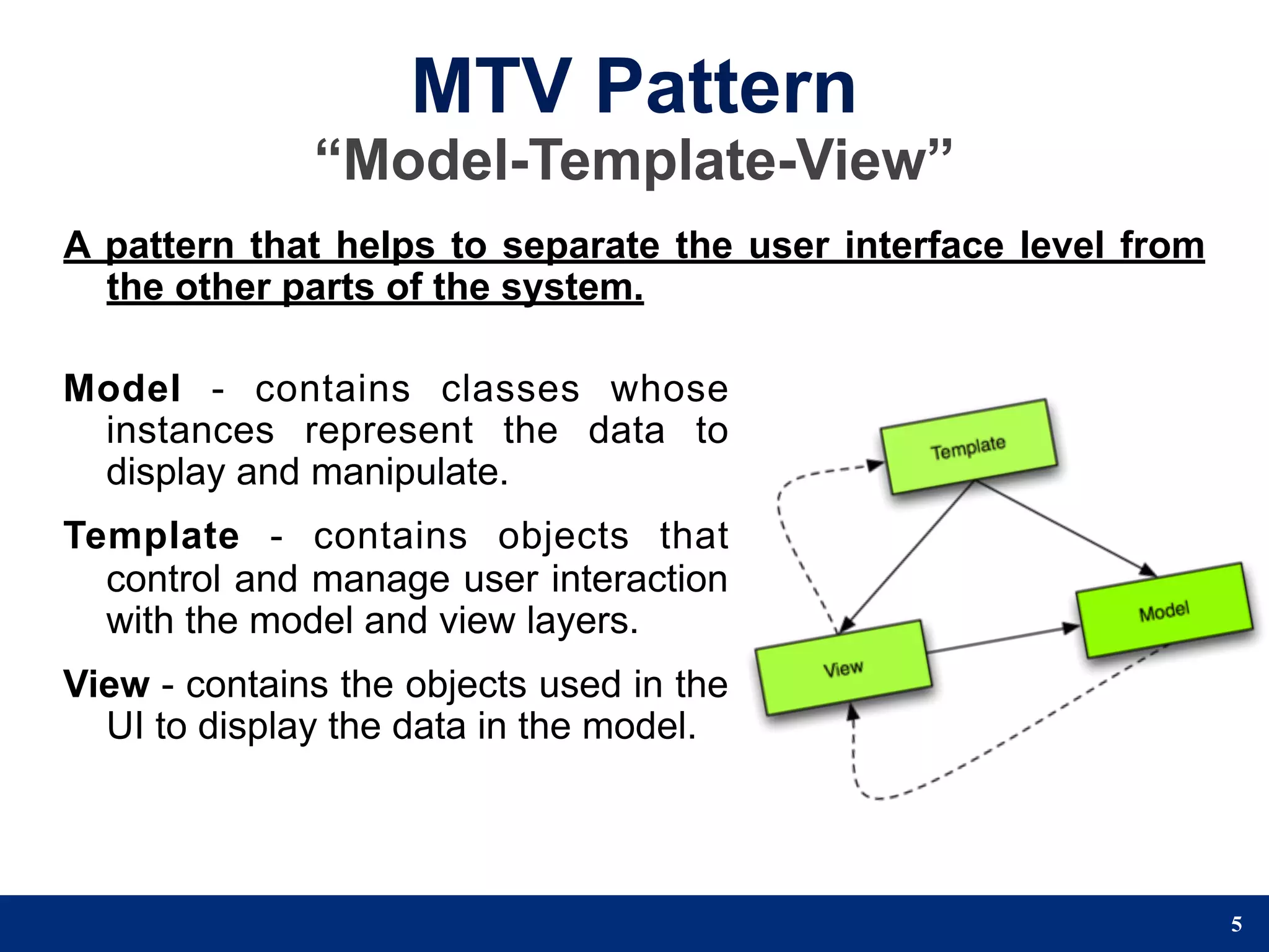
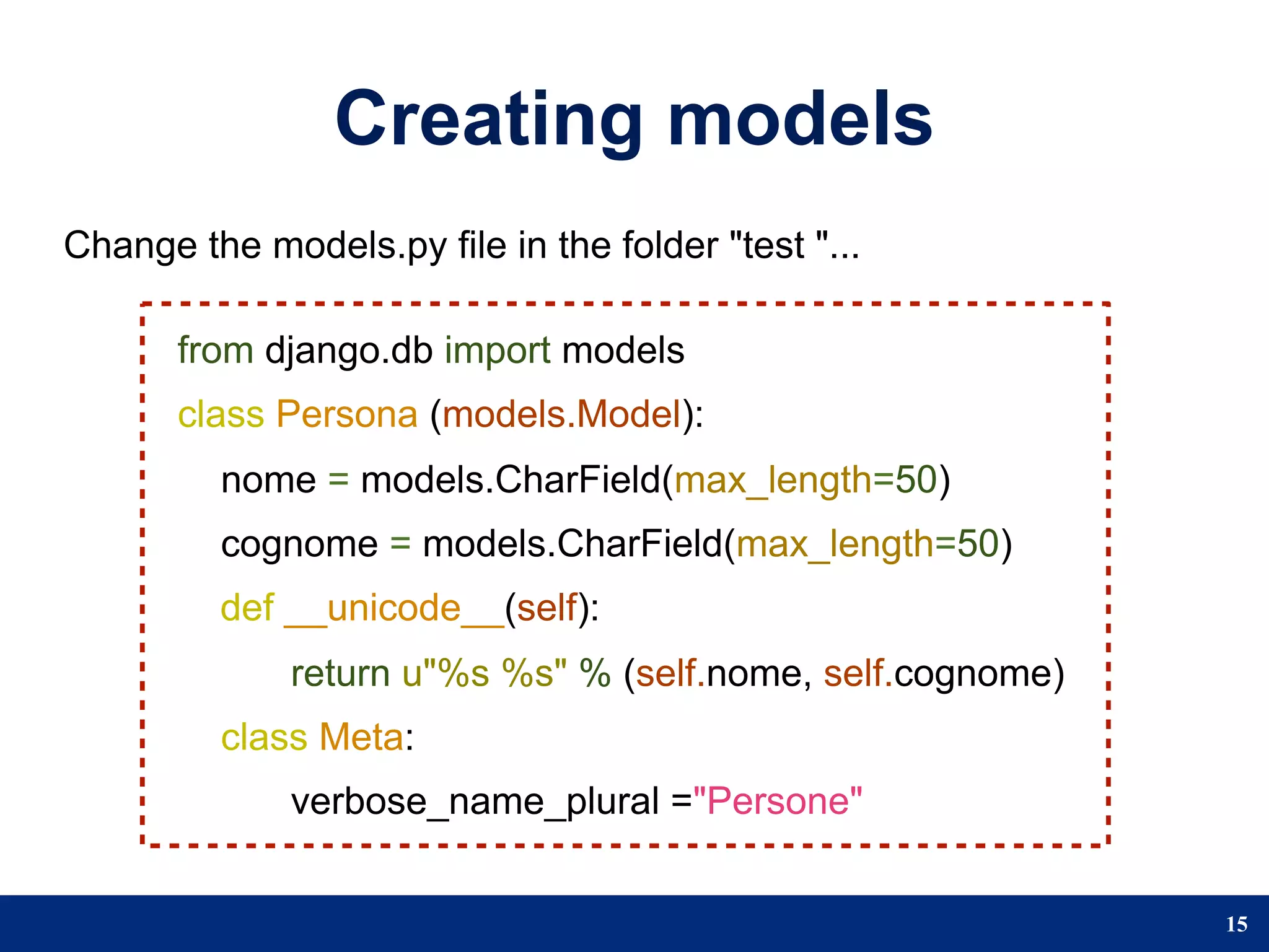
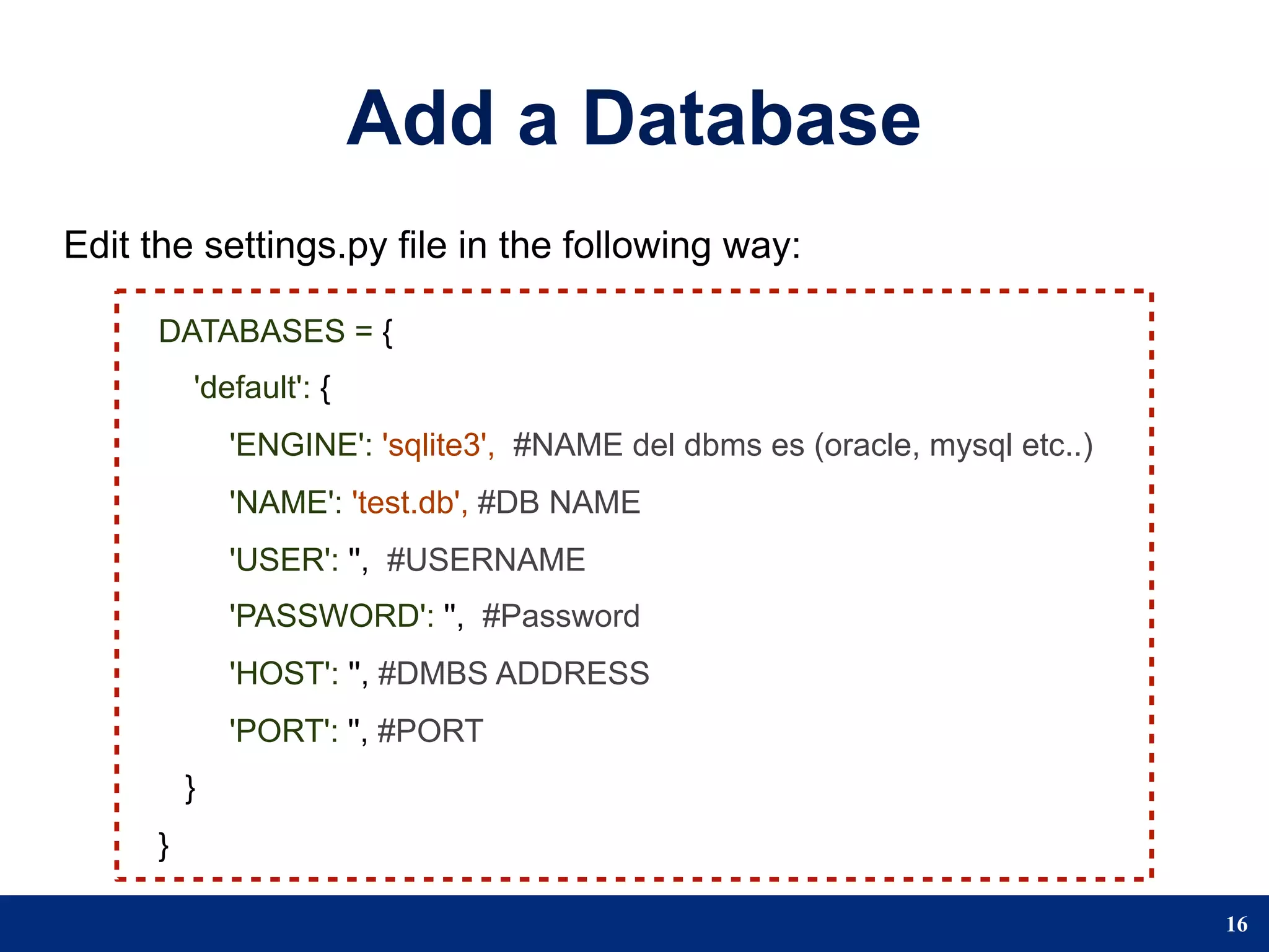
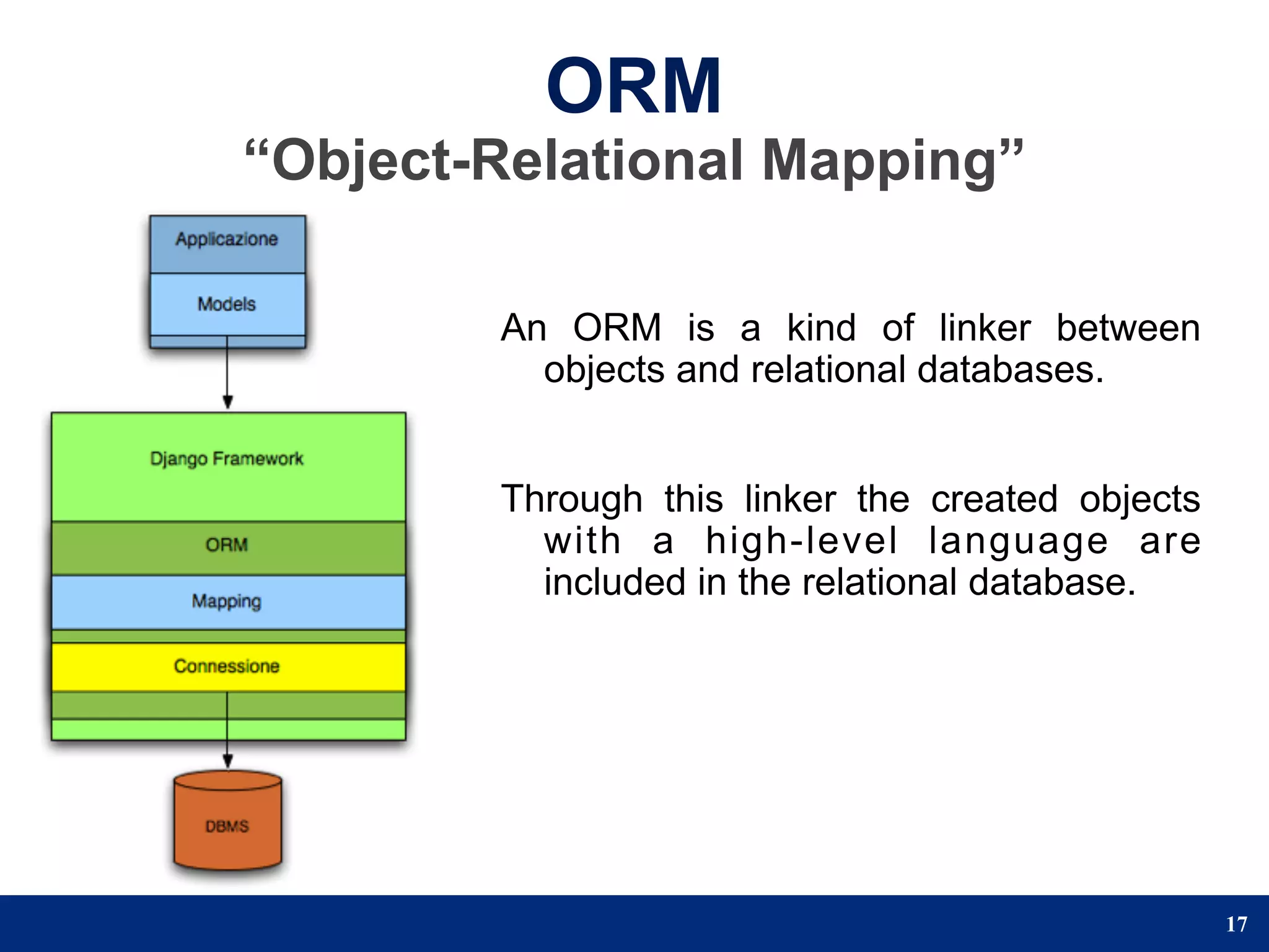
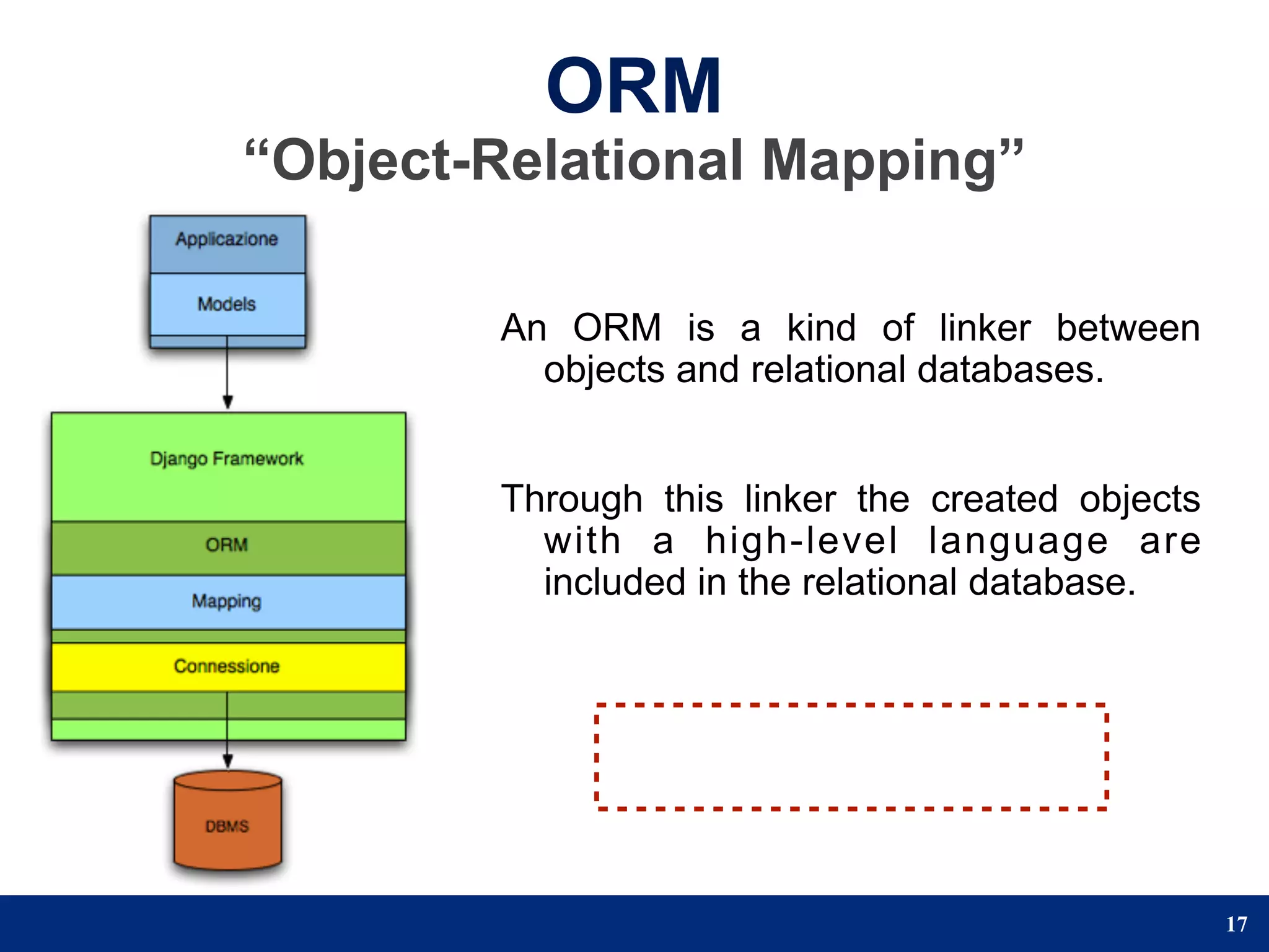
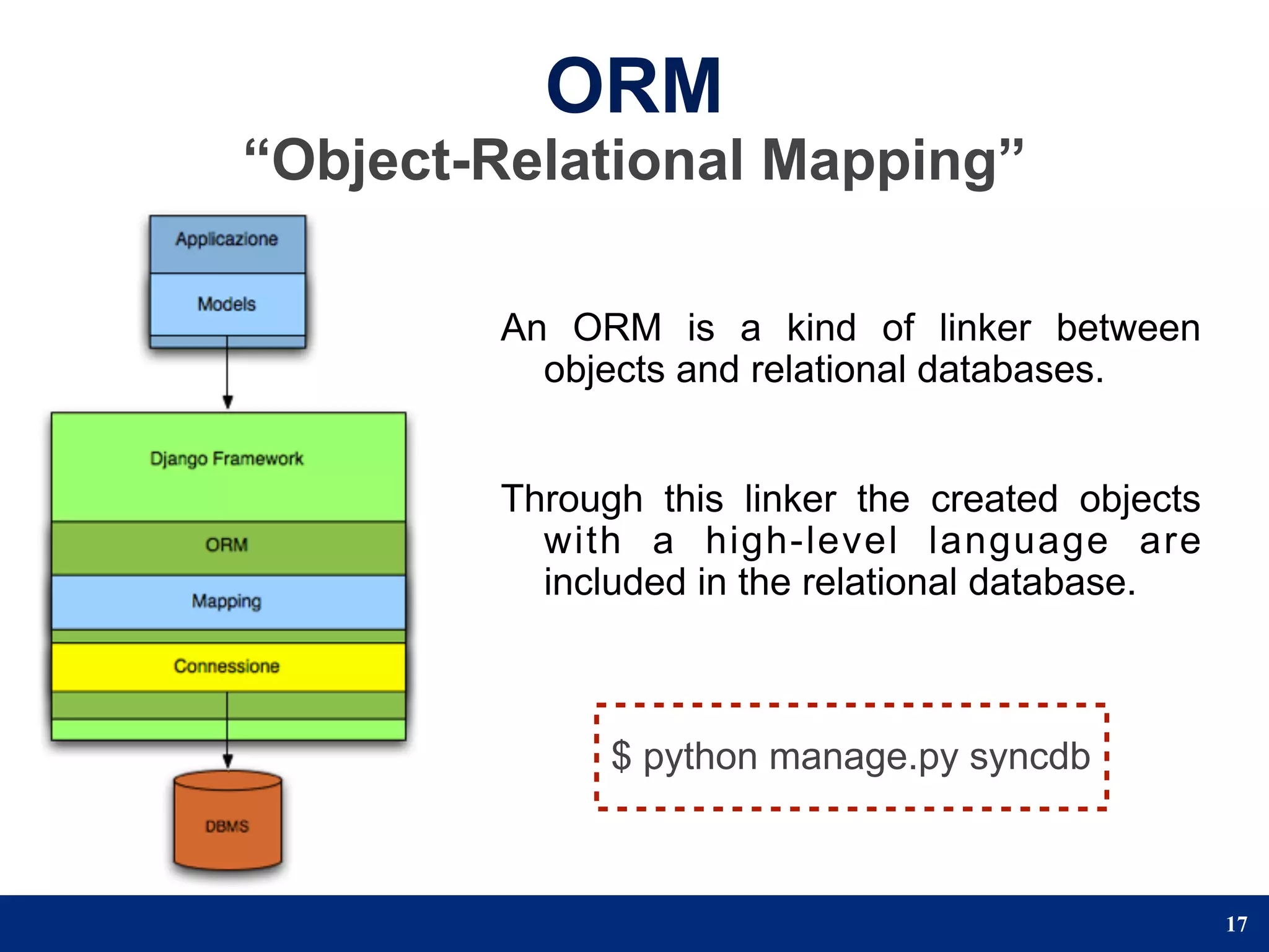
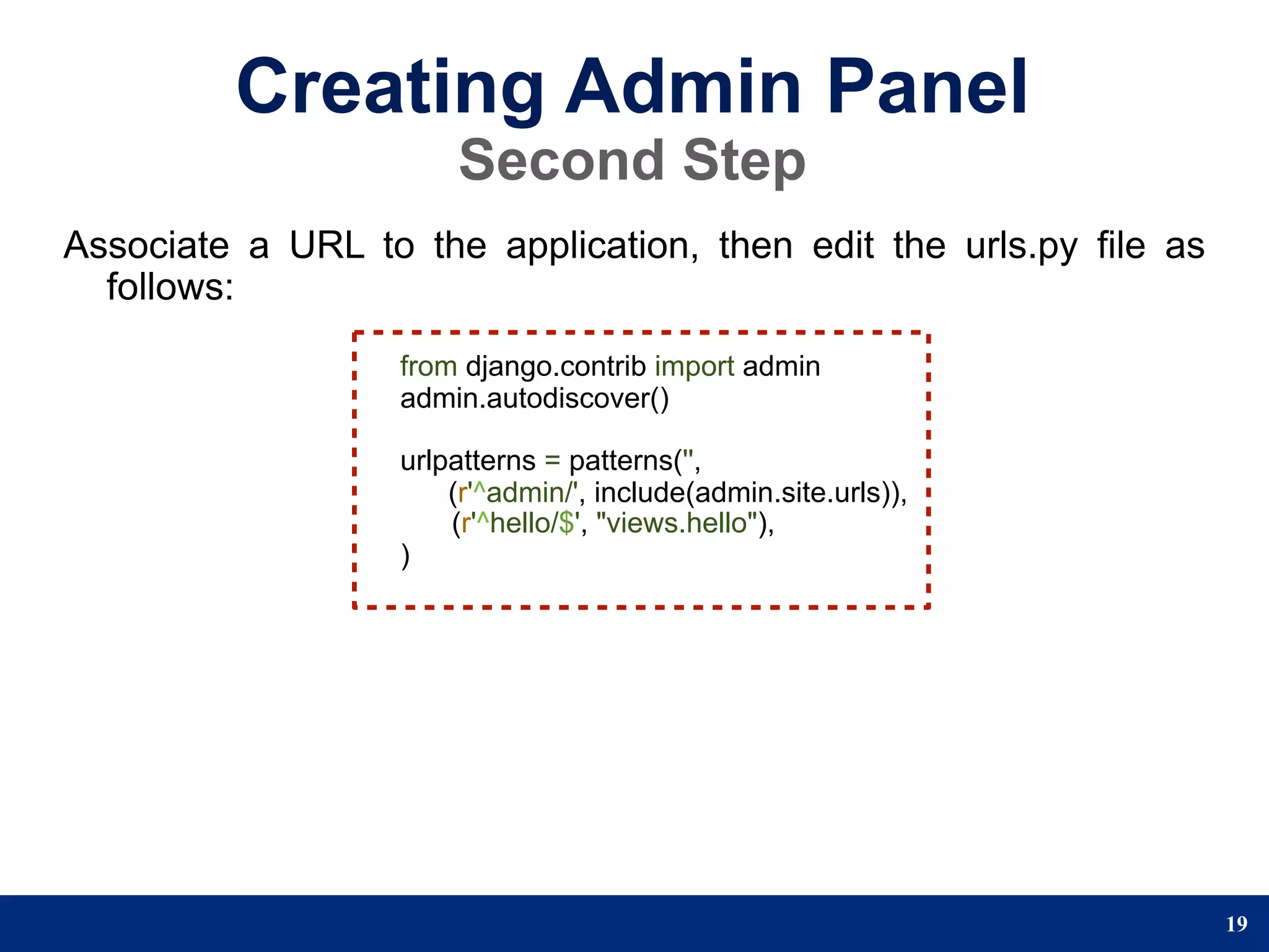
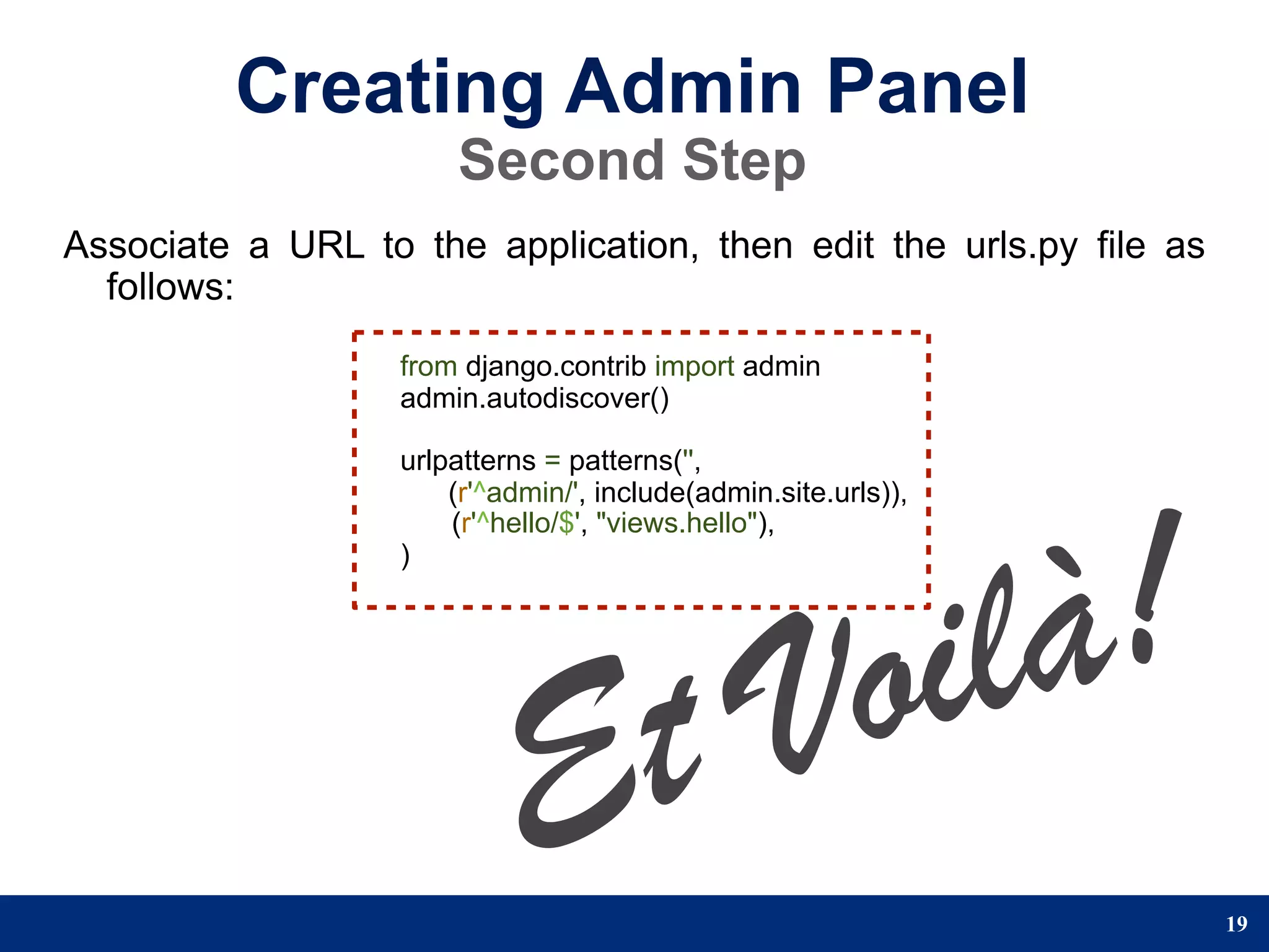
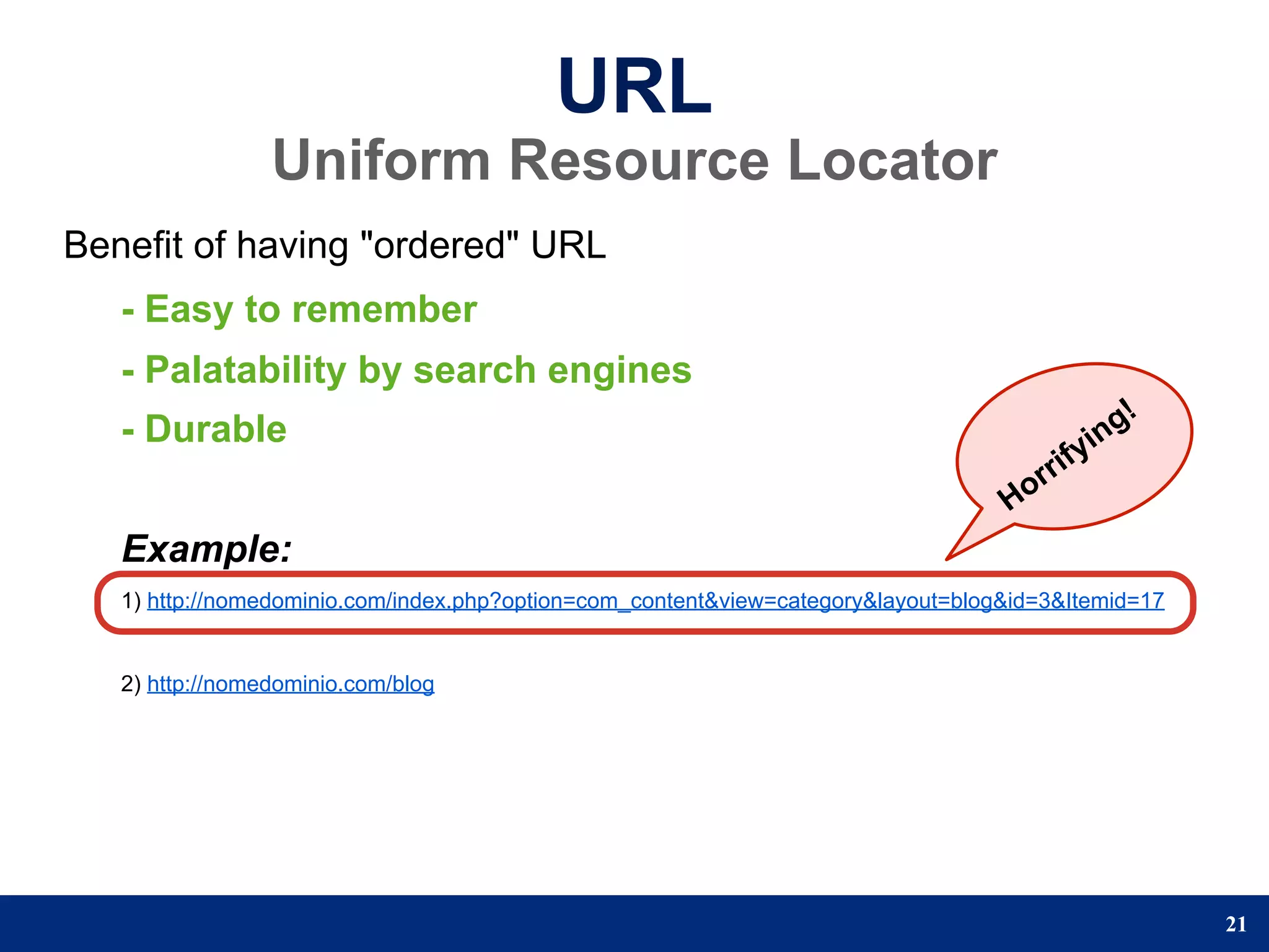
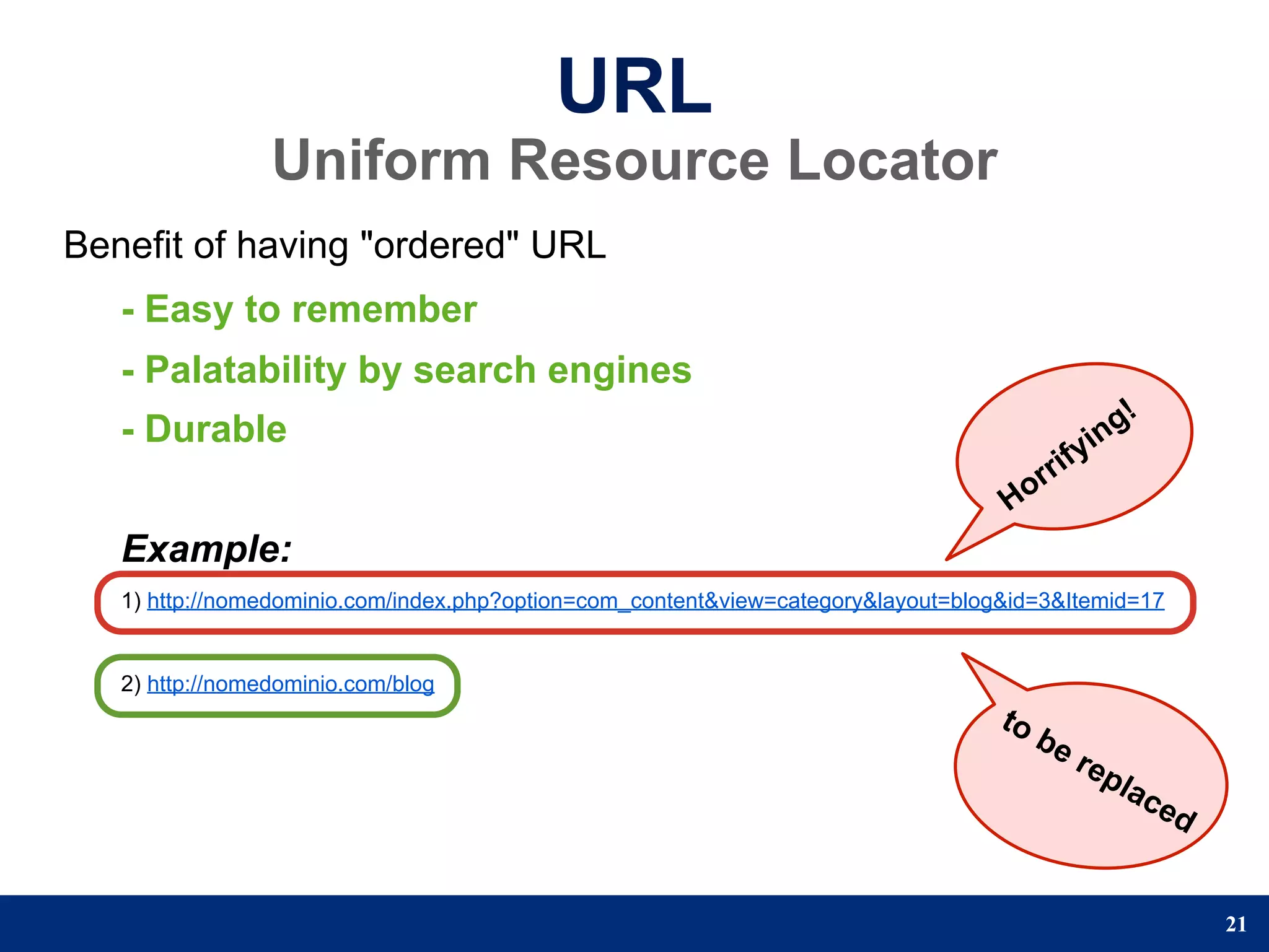
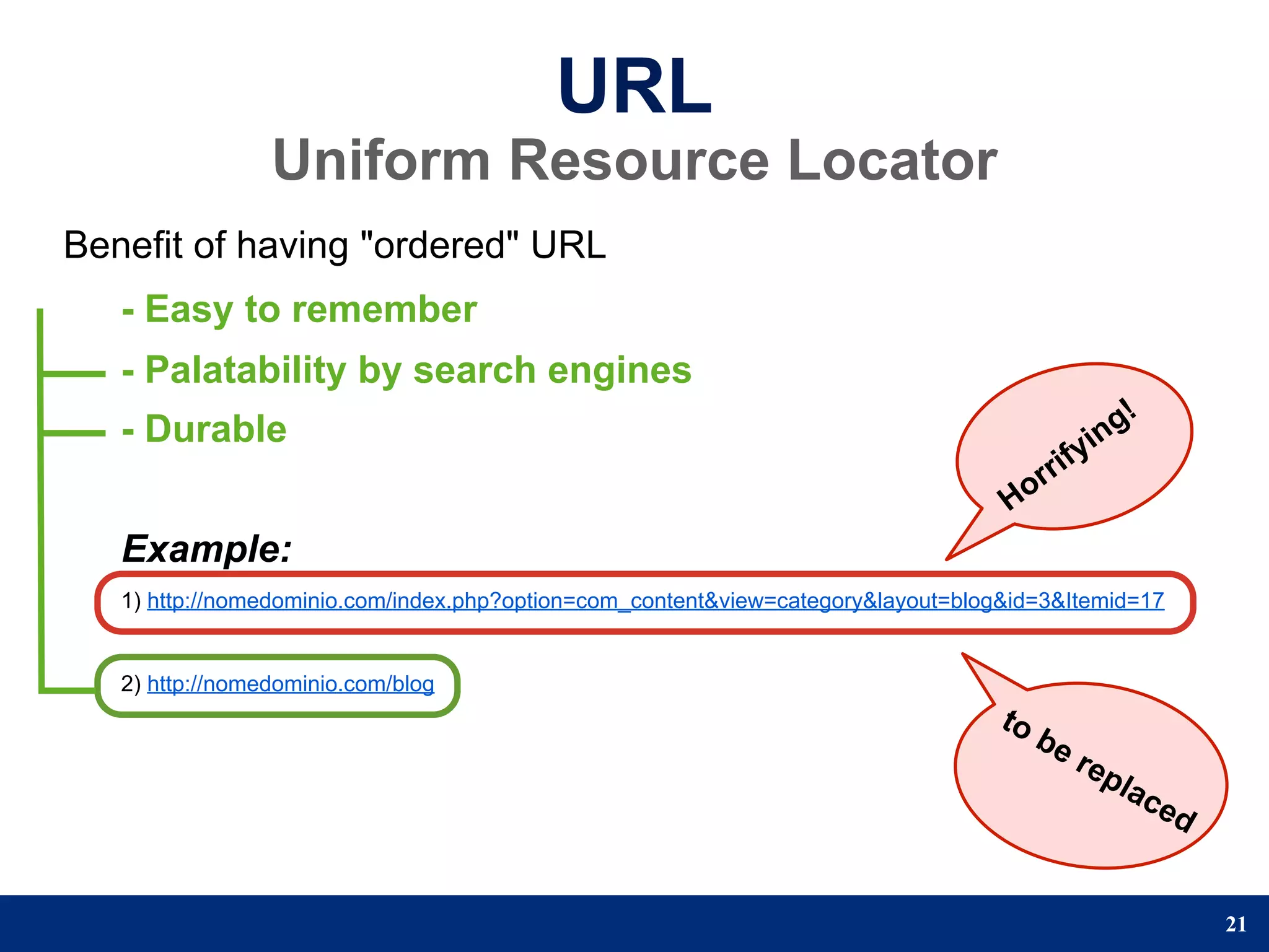
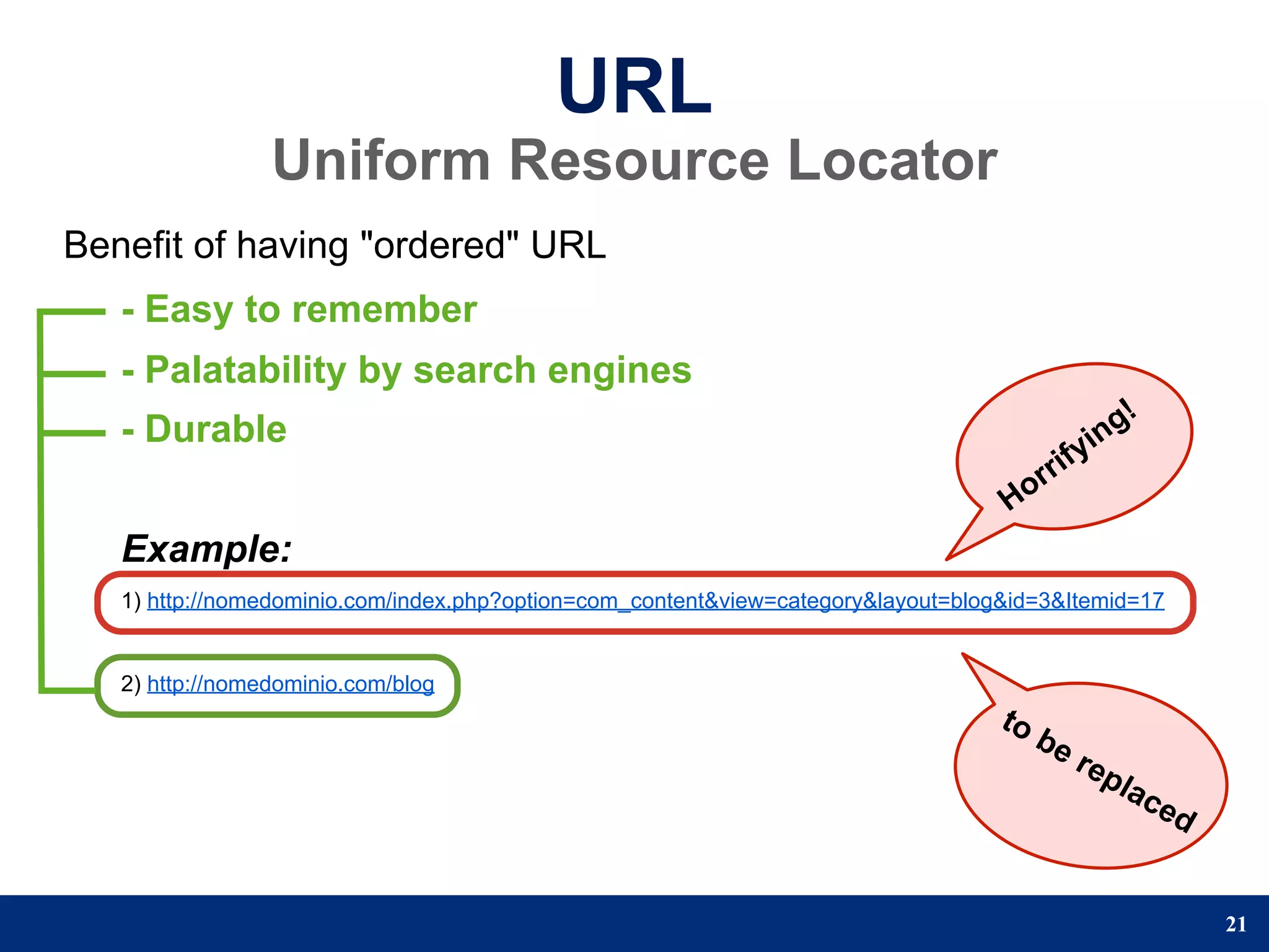
The document provides a step-by-step guide to developing a web application using the Django framework. It introduces Django and describes the Model-Template-View pattern. It then outlines the steps to setup a Django project, create models, add a database, and setup the admin panel. The steps include creating applications, models, associating a URL pattern to views, and registering the admin application.