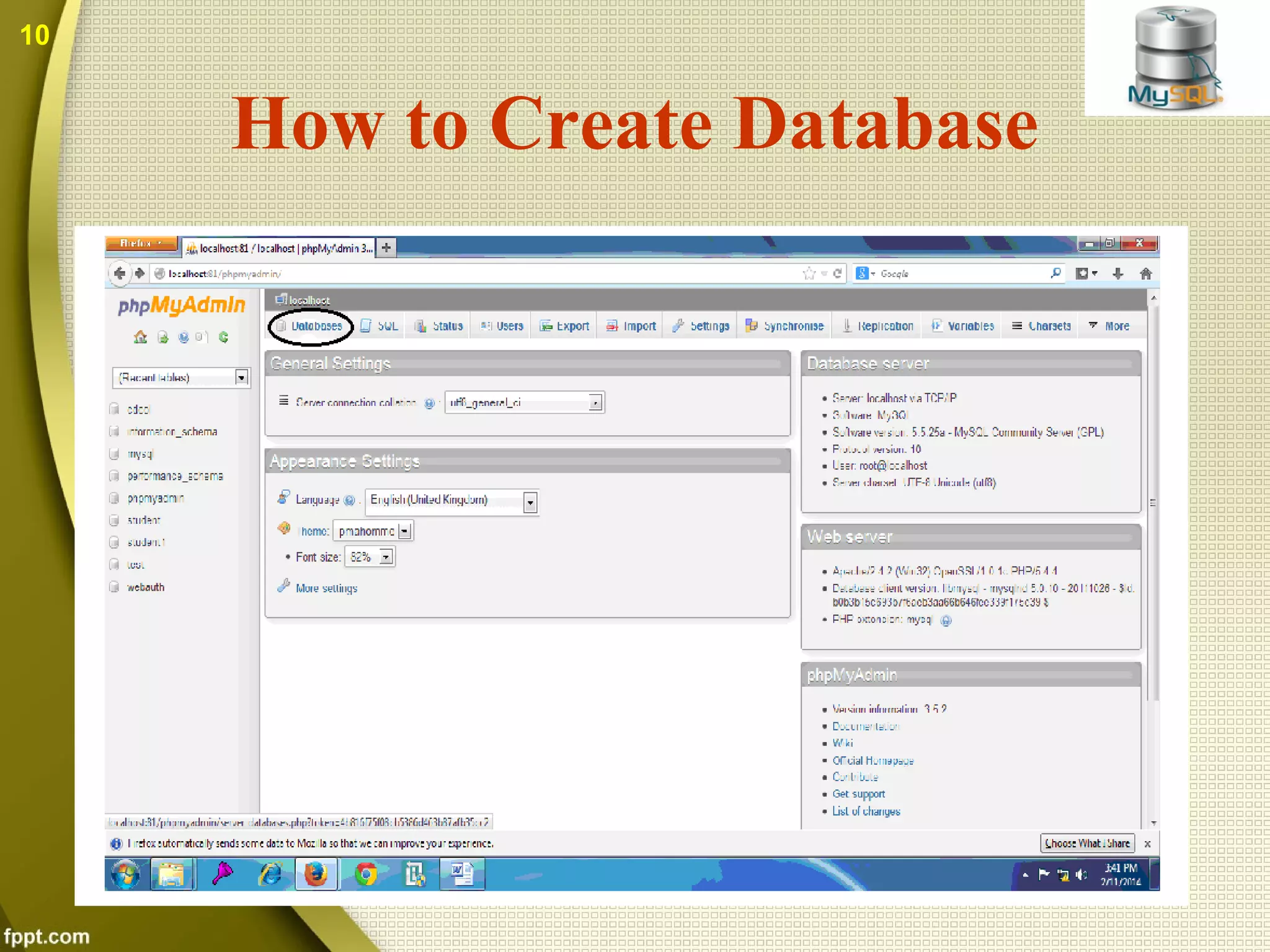
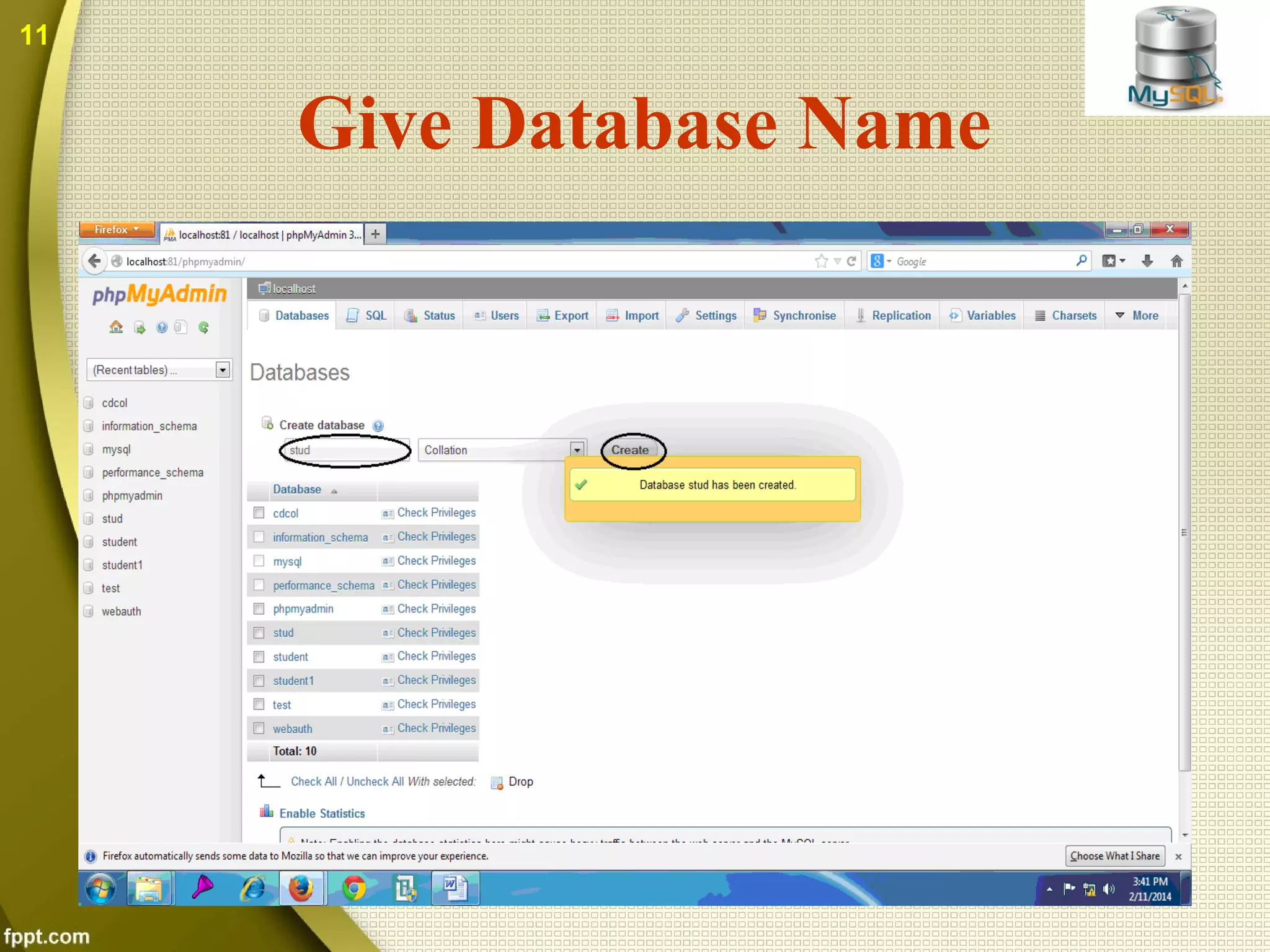
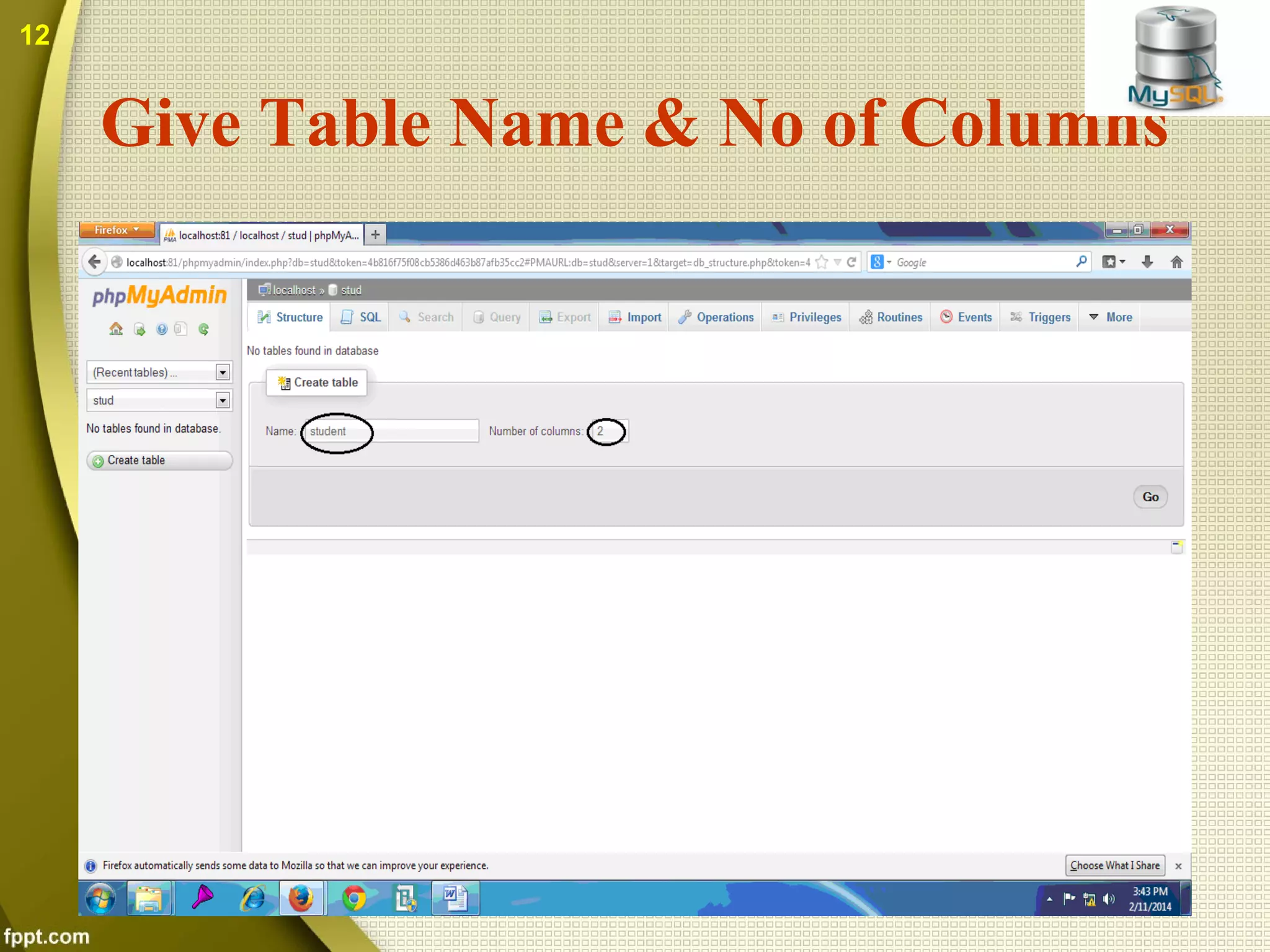
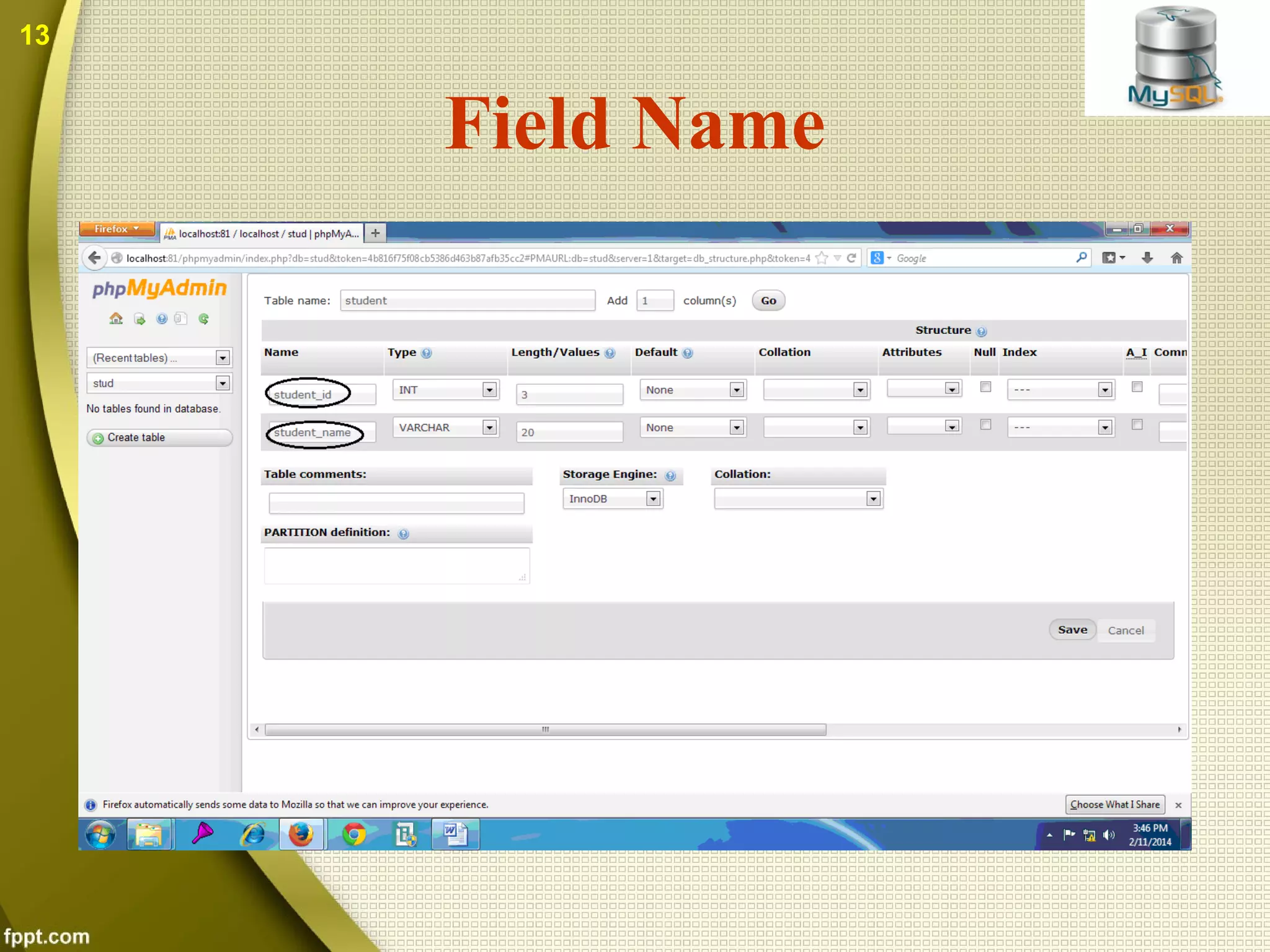
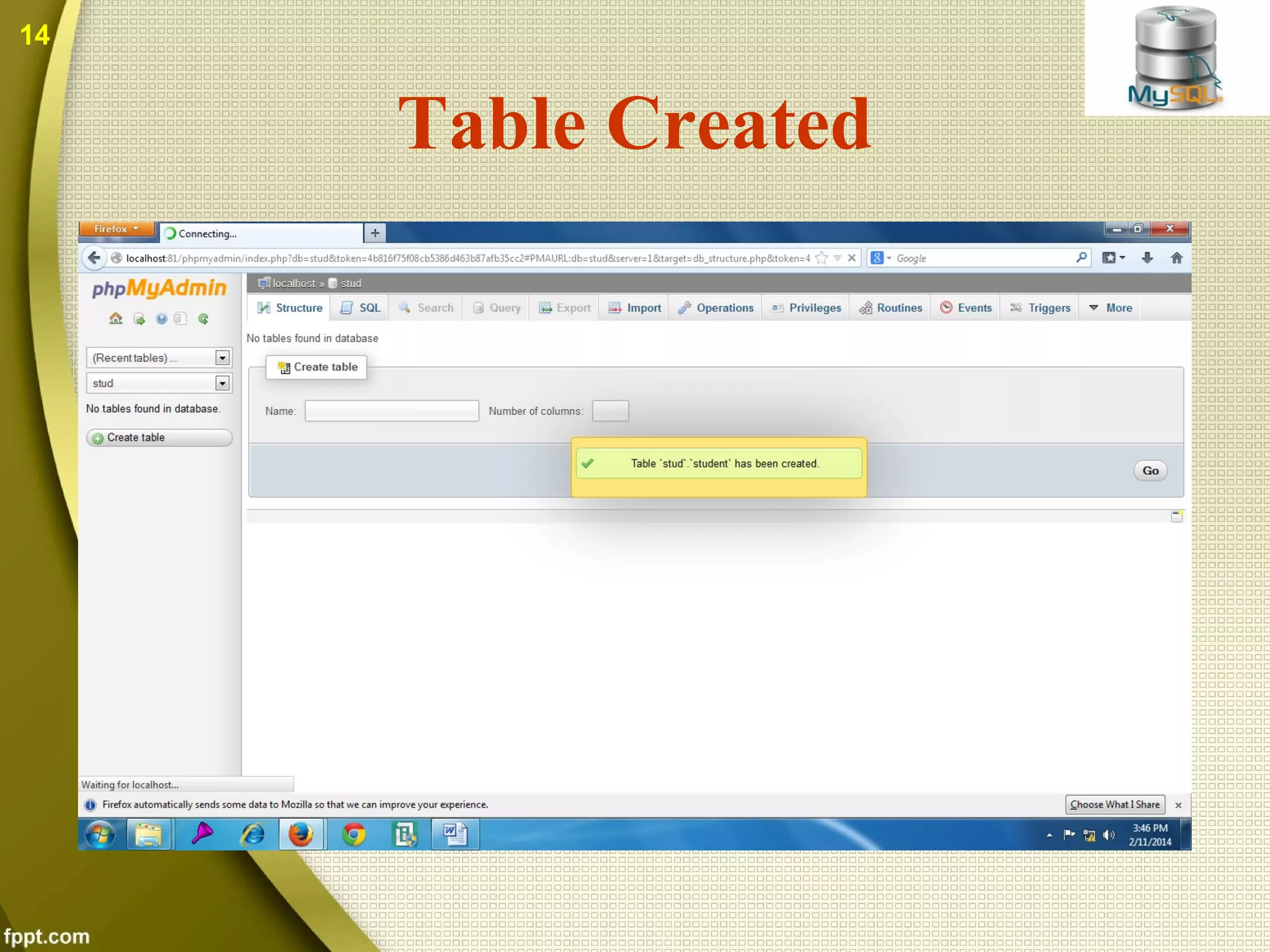
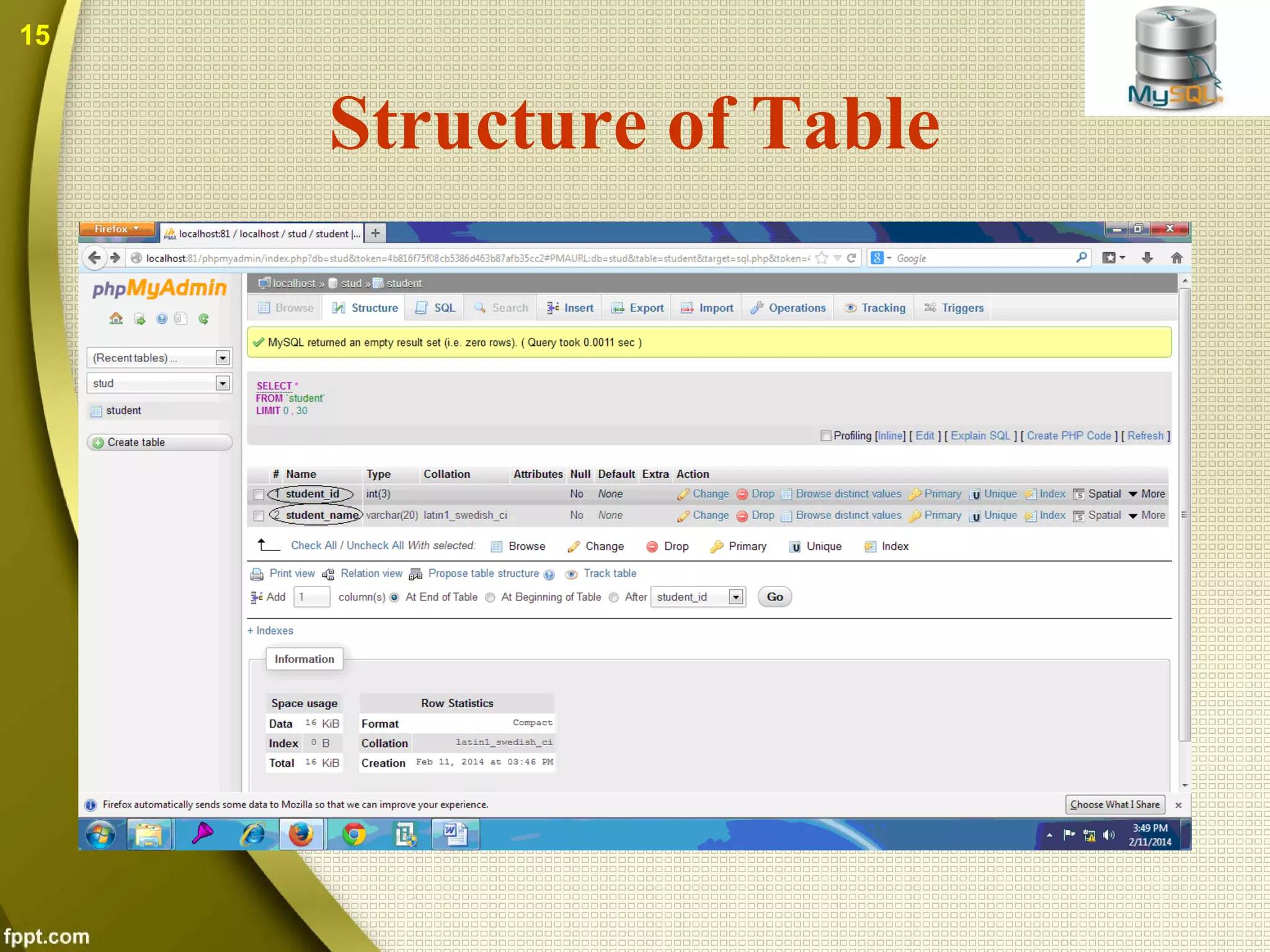
The document introduces MySQL, including what it is, how to create databases and tables, basic operations and functions. MySQL is an open source database that stores data in tables within databases. It can be used with many programming languages. The document discusses how to connect to a MySQL database, select tables, perform queries, and other common functions. Both benefits like being open source and cross-platform, and drawbacks like limited capabilities with large databases are covered.