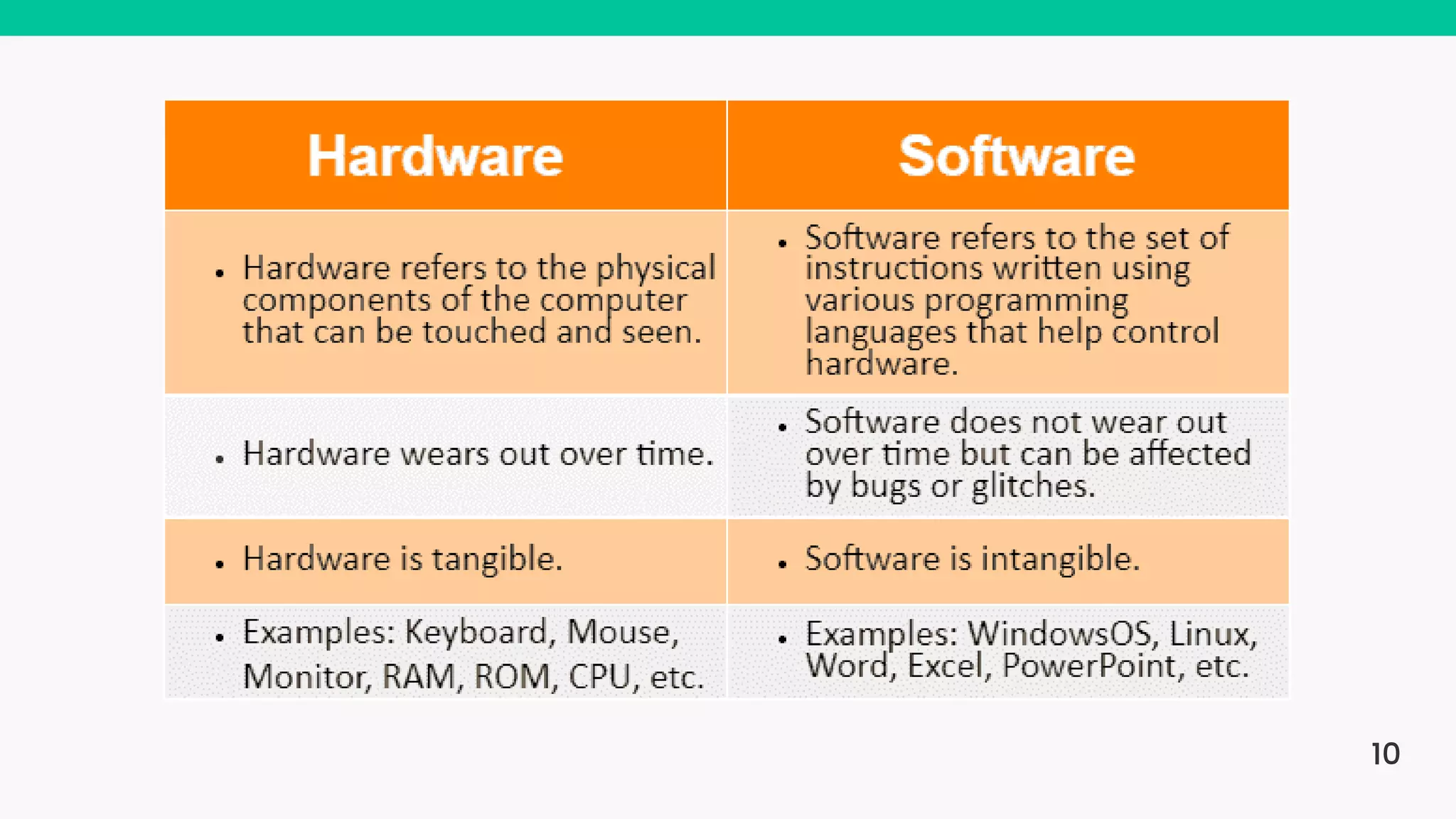
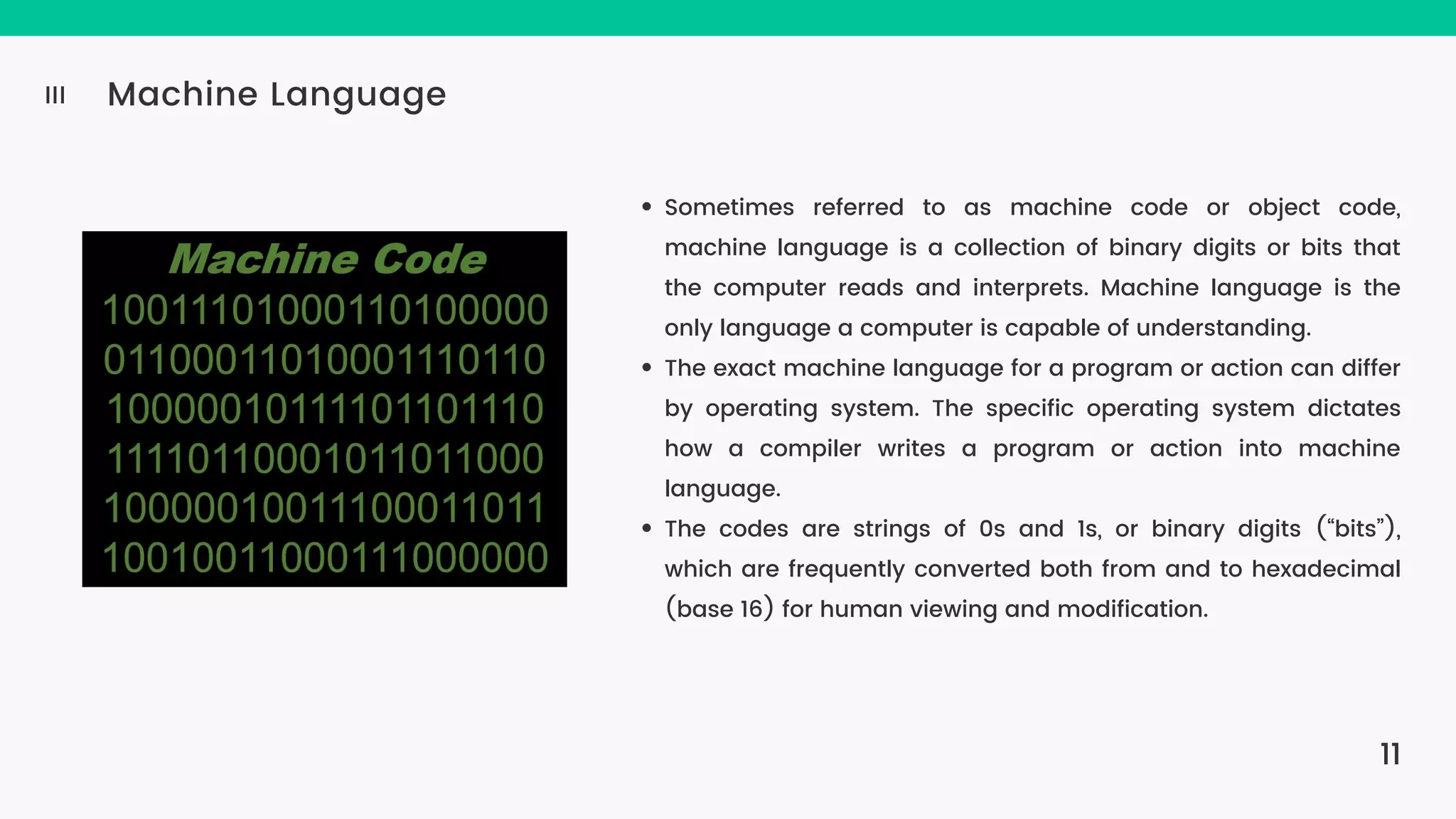
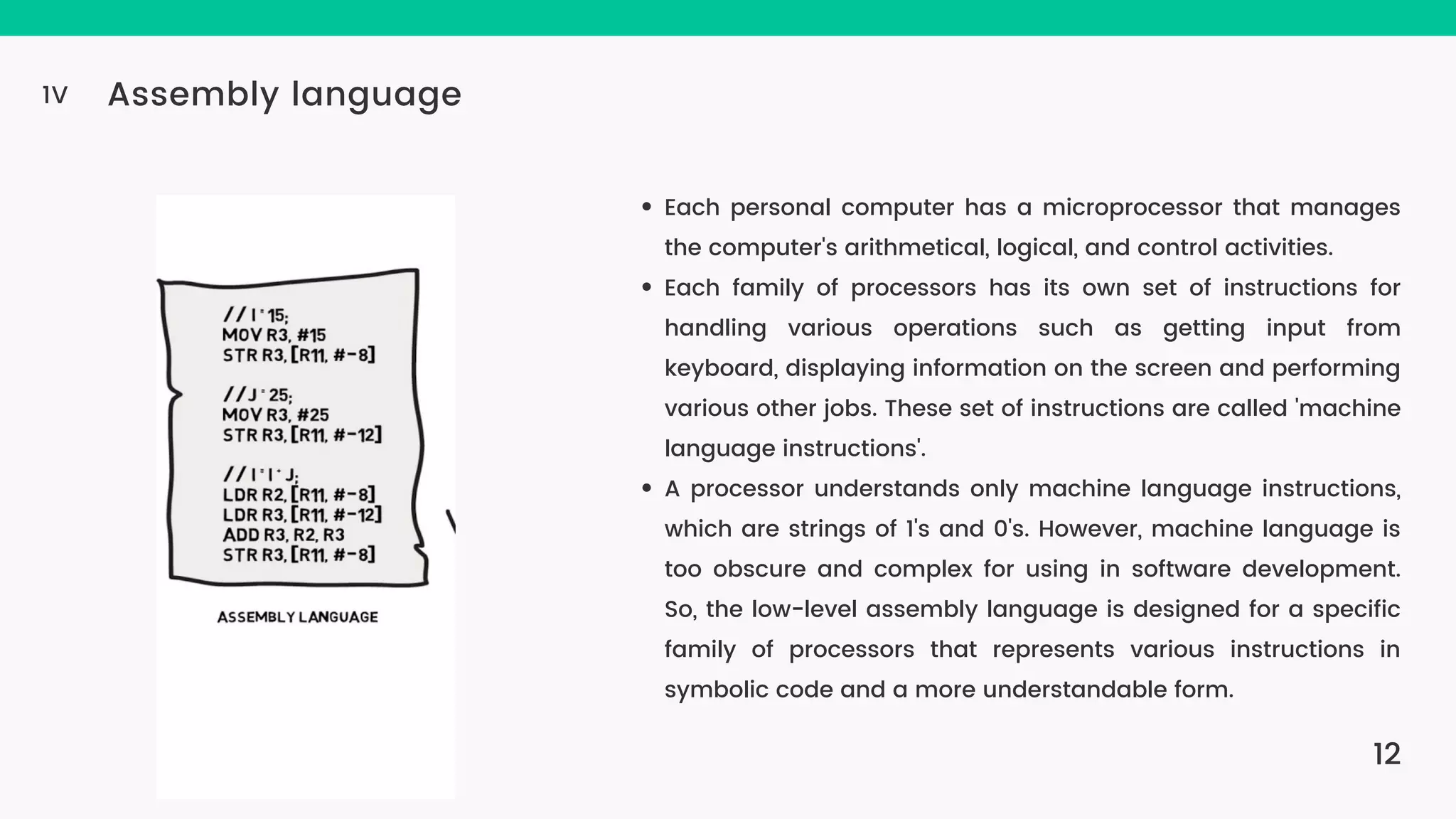
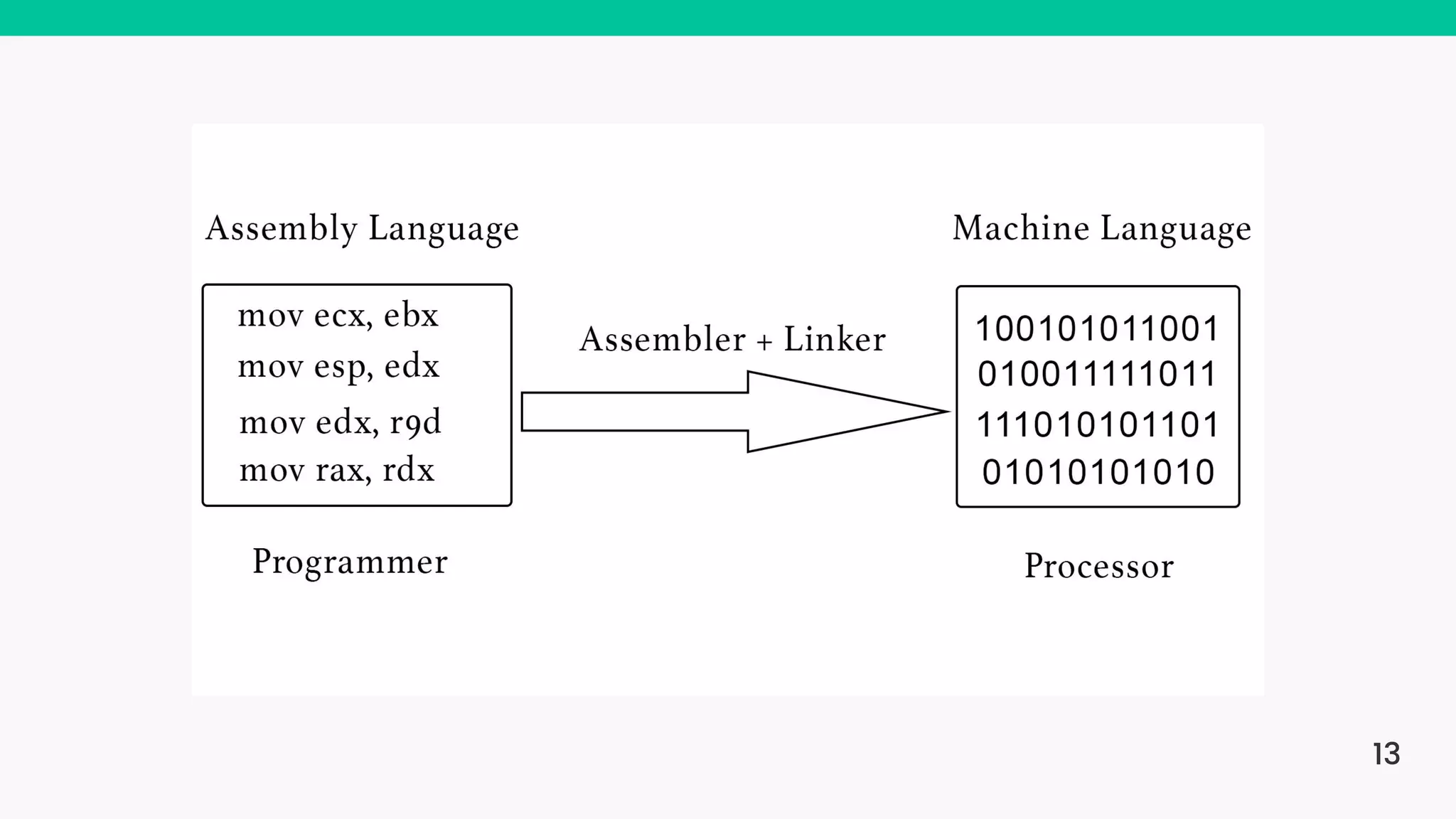
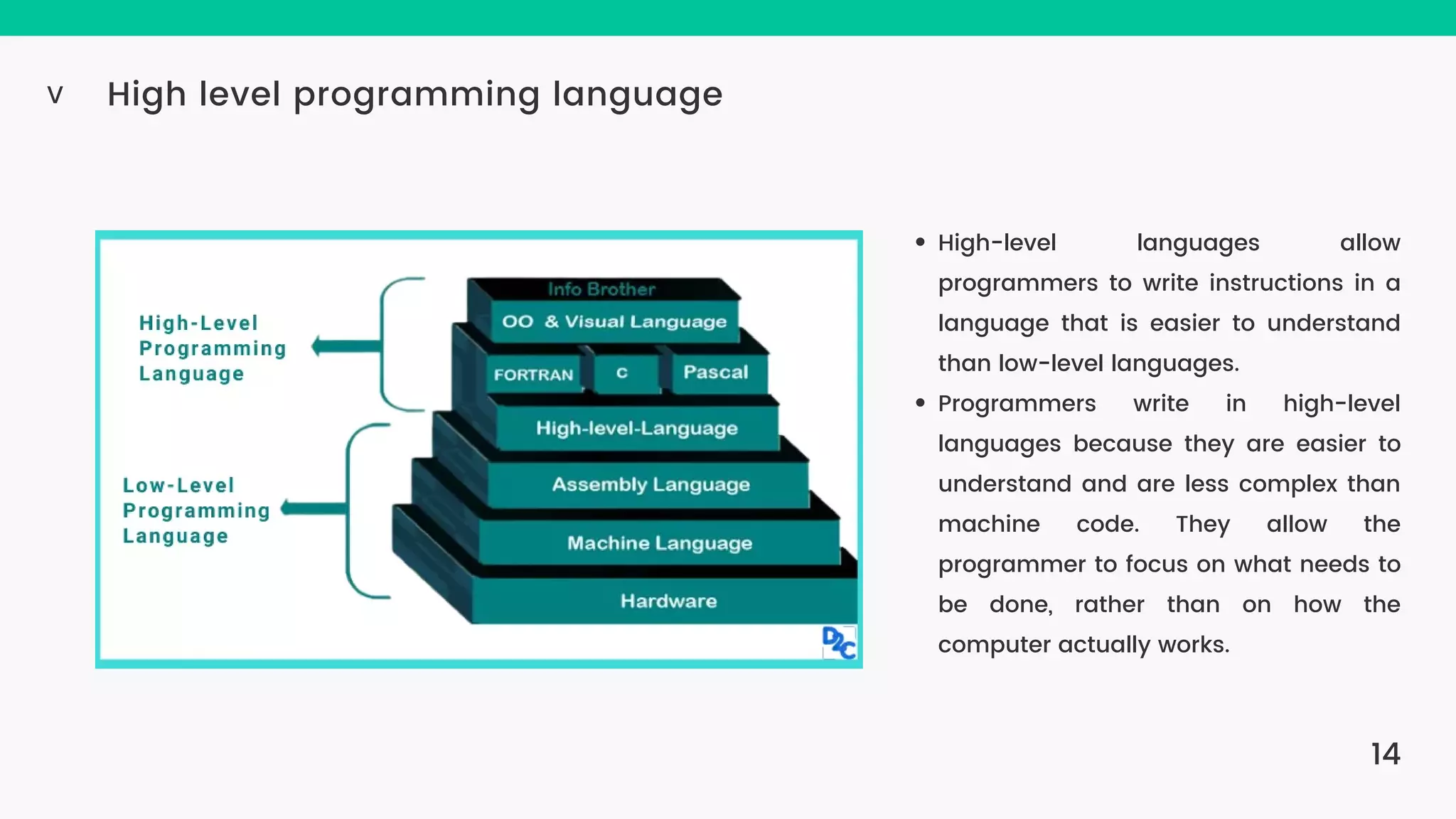
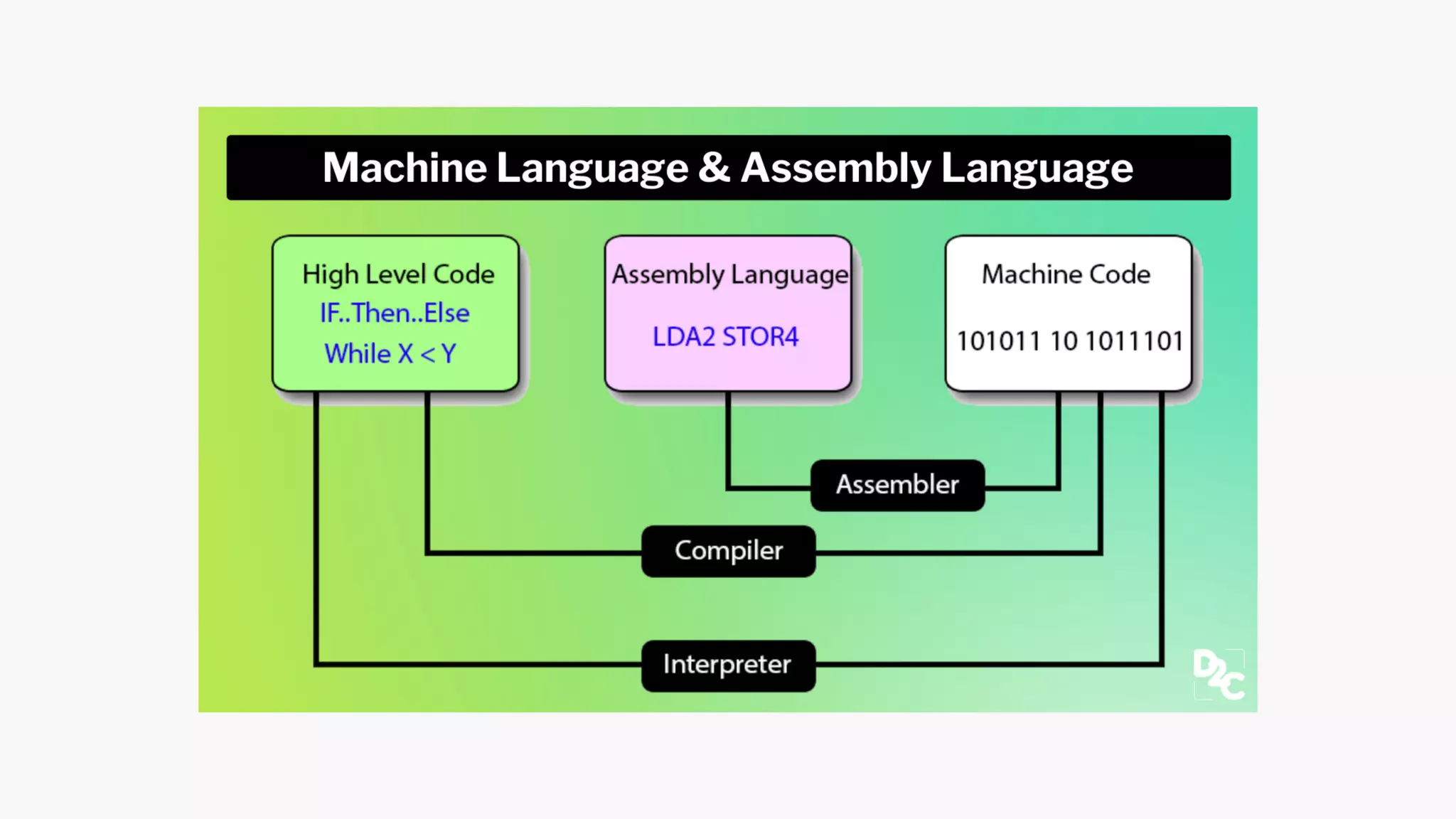
The document provides an introduction to computers, highlighting their basic components, the distinction between hardware and software, and the evolution of programming languages from machine language to high-level languages. It discusses the capabilities of computers, including complex tasks and their applications in various fields, and emphasizes the interplay between hardware and software for efficient functioning. Additionally, it briefly mentions the advancements in computing, such as quantum computers and the current most powerful supercomputer, Fugaku.