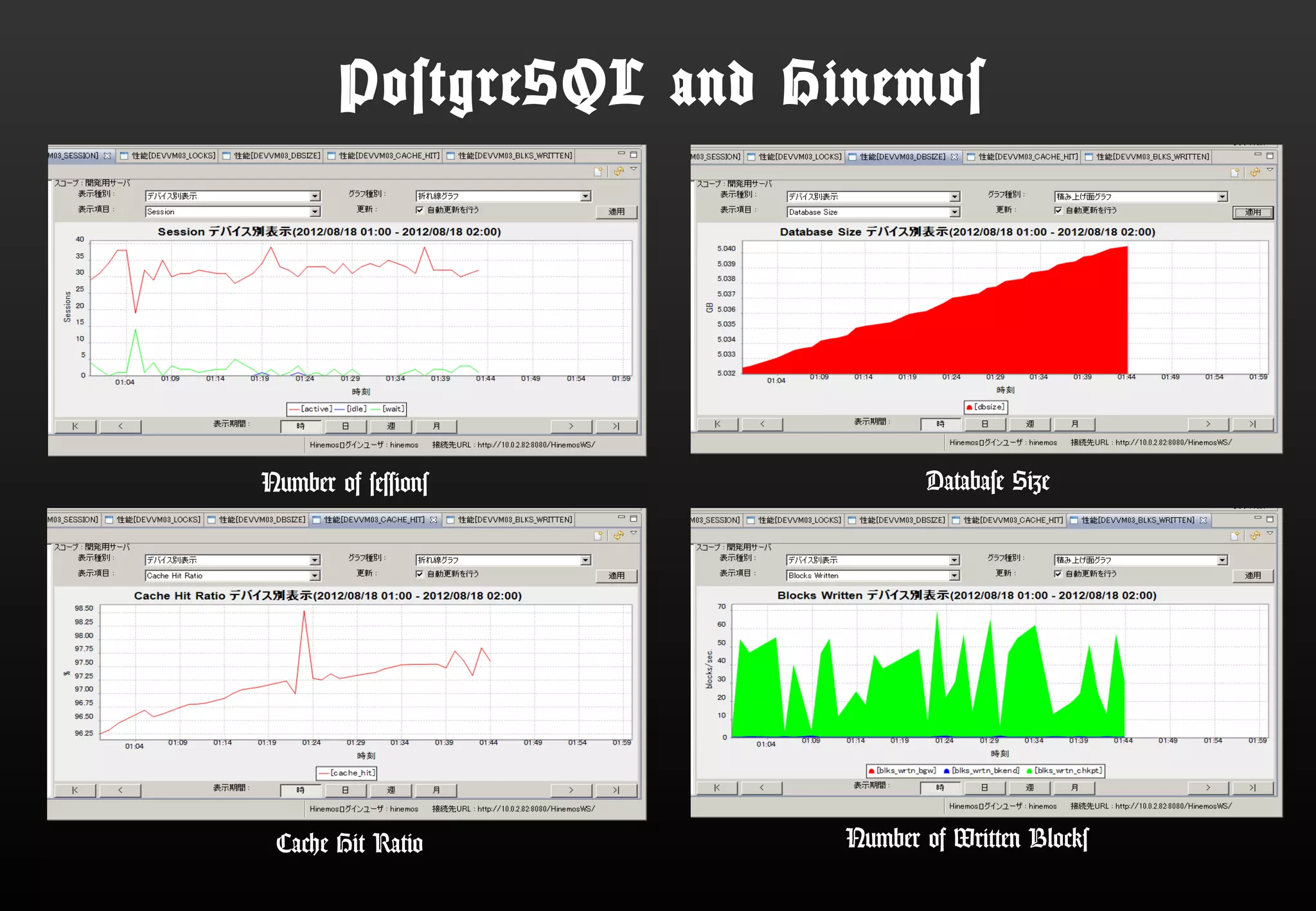
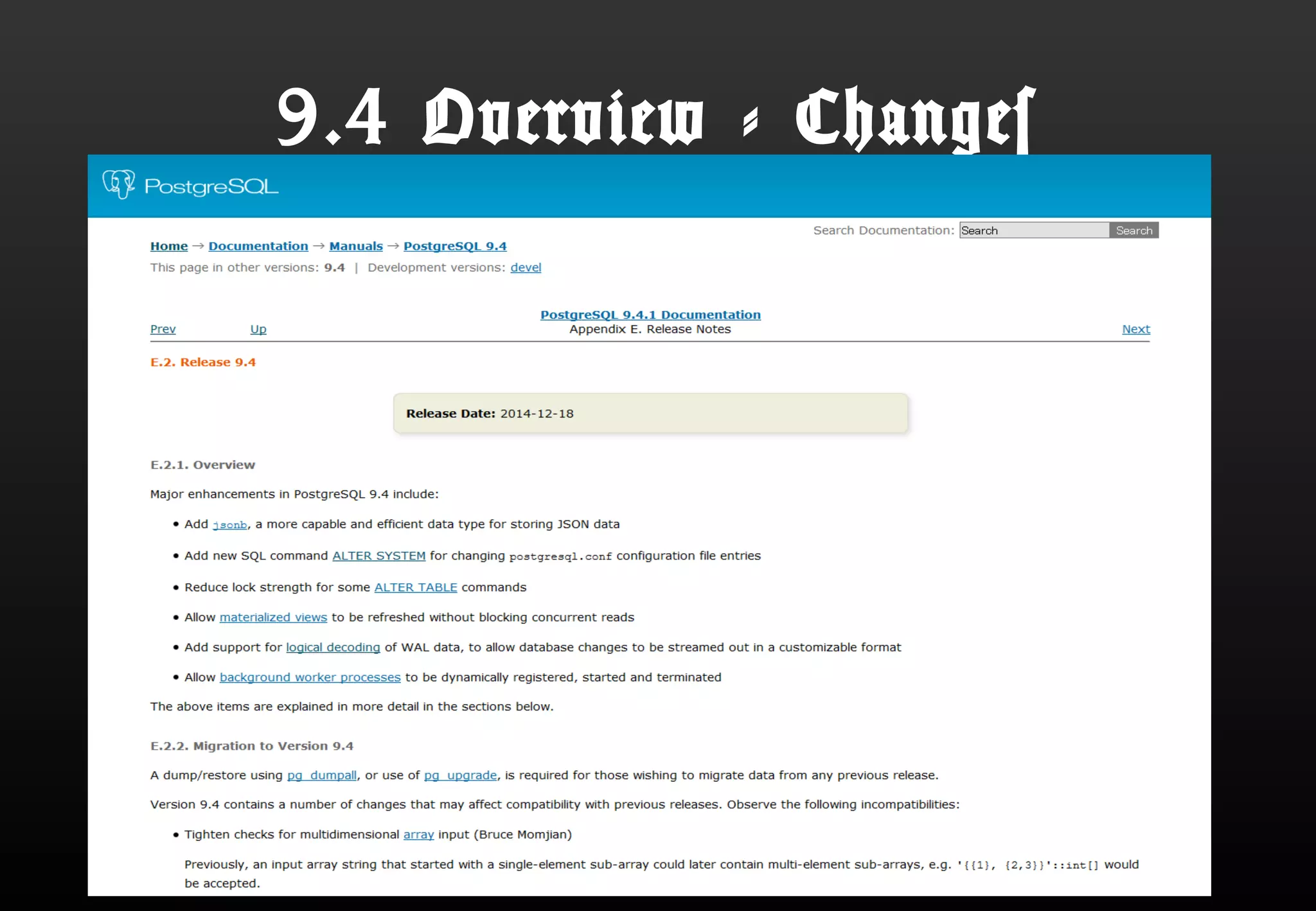
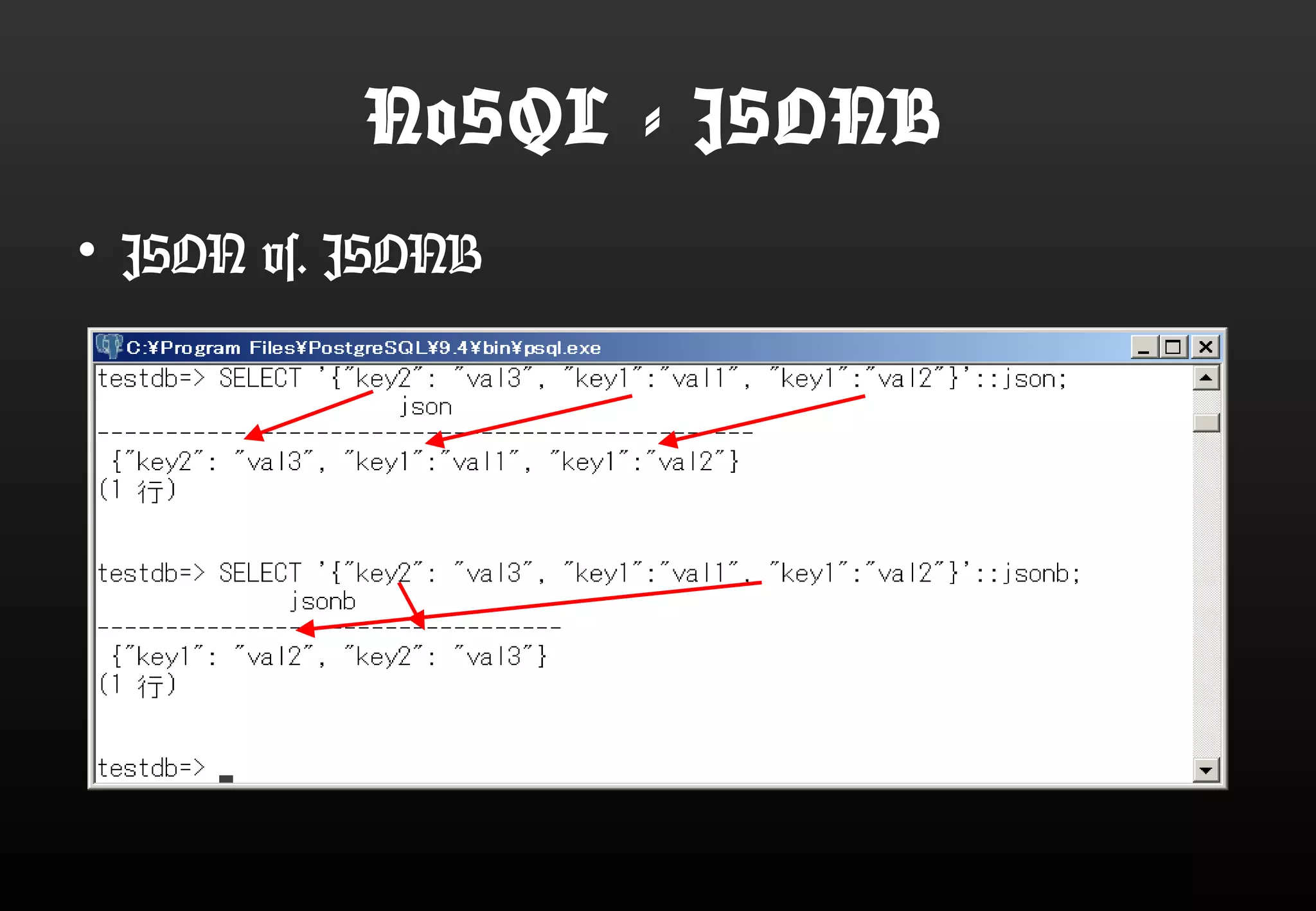
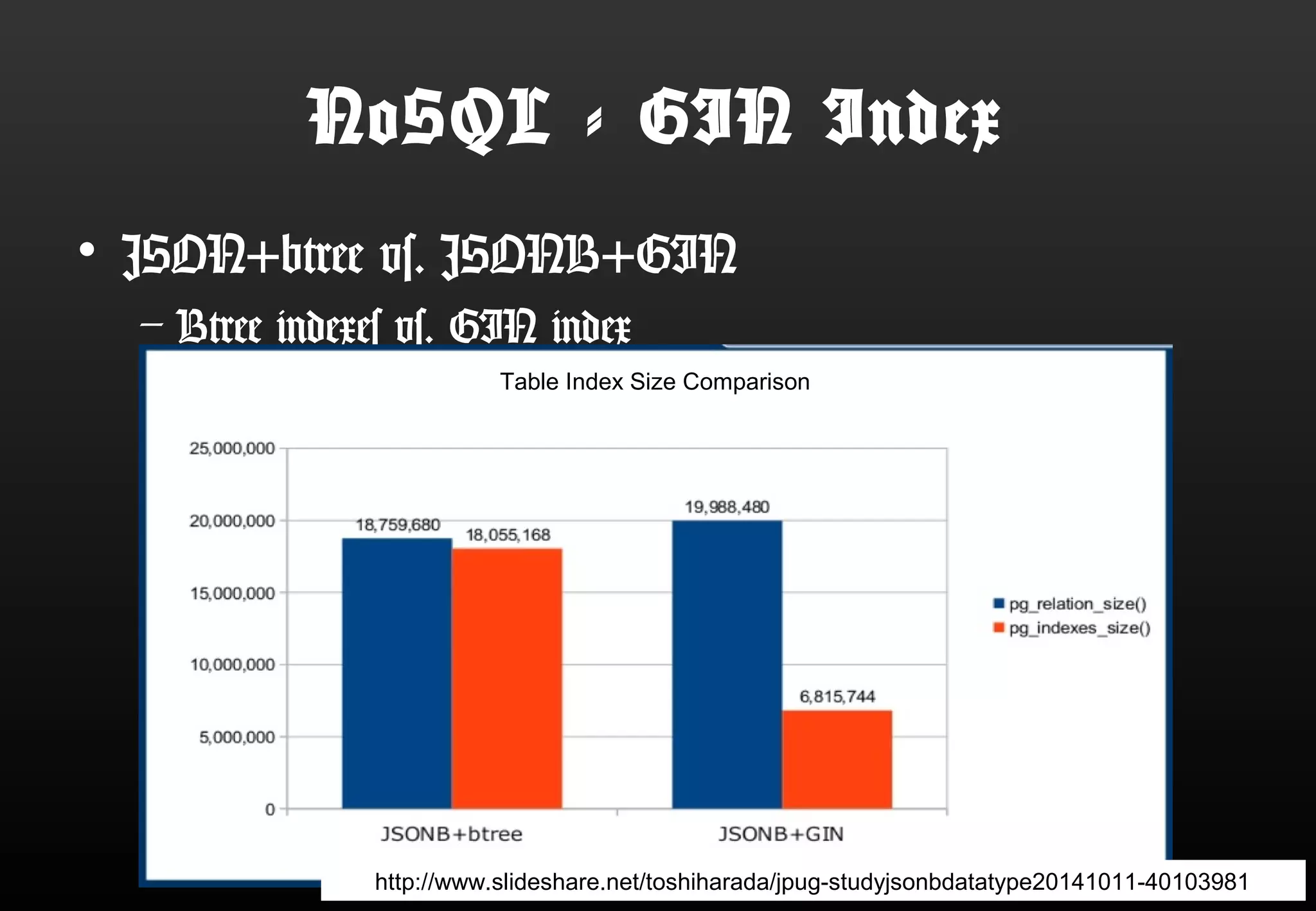
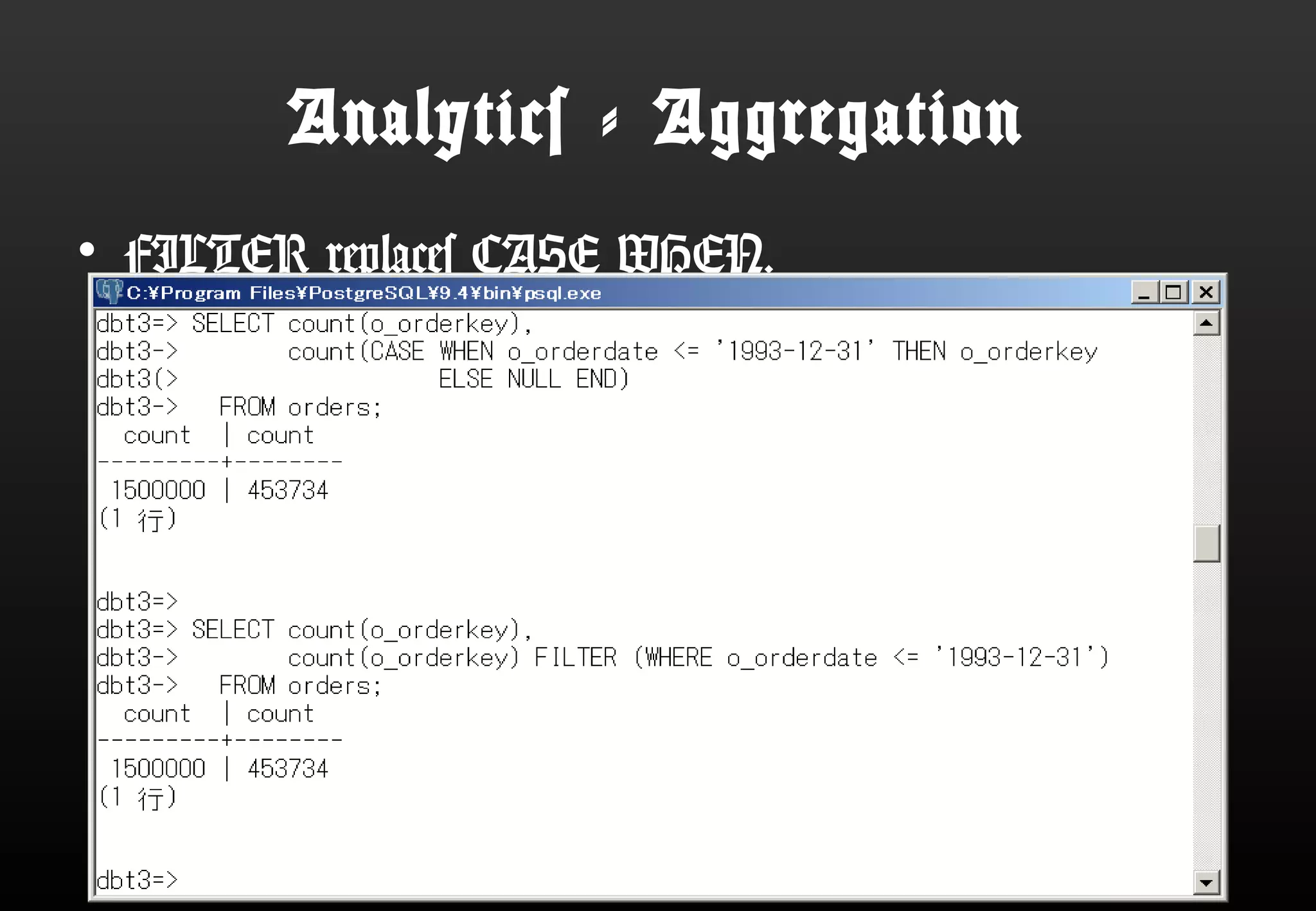
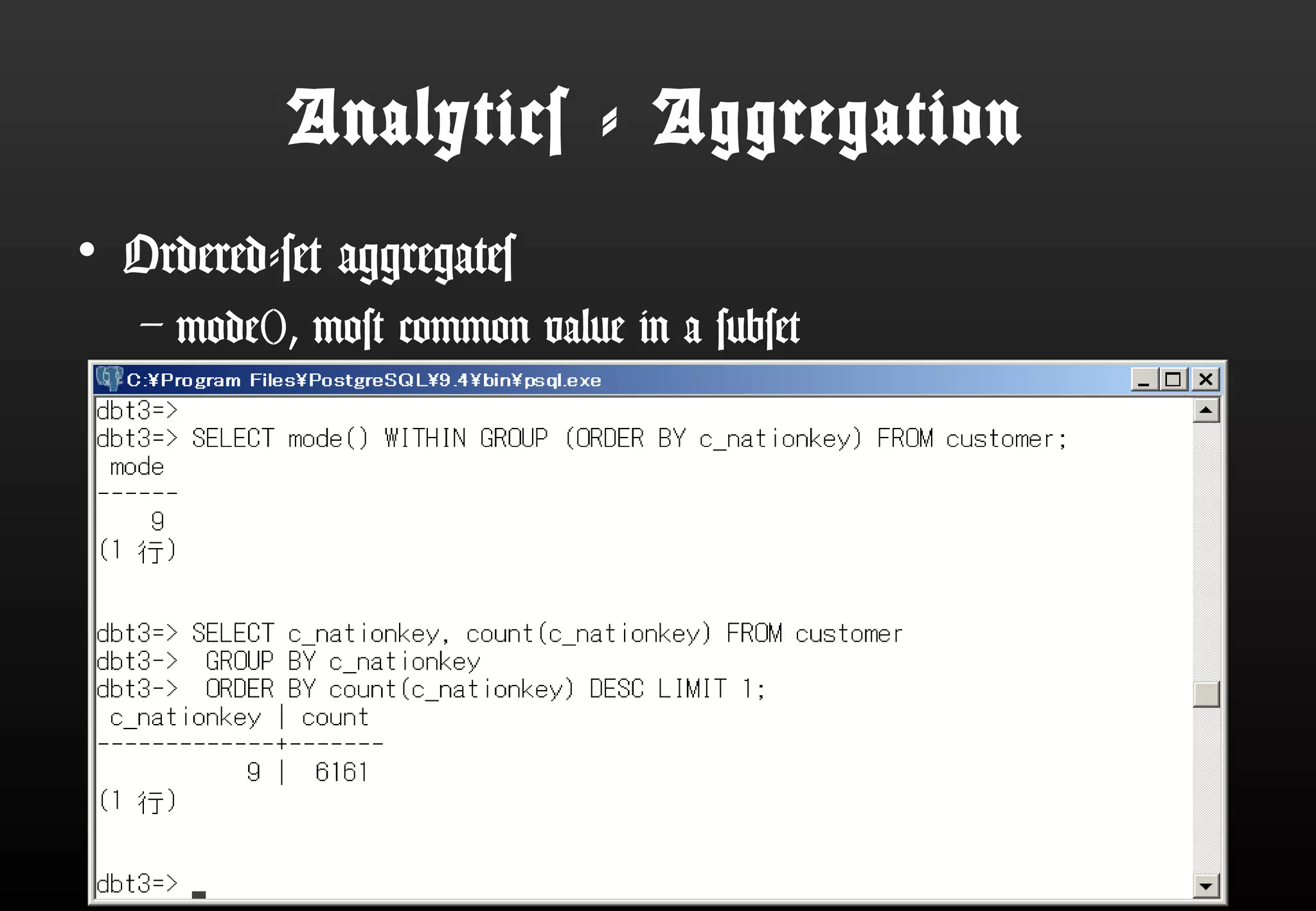
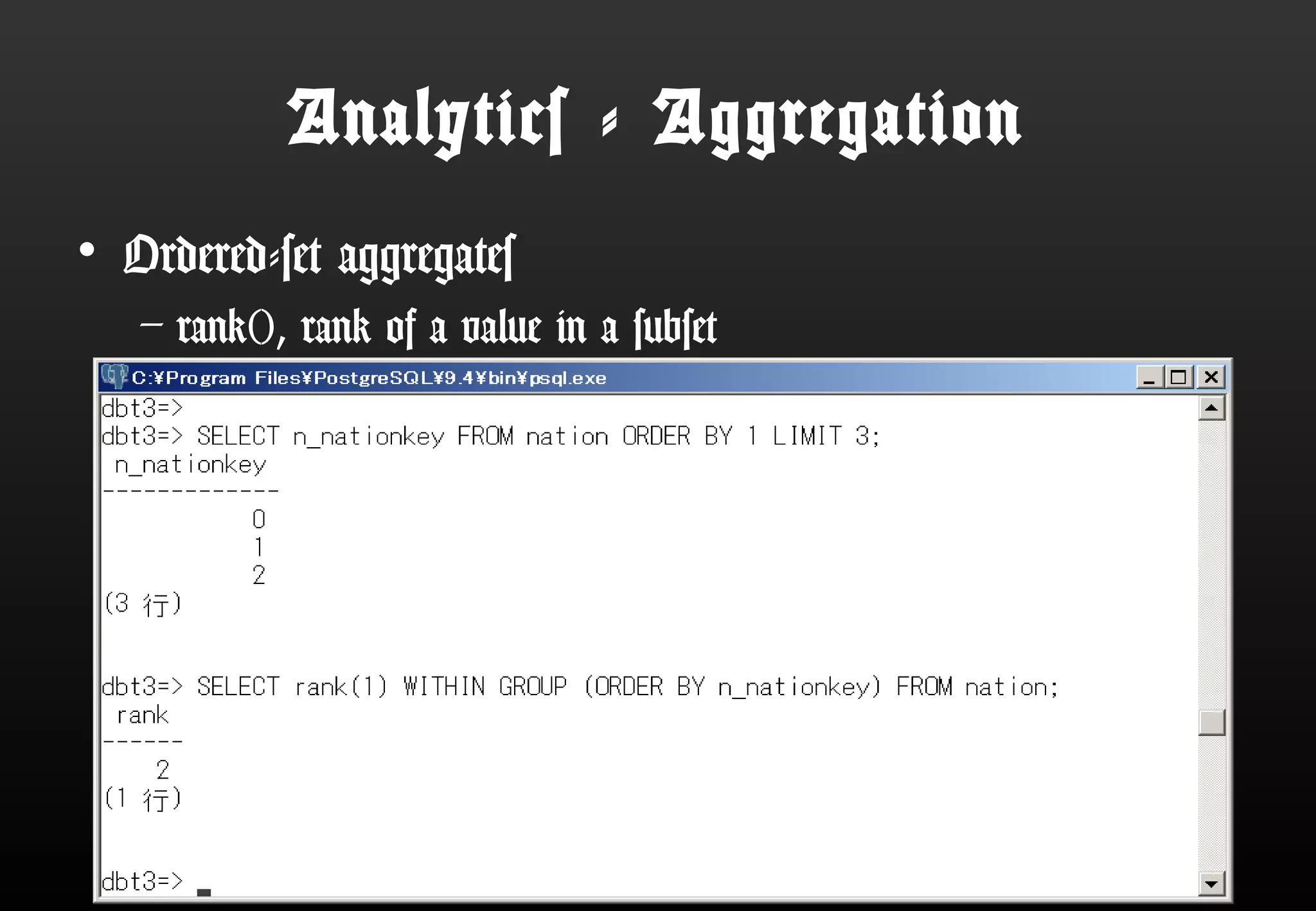
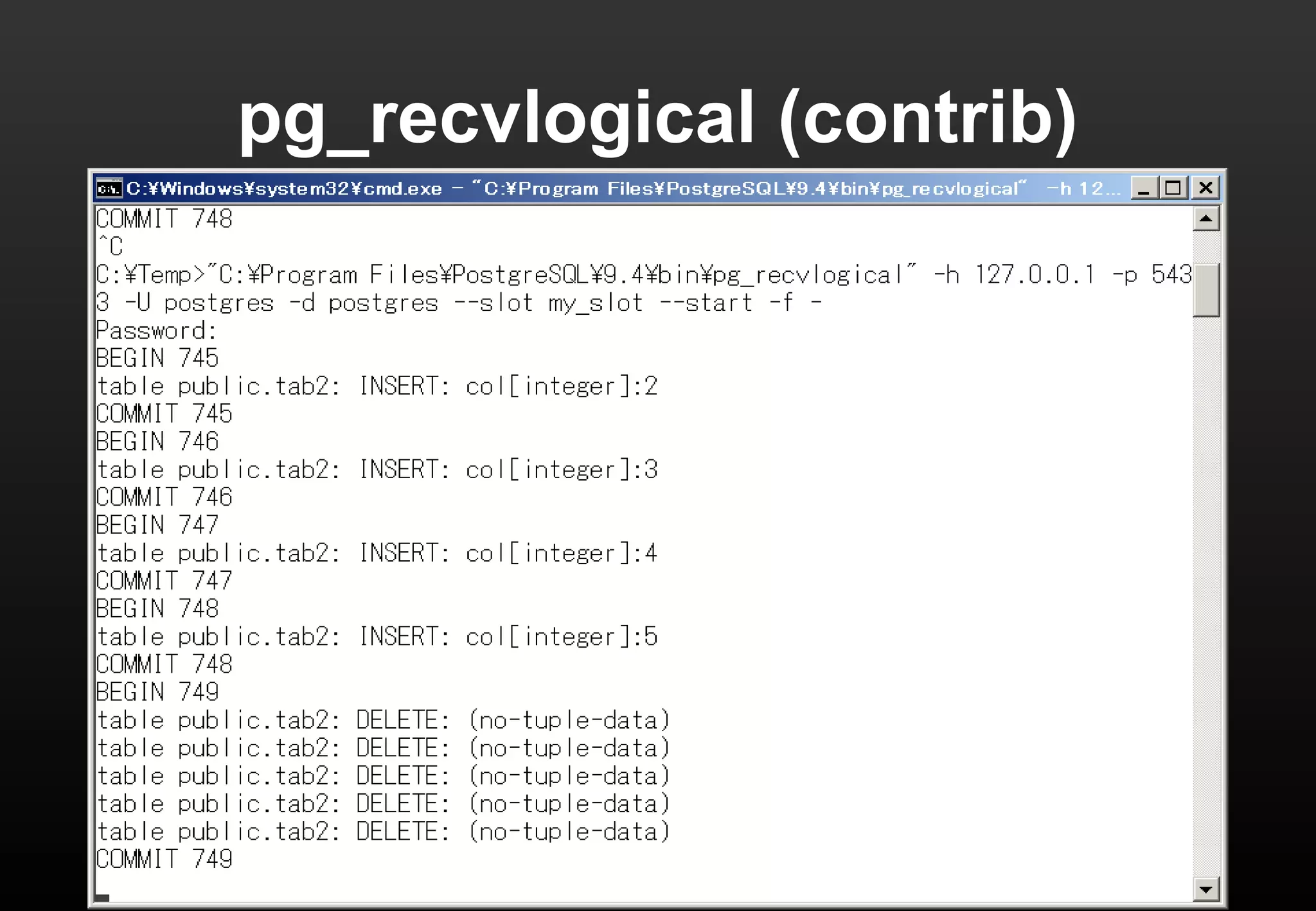
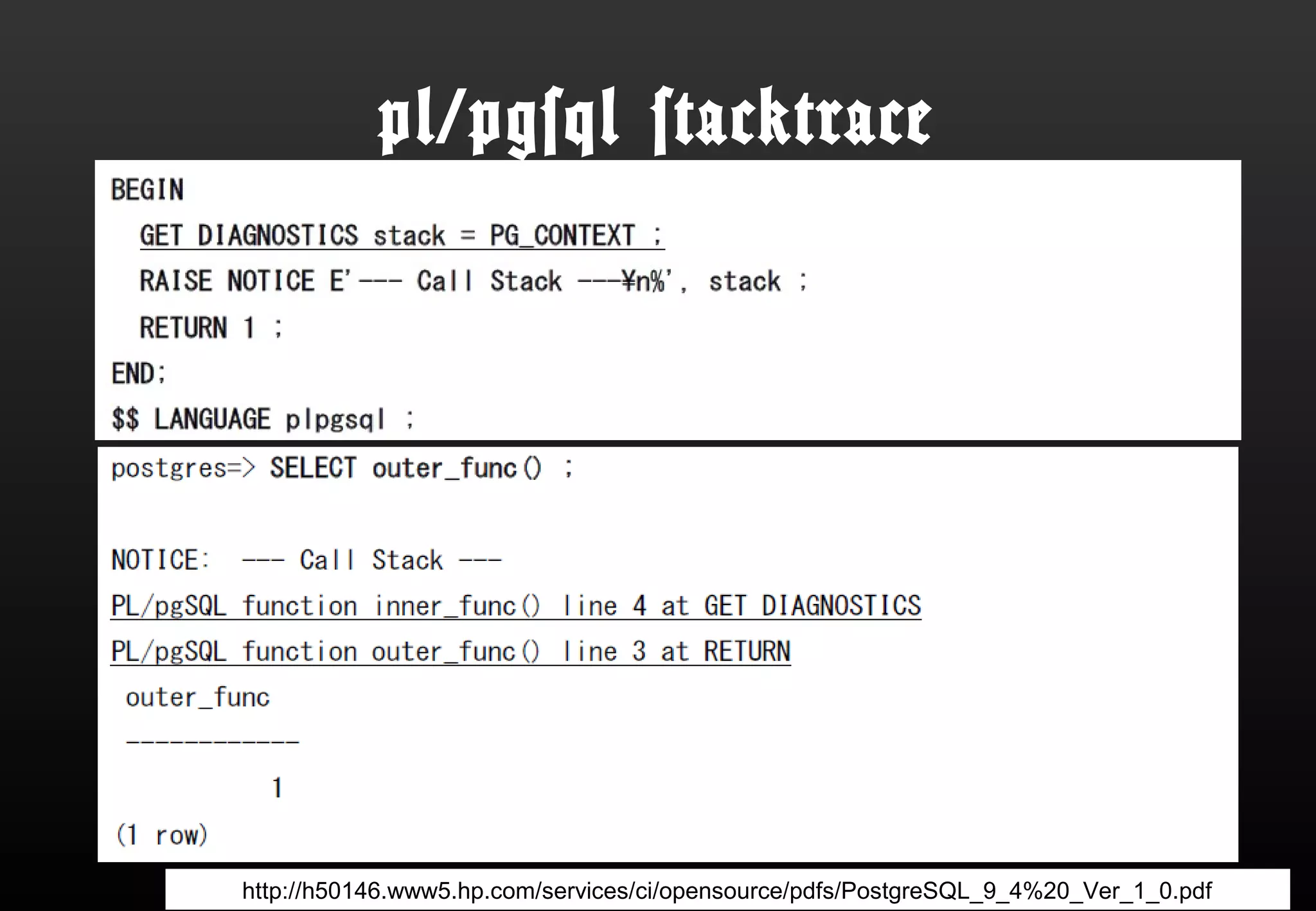
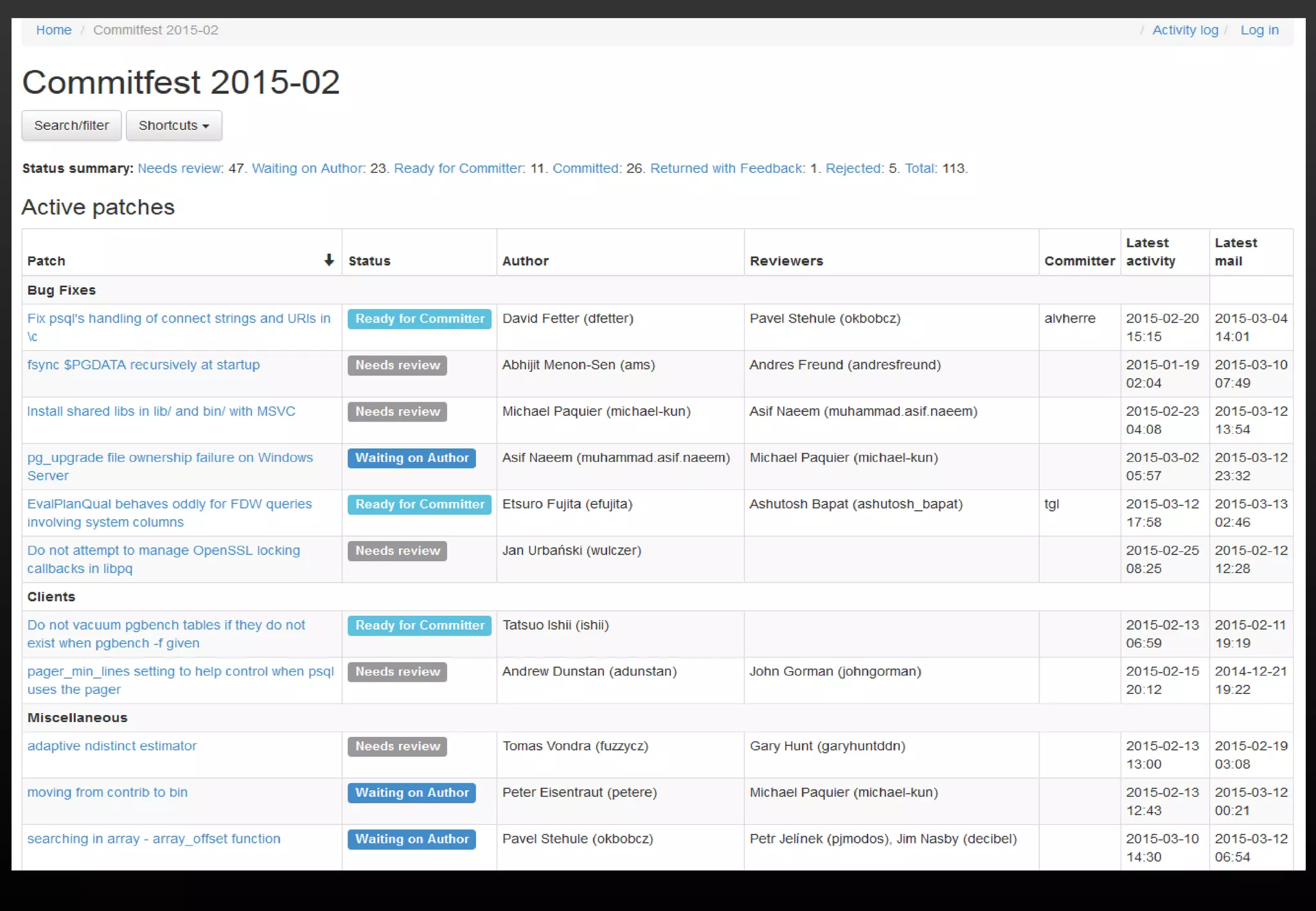
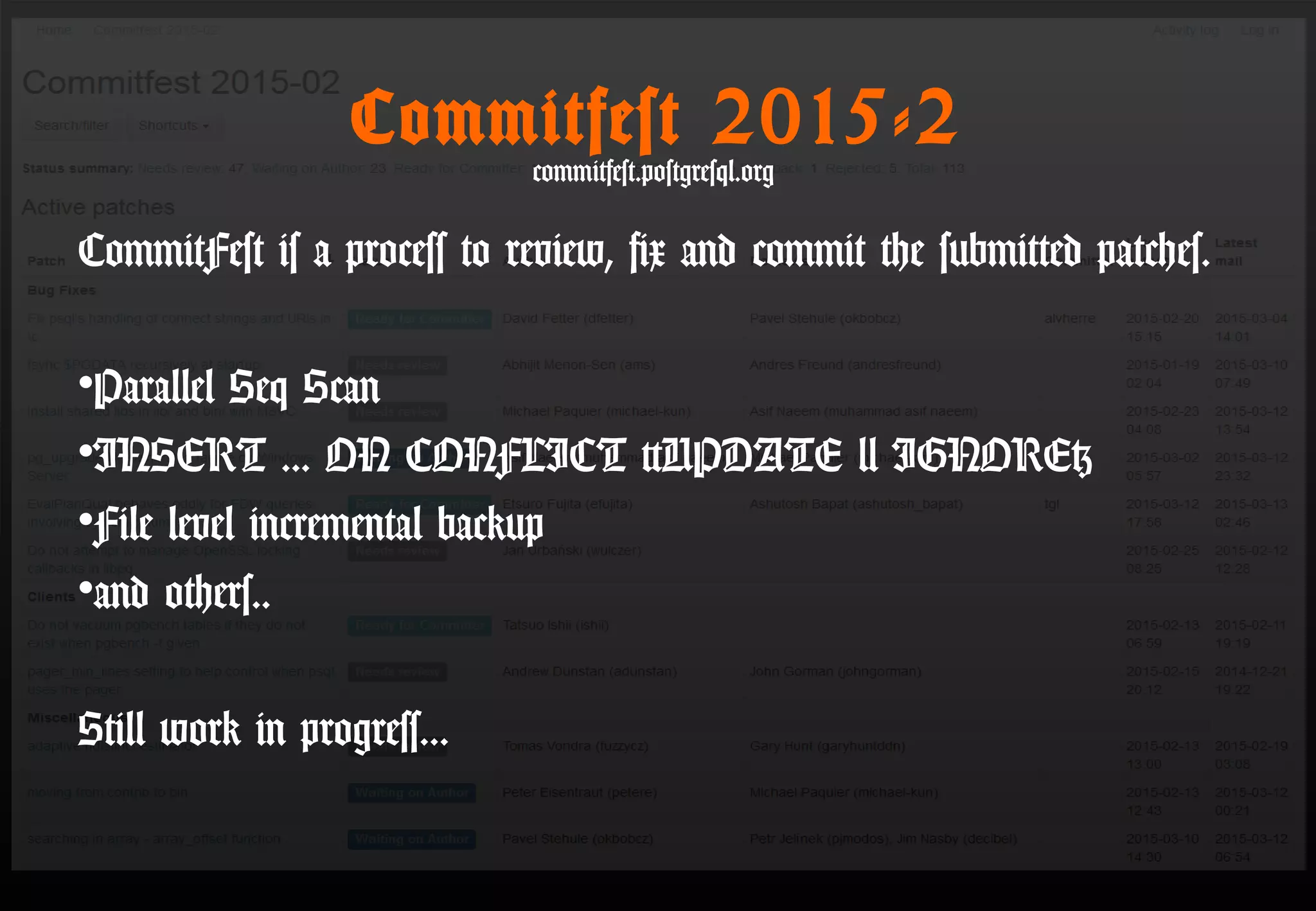
This document summarizes Satoshi Nagayasu's presentation on PostgreSQL 9.4 and beyond. Key highlights include: improvements to JSON support with the new JSONB data type and GIN indexes; new aggregation functions and materialized views for analytics; logical decoding for more flexible replication; and infrastructure changes like dynamic background workers and shared memory to support parallelization. Upcoming features like BRIN indexes are also mentioned.