Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to work with the SQLite date and time values and use the built-in dates and times functions to handle date and time values.
SQLite does not support built-in date and/or time storage class. Instead, it leverages some built-in date and time functions to use other storage classes such as TEXT, REAL, or INTEGER for storing the date and time values.
Using the TEXT storage class for storing SQLite date and time
If you use the TEXT storage class to store date and time value, you need to use the ISO8601 string format as follows:
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.SSSCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, 2016-01-01 10:20:05.123
First, create a new table named datetime_text for demonstration.
CREATE TABLE datetime_text( d1 text, d2 text );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The table contains two column d1 and d2 with TEXT datatype.
To insert date and time values into the datetime_text table, you use the DATETIME function.
For example, to get the current UTC date and time value, you pass the now literal string to the function as follows:
SELECT datetime('now');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To get the local time, you pass an additional argument localtime.
SELECT datetime('now','localtime');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert the date and time values into the datetime_text table as follows:
INSERT INTO datetime_text (d1, d2) VALUES(datetime('now'),datetime('now', 'localtime'));Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, query the data from the datetime_text table.
SELECT d1, typeof(d1), d2, typeof(d2) FROM datetime_text;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Using REAL storage class to store SQLite date and time values
You can use the REAL storage class to store the date and/ or time values as Julian day numbers, which is the number of days since noon in Greenwich on November 24, 4714 B.C. based on the proleptic Gregorian calendar.
Let’s take a look at an example of using the REAL storage class to store date and time values.
First, create a new table named datetime_real.
CREATE TABLE datetime_real( d1 real );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert the “current” date and time value into the datetime_real table.
INSERT INTO datetime_real (d1) VALUES(julianday('now'));Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We used the julianday() function to convert the current date and time to the Julian Day.
Third, query data from the datetime_real table.
SELECT d1 FROM datetime_real;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)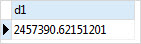
The output is not human readable.
Fortunately, you can use the built-in date() and time() functions to format a date and time value as follows:
SELECT date(d1), time(d1) FROM datetime_real;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)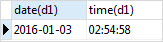
Using INTEGER to store SQLite date and time values
Besides TEXT and REAL storage classes, you can use the INTEGER storage class to store date and time values.
We typically use the INTEGER to store UNIX time which is the number of seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC. See the following example:
First, create a table that has one column whose data type is INTEGER to store the date and time values.
CREATE TABLE datetime_int (d1 int);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert the current date and time value into the datetime_int table.
INSERT INTO datetime_int (d1) VALUES(strftime('%s','now'));Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, query data from the datetime_int table.
SELECT d1 FROM datetime_int;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It’s an integer.
To format the result, you can use the built-in datetime() function as follows:
SELECT datetime(d1,'unixepoch') FROM datetime_int;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)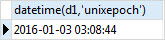
Using SQLite, you can freely choose any data types to store date and time values and use the built-in dates and times function to convert between formats.
For the detailed information on SQLite dates and times functions, check it out the built-in dates and times functions.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the TEXT, REAL, and INTEGER storage classes to store date and time values. In addition, you learned how to use the built-in dates and times functions to convert the stored date and times values into readable formats.