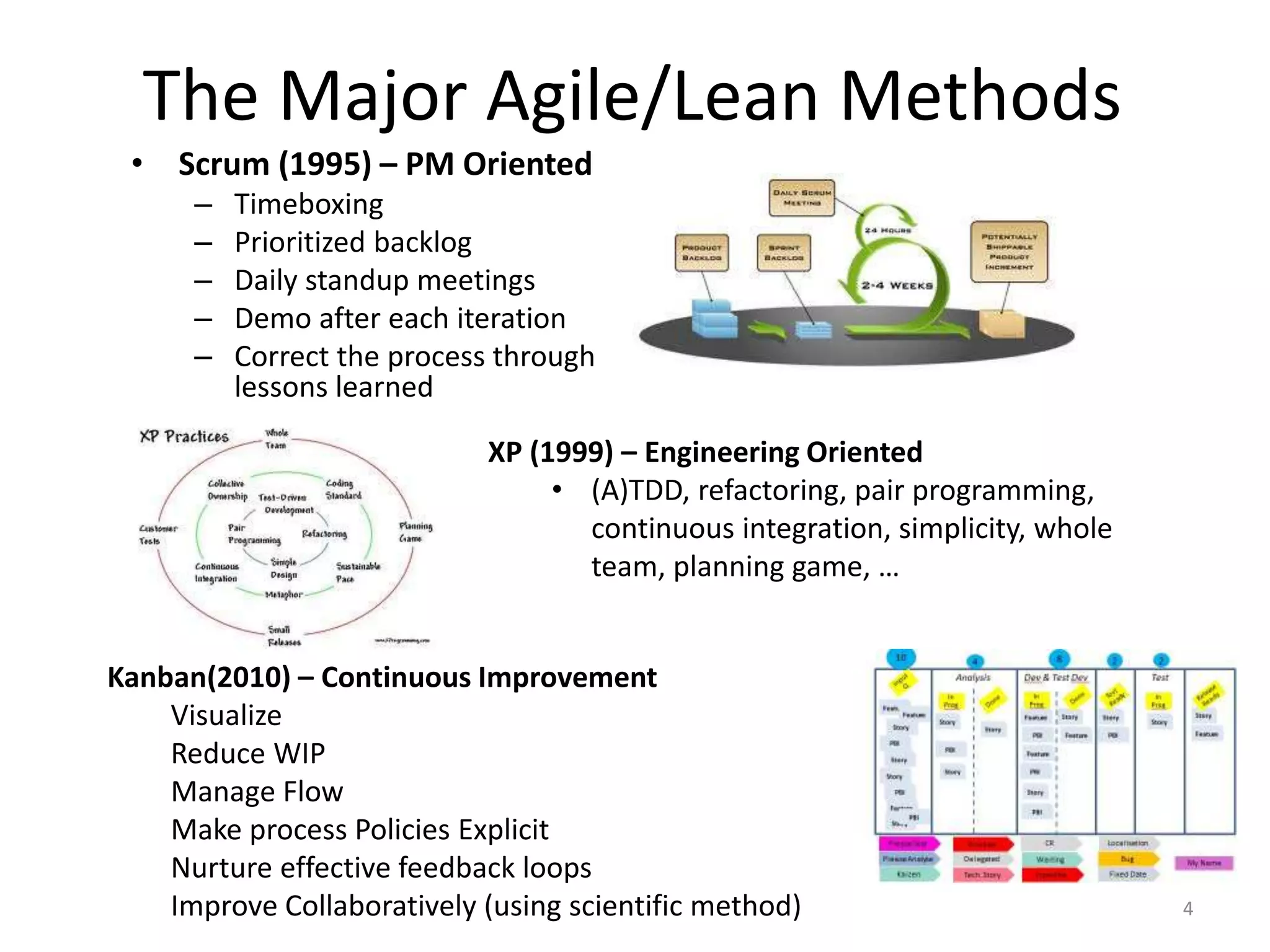
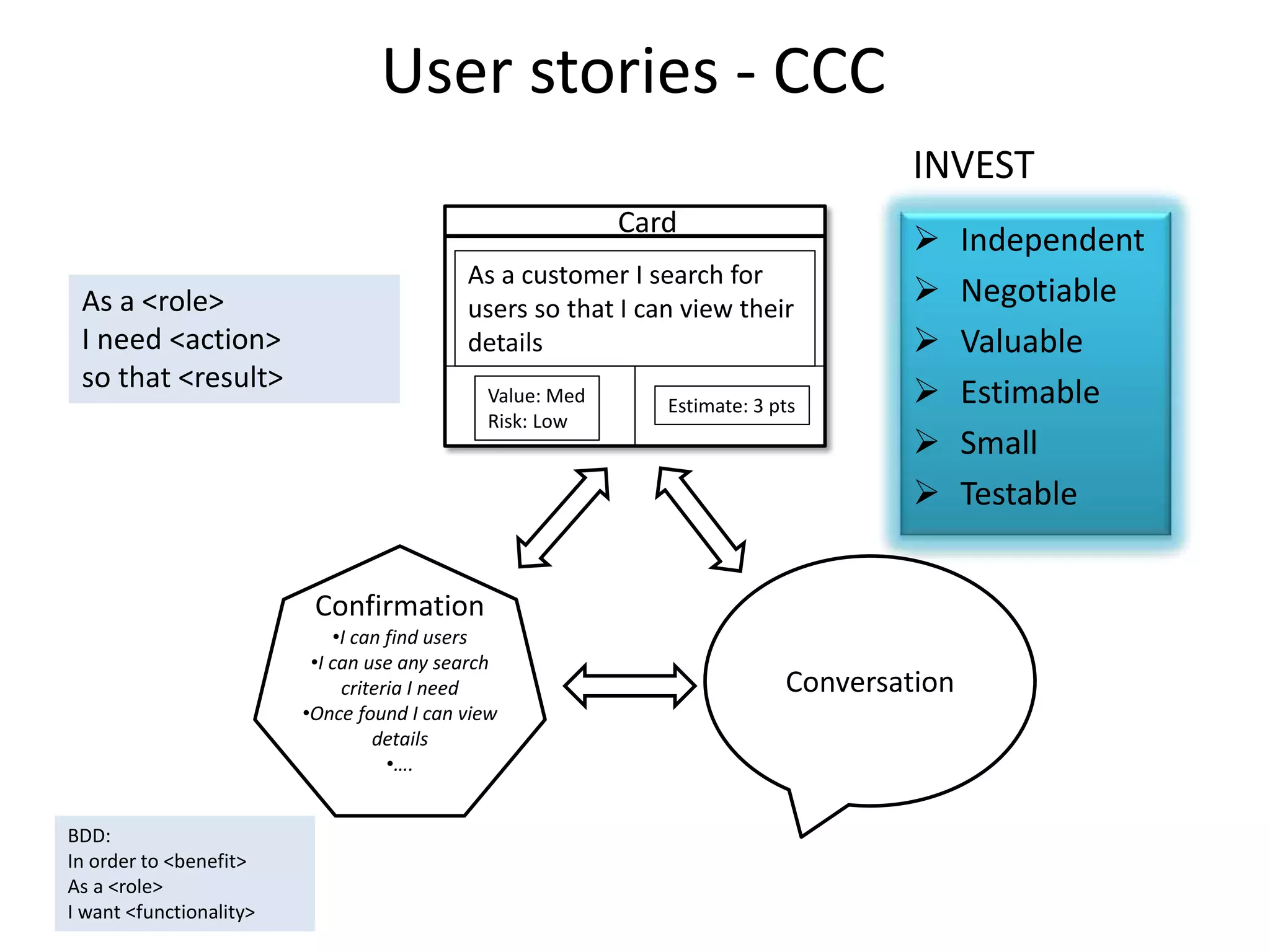
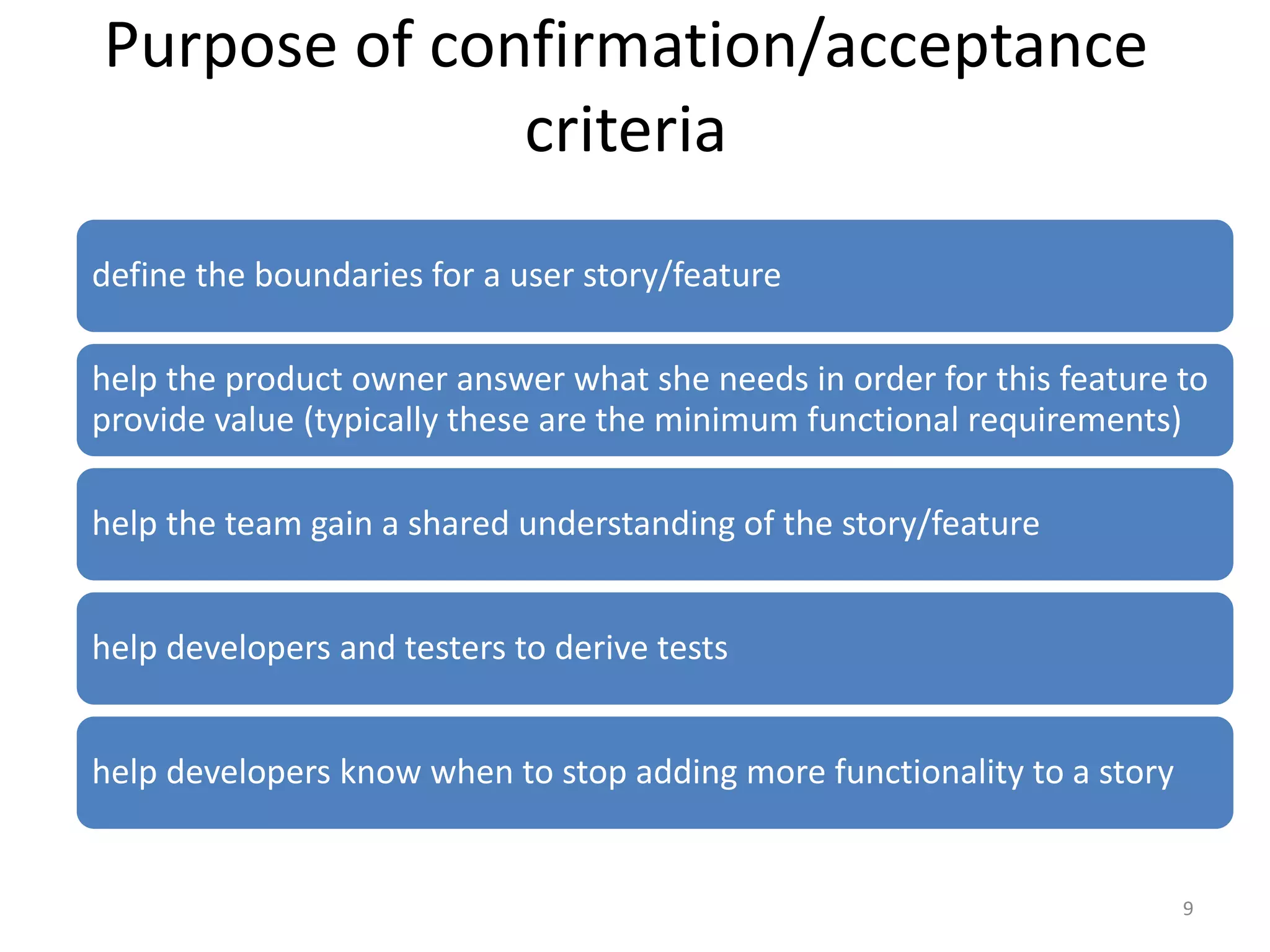
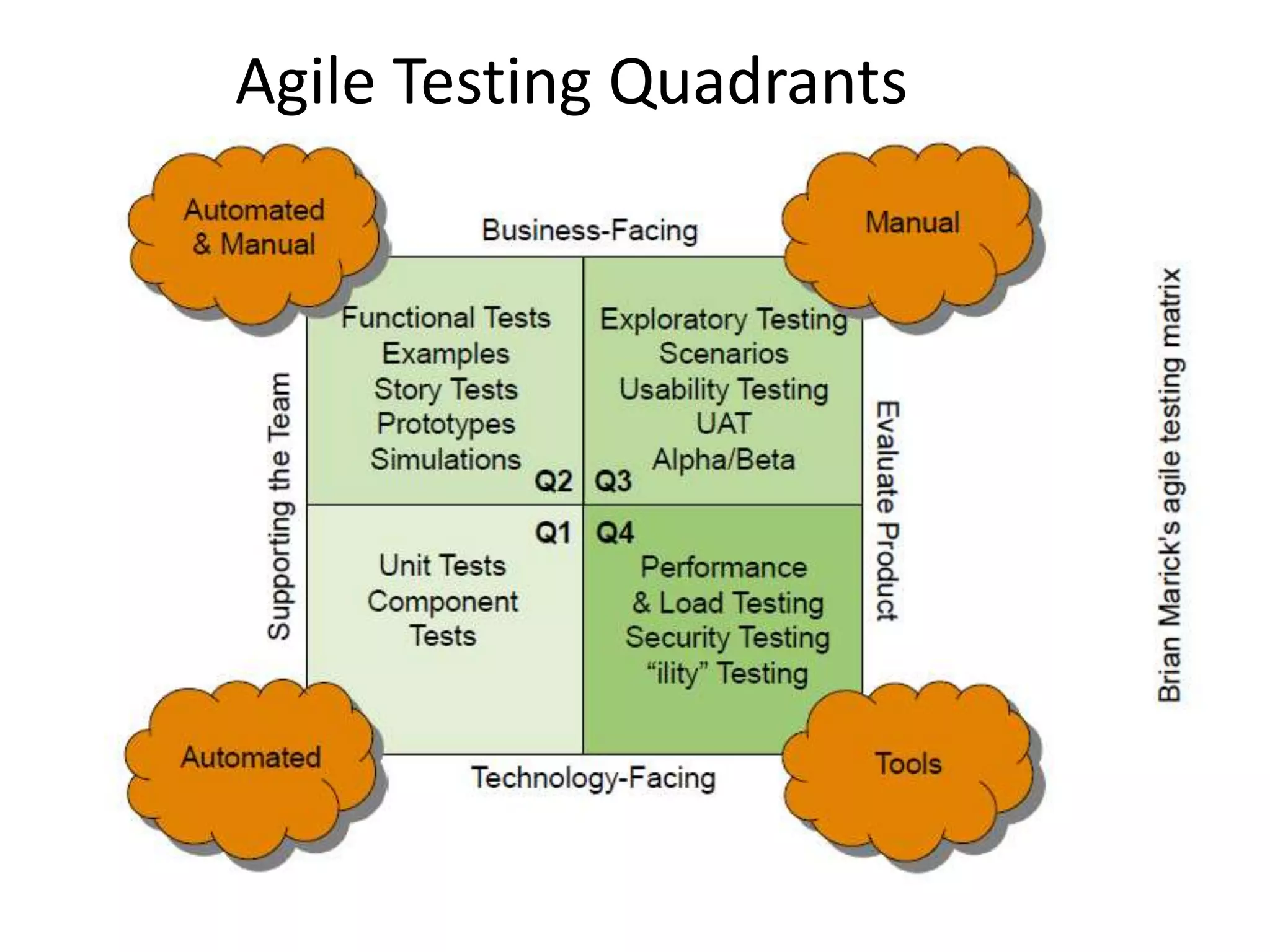
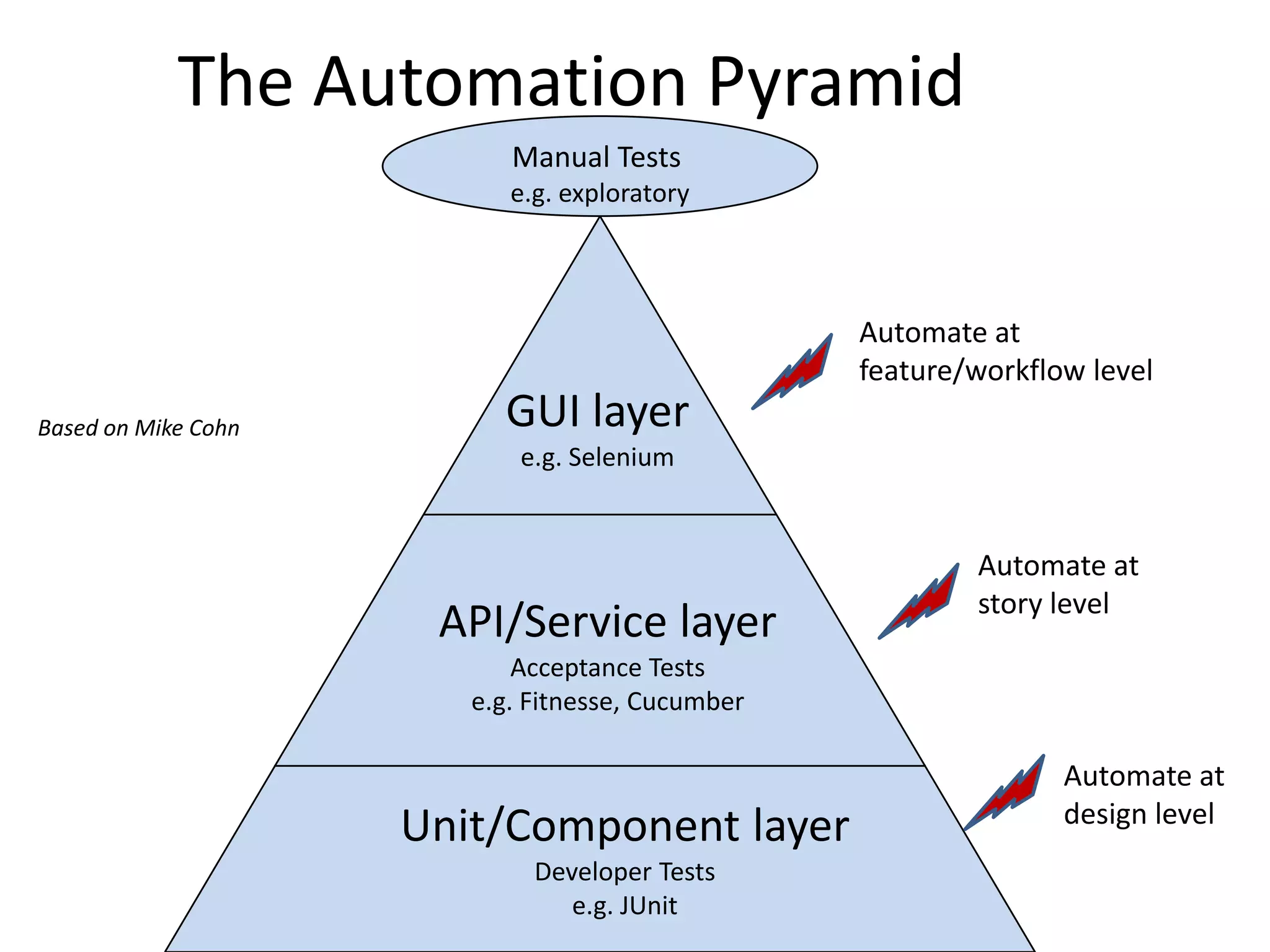
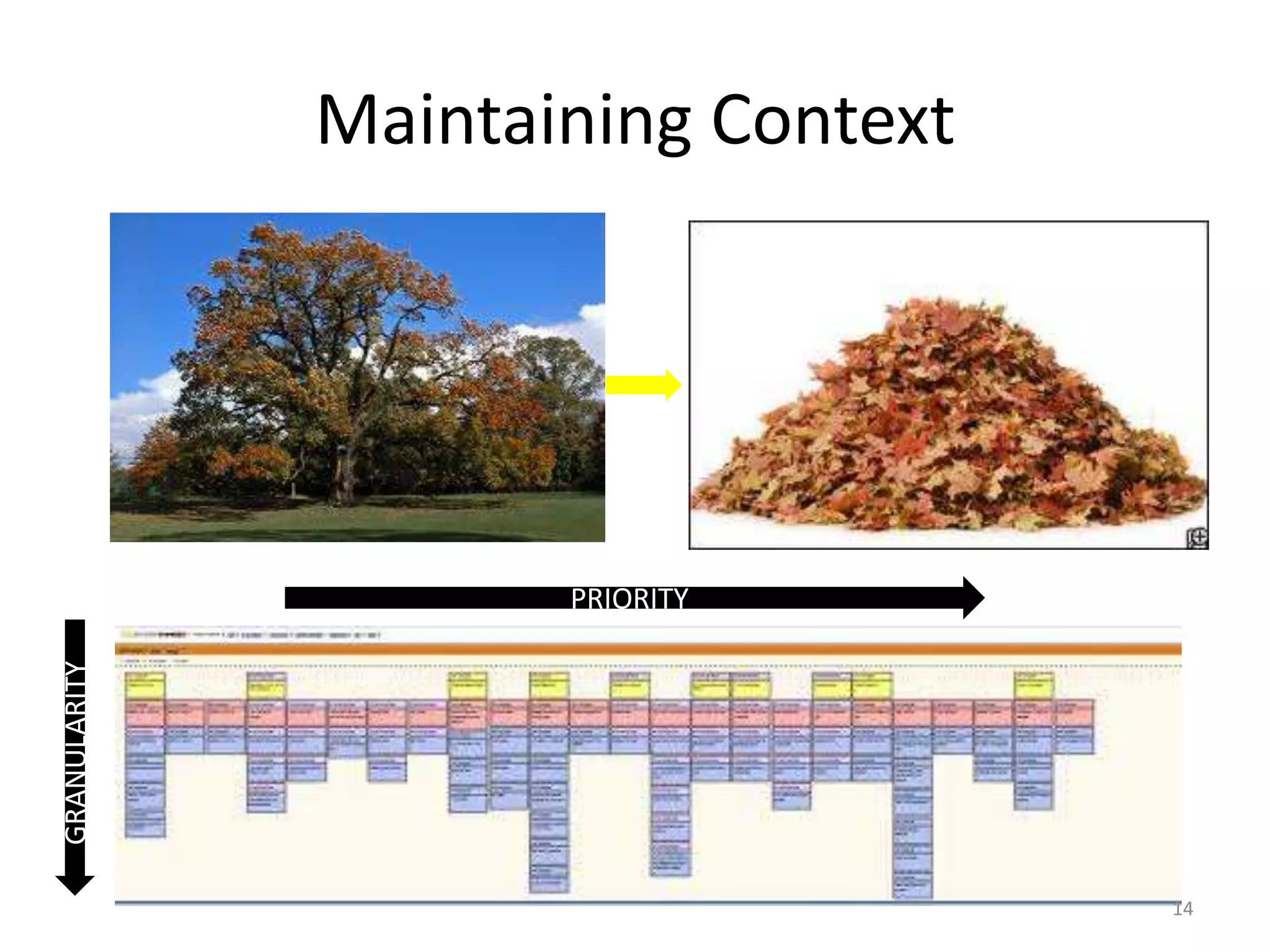
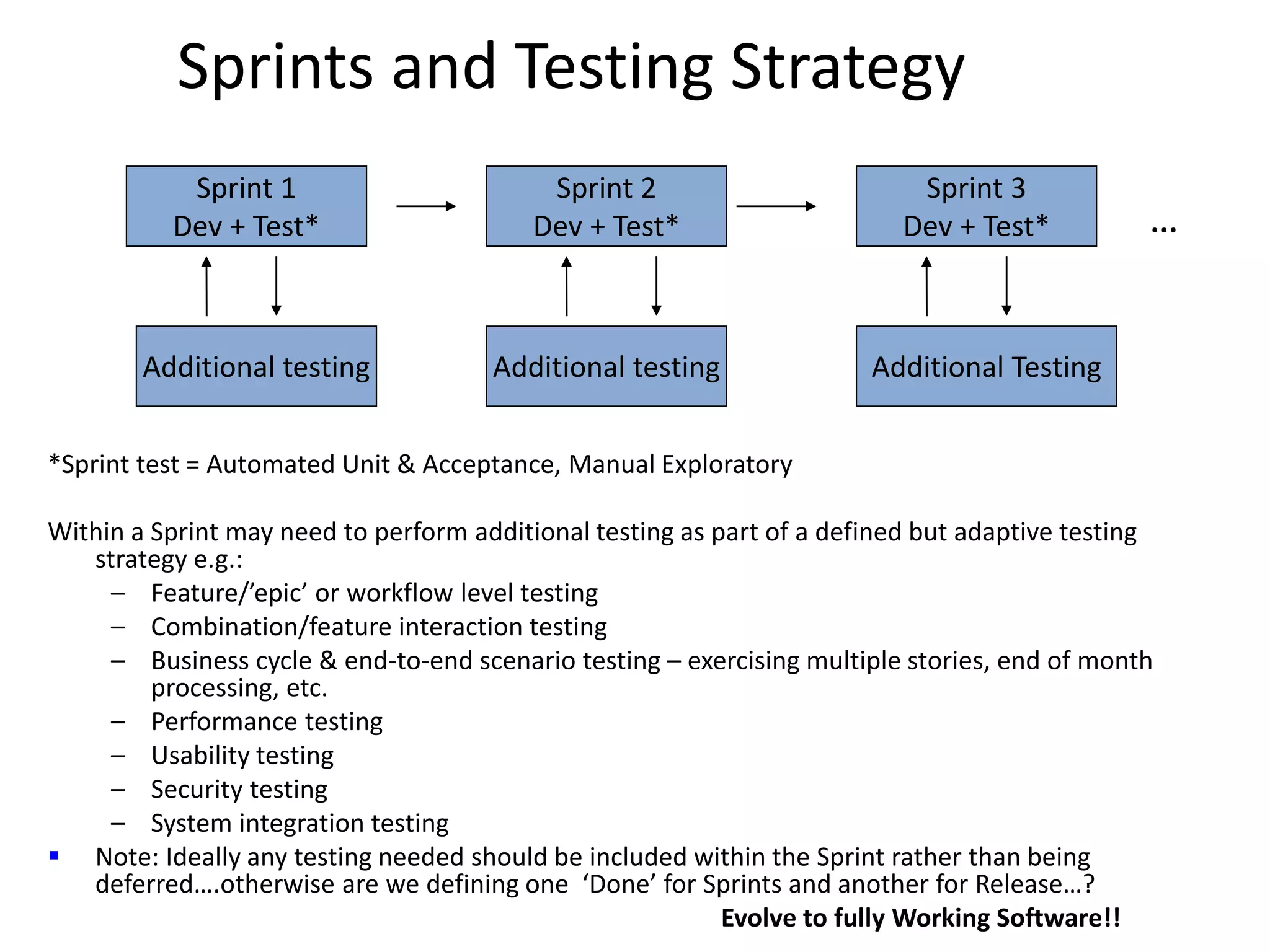
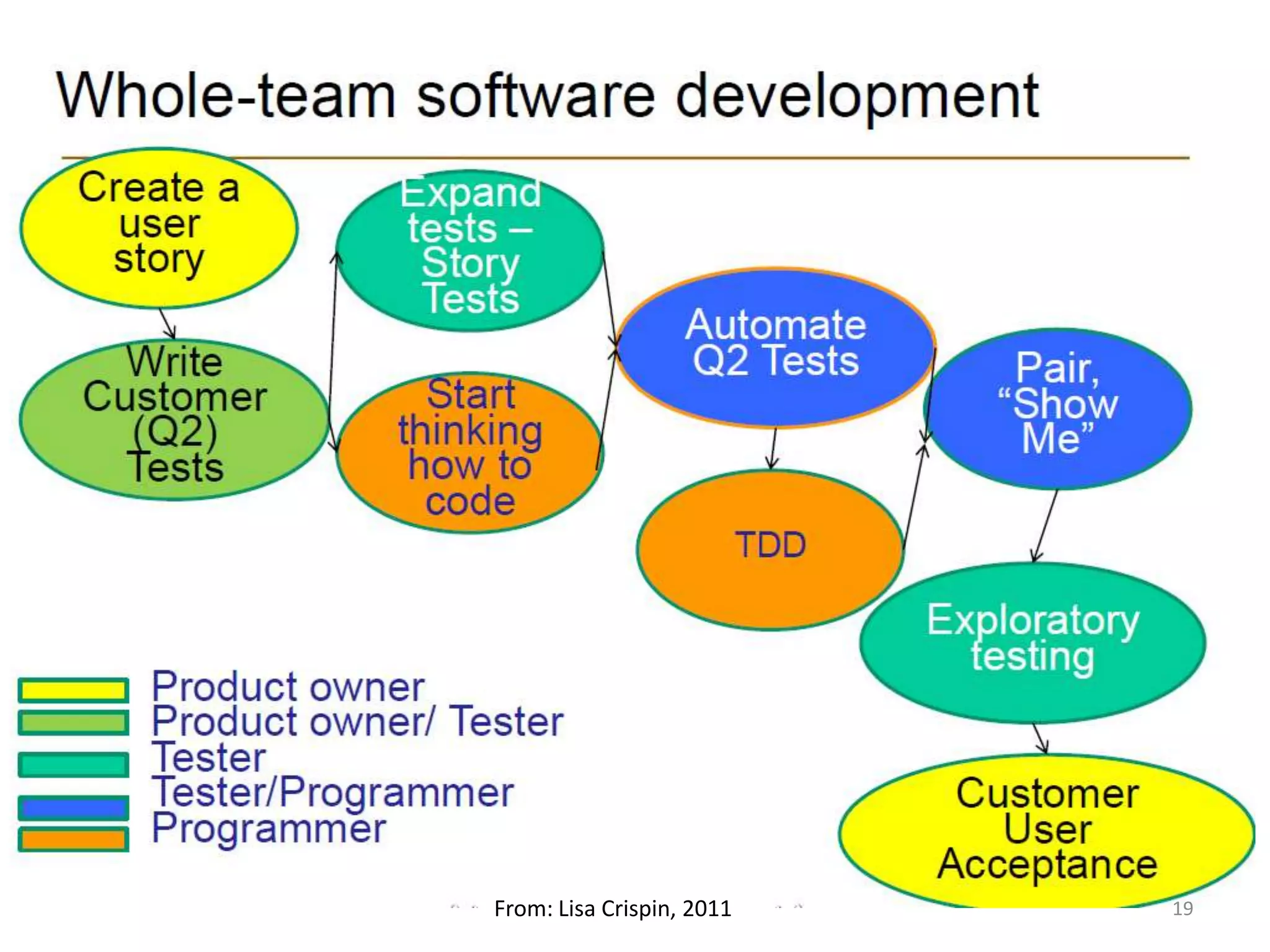
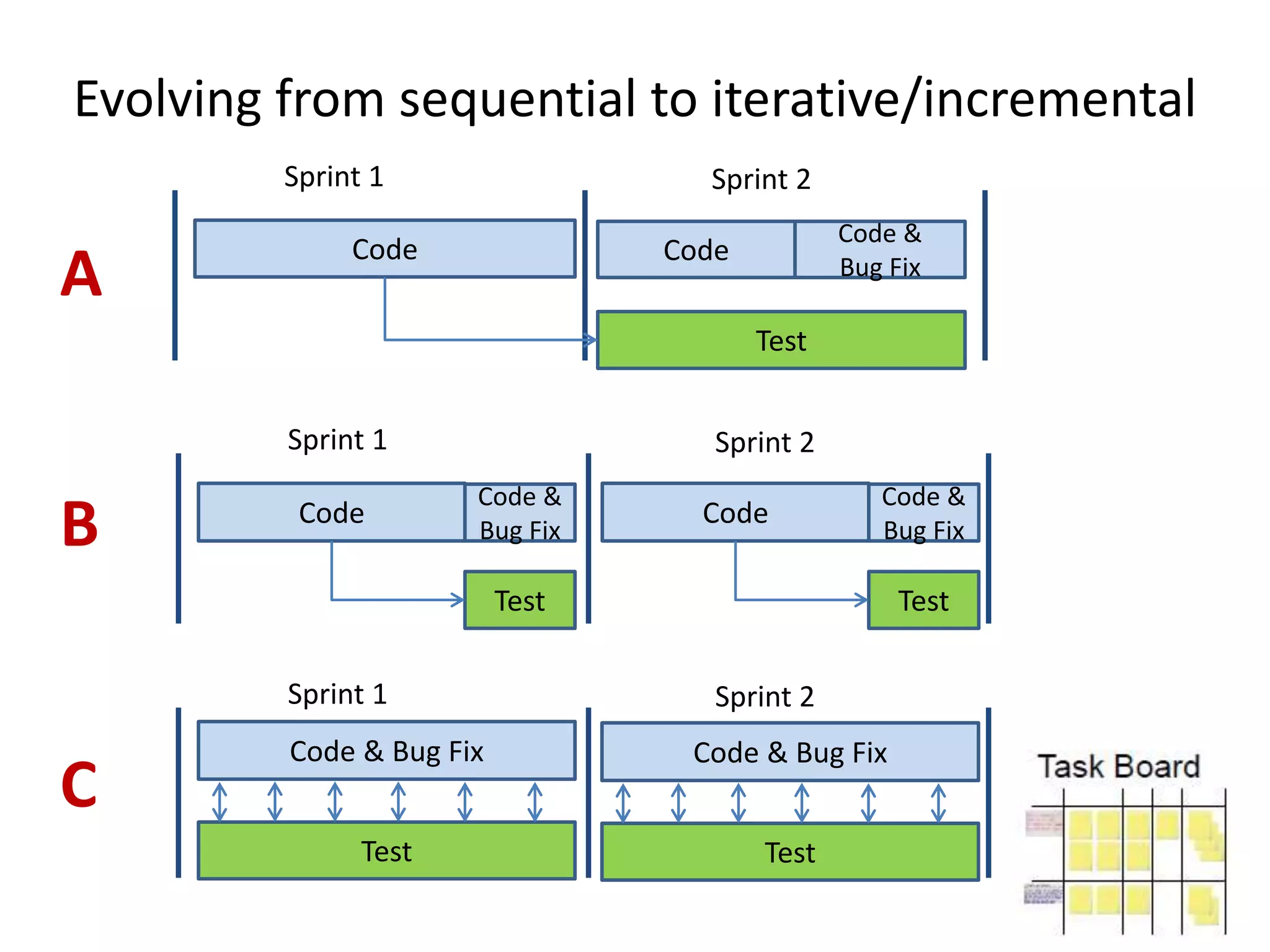
The document outlines agile testing services provided by Fran O'Hara and key methodologies including Scrum, XP, and Kanban. It emphasizes the integration of testing and development, early feedback, and the importance of setting clear acceptance criteria and user stories. Additionally, it discusses the evolving role of testers and developers in agile environments to ensure continuous communication, validation of requirements, and effective testing strategies.