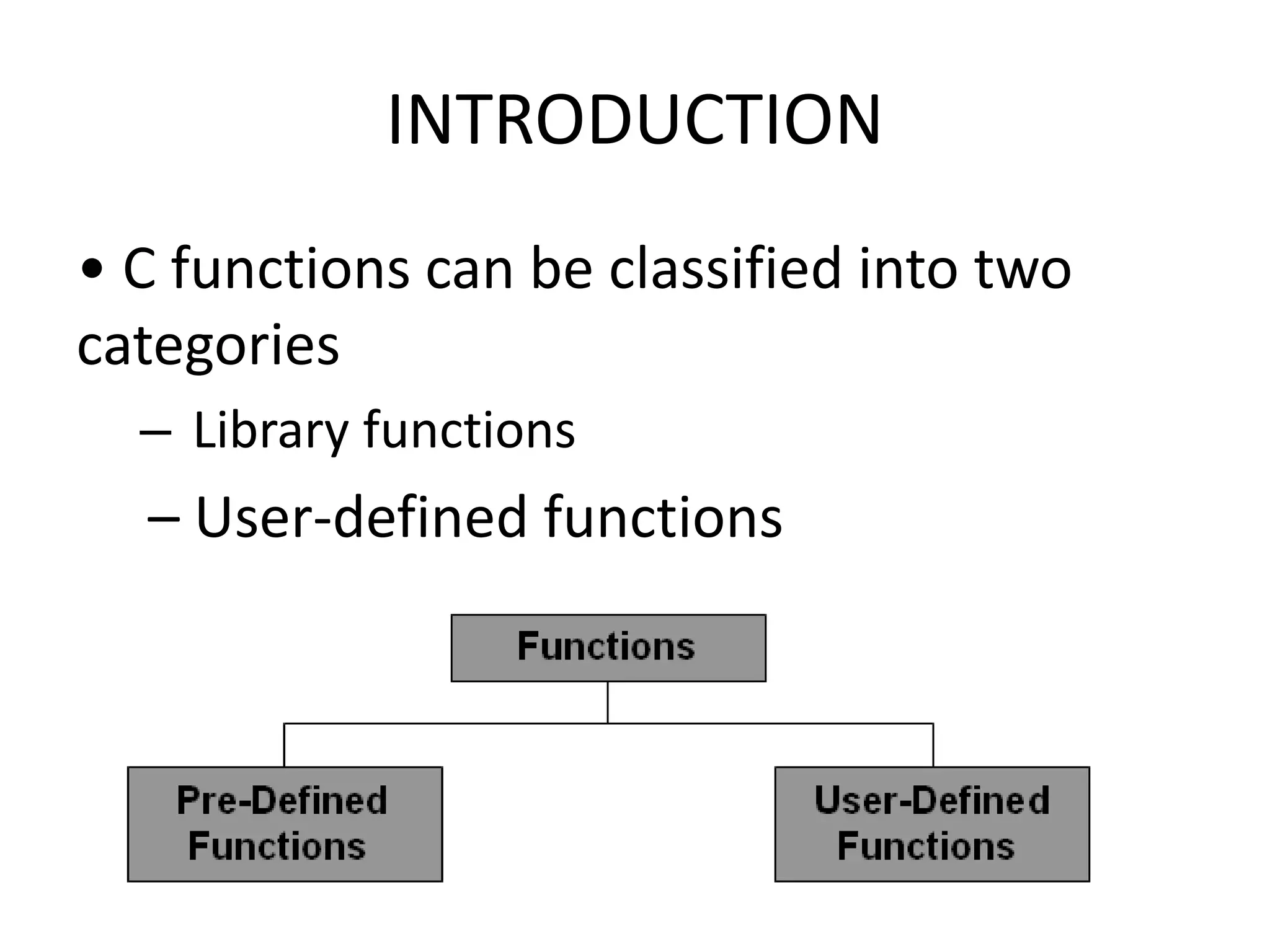
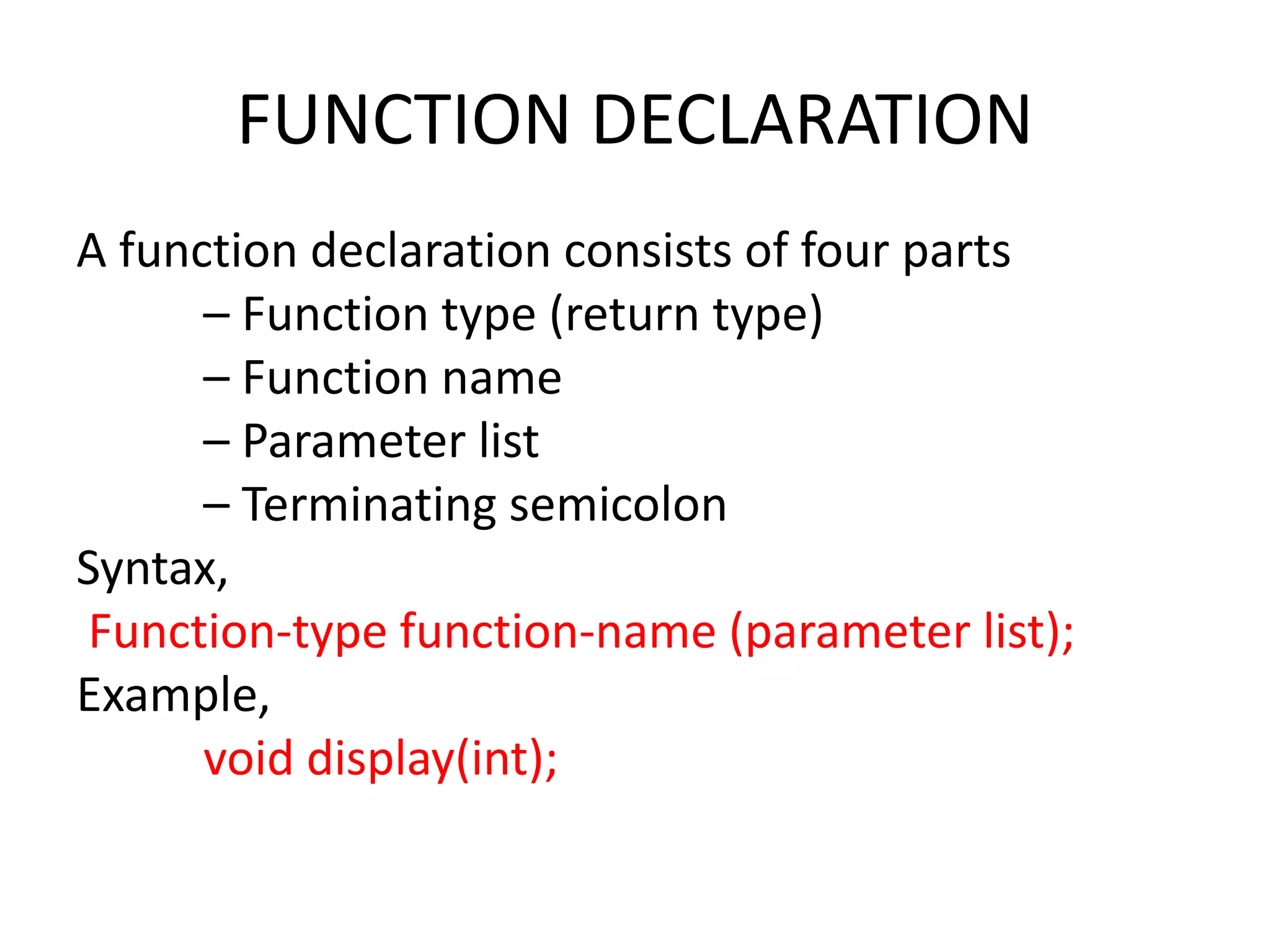
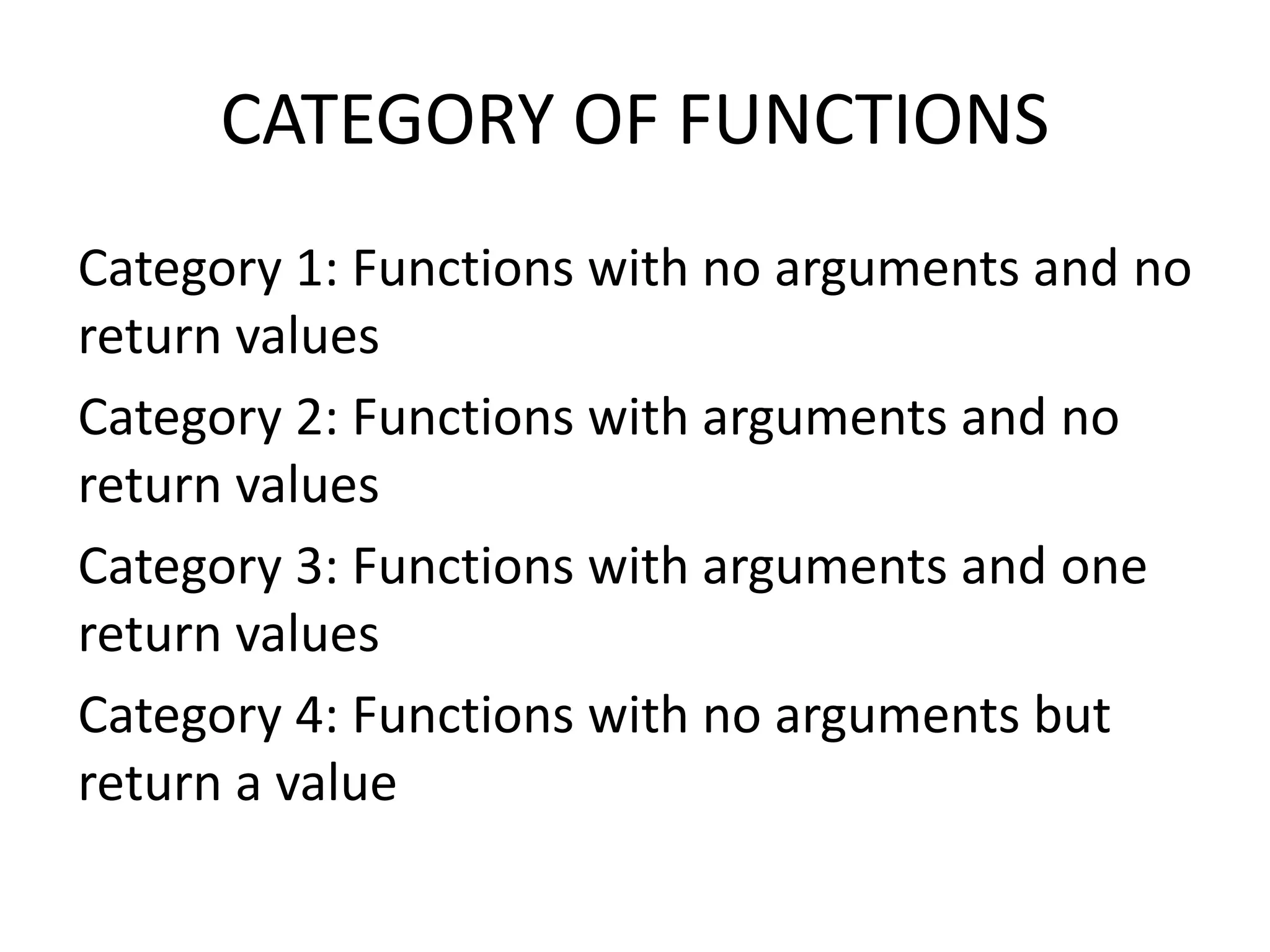
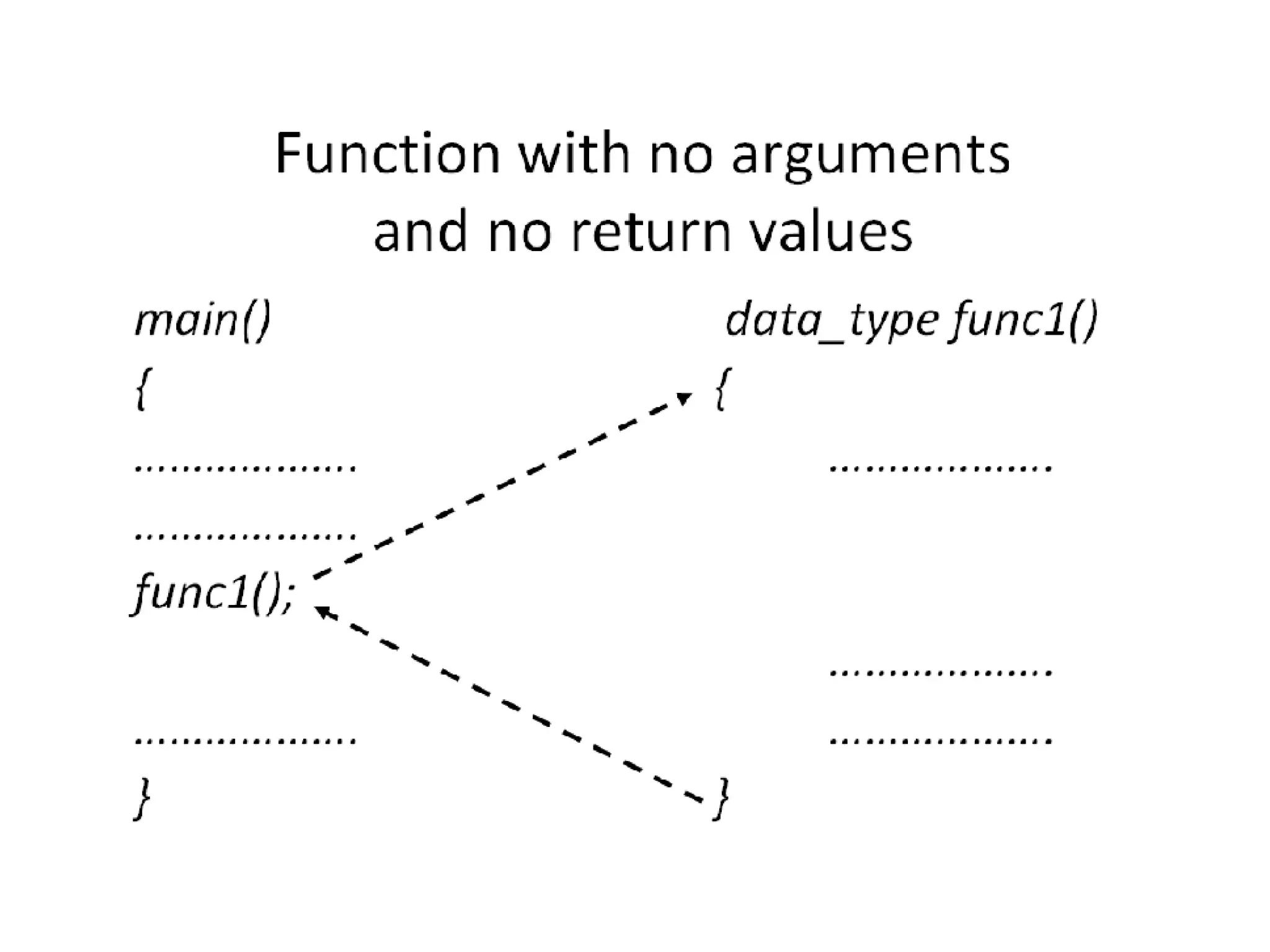
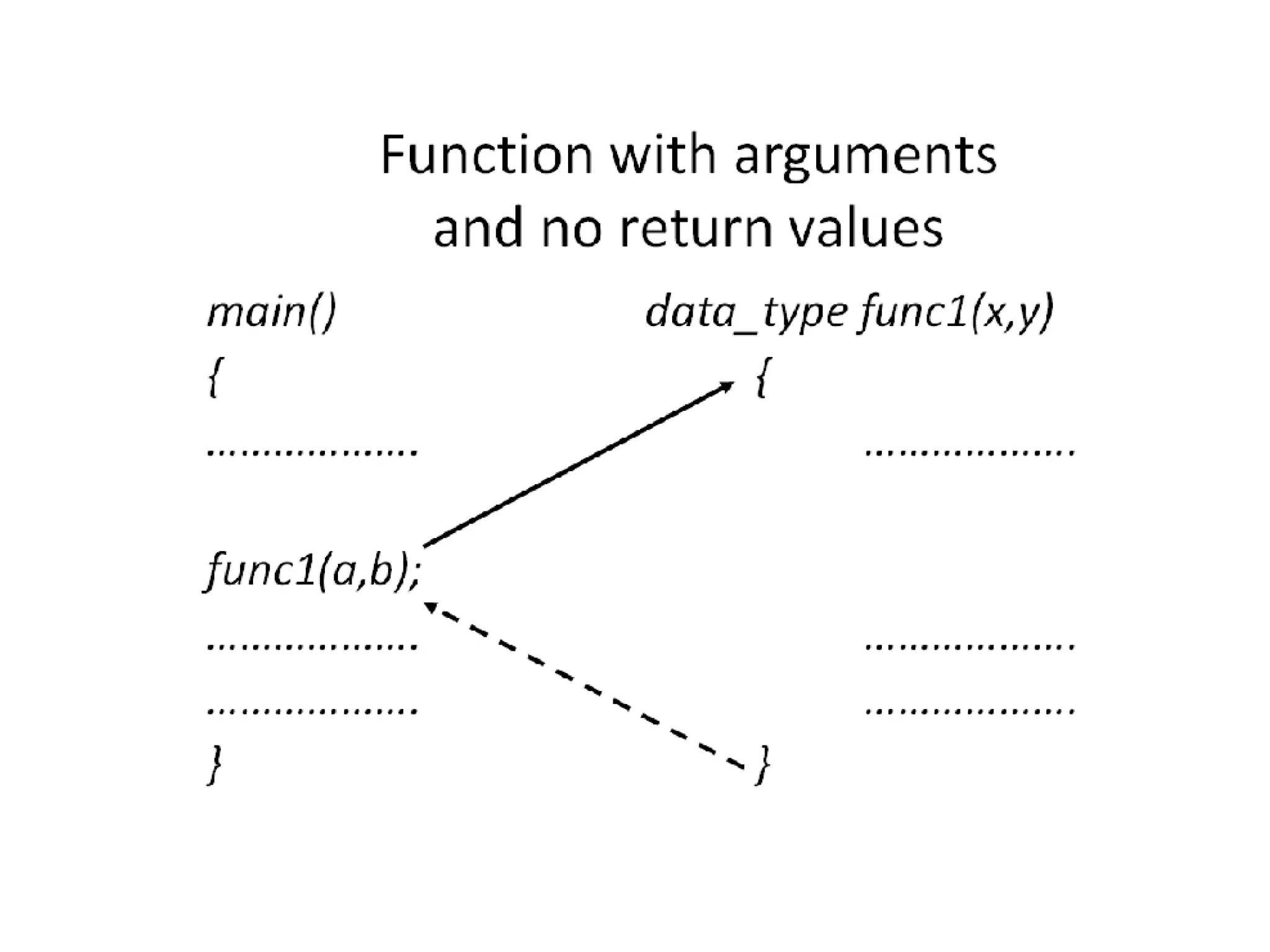
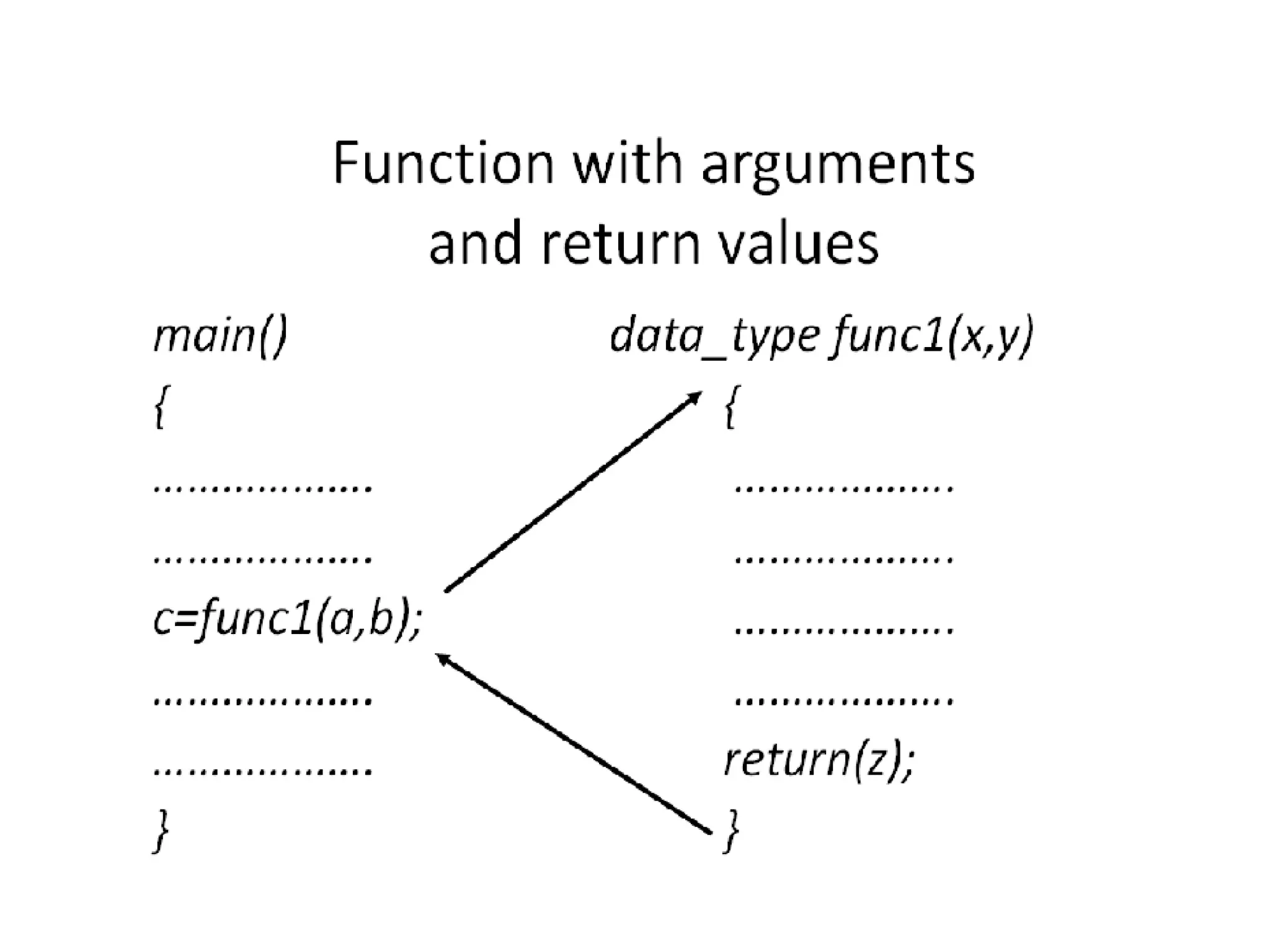
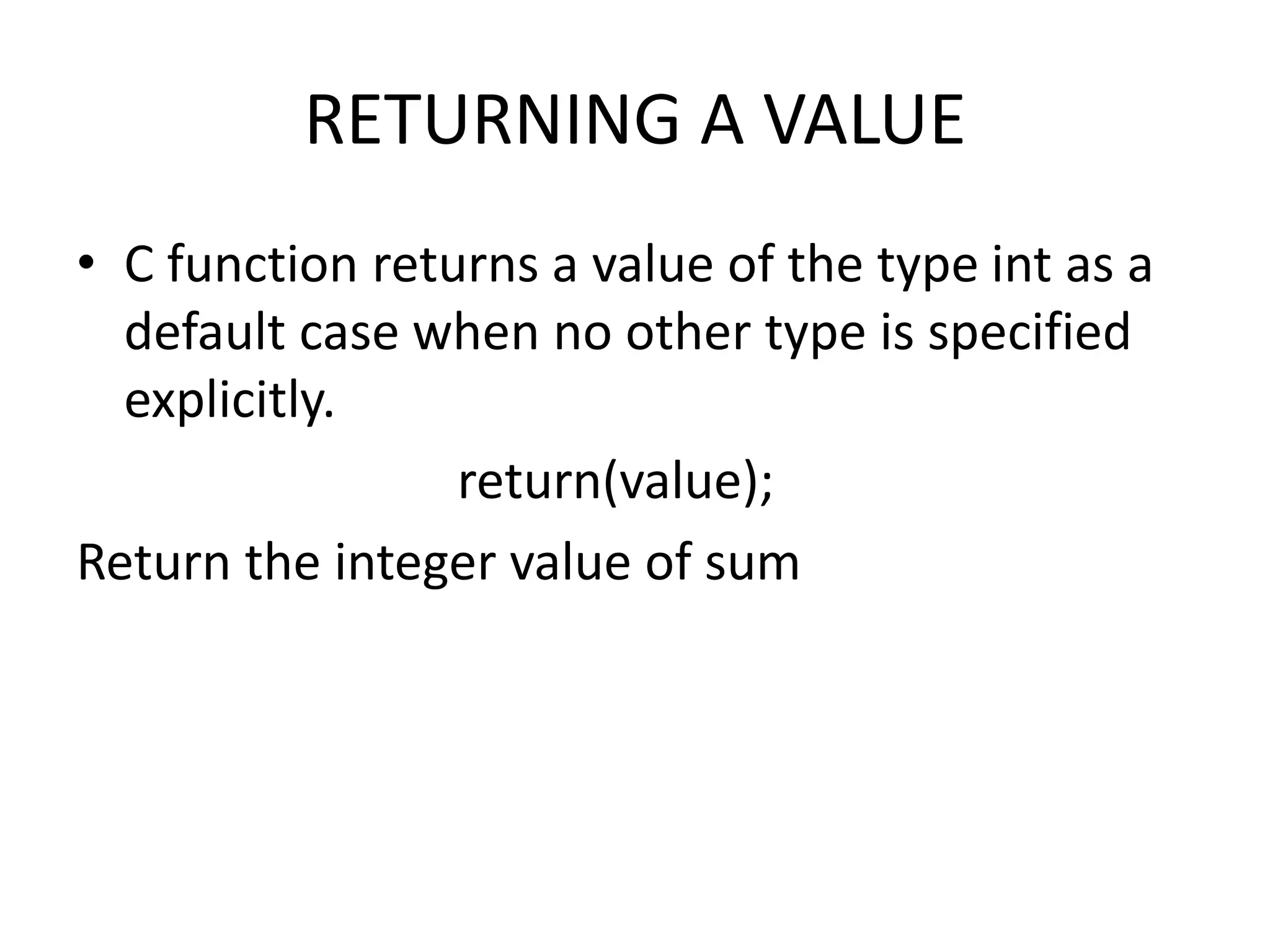
This document discusses C functions and their elements. It describes two categories of functions - library functions and user-defined functions. The key elements of user-defined functions are the function definition, function call, and function declaration. A function declaration specifies the return type, name, and parameters. A function definition implements the function with its name, return type, parameters, local variables, statements, and return statement. Functions can be called by using their name in a statement.