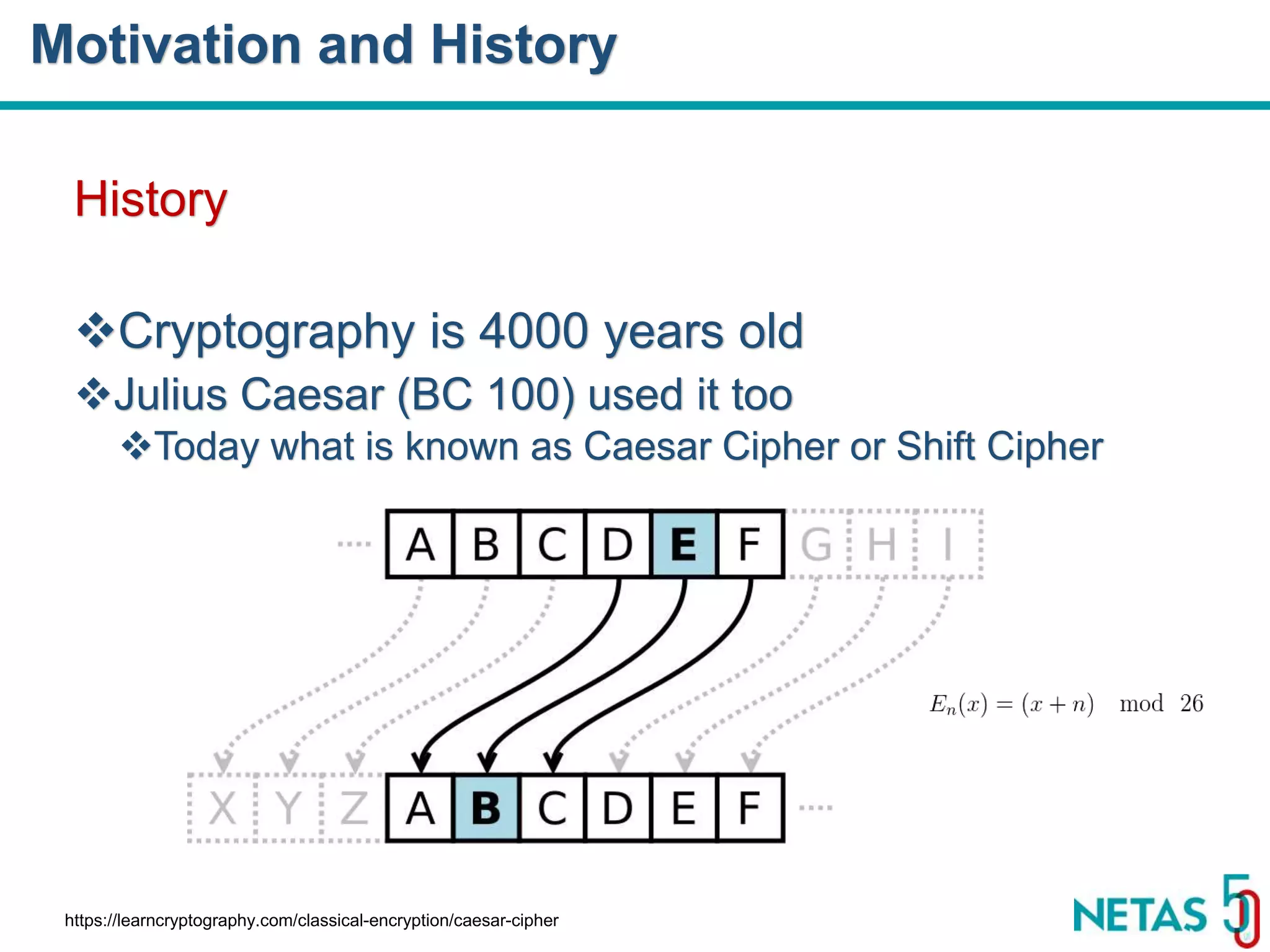
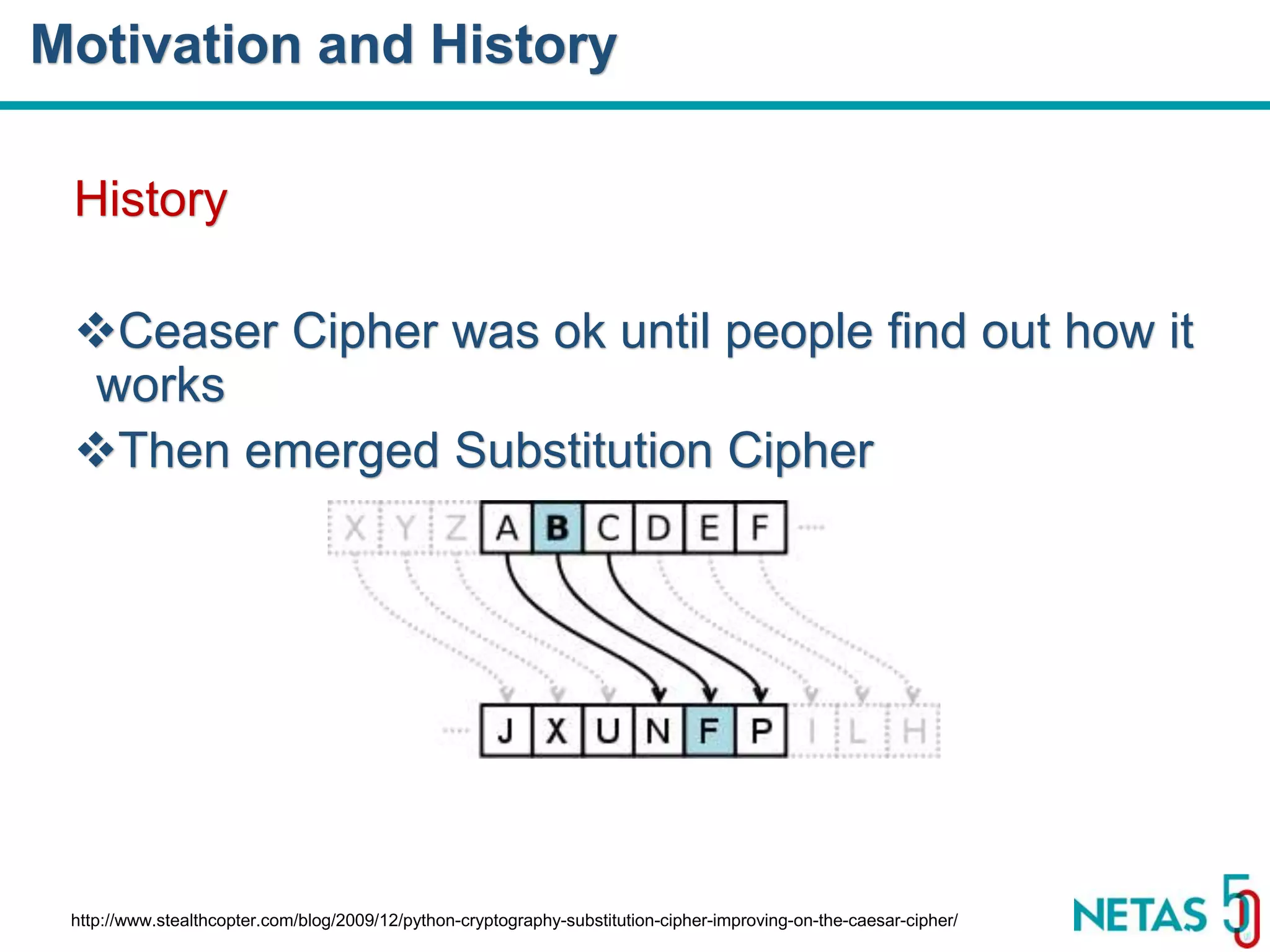
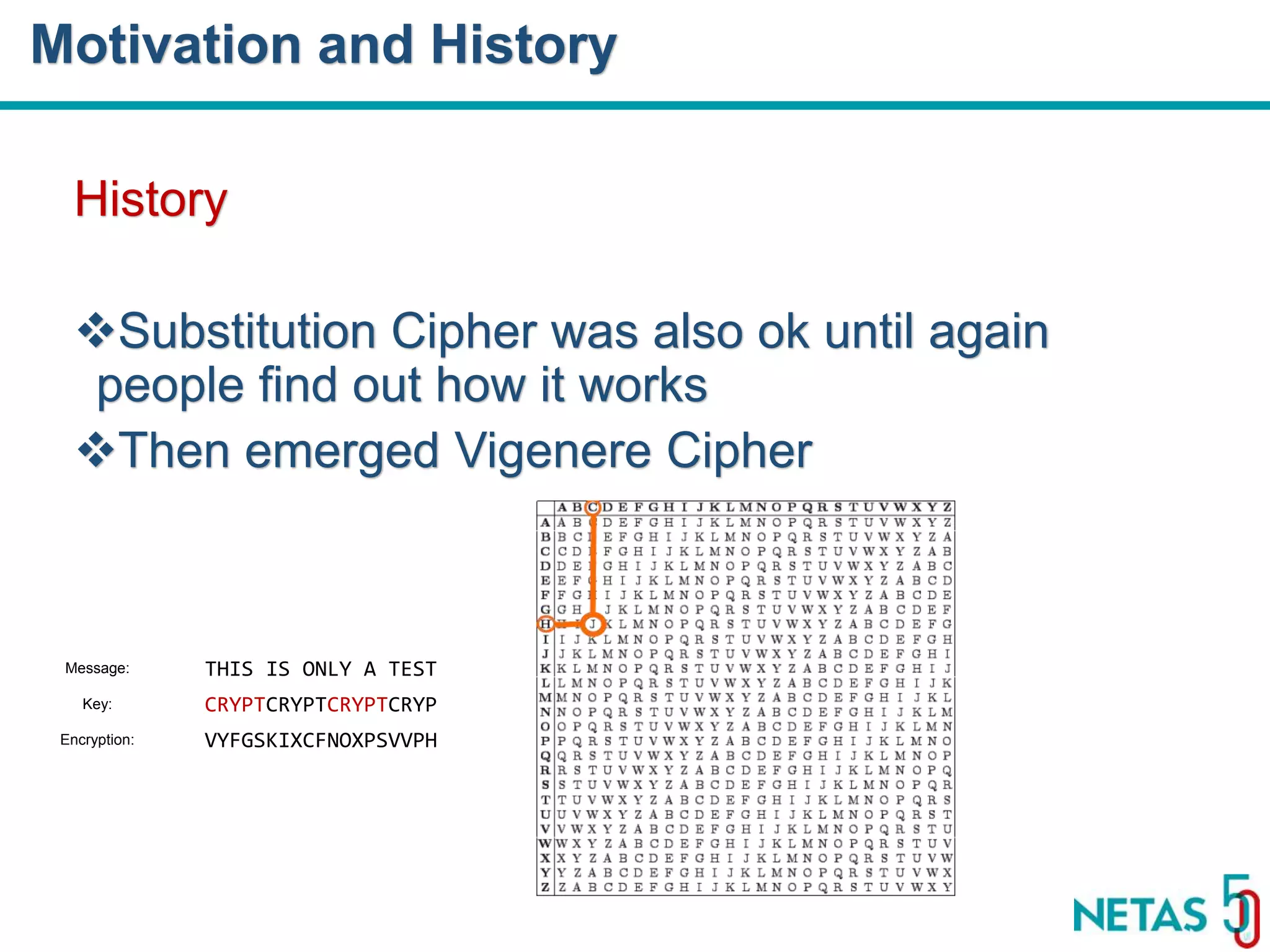
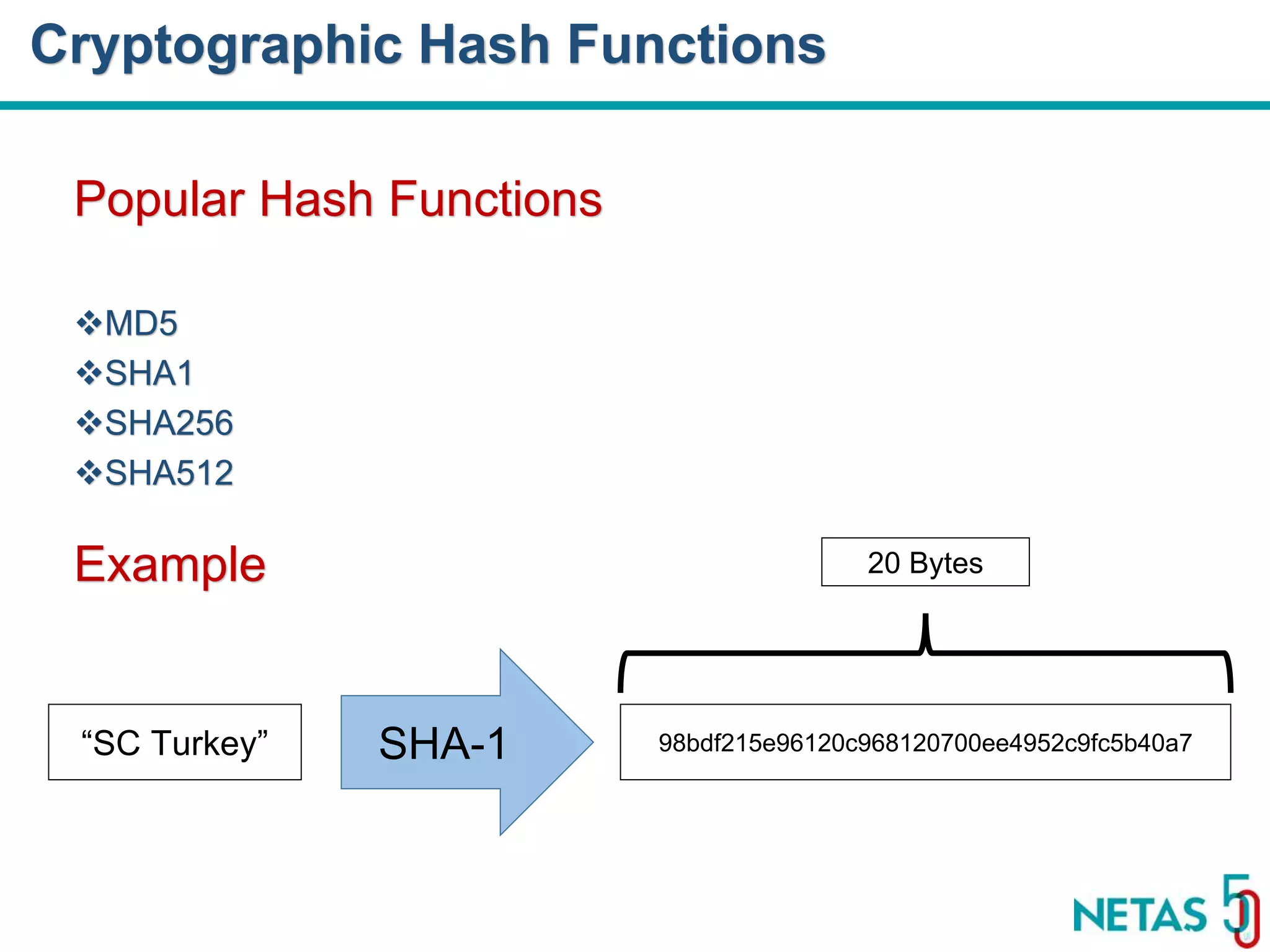
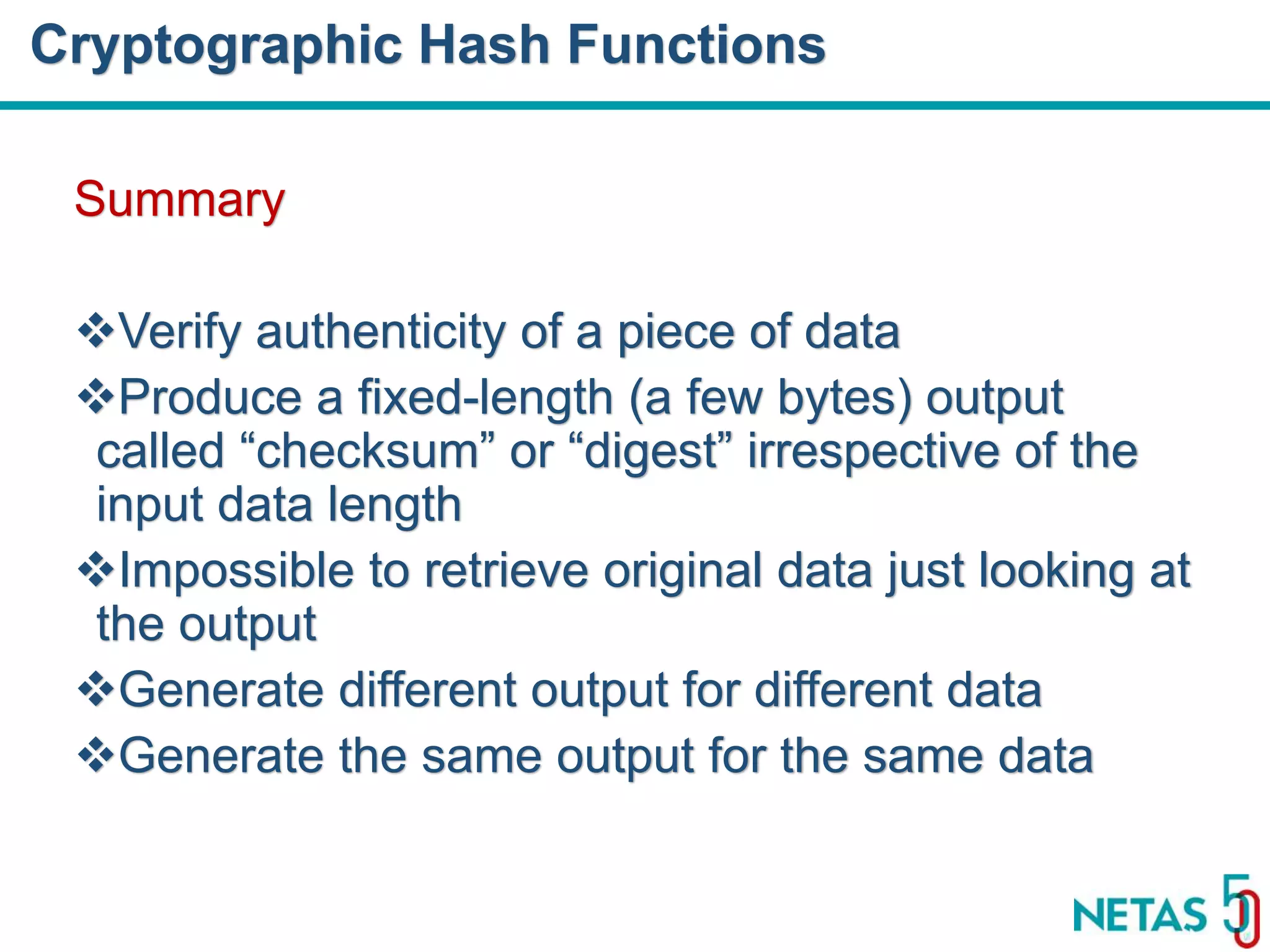
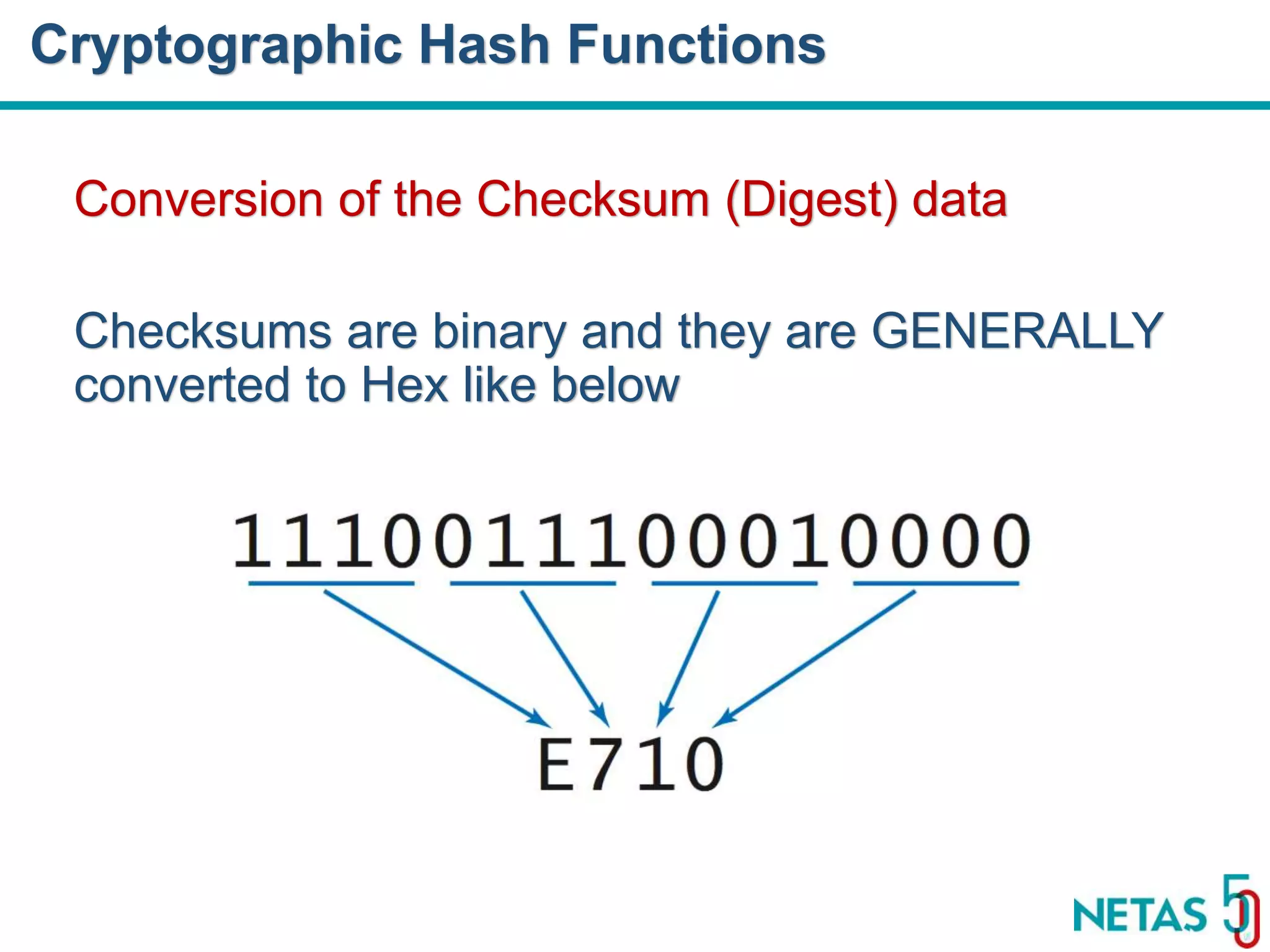
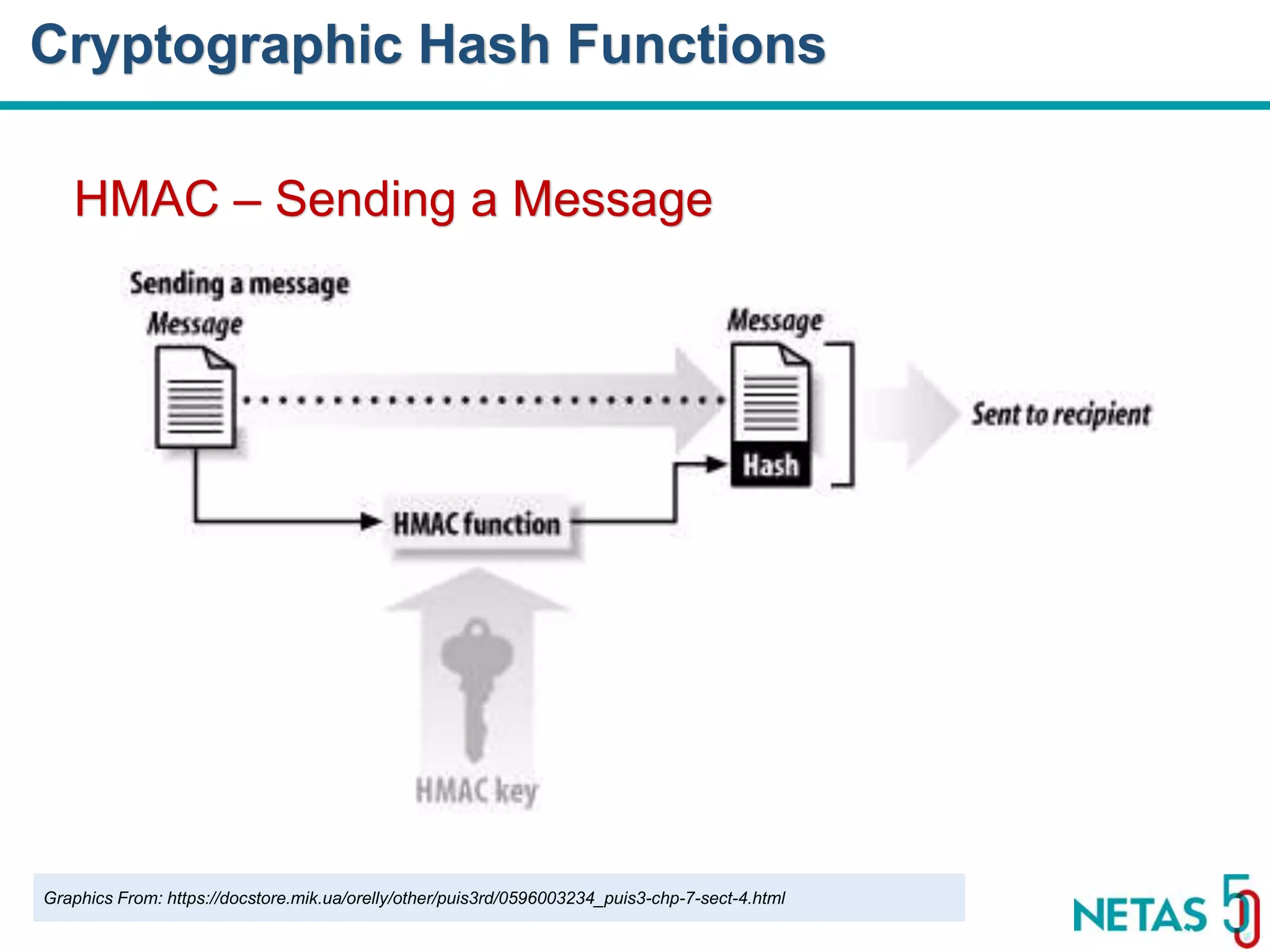
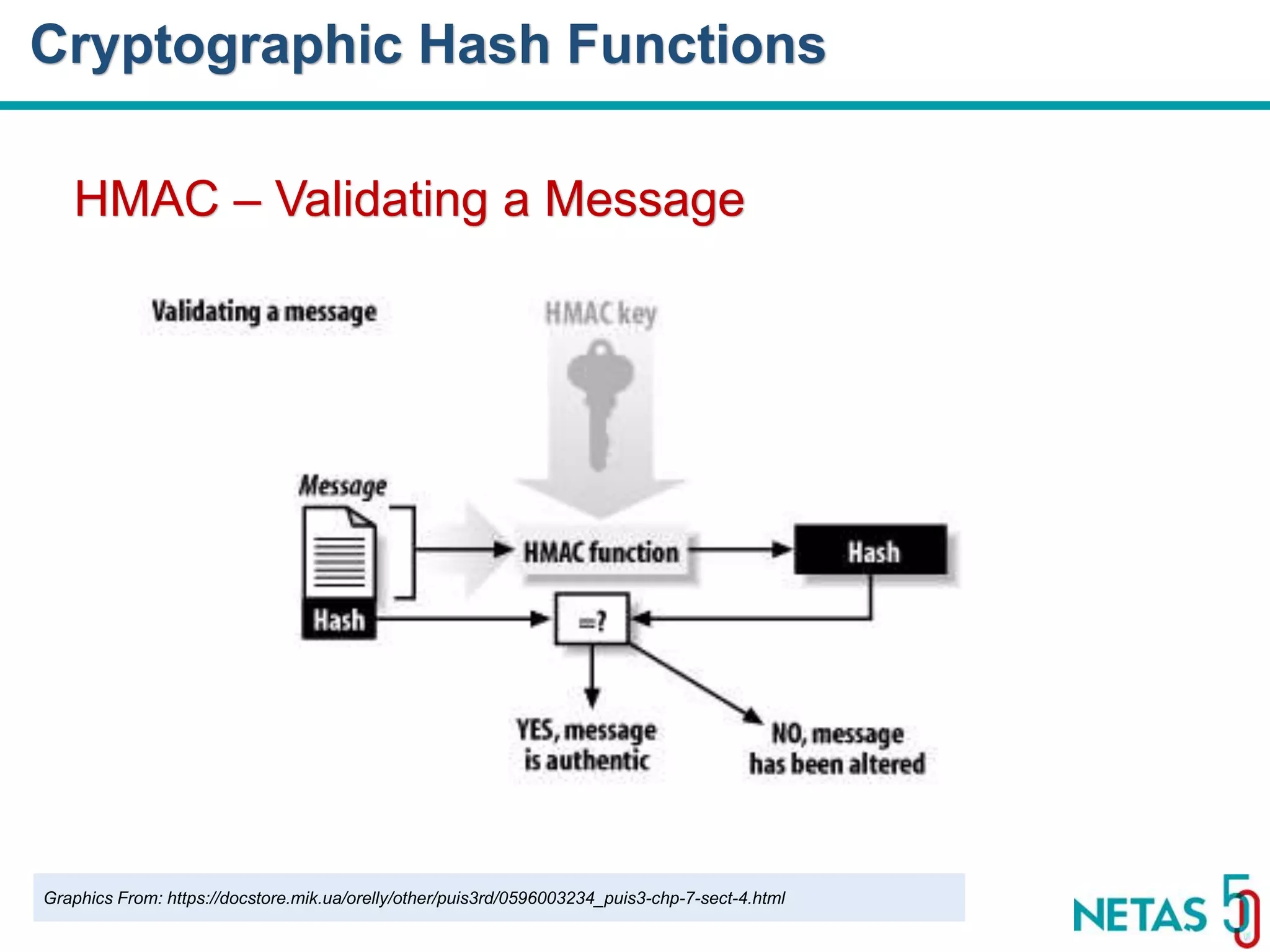
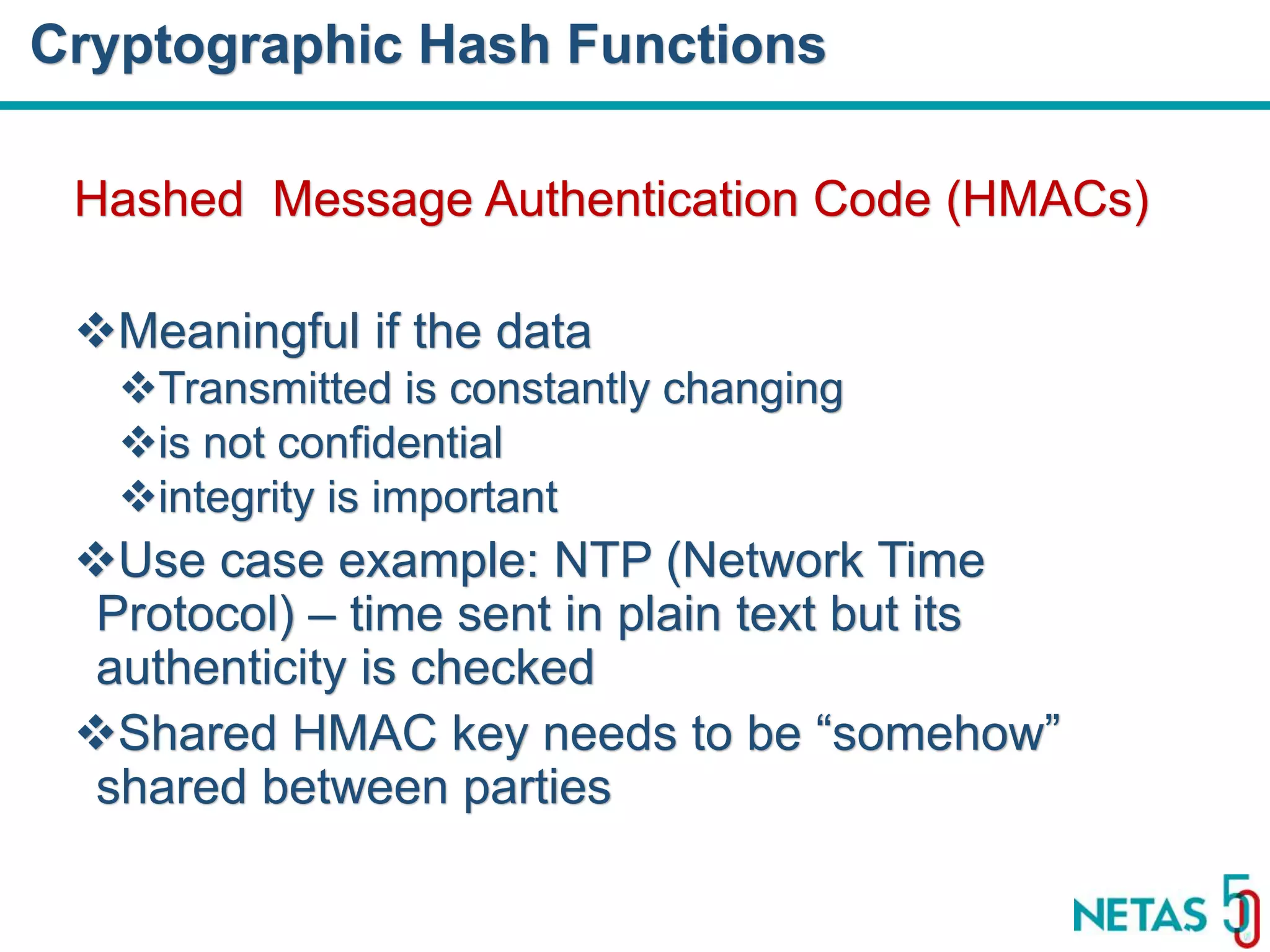
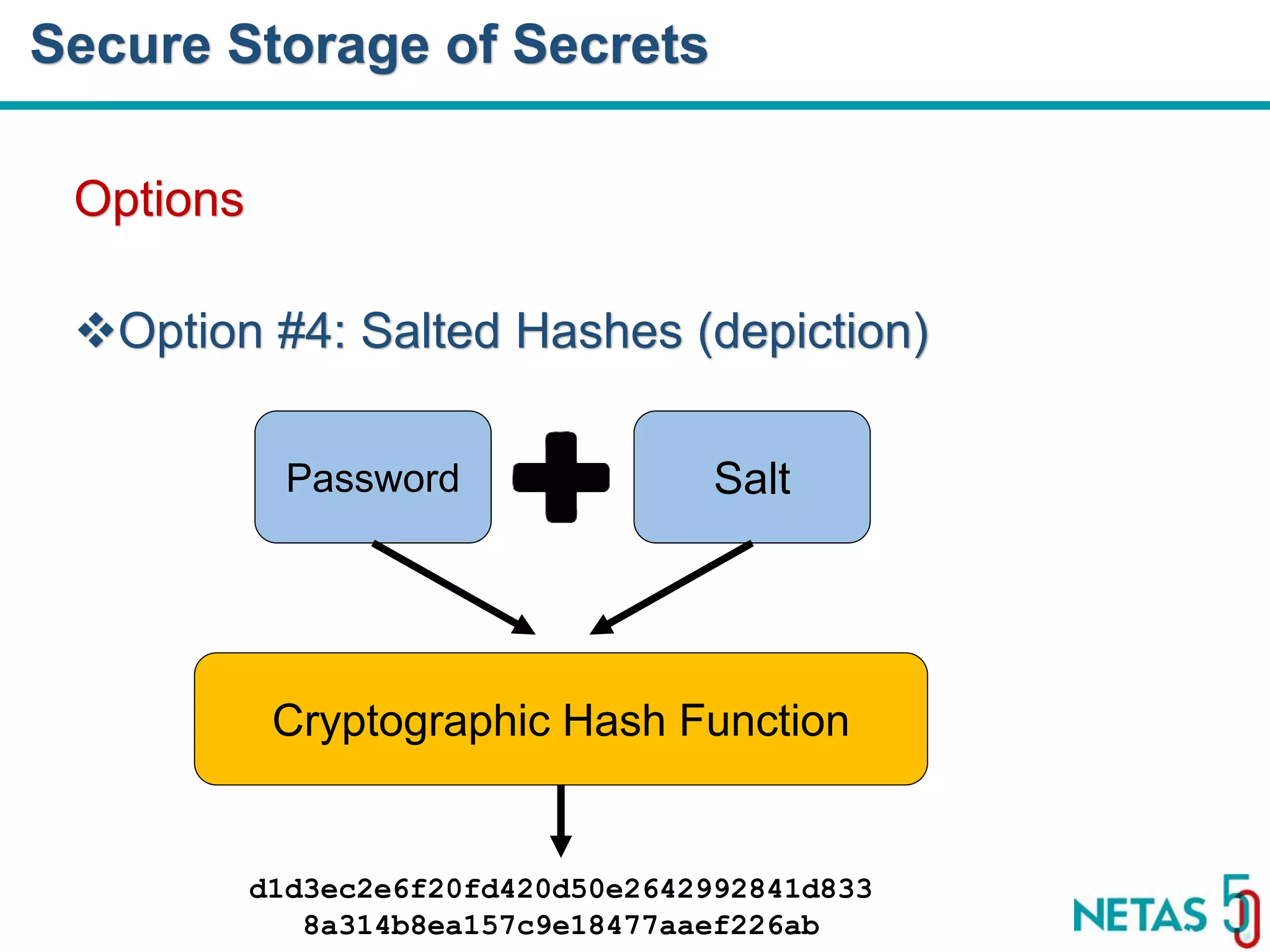
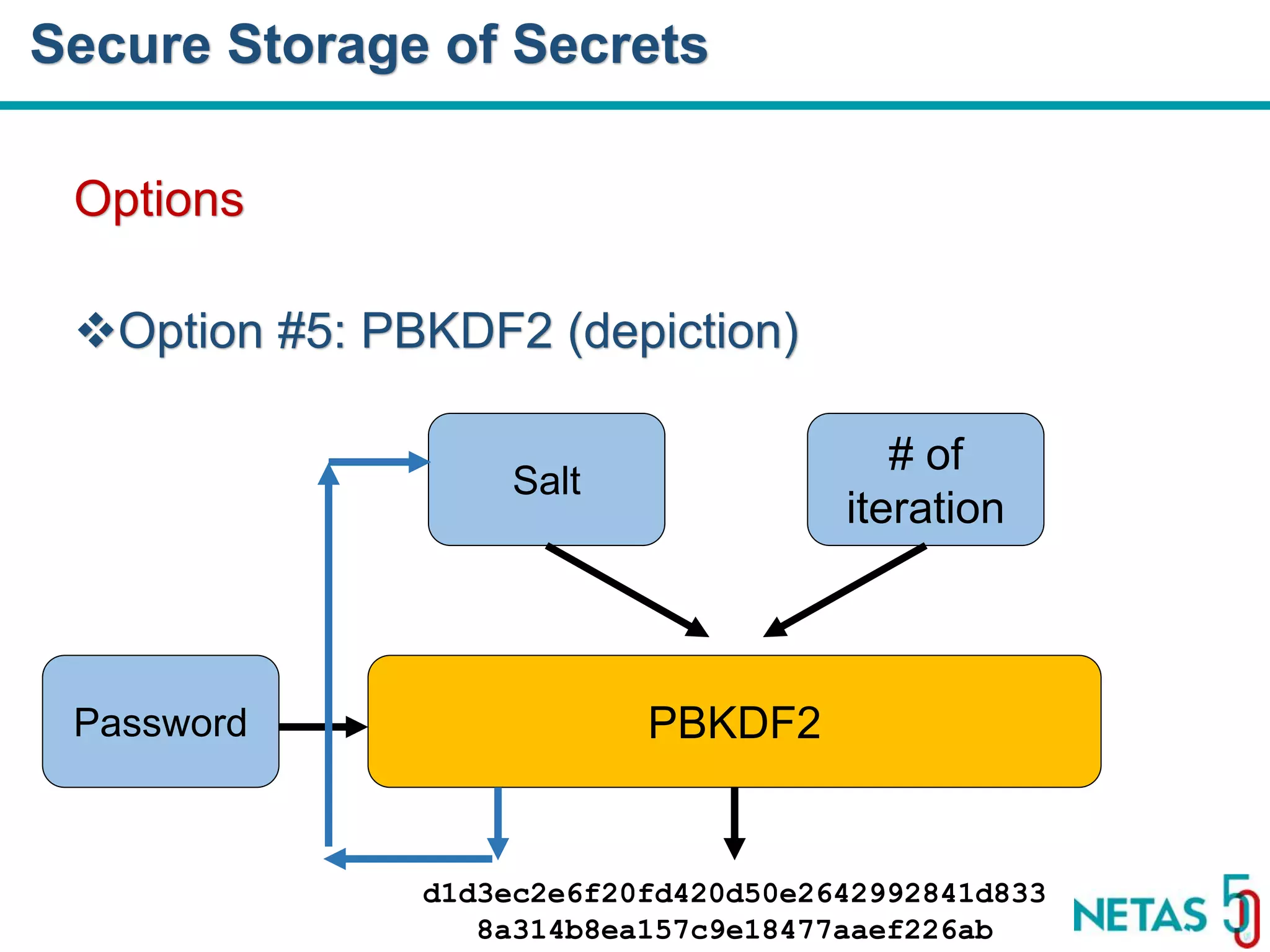
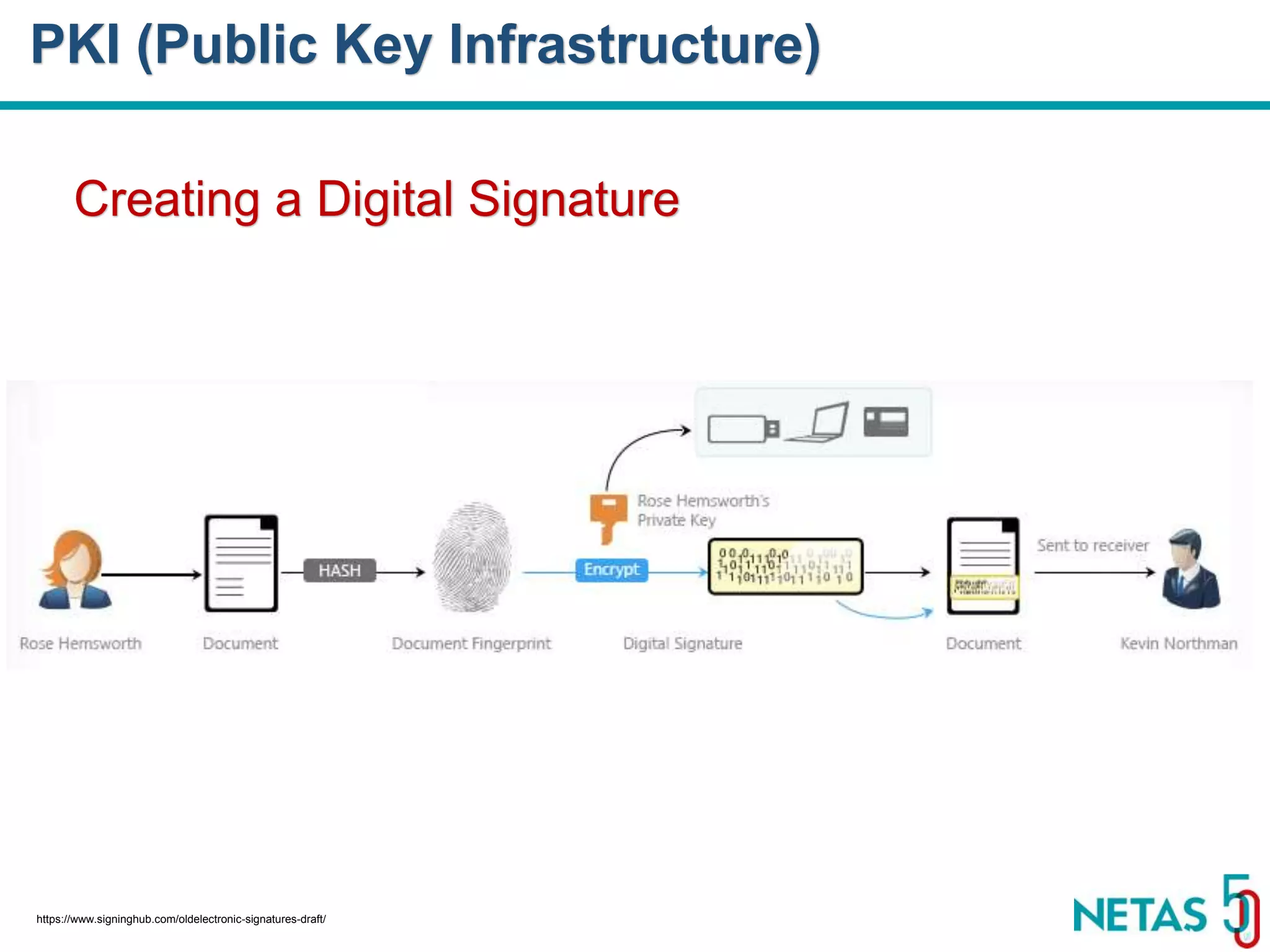
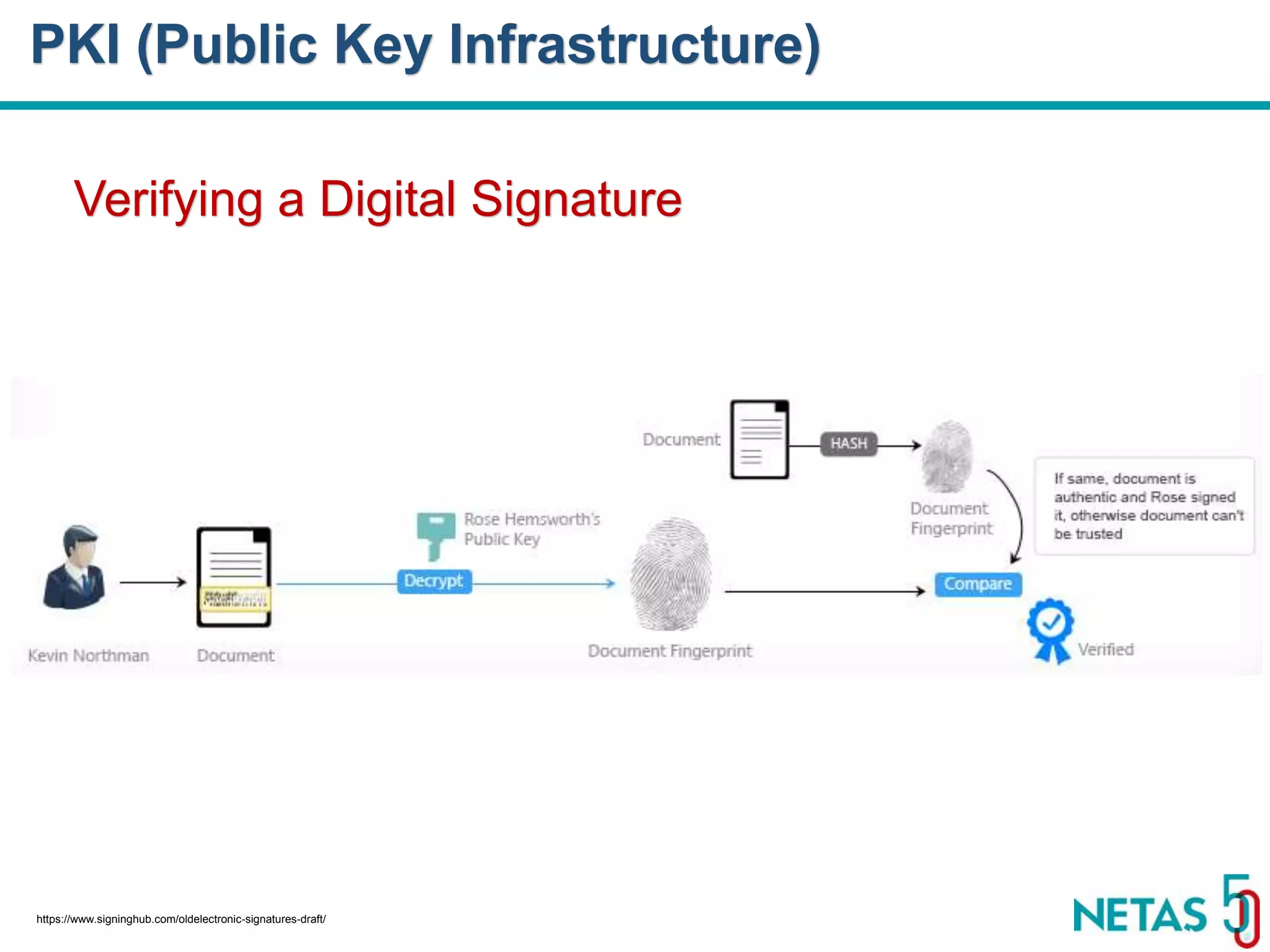
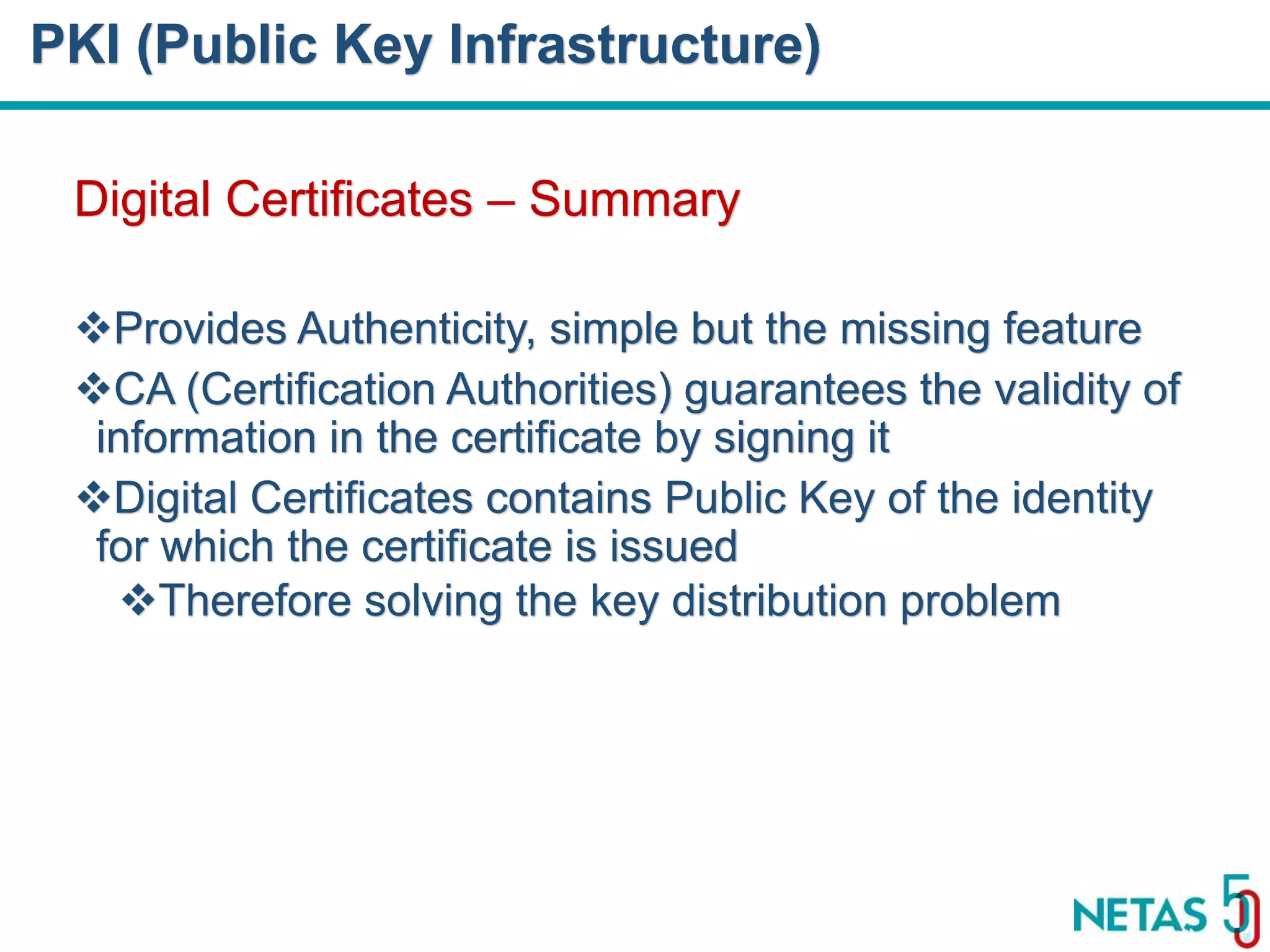
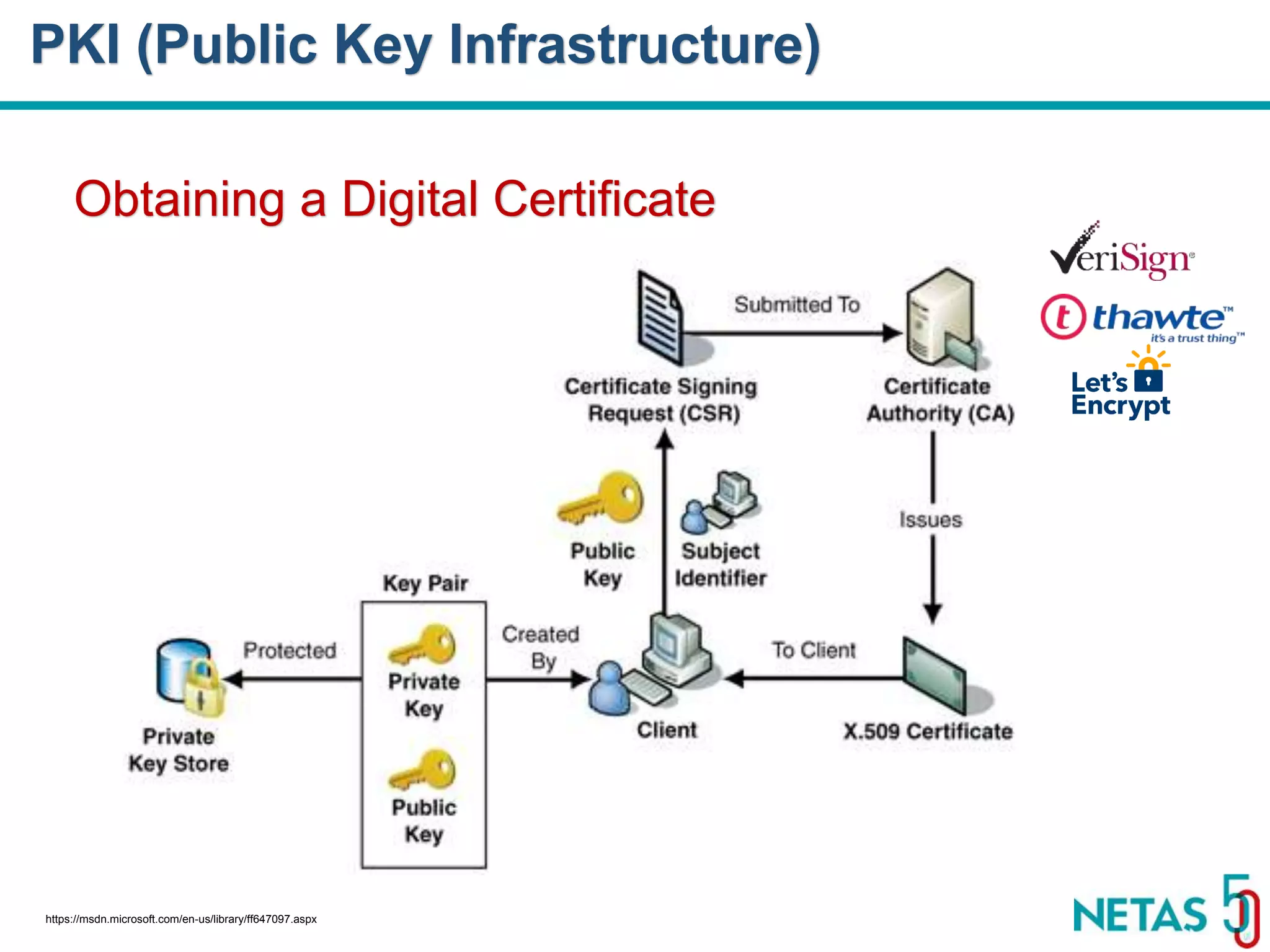
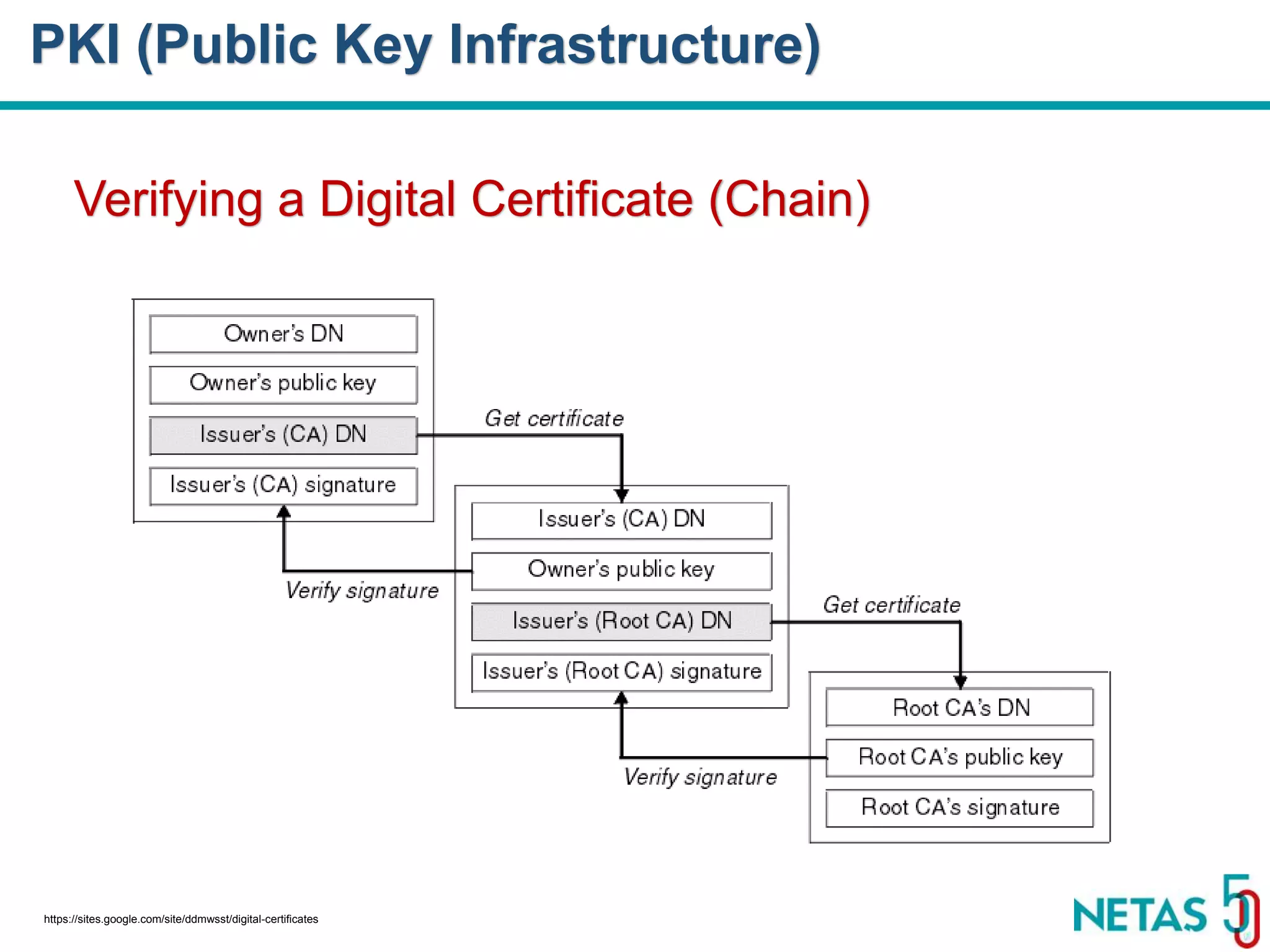
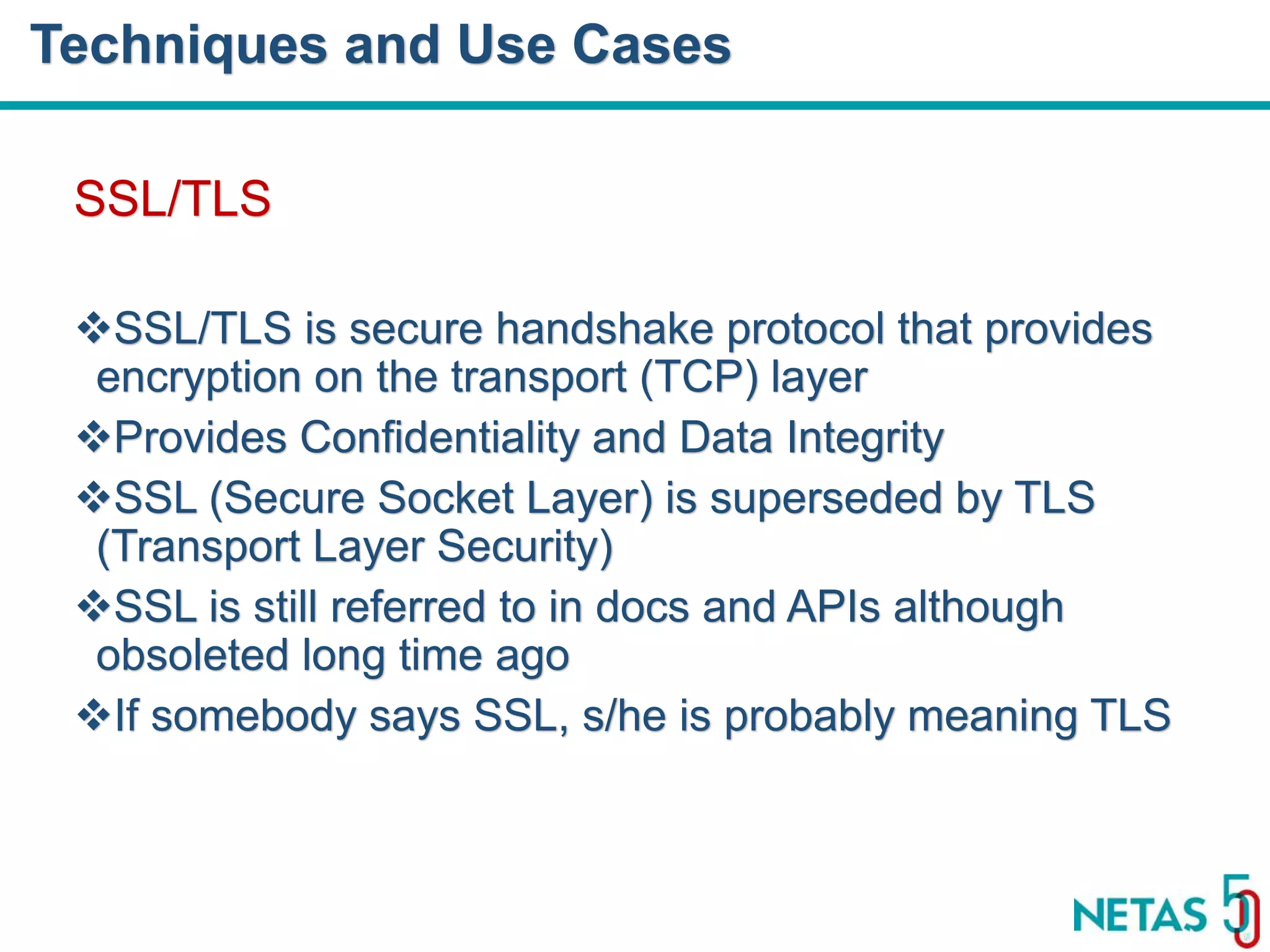
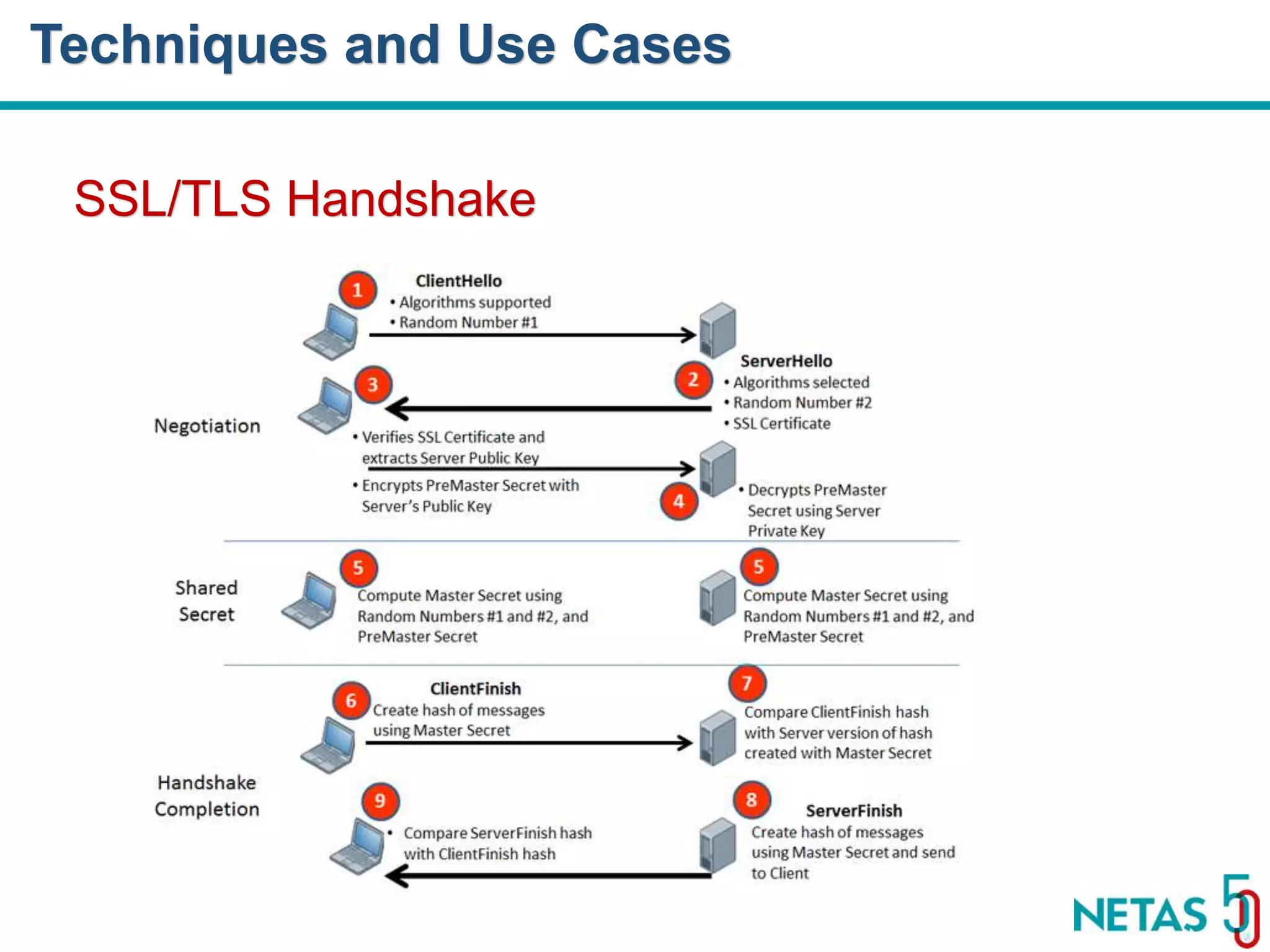
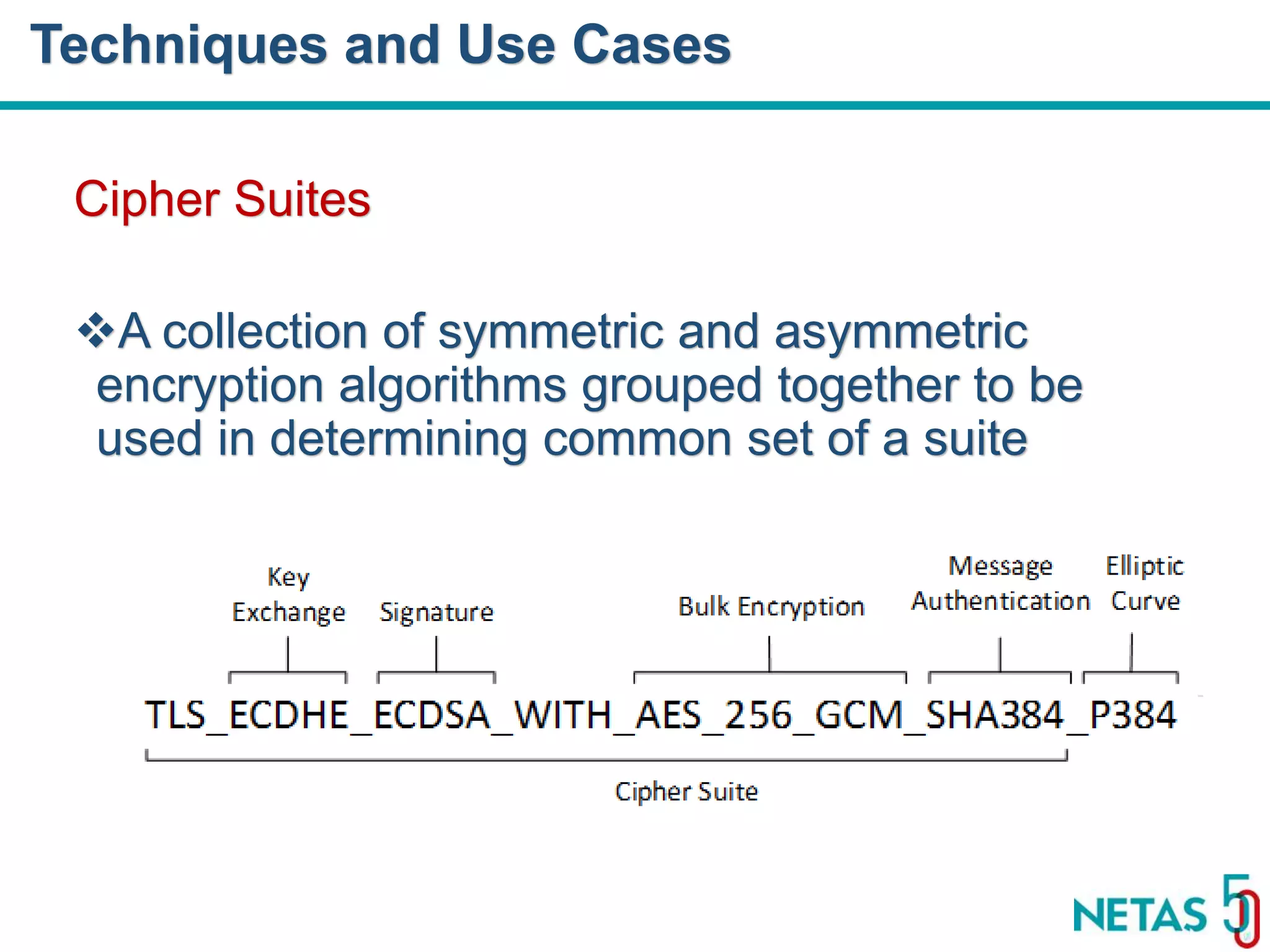
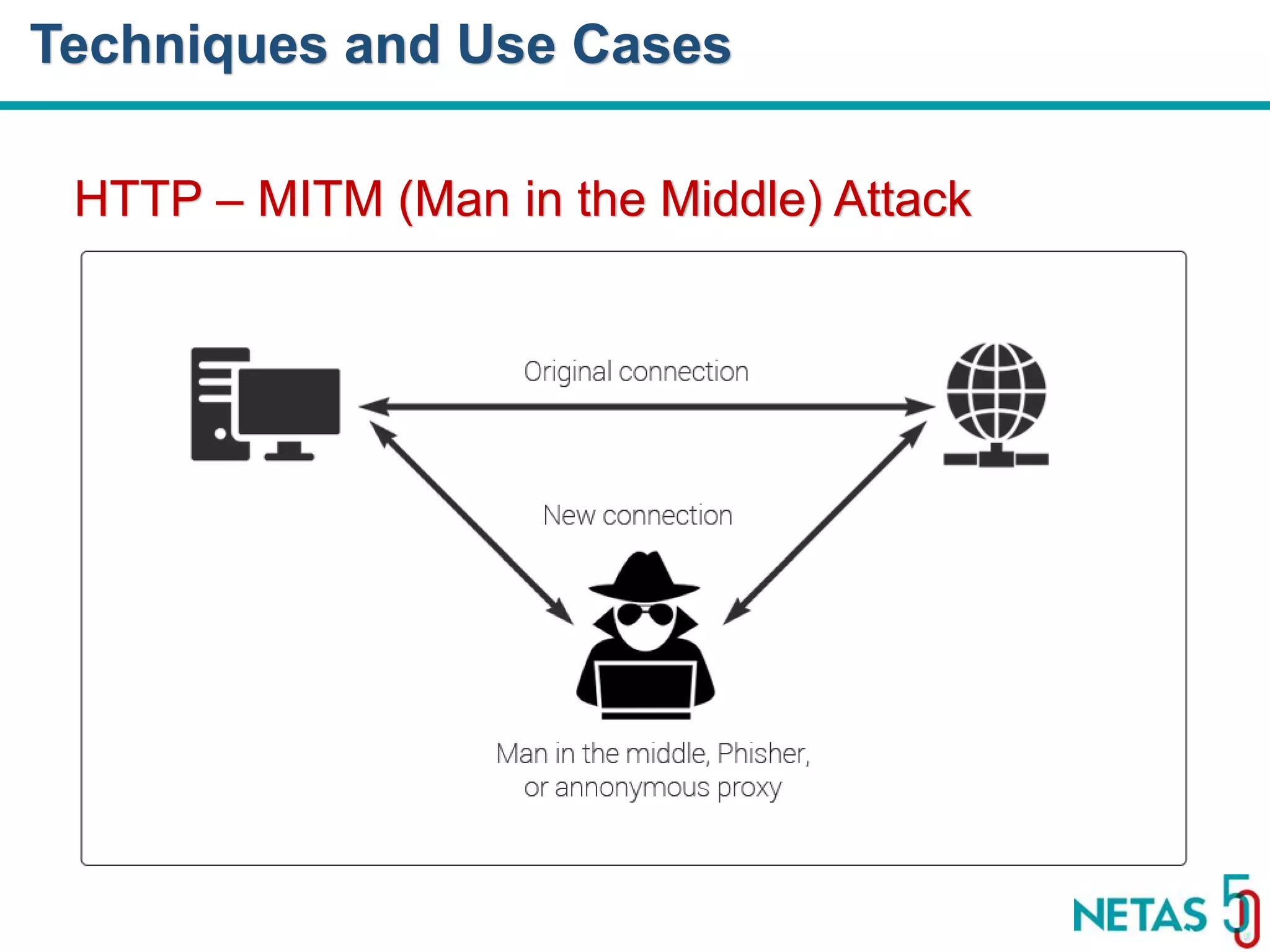
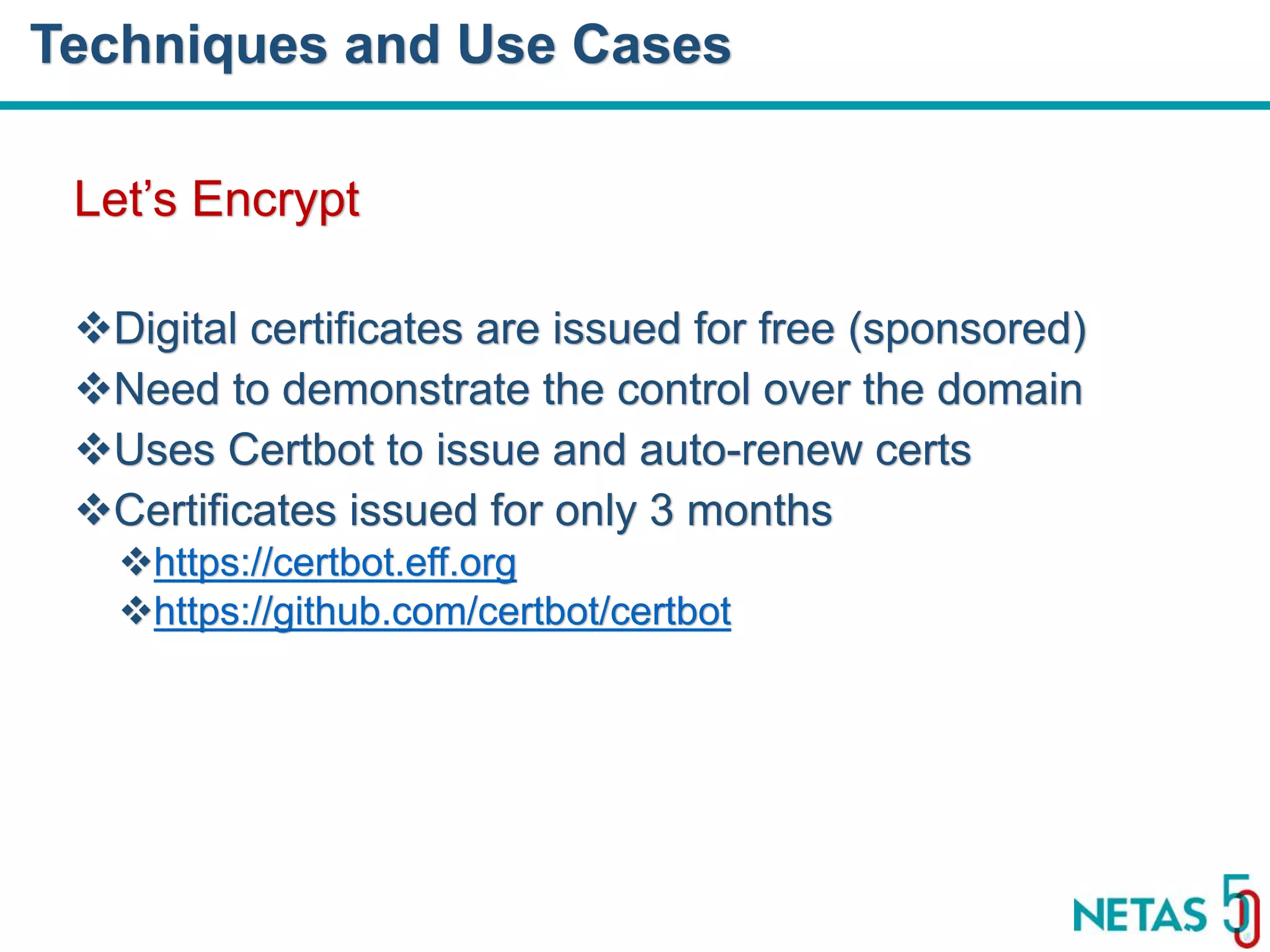
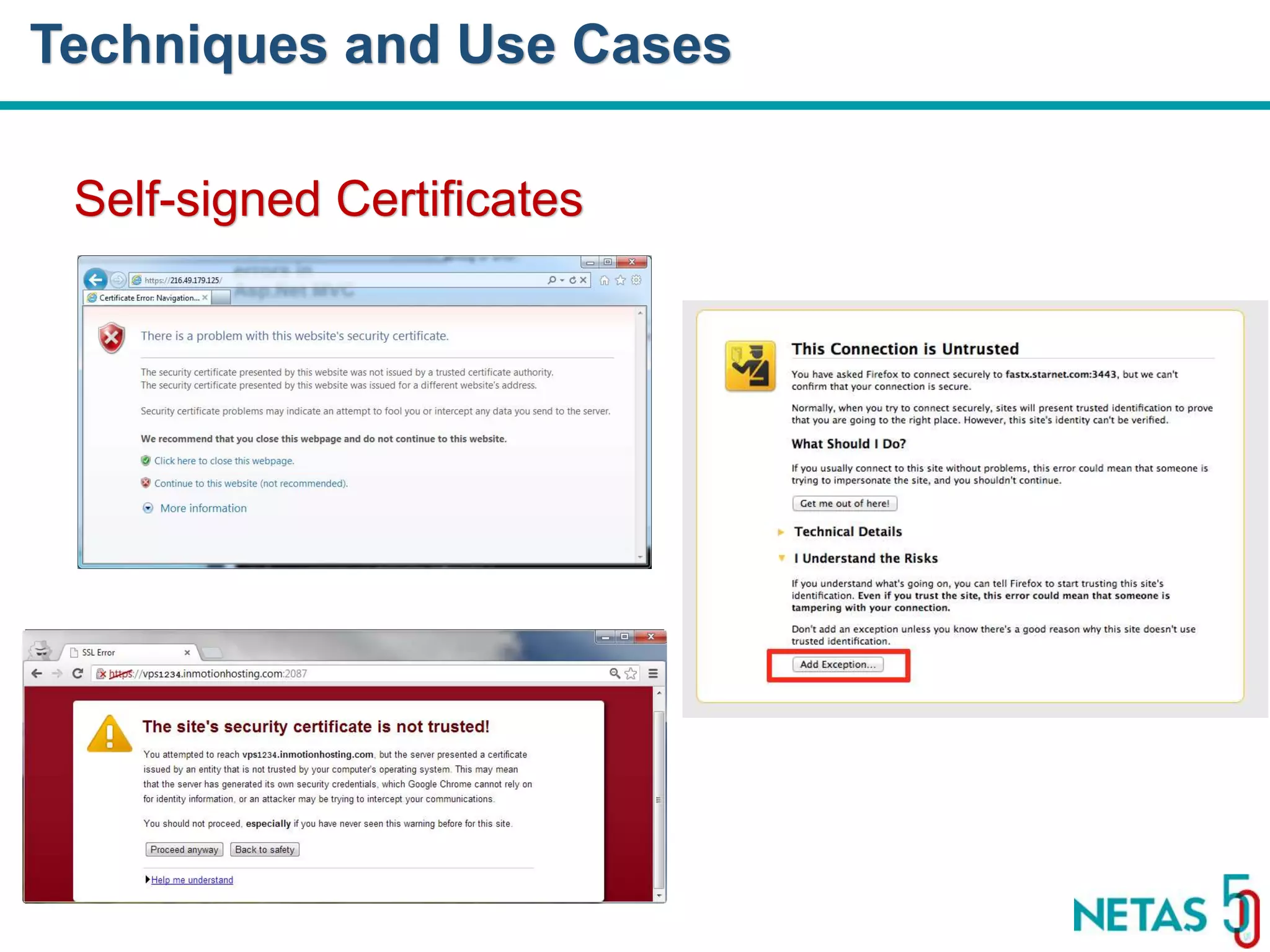
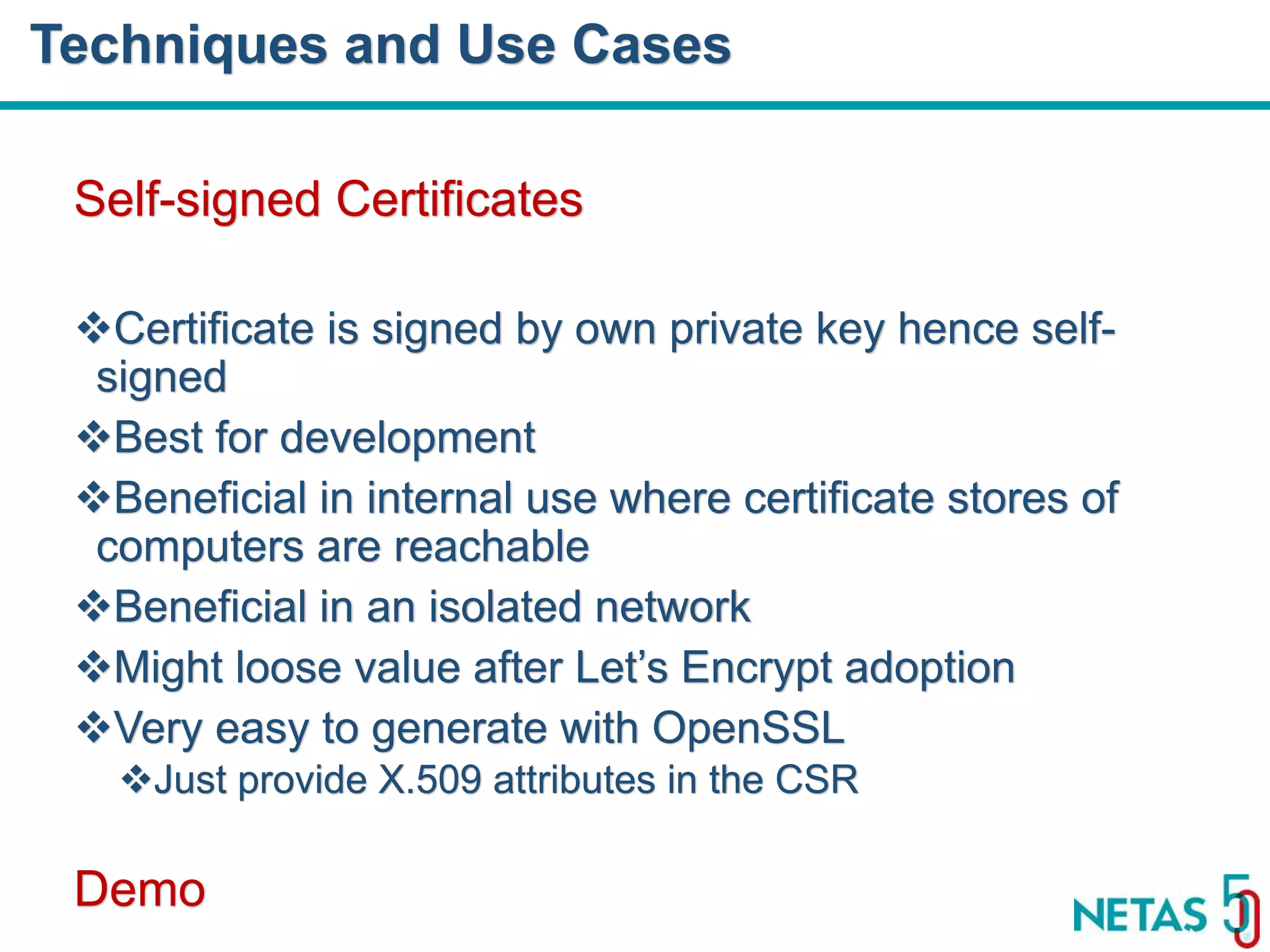
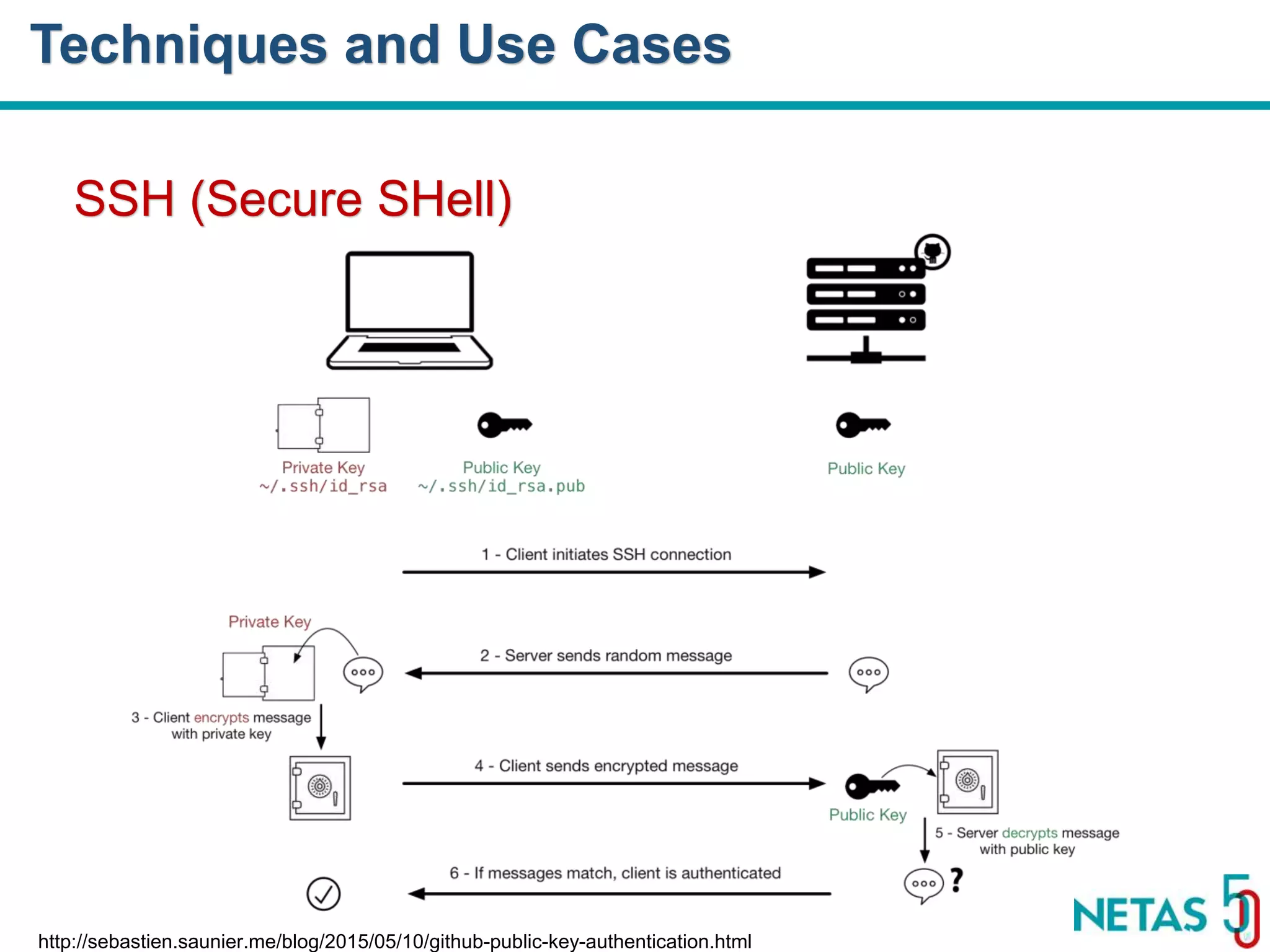
This document summarizes Gökhan Şengün's presentation on practical cryptography and security concepts for developers at DEVOPS Zirvesi 2017. The presentation covers the history of cryptography, cryptographic hash functions, secure storage of secrets, symmetric and asymmetric encryption, public key infrastructure (PKI) and digital signatures, and techniques and use cases including HTTPS and SSL/TLS handshakes. The presentation aims to help developers understand basic cryptography concepts and how they apply to building secure systems.