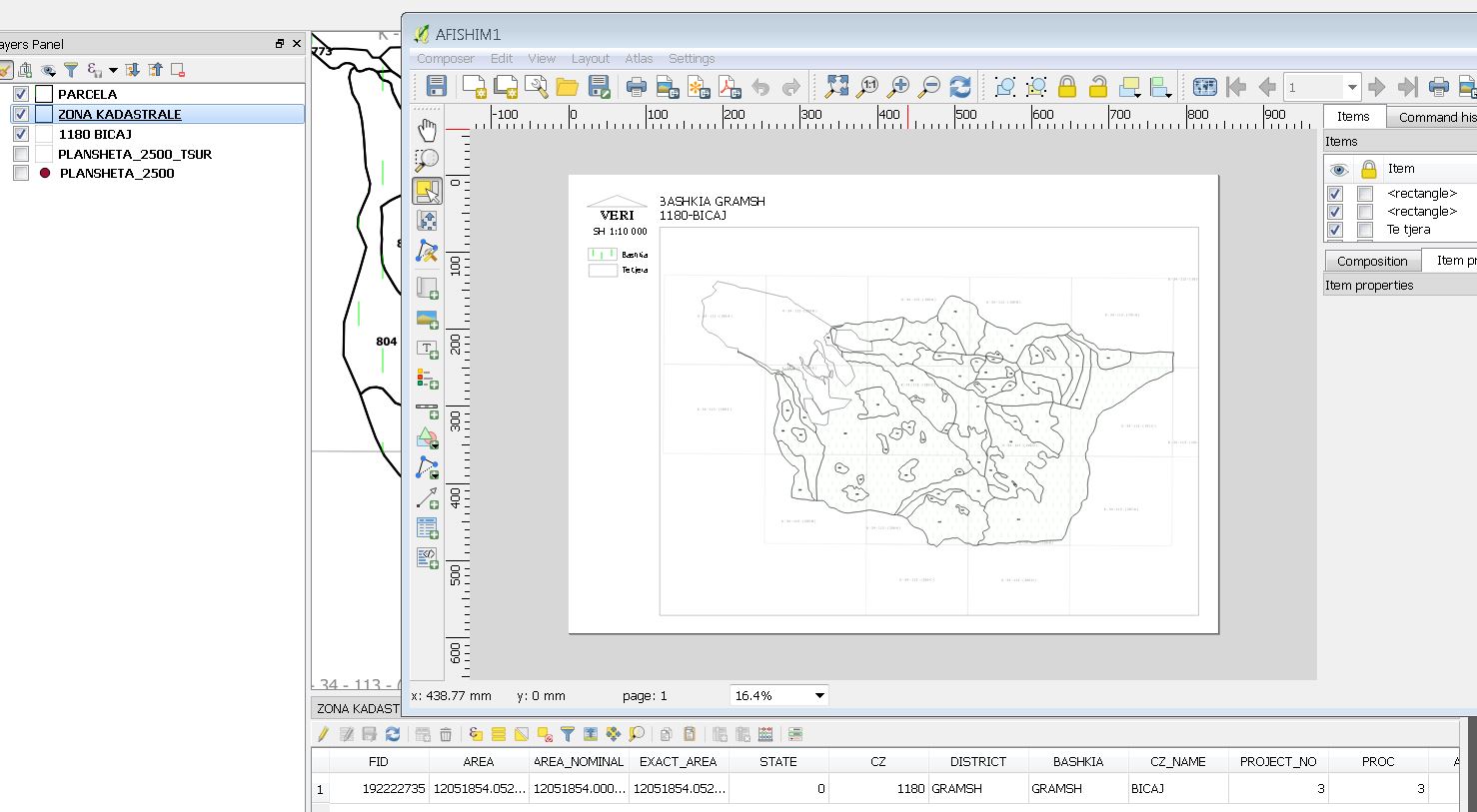
When you wish to display attribute values from your layer using a text label, you can define an expression that references the attribute name. For example, if you need the value of the CZ_NAME attribute from your coverage layer (the one set as such in the atlas settings), you can use:
[%"CZ_NAME"%]
If you want to concatenate this value with another attribute or text, you can do so with the following expression:
[% concat("CZ", '-', "CZ_NAME") %]
In addition to this standard approach, you may want to dynamically retrieve data from a secondary data source. This is where the aggregate function comes into play. Suppose you need to display dynamically the sum of the burned area (attribute superficie_indic_ha) from a thematic fact table such as vue_dtm_zb_administ. This table is filtered according to both spatial and temporal dimensions. When you want this in Atlas, this is realy powerfull. The spatial filter uses the @atlas_pagename (from the atlas coverage layer) and the temporal filter relies on the environment variable ATLAS_YEAR. The corresponding QGIS expression for the filter might look like:
id_spatial = @atlas_pagename and year = env('ATLAS_YEAR')
Then, using the aggregate function, you can sum the values as follows:
aggregate( layer := 'vue_dtm_zb_administ', aggregate := 'sum', expression := "superficie_indic_ha", filter := type_spatial = 'commune' and id_spatial = @atlas_pagename )
Explanation
Text Label Approach:
You simply reference the attribute by enclosing its name in the expression syntax ([%"CZ_NAME"%]). You can further manipulate the output, for instance by concatenating strings or additional attributes.
Aggregate Function Approach:
This method allows you to pull in data from another layer or table (in this case, a thematic fact table). The parameters include:
- layer: the data source (
'vue_dtm_zb_administ'). - aggregate: the type of aggregation operation (here,
'sum'). - expression: the field you wish to aggregate (
"superficie_indic_ha"). - filter: conditions that limit the data aggregated (using both spatial and, if needed, temporal filters like year from env variable for exemple).
This dual approach empowers you to dynamically incorporate and aggregate data from multiple sources, ensuring that your atlas pages can display up-to-date and contextually relevant information based on spatial and temporal parameters.