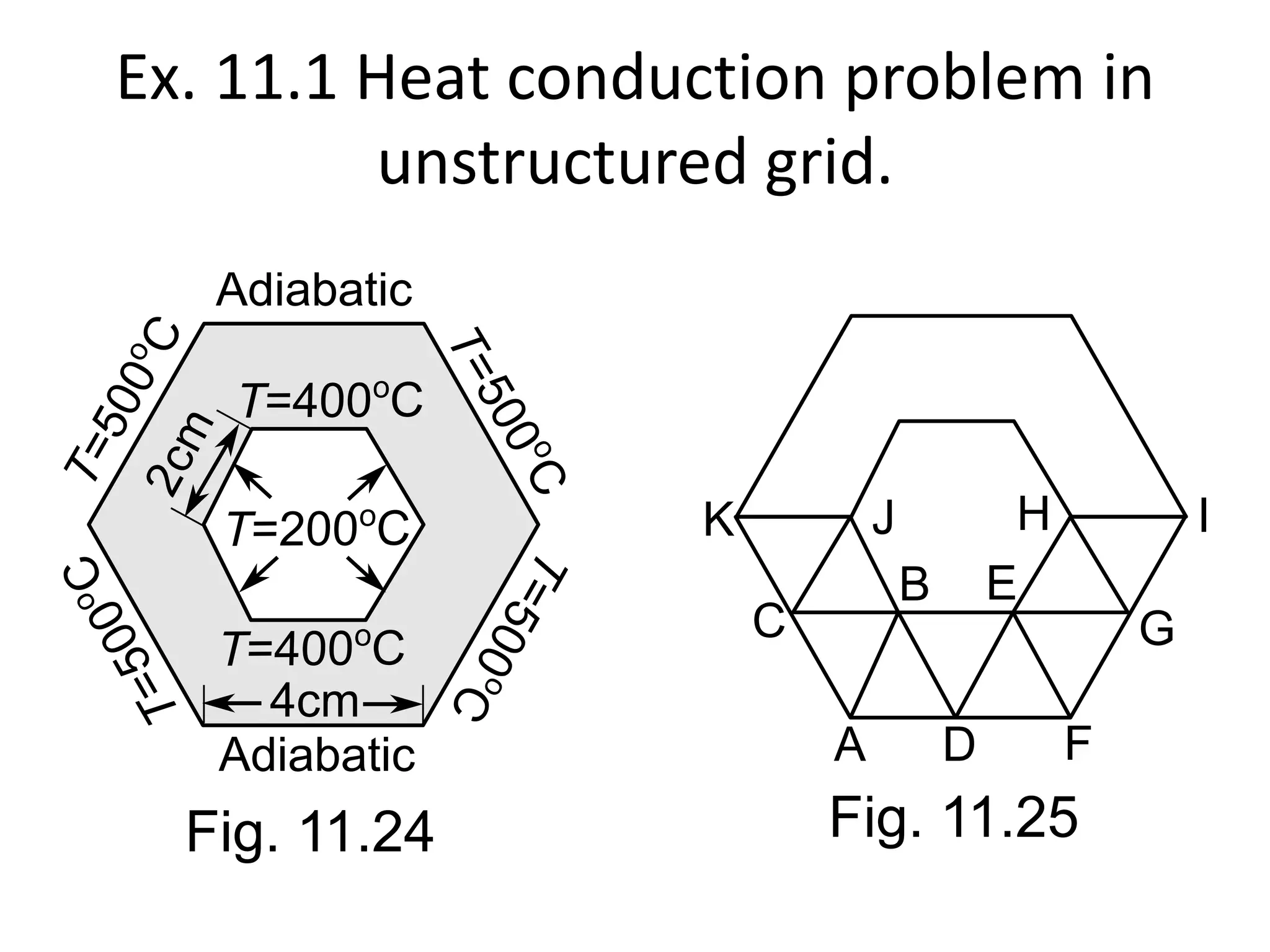
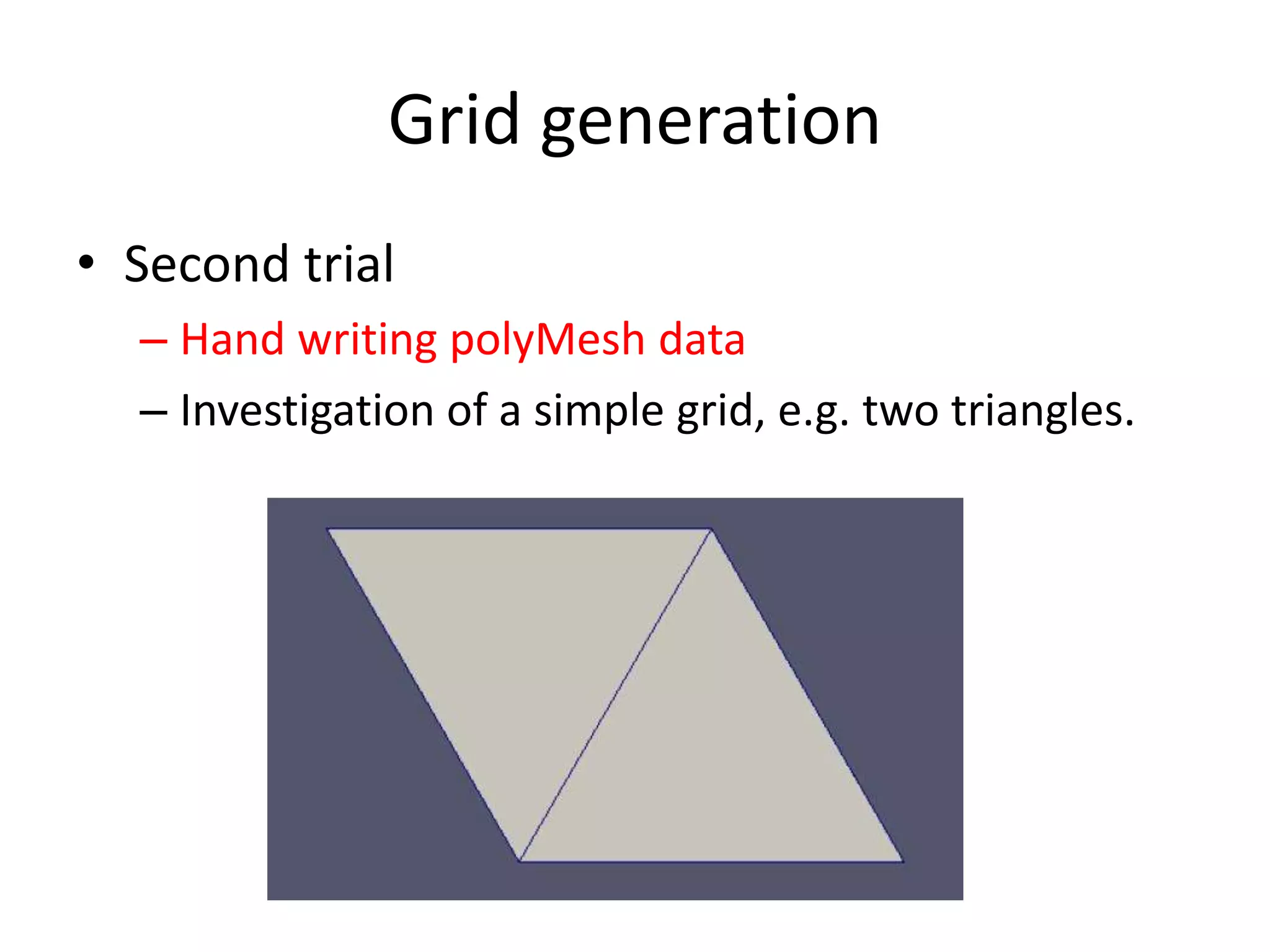
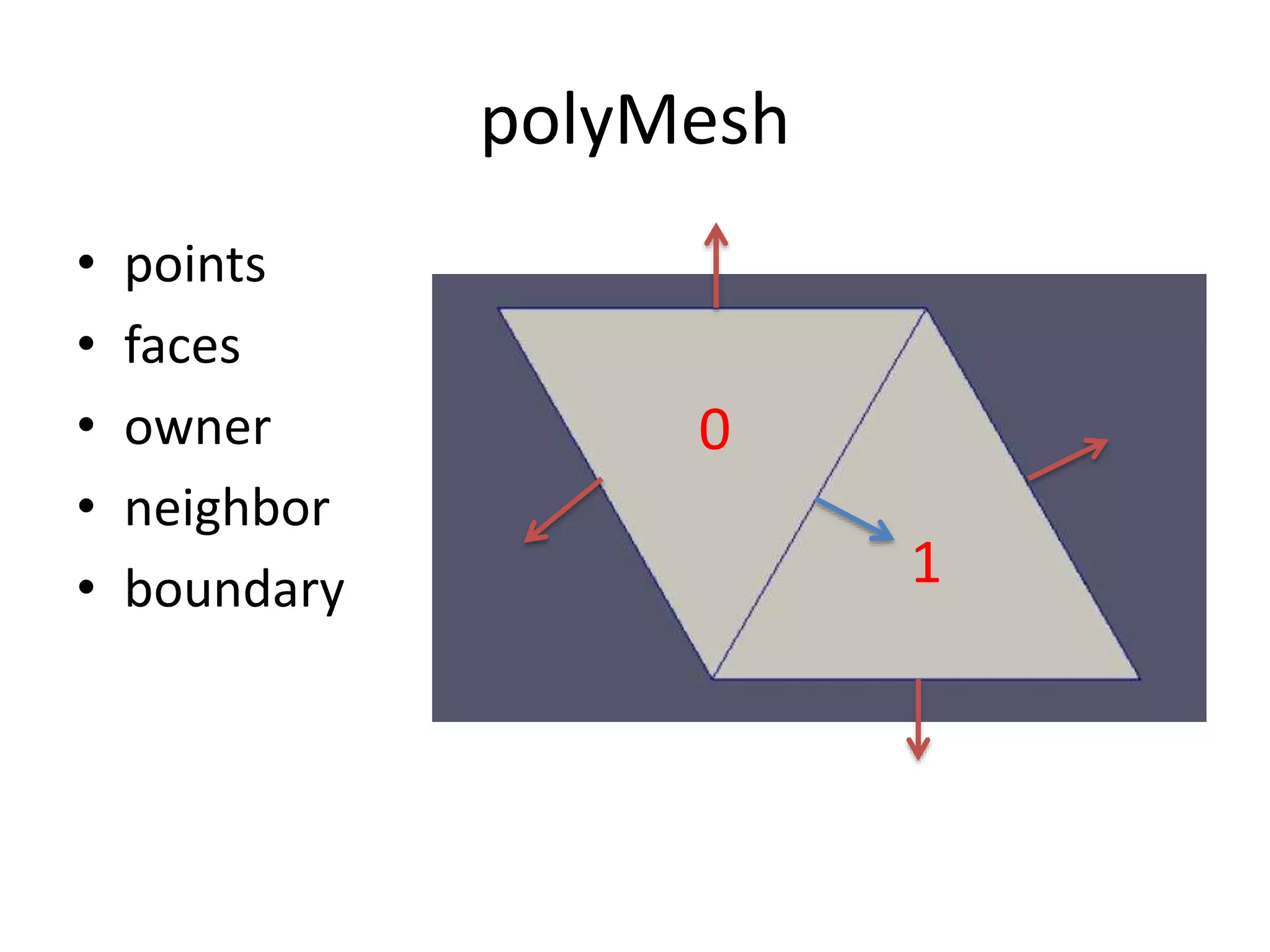
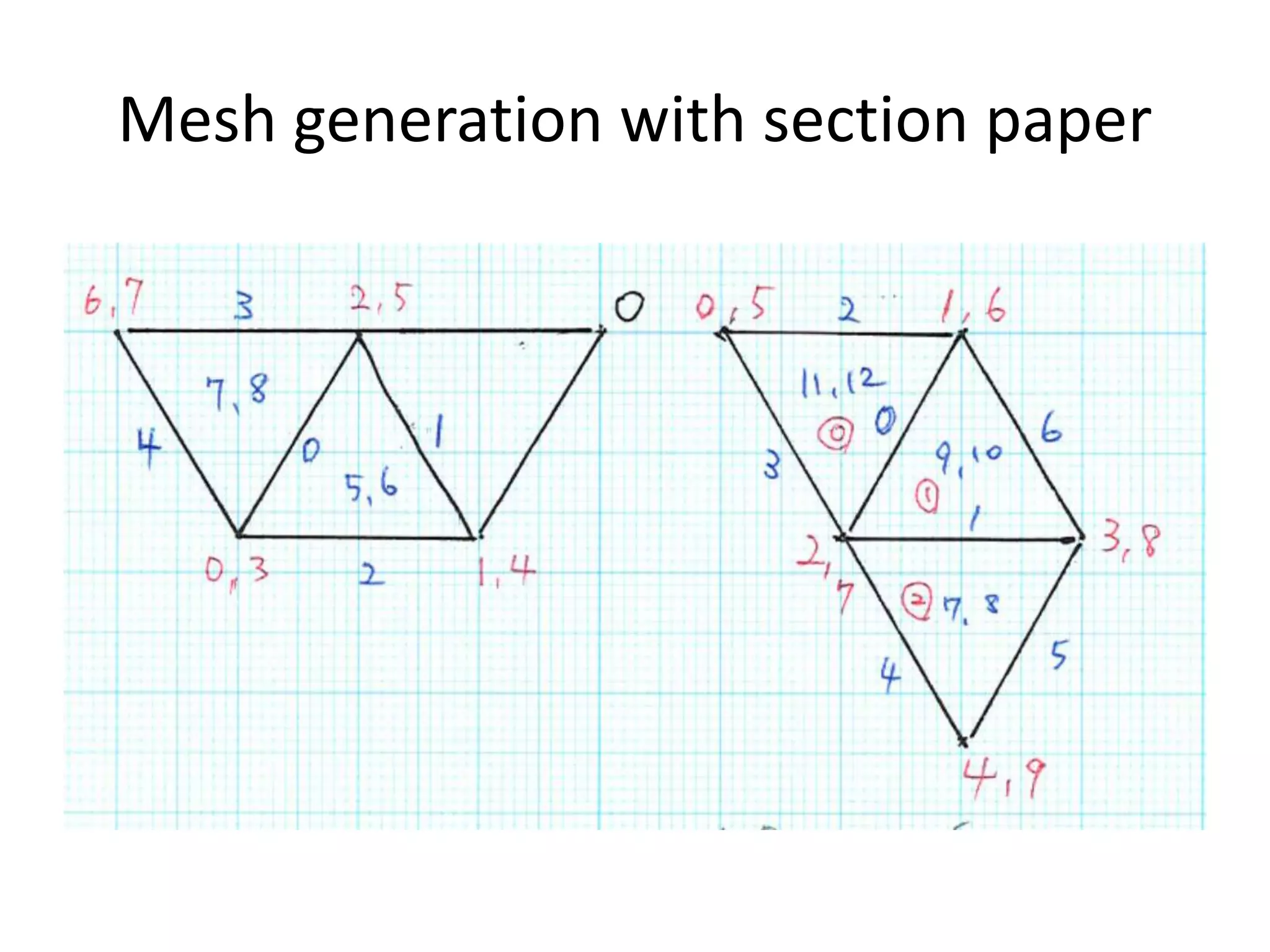
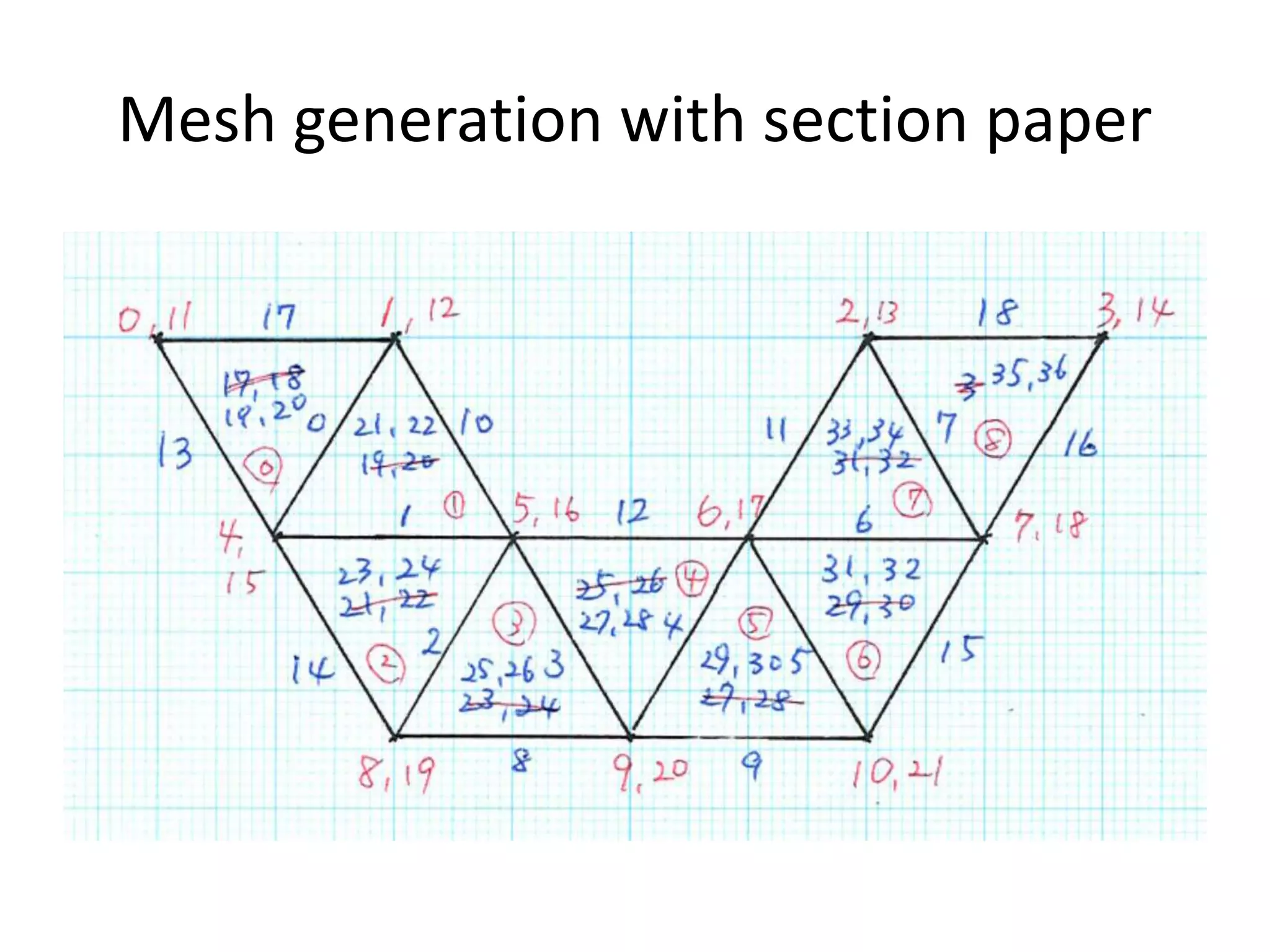
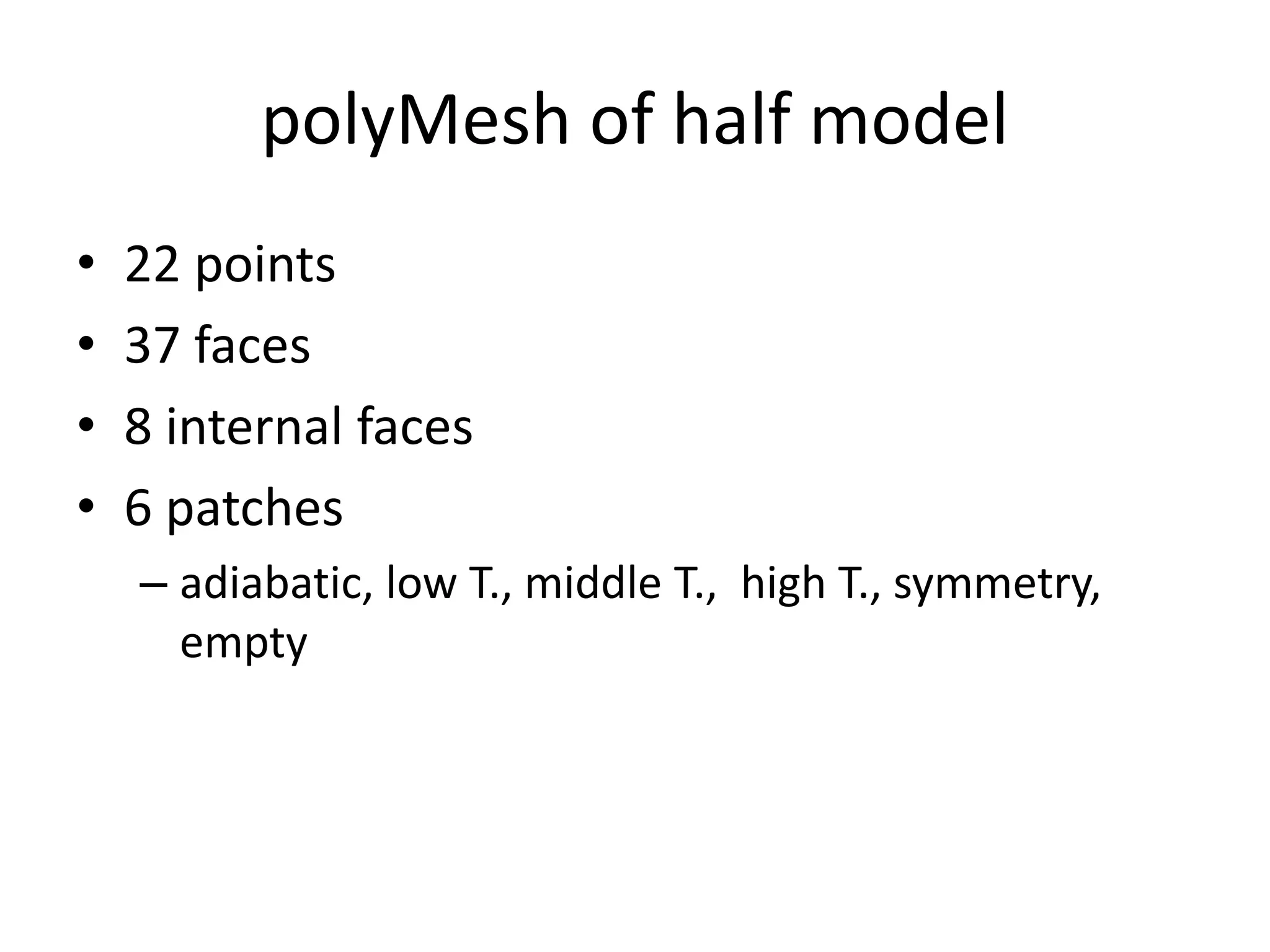
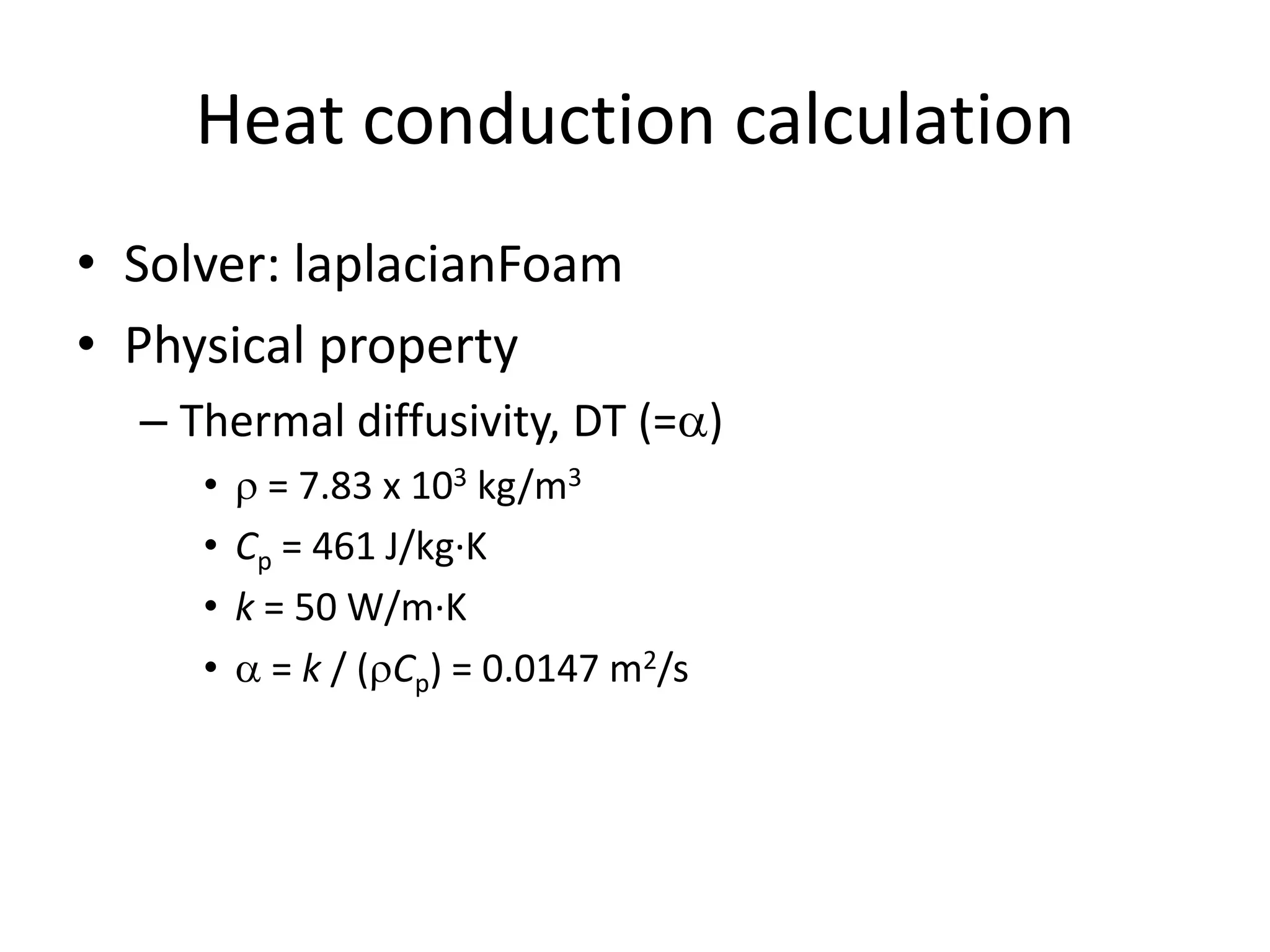
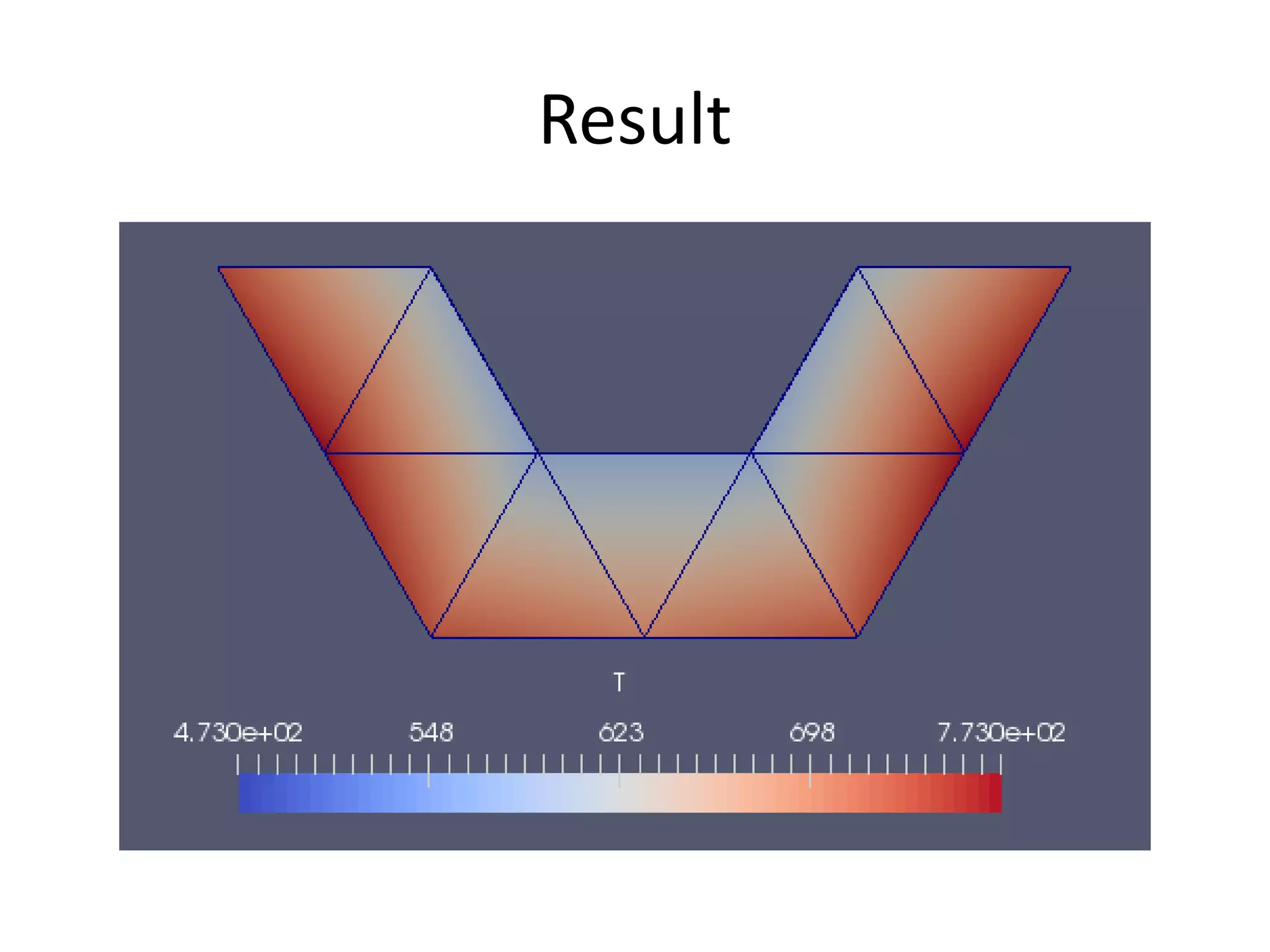
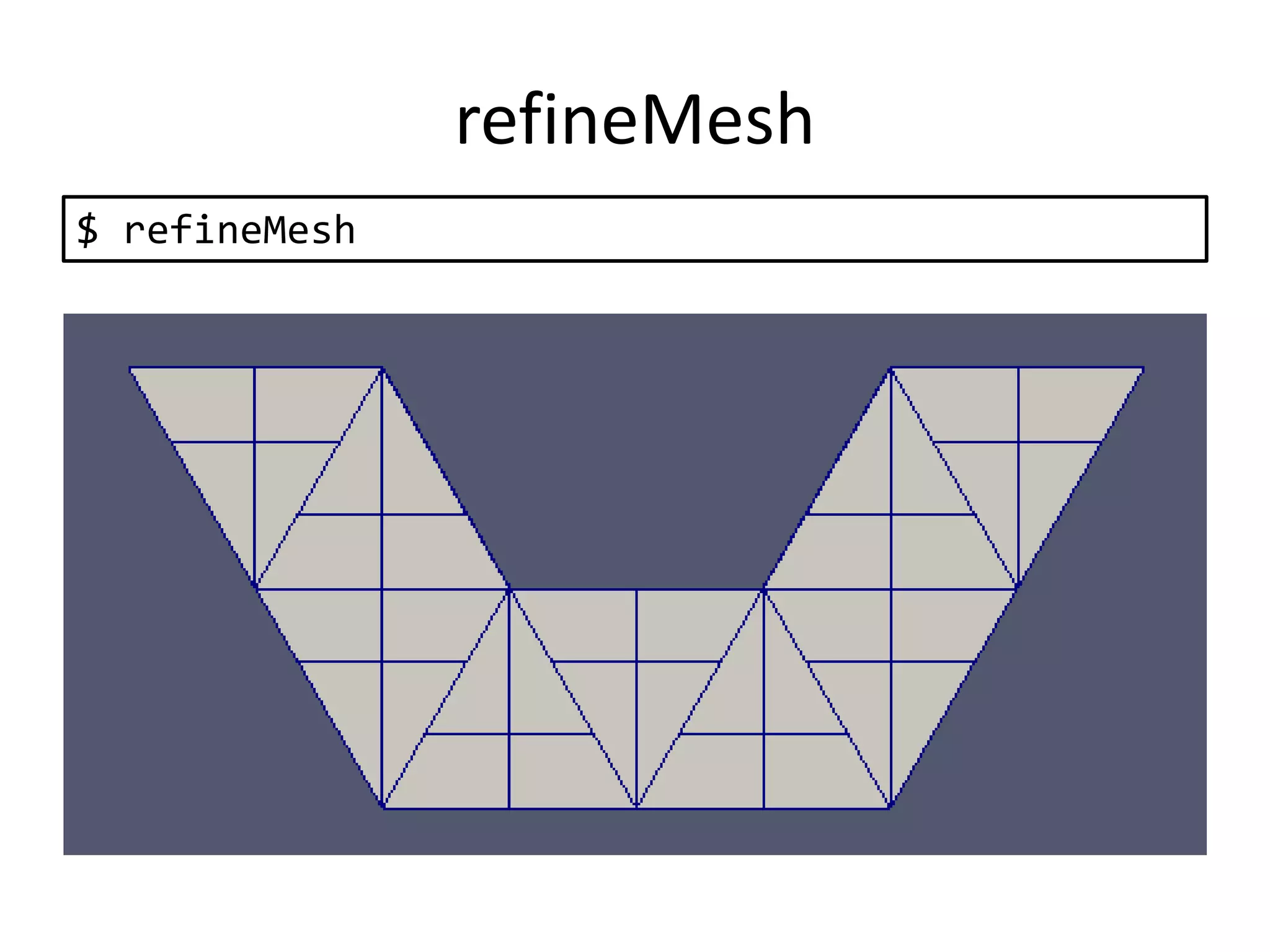
This document discusses generating and refining an unstructured mesh for a heat conduction simulation. It describes manually generating a simple triangular mesh with 22 points and 37 faces, specifying boundary conditions and material properties, and solving the problem with the laplacianFoam solver. It also includes a refineMeshDict file to refine the mesh along coordinate directions or faces.