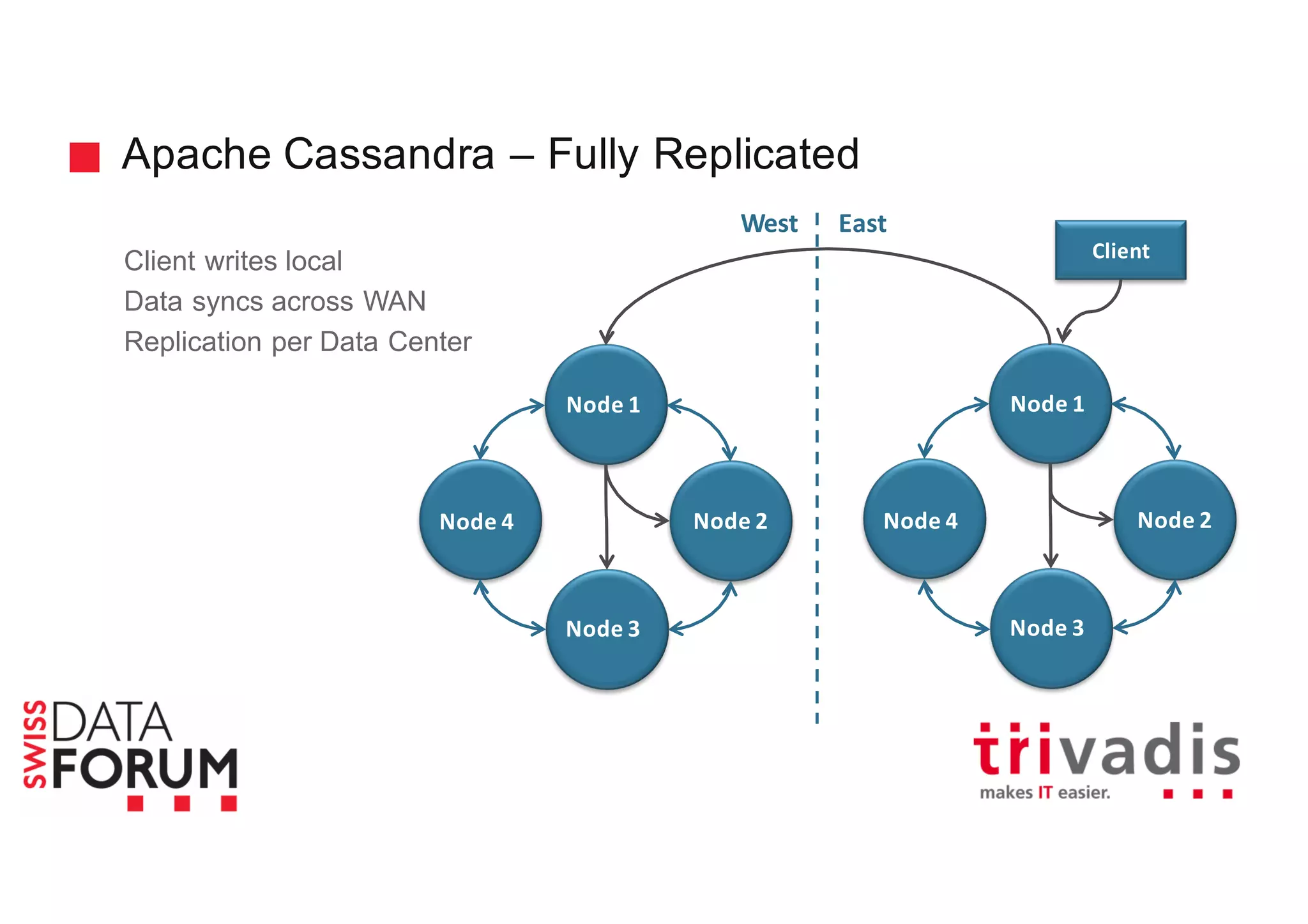
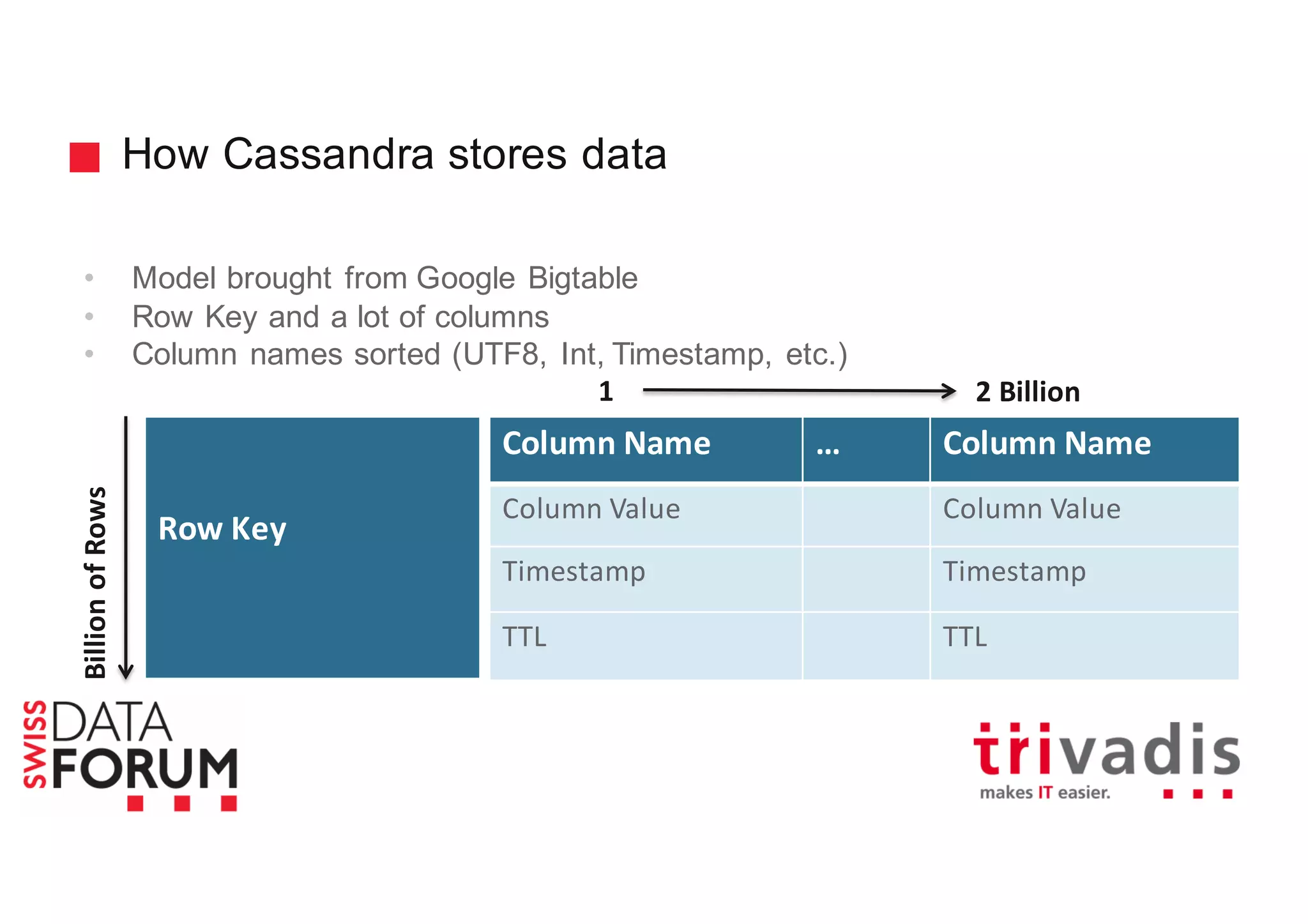
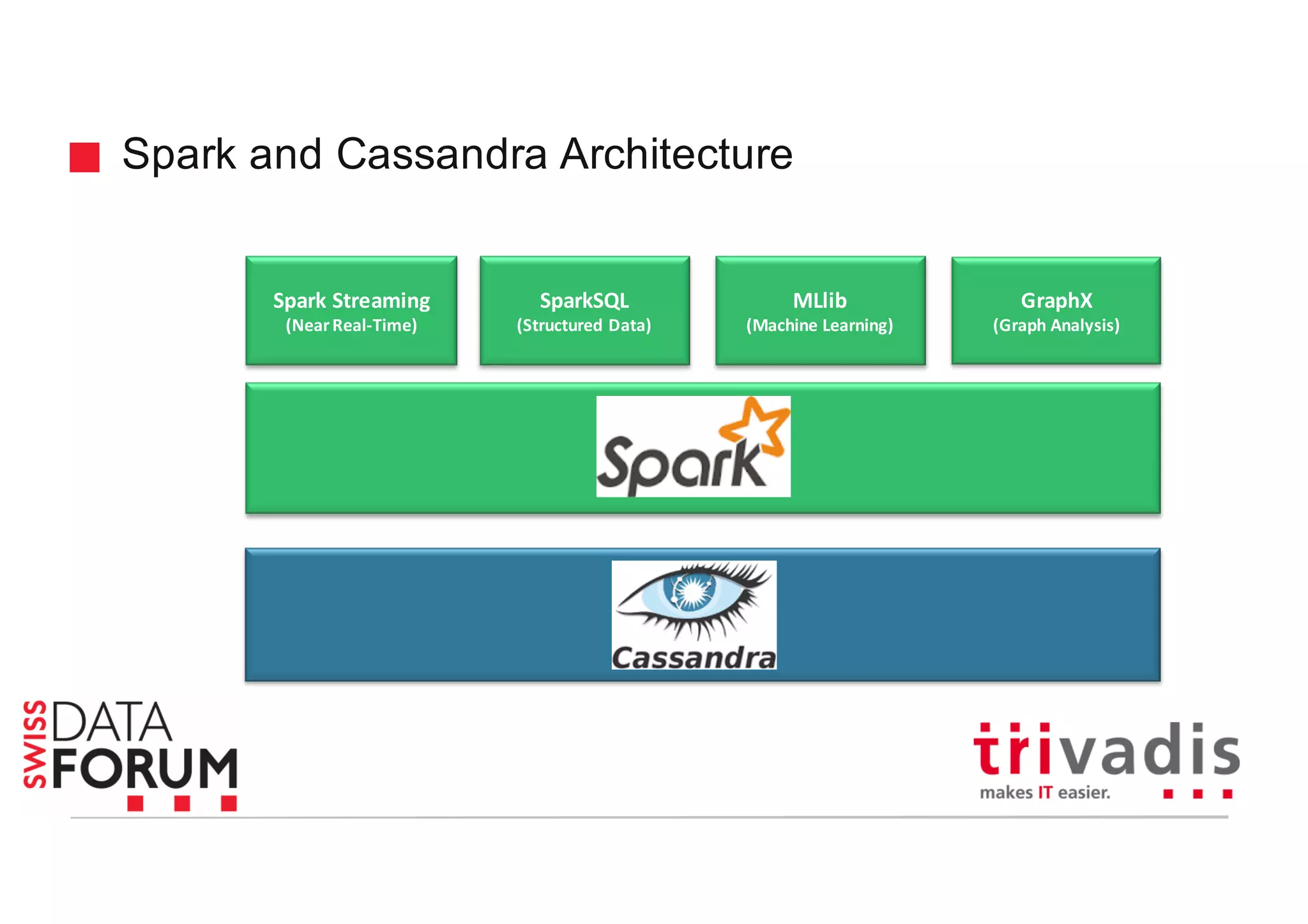
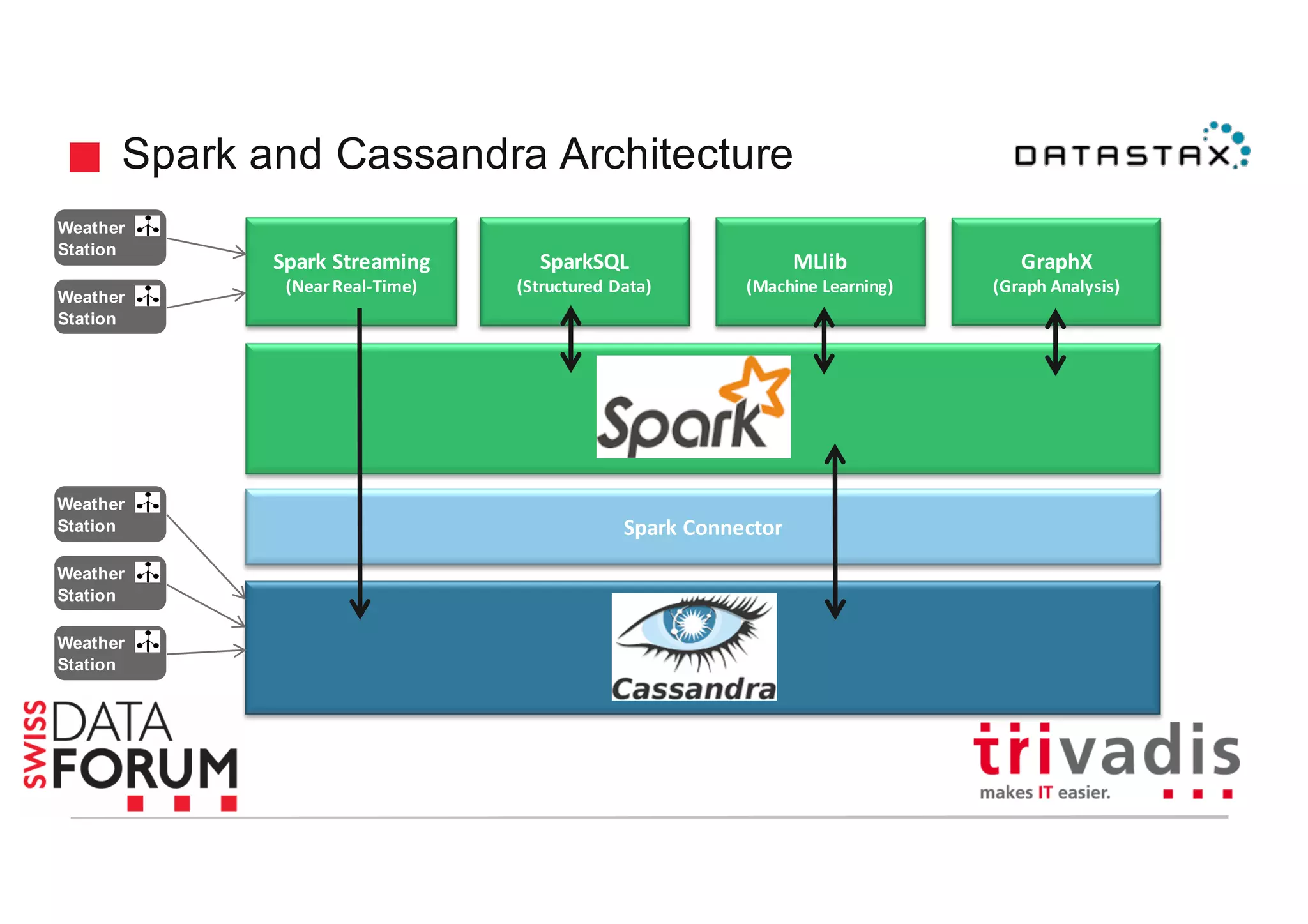
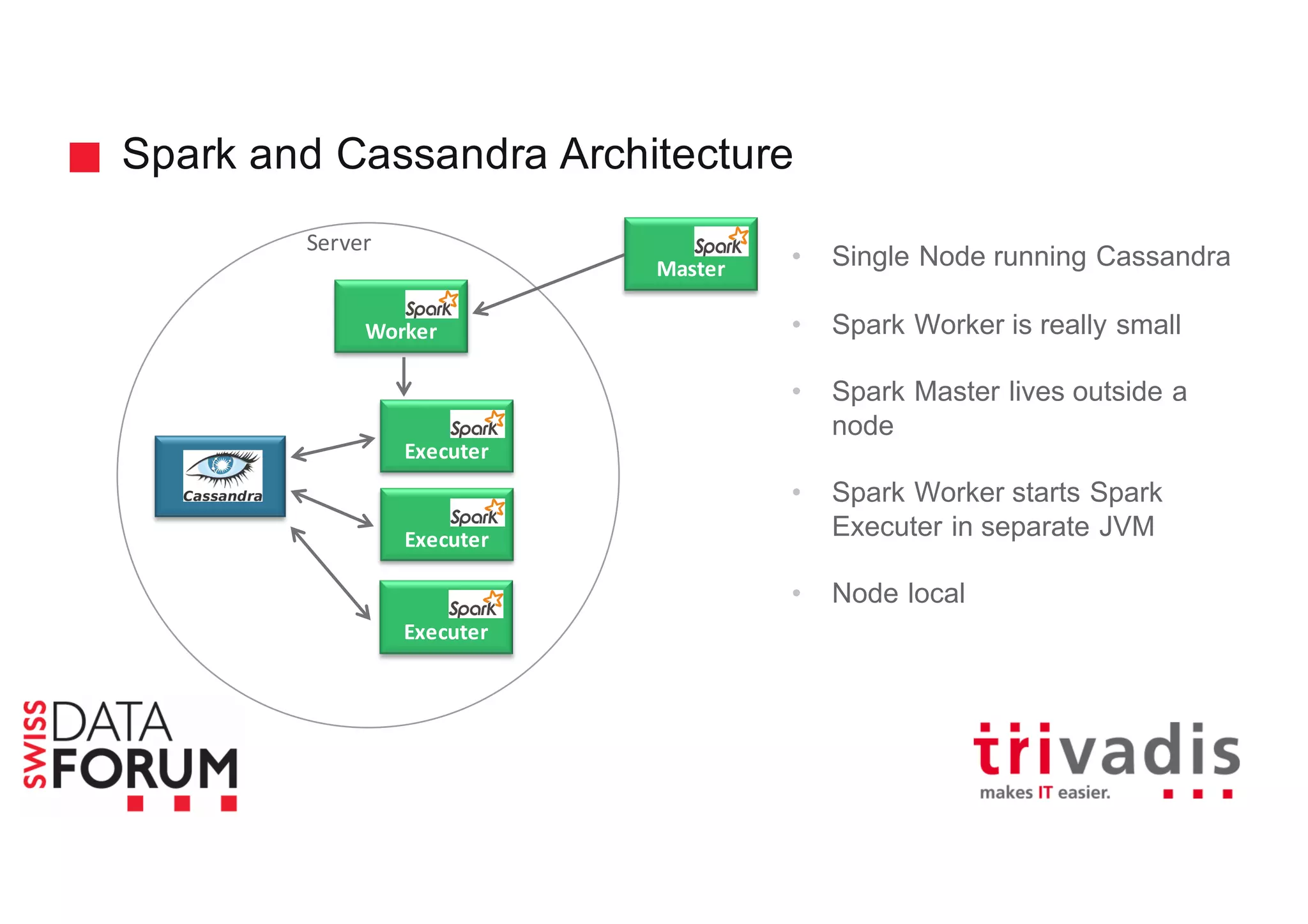
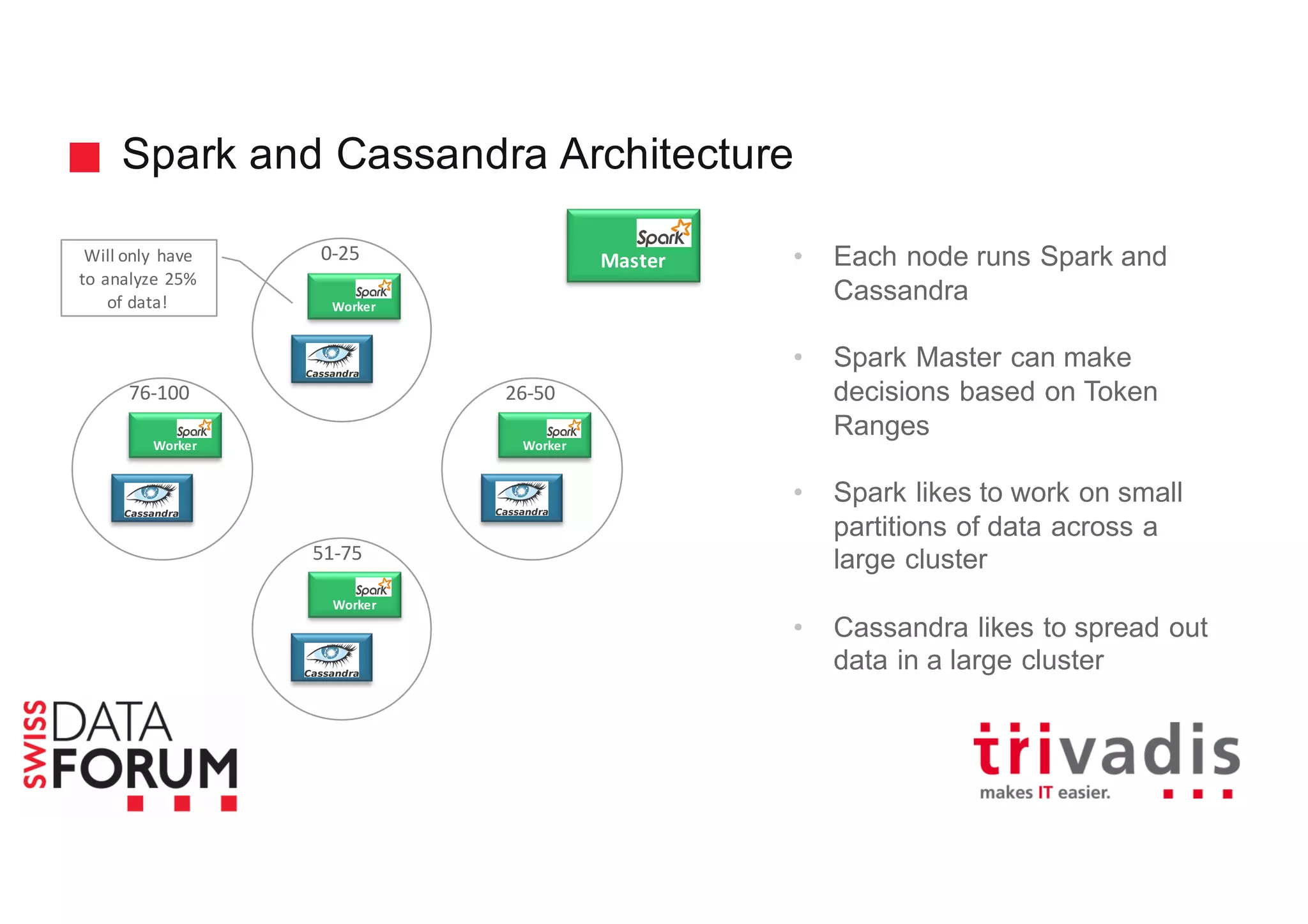
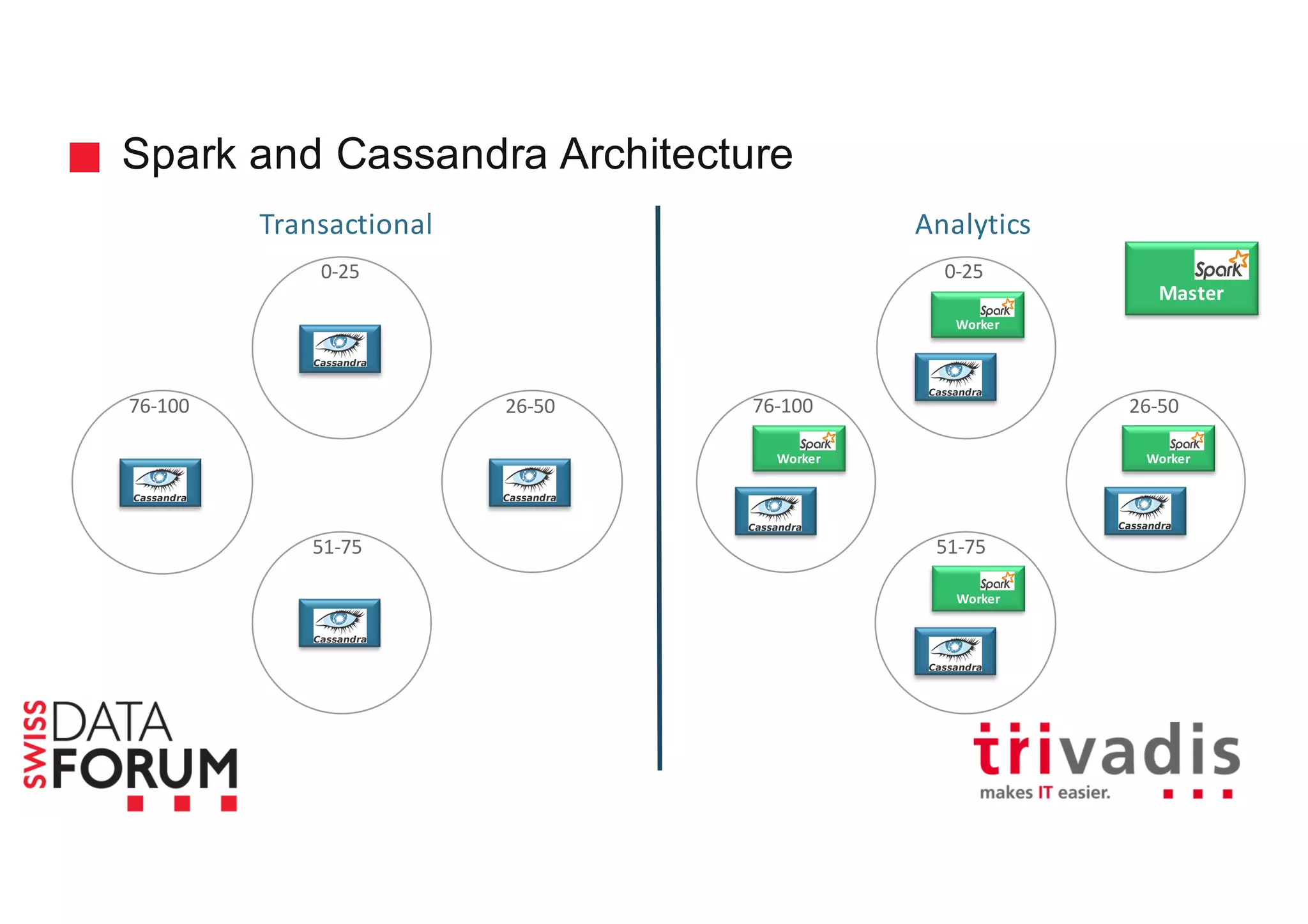
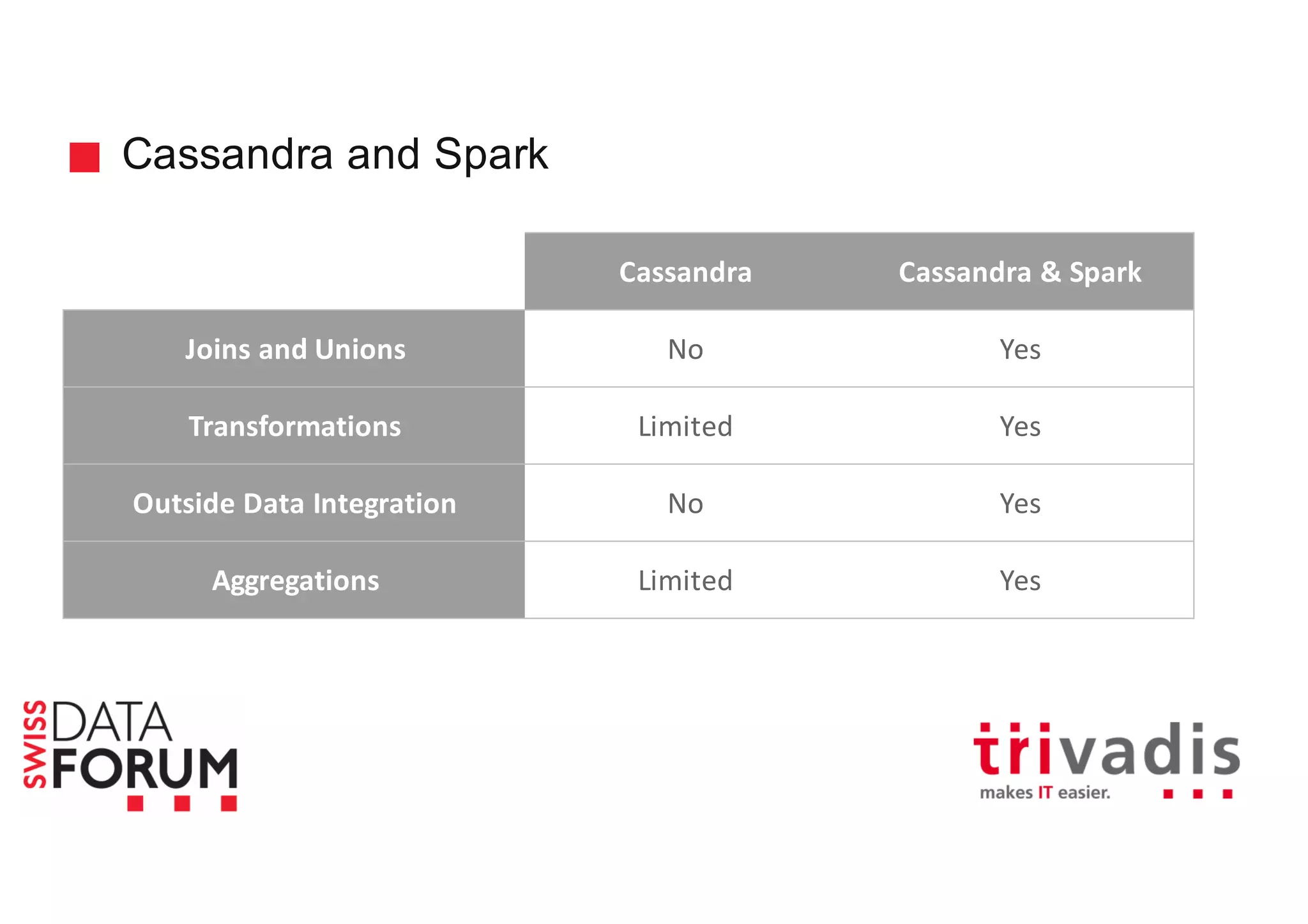
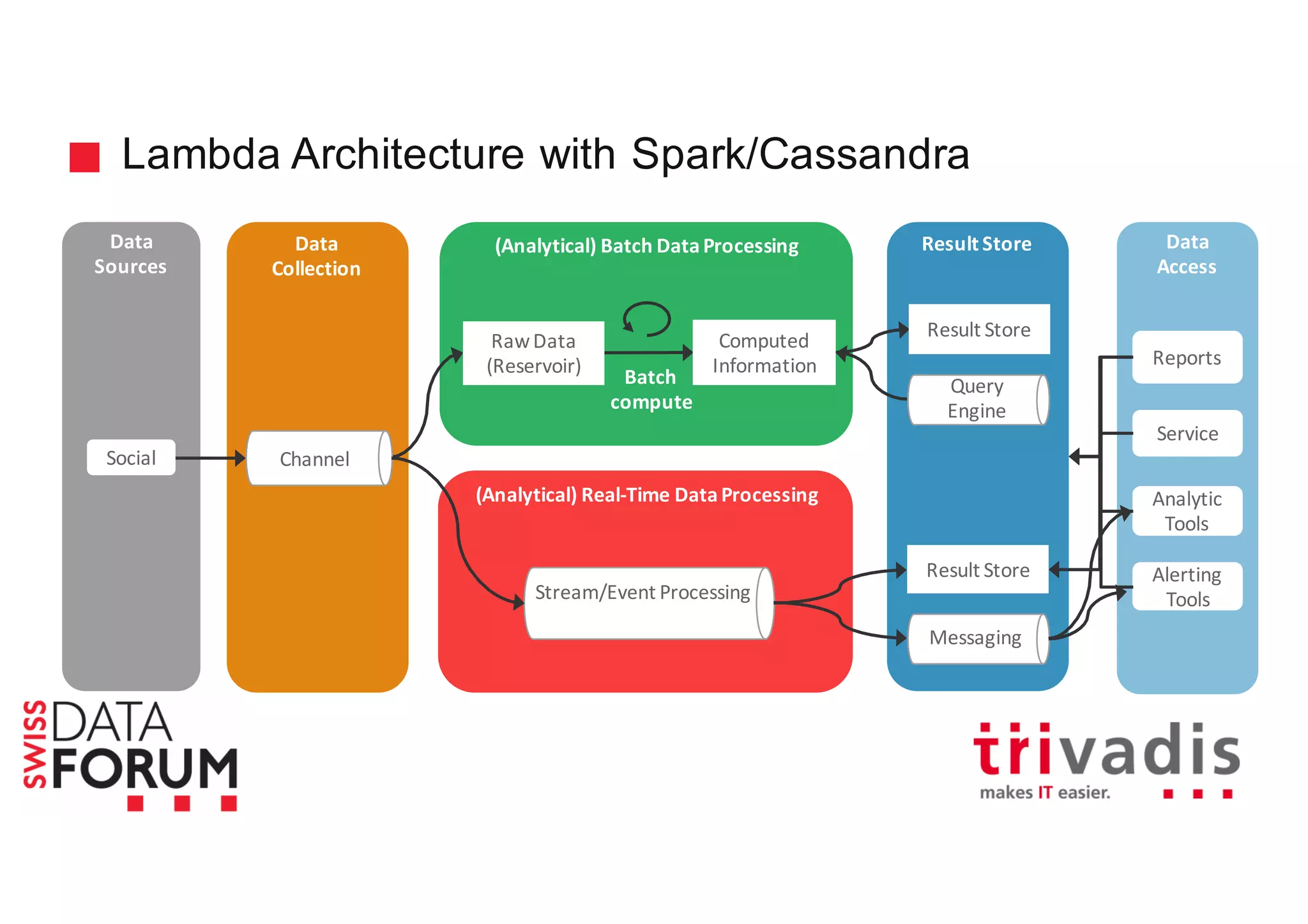
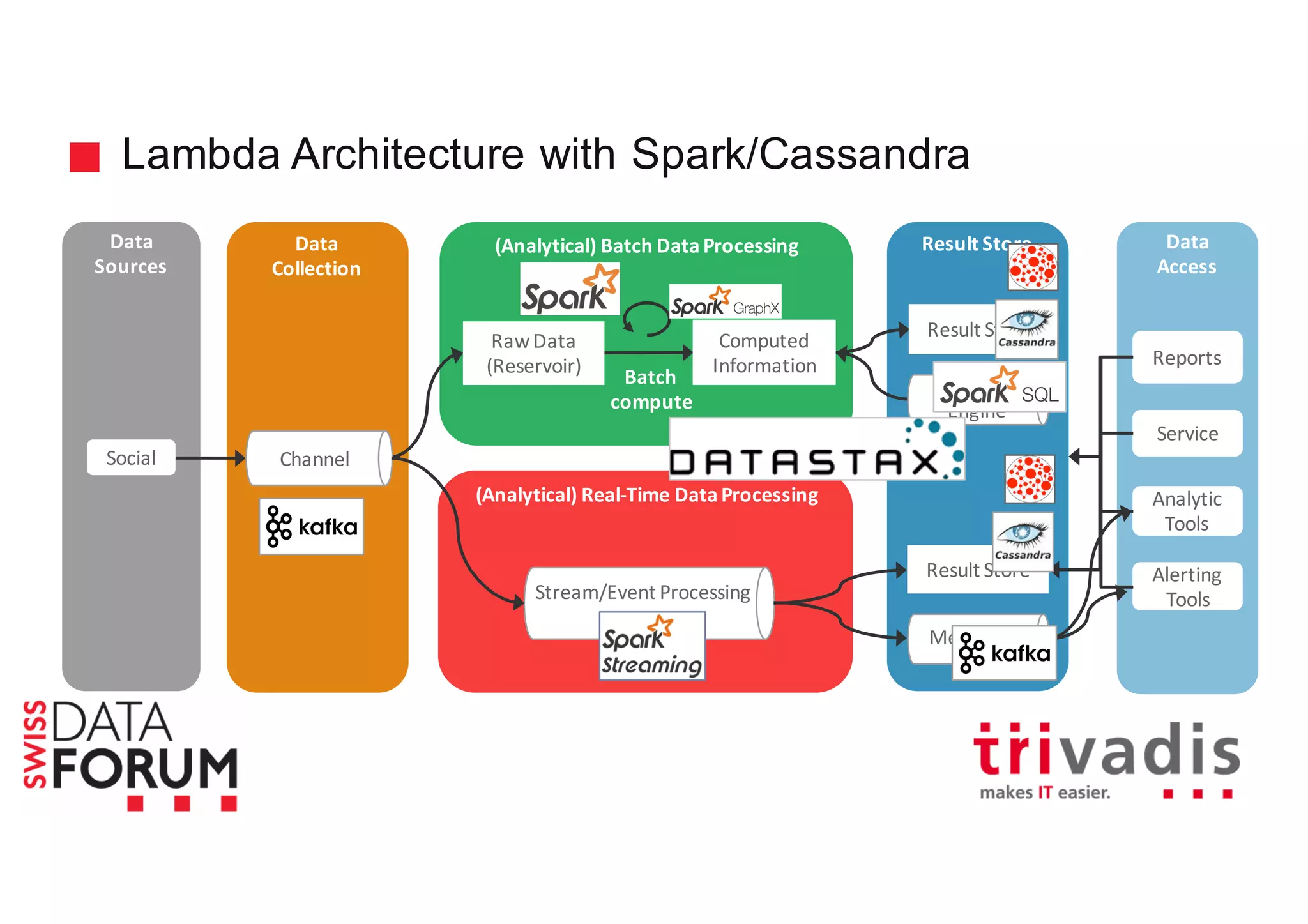
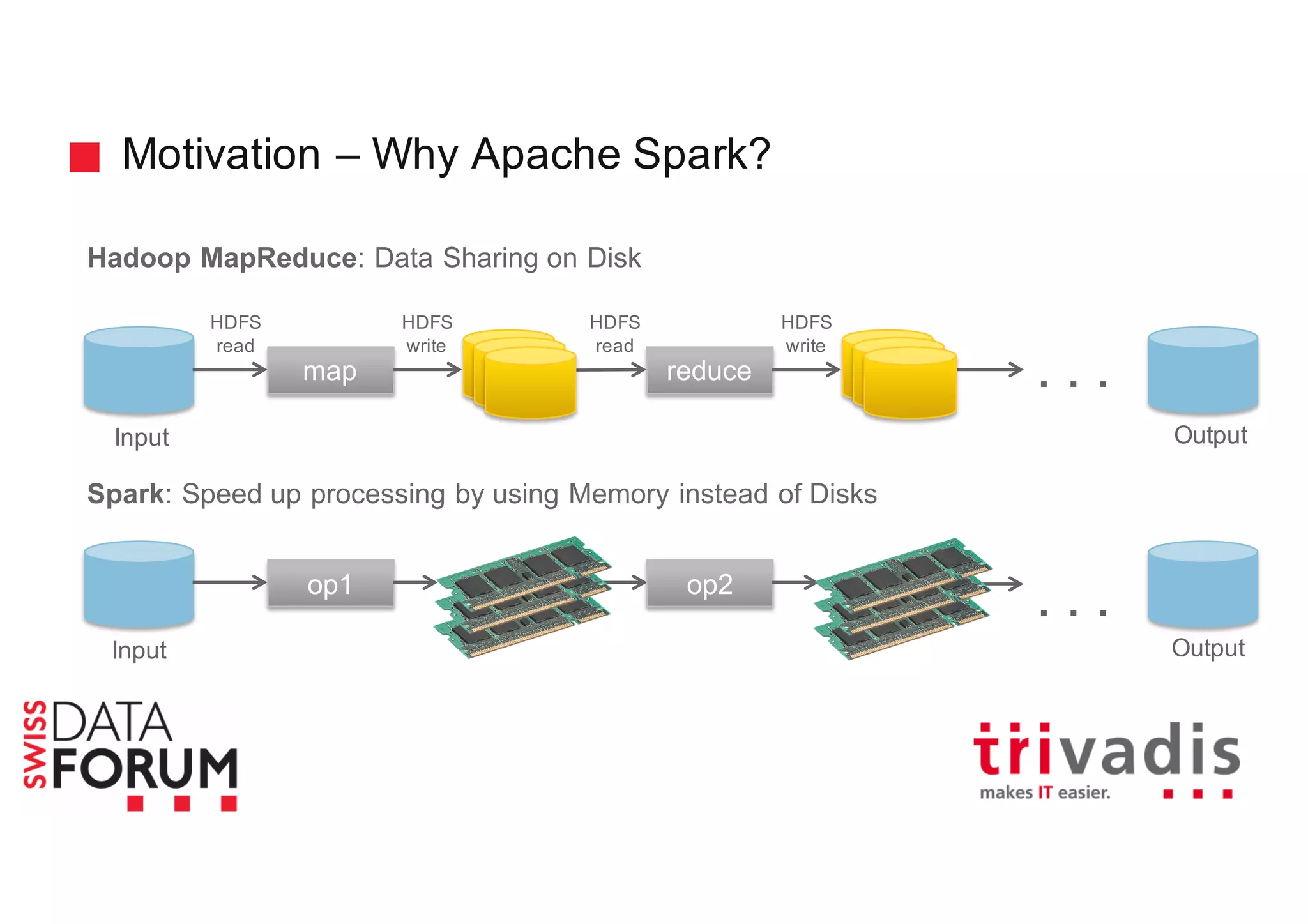
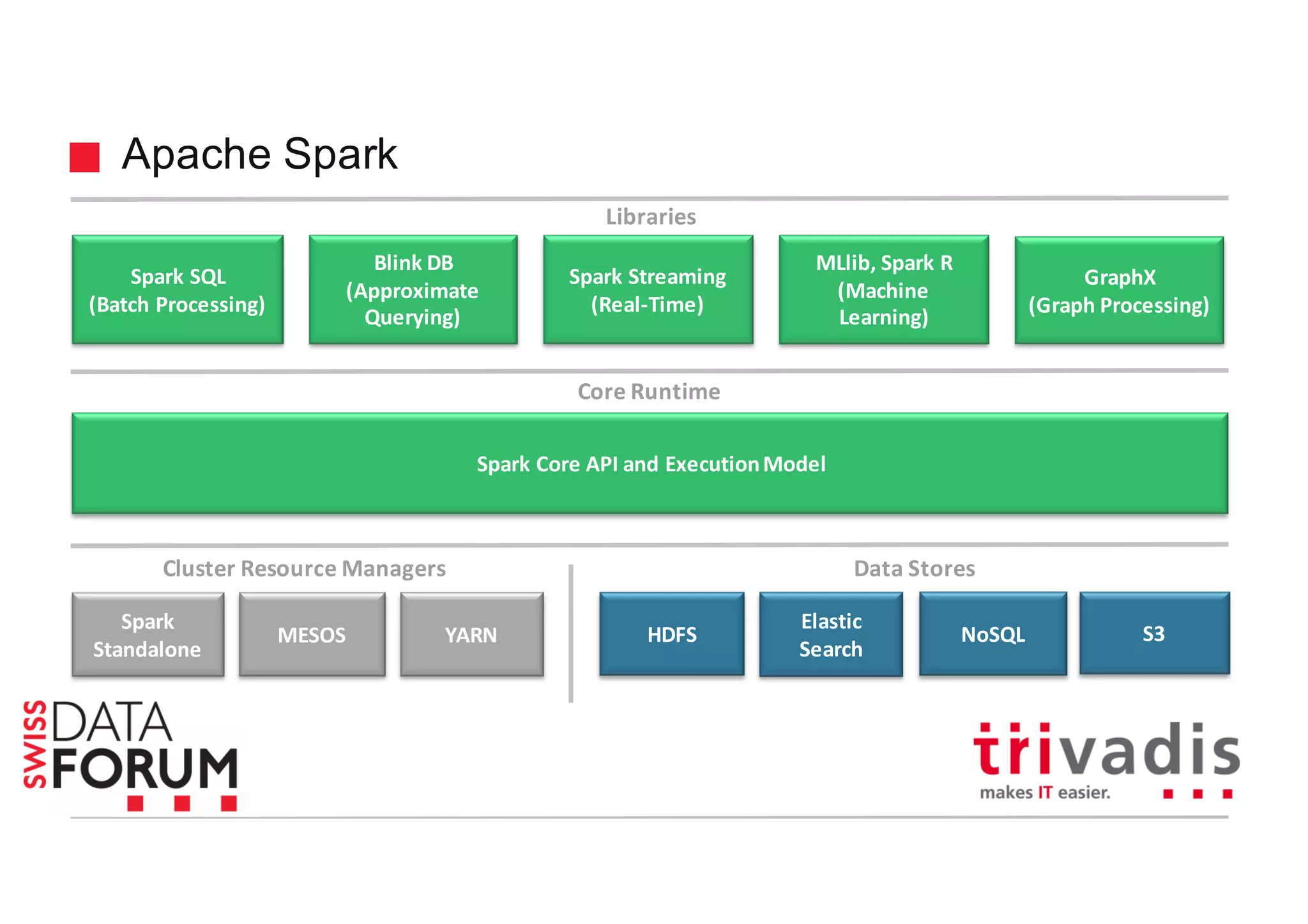
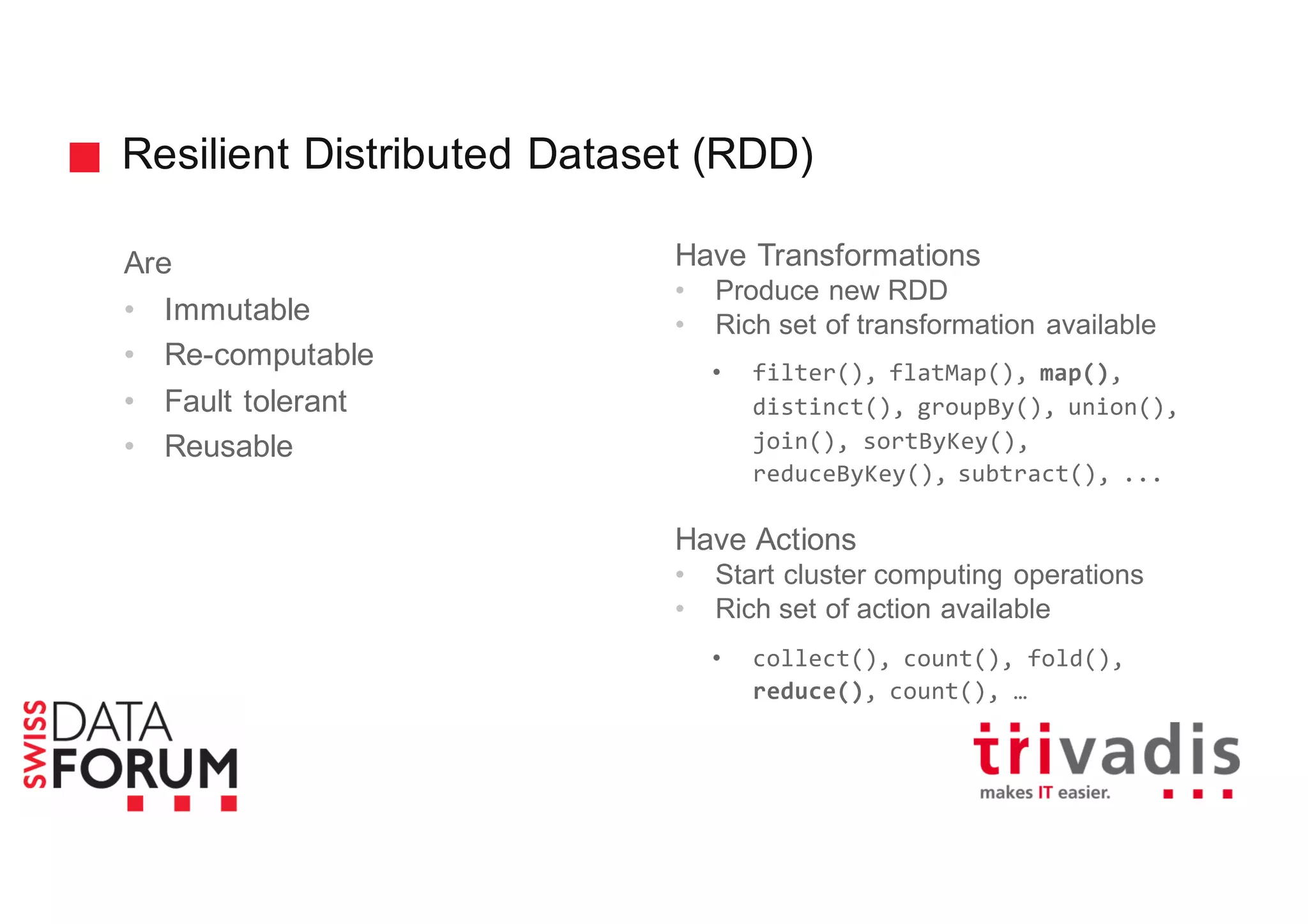
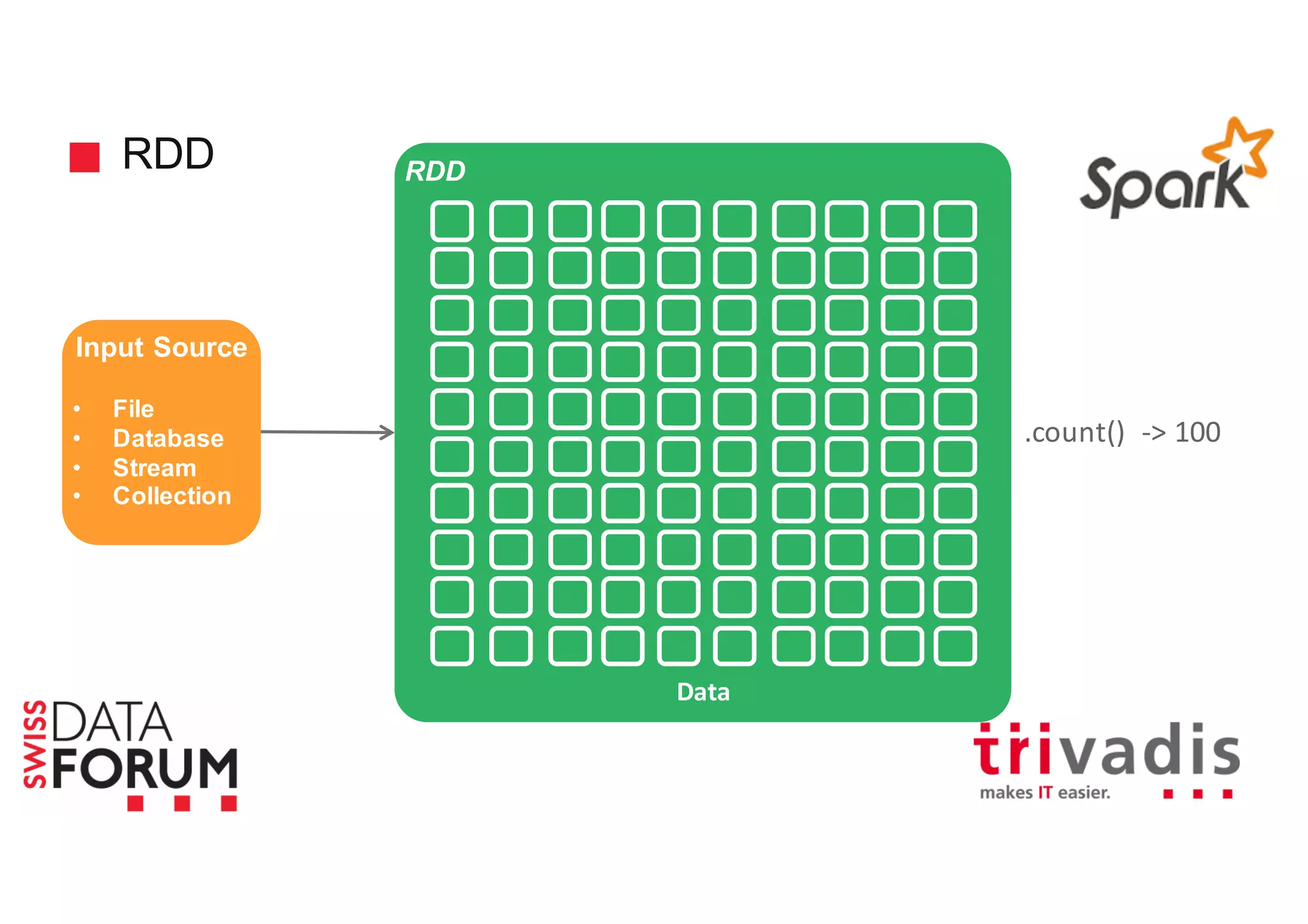
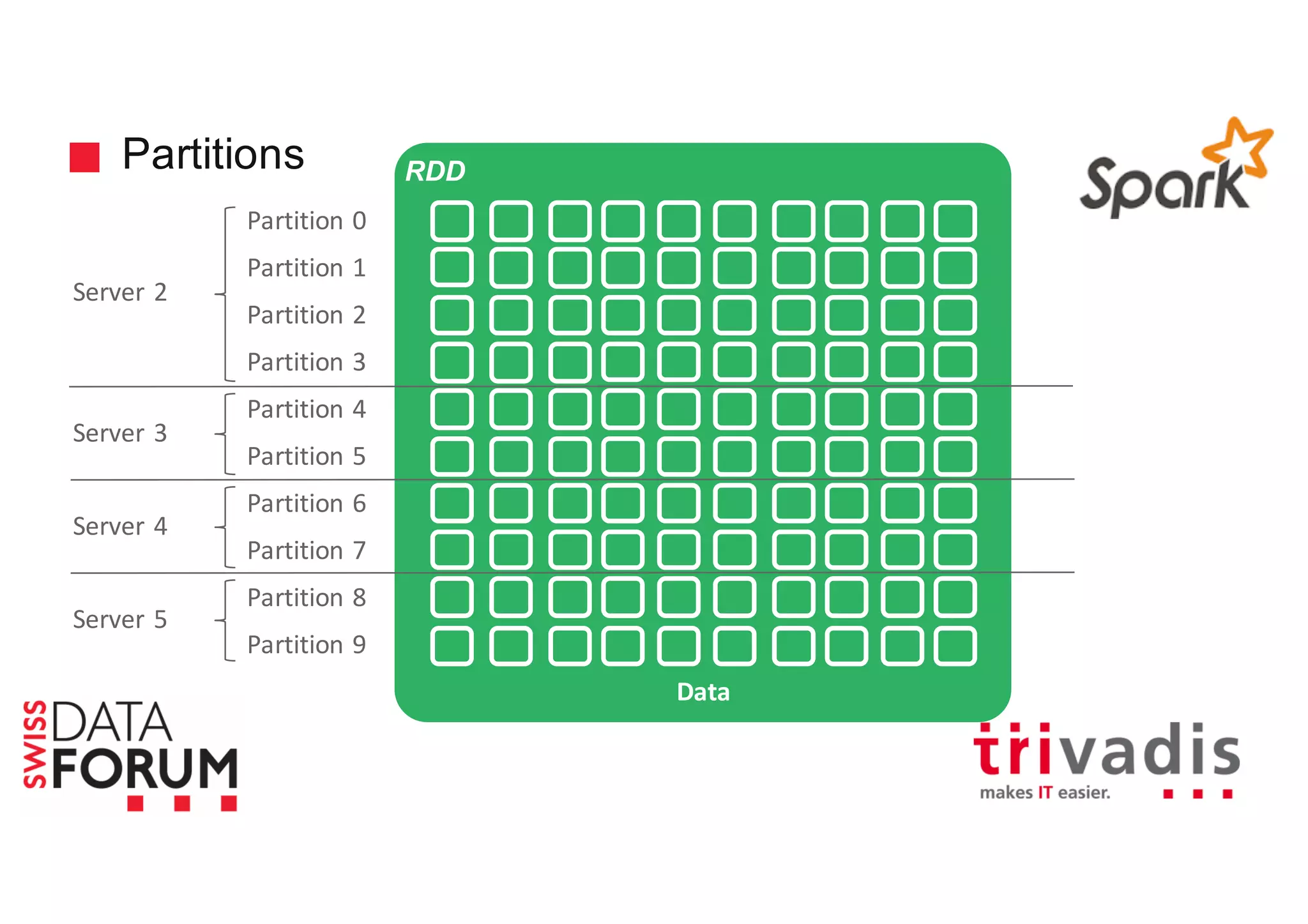
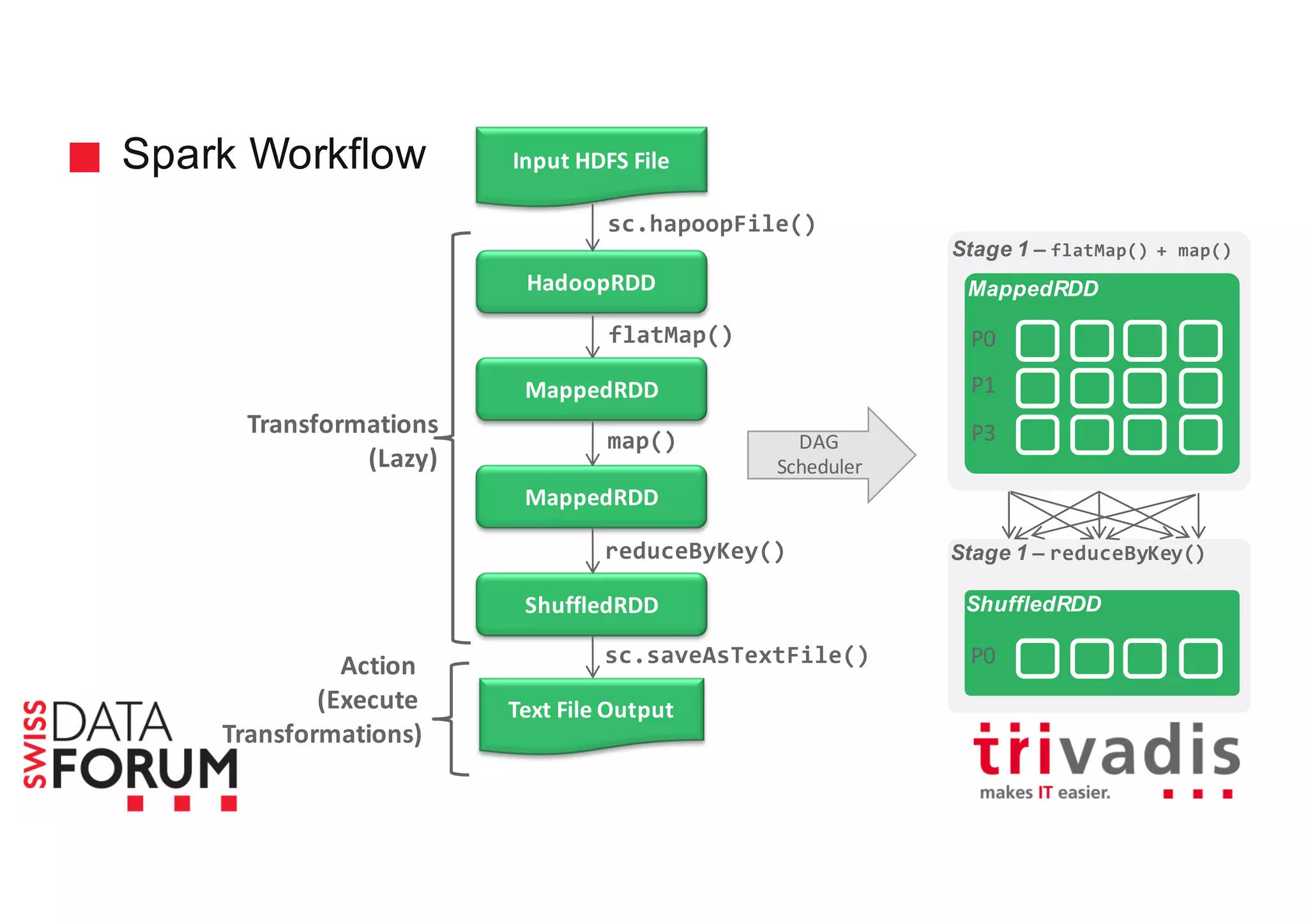
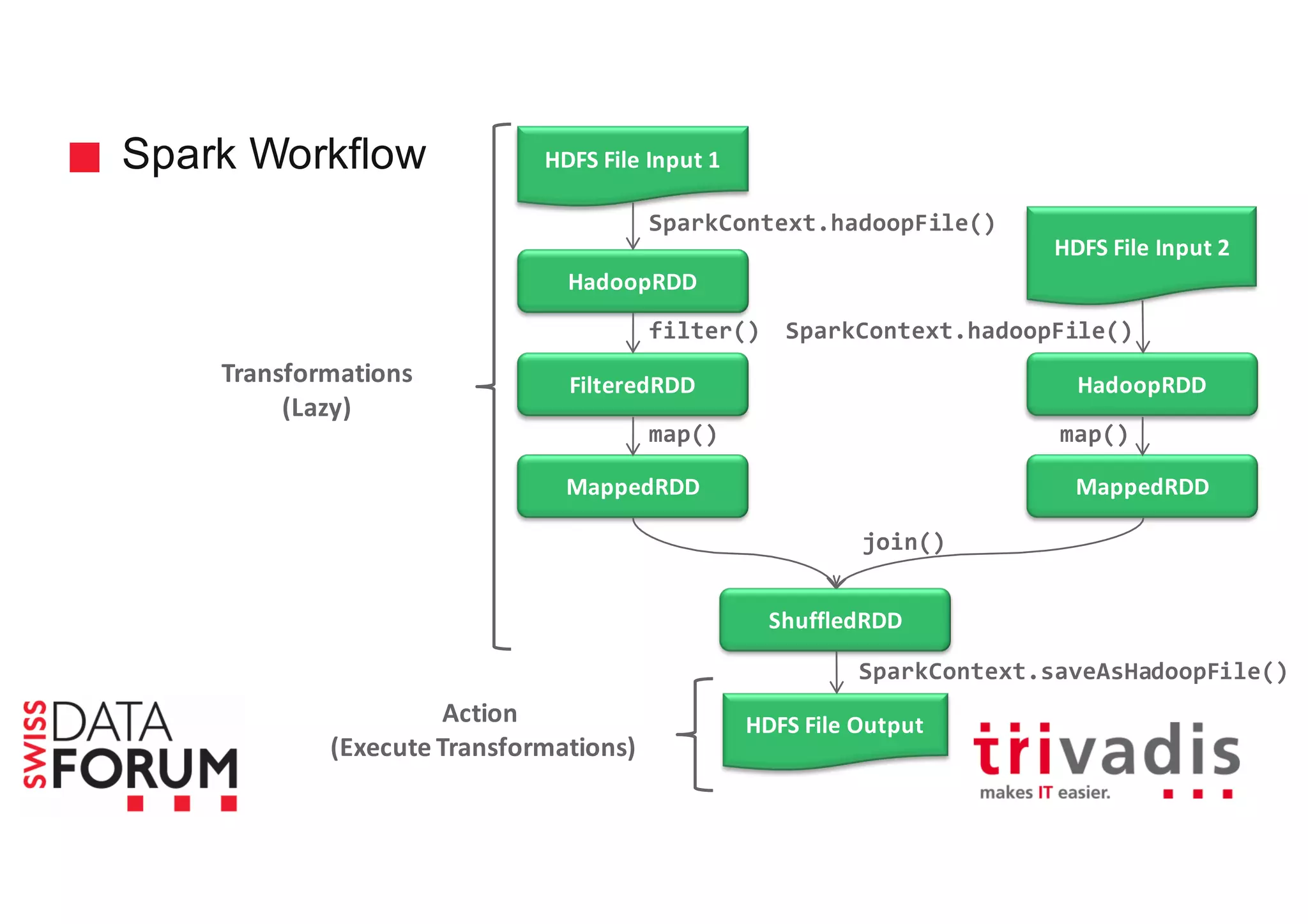
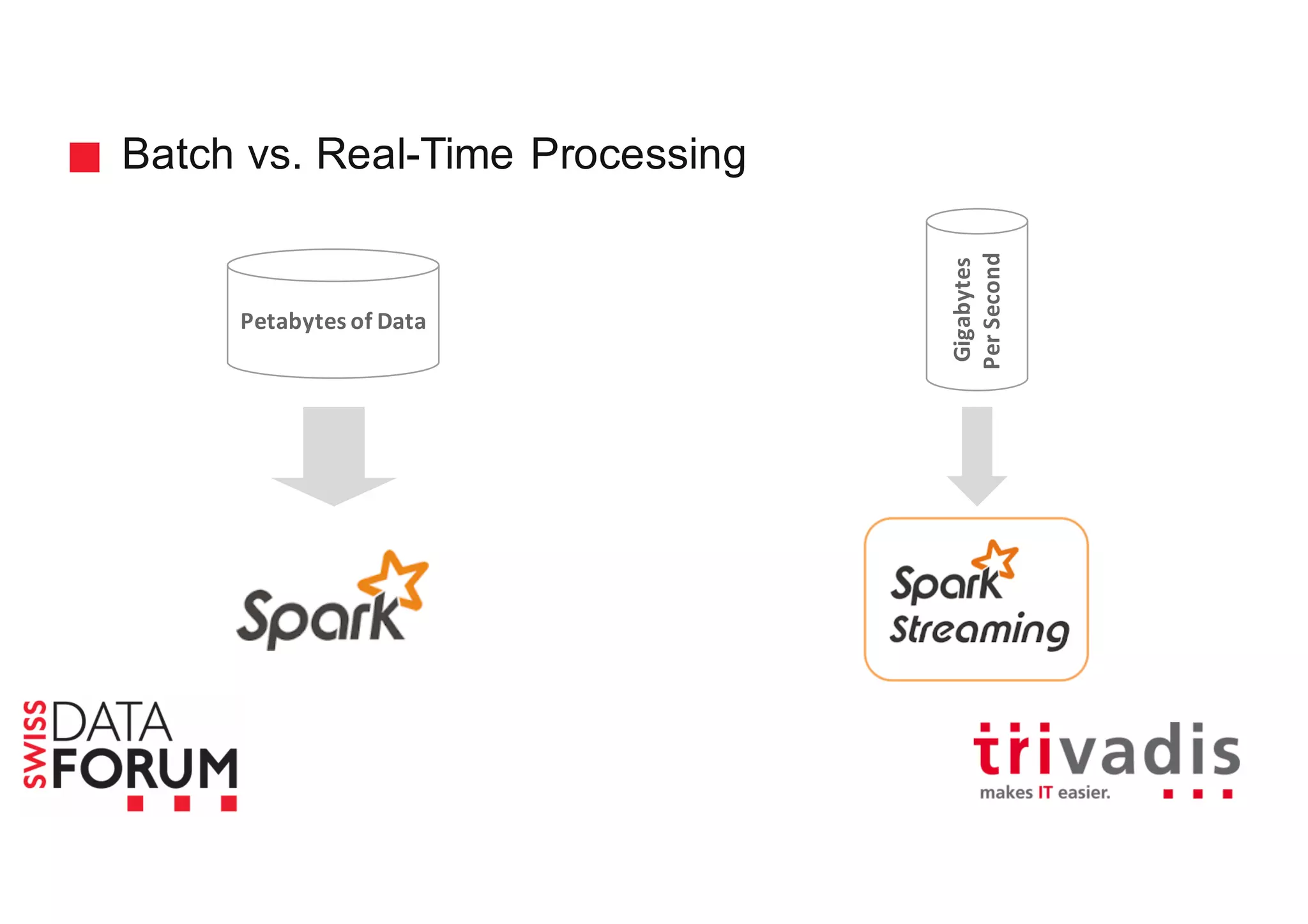
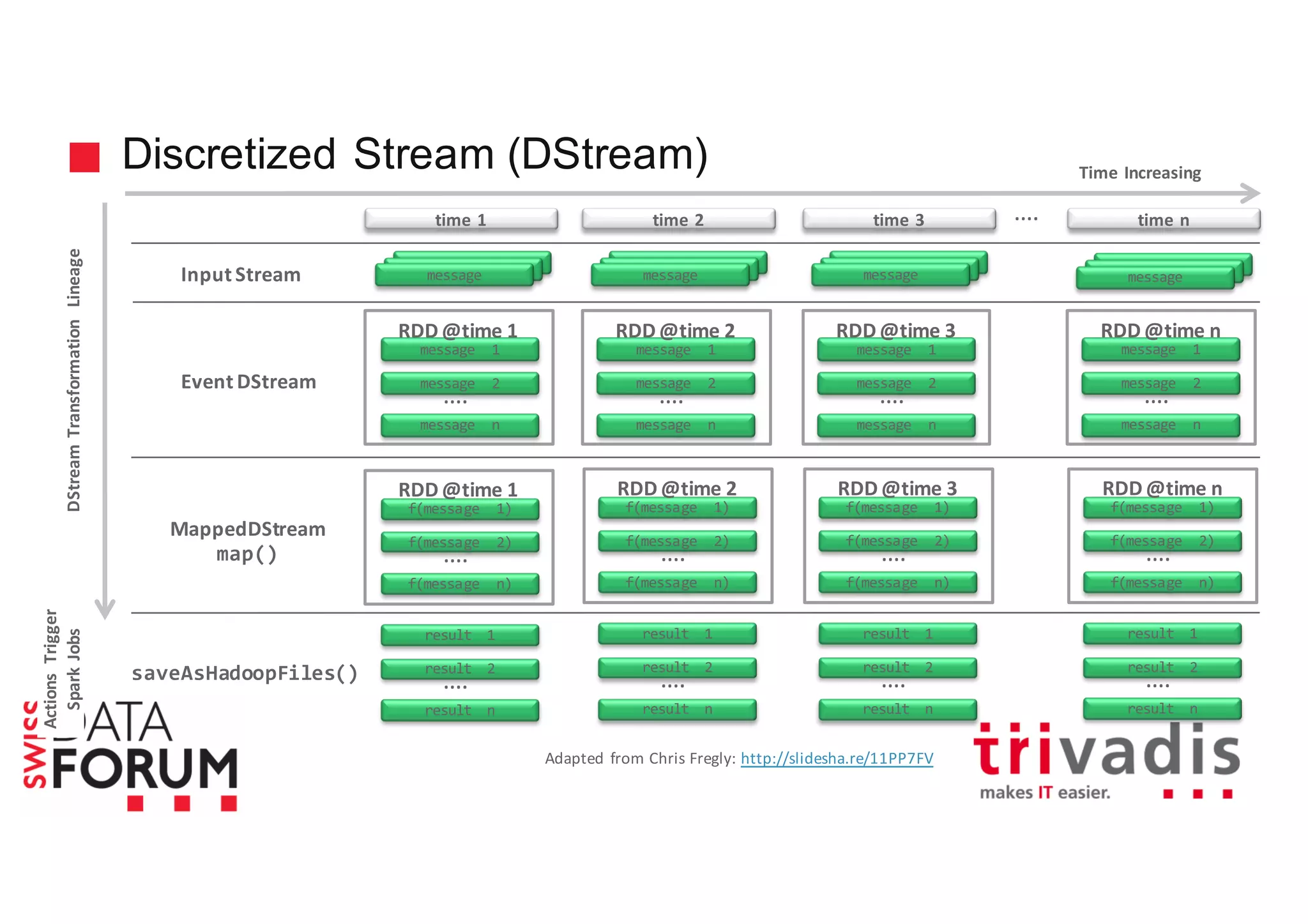
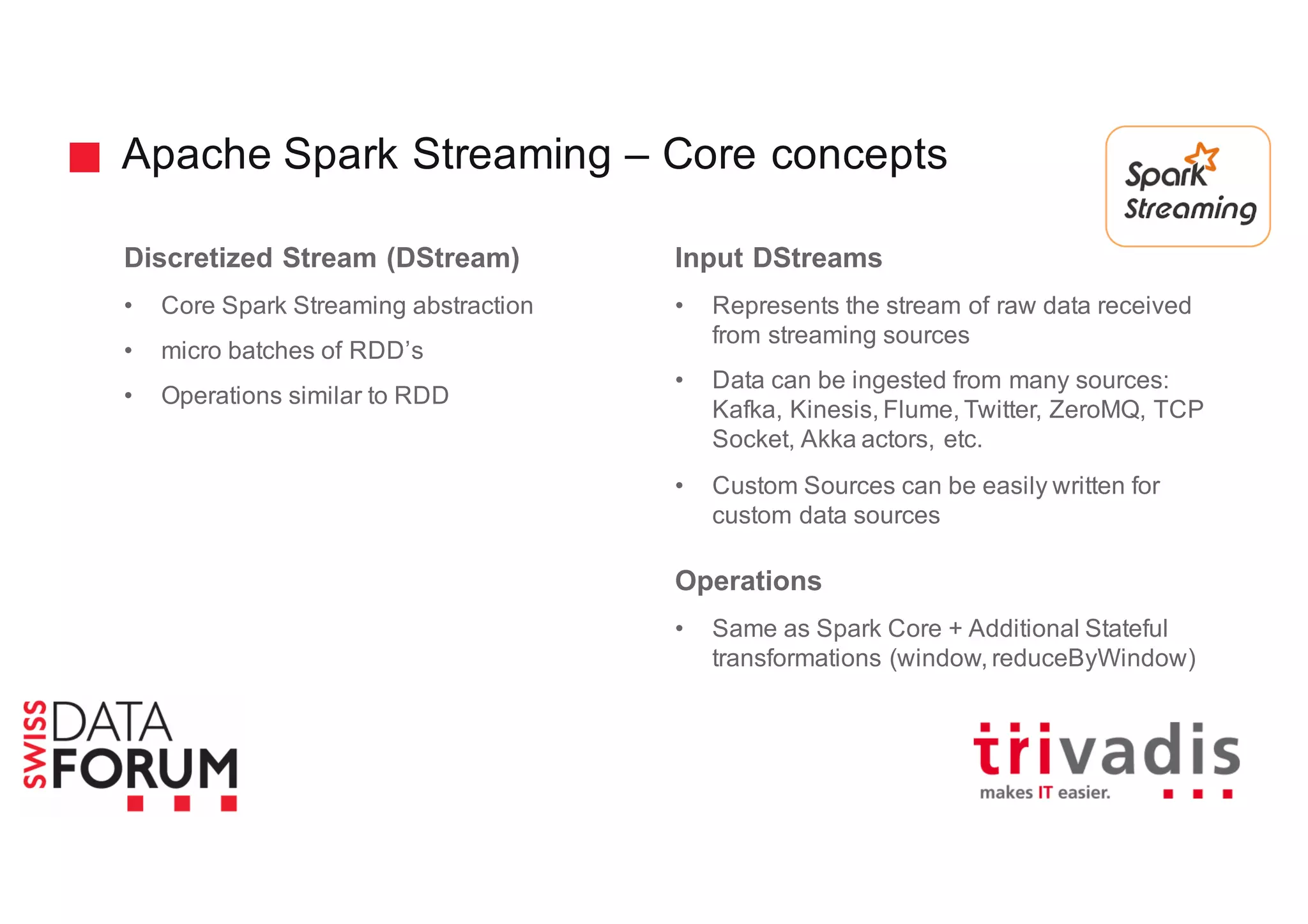
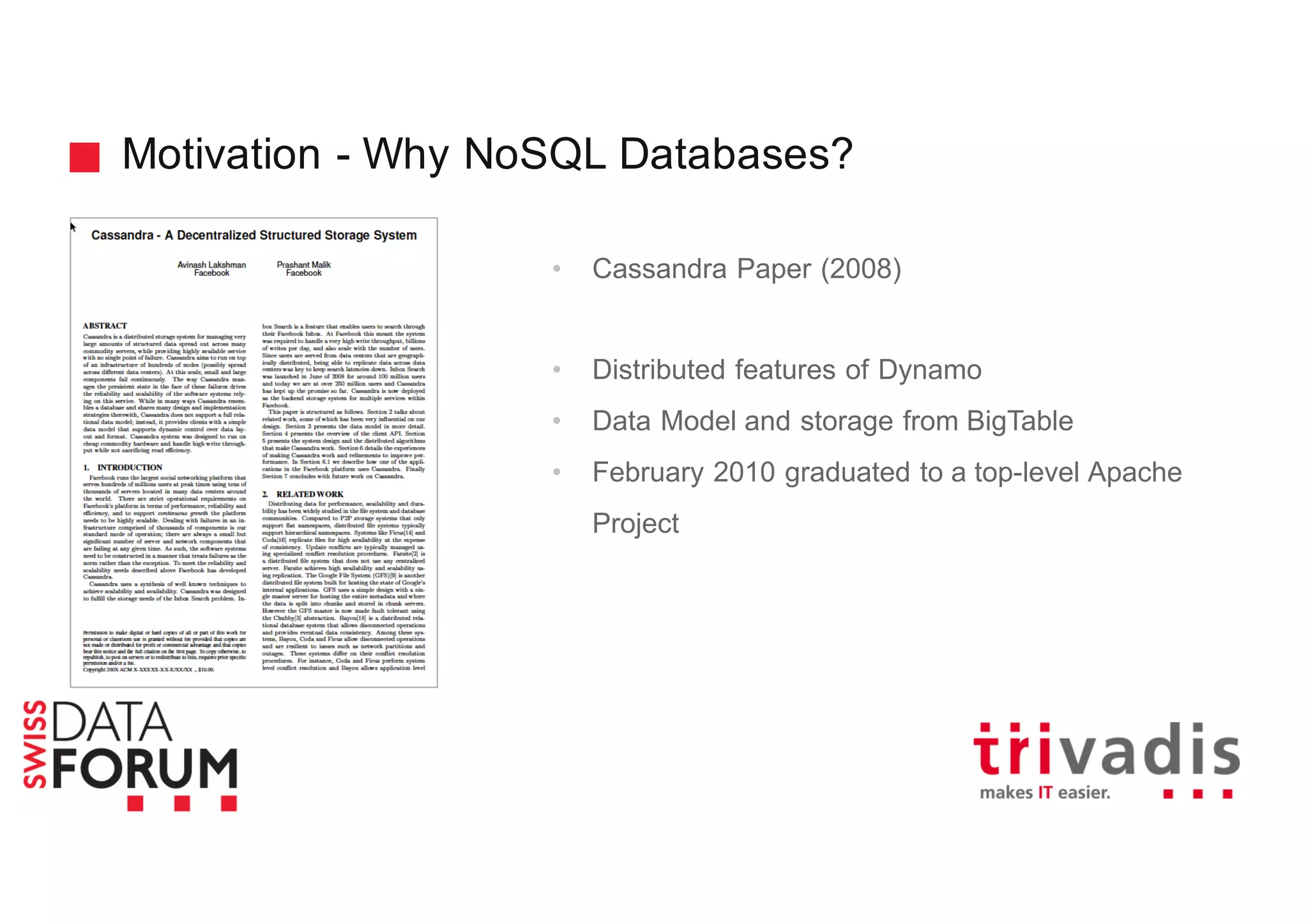
This document provides an overview of real-time analytics with Apache Cassandra and Apache Spark. It discusses how Spark can be used for stream processing over Cassandra for storage. Spark Streaming ingests real-time data from sources like Kafka and processes it using Spark transformations and actions. The processed data can be stored in Cassandra for querying. Cassandra is well suited for high write throughput and storing large amounts of data, while Spark enables fast in-memory processing and machine learning capabilities. Together, Spark and Cassandra provide a scalable solution for real-time analytics and querying of large datasets.



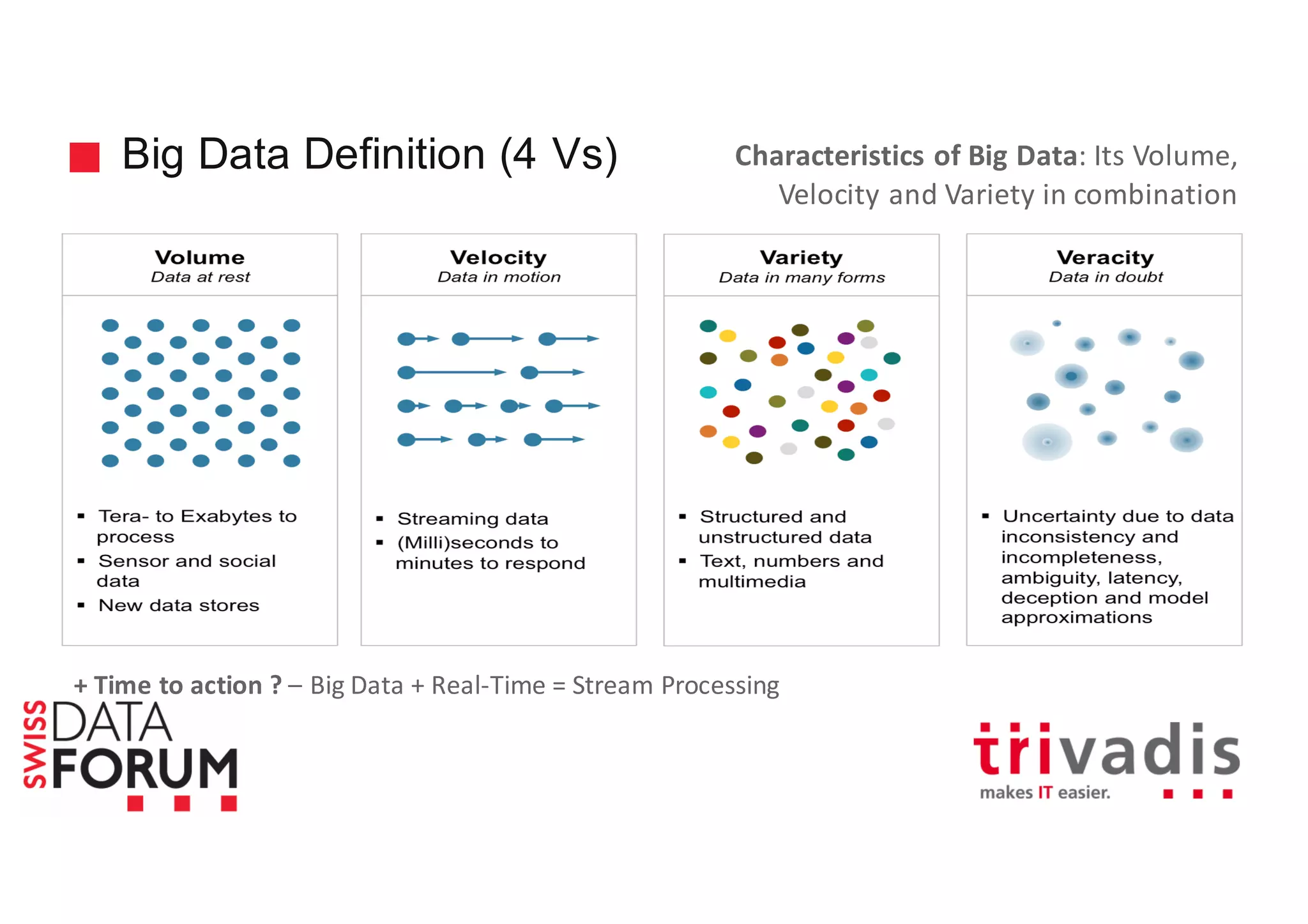
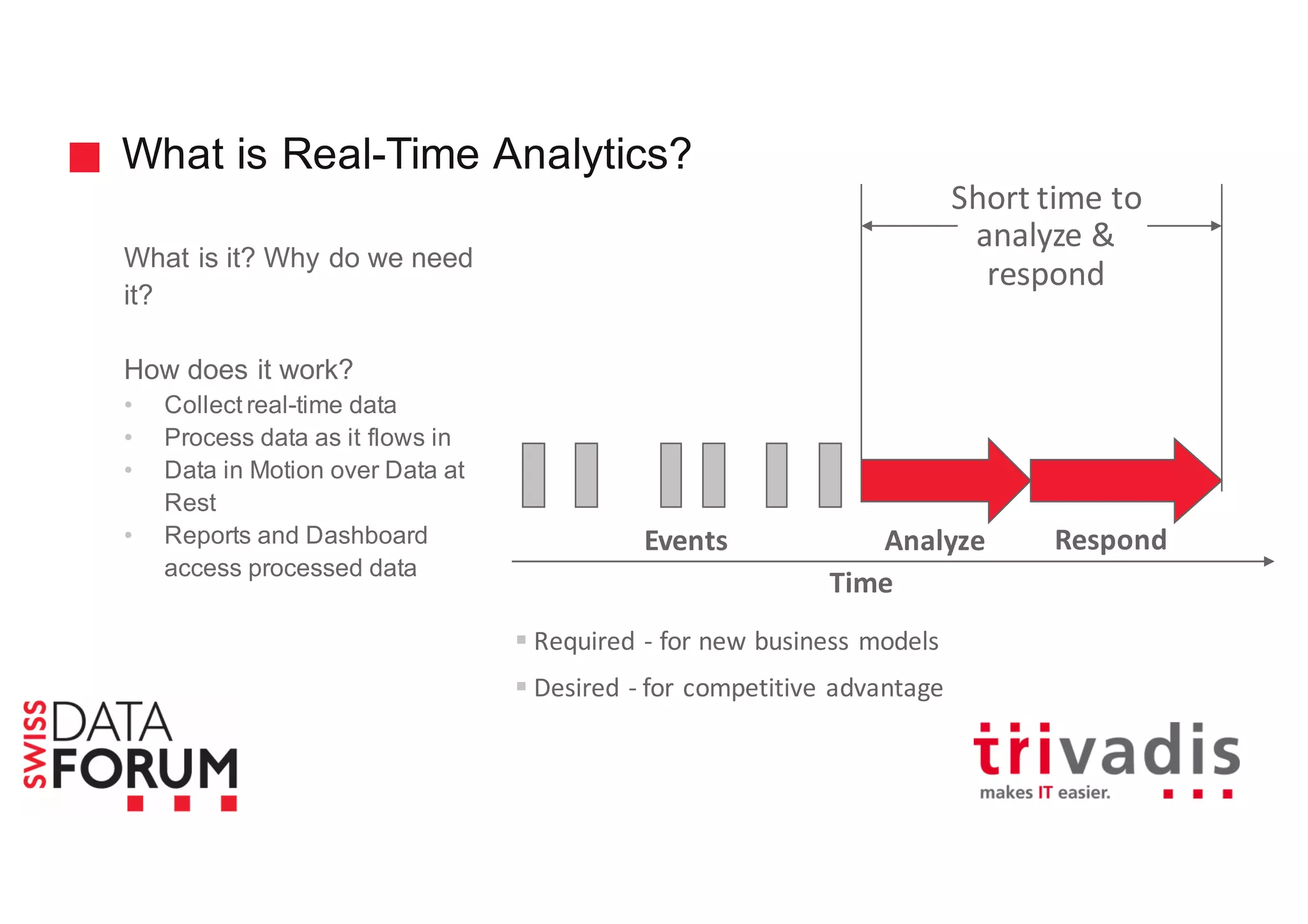






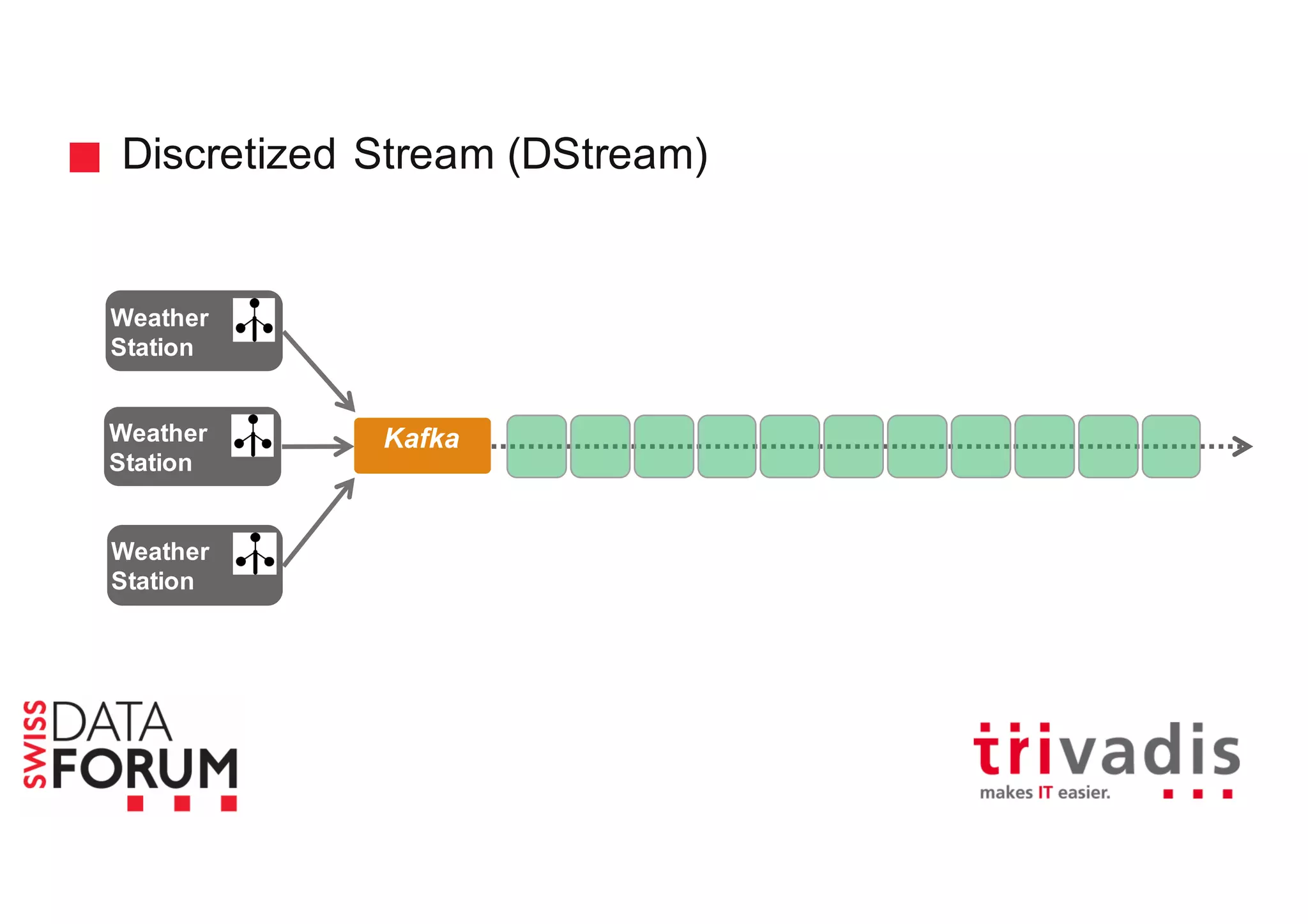
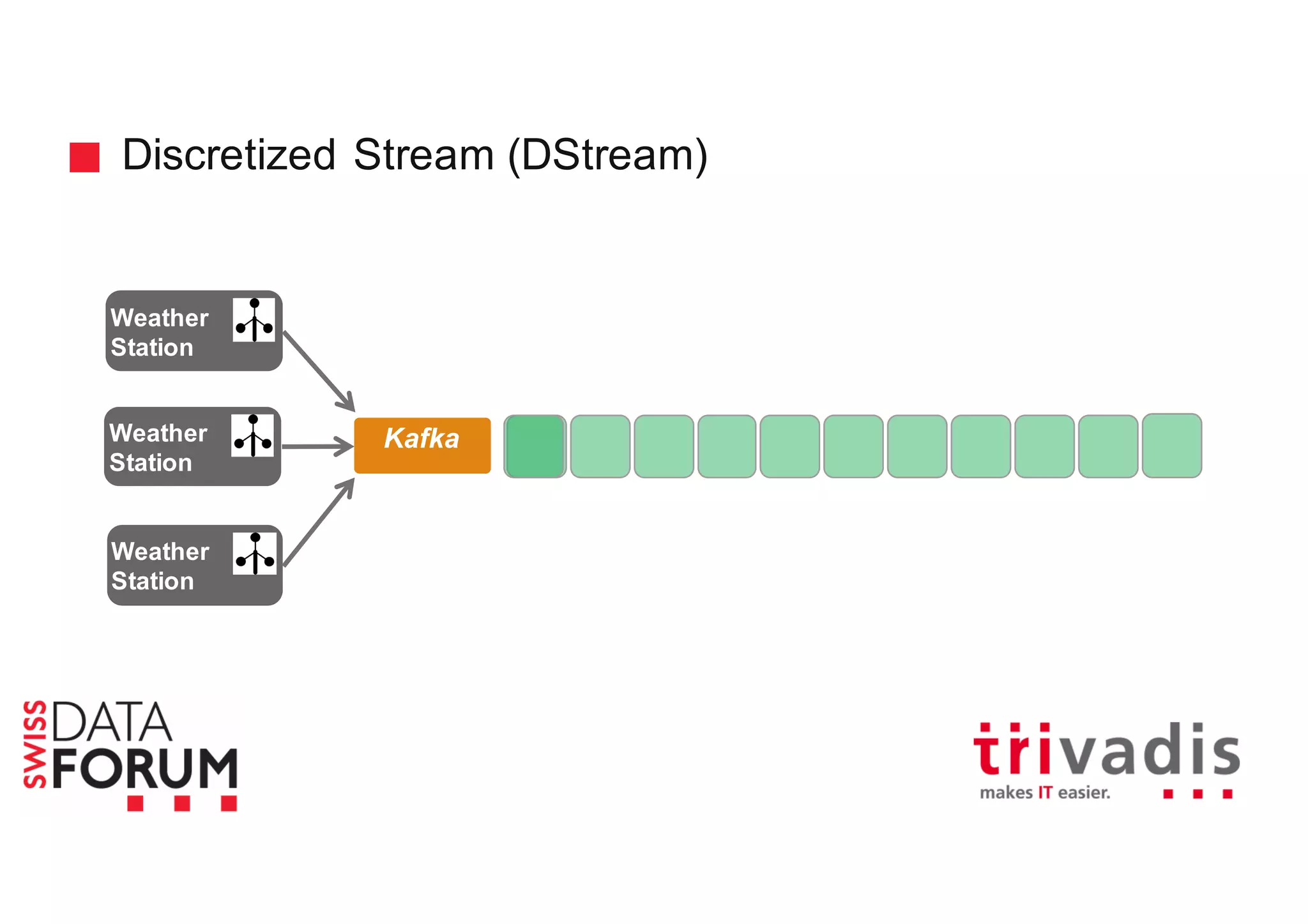
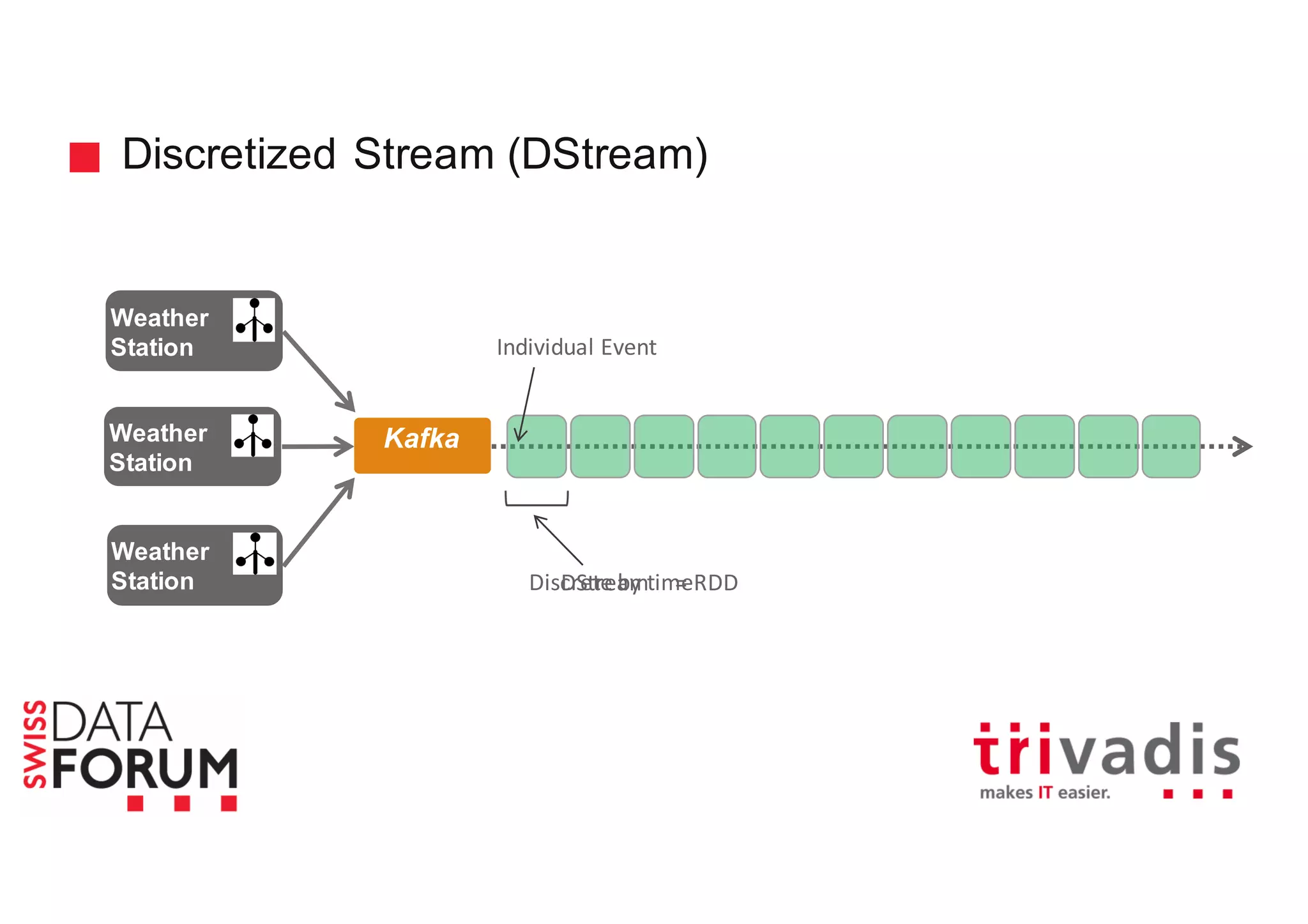
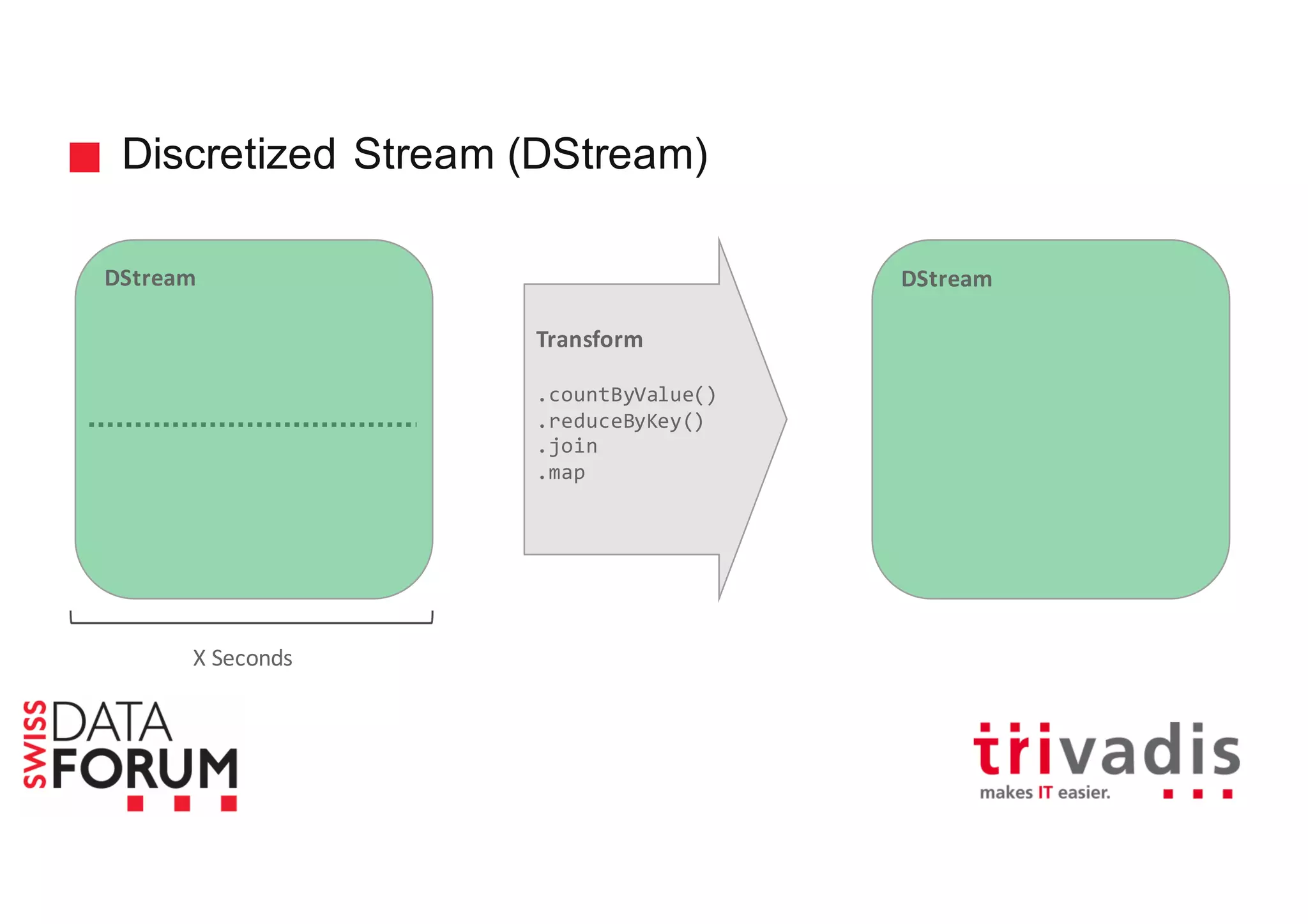





![Apache Cassandra – More than one server All nodes participate in a cluster Shared nothing Add or remove as needed More capacity? Add more servers Node is a basic unit inside a cluster Each node owns a range of partitions Consistent Hashing Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 Node 4 [26-50] [0-25] [51-75] [76-100] [0-25] [0-25] [26-50] [26-50] [51-75] [51-75] [76-100] [76-100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-time-analytics-with-spark-and-cassandra-v1-151125191956-lva1-app6892/75/Real-Time-Analytics-with-Apache-Cassandra-and-Apache-Spark-40-2048.jpg)