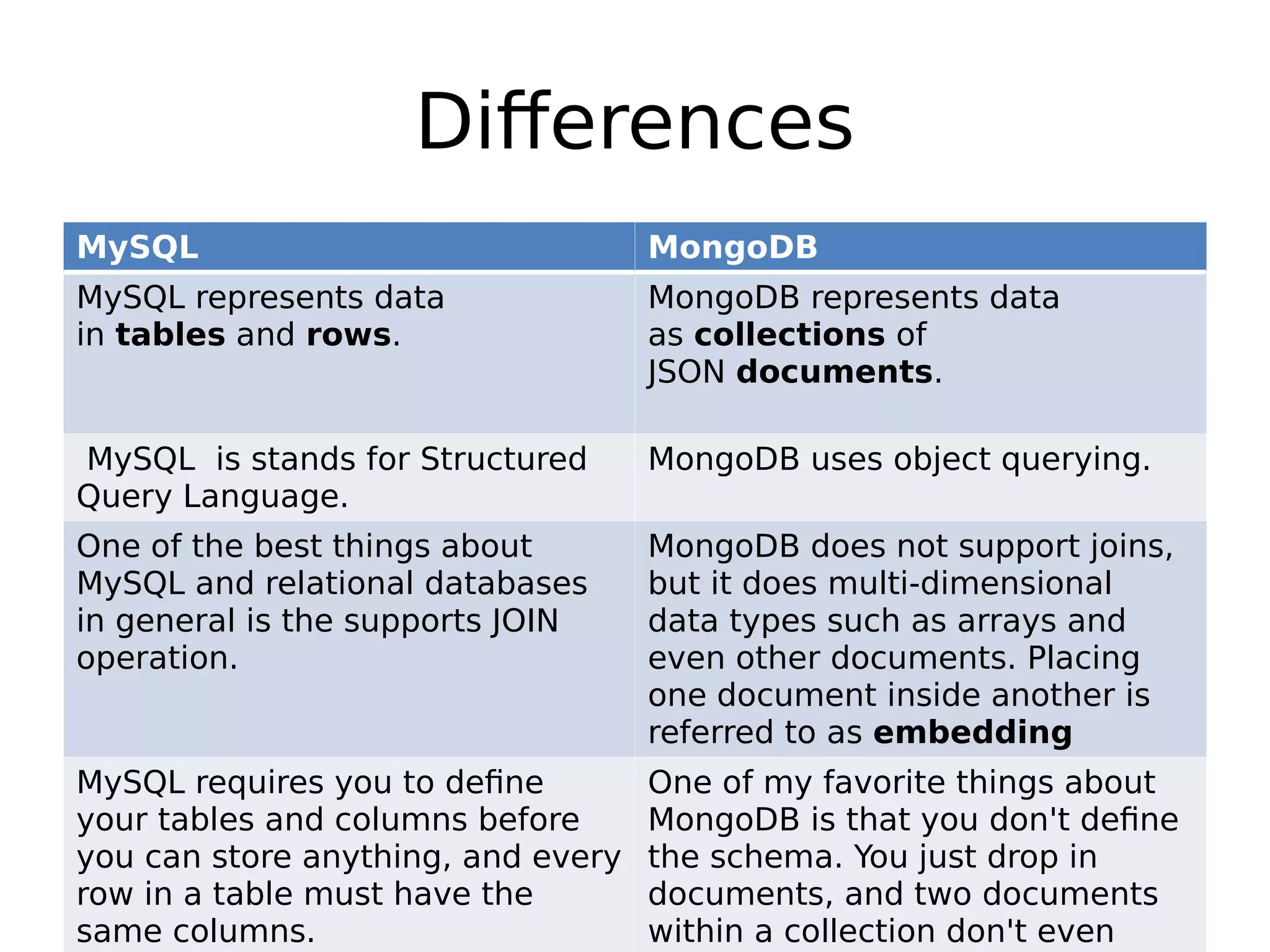
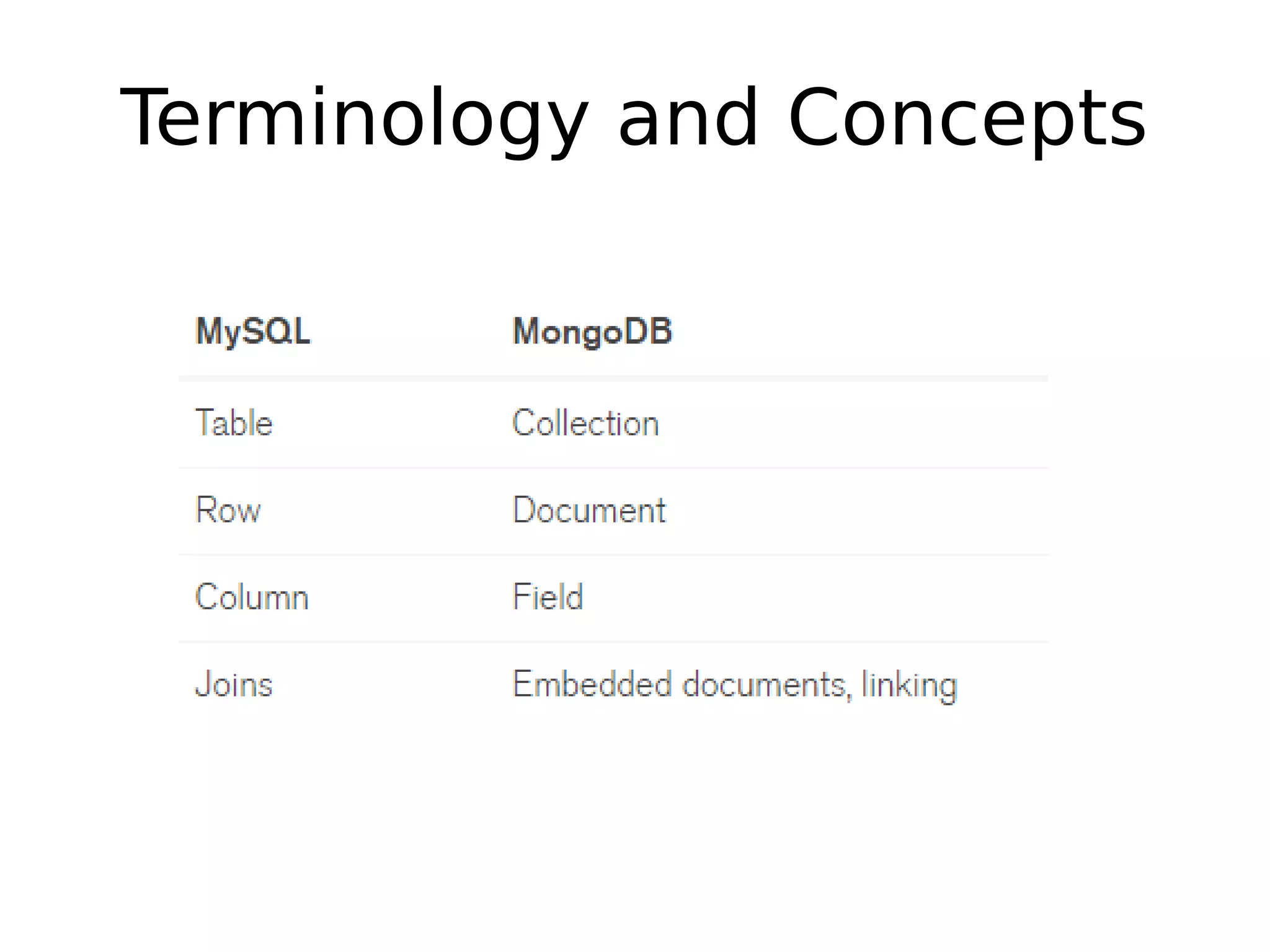
MySQL and MongoDB are database management systems that differ in how they structure and store data. MySQL uses a relational model where data is stored in tables and rows and uses SQL, requiring the schema to be defined beforehand. MongoDB is non-relational and stores data as JSON-like documents that can vary in structure and do not require a predefined schema. Key differences include that MySQL uses joins while MongoDB embeds documents and supports arrays, and that MySQL requires a defined schema while MongoDB allows dynamic schemas.