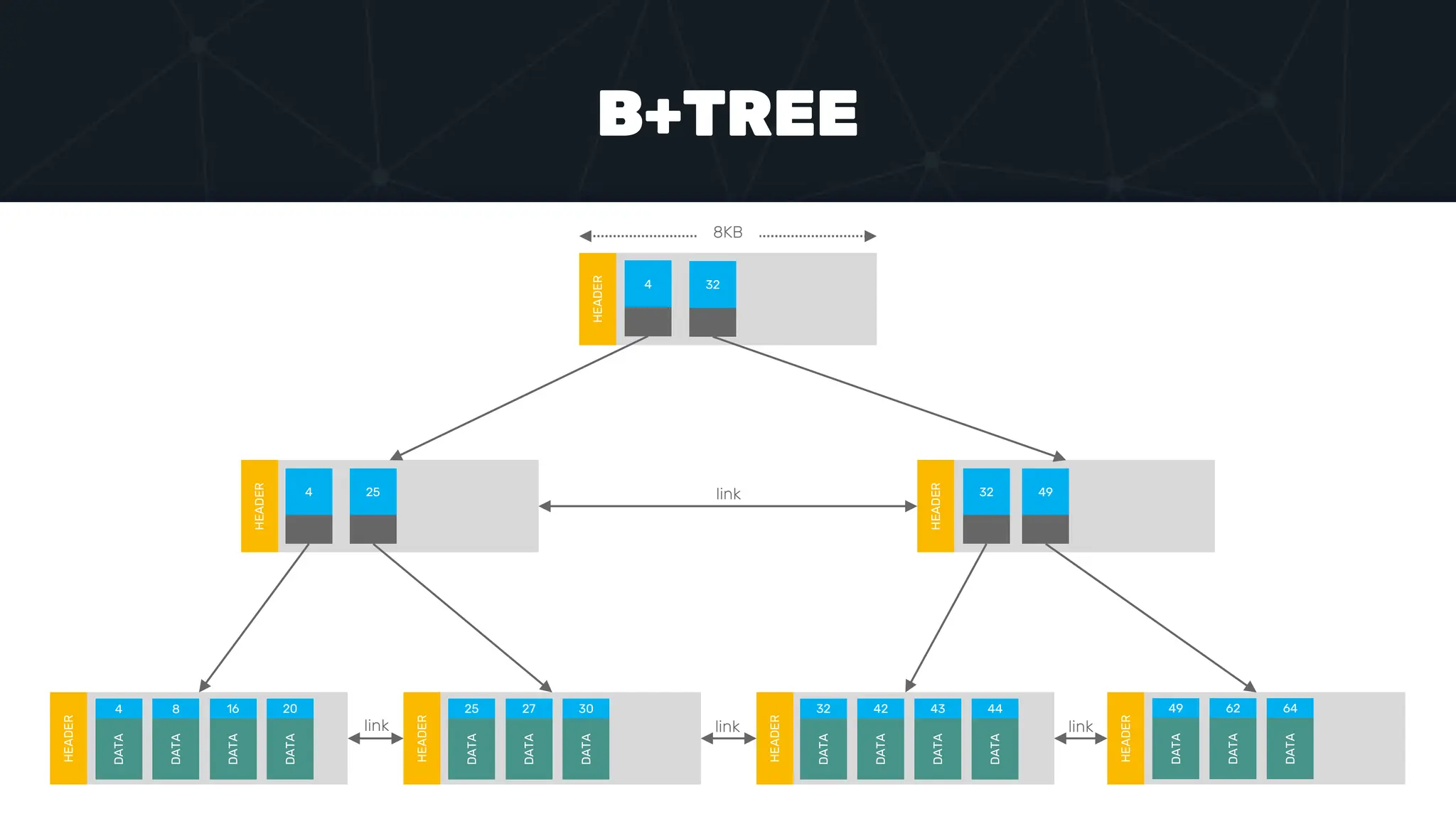
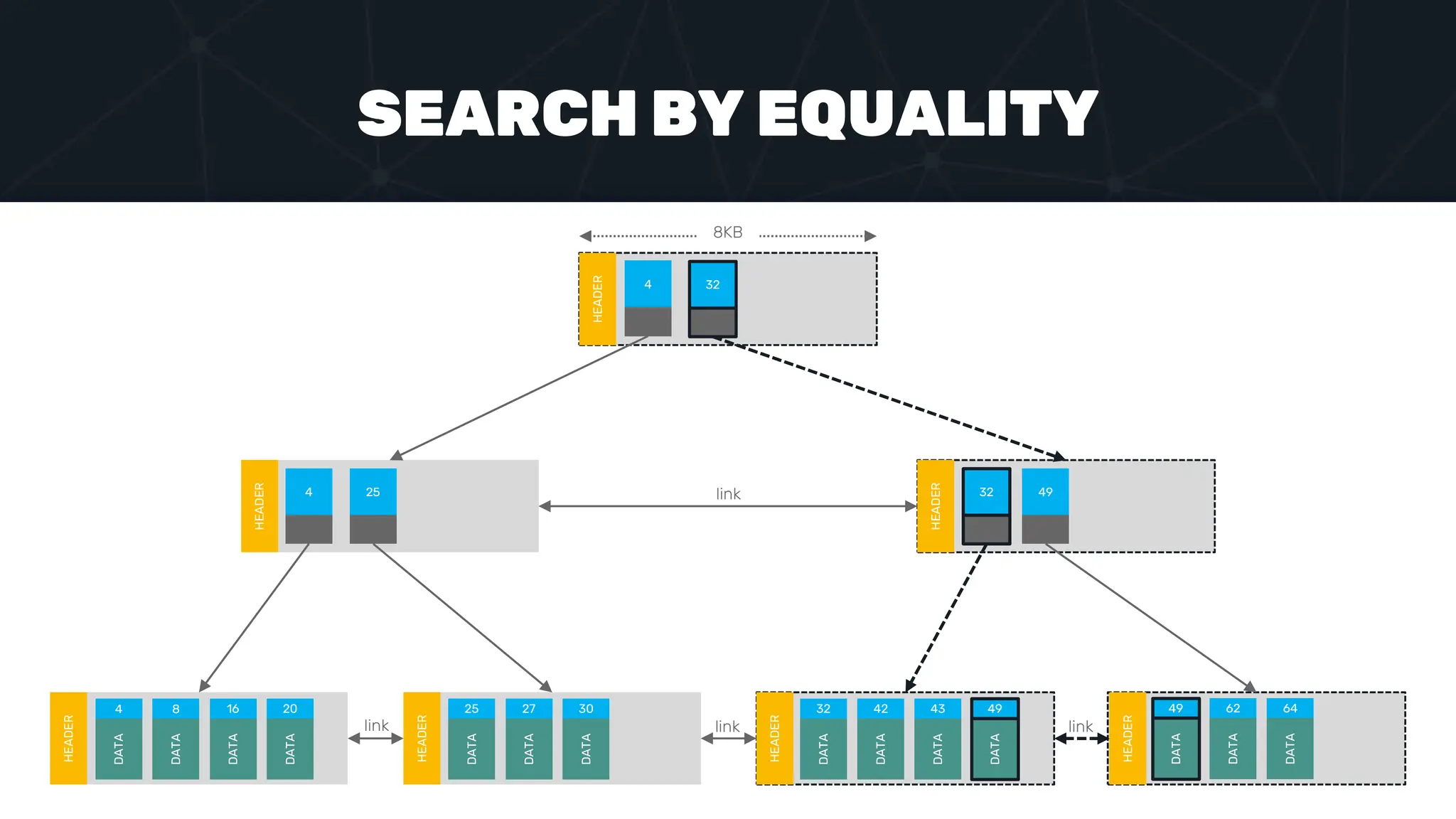
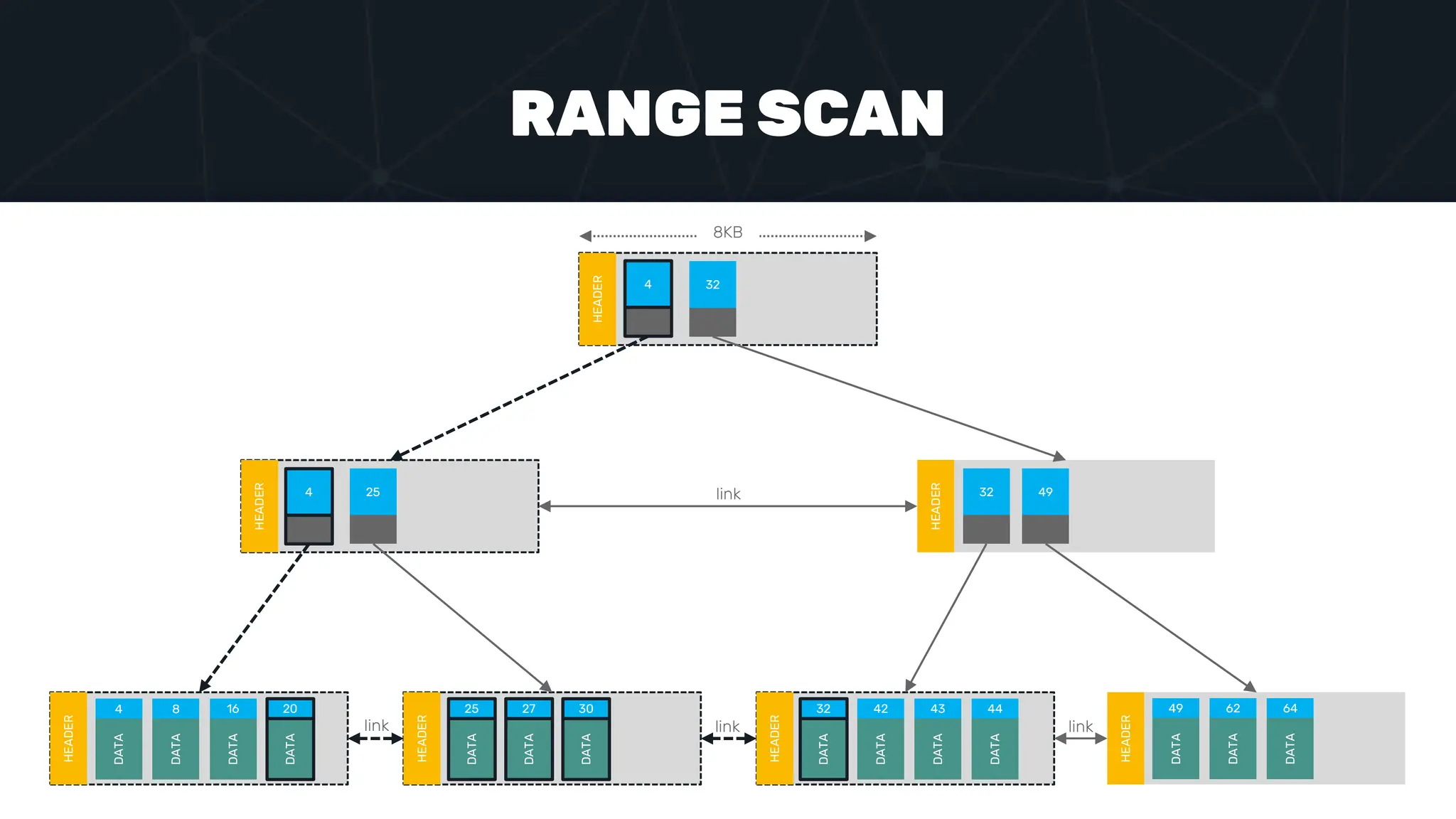
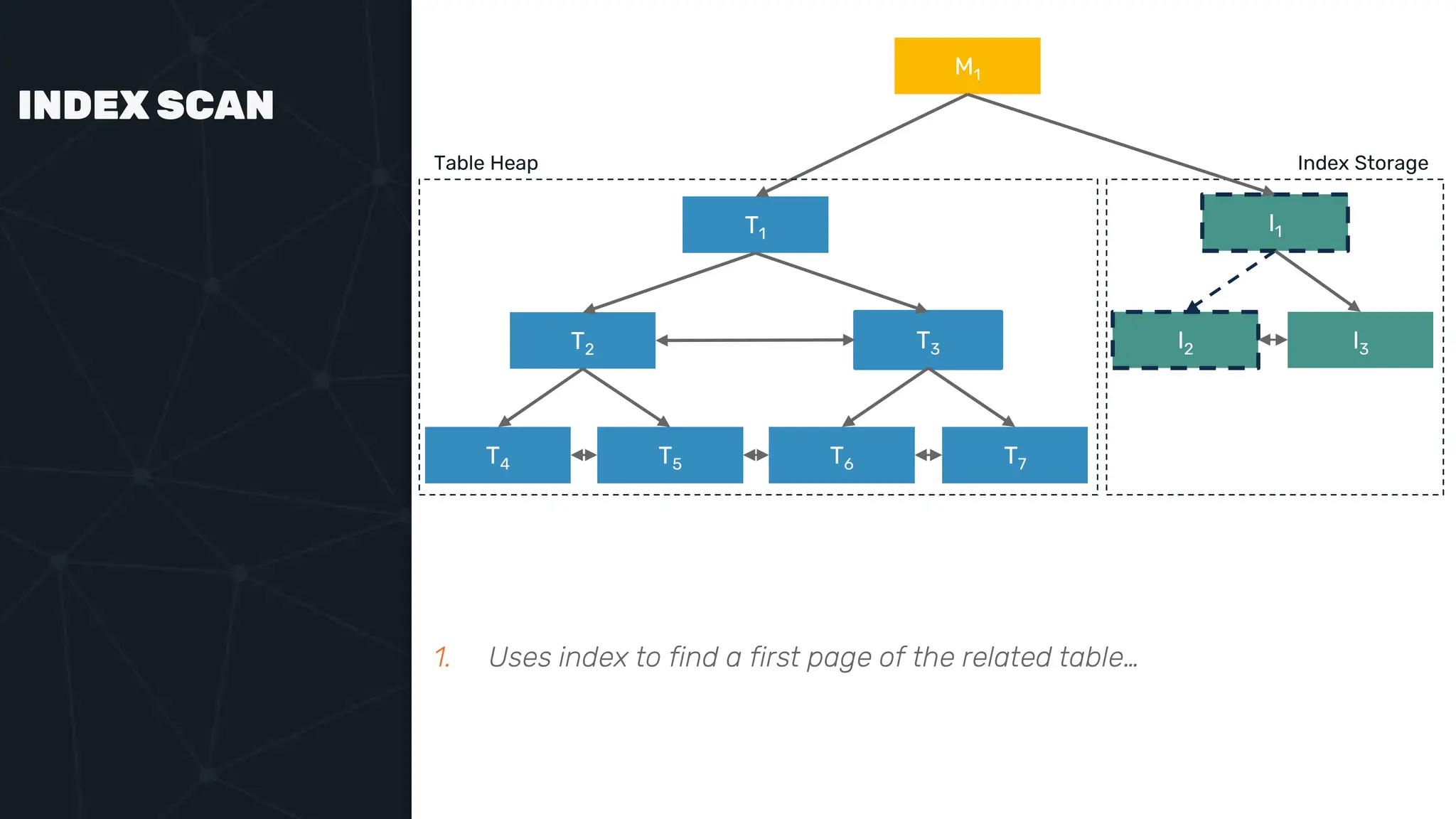
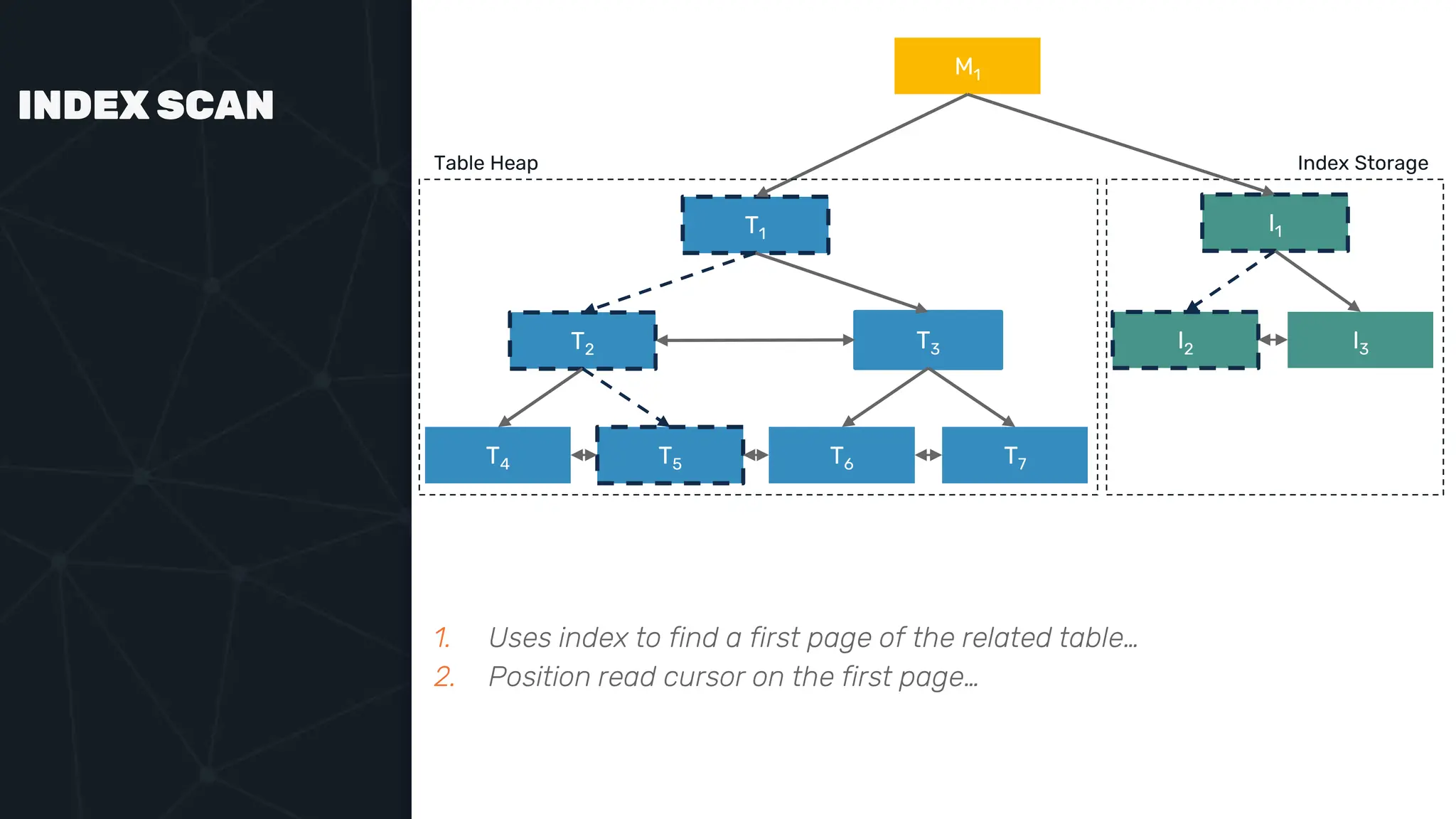
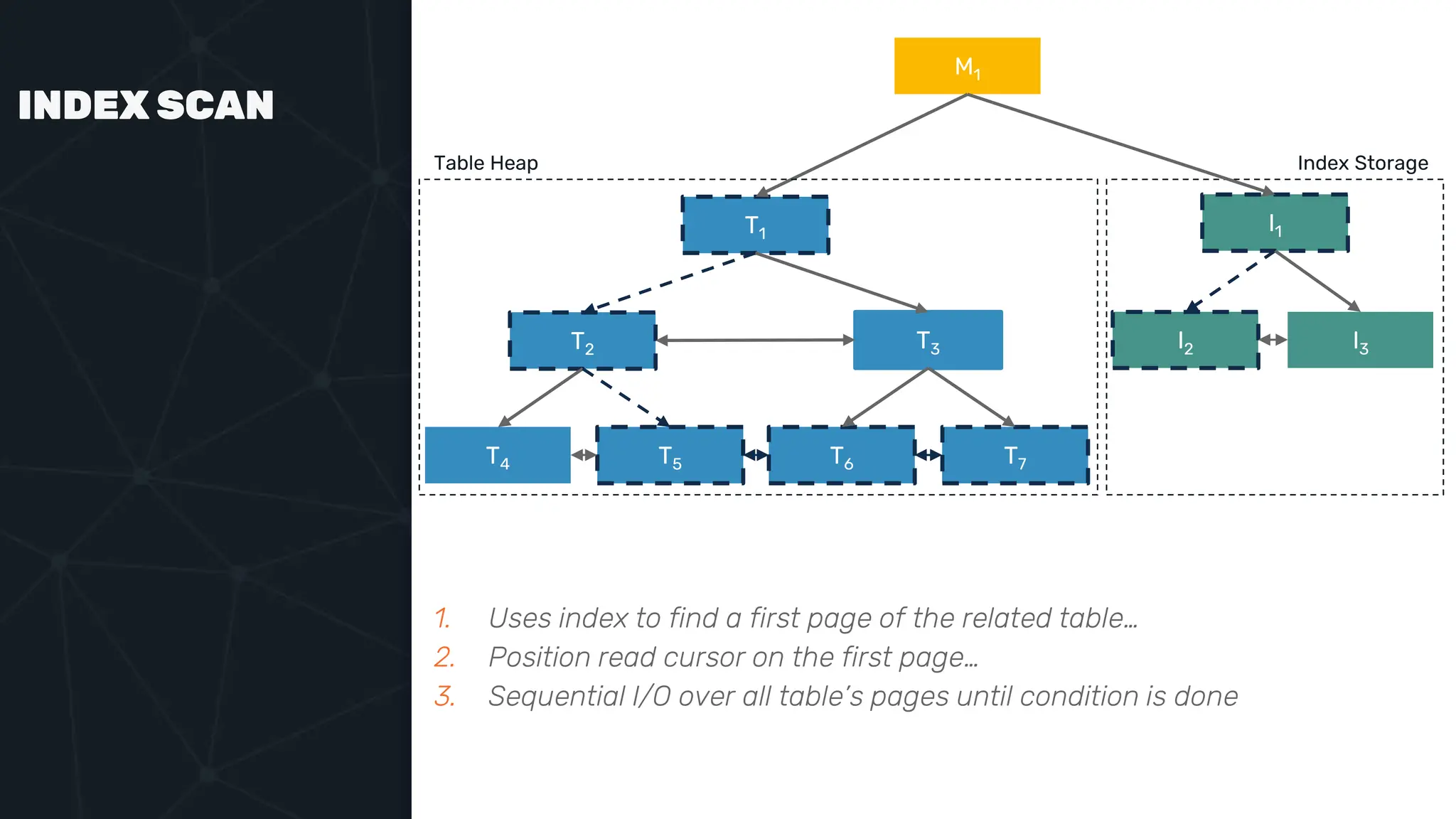
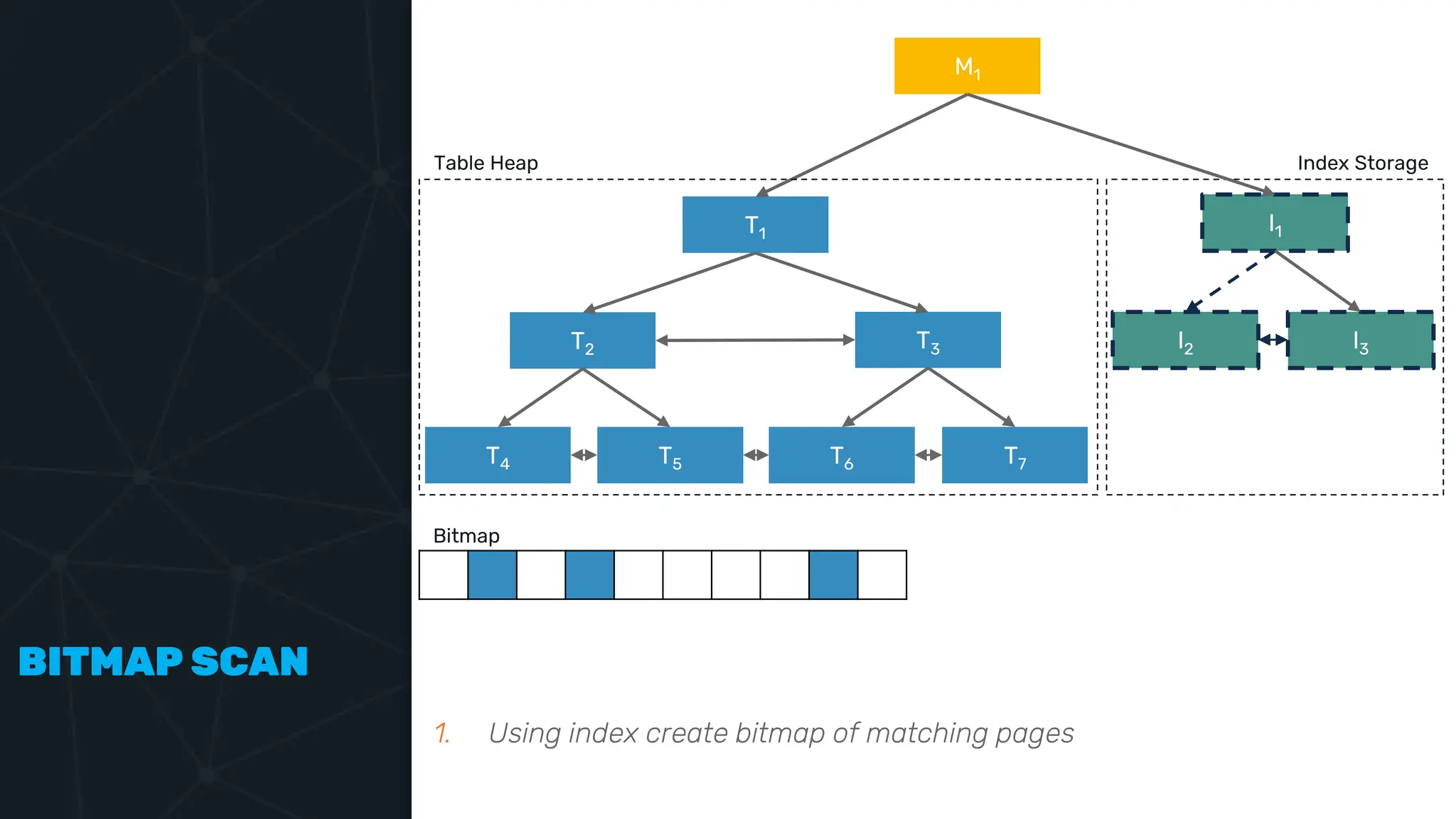
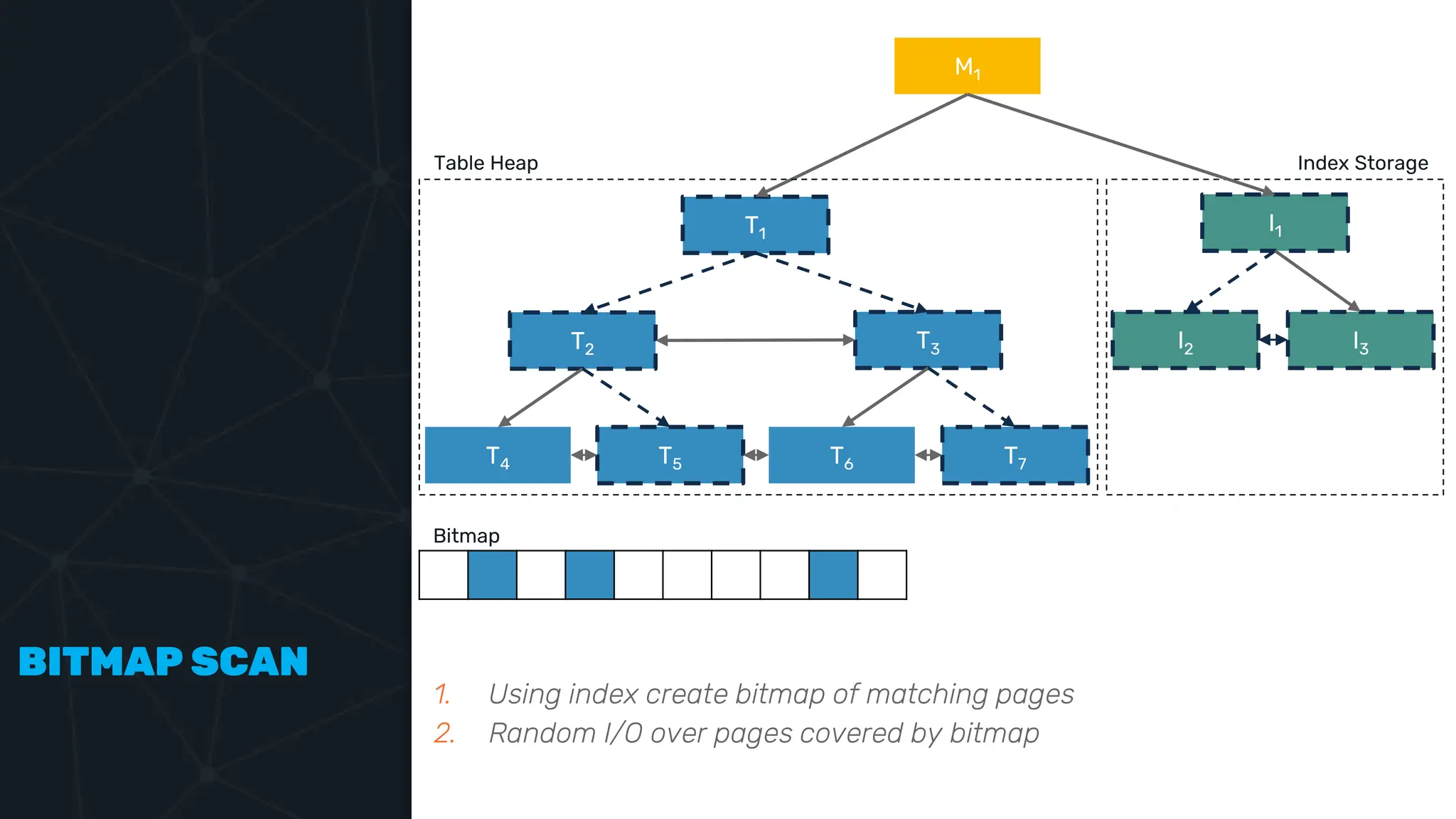
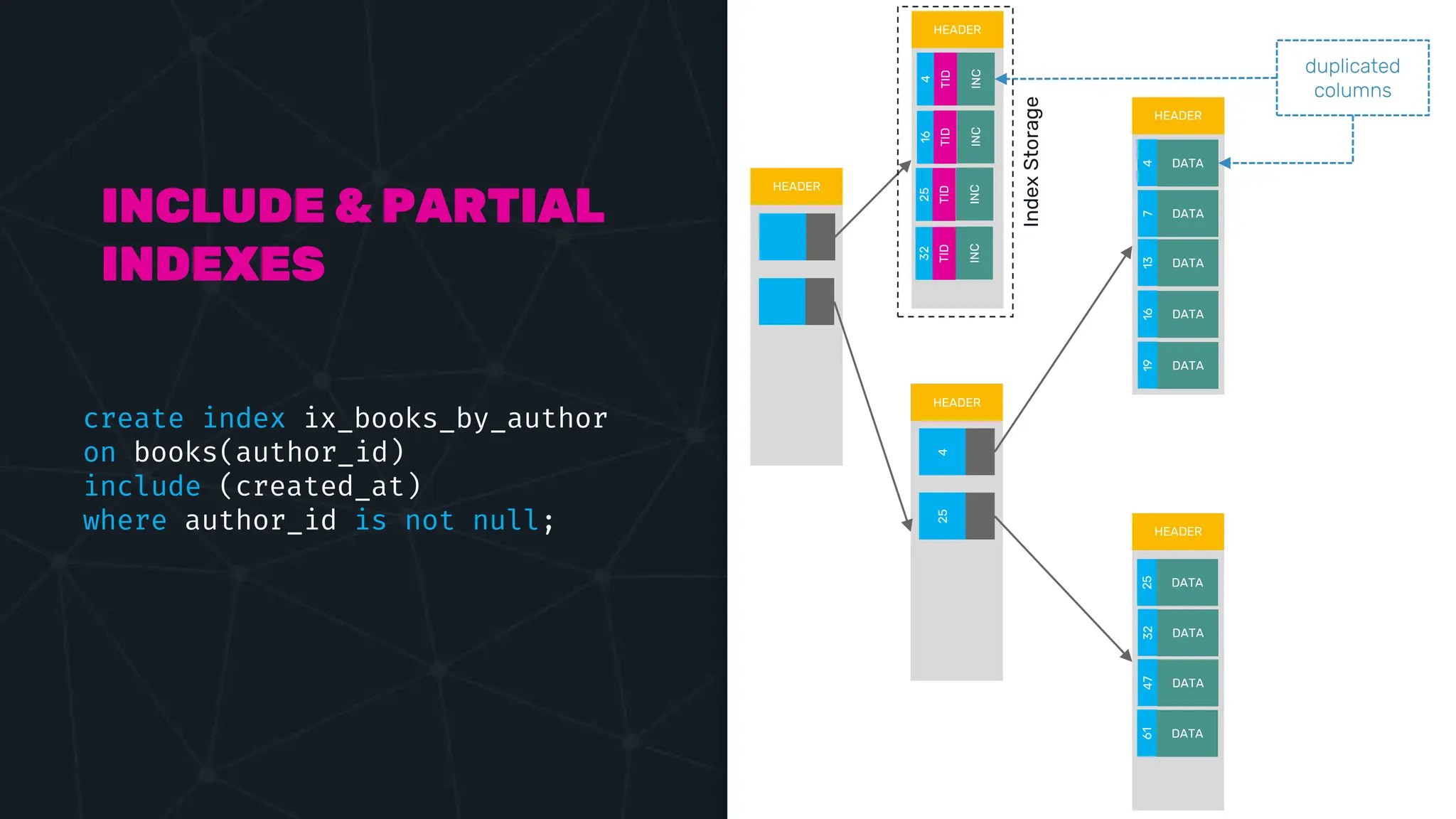
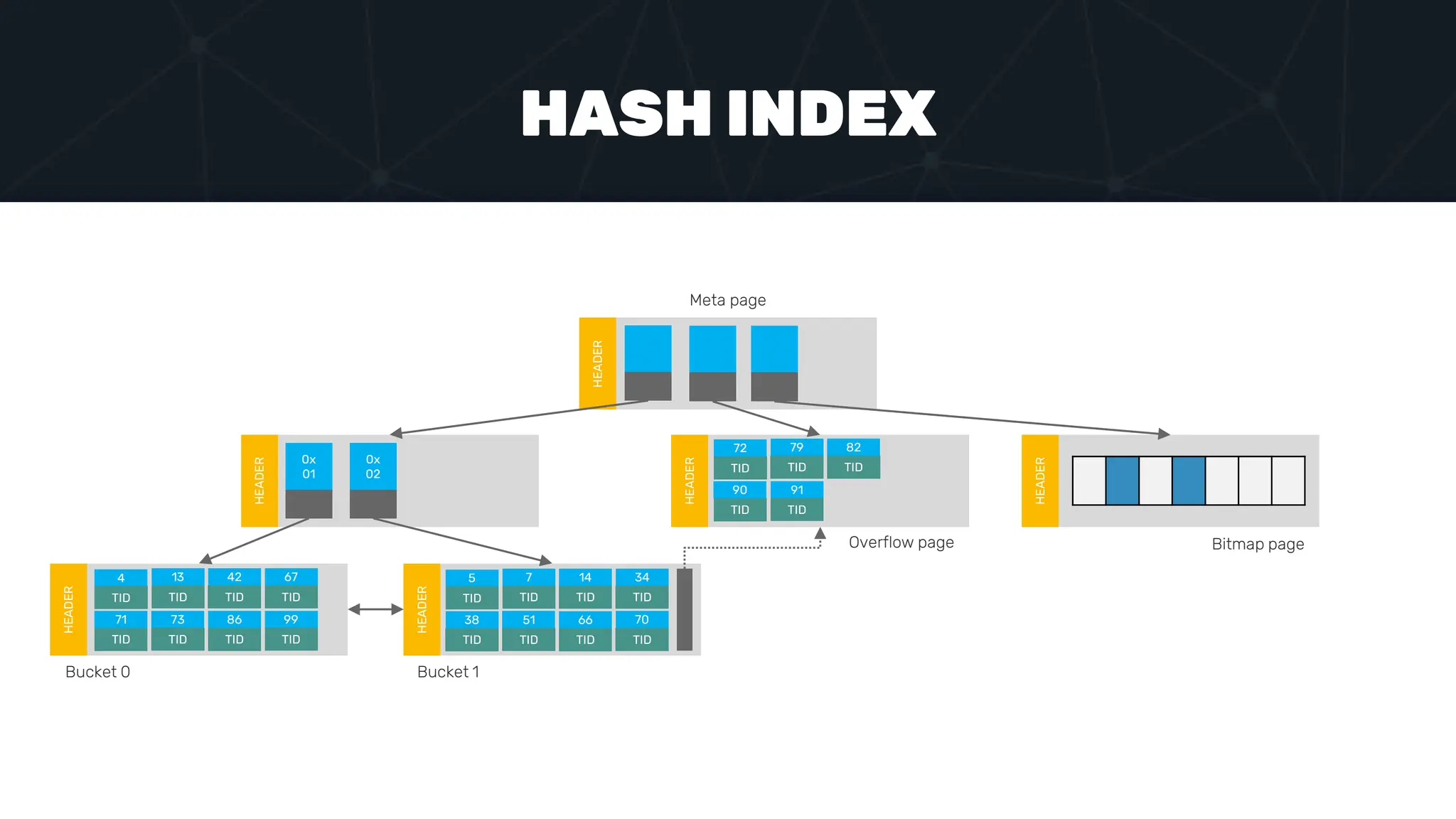
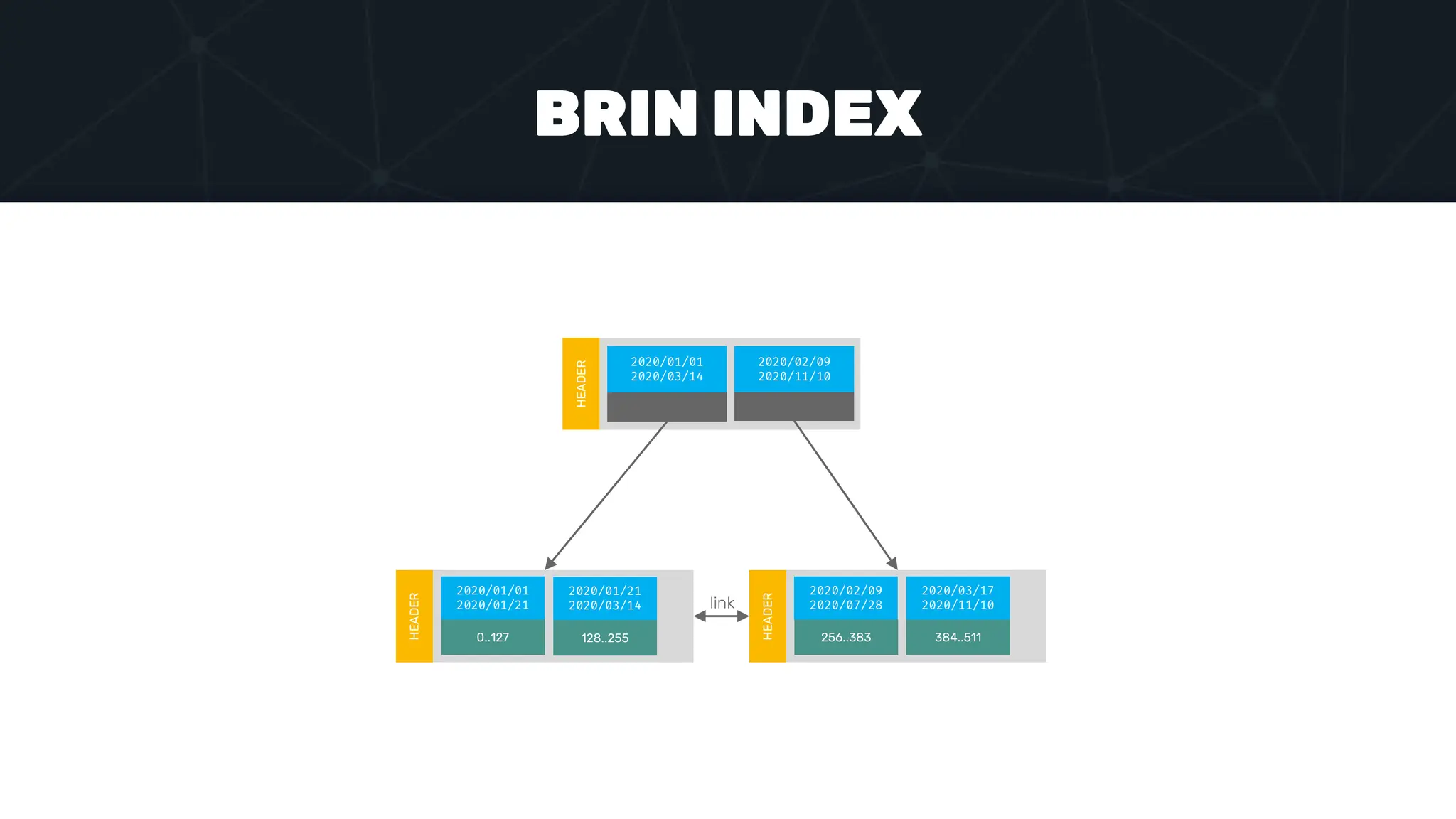
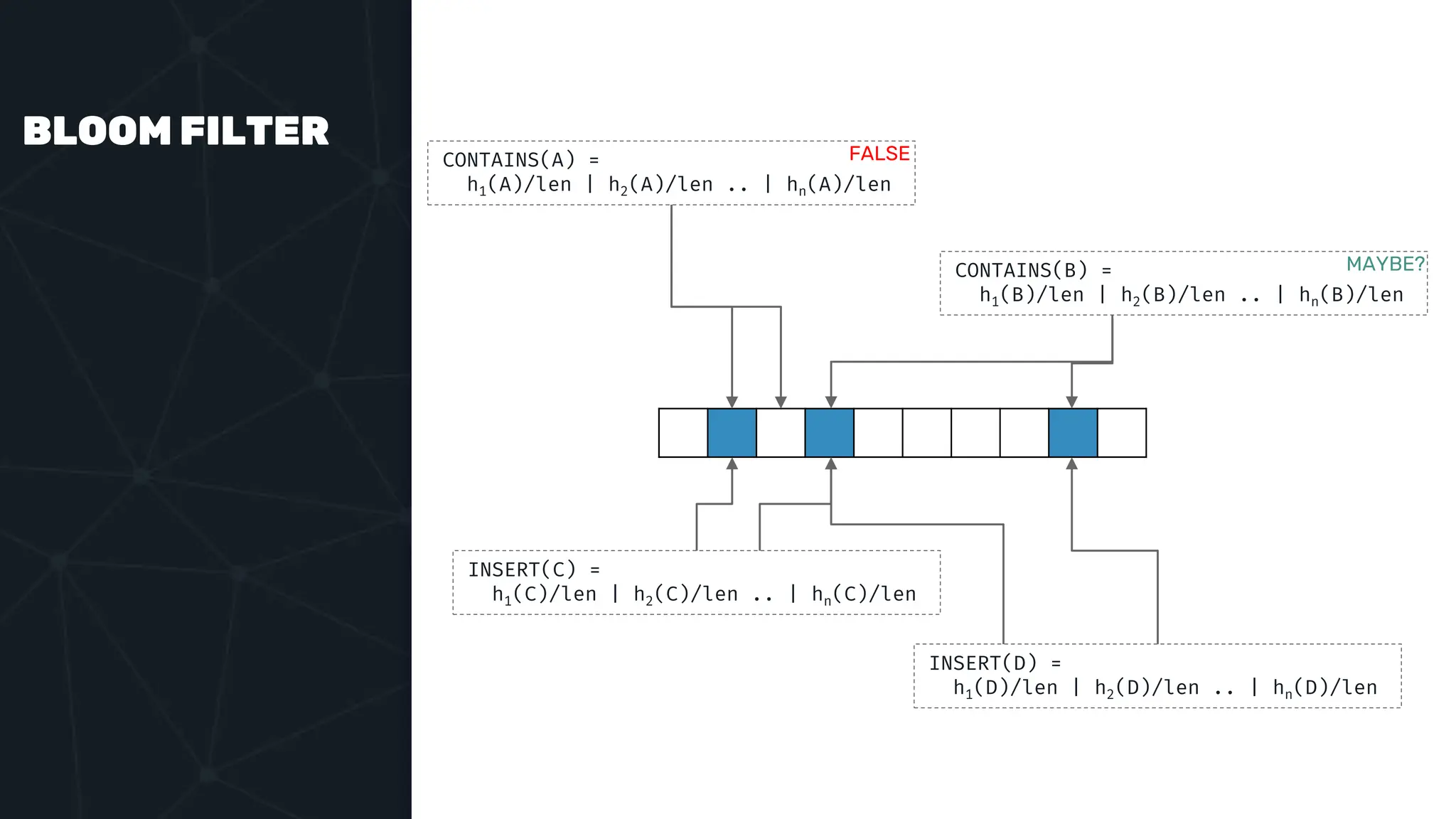
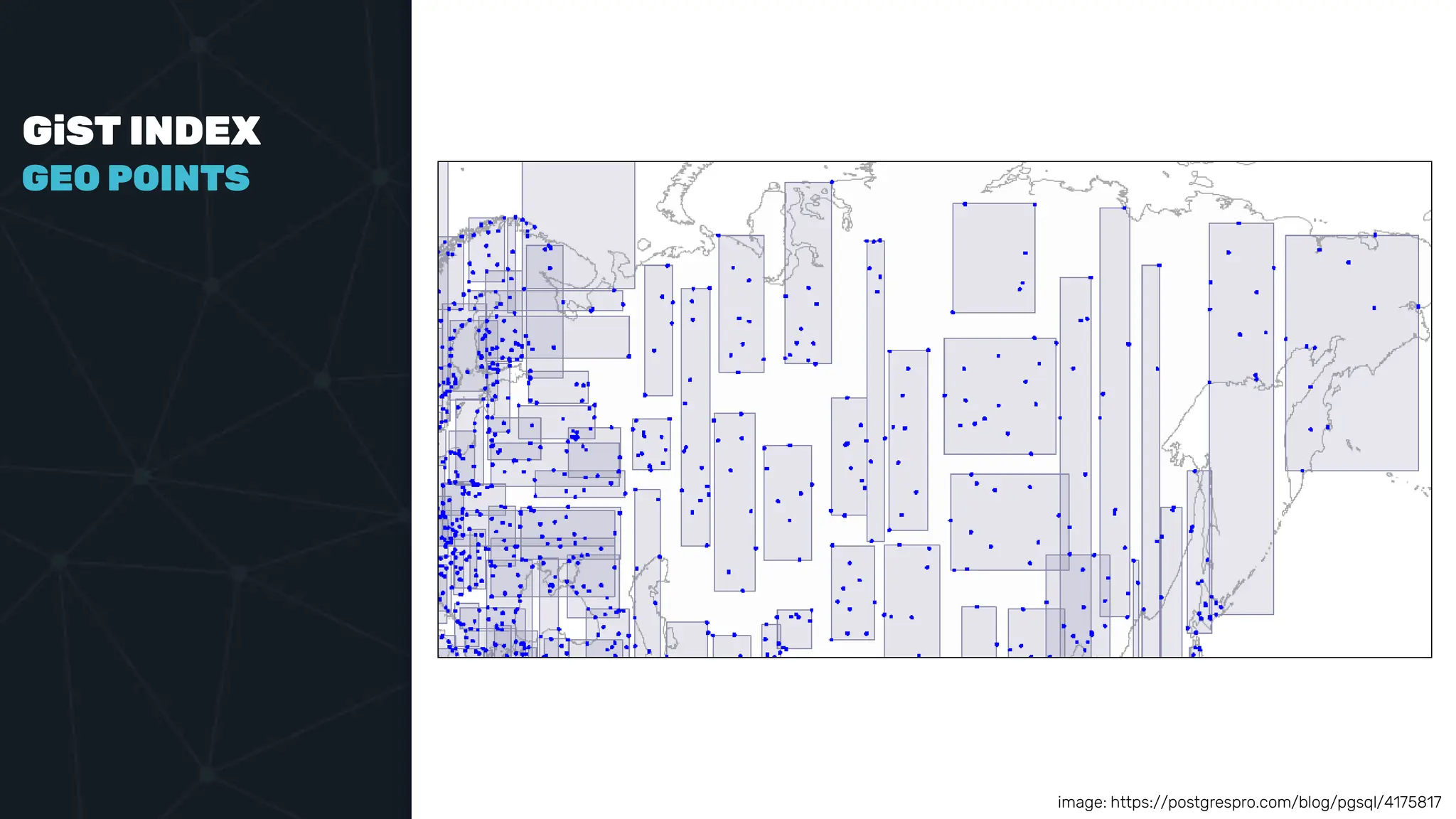
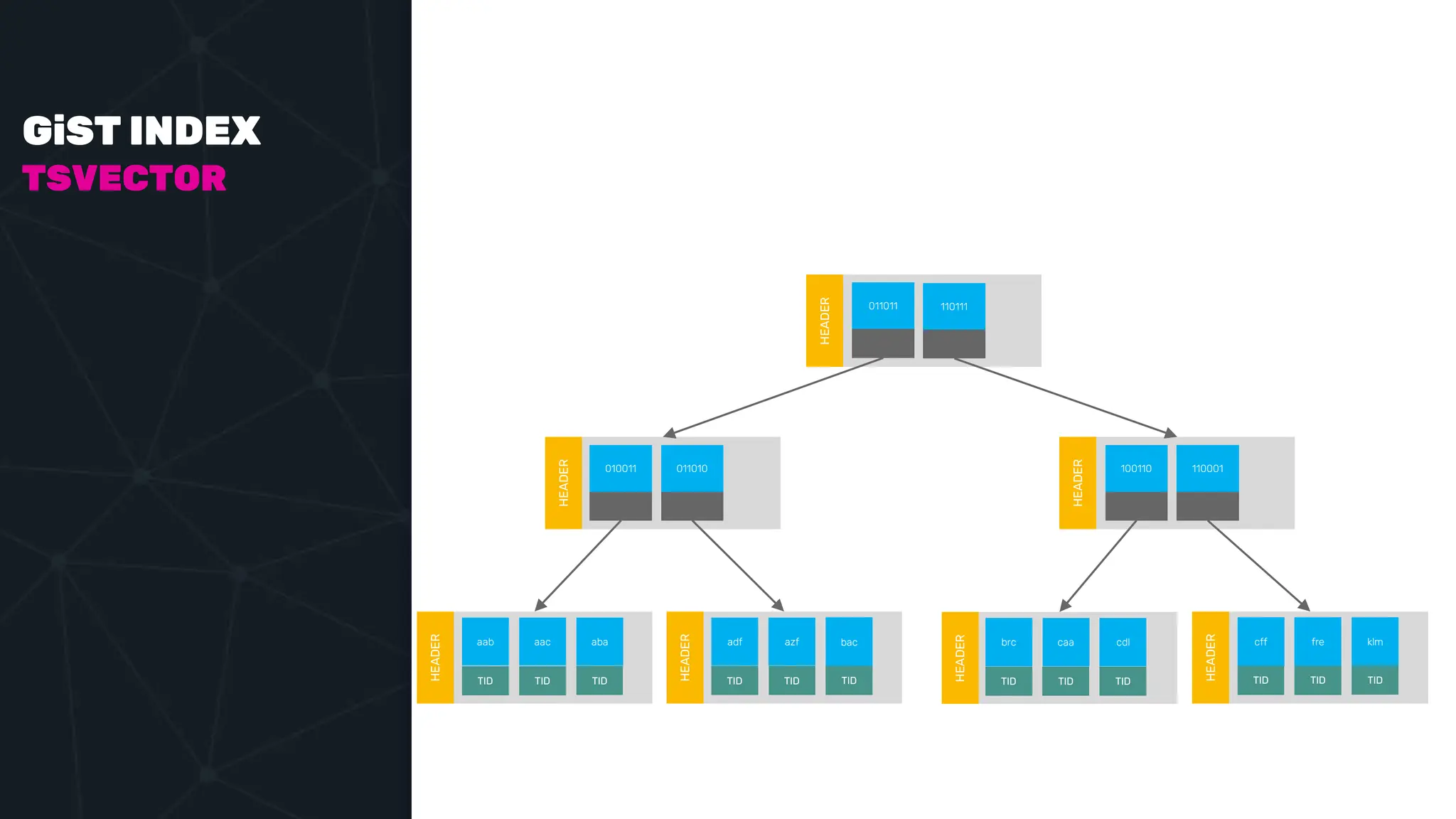
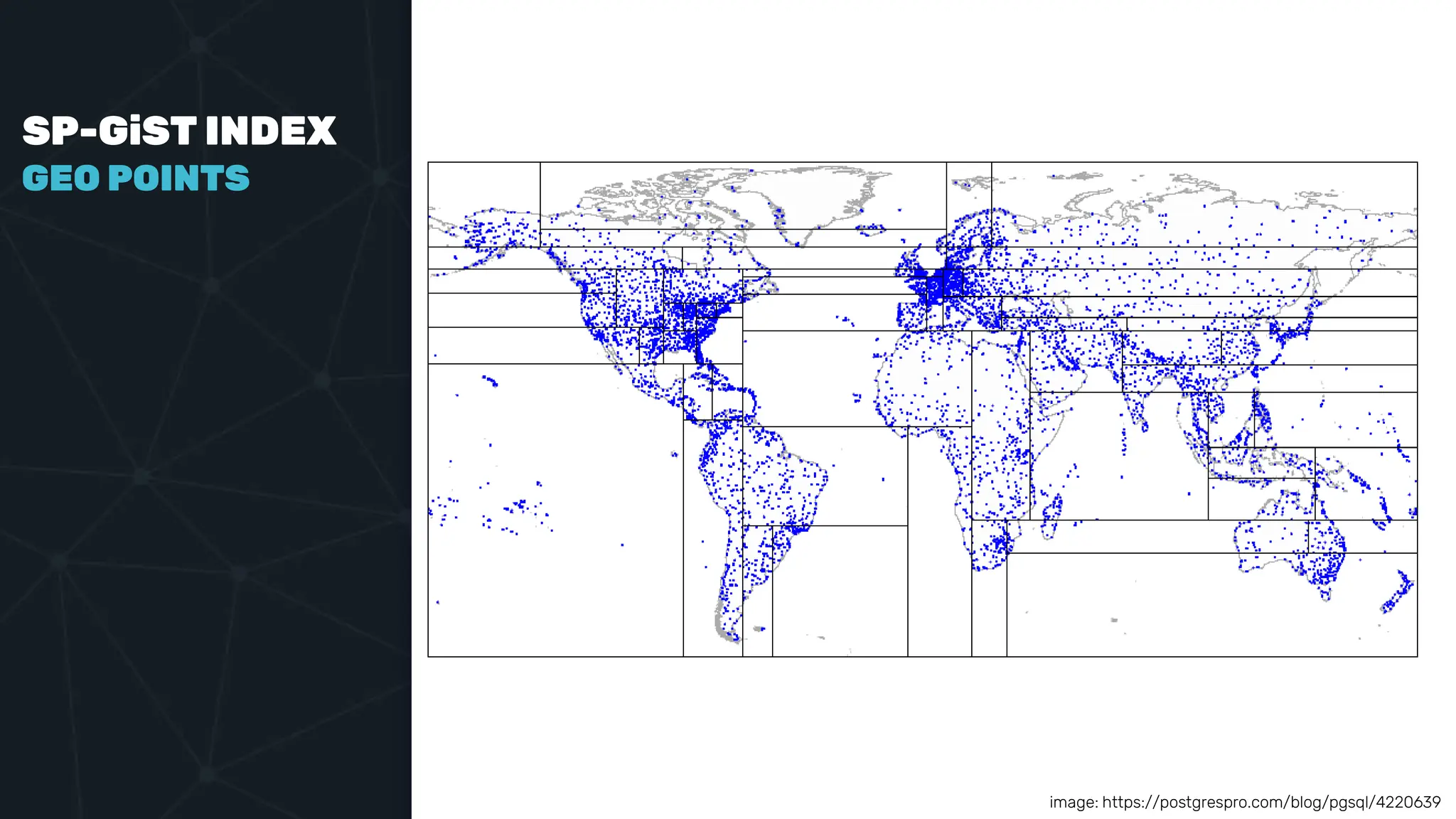
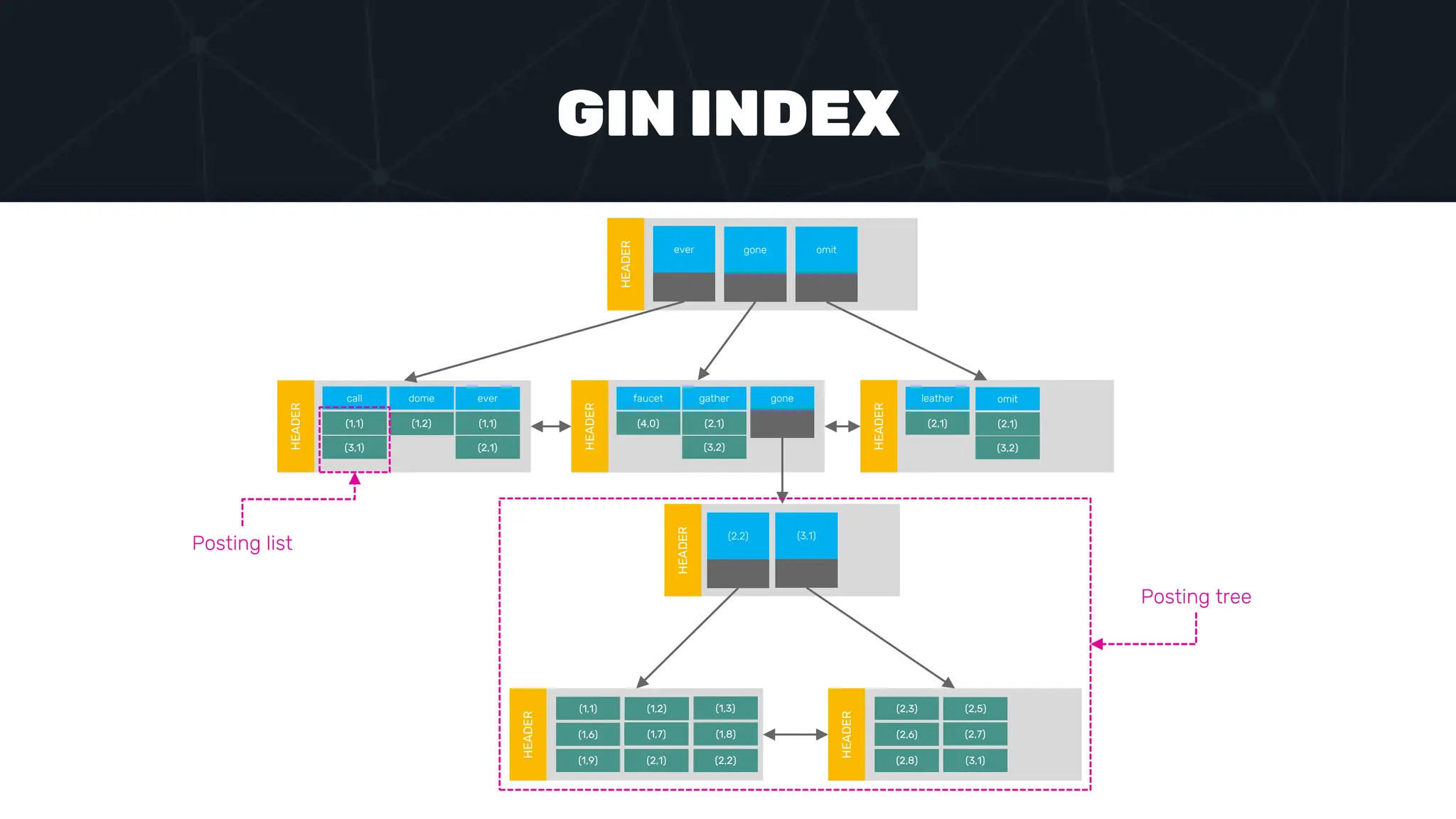
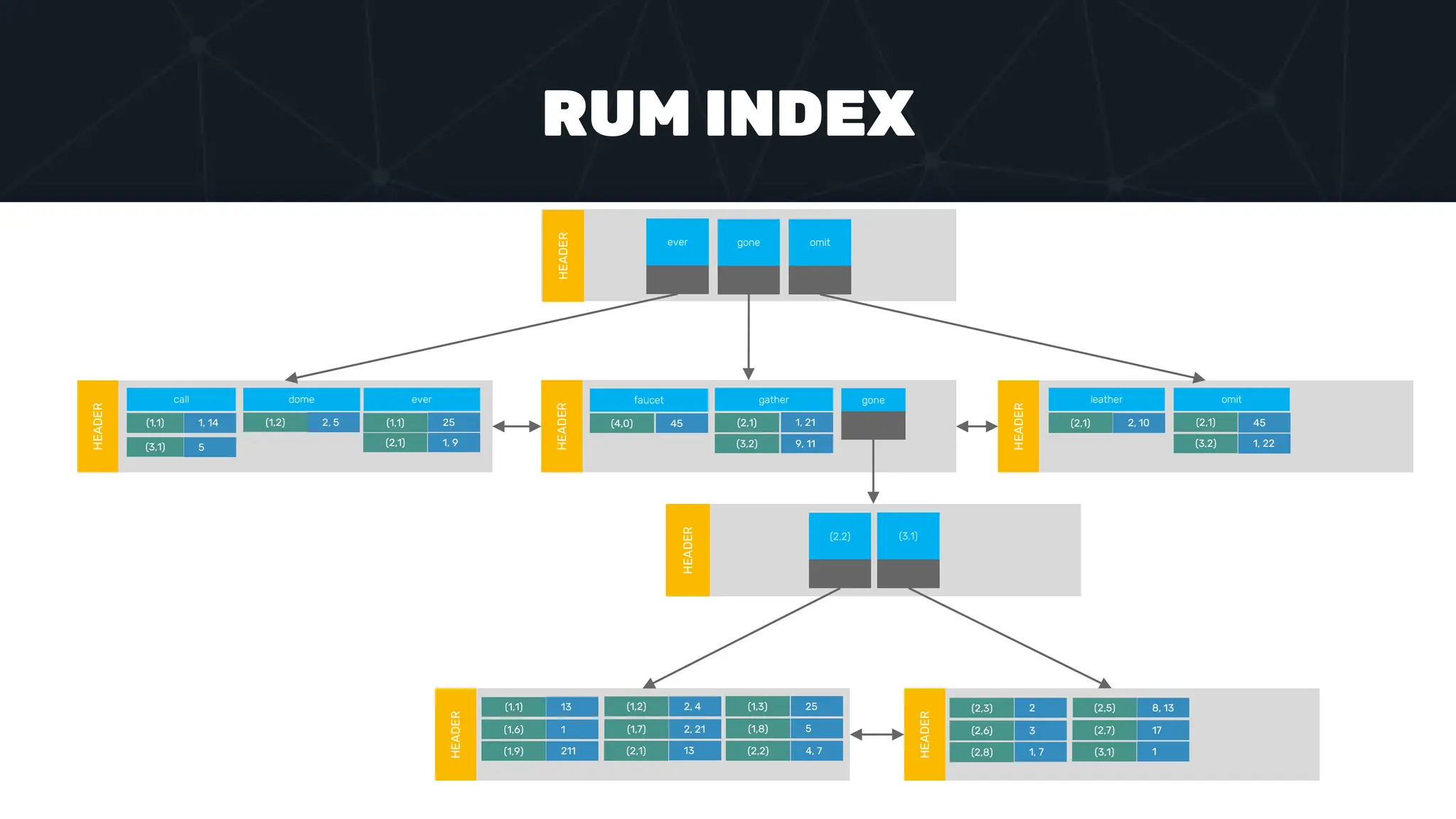
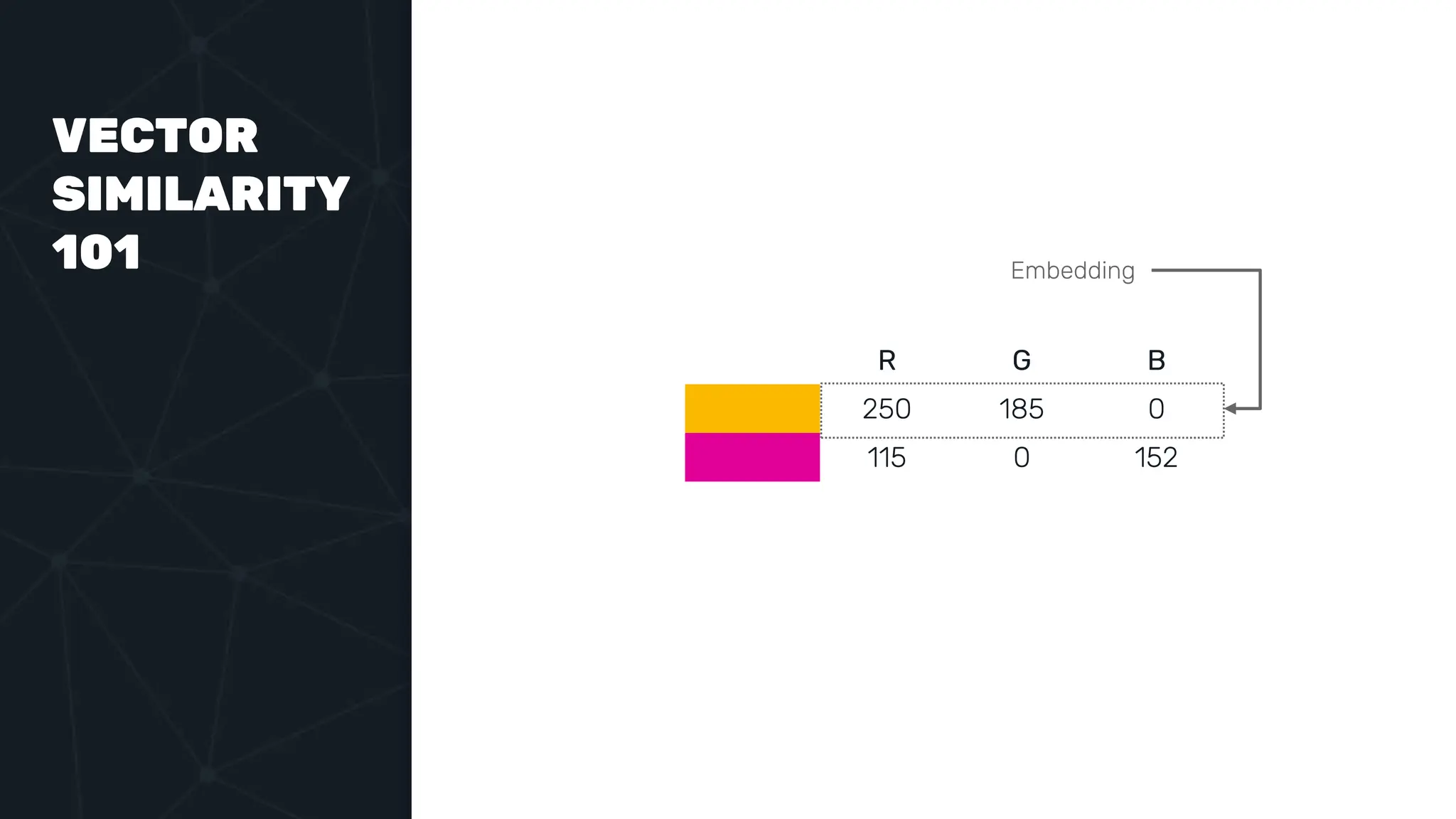
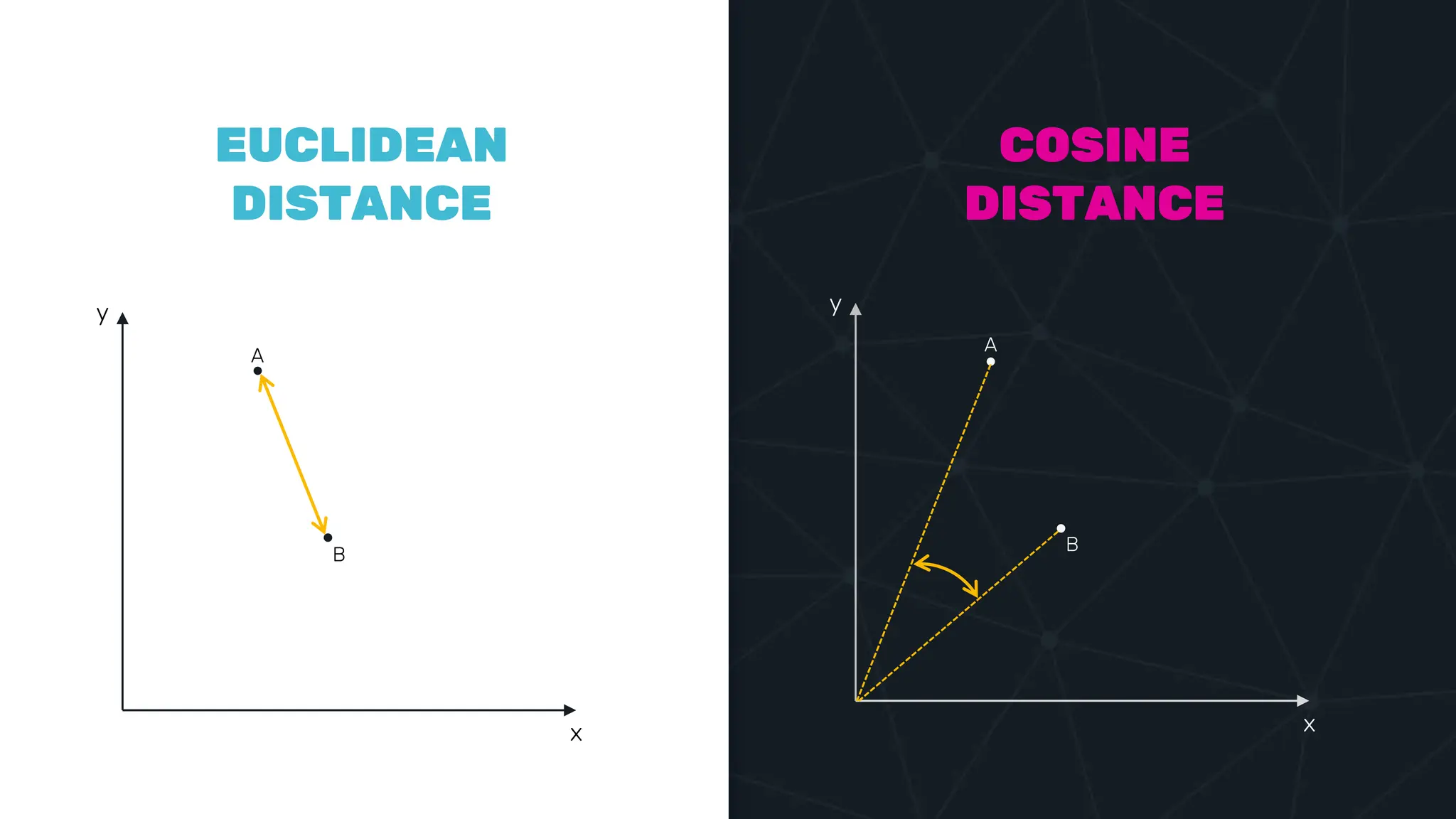
The document provides an in-depth examination of PostgreSQL indexes, covering various types such as B-Tree, Hash, and GIN indexes, and their functionalities in querying and data management. It discusses query execution methods and optimizations, highlighting how different indexes can significantly impact performance. Additionally, the document includes examples of creating and utilizing different indexes for efficient data retrieval and search matching.




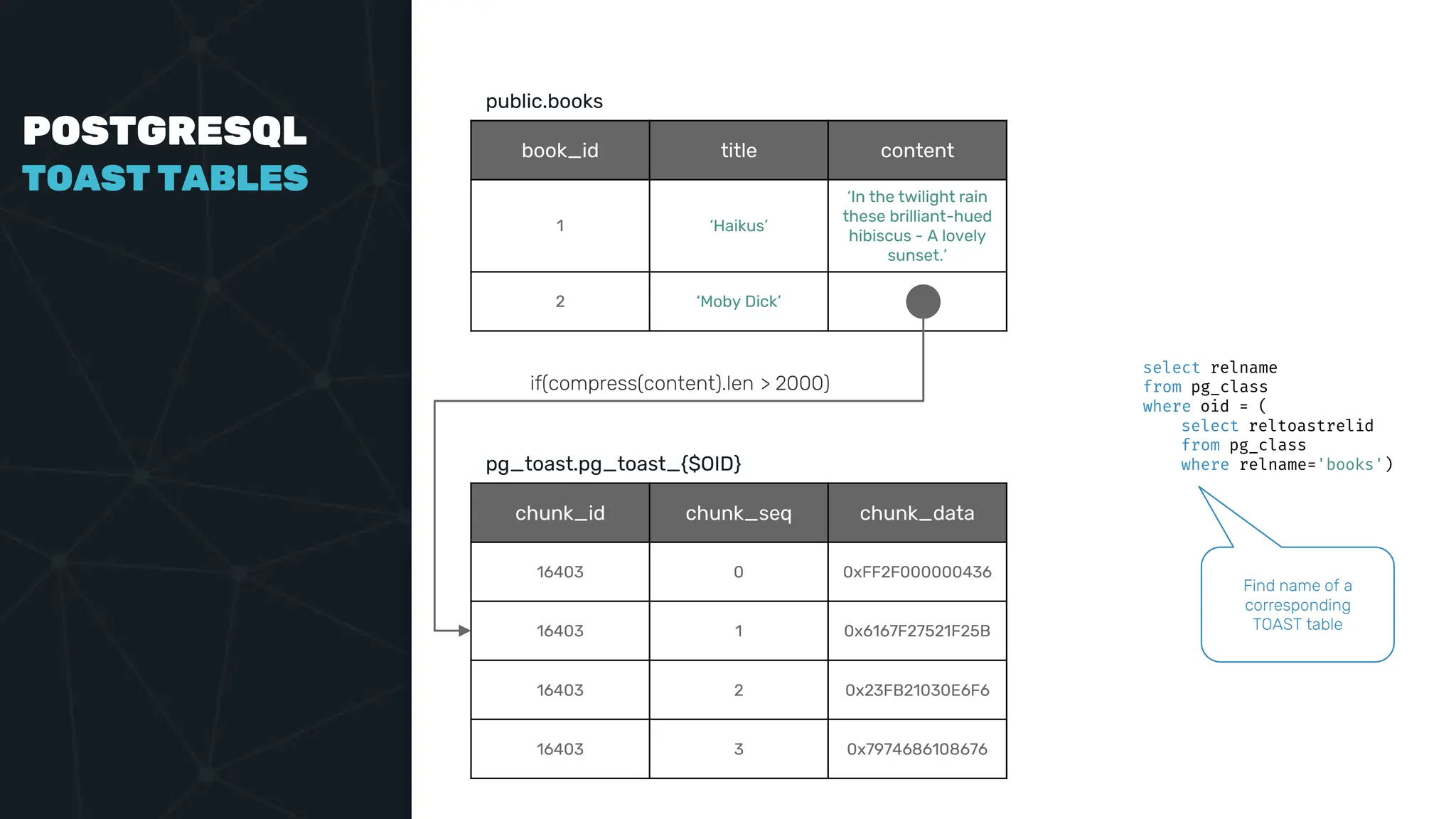
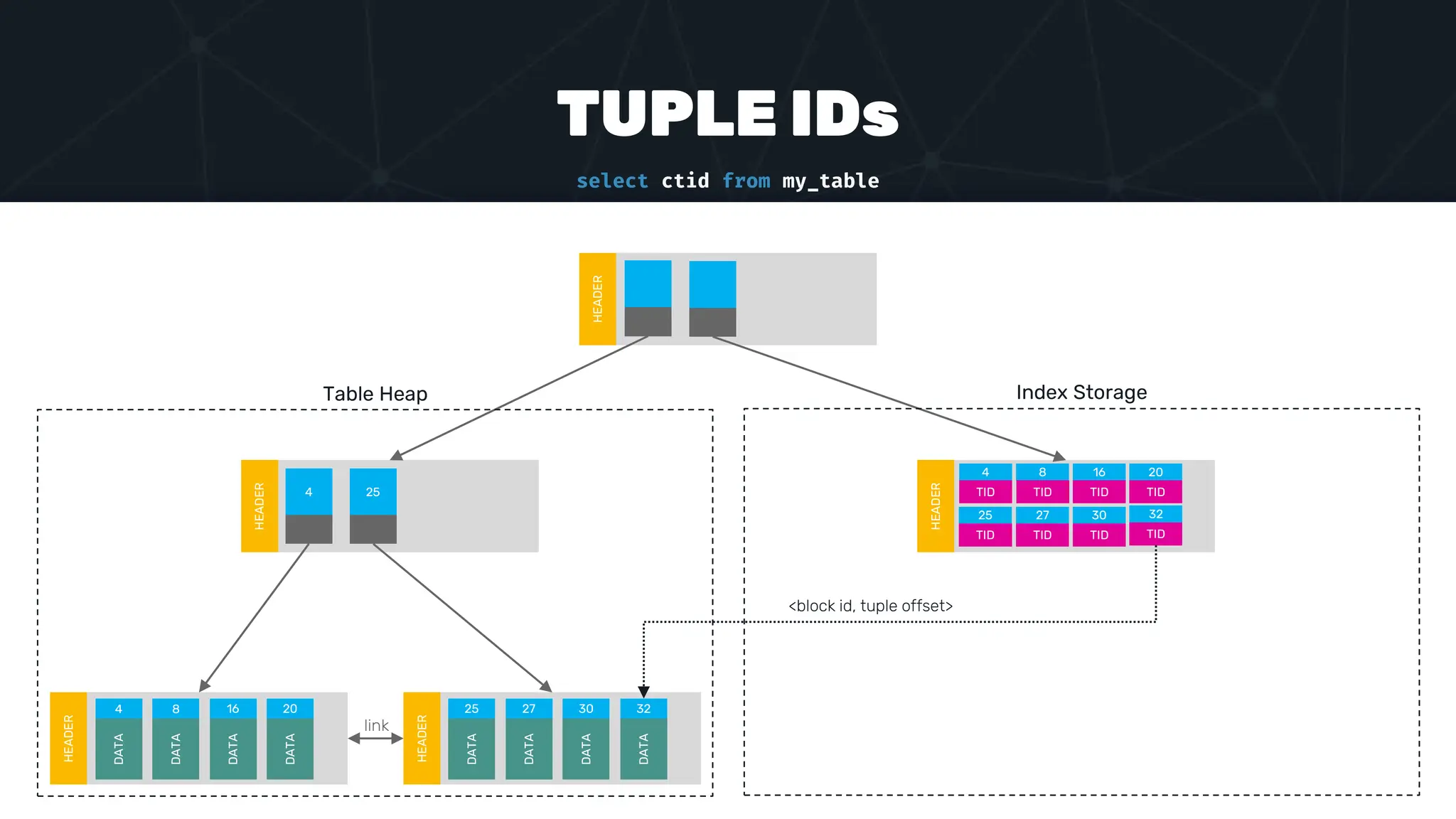


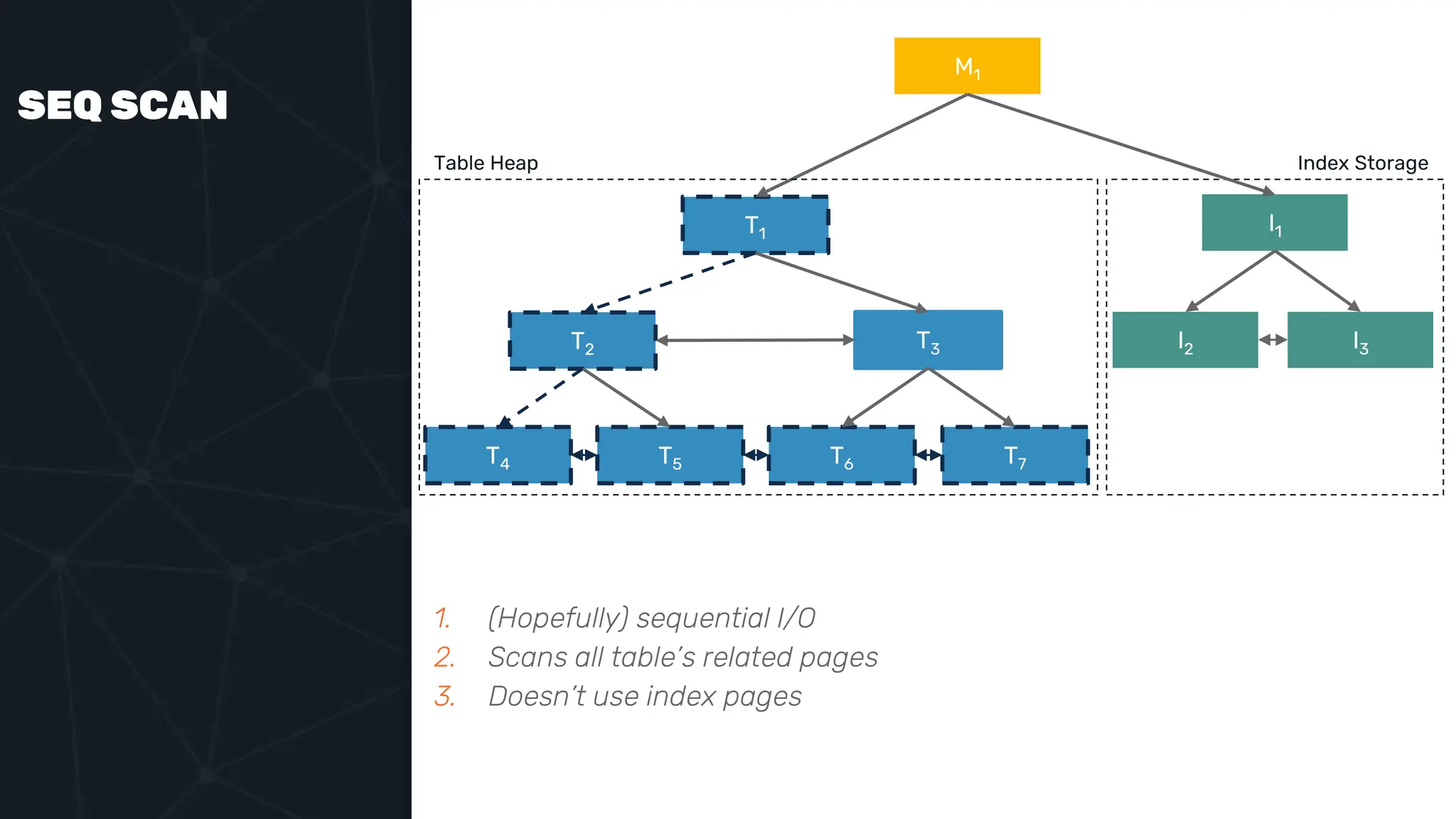

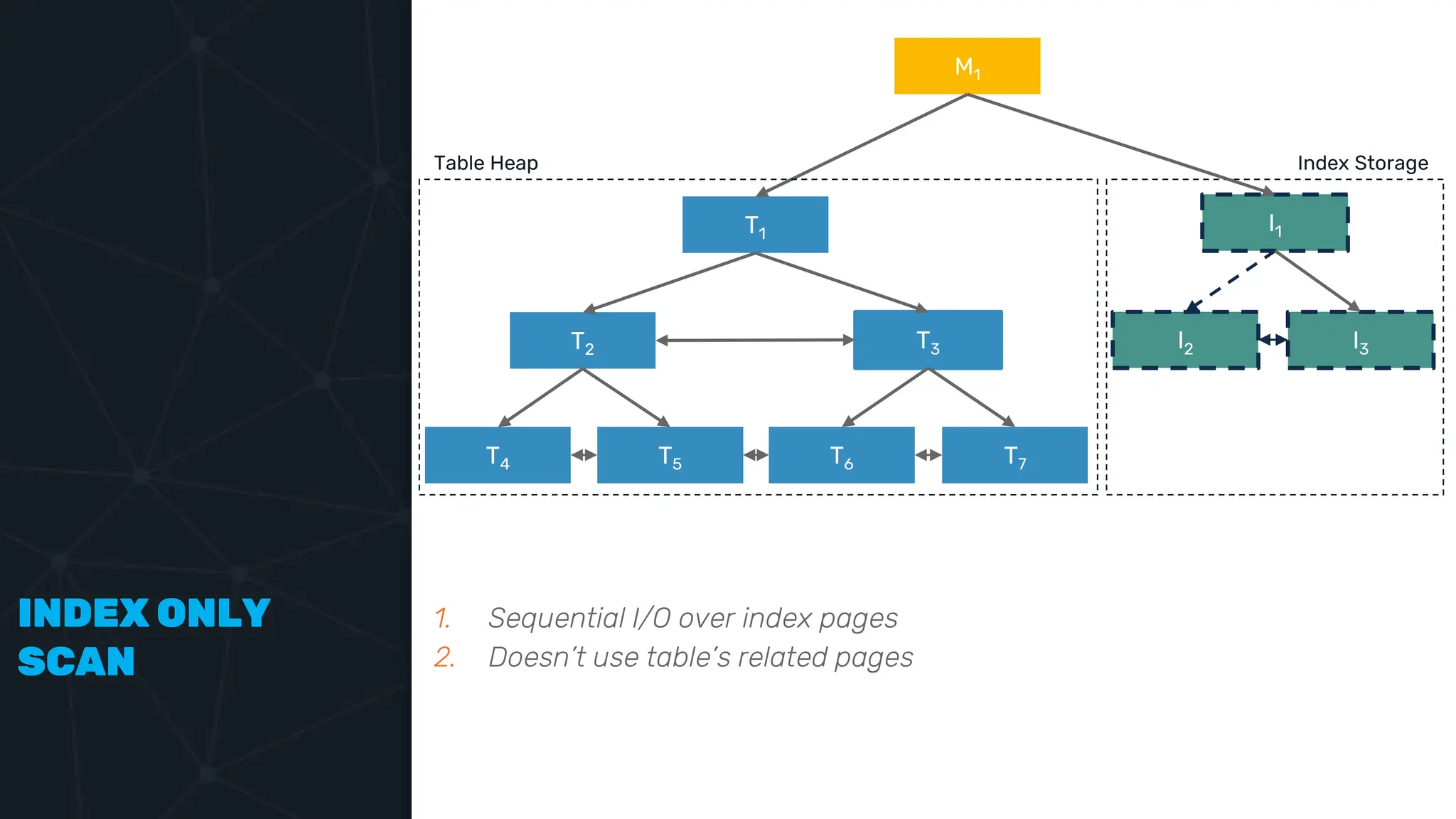







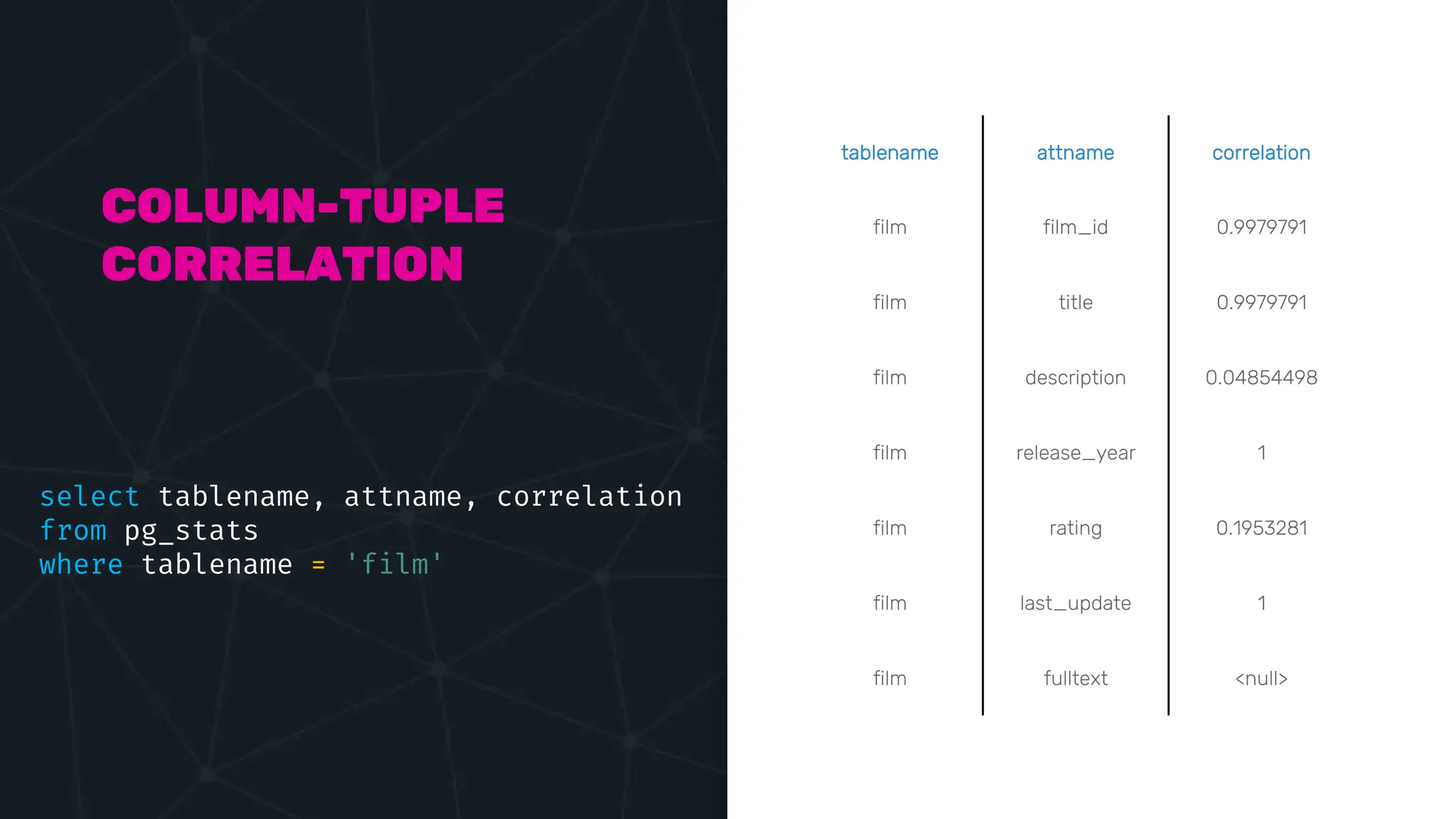


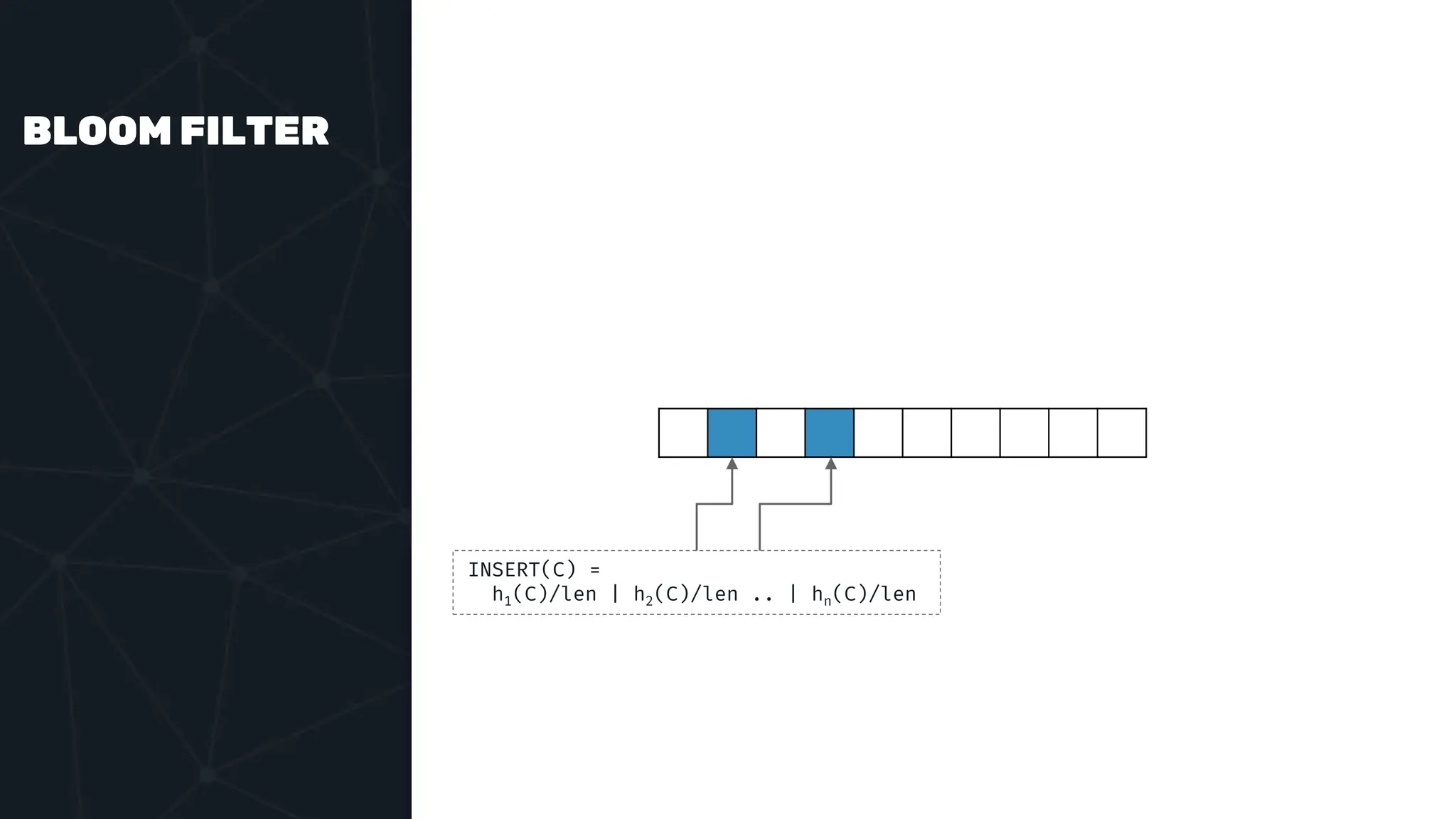
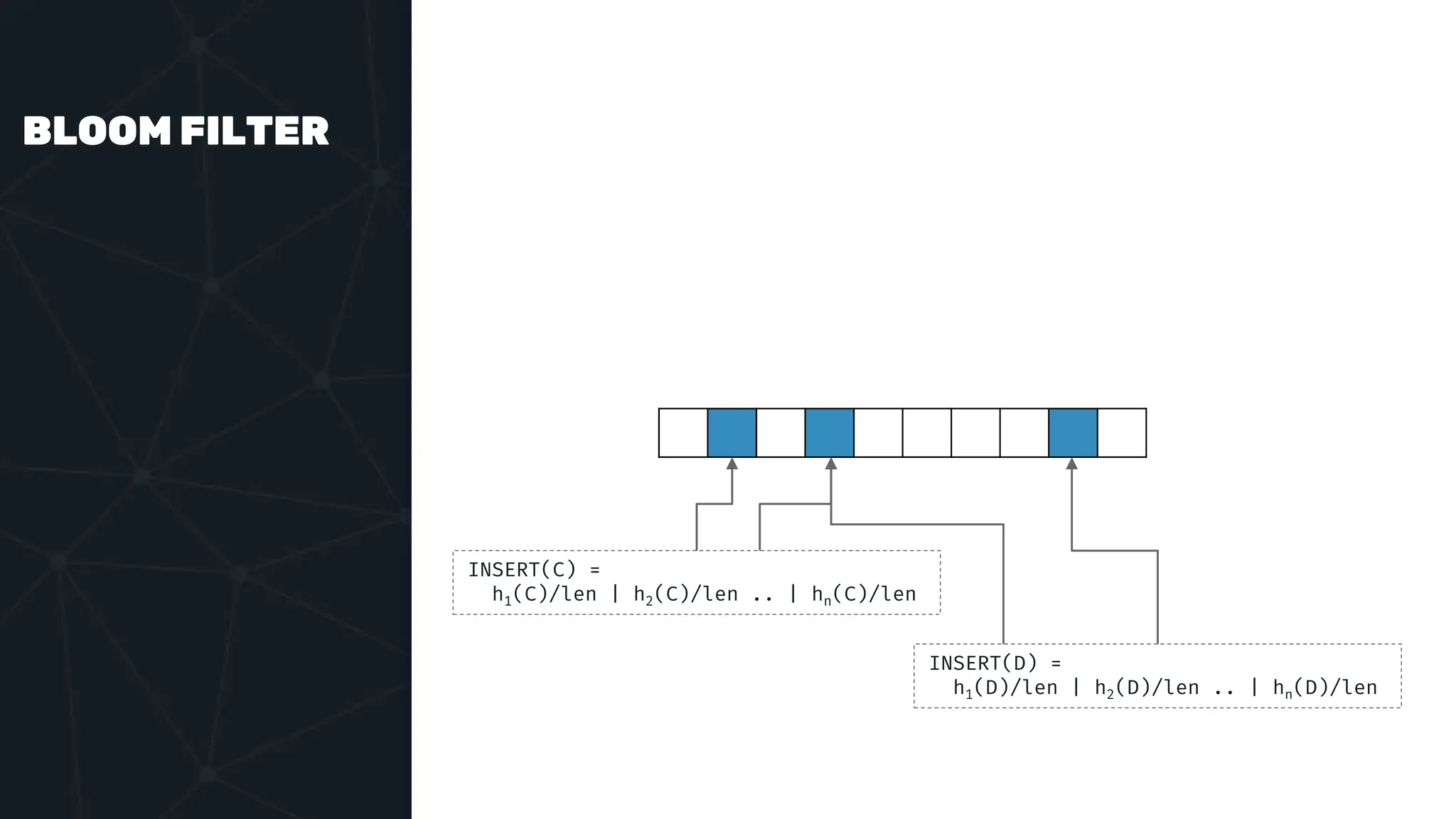
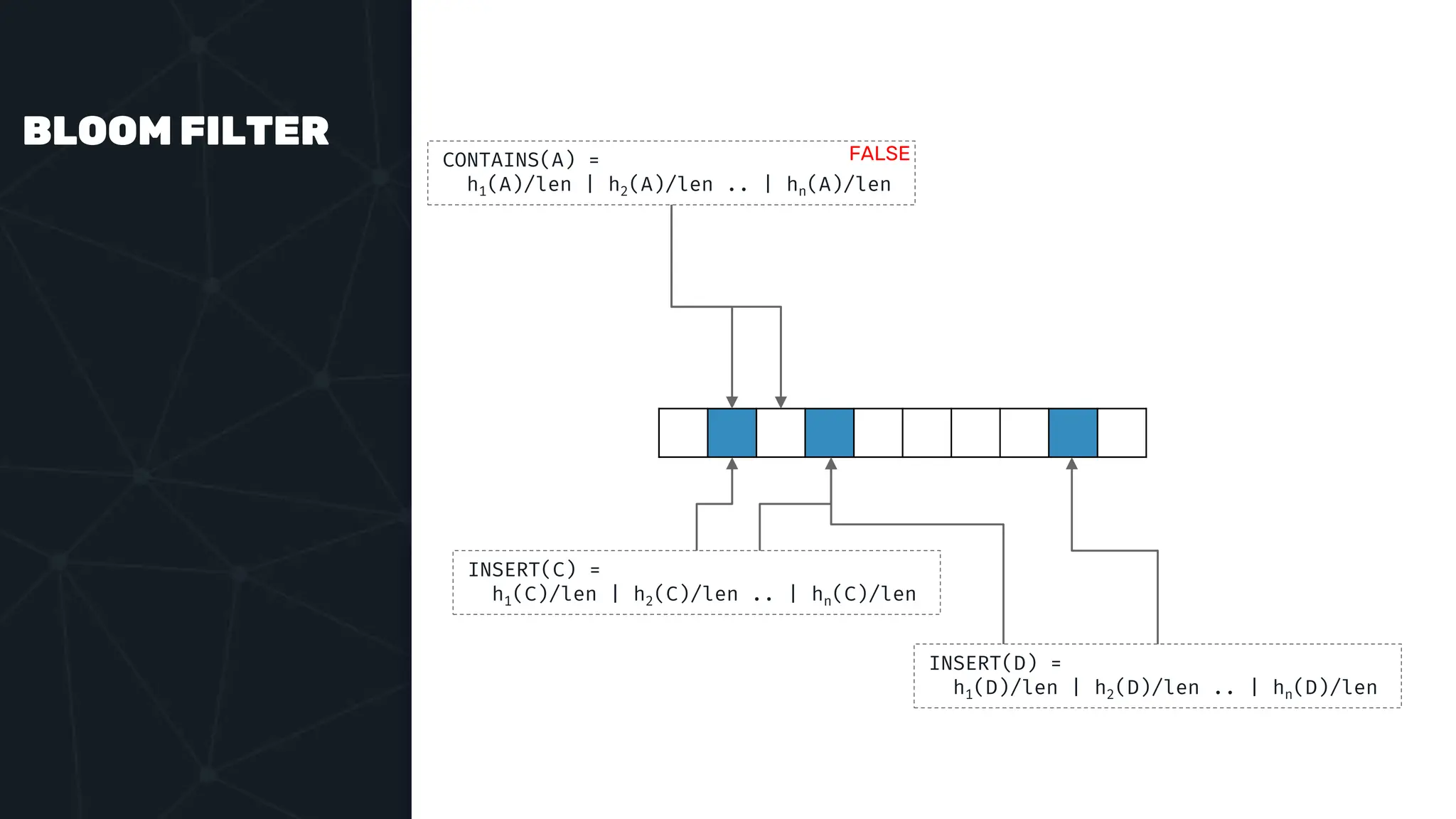












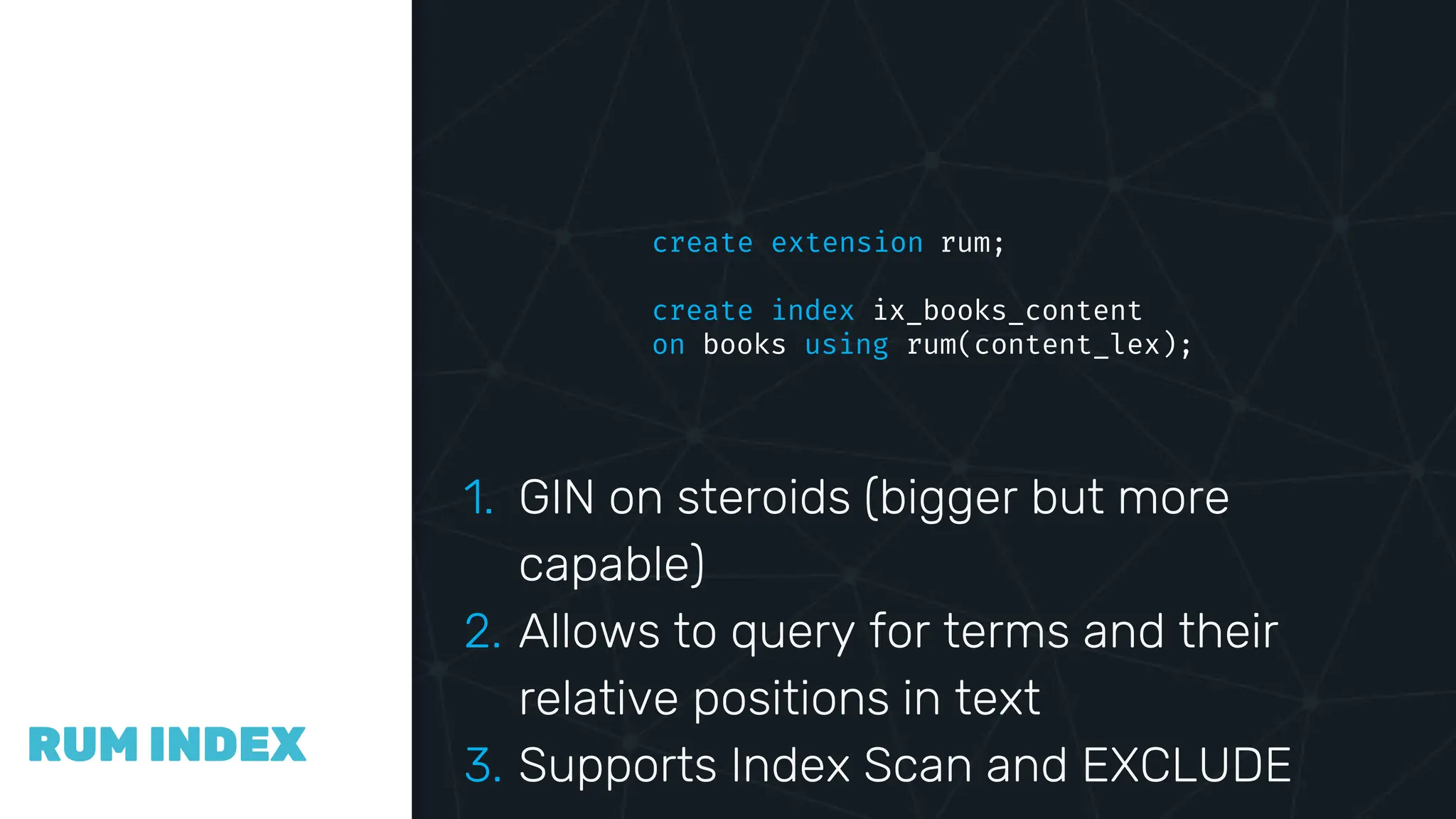


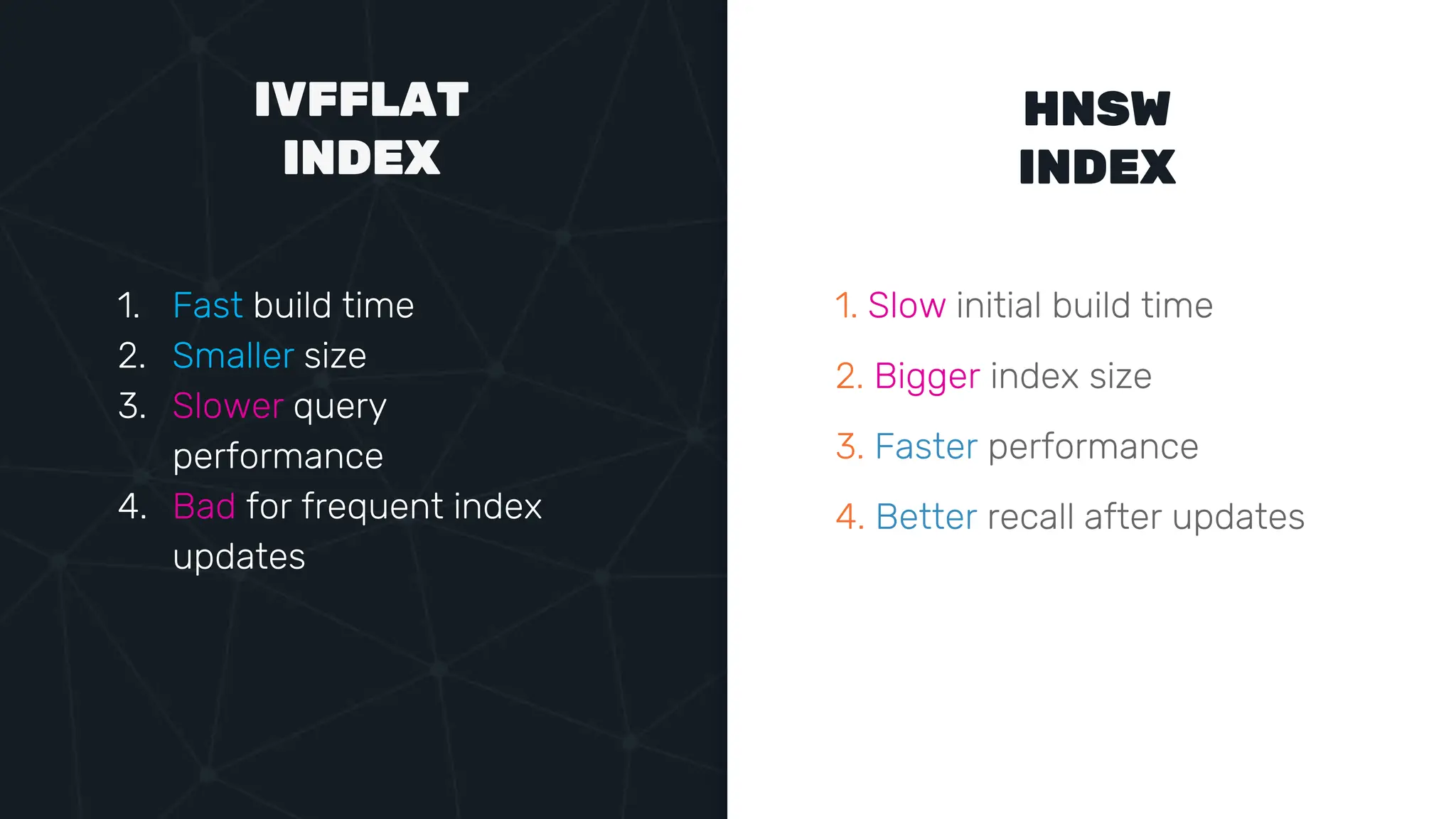
![IVFFLAT VECTOR INDEX create index ix_books_content on books using ivfflat(embedding content_lex) with (lists = 1000); select * from items where embedding <-> ‘[3,1,2]’ < 5;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-59-2048.jpg)

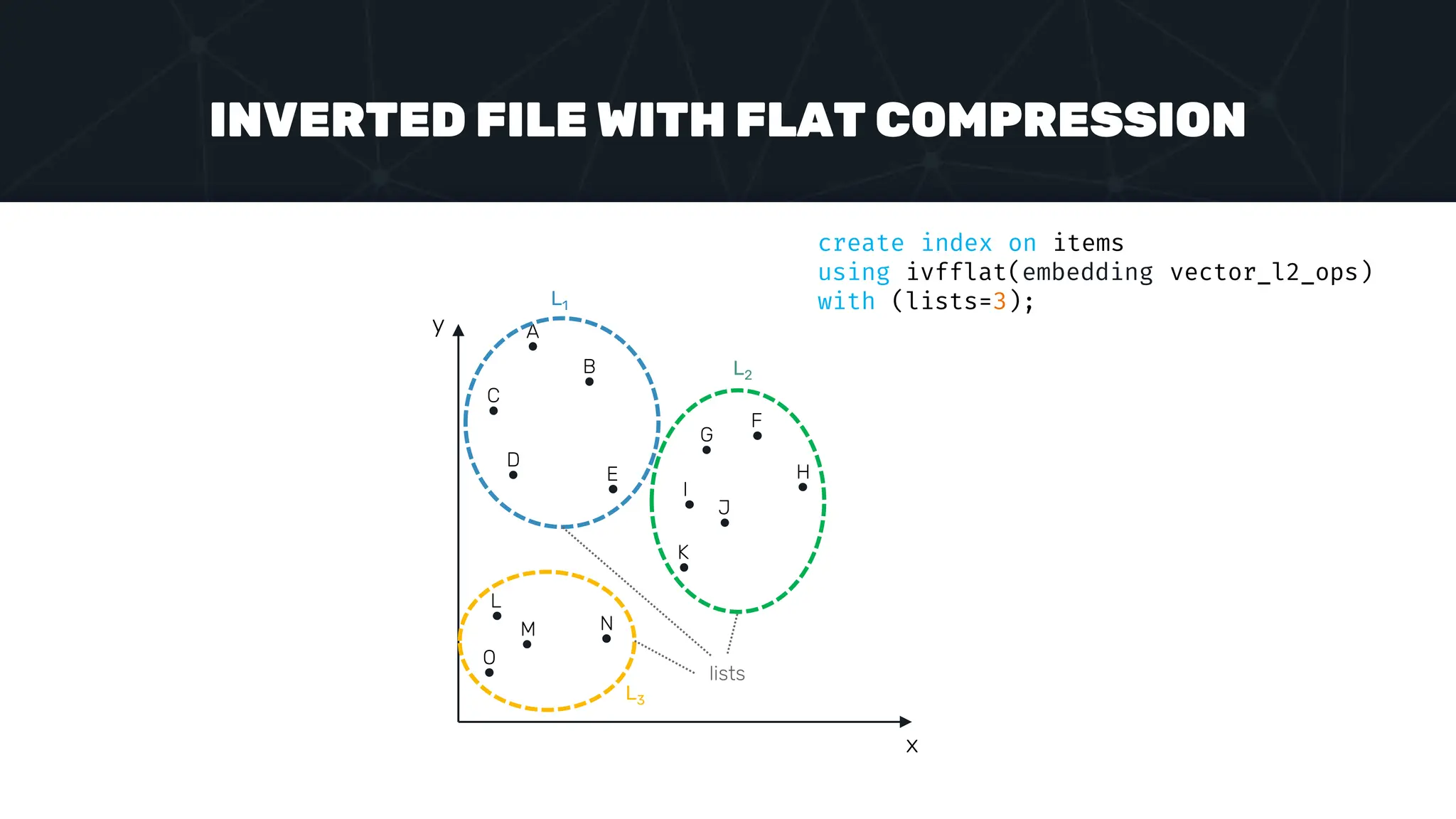
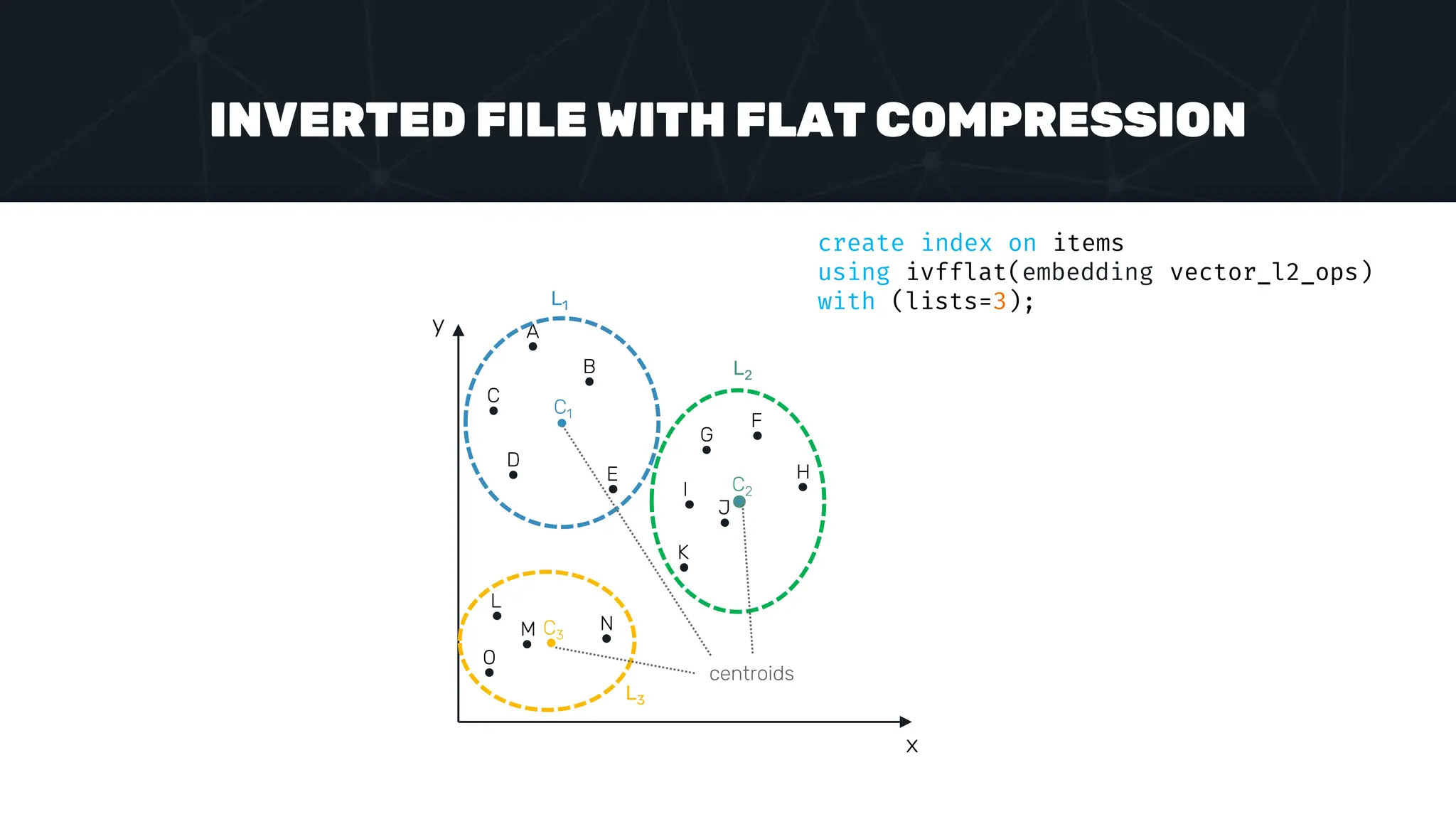

![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H L1 L2 L3 C1 C2 C3 set ivfflat.probes = 2; select * from items where embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ < 5; [1,2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-64-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H L1 L2 L3 C1 C2 C3 set ivfflat.probes = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4; [1,2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-65-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H L1 L2 L3 C1 C2 C3 [1,2] set ivfflat.probes = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-66-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H L1 L2 L3 C1 C2 C3 [1,2] set ivfflat.probes = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-67-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H L1 L2 L3 C1 C2 C3 [1,2] set ivfflat.probes = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-68-2048.jpg)




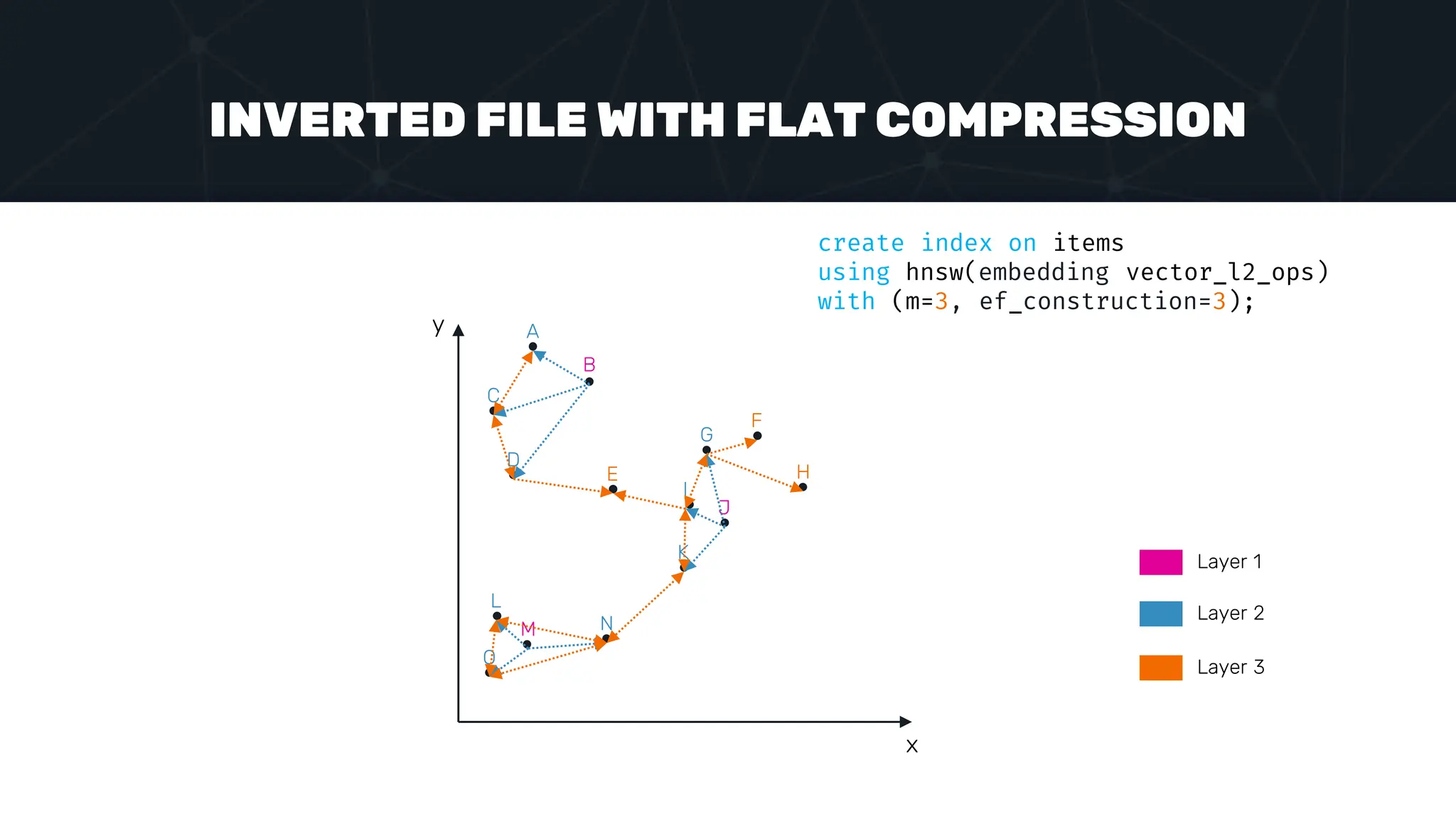

![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H [1,2] set hnsw.ef_search = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-75-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H [1,2] set hnsw.ef_search = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-76-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H [1,2] set hnsw.ef_search = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-77-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H [1,2] set hnsw.ef_search = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-78-2048.jpg)
![INVERTED FILE WITH FLAT COMPRESSION x y A C B D G E L O M N F I K J H [1,2] set hnsw.ef_search = 2; select * from items order by embedding <-> ‘[1,2]’ take 4;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgres-indexes-240403044341-59b20184/75/Postgres-indexes-how-to-make-them-work-for-your-application-79-2048.jpg)