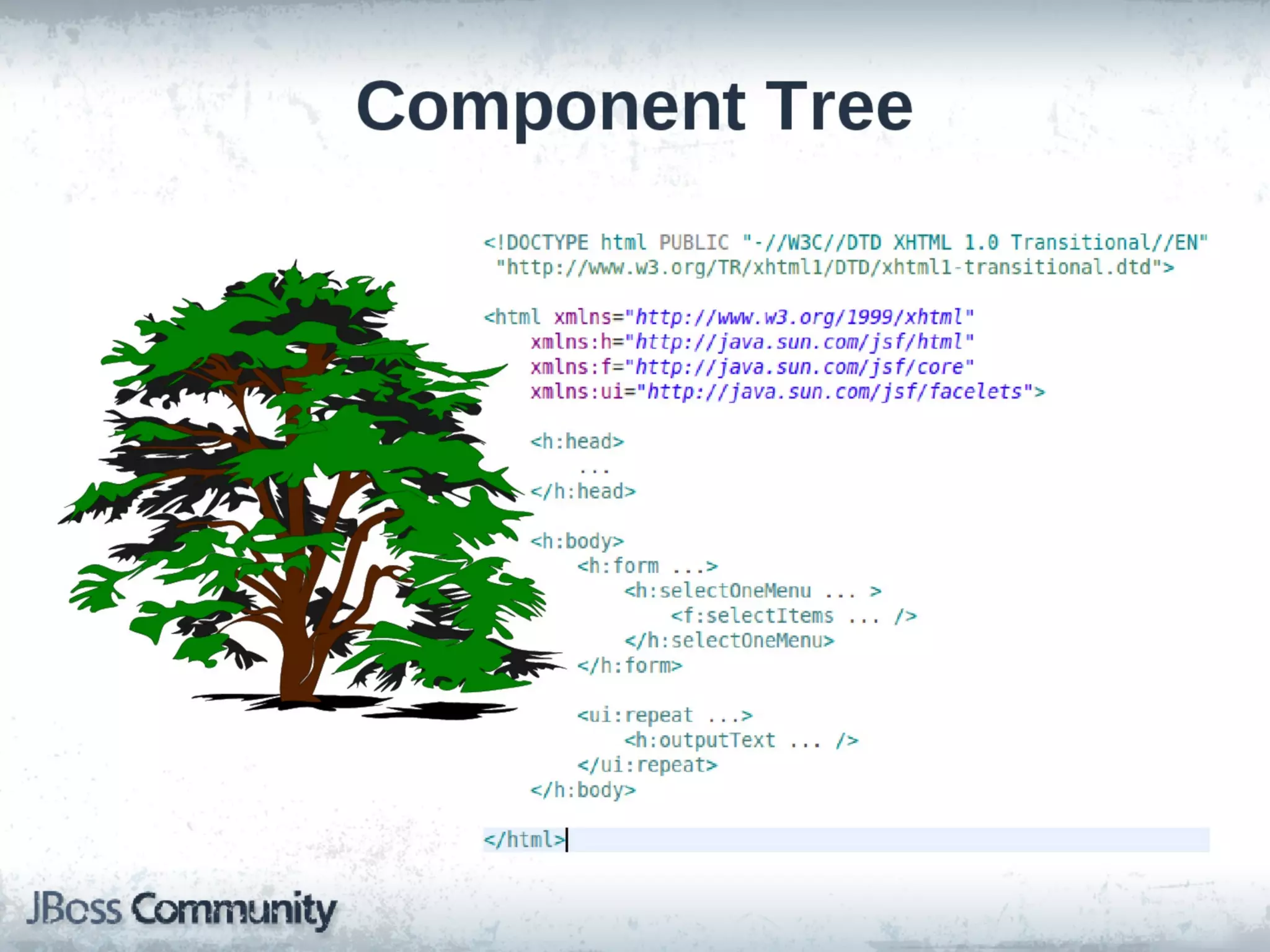
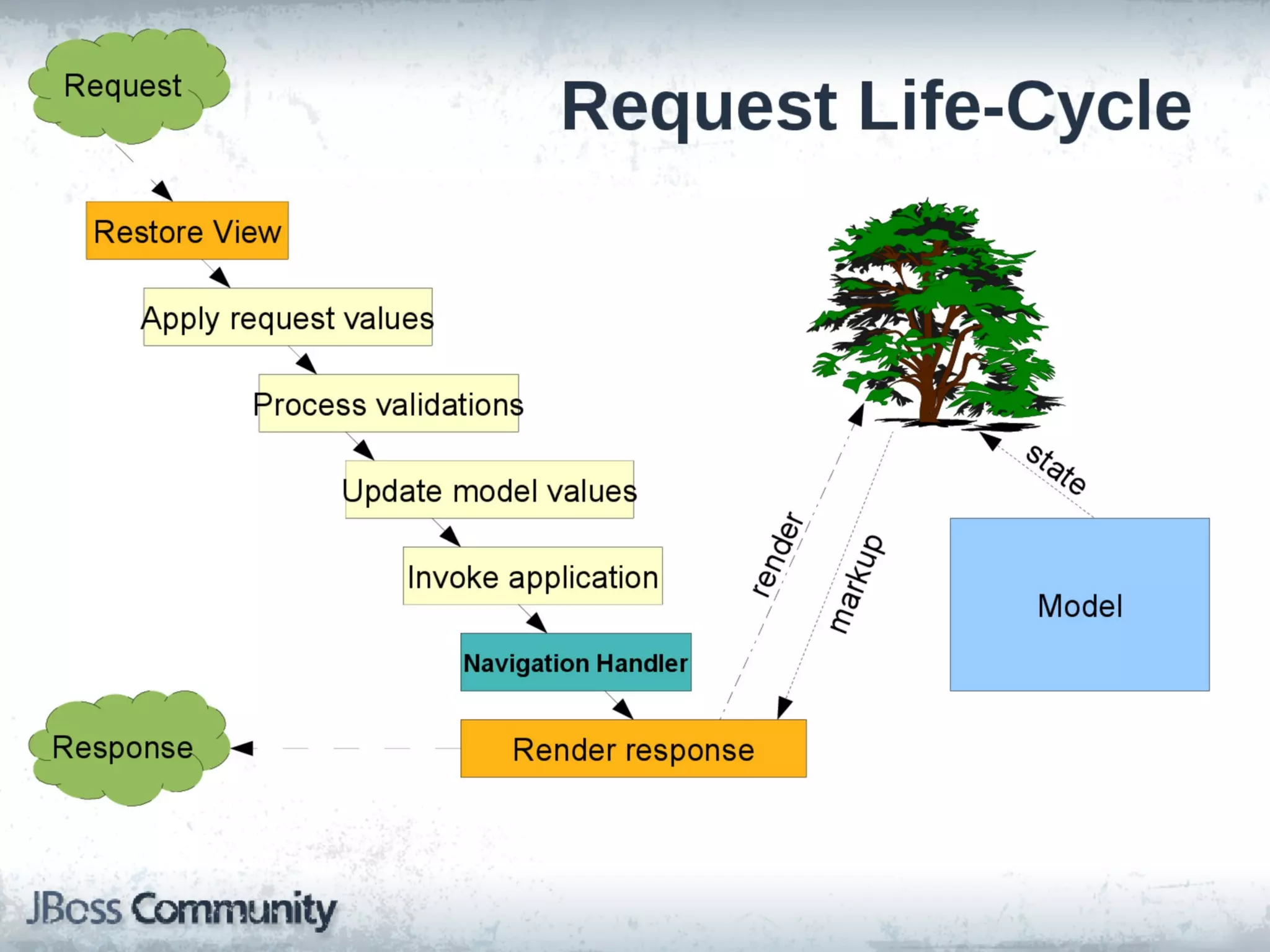
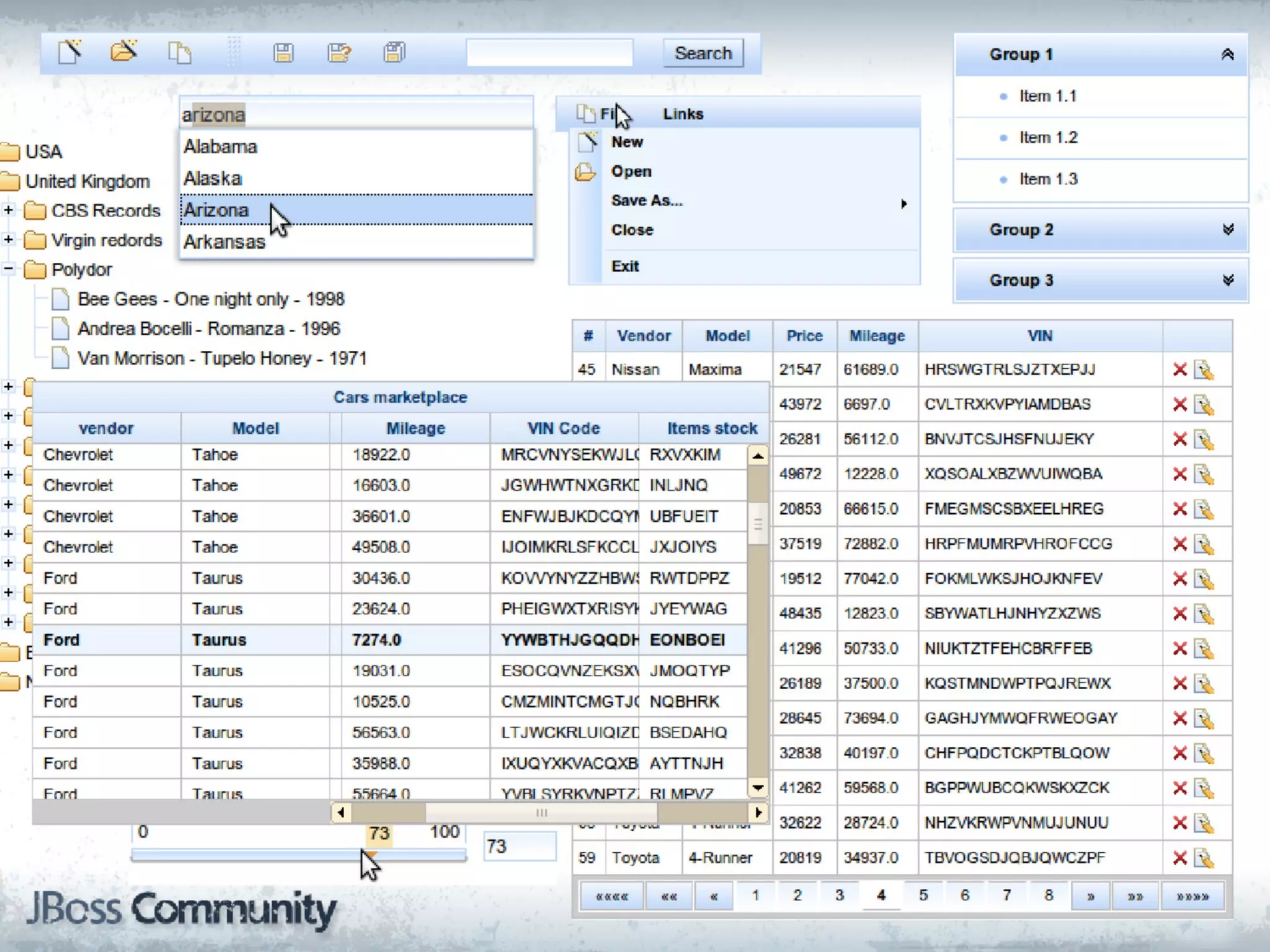
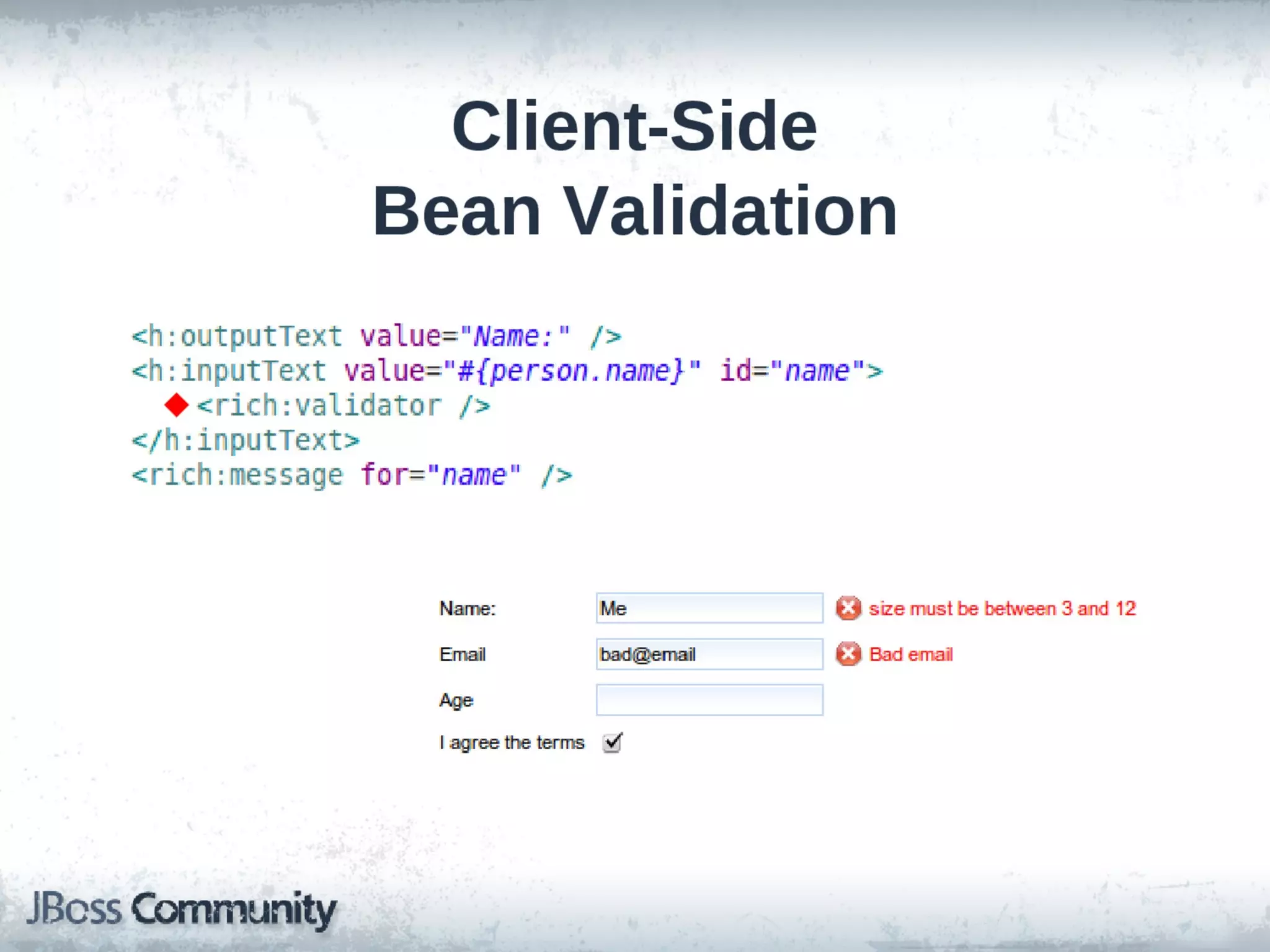
This document discusses various web technologies in Java EE including JSF 2.2, JAX-RS 2.0, JSON-P, and WebSocket. It provides an overview of client-side vs server-side web approaches, describes the capabilities and goals of each technology, and demonstrates examples of using JAX-RS for RESTful services, the JSON processing APIs, and WebSocket. The document is presented by Lukas Fryc, a software engineer at Red Hat interested in Java EE, HTML5, and Web Components.




















![Method Parameters • Session • Implicitly supported types – String, byte[] – JsonArray, JsonObject • More types supported by Encoders](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-technologies-in-java-ee-131211082145-phpapp02/75/Web-Technologies-in-Java-EE-7-50-2048.jpg)