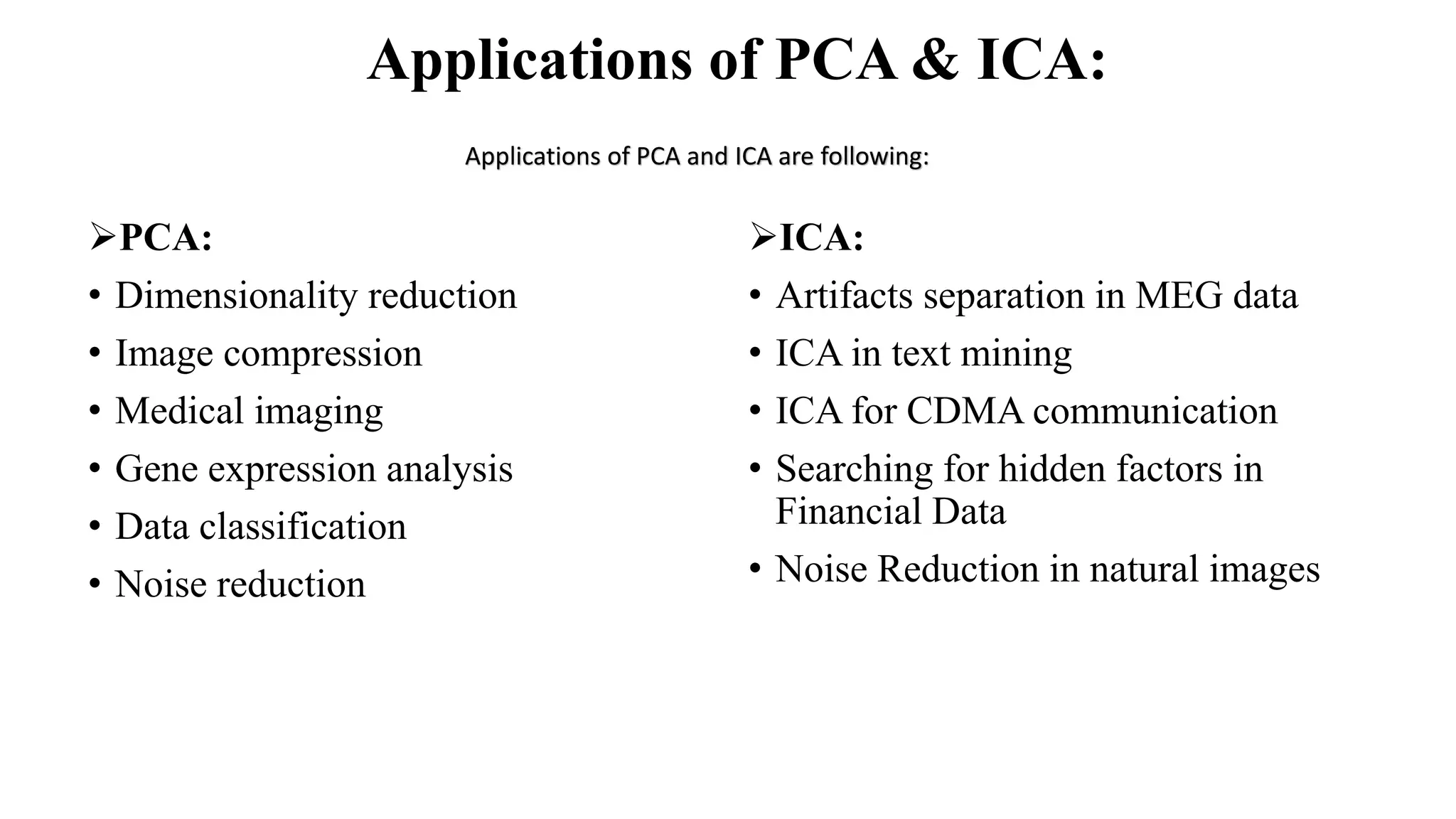
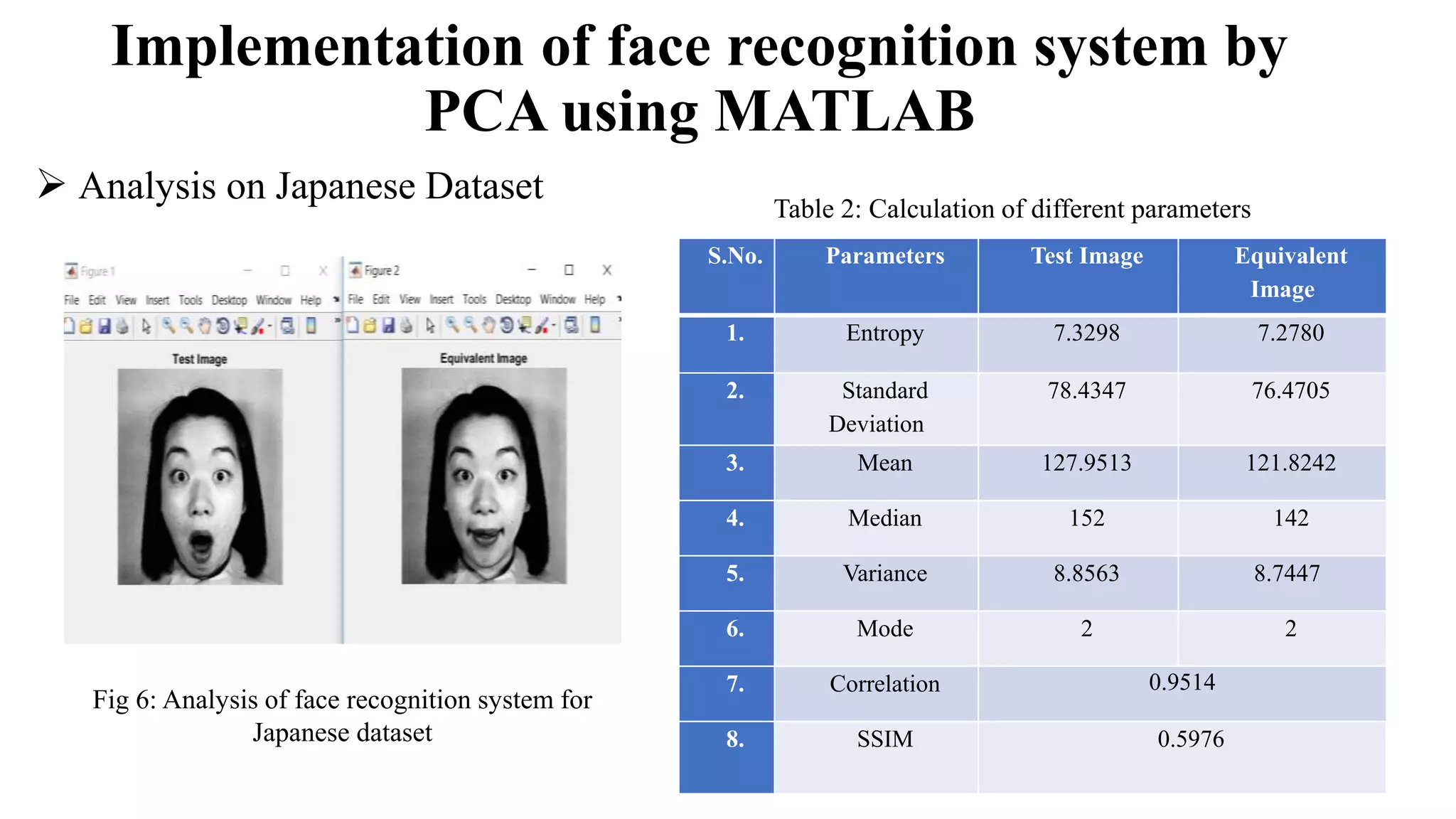
This document compares Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Independent Component Analysis (ICA) and their application to facial image analysis. It provides an introduction to both PCA and ICA, including their processes and differences. The document then summarizes previous literature comparing PCA and ICA, describes implementations of PCA for facial recognition on Japanese, African, and Asian datasets in MATLAB, and calculates statistical metrics for the original and recognized images. It concludes that PCA is effective for pattern recognition and dimensionality reduction in facial analysis applications.
![Introduction • The two most important techniques have been explored here as these approaches are very useful in many fields. One of the most interesting field, scilicet as face recognition has become a hot topic in computer vision algorithms. Similarly, dimensionality reduction, compression, signal separation, image filtering, and many other statistical approaches are becoming popular and of great use in many fields day by day. • In the computer vision, PCA is a popular method and applied mainly in face recognition whereas ICA was initially originated for distinct and the mixed audio signals into independent sources[10]. • The literature on the subject is conflicting. Some assert that PCA outperforms ICA others claim that ICA outperforms PCA and some claims that there is no difference in their performance statistically[8]. Thus, this paper compares the PCA technique to a newer technique ICA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-200229160317/75/Standard-Statistical-Feature-analysis-of-Image-Features-for-Facial-Images-using-Principal-Component-Analysis-and-its-Comparative-study-with-Independent-Component-Analysis-3-2048.jpg)

![Principal Component Analysis • The main idea of principal component analysis (PCA) is to reduce the dimensionality of a data set consisting of many variables correlated with each other. • The same is done by transforming the variables to a new set of variables, which are known as the principal components (or simply, the PCs)[2] and are orthogonal. • The principal components are the eigenvectors of a covariance matrix, and hence they are orthogonal. • The direction of the PCA space serves as the direction of the maximum variance of the given data points[9].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-200229160317/75/Standard-Statistical-Feature-analysis-of-Image-Features-for-Facial-Images-using-Principal-Component-Analysis-and-its-Comparative-study-with-Independent-Component-Analysis-5-2048.jpg)

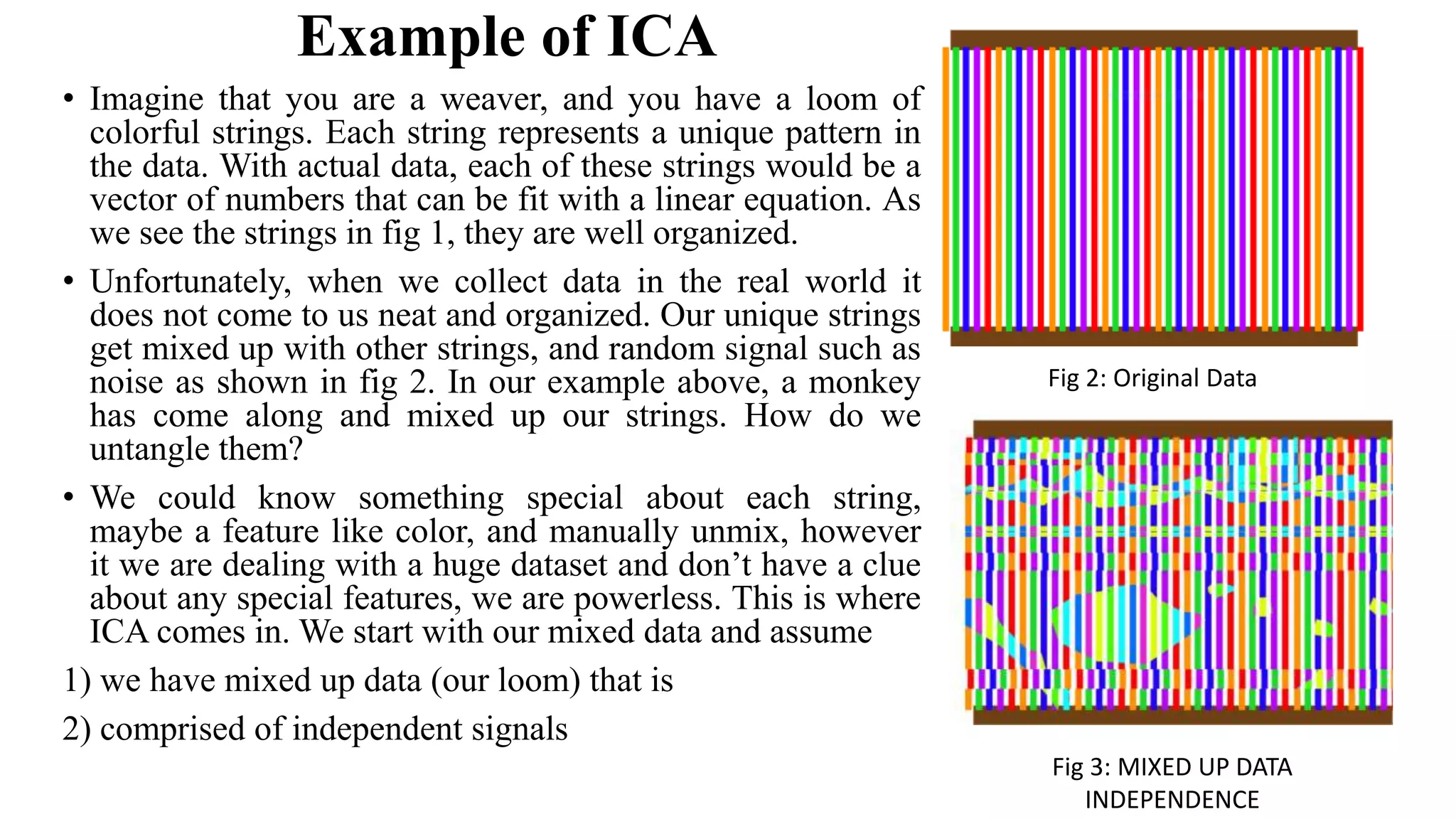
![Independent Component Analysis • In the method of ICA, not only statistical characteristics in second order or higher order are considered, but also basis vectors decomposed from face images obtained by ICA are more localized in distribution space than those by PCA[12]. • Localized characteristics are favorable for face recognition, because human faces are non-rigid bodies, and because localized characteristics are not easily influenced by face expression changes, location position, or partial occlusion [11]. • Independent Component Analysis is basically used to solve the Blind Source Seperation/ Cocktail Party Problem[8]. ICAAmbiguities: • The two most common ambiguities arise in ICA are that the method to calculate the variances of the independent components cannot be determined. Another problem is that the order of the independent components is also cannot be identifiable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-200229160317/75/Standard-Statistical-Feature-analysis-of-Image-Features-for-Facial-Images-using-Principal-Component-Analysis-and-its-Comparative-study-with-Independent-Component-Analysis-7-2048.jpg)

![Comparison between PCA & ICA S.No. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Independent Component Analysis (ICA) 1. In the image database, PCA relies only on pairwise relationships between pixels. Detecting the component from a multivariate data is done by ICA. 2. PCA takes details of statistical changes from second order statistics. It can have details up to higher order statistics. 3. With the help of PCA, higher order relations cannot be removed but it is useful for removing correlations. ICA, on the other hand removes both correlations as well as higher order dependence. 4. It works with the Gaussian model. ICA works with the non-Gaussian model. 5. Based on their eigenvalues some of the components in PCA are given more importance with respect to others. In ICA, all of the components are of equal importance. 6. It prefers orthogonal vectors. Non-orthogonal vectors are used. 7. PCA performance is based on the task statement, the subspace distance metric, and the number of subspace dimensions retained. The performance of ICA depends on the task, the algorithm used to approximate ICA, and the number of subspace dimensions retained. 8. For compression purpose, PCA uses low-rank matrix It uses full rank matrix factorization to eliminate Table 1: Comparison between PCA & ICA[7][12] :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-200229160317/75/Standard-Statistical-Feature-analysis-of-Image-Features-for-Facial-Images-using-Principal-Component-Analysis-and-its-Comparative-study-with-Independent-Component-Analysis-10-2048.jpg)