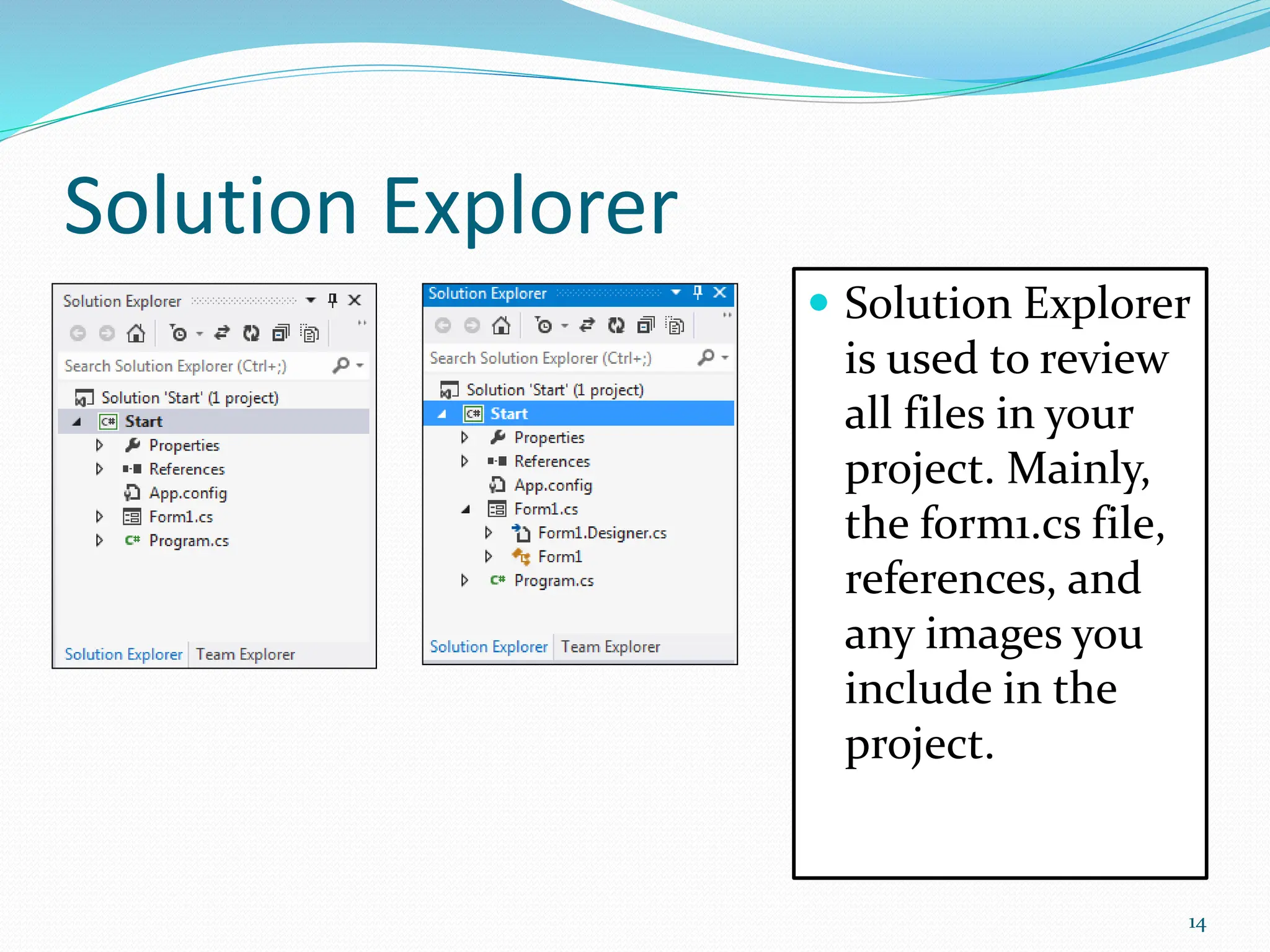
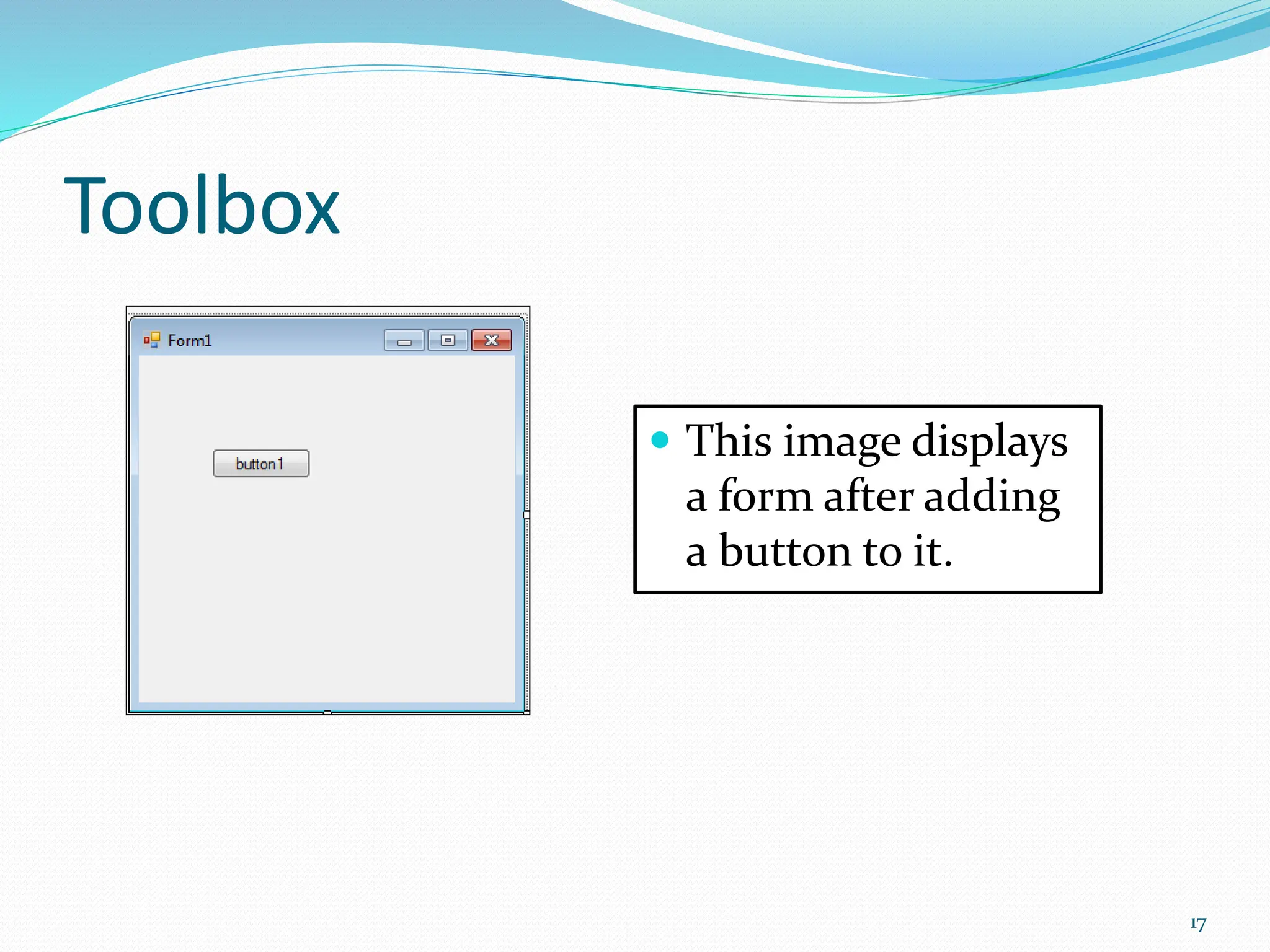
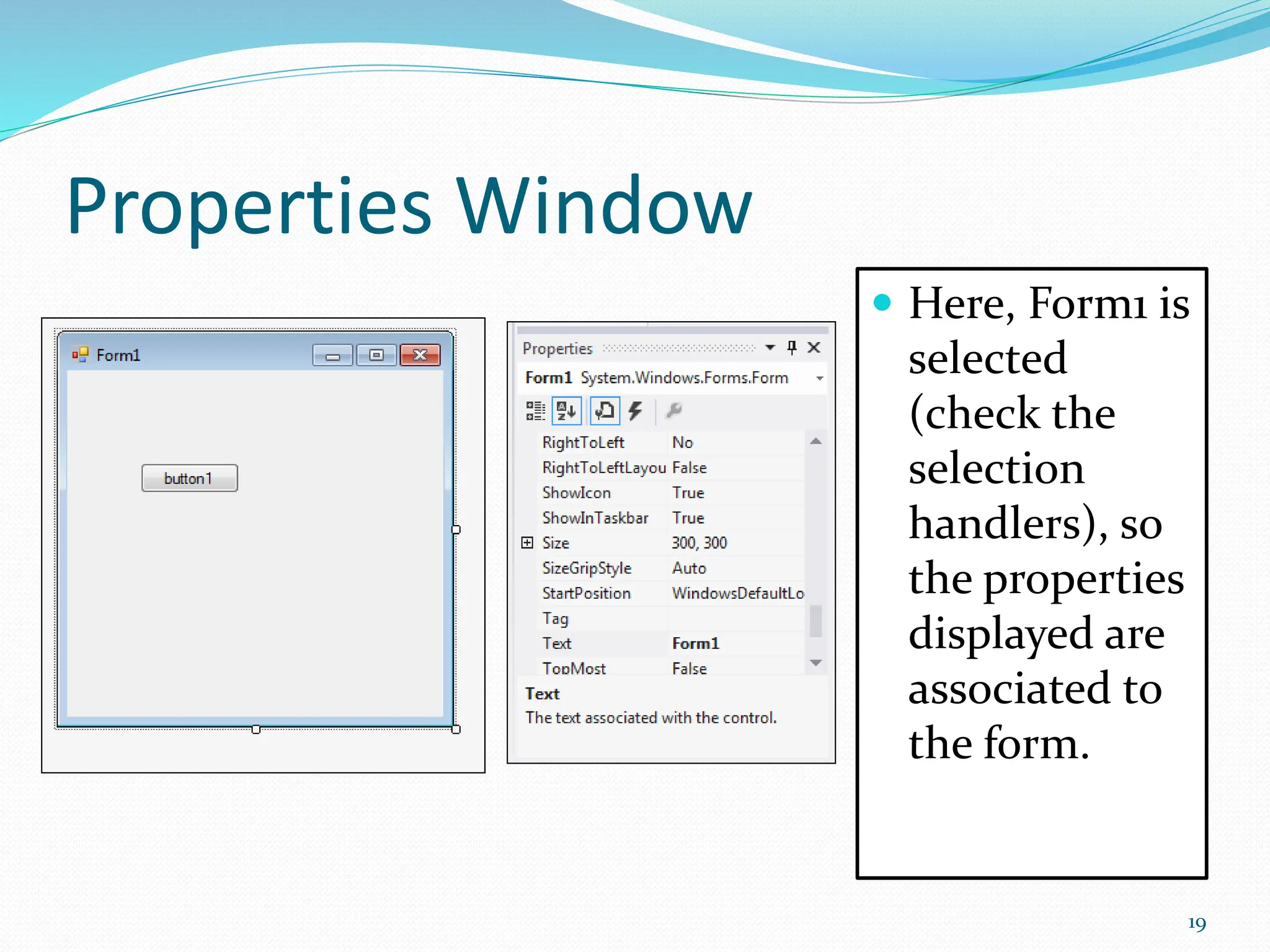
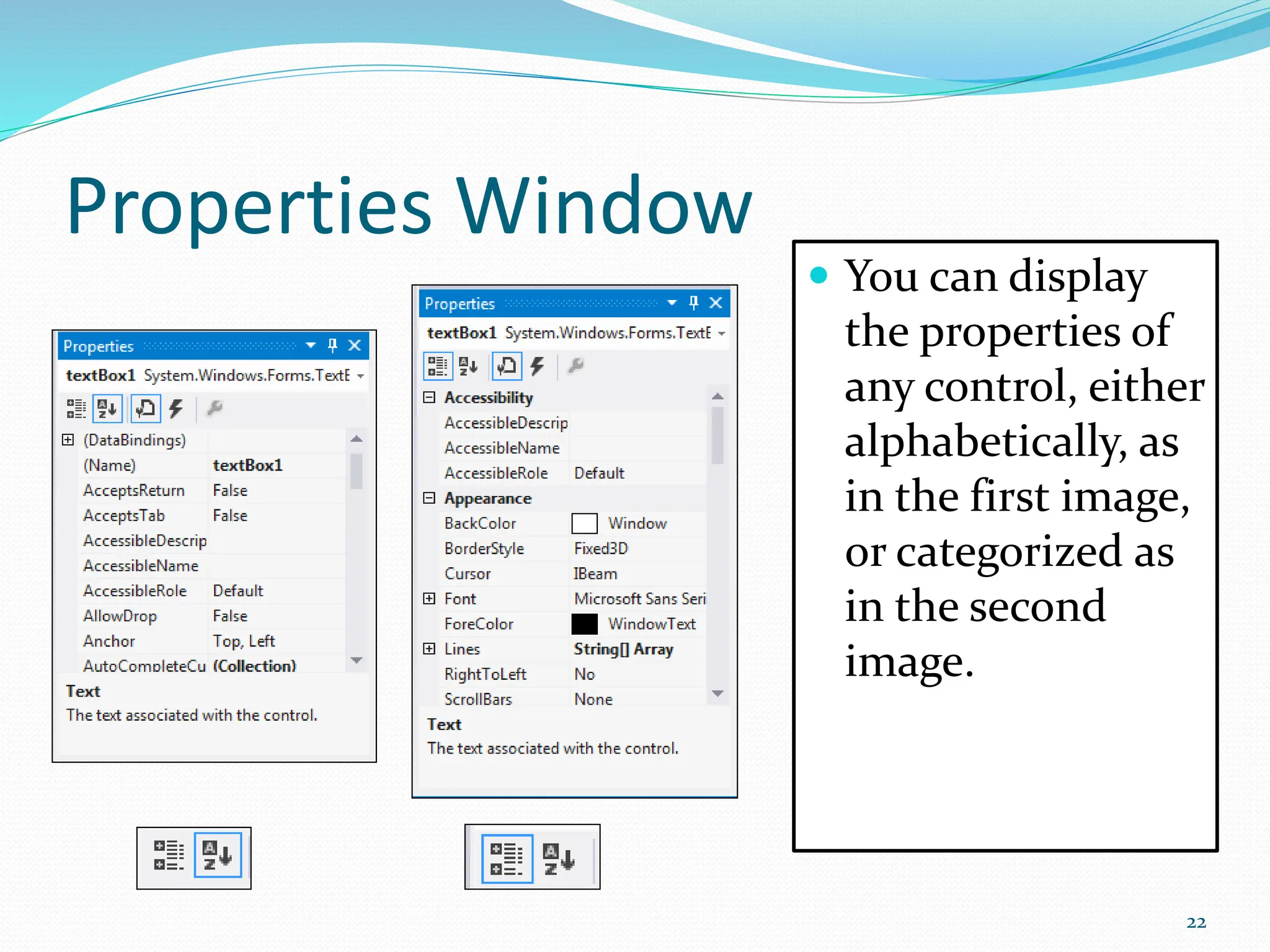
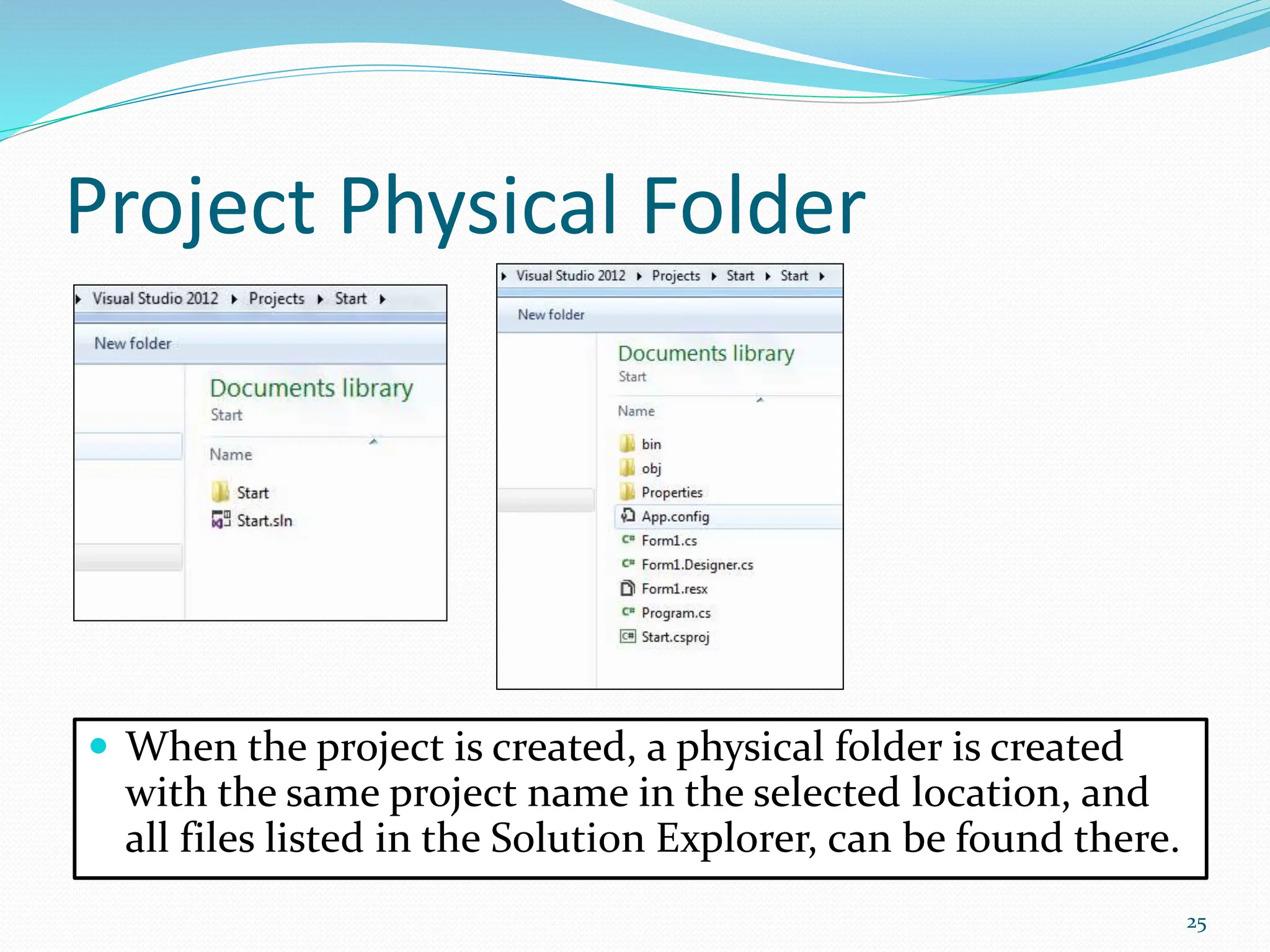
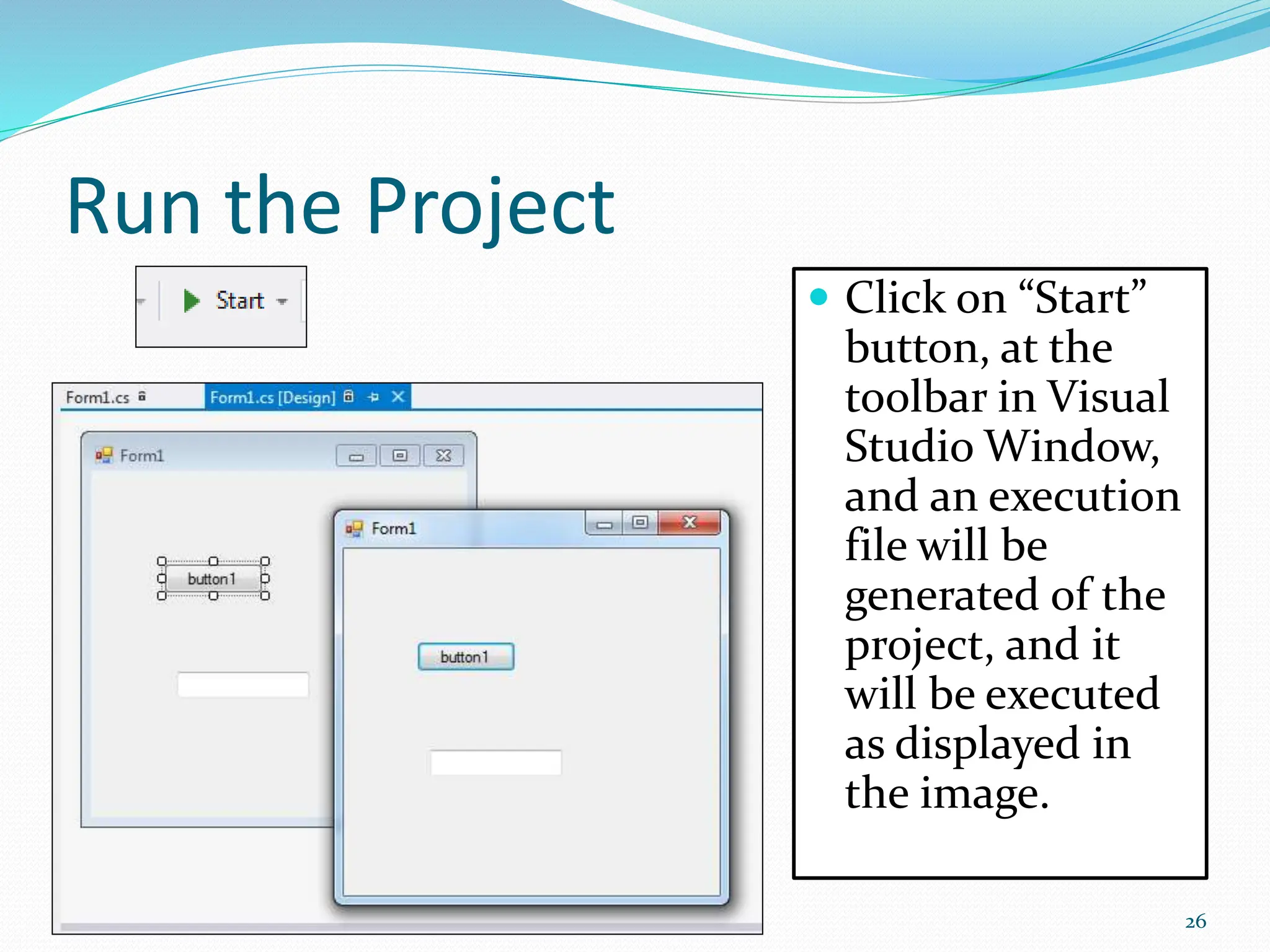
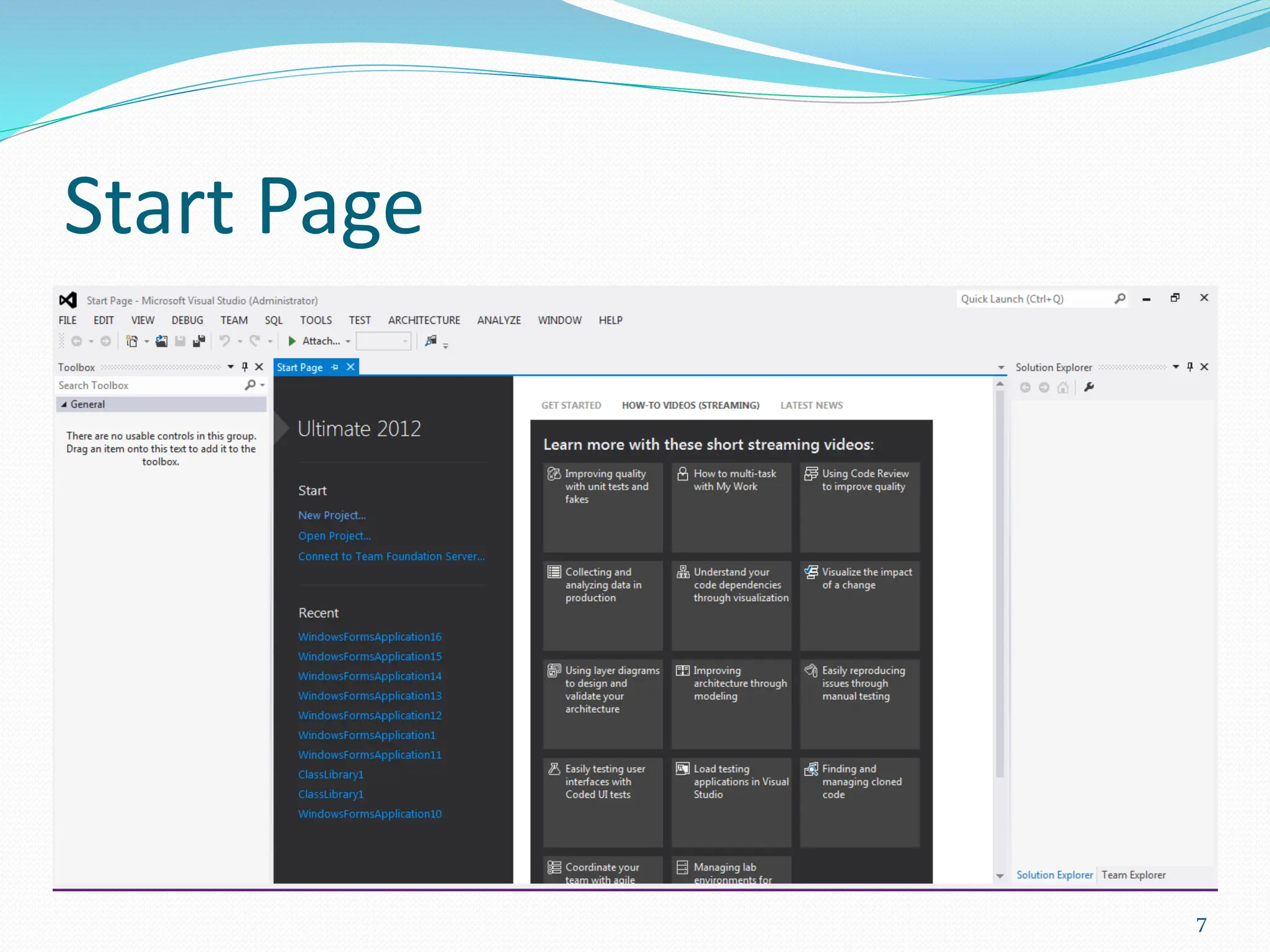
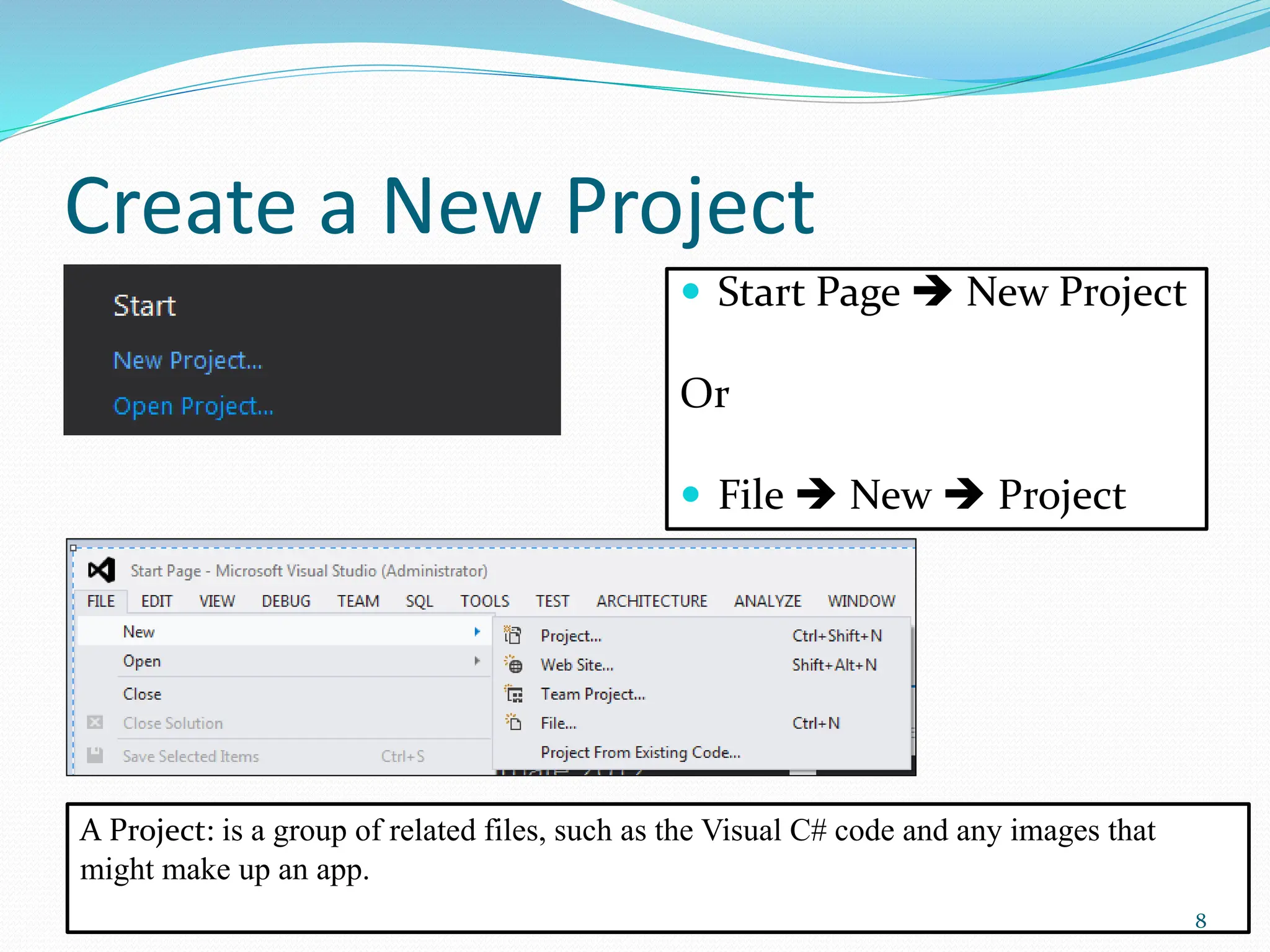
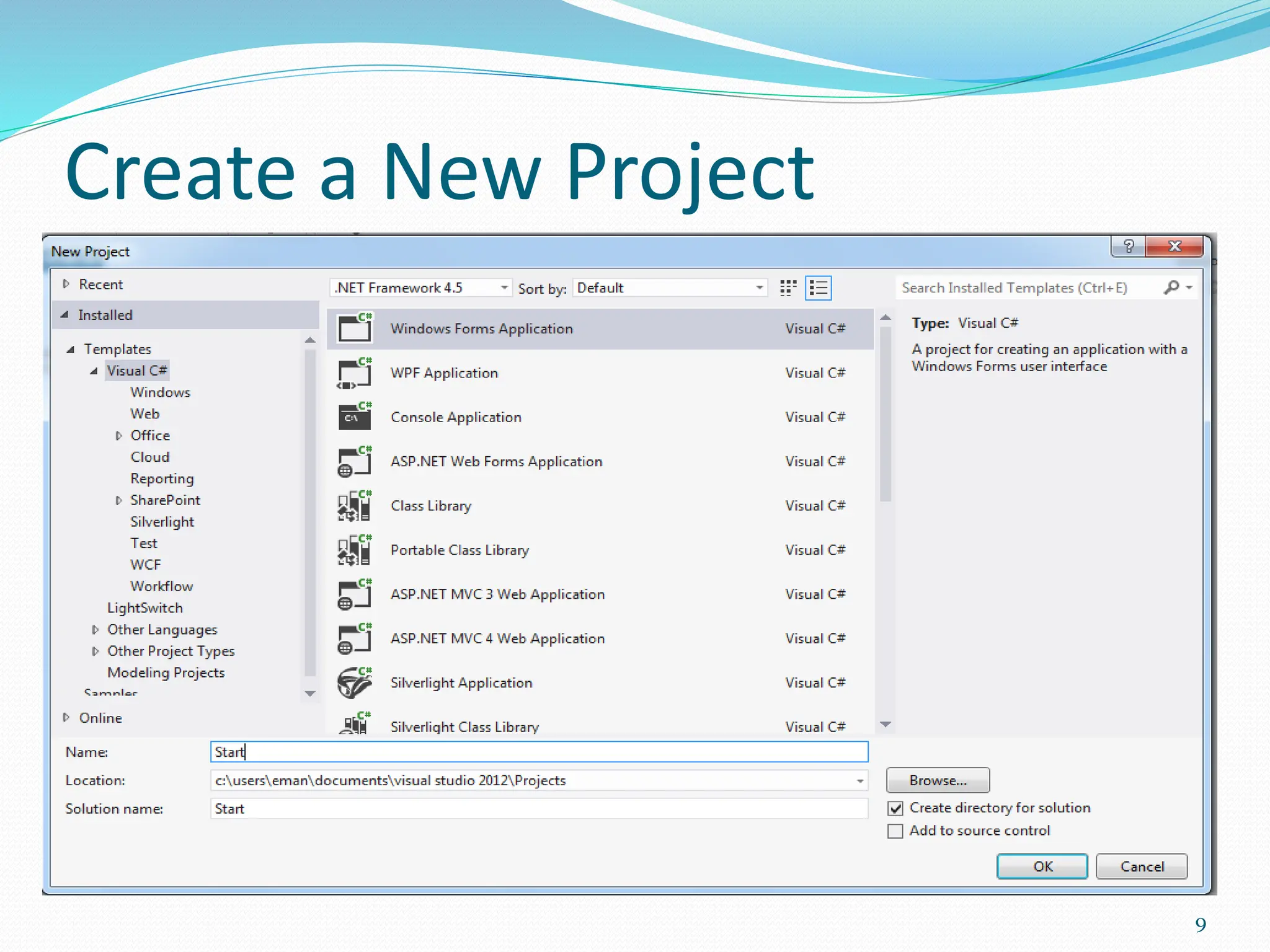
Visual programming allows creating software applications graphically without writing code. Visual Studio is a development environment for building applications with languages like C#. It contains tools like the toolbox, properties window, and solution explorer. The toolbox has common controls that can be dragged onto forms to build an application's interface. Properties configure the controls and forms. Running the project generates an executable file to distribute the completed application.







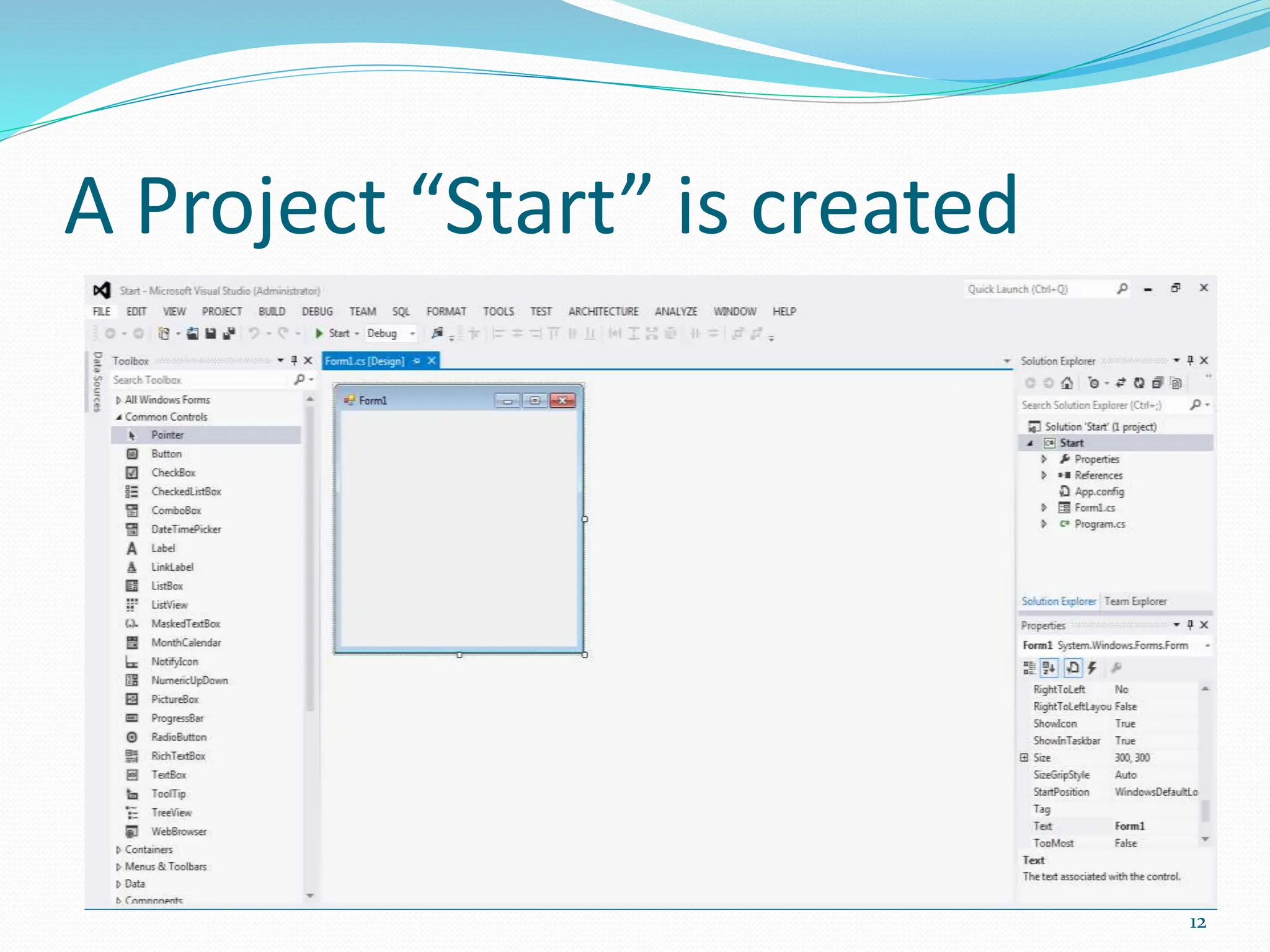
![Forms.cs Form1.cs [Design] This window displays the file form1.cs in design mode. In this window you can add the needed controls to the form. Your project may contain several forms that act as the windows of the application. 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/visualprogrammingbasic-240228101744-036456a7/75/Visual-programming-basic-ppt-bs-cs5th-class-13-2048.jpg)