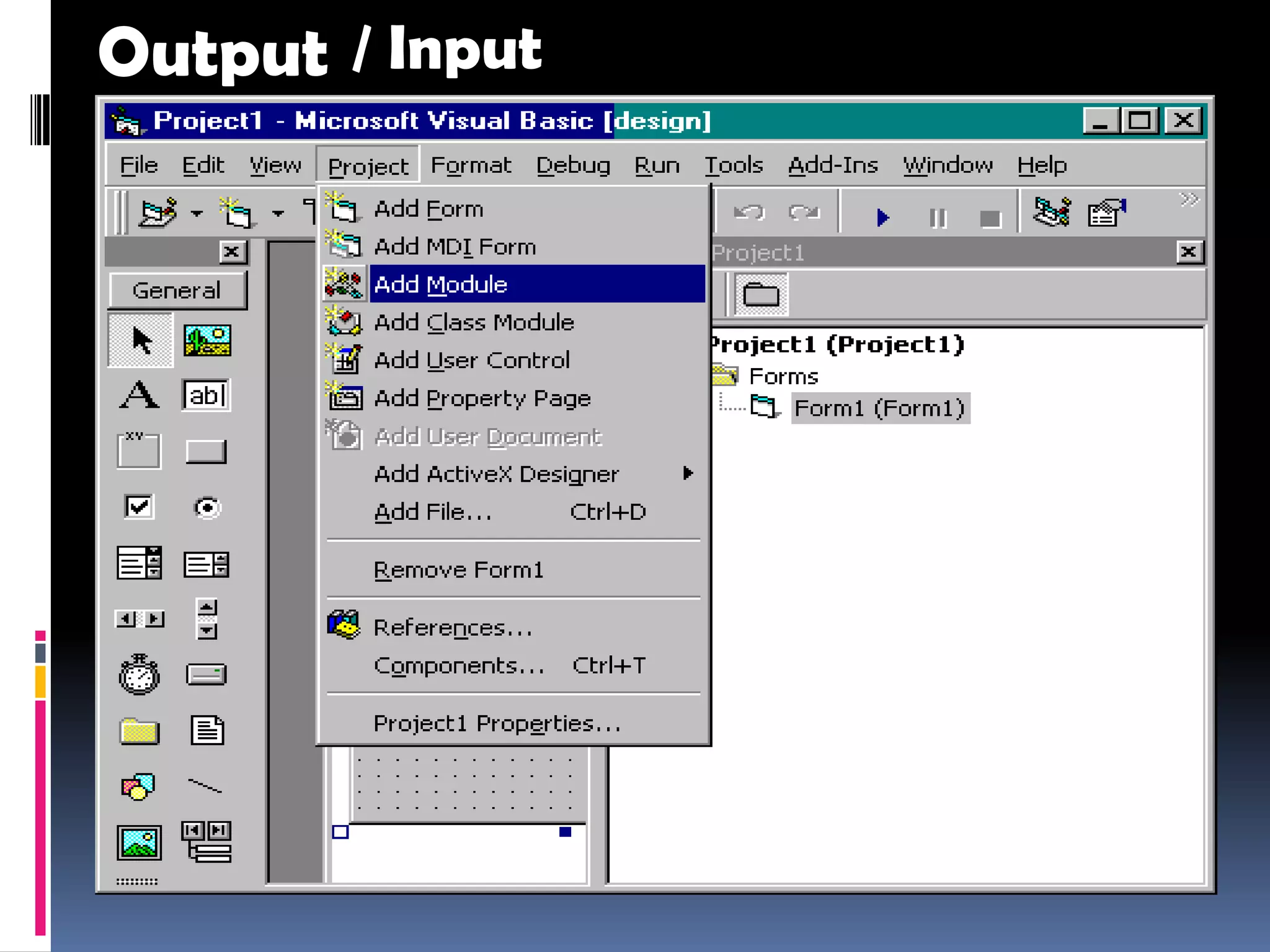
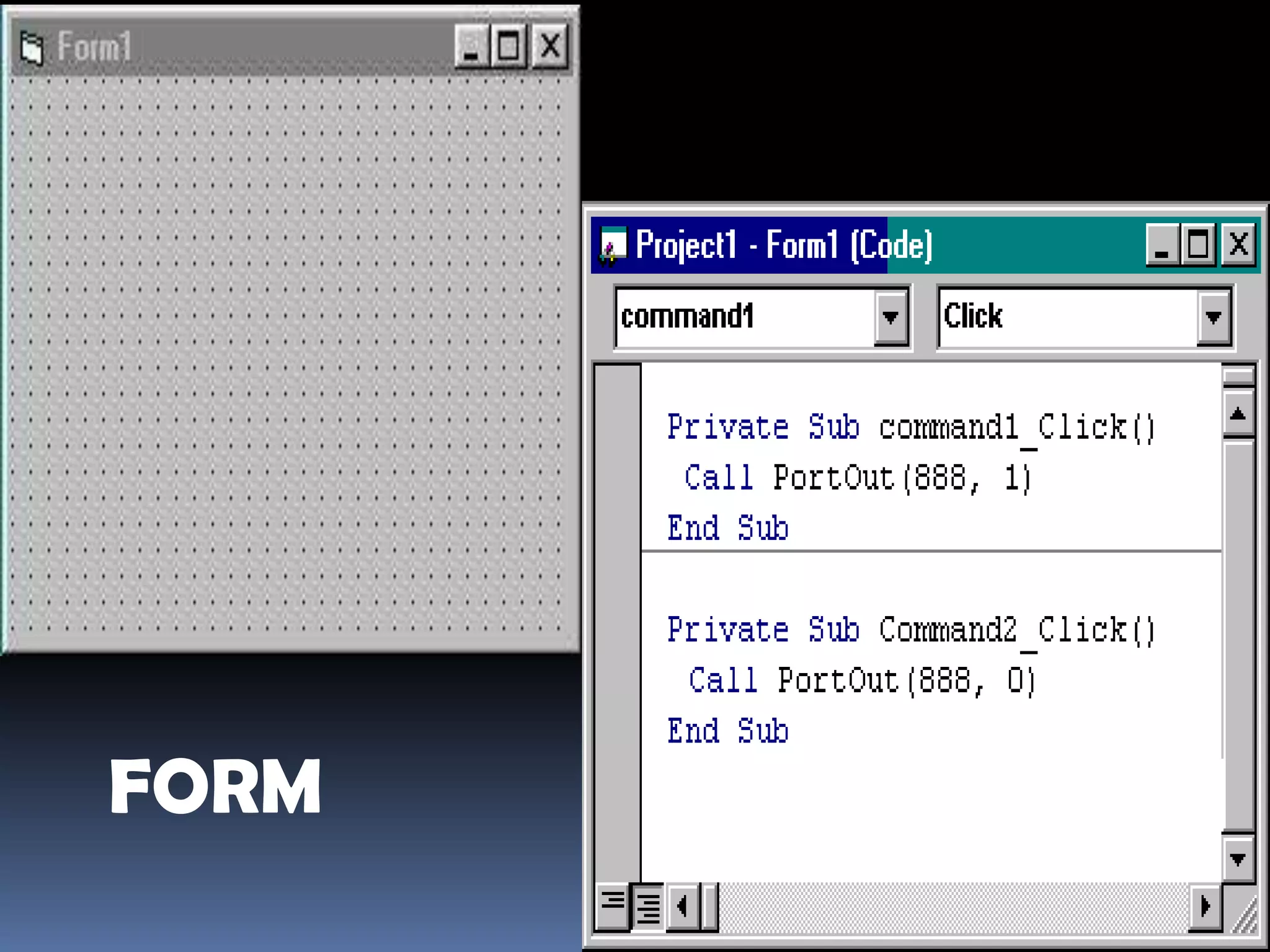
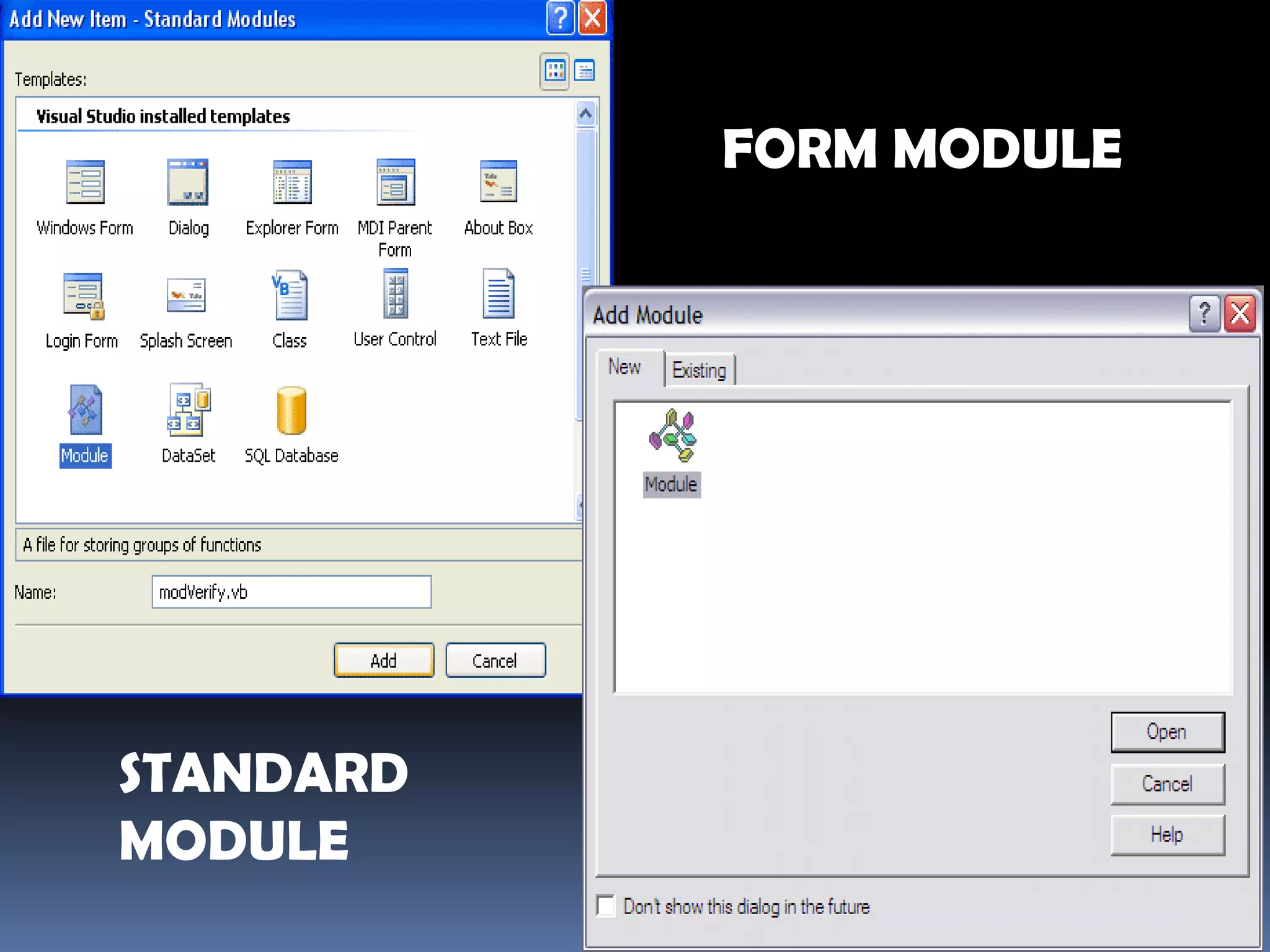
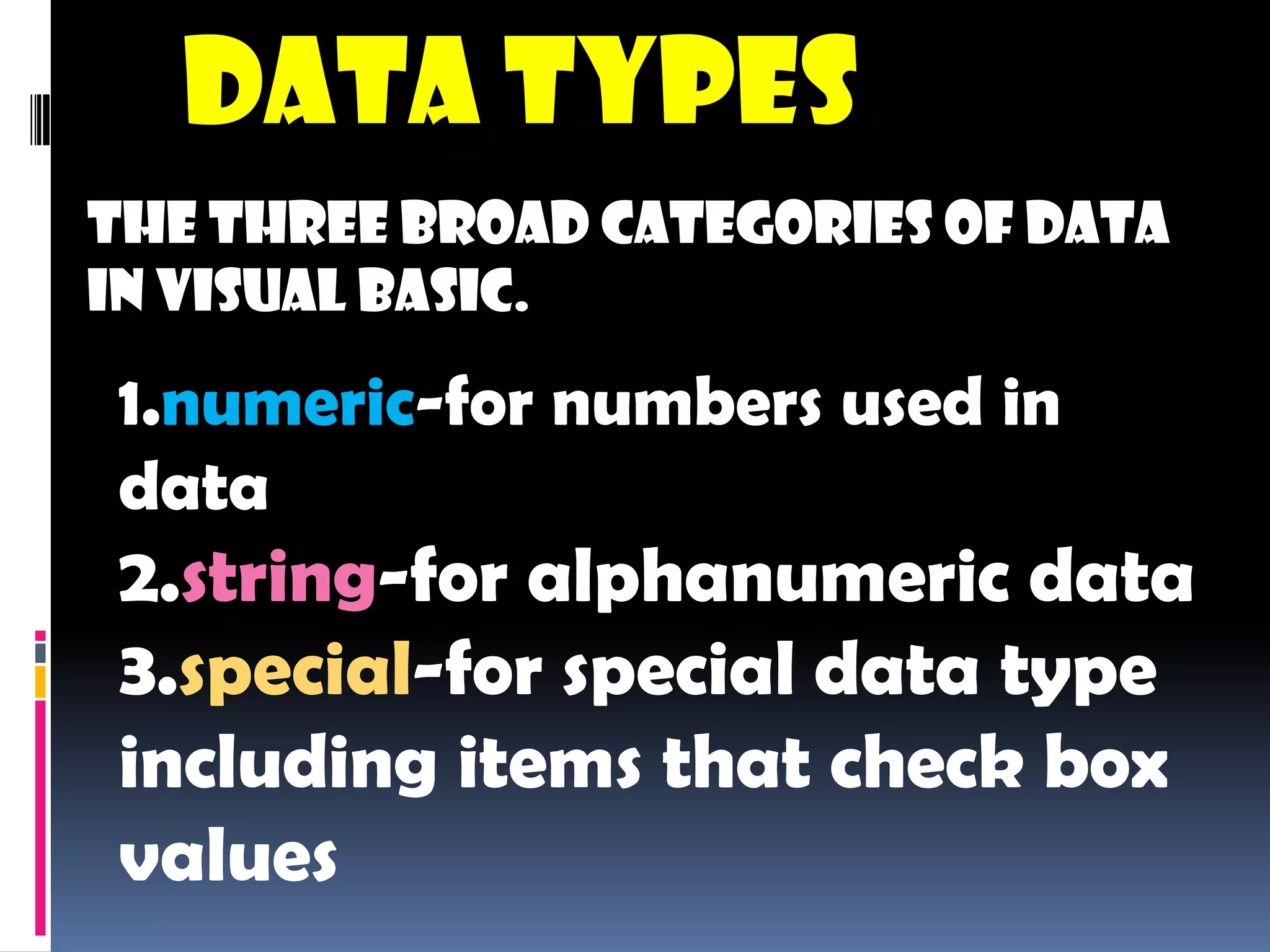
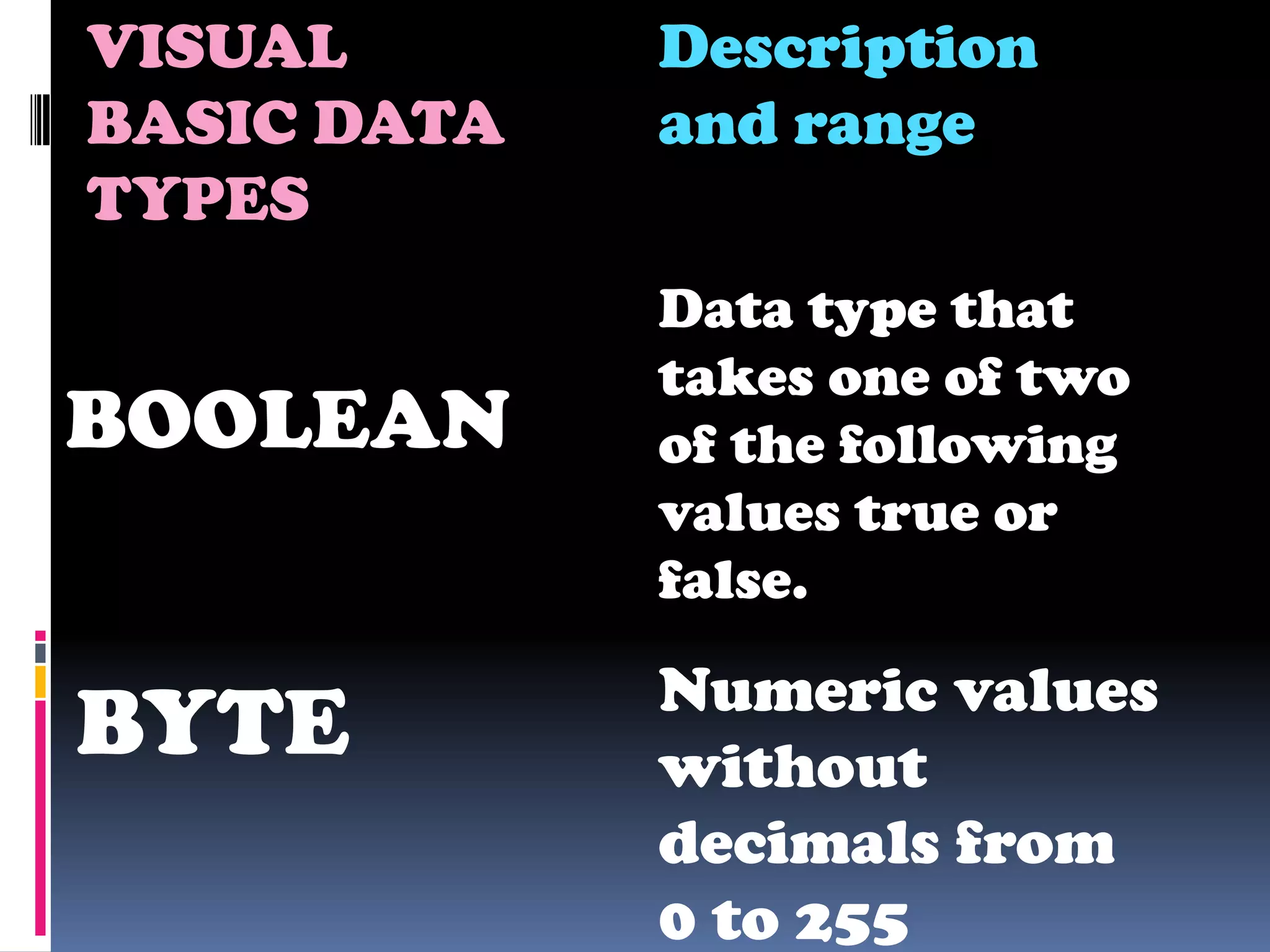
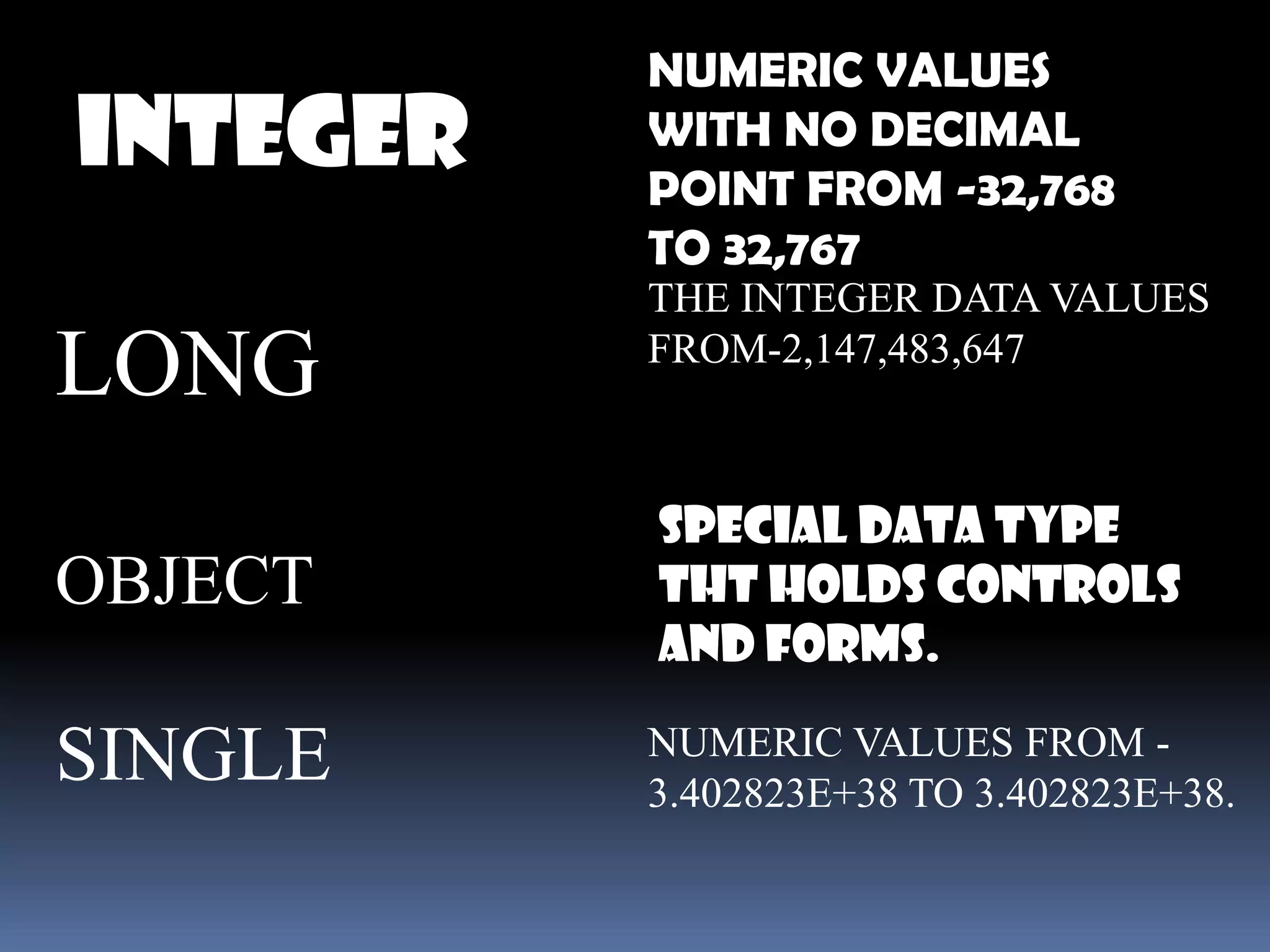
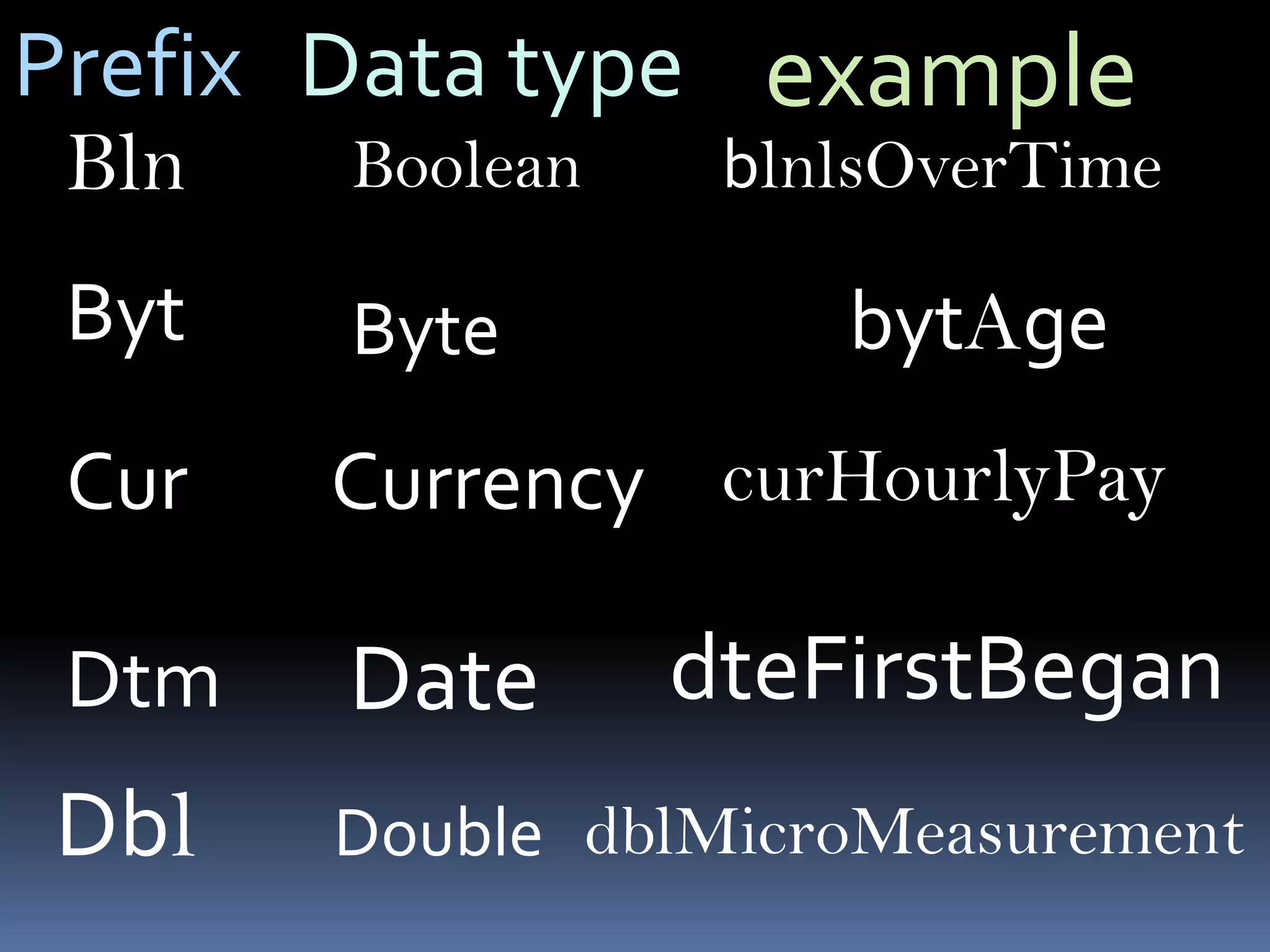
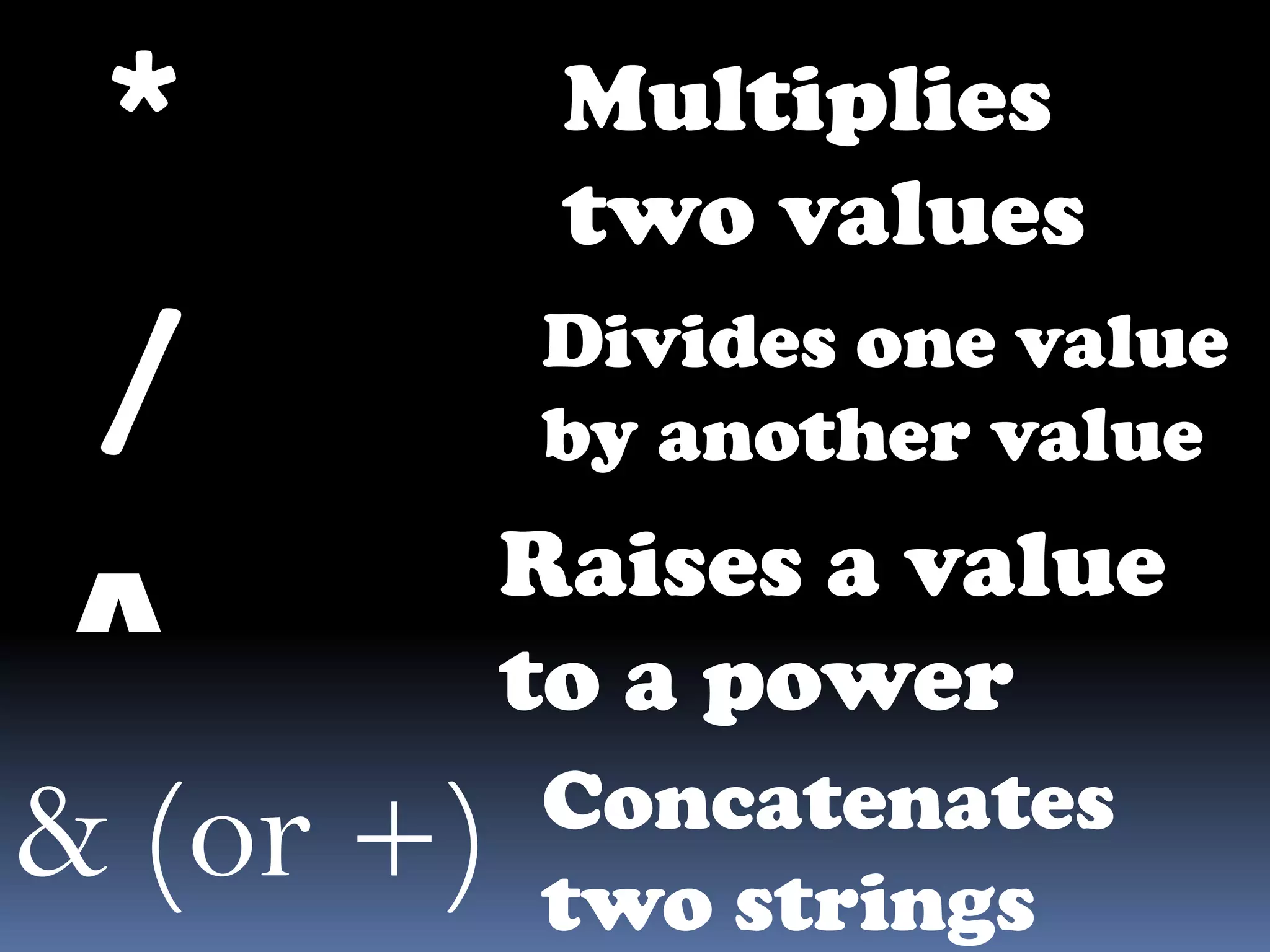
The document discusses various aspects of code for Visual Basic, including where to find code examples within the Visual Basic documentation, the typical components of a Visual Basic application like forms and controls, and some basic data types like numeric, string, and special. It also covers topics like input and output, form modules, standard modules, strings, data types, variables, expressions, and math operators.