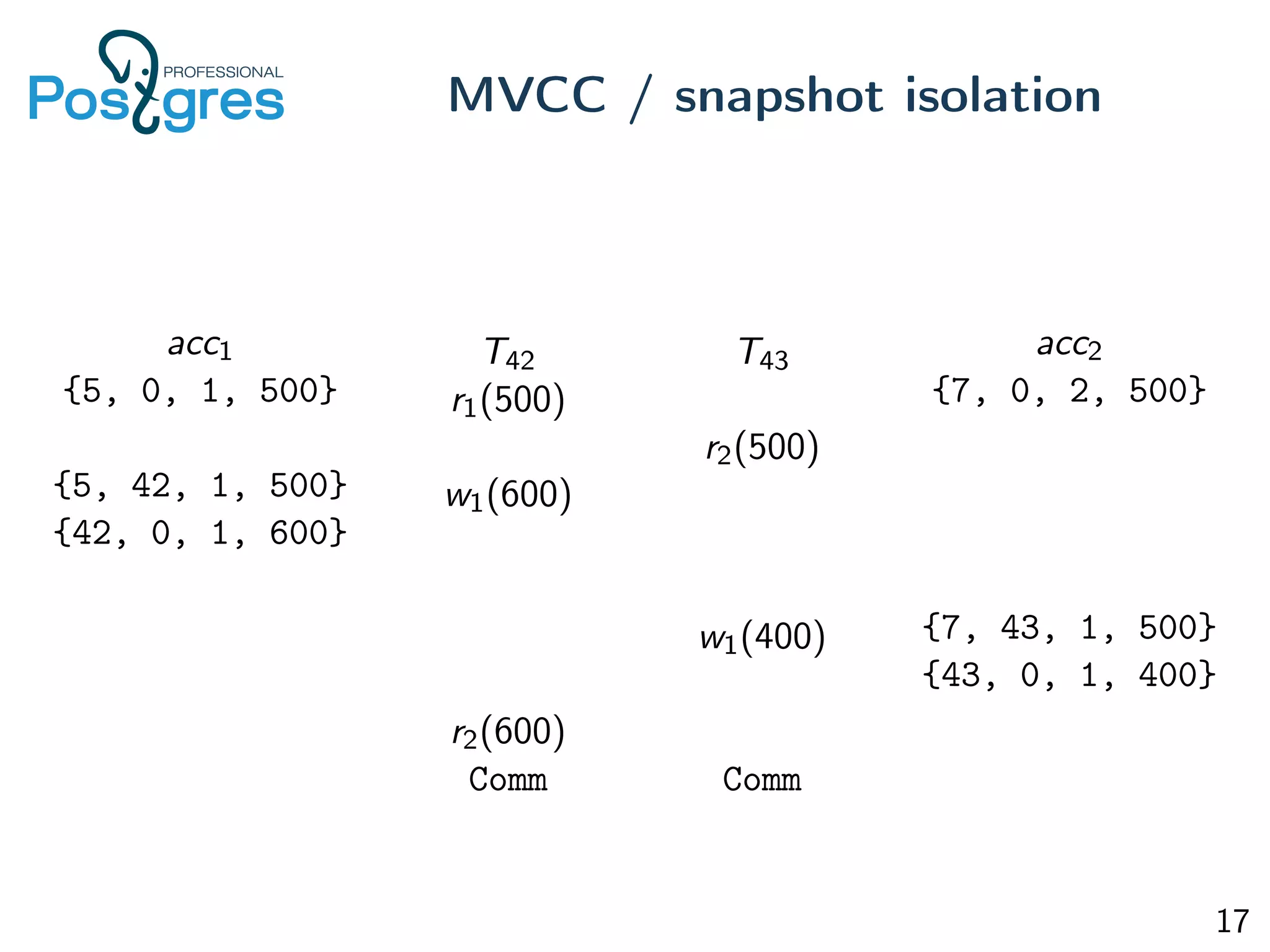
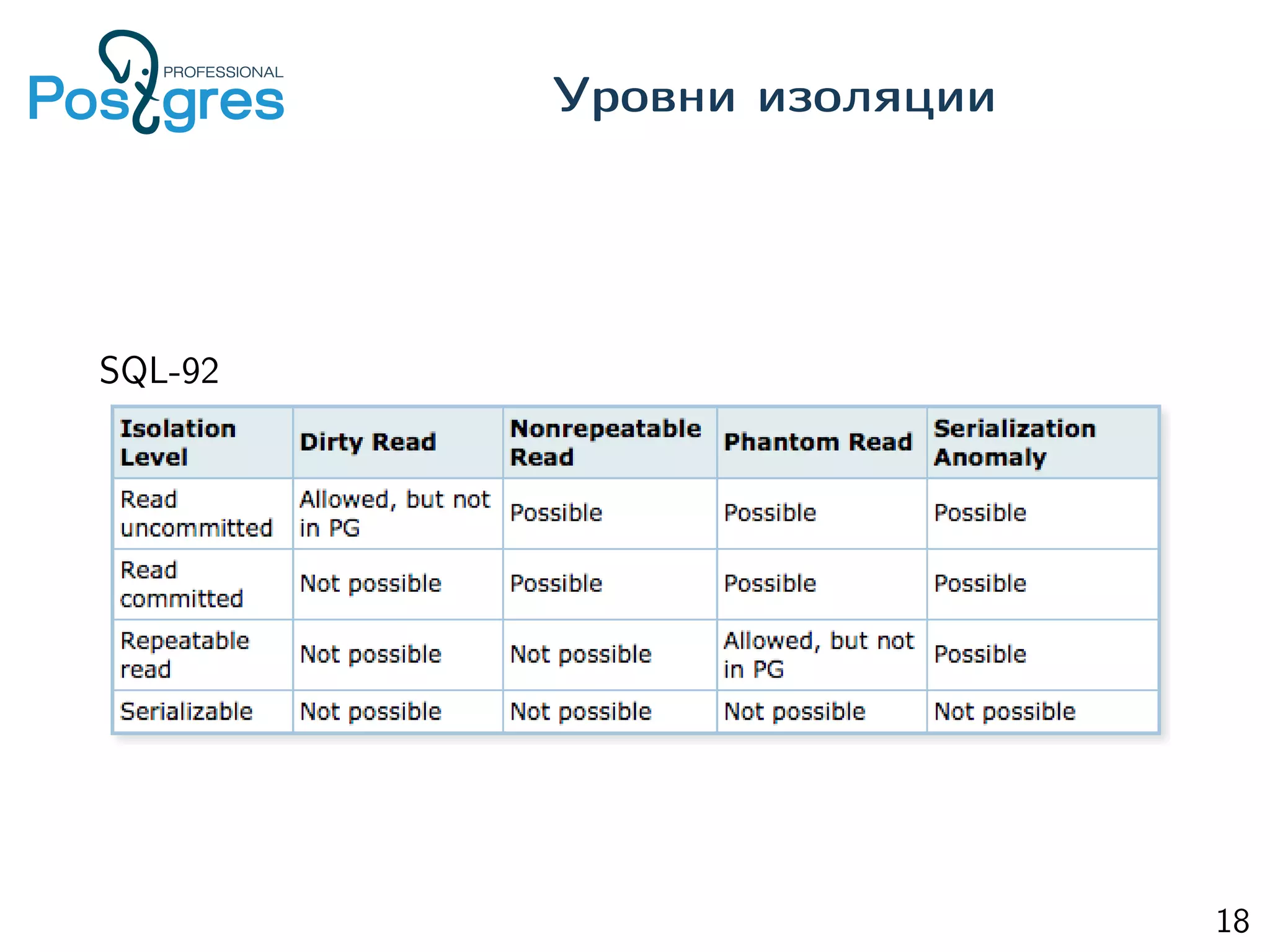
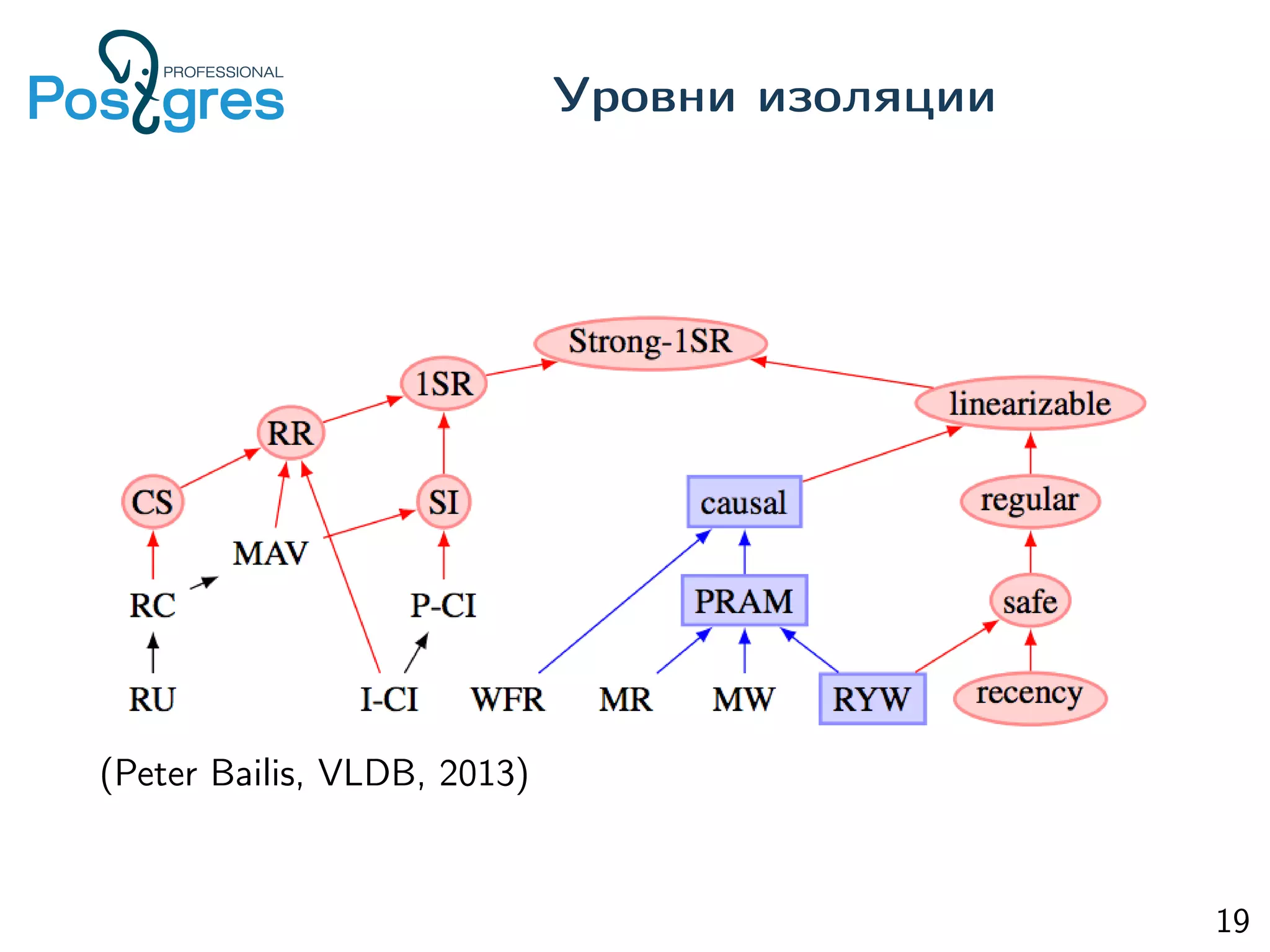
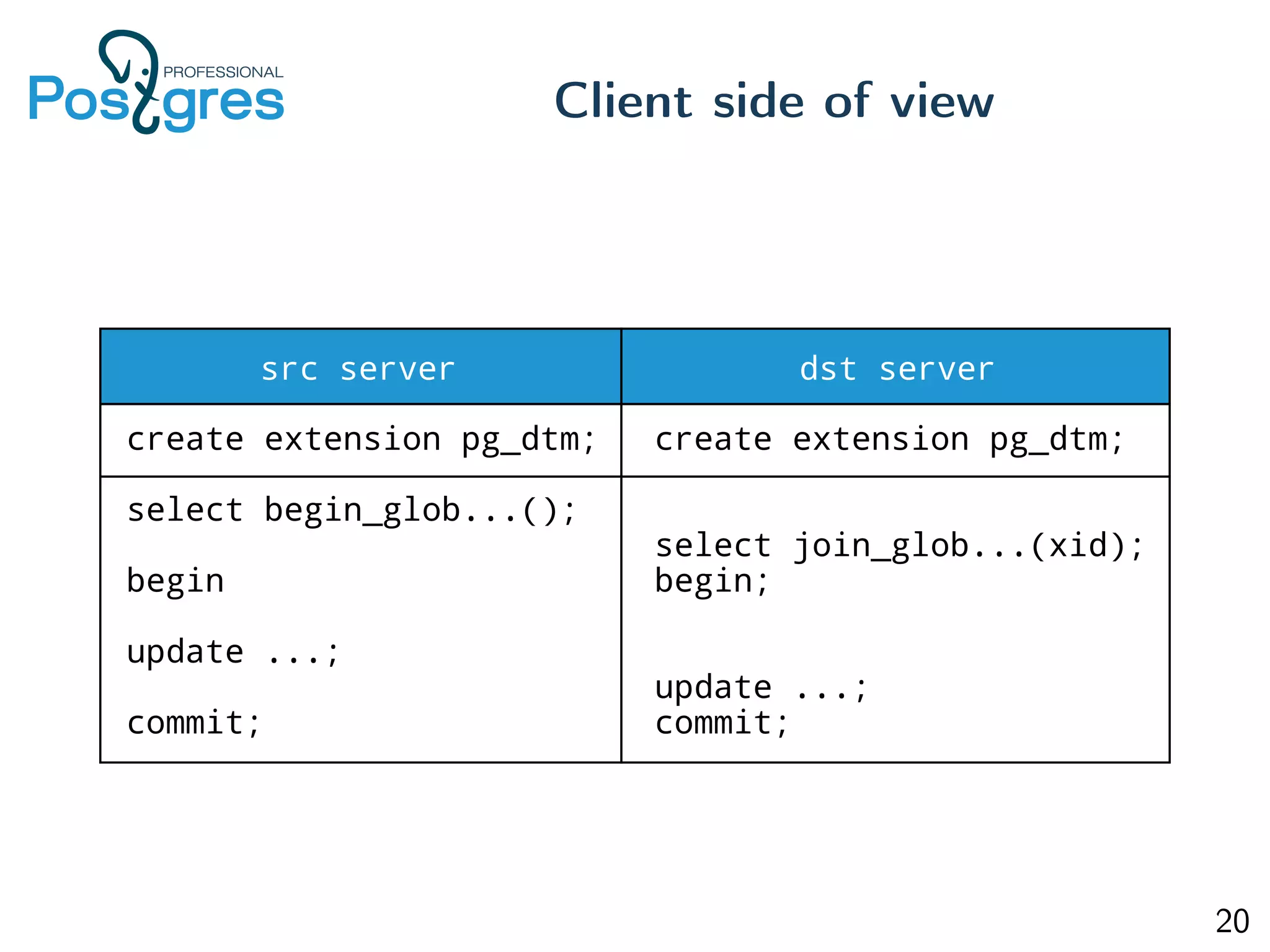
This document provides an overview of Postgres clustering solutions and distributed Postgres architectures. It discusses master-slave replication, Postgres-XC/XL, Greenplum, CitusDB, pg_shard, BDR, pg_logical, and challenges around distributed transactions, high availability, and multimaster replication. Key points include the tradeoffs of different approaches and an implementation of multimaster replication built on pg_logical and a timestamp-based distributed transaction manager (tsDTM) that provides partition tolerance and automatic failover.














![More nodes, higher probability of failure in system. Possible problems with nodes: Node stopped (and will not be back); Node was down small amount of time (and we should bring it back to operation); Network partitions (avoid split-brain). If we want to survive network partitions than we can have not more than [N/2] - 1 failures. HA/autofailover 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgresclusters-161214115253/75/Postgres-clusters-29-2048.jpg)



