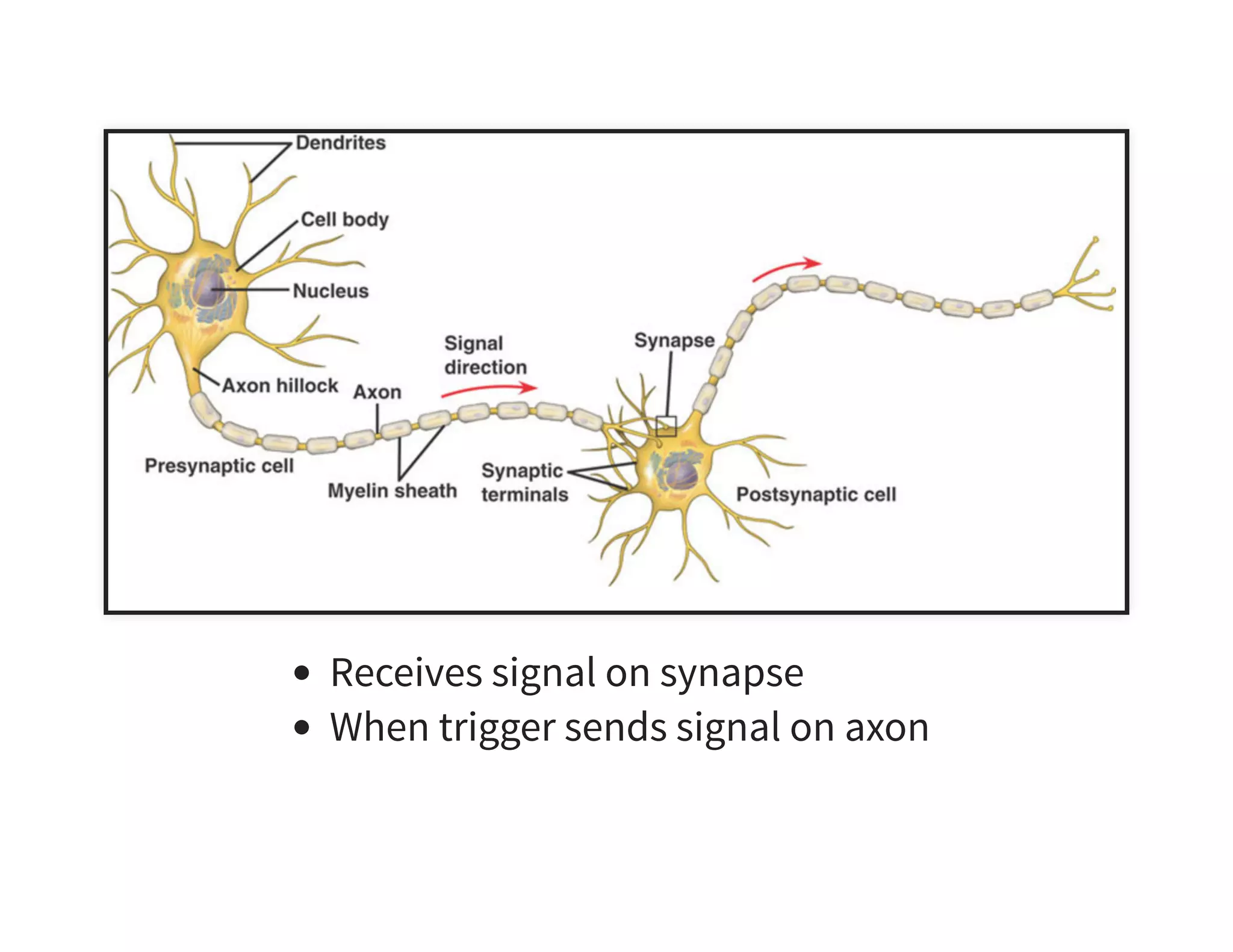
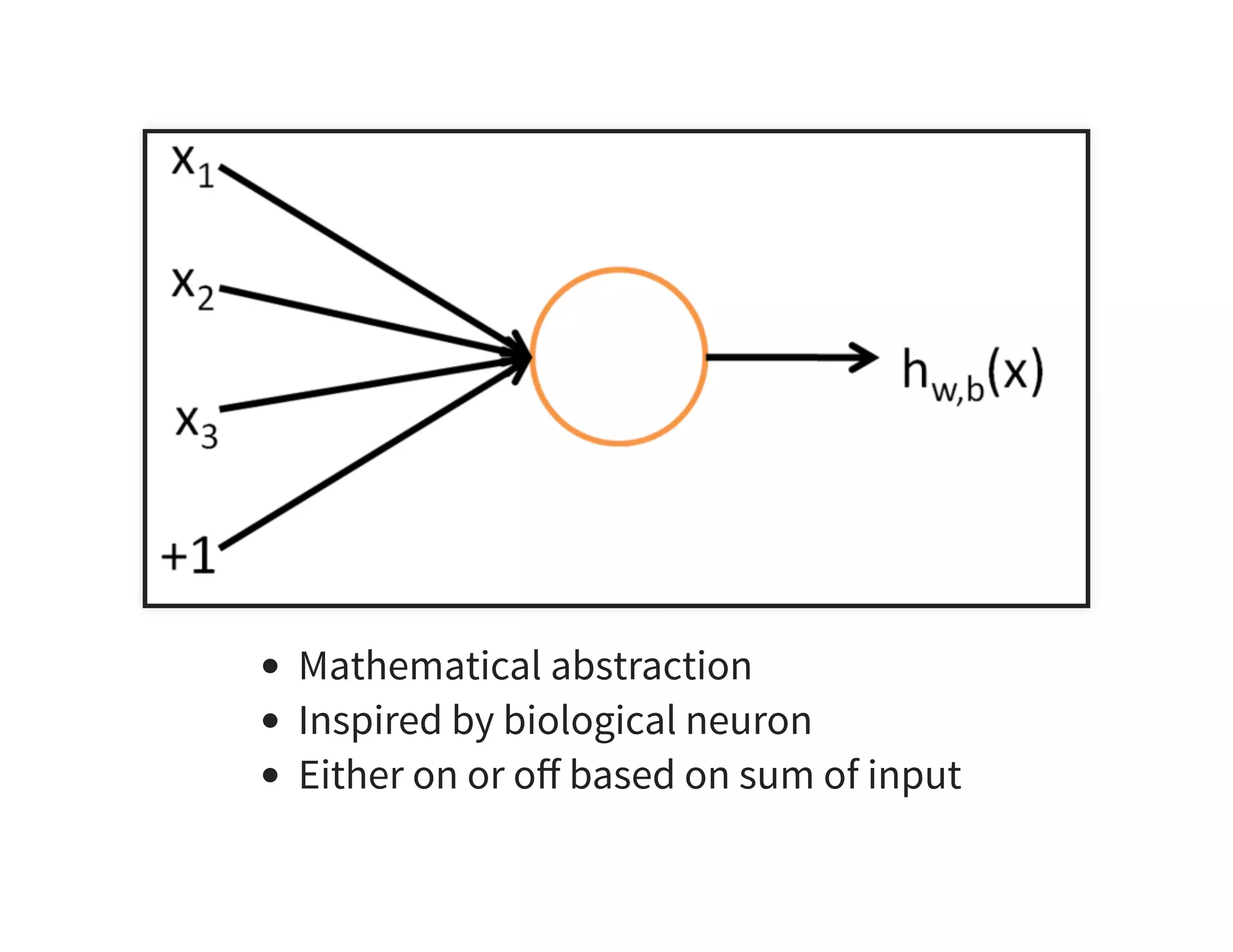
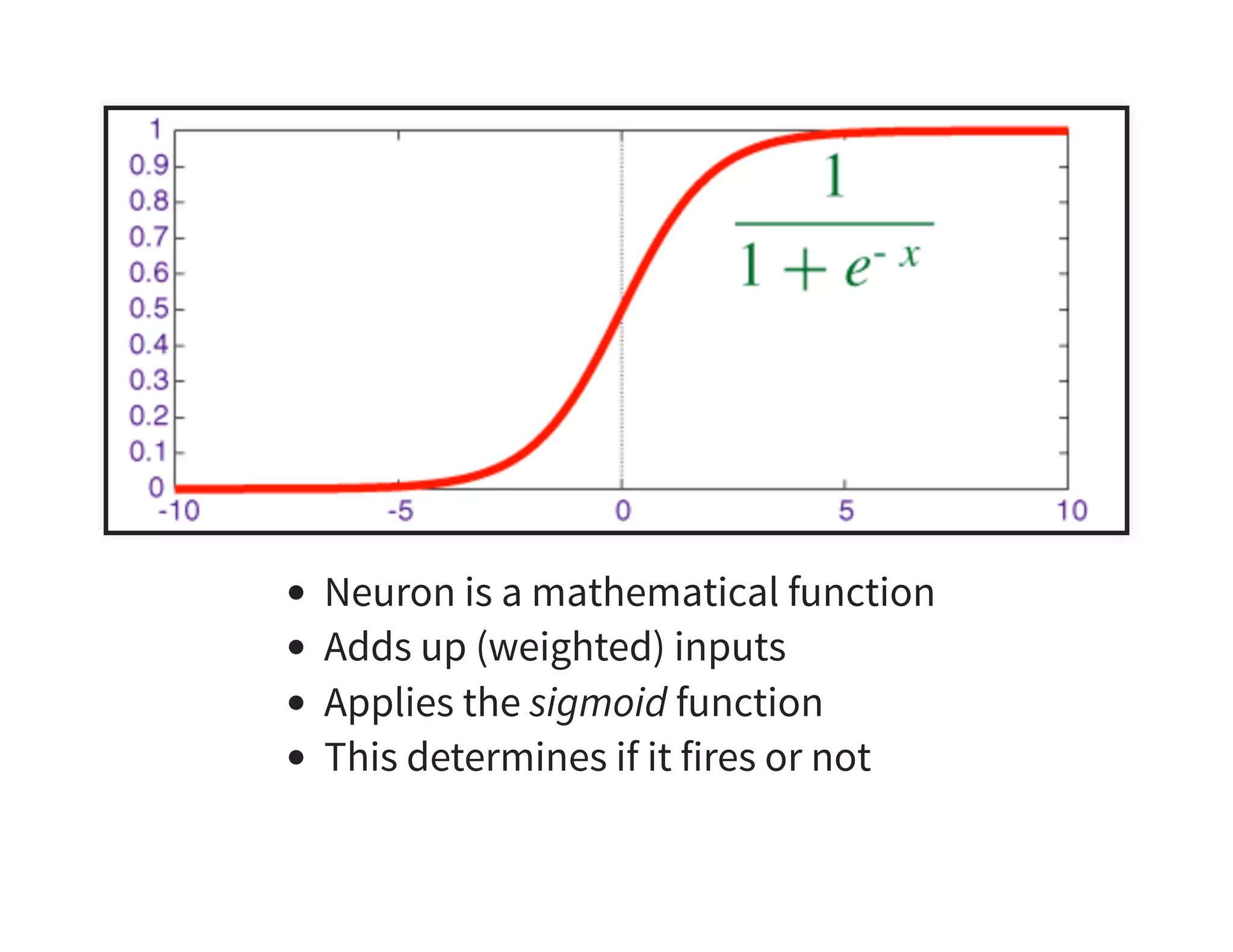
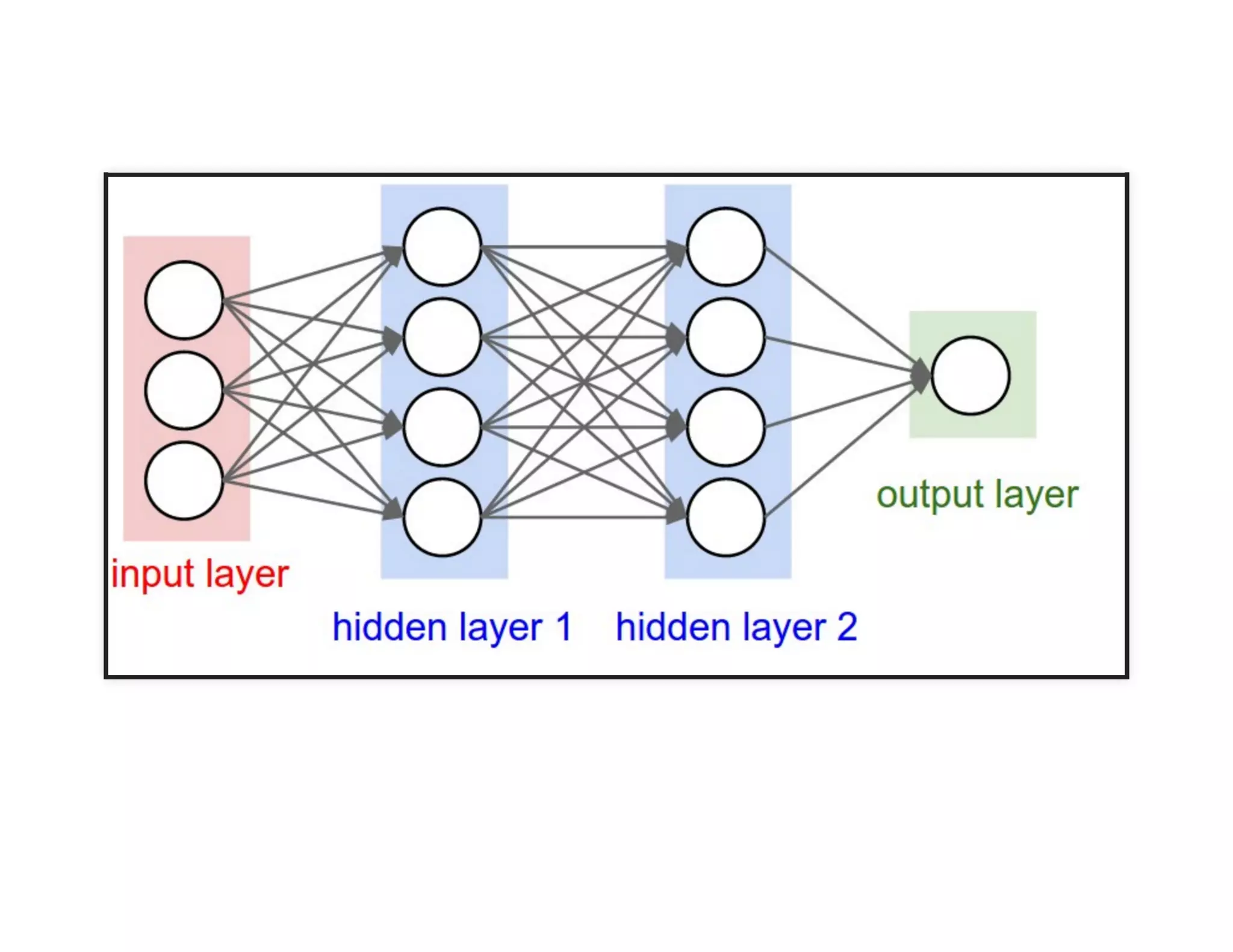
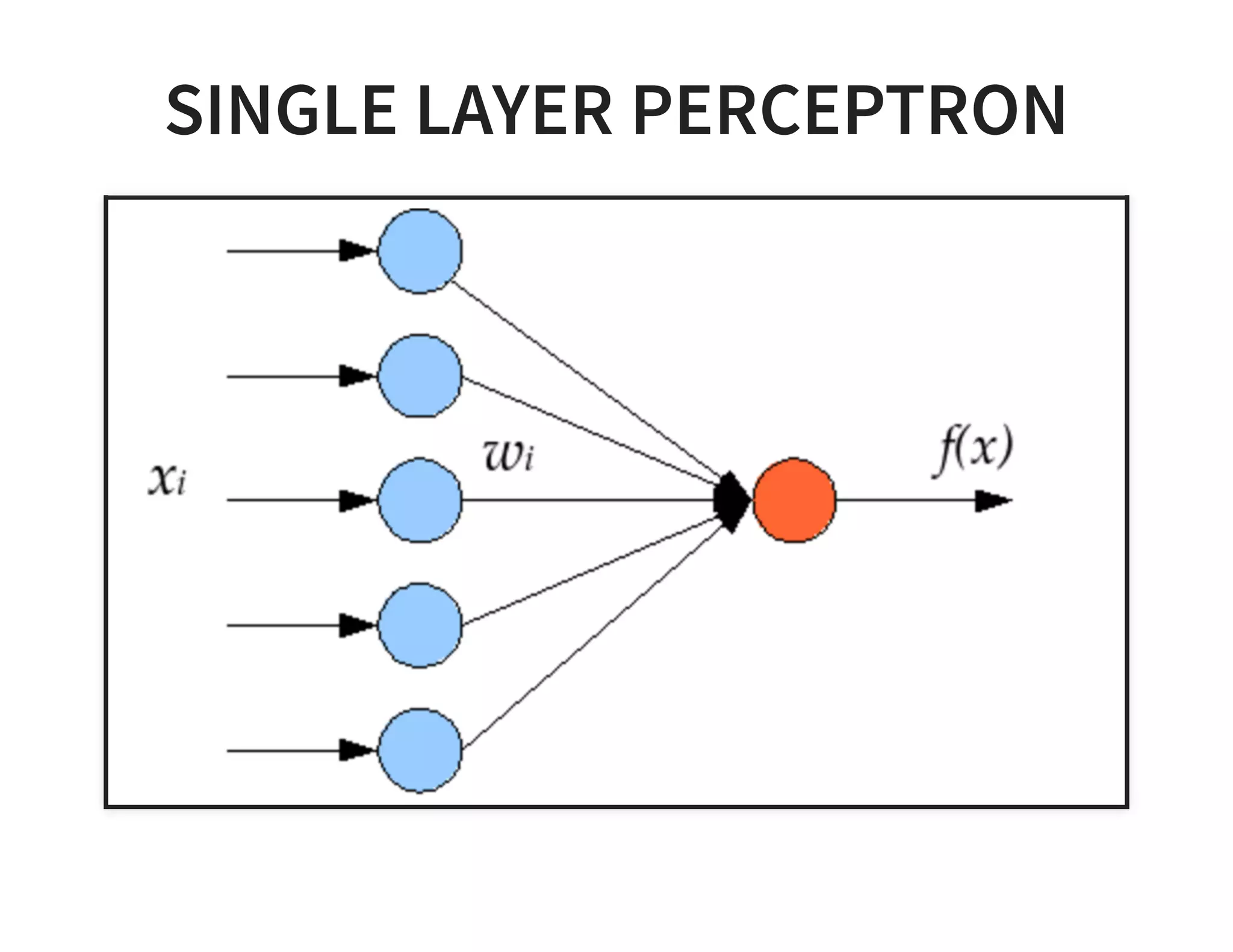
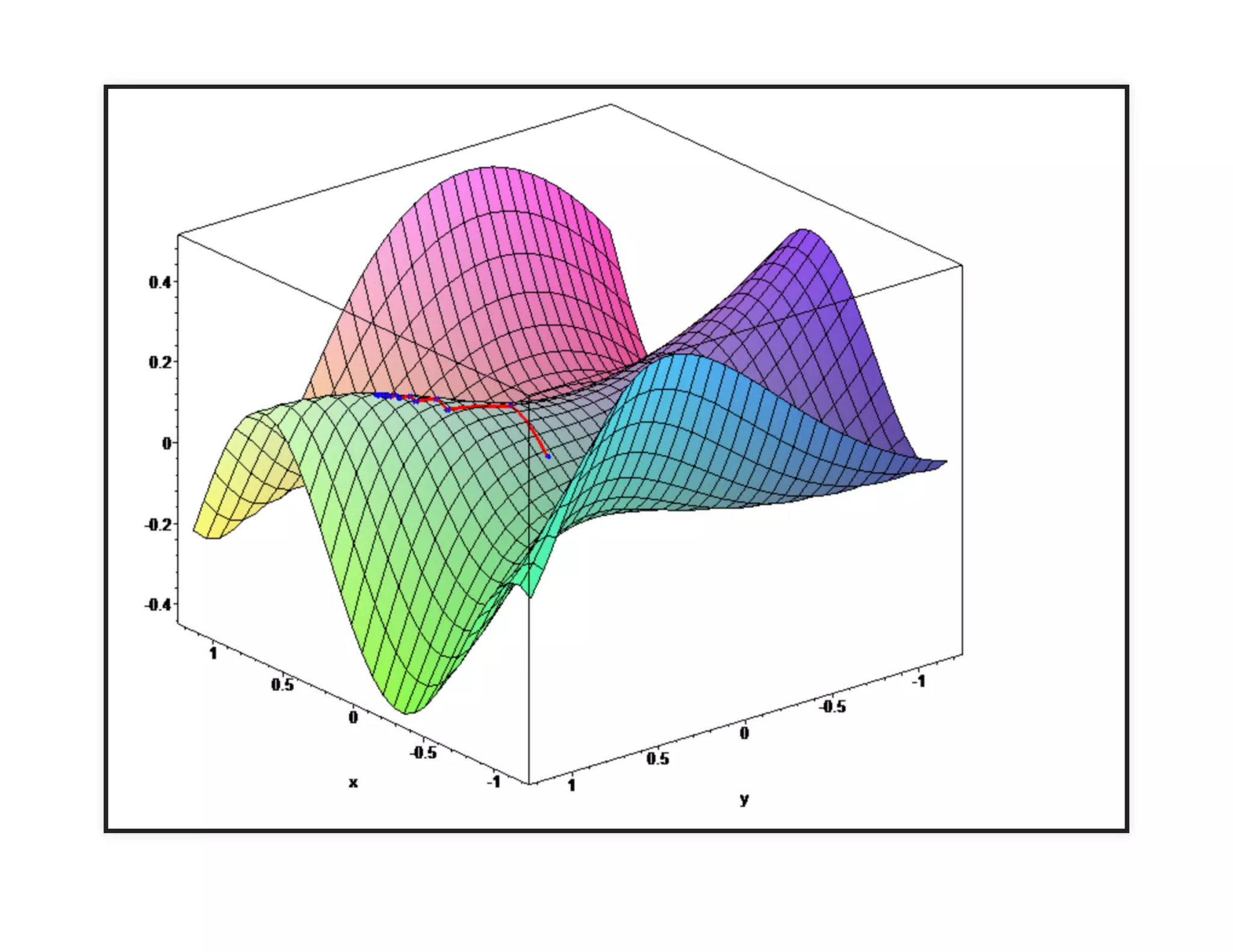
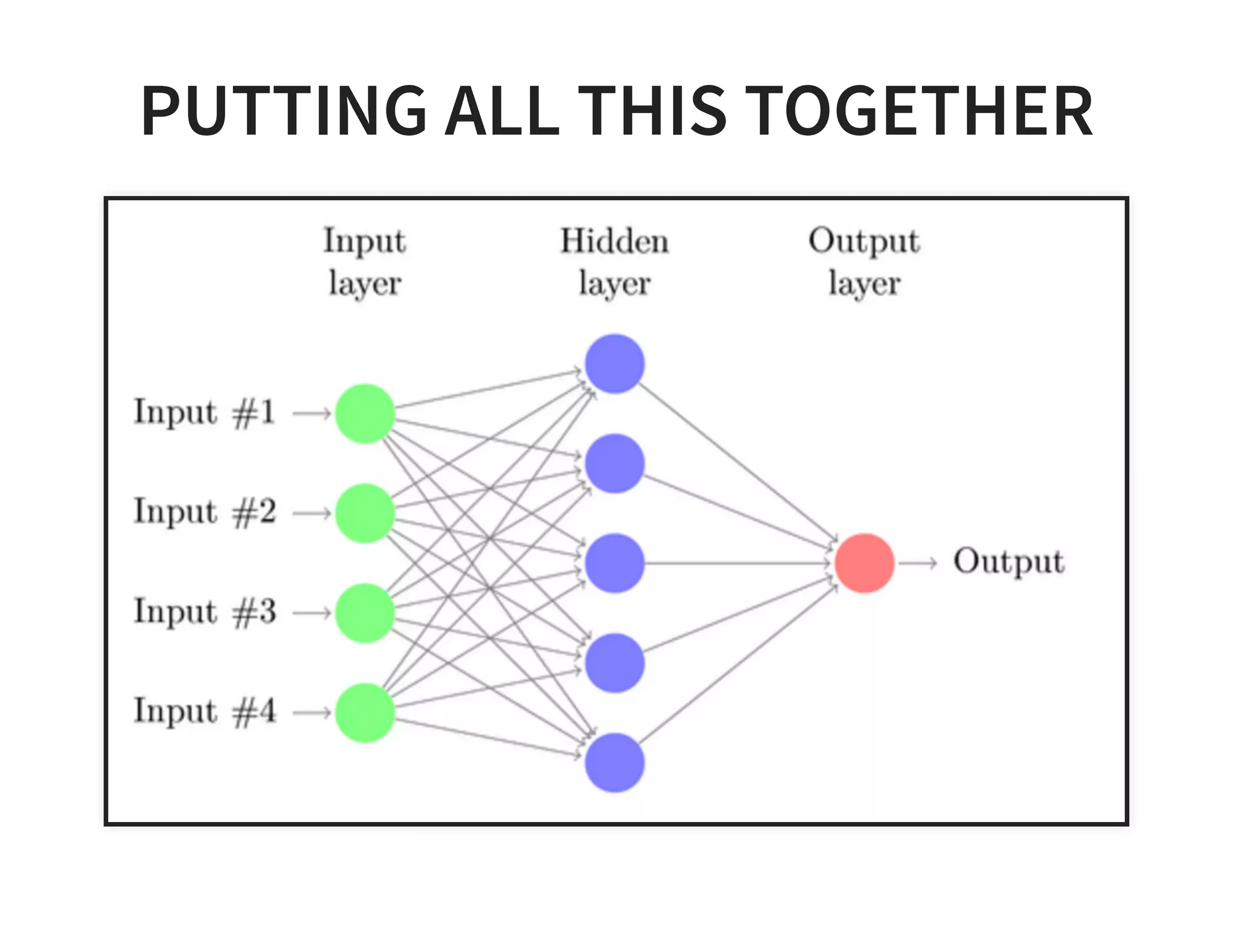
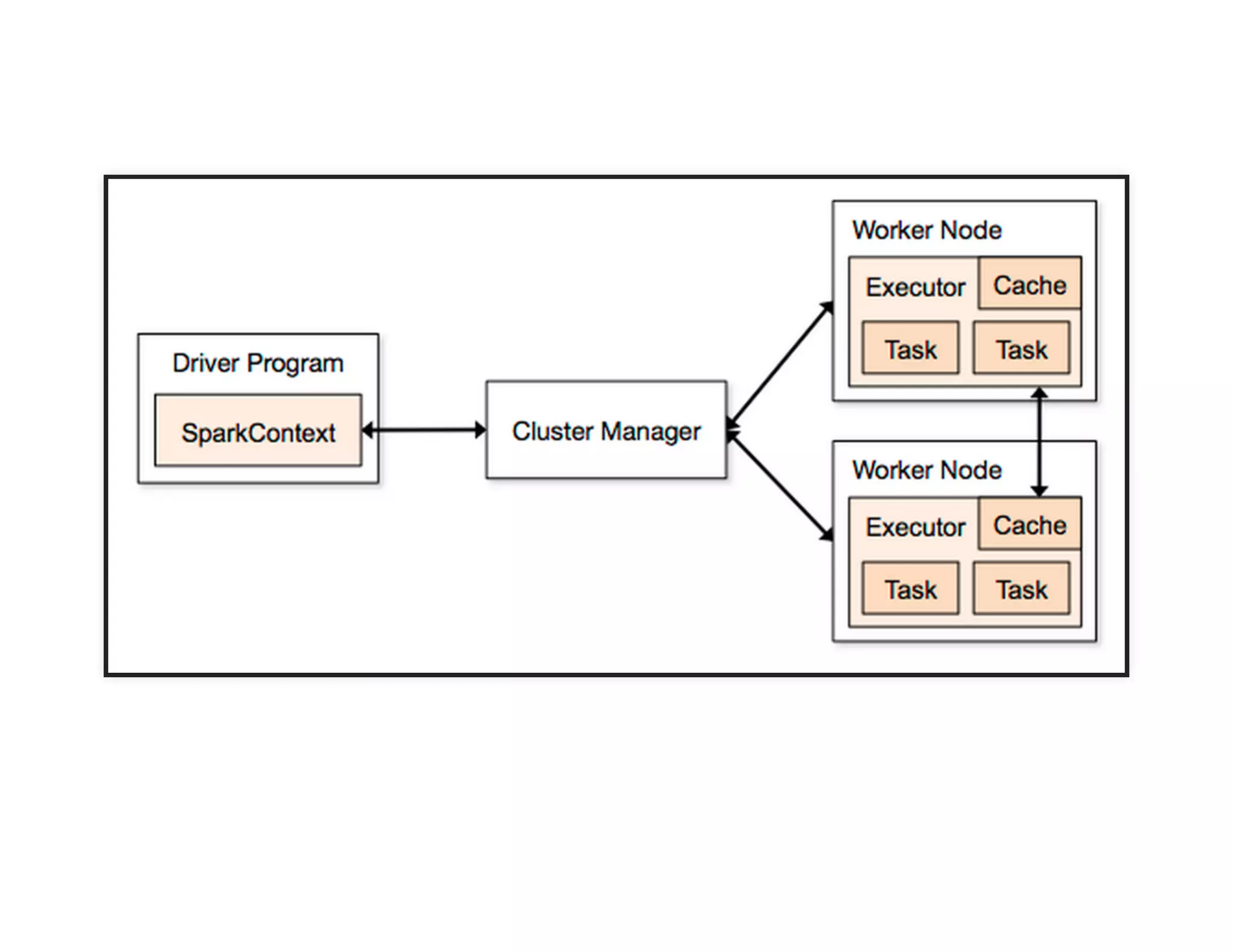
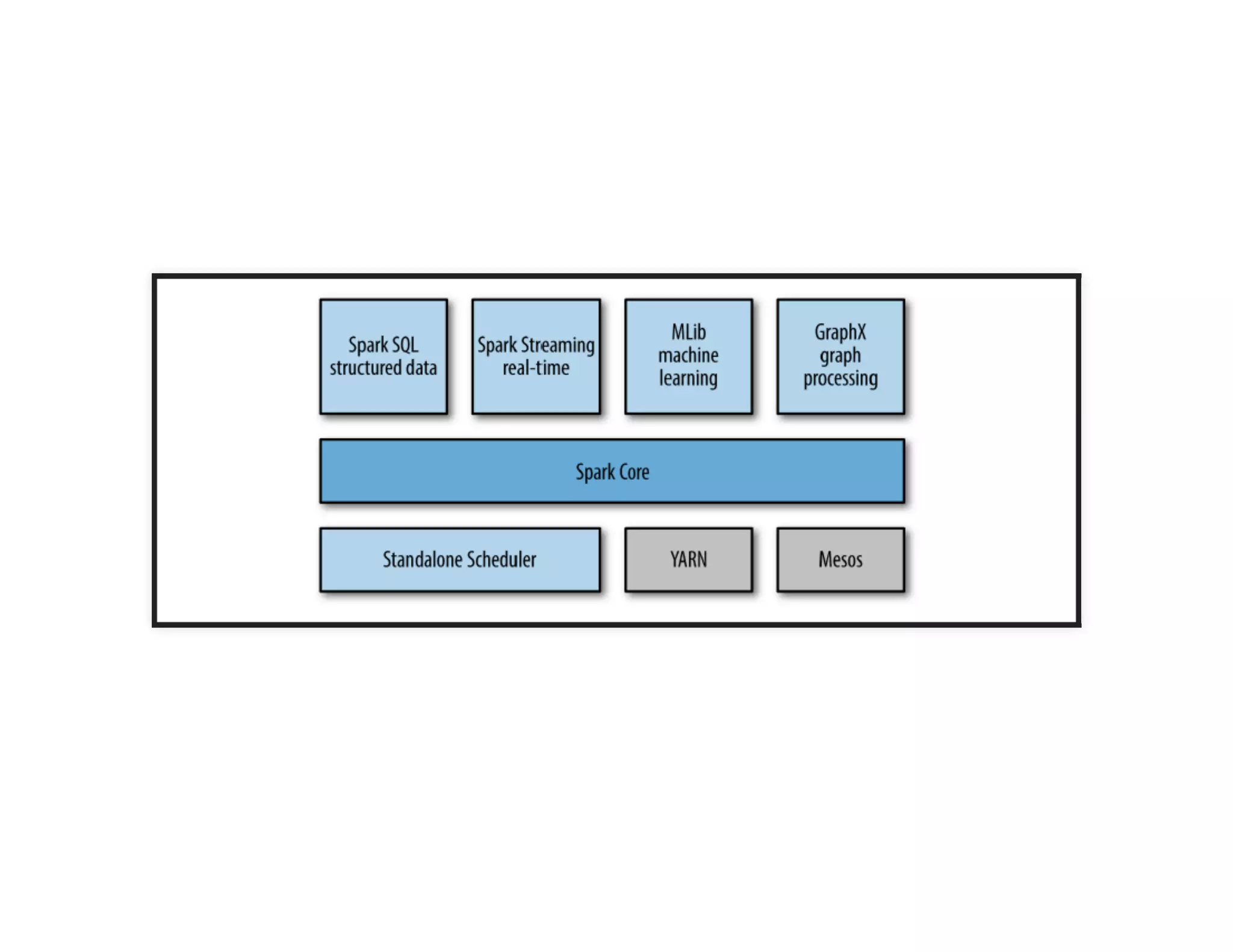
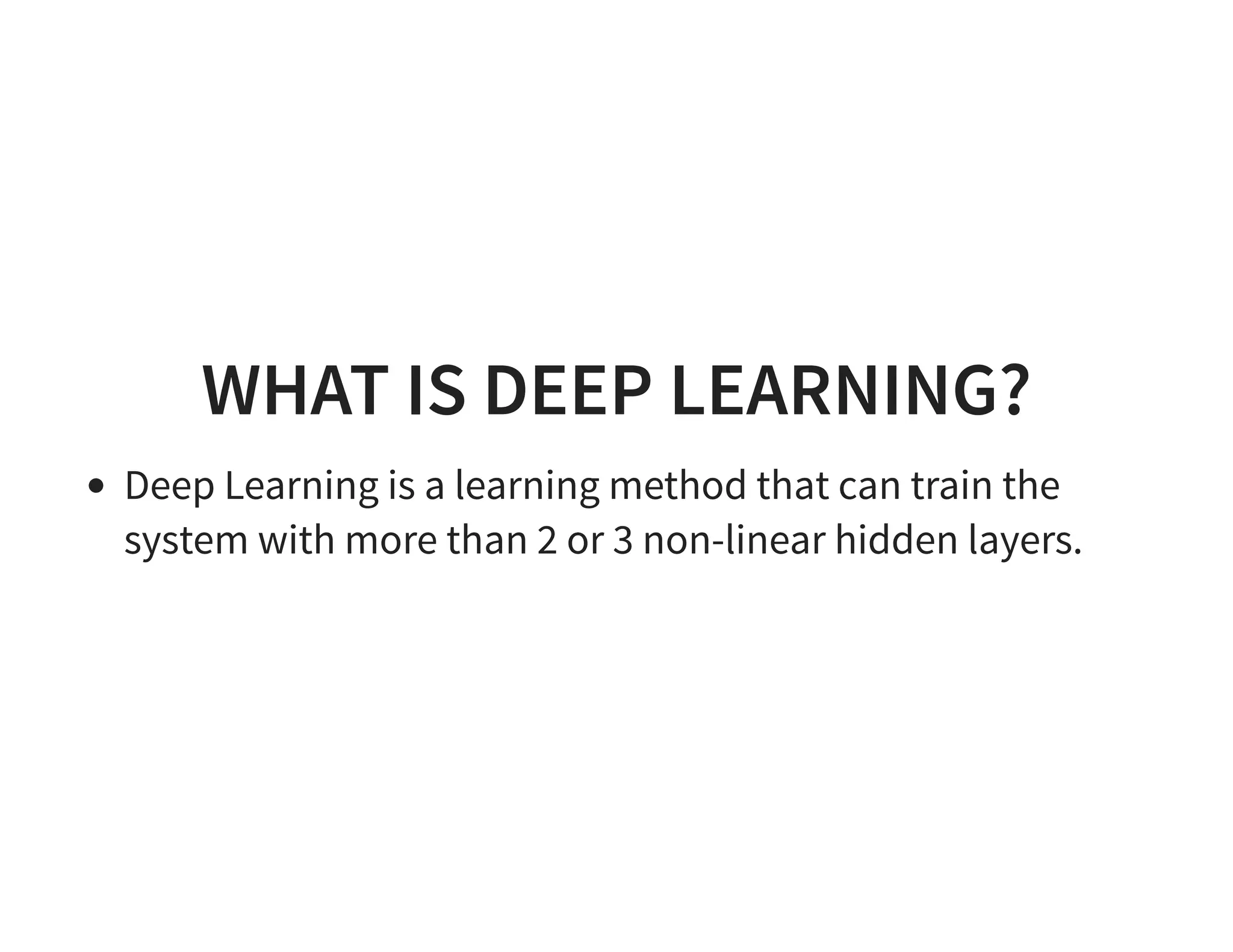
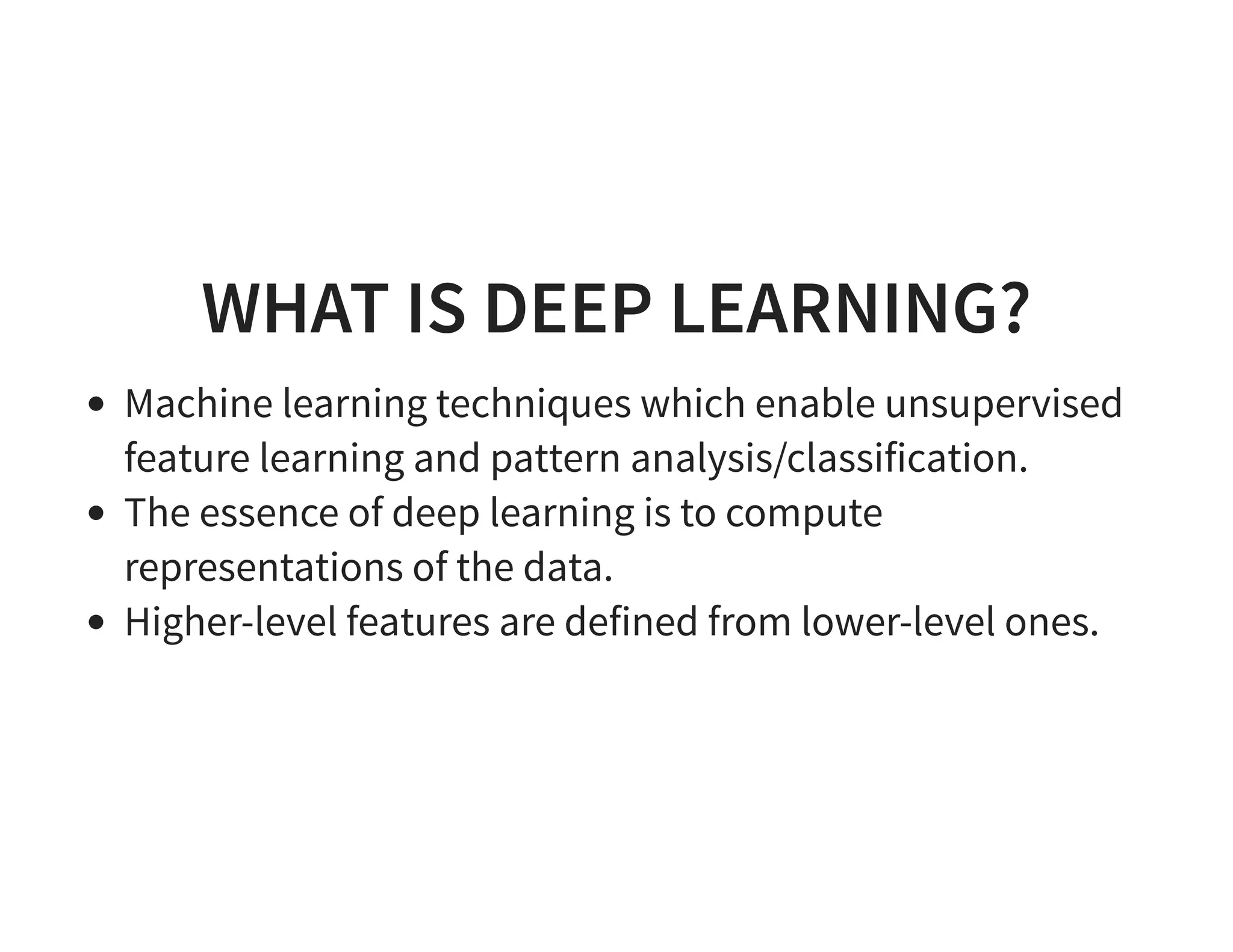
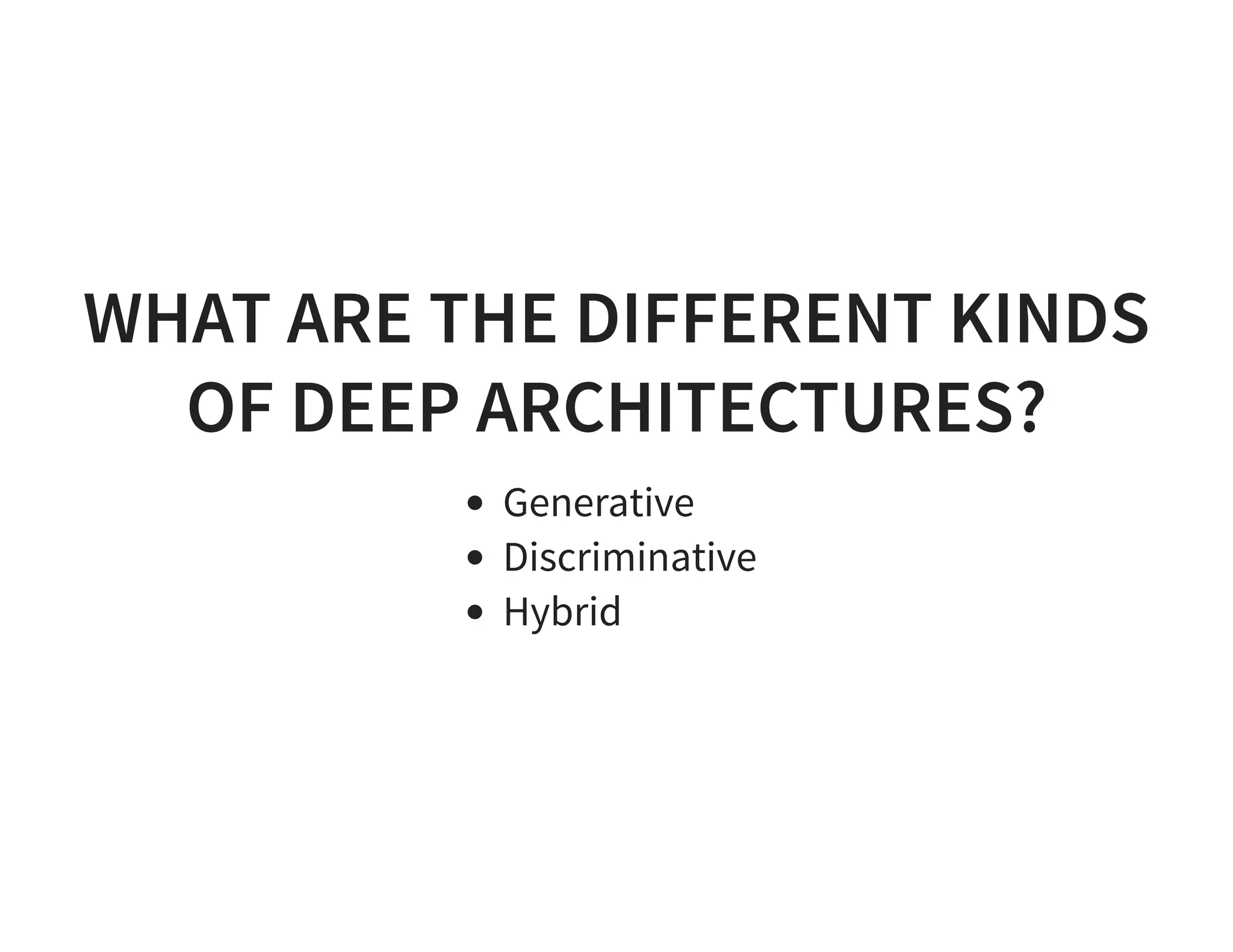
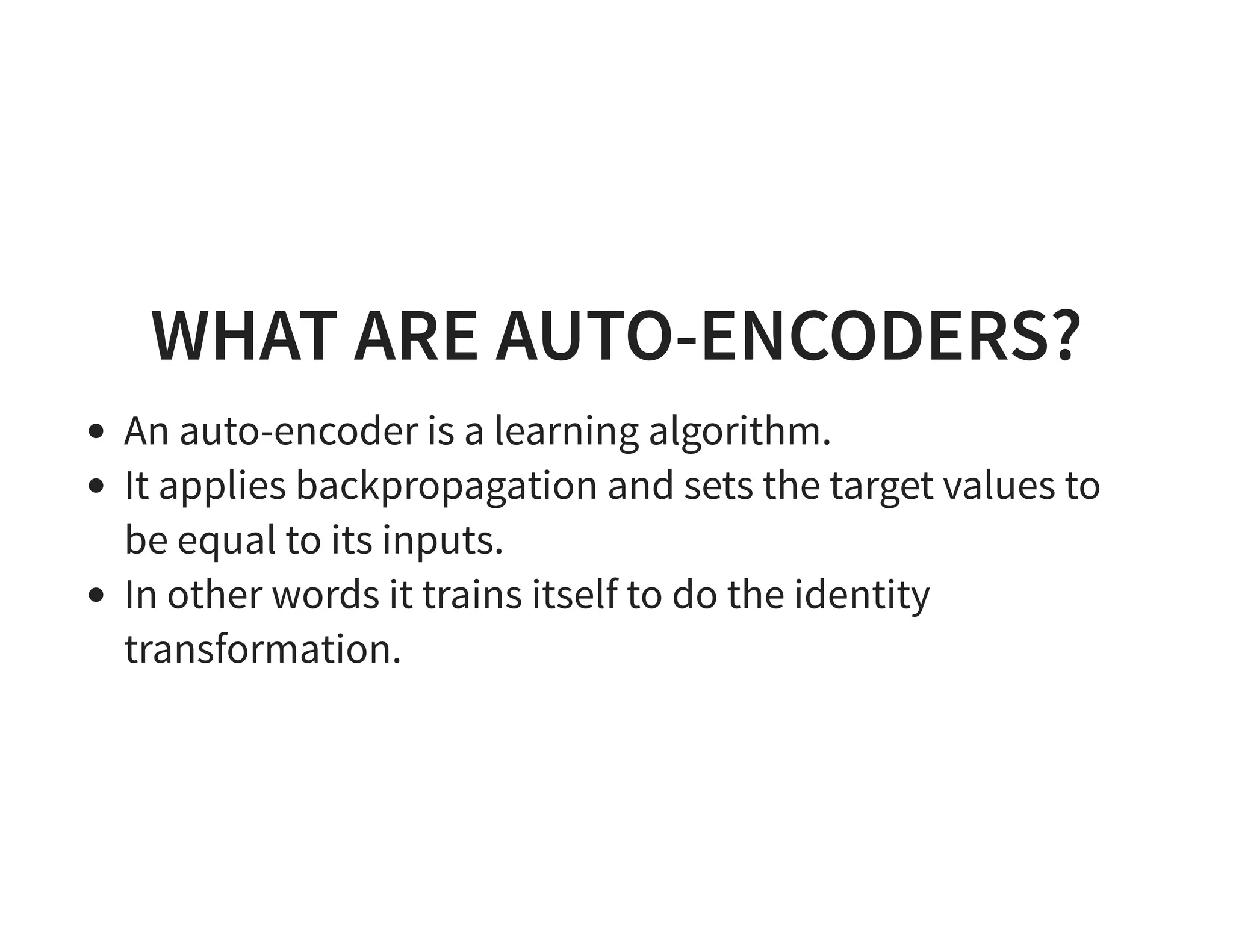
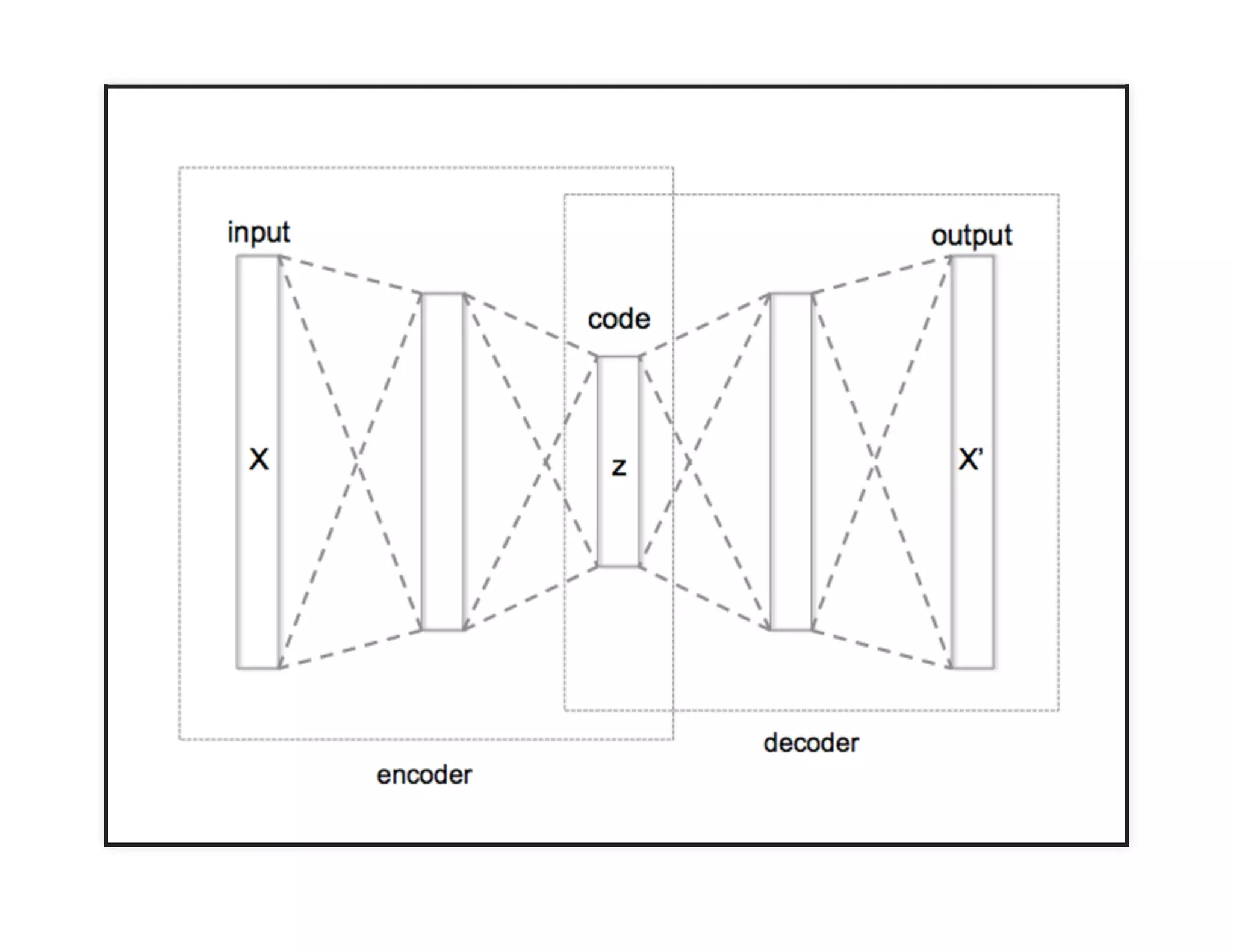
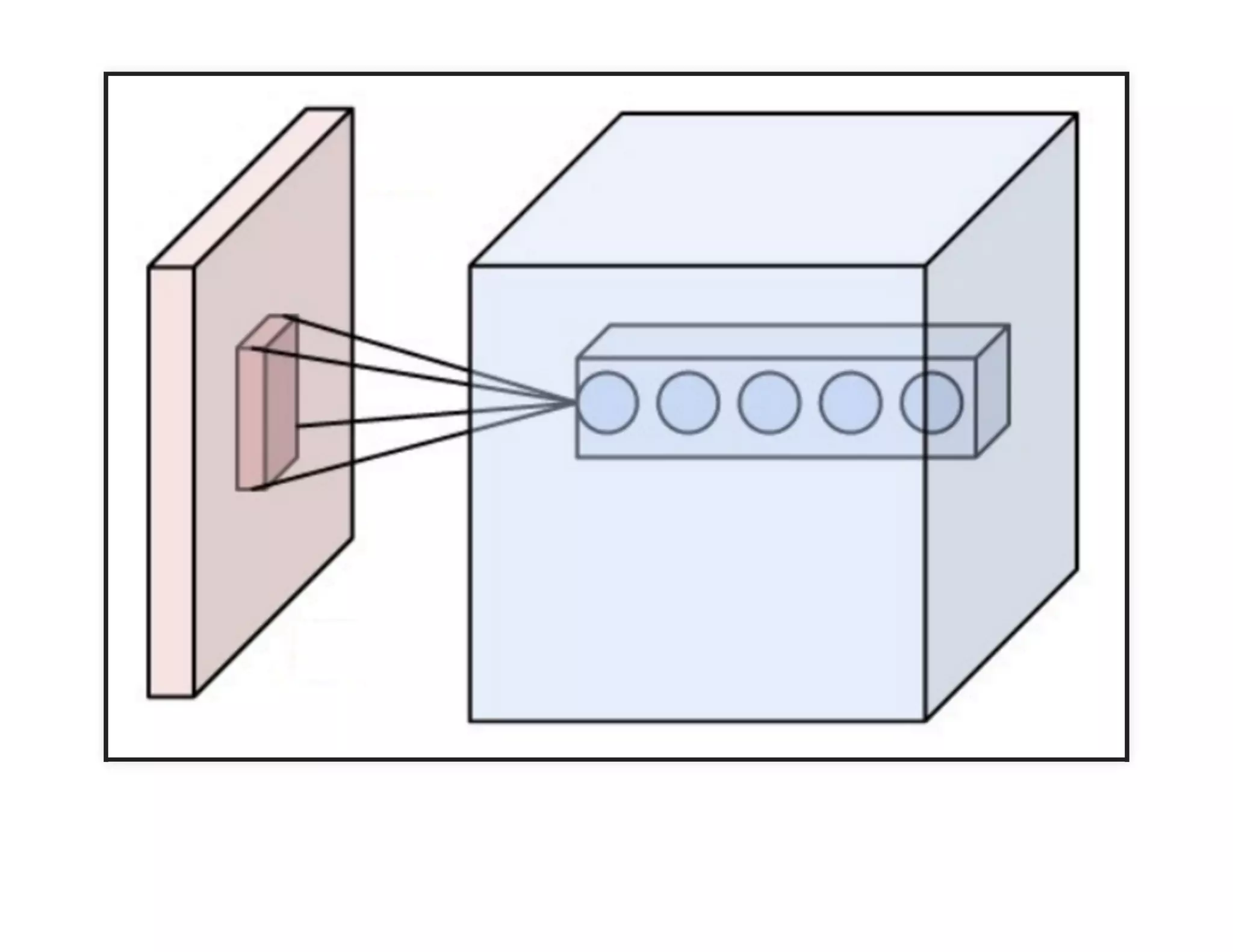
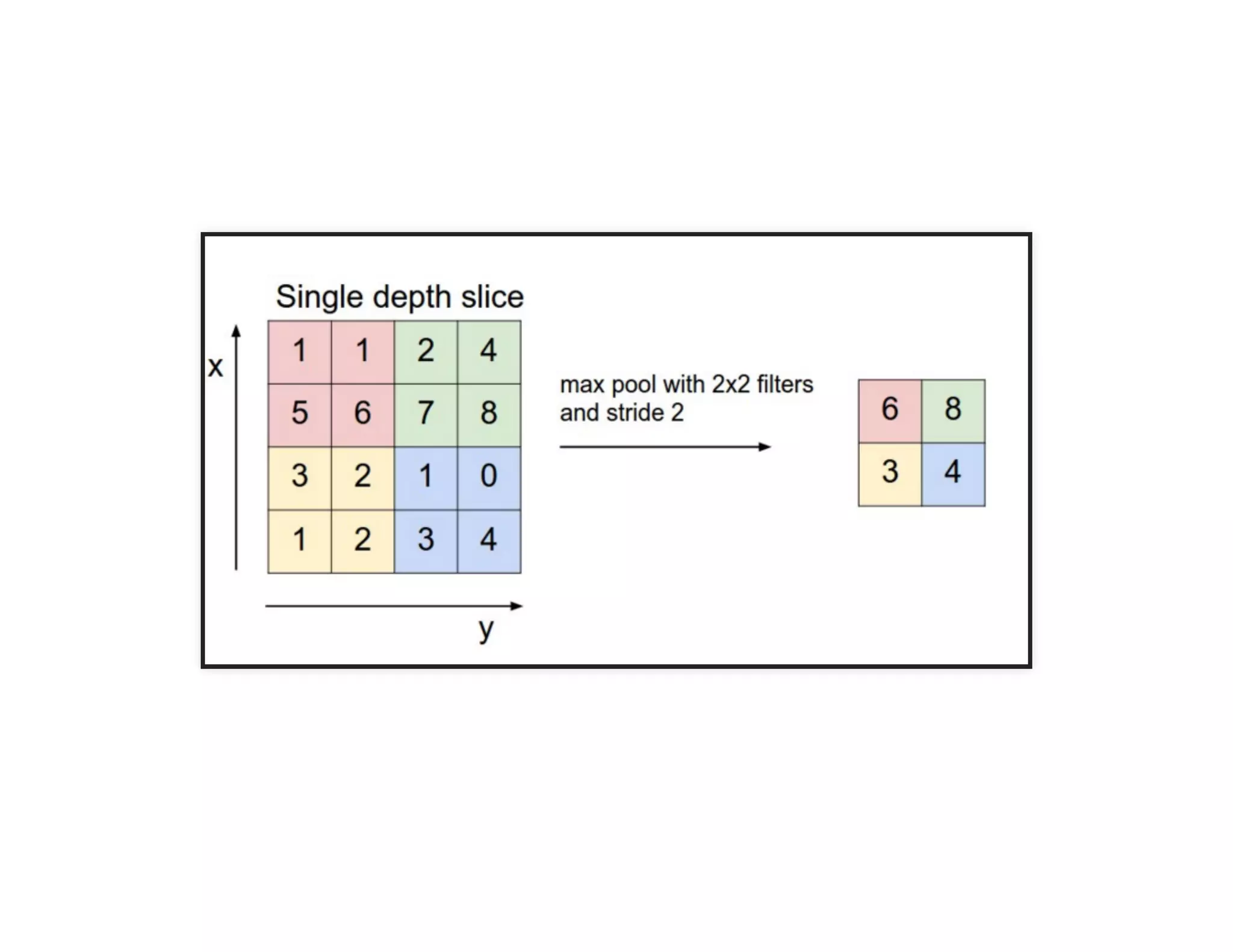
The document discusses neural networks and deep learning, covering their definitions, functionalities, and differences, as well as practical applications in Apache Spark. It outlines the processes of training neural networks, including concepts like feedforward, backpropagation, and gradient descent. Additionally, it highlights various architectures within deep learning, such as auto-encoders and convolutional networks, along with major deep learning platforms.