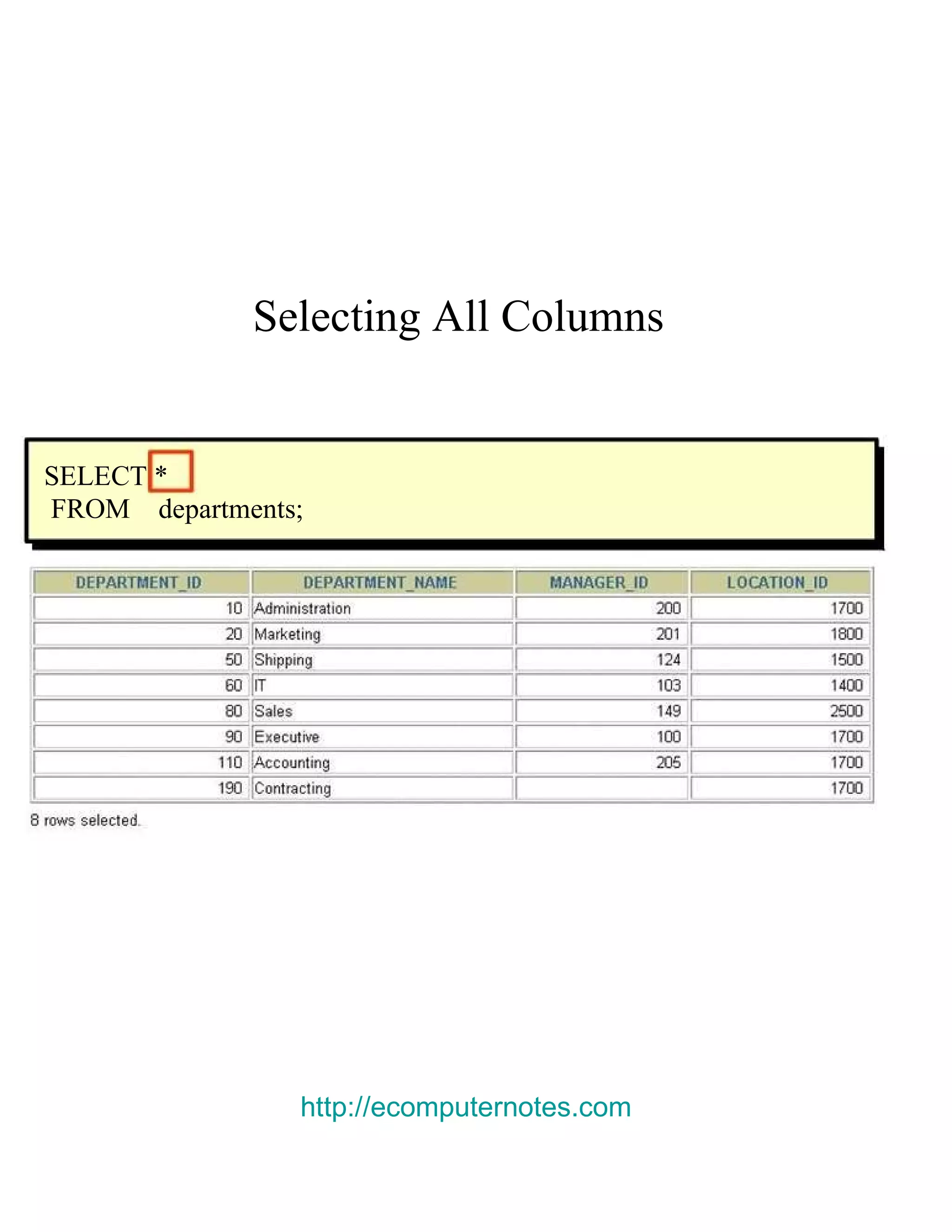
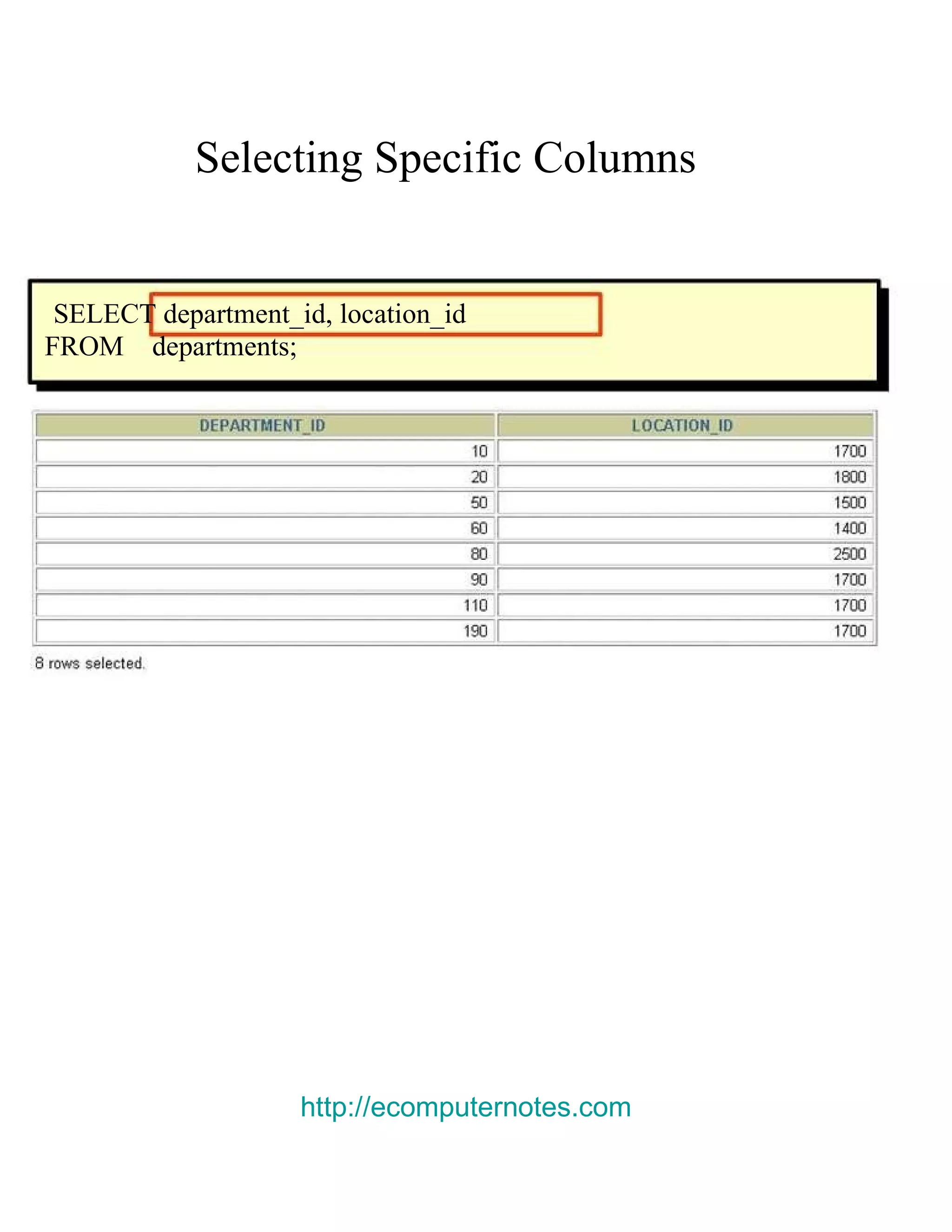
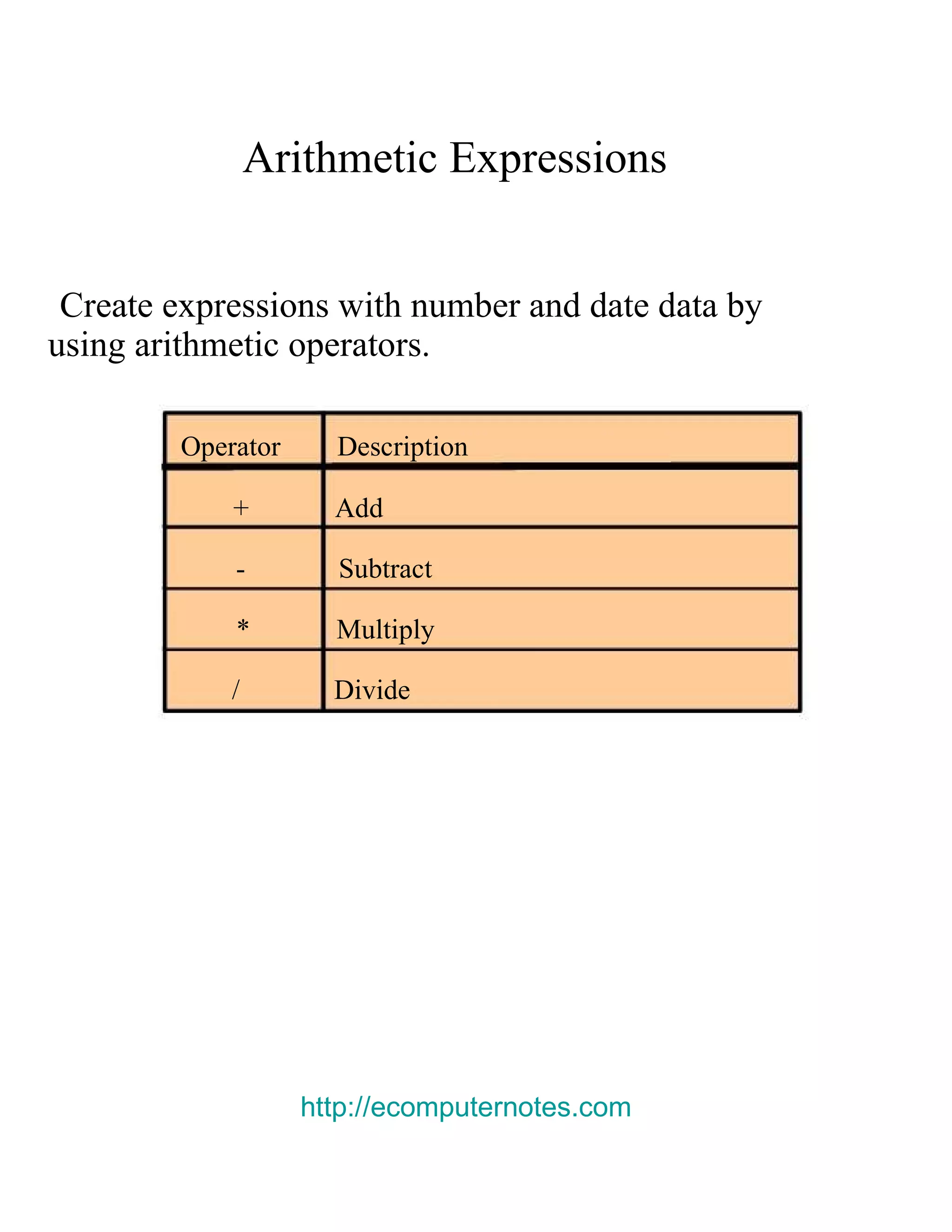
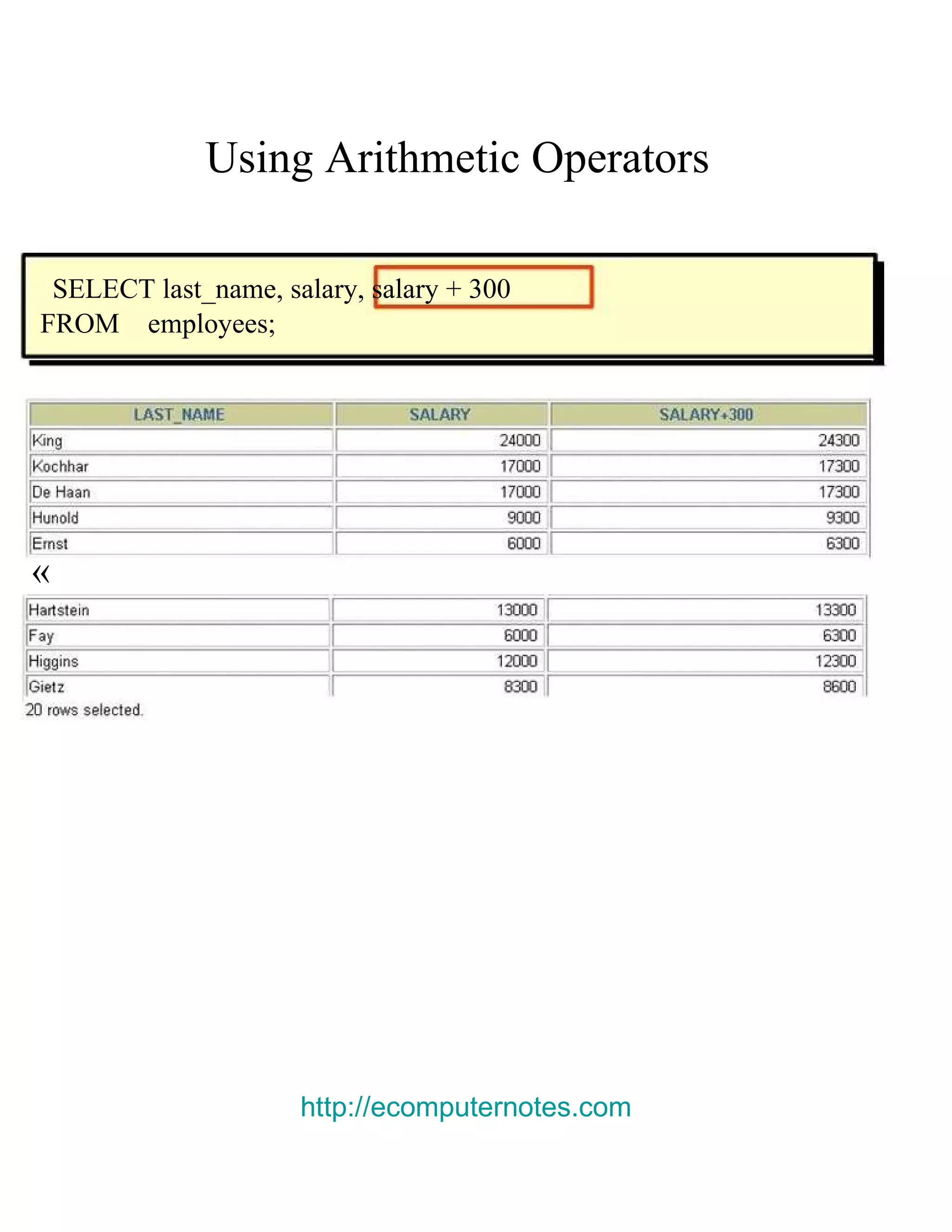
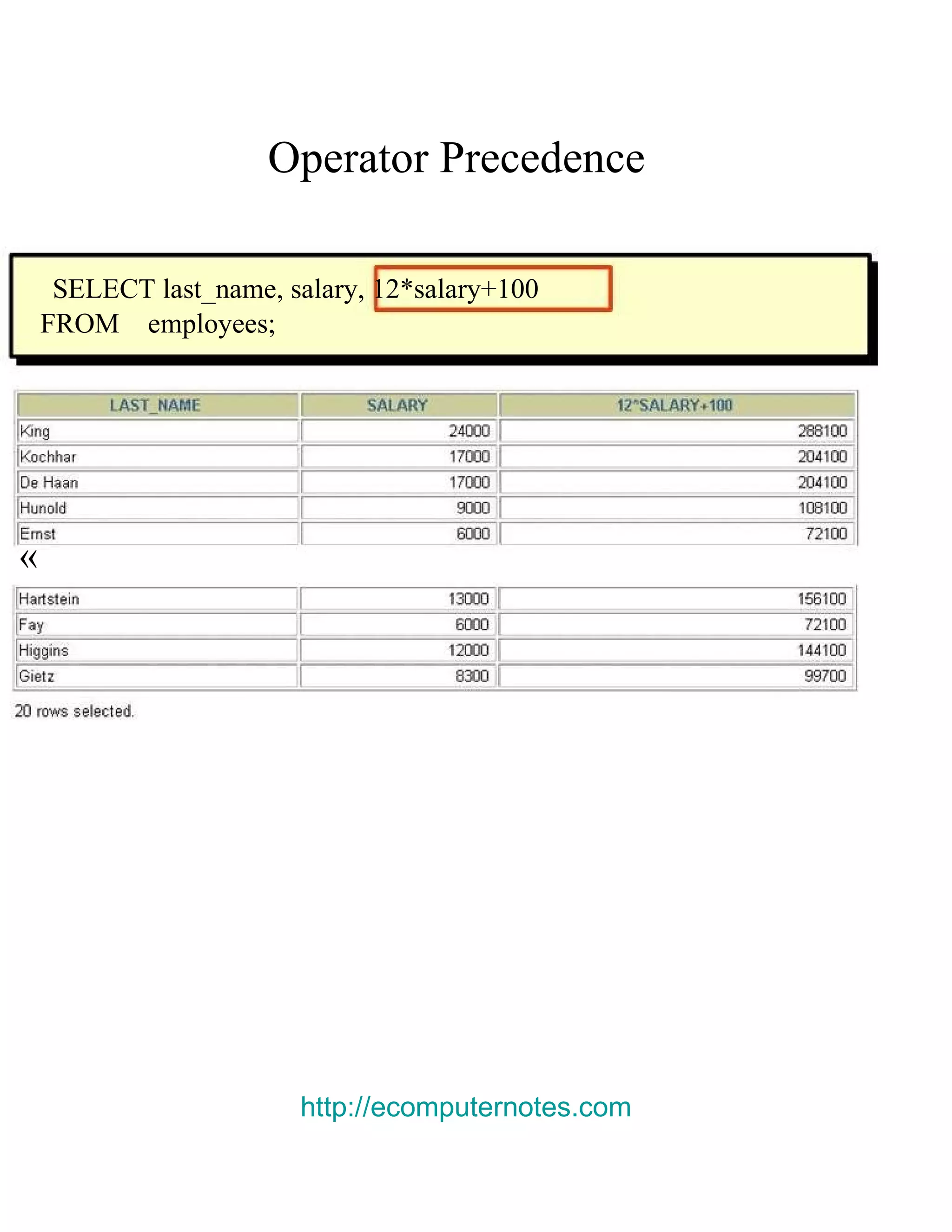
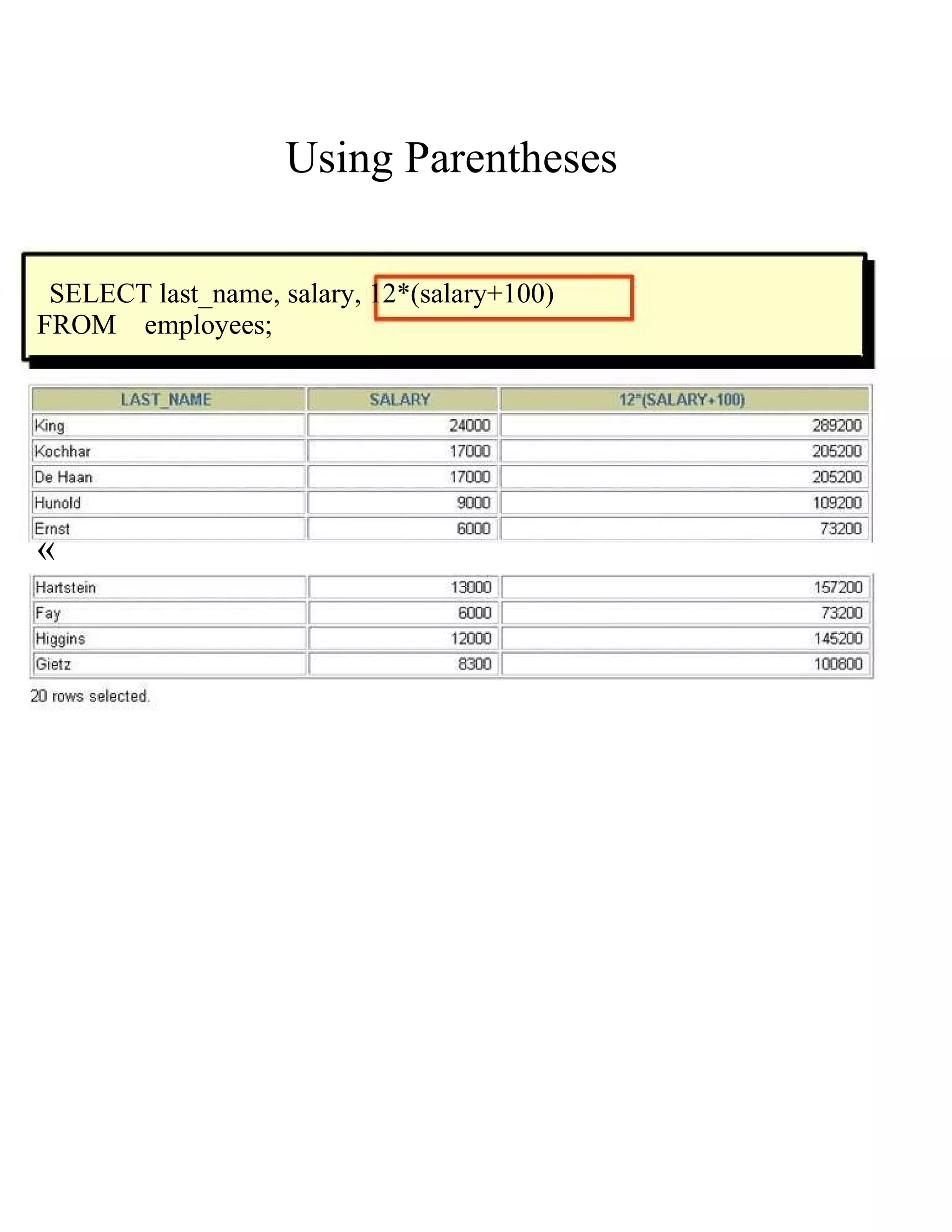
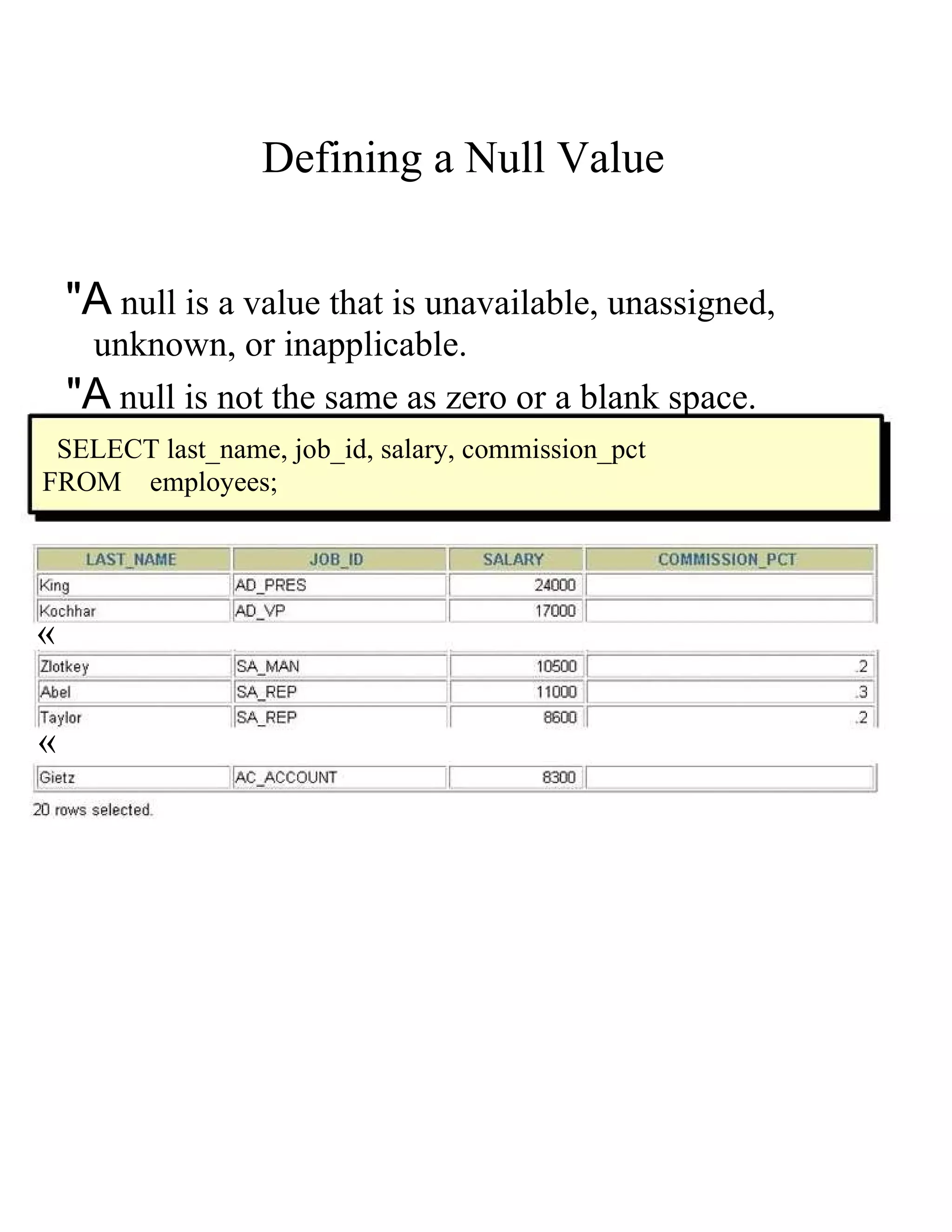
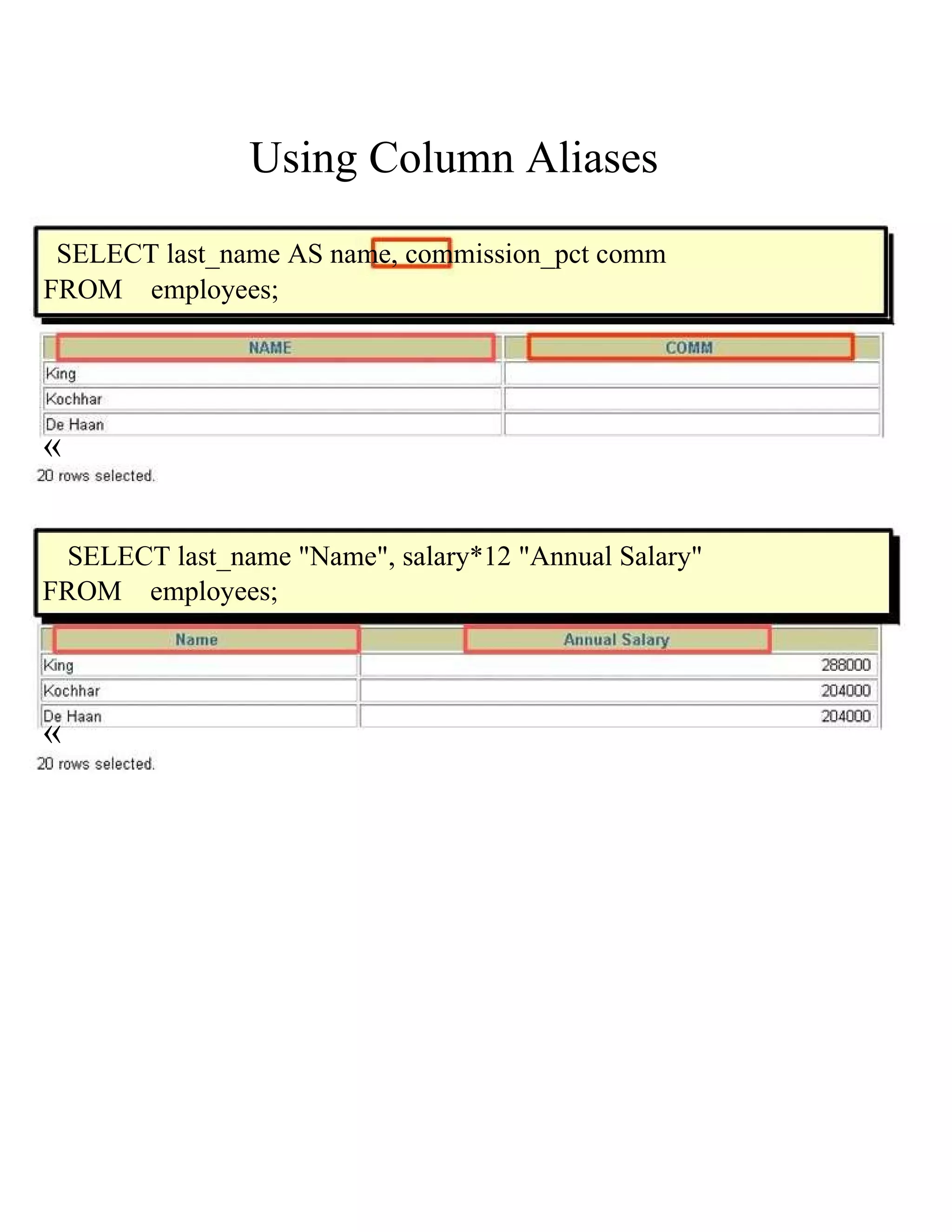
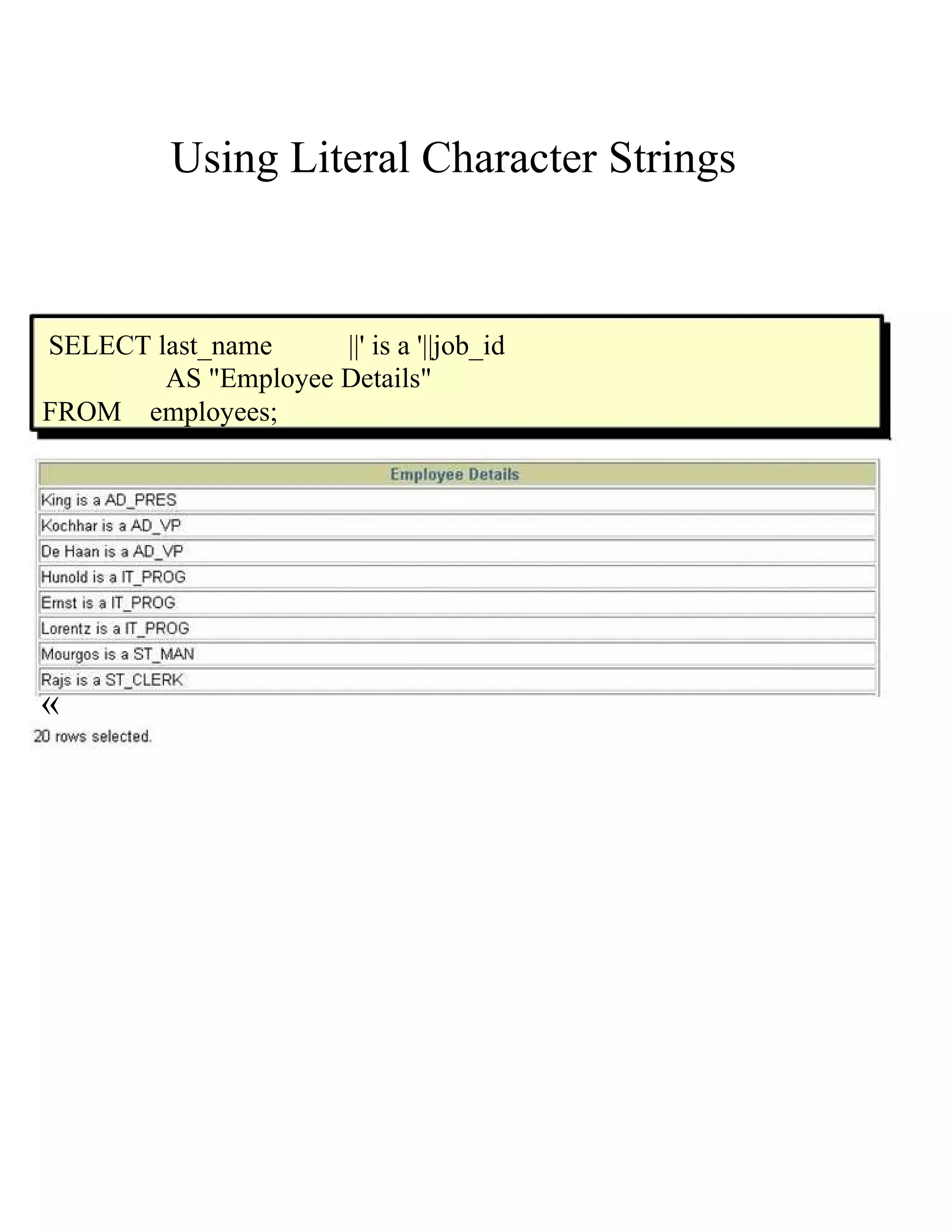
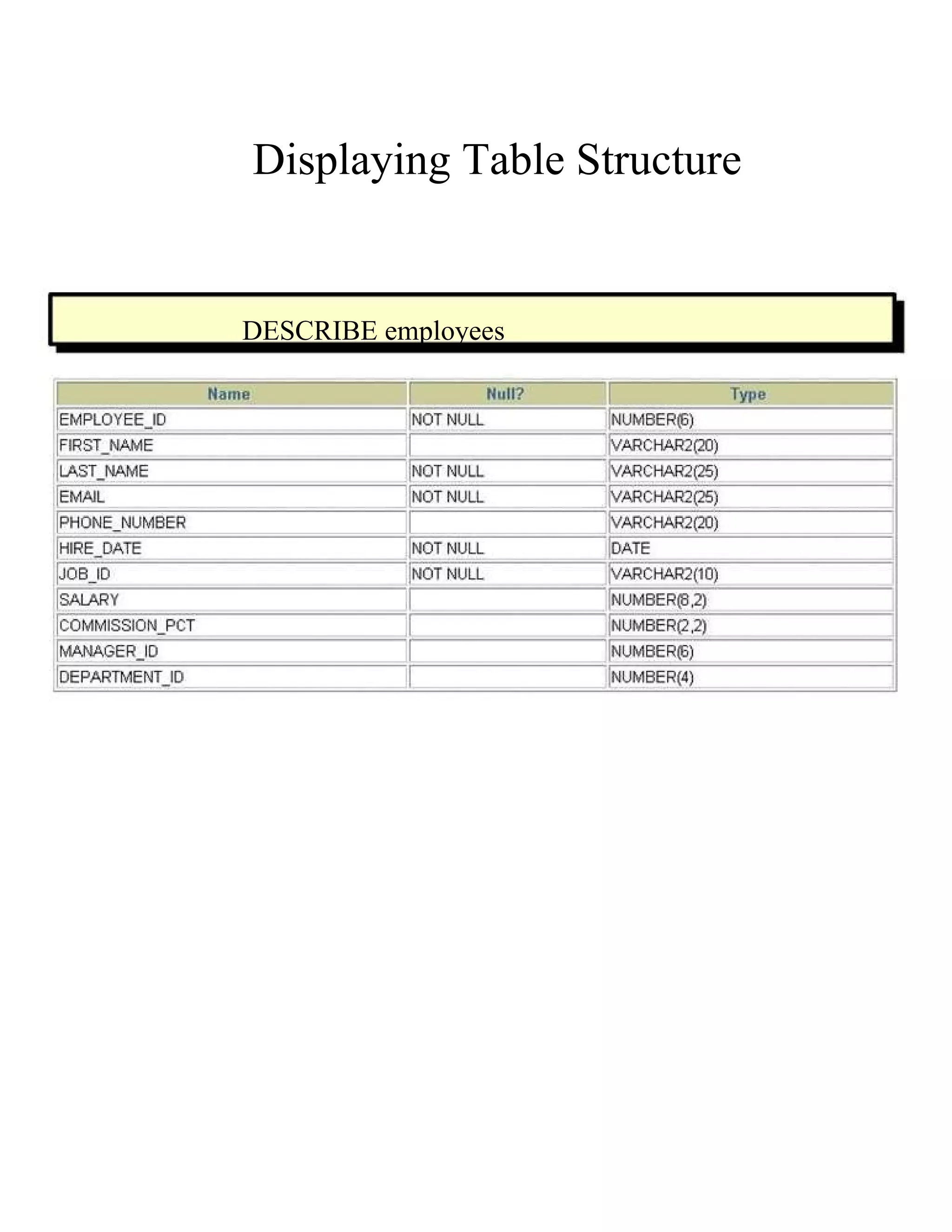
This document provides an overview of basic SELECT statements in SQL, including: - The SELECT clause identifies columns to retrieve from tables identified in the FROM clause. - Arithmetic expressions can be used to manipulate number and date columns. Operators like +, -, *, / follow standard order of operations rules. - Column aliases can rename columns and make column headings more readable. - Concatenation using || combines character strings from different columns into one column. - Literal strings and values can be included in the output. - The DISTINCT keyword eliminates duplicate rows from the results. - DESCRIBE shows the structure of a table.

![" " http://ecomputernotes.com Basic SELECT Statement SELECT * | { [DISTINCT] column | expression [ alias ],...} FRO M table; SELECT identifies what columns FROM identifies which table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writingbasicsqlselectstatements-111224104359-phpapp02/75/e-computer-notes-Writing-basic-sql-select-statements-2-2048.jpg)