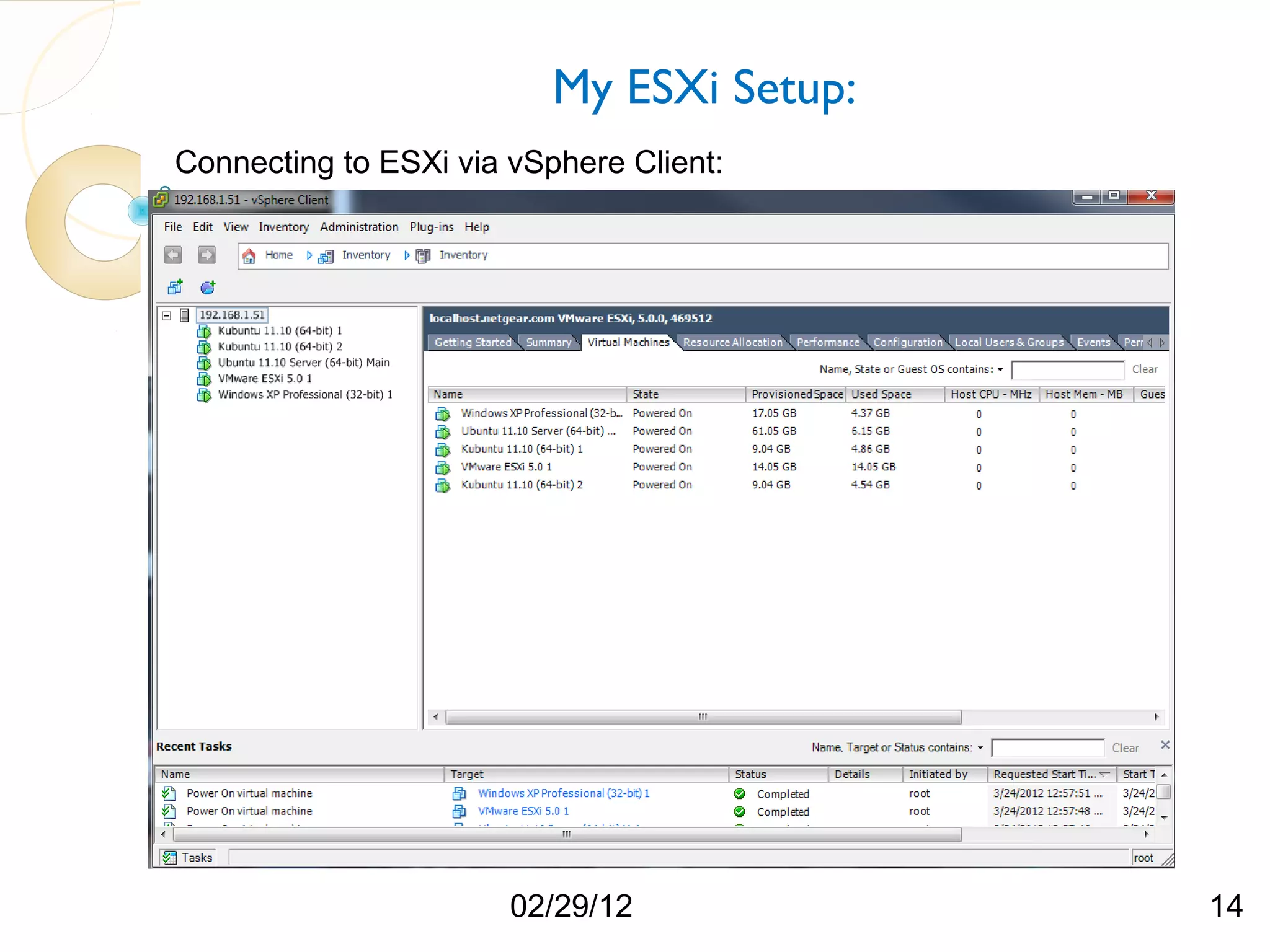
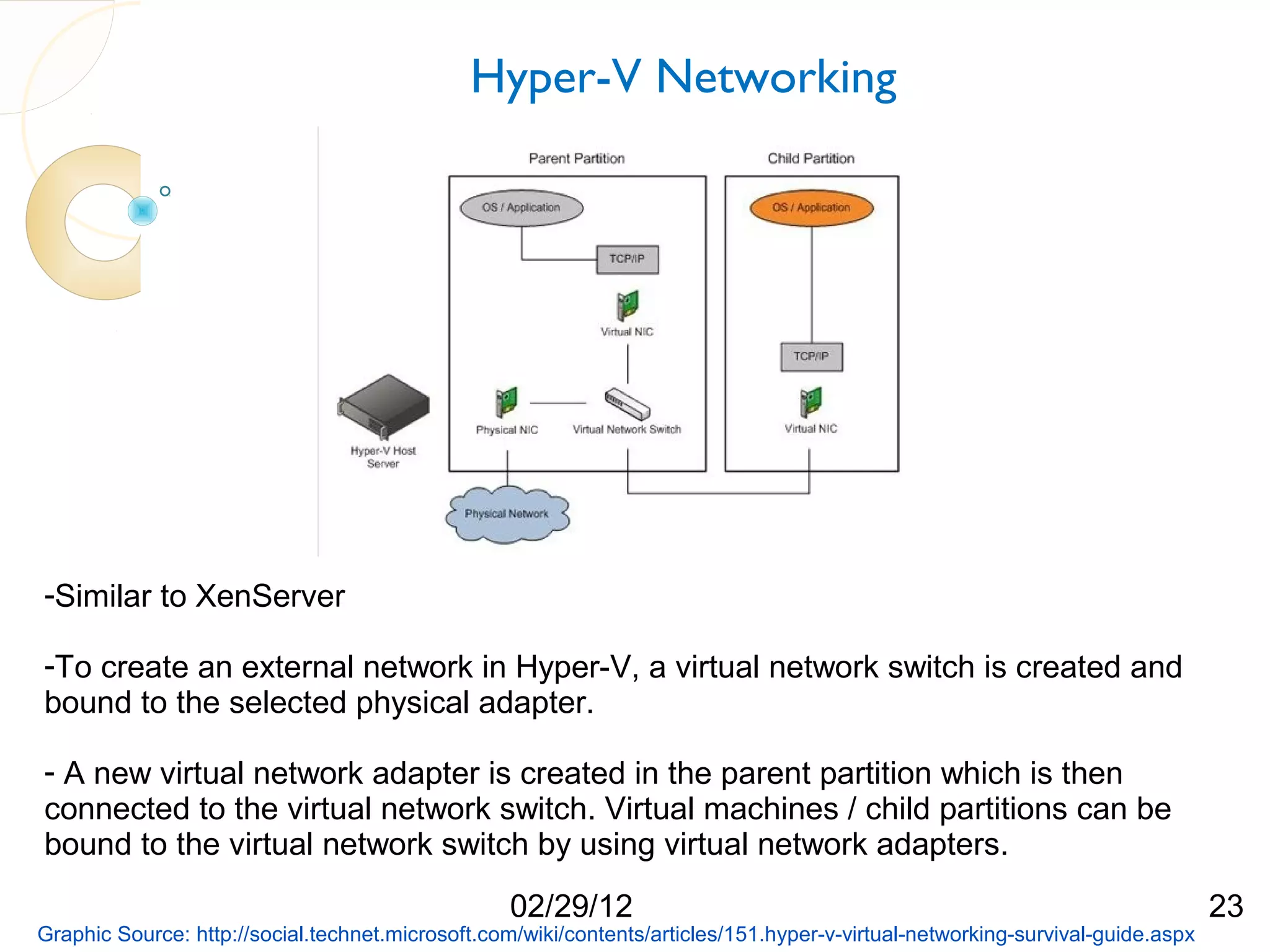
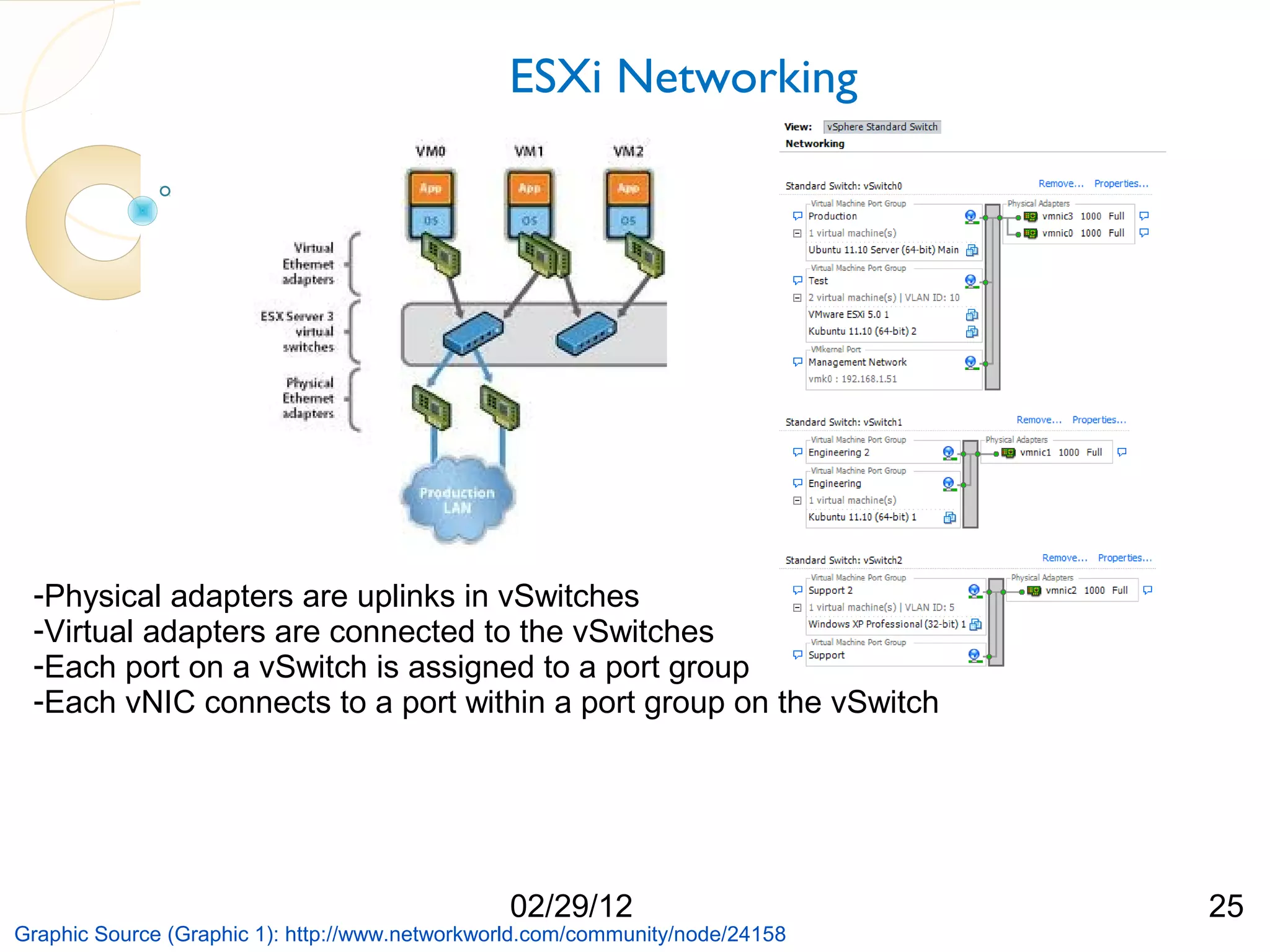
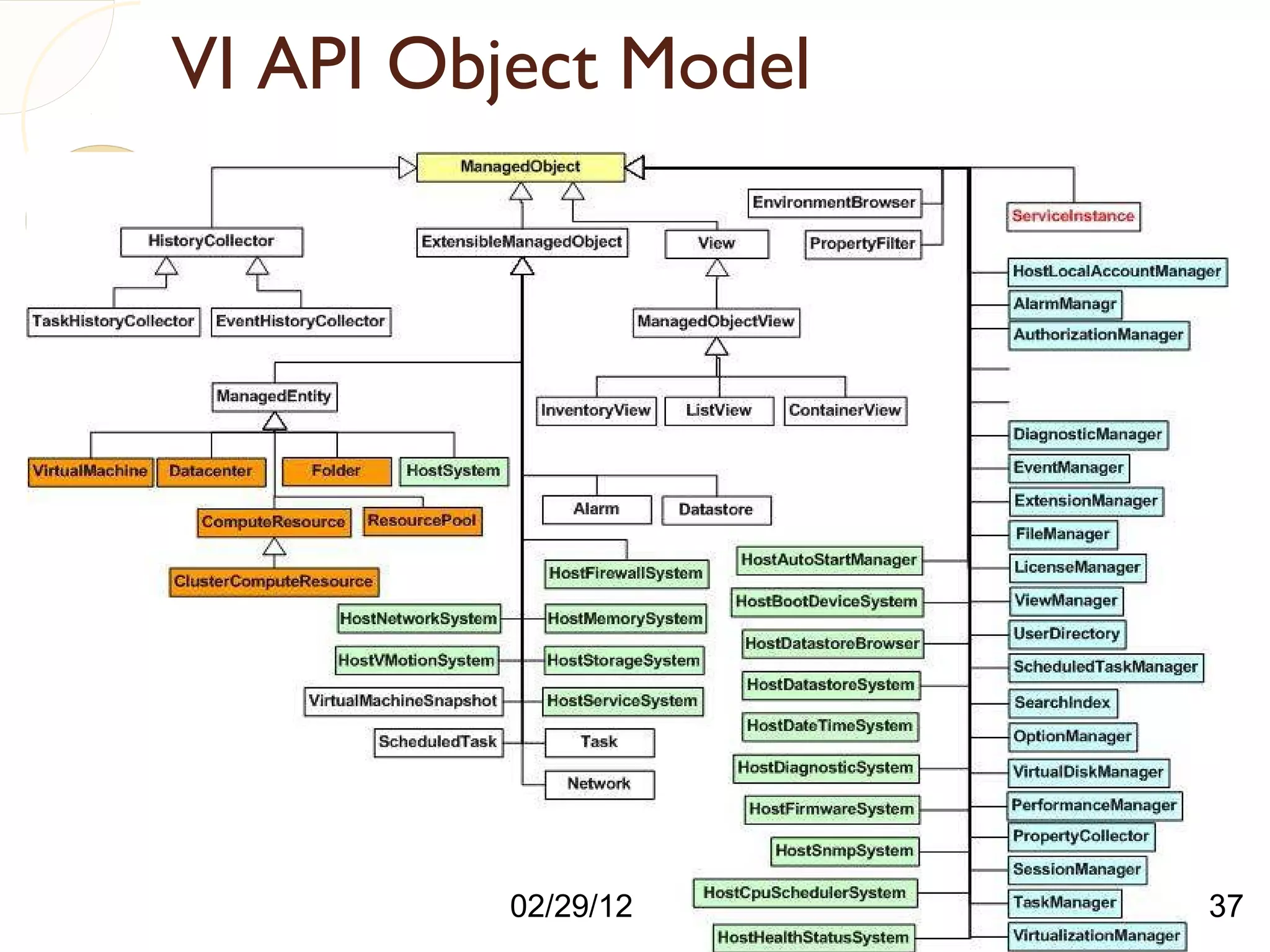
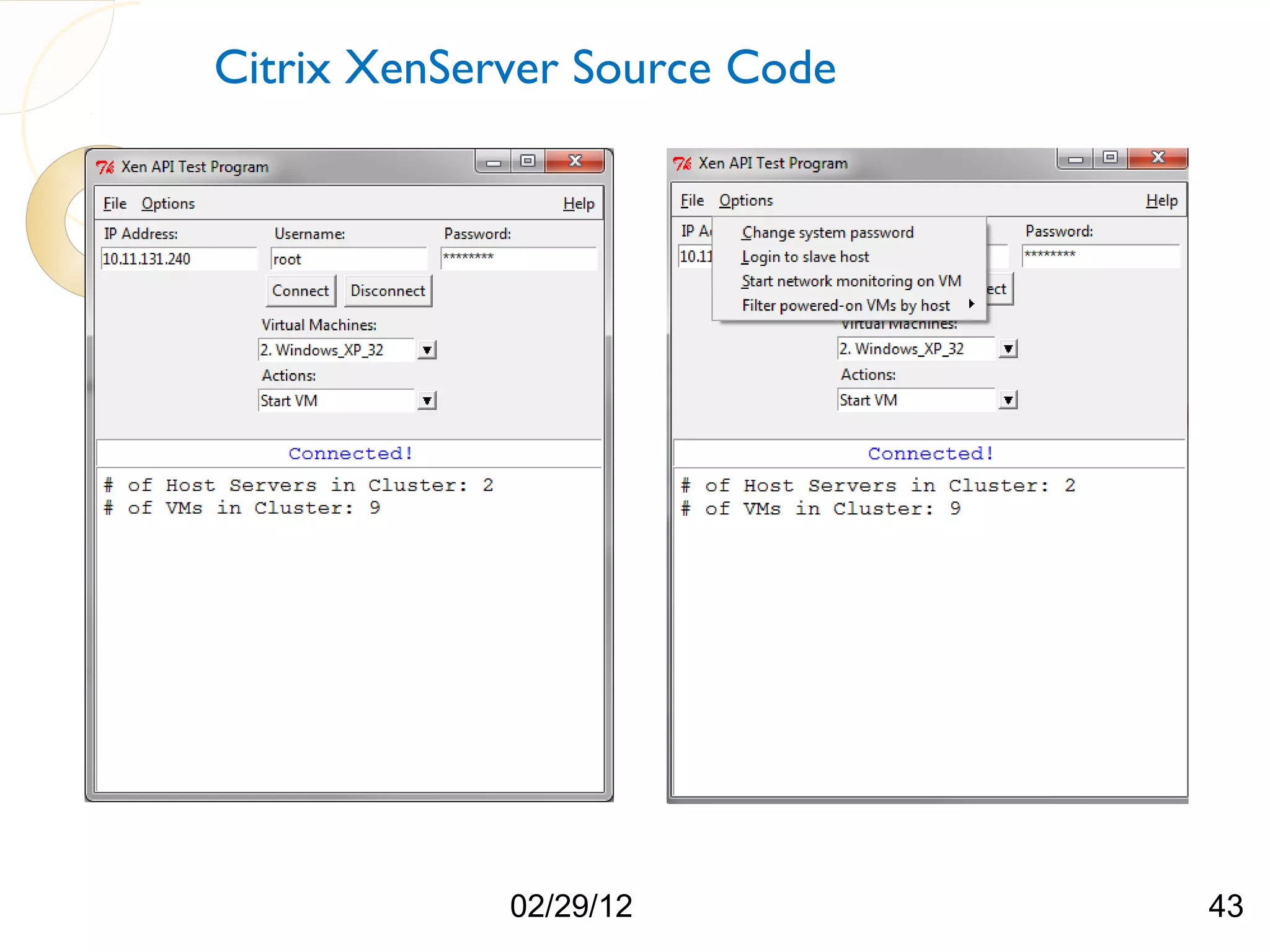
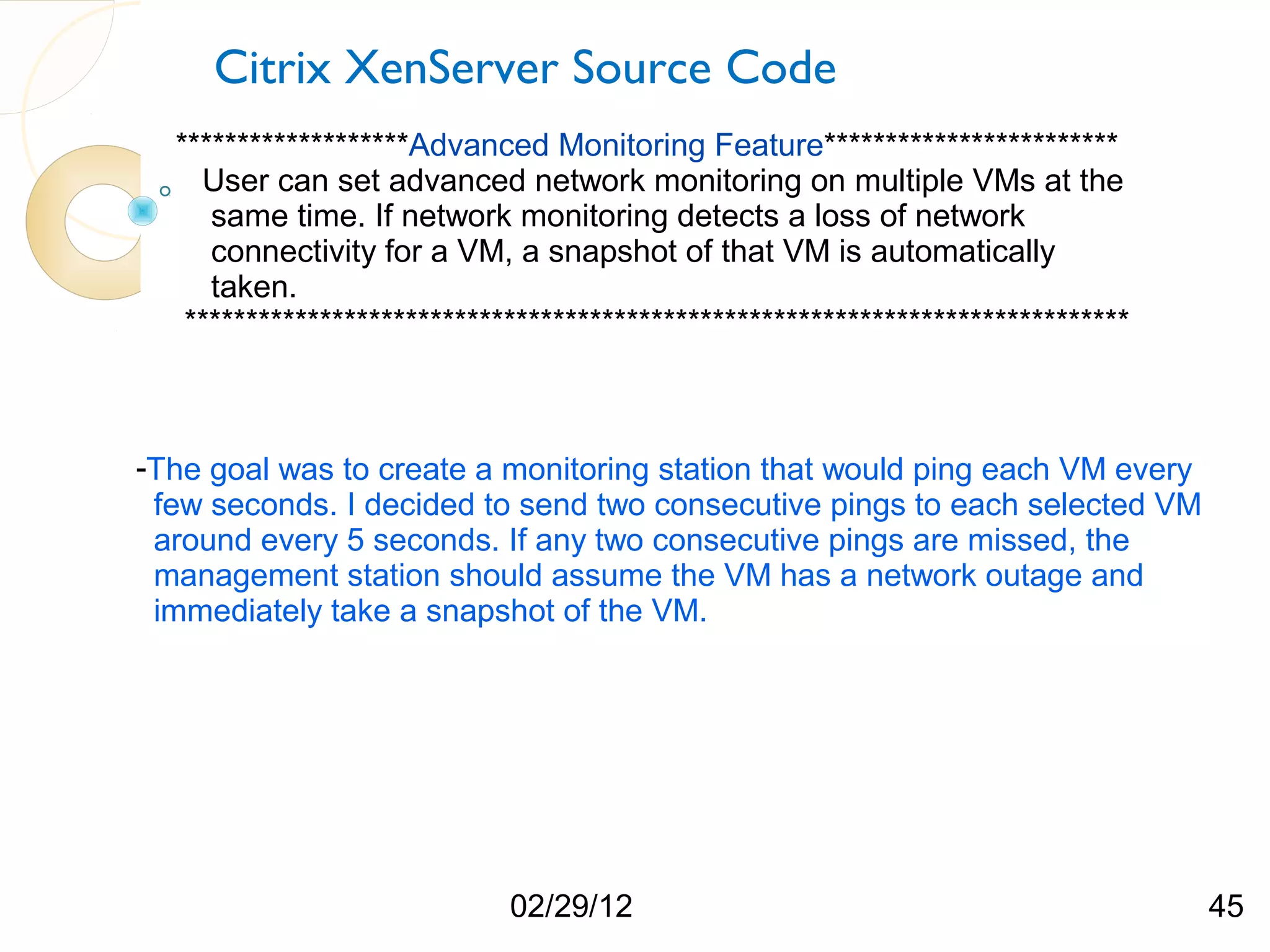
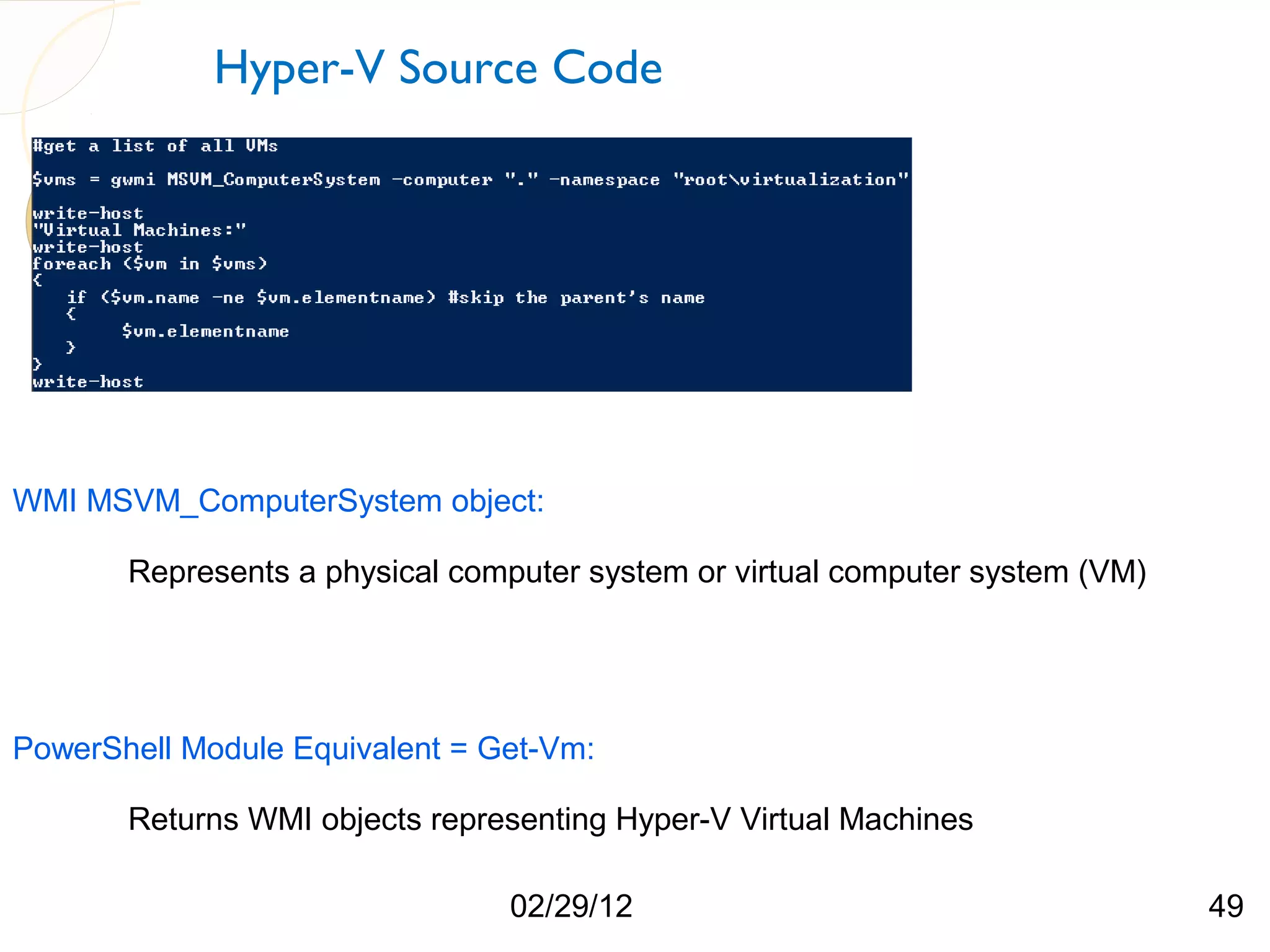
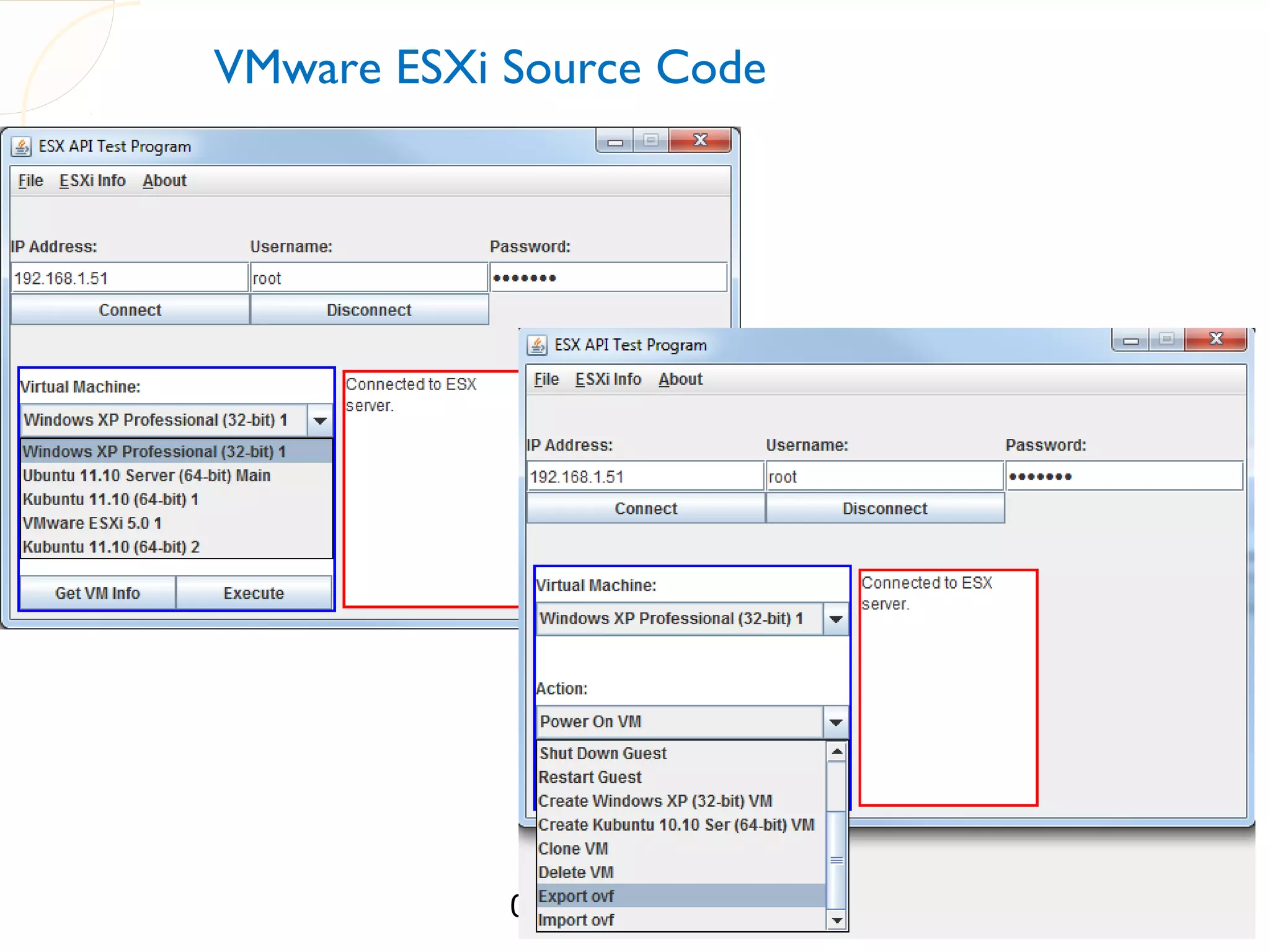
The document compares three hypervisors: XenServer, Hyper-V, and ESXi, covering aspects such as architecture, installation, and APIs. It includes personal setups for each hypervisor, networking configurations, and details about API interactions for XenServer and Hyper-V, including examples of code written to manage and monitor virtual machines. Additionally, it provides links to the full source code accessible on GitHub and personal website.