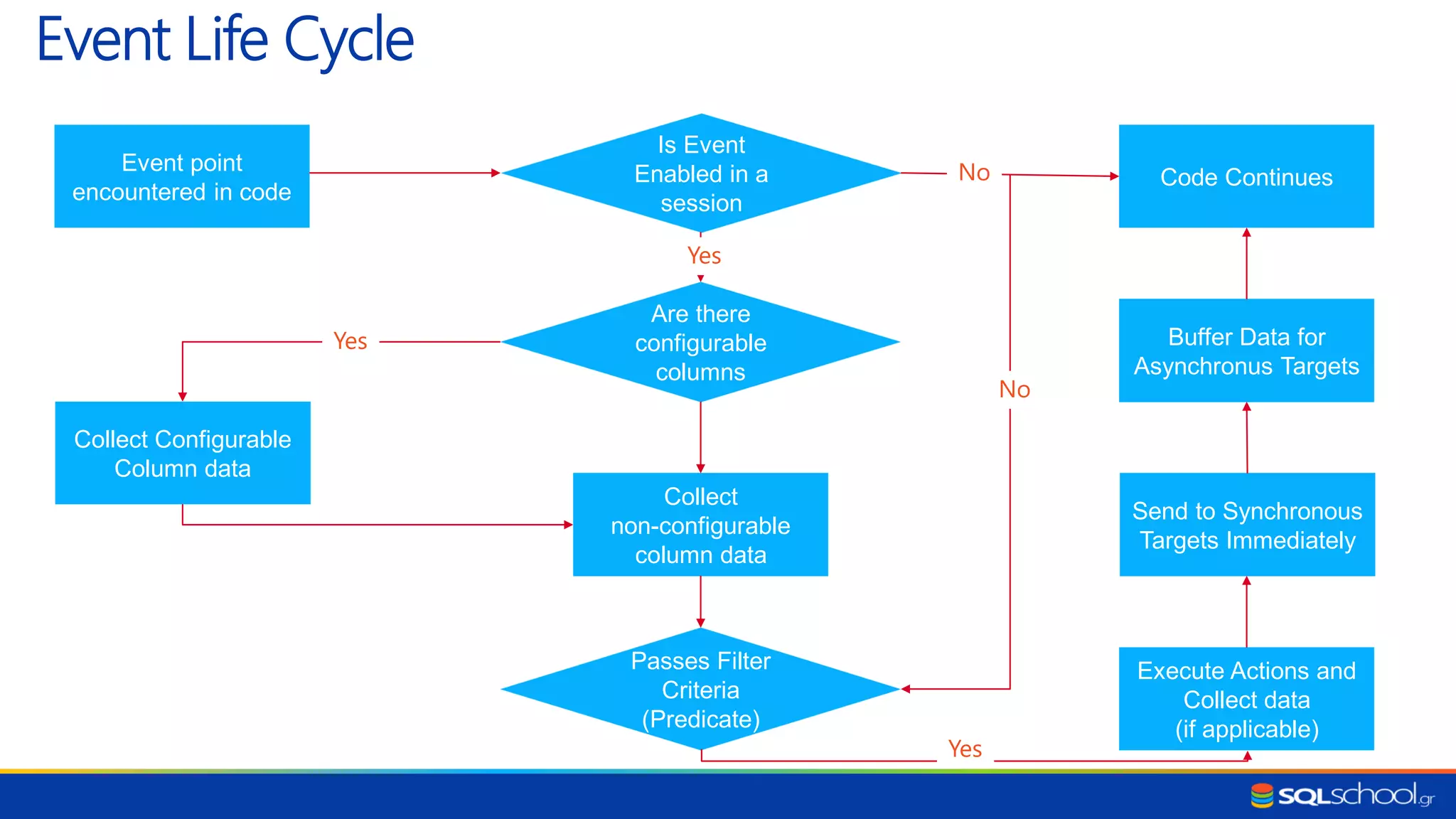
The document discusses the introduction and advantages of Extended Events in SQL Server, highlighting its role in future troubleshooting and diagnostic data collection. It compares Extended Events with the deprecated SQL Trace feature, emphasizing its efficiency, flexibility, and lower overhead. Additionally, it outlines the architecture of Extended Events, including event life cycles, sessions, predicates, and various targets for data collection.