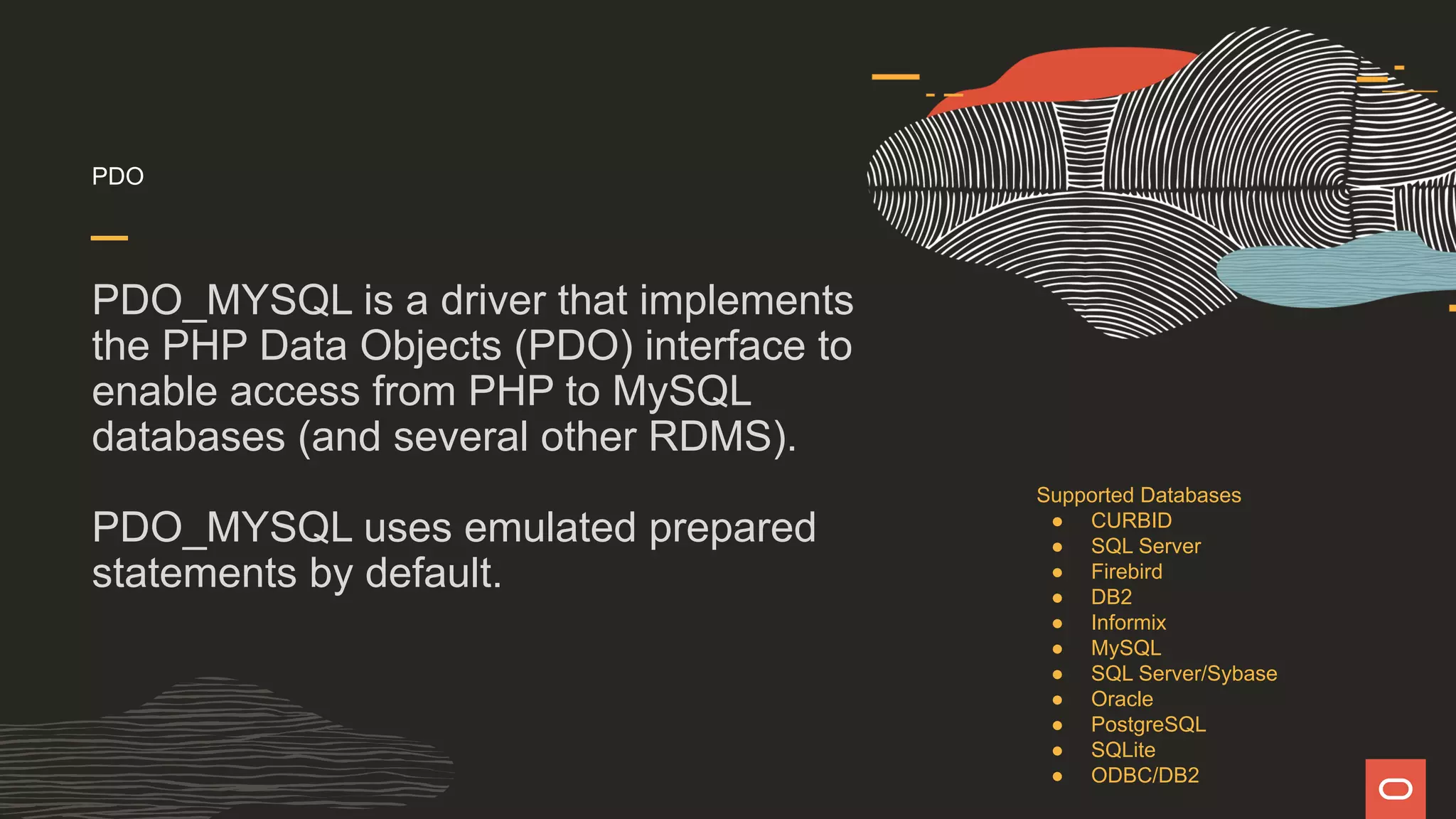
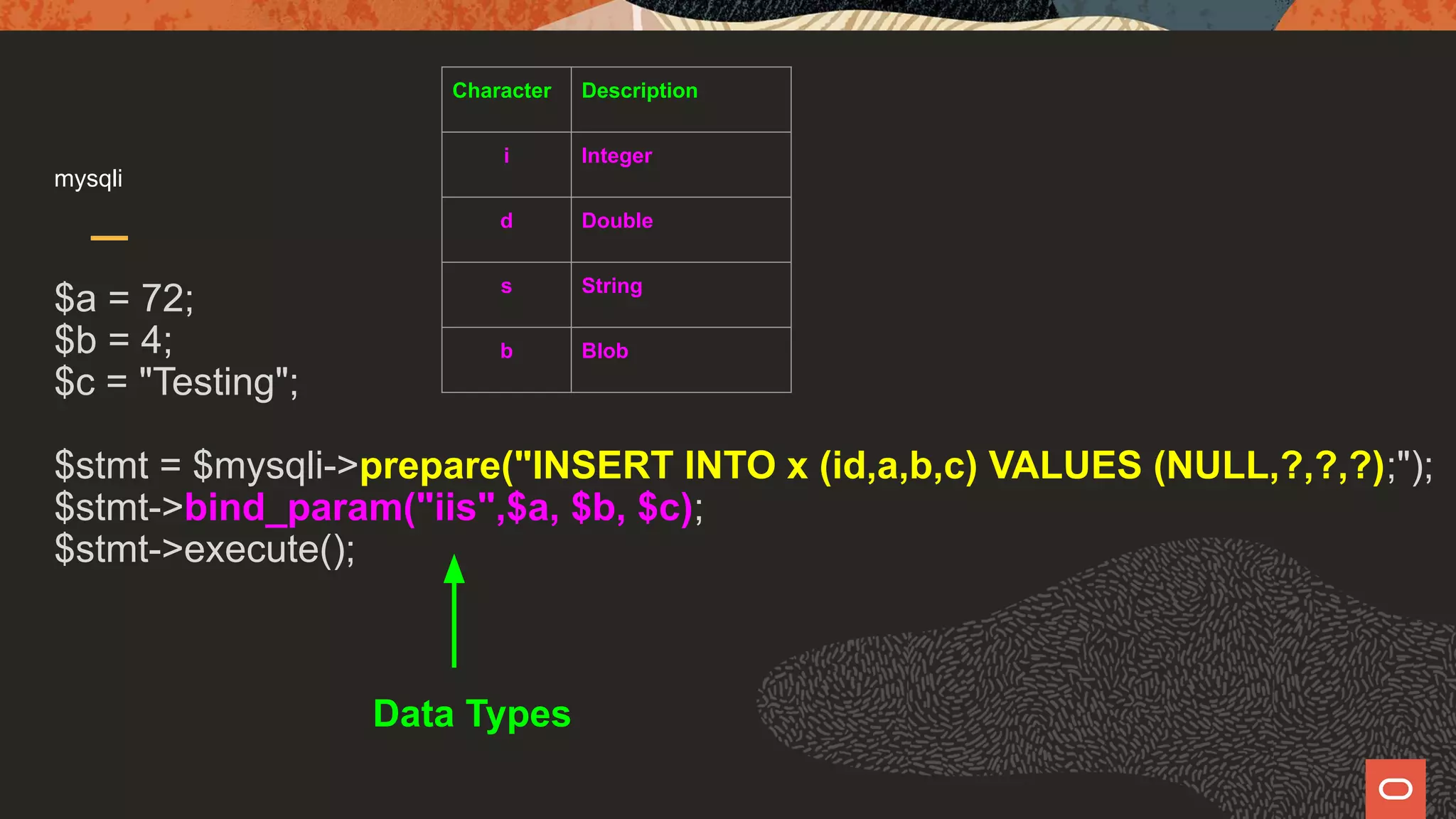
The document discusses various PHP APIs for connecting to MySQL databases, specifically focusing on mysqli, PDO, and X DevAPI, highlighting their functionalities and optimizations through the mysqlnd driver. It compares the features of each API, including prepared statements, authentication methods, and SQL execution examples, while also noting the disadvantages of using emulated prepared statements in PDO. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of secure practices and provides code snippets for establishing database connections and executing queries.


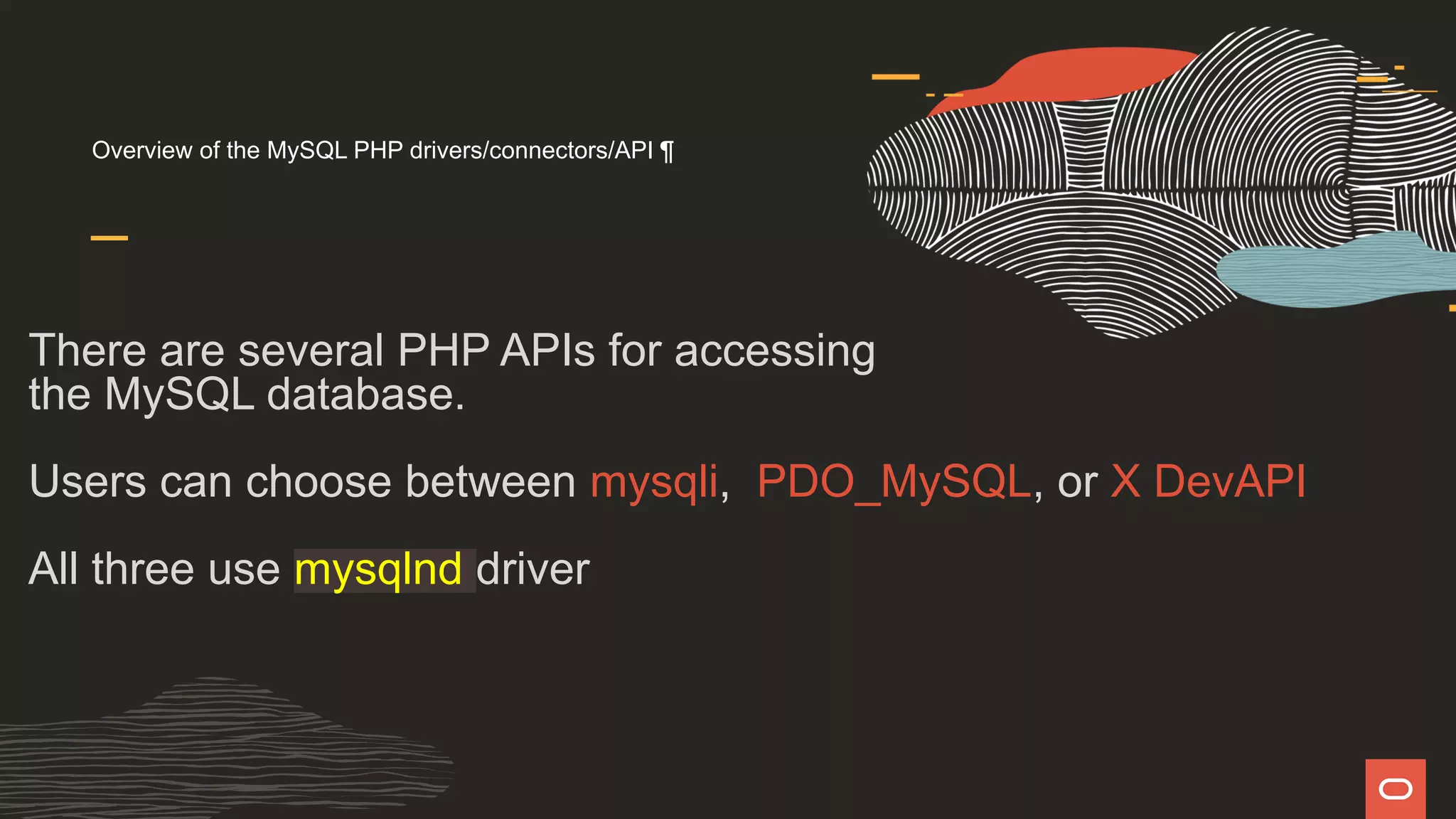












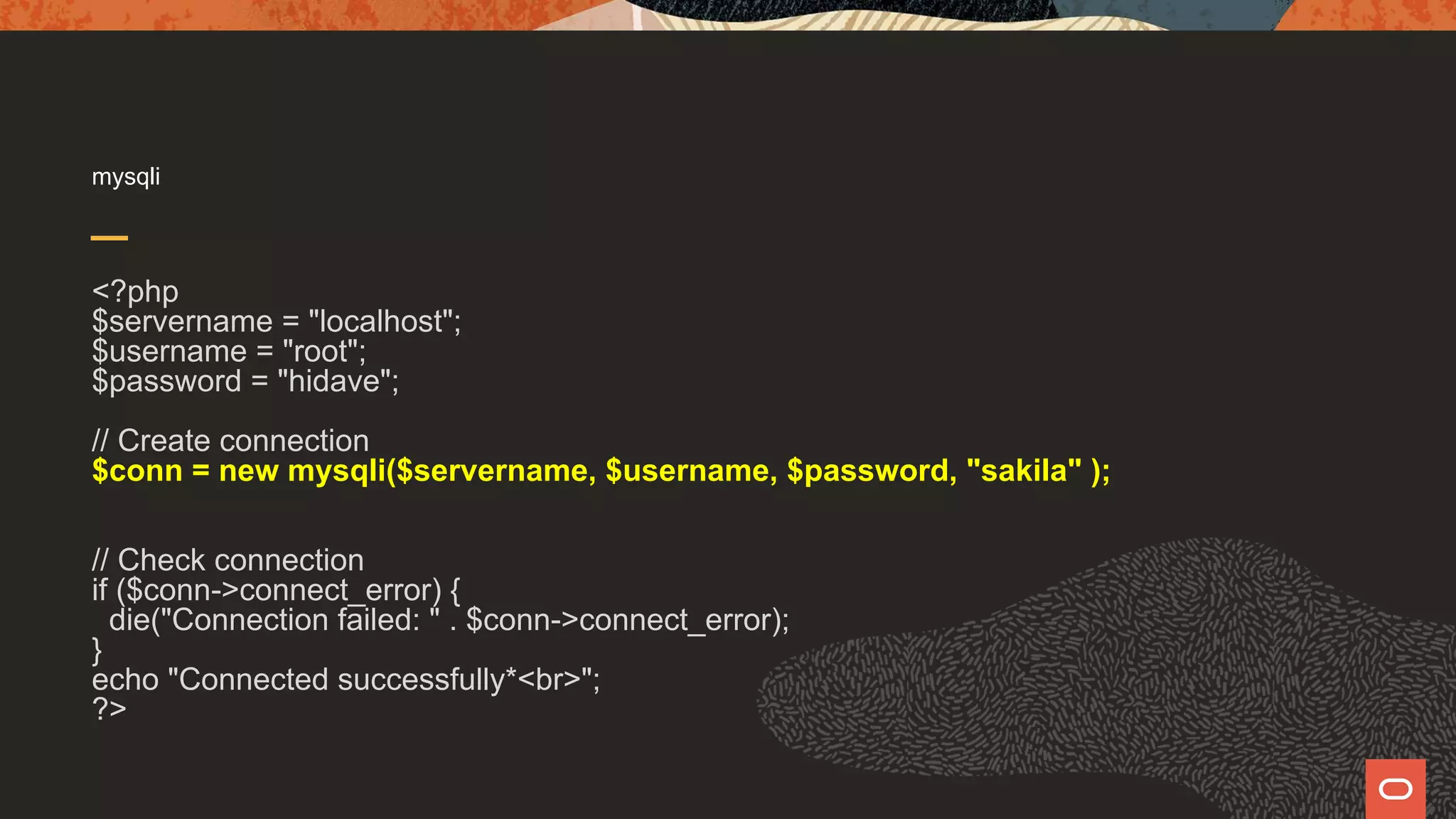


![mysqli <?php $servername = "localhost"; $username = "root"; $password = "hidave"; // Create connection $conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, "world" ); // Check connection if ($conn->connect_error) { die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error); } $result = $conn->query("SELECT * FROM country WHERE Code='USA'"); while ($row = $result->fetch_row()) { printf("%s (%s)n", $row[0], $row[1]); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-24-2048.jpg)
![pdo <?php $servername = "localhost"; $username = "dave"; $password = "Passw0rd!"; try { $conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=world", $username, $password); // set the PDO error mode to exception $conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION); } catch(PDOException $e) { echo "Connection failed: " . $e->getMessage(); } foreach($conn->query("SELECT * FROM country WHERE Code = 'USA'") as $row) { printf("%s (%s)n", $row[0], $row[1] ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-25-2048.jpg)
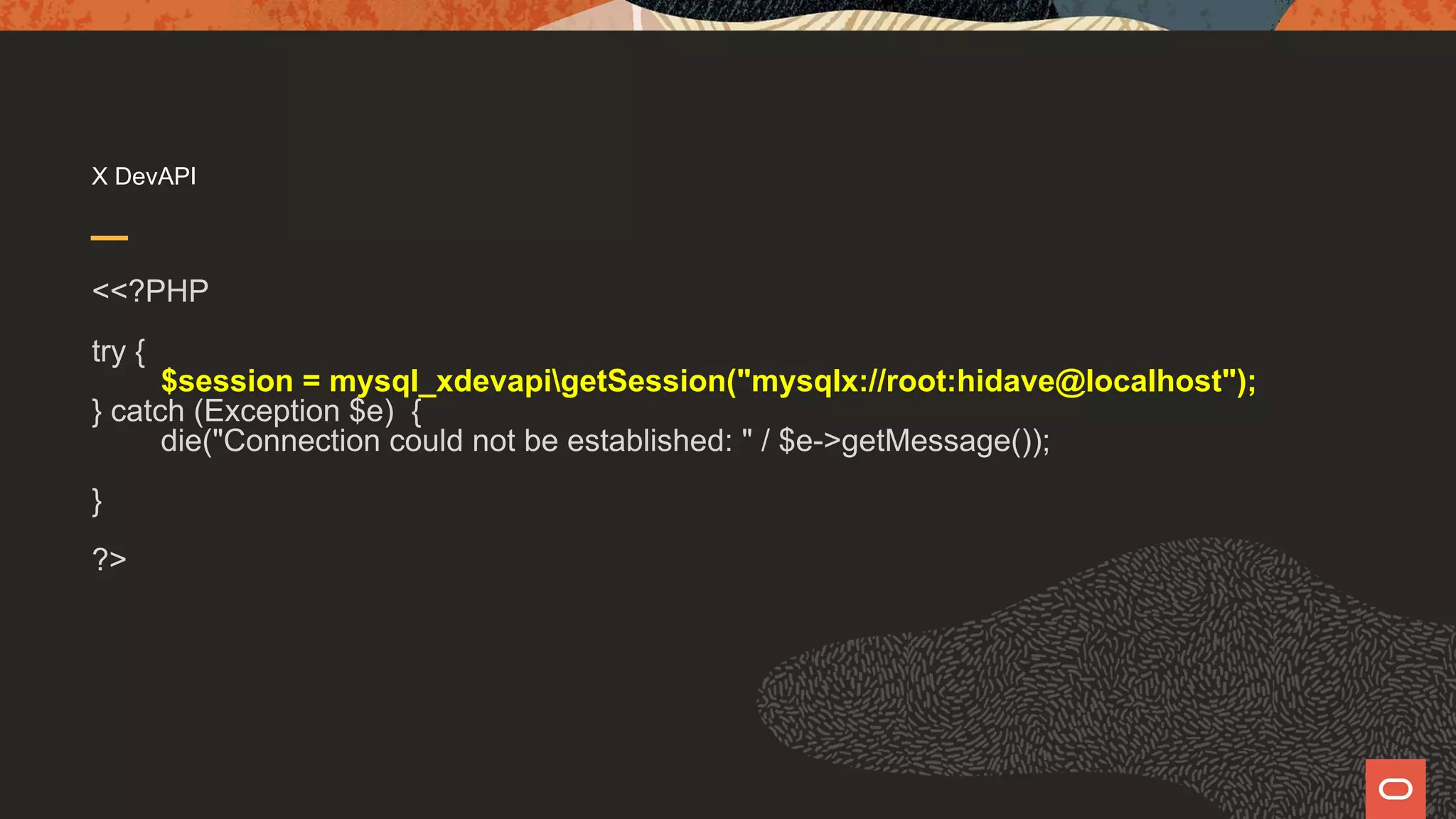
![X DevAPI JSON <?PHP try { $session = mysql_xdevapigetSession("mysqlx://root:hidave@localhost"); } catch (Exception $e) { die("Connection could not be established: " / $e->getMessage()); } $schema = $session->getSchema("world_x"); $collection = $schema->getCollection("countryinfo"); print_r($collection->find("Code = 'USA'") ->fields("[Code,Name]") ->execute() ->fetchOne());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-26-2048.jpg)

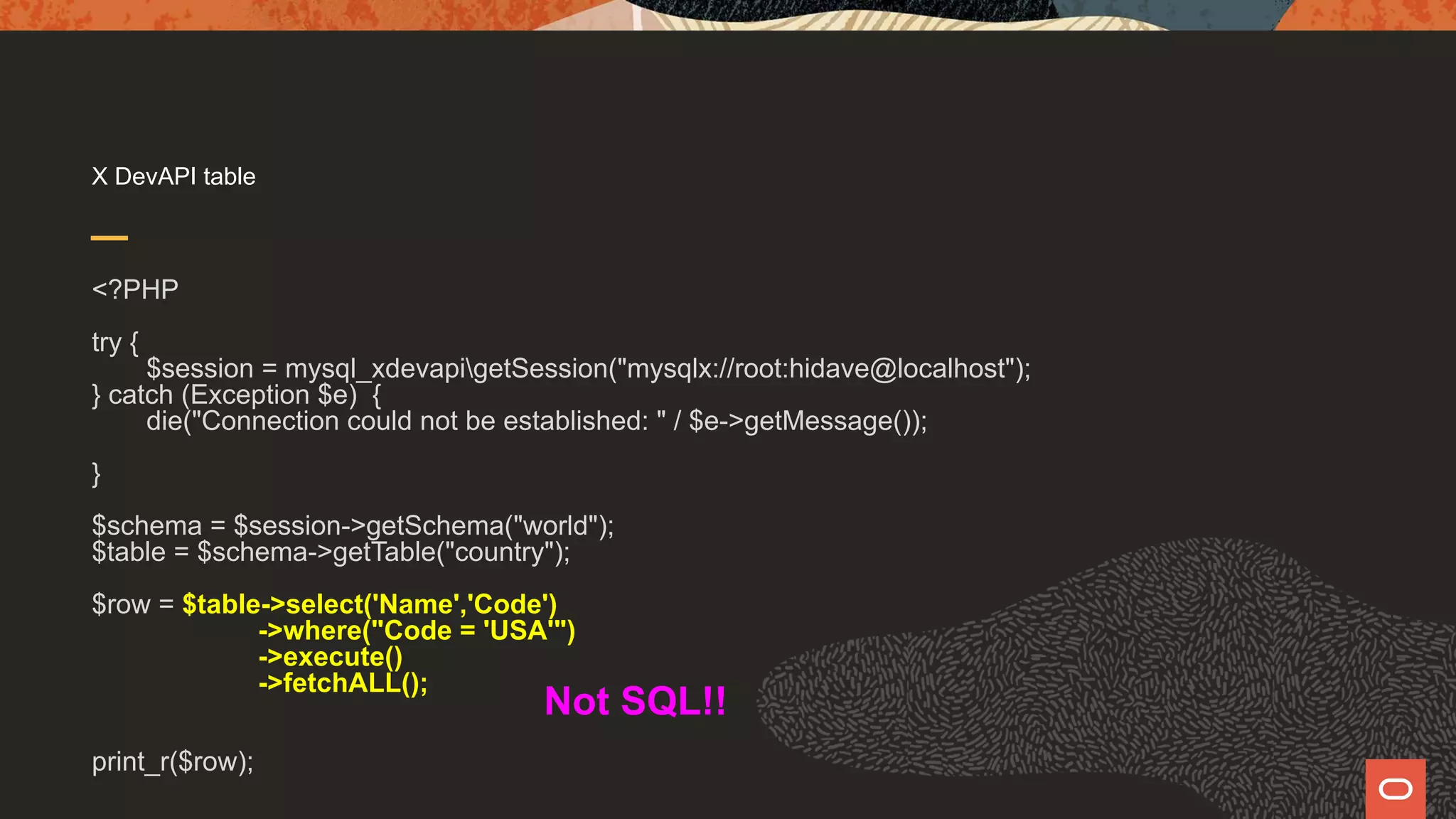
![Document Store vs. Relational Tables Document Store $schema = $session->getSchema("world_x"); $collection = $schema->getCollection("countryinfo"); print_r($collection->find("Code = 'USA'")->fields("[Code,Name]")->execute()->fetchOne()); Relational Table $schema = $session->getSchema("world"); $table = $schema->getTable("country"); $row = $table->select('Name','Code')->where("Code = 'USA'")->execute()->fetchALL(); print_r($row);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-29-2048.jpg)
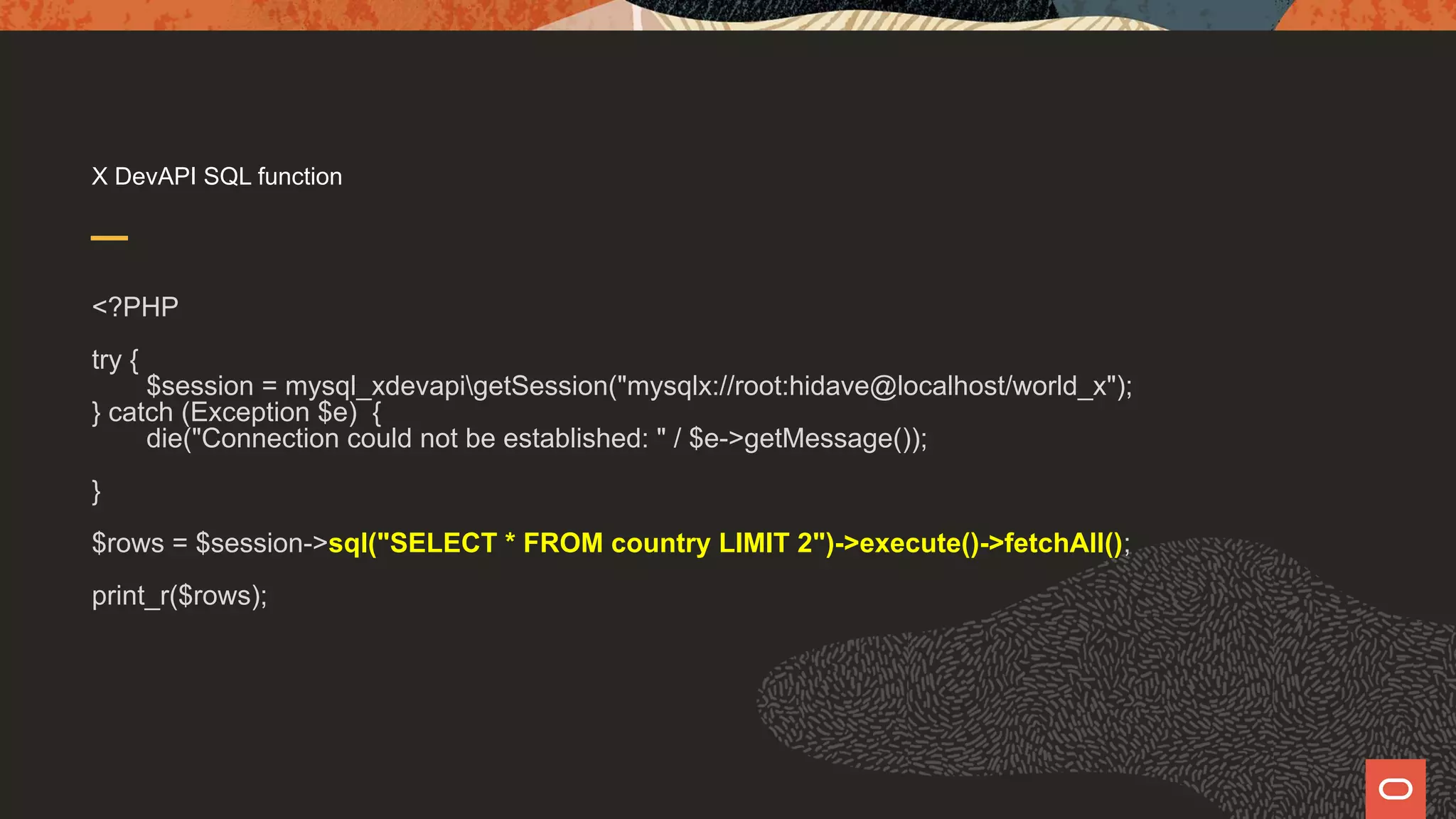









![pdo $a = 33; $b = 101; $c = "Whohoo!"; $conn=->setAttributes(PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES,false); $stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO x (id,a,b,c) VALUES (NULL, :a, :b, :c)"); $stmt->execute([':a' => $a, ':b' => $b, ':c' => $c]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-43-2048.jpg)
![pdo $a = 33; $b = 101; $c = "Whohoo!"; $conn=->setAttributes(PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES,false); $stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO x (id,a,b,c) VALUES (NULL, :a, :b, :c)"); $stmt->execute([':a' => $a, ':b' => $b, ':c' => $c]); This says to use prepared statements not emulated prepared statements!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-44-2048.jpg)

![xdevapi $collection->find("Code = :code") ->fields("[Code,Name]") ->bind(['code' => 'USA']) ->execute() ->fetchOne();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-46-2048.jpg)






![for ($x=0; $x < 1000000 ; $x++) { $y=rand(1,10000); $result= = $conn->query(“SELECT * FROM x WHERE id=$y;”); } m06-mt.php real 1m11.647s user 0m5.911s sys 0m8.310s p06-mt.php real 1m9.242s user 0m8.578s sys 0m7.987s x06x-mt.php real 3m5.109s user 1m42.753s sys 0m27.542s select(‘*’) ->where(“id = :id”) ->bind([‘id’ => $y]) ->execute()-fetchone(); Averages of 10 runs, high/low tossed out](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysql-howdopdomysqliandxdevapidowhattheydo-211015155331/75/Php-amp-my-sql-how-do-pdo-mysq-li-and-x-devapi-do-what-they-do-54-2048.jpg)