Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use SQLite GROUP BY clause to make a set of summary rows from a set of rows.
Introduction to SQLite GROUP BY clause
The GROUP BY clause is an optional clause of the SELECT statement. The GROUP BY clause a selected group of rows into summary rows by values of one or more columns.
The GROUP BY clause returns one row for each group. For each group, you can apply an aggregate function such as MIN, MAX, SUM, COUNT, or AVG to provide more information about each group.
The following statement illustrates the syntax of the SQLite GROUP BY clause.
SELECT column_1, aggregate_function(column_2) FROM table GROUP BY column_1, column_2; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The GROUP BY clause comes after the FROM clause of the SELECT statement. In case a statement contains a WHERE clause, the GROUP BY clause must come after the WHERE clause.
Following the GROUP BY clause is a column or a list of comma-separated columns used to specify the group.
SQLite GROUP BY examples
We use the tracks table from the sample database for the demonstration.
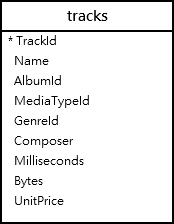
SQLite GROUP BY clause with COUNT function
The following statement returns the album id and the number of tracks per album. It uses the GROUP BY clause to groups tracks by album and applies the COUNT() function to each group.
SELECT albumid, COUNT(trackid) FROM tracks GROUP BY albumid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)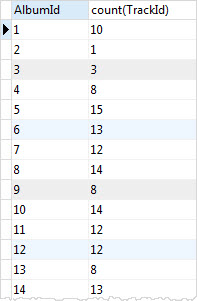
You can use the ORDER BY clause to sort the groups as follows:
SELECT albumid, COUNT(trackid) FROM tracks GROUP BY albumid ORDER BY COUNT(trackid) DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)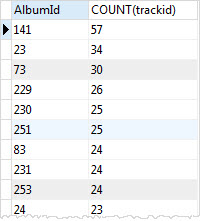
SQLite GROUP BY and INNER JOIN clause
You can query data from multiple tables using the INNER JOIN clause, then use the GROUP BY clause to group rows into a set of summary rows.
For example, the following statement joins the tracks table with the albums table to get the album’s titles and uses the GROUP BY clause with the COUNT function to get the number of tracks per album.
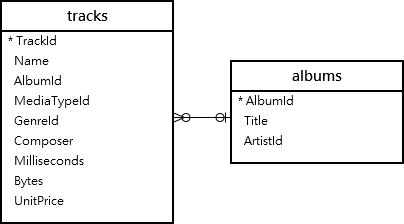
SELECT tracks.albumid, title, COUNT(trackid) FROM tracks INNER JOIN albums ON albums.albumid = tracks.albumid GROUP BY tracks.albumid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)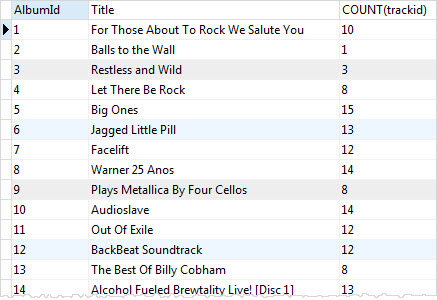
SQLite GROUP BY with HAVING clause
To filter groups, you use the GROUP BY with HAVING clause. For example, to get the albums that have more than 15 tracks, you use the following statement:
SELECT tracks.albumid, title, COUNT(trackid) FROM tracks INNER JOIN albums ON albums.albumid = tracks.albumid GROUP BY tracks.albumid HAVING COUNT(trackid) > 15;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)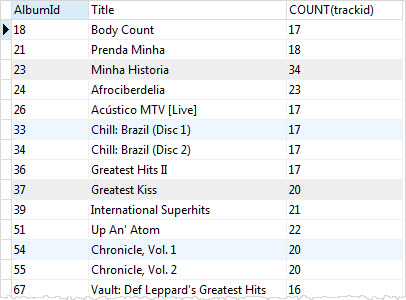
SQLite GROUP BY clause with SUM function example
You can use the SUM function to calculate total per group. For example, to get total length and bytes for each album, you use the SUM function to calculate total milliseconds and bytes.
SELECT albumid, SUM(milliseconds) length, SUM(bytes) size FROM tracks GROUP BY albumid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)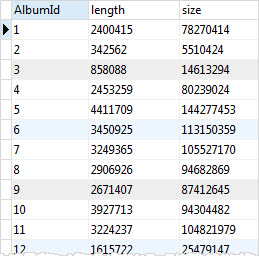
SQLite GROUP BY with MAX, MIN, and AVG functions
The following statement returns the album id, album title, maximum length, minimum length, and the average length of tracks in the tracks table.
SELECT tracks.albumid, title, min(milliseconds), max(milliseconds), round(avg(milliseconds),2) FROM tracks INNER JOIN albums ON albums.albumid = tracks.albumid GROUP BY tracks.albumid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)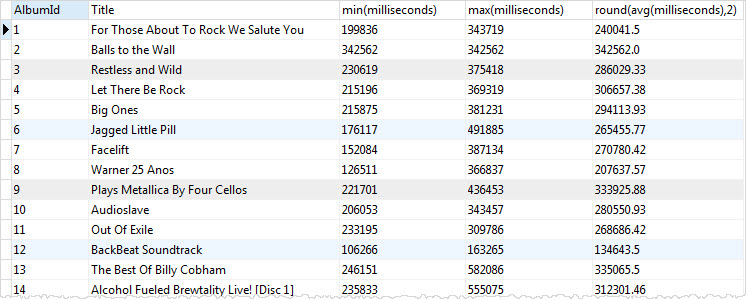
SQLite GROUP BY multiple columns example
In the previous example, we have used one column in the GROUP BY clause. SQLite allows you to group rows by multiple columns.
For example, to group tracks by media type and genre, you use the following statement:
SELECT MediaTypeId, GenreId, COUNT(TrackId) FROM tracks GROUP BY MediaTypeId, GenreId;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)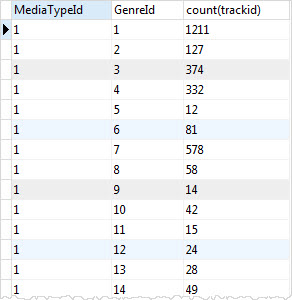
SQLite uses the combination of values of MediaTypeId and GenreId columns as a group e.g., (1,1) and (1,2). It then applies the COUNT function to return the number of tracks in each group.
SQLite GROUP BY date example
See the following invoices table from the sample database:
The following statement returns the number of invoice by years.
SELECT STRFTIME('%Y', InvoiceDate) InvoiceYear, COUNT(InvoiceId) InvoiceCount FROM invoices GROUP BY STRFTIME('%Y', InvoiceDate) ORDER BY InvoiceYear;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
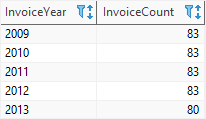
In this example:
- The function
STRFTIME('%Y', InvoiceDate)returns a year from a date string. - The
GROUP BYclause groups the invoices by years. - The function
COUNT()returns the number of invoice in each year (or group).
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the SQLite GROUP BY clause to group rows into a set of summary rows.