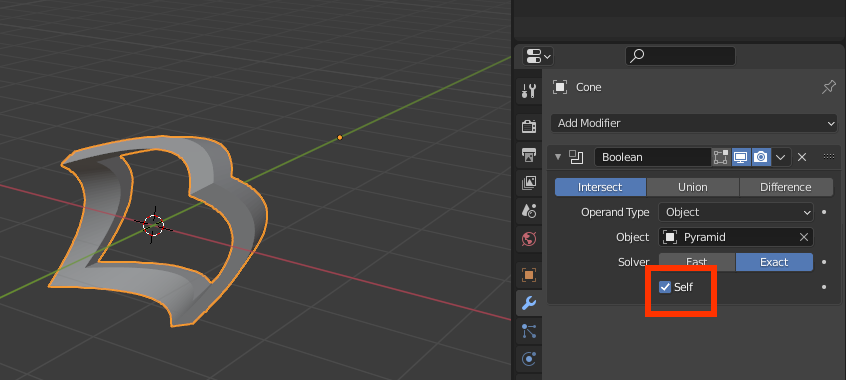
Most of the common problems people experience with the Boolean modifier are generally down to only 2 or 3 things: Normals, Doubles (or overlapping geometry), Non-Manifold geometry.
#Normals
Faces have a direction, it may seem like a weird idea but it's necessary in computer graphics to give a polygon (different word for face) a direction.

The fact that faces have a direction is included in the word "face", for English speakers: "what direction is it facing? it's facing that direction". Blender will give the new faces you create a direction that corresponds to the faces around it, it's up to you as a modeler to be aware of this.
While in Edit Mode, you can visualize the direction of Normals like vertex and face normals by enabling the appropriate options under the Mesh Edit Mode menu. Look for the buttons labeled Display Vertex Normals, Display Split Normals, and Display Face Normals to toggle them on as needed.

You can also enable Face Orientation, which highlights faces in red if their Normals are inverted. In the example below, there are two cubes: one with face Normals pointing outward (the correct direction), and another with normals pointing inward (inverted), which Blender marks in red. To visualize and check for inverted normals, enable Face Orientation under Viewport Overlays:

The direction of the Normals determines how the objects combine when using a Boolean Modifier:
On the first image the cube and the torus have their normals facing out:
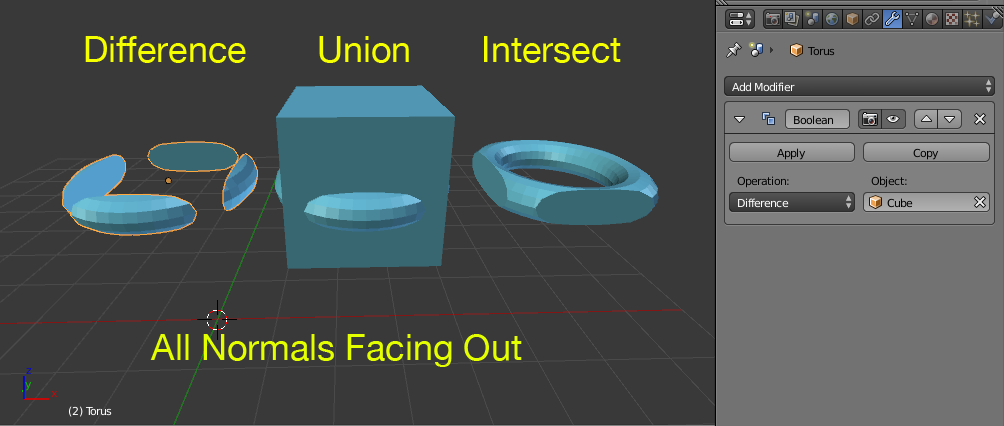
On the second image the Torus has the normals facing in:

On the third image both objects have their normals facing in:
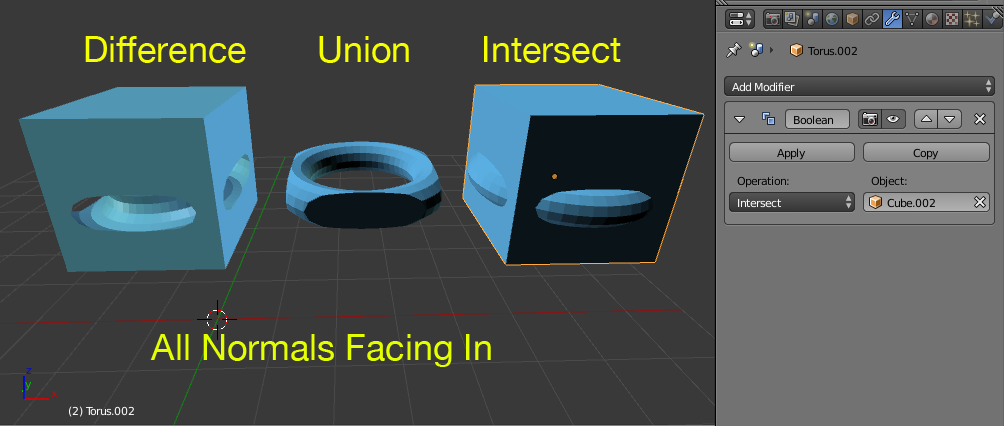
What are Difference, Union, and Intersect supposed to produce?
- Difference: The result will be those parts of the mesh which do not share volume in 3D space. see here a good expose on how to do this, and what to expect
- Union: Returns the two meshes joined as one, the two meshes do need to have at least some common volume in 3D space. If they don't you can use the Join command (Ctrl+j) instead of a boolean.
- Intersect: will return the shared 3d volume of the two meshes.
Quote from the manual:
The modified mesh is subtracted from the target mesh.
If the target Mesh has inverted normals, Blender will Intersect the modified mesh.
If the modified Mesh has inverted normals, Blender will add both meshes (Union).
If both Meshes use inverted normals, Blender will Intersect the target Mesh.
The target mesh is added to the modified mesh.
If the target Mesh has inverted normals, Blender will Intersect the target Mesh.
If the modified Mesh has inverted normals, Blender will subtract the target Mesh.
If both Meshes use inverted normals, Blender will Intersect the modified Mesh.
The target mesh is subtracted from the modified mesh.
If the target Mesh has inverted normals, Blender will subtract the target Mesh.
If the modified Mesh has inverted normals, Blender will intersect the target Mesh.
If both Meshes use inverted normals, Blender will add both meshes (Union).
Fixes for problems caused by normals in boolean operations are generally easy: Faces of both objects should all be outward facing with no exceptions.
To recalculate normals enter Edit Mode (Tab).
Select all faces and press ShiftN To have the normals face out
Or CtrlShiftN to have normals face inside the mesh.
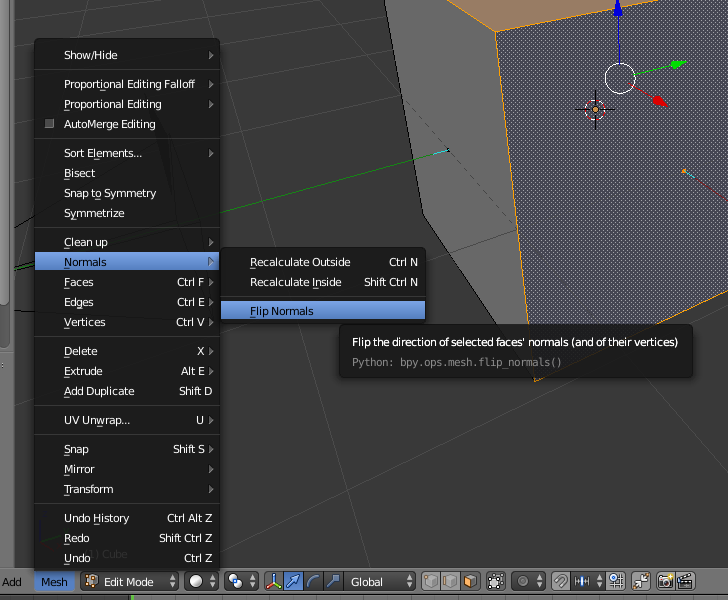
To flip a single face, select it and use Mesh>Normals>Flip Normals.
You can toggle the display of normals in the Properties Panel (right panel N): 
#Doubles
Doubles (overlapping vertices) refer to multiple vertices that share the same 3D location. These can cause problems with modifiers like Boolean, as they may indicate degenerate geometry (e.g., zero-area faces, overlapping edges), or a mesh that appears connected but isn't.
To remove doubles:
- Enter Edit Mode (Tab)
- Select everything (A)
- Press M and choose Merge by Distance
You can adjust the Merge Distance in the Adjust Last Operation panel that appears in the bottom-left corner of the viewport to control how close vertices must be to merge.
( insert images of example tell-tale signs of doubles )
- Overlapping geometry between objects:
If you've removed doubles and flipped normals the right way, then a third cause of Boolean Failure is that some of your edges are shared by more than 2 faces. Inspect your Objects closely. Multiple vertices in the same location will often cause the boolean modifier to act up. In addition to Double geometry on Object A or B, object B should also not share any duplicated geometry with A. You can always prevent this by adjusting one of your Objects to comply with this limitation of the Boolean Algorithm. From this bug report:
this is a known bug in Carve upstream (a library we're using for boolean operations)
#Non-Manifold Geometry
Boolean operations will fail when using Non-manifold objects.
For all intents are purposes manifold means 'is it air-tight', meaning it has no holes. Examples of non-manifold objects could be objects like planes with no thickness, or objects that are self-intersecting or that have Zero-area faces or have Open volumes.
For some operations it helps if you use the Outliner to hide the object you are doing the boolean operation with from view/render so you can see clearly the effect of the operation before applying the modifier (apply at the last possible moment!)
Other cases where boolean operations can fail:
- Using Curve objects instead of Mesh objects
Blender doesn't let you use a curve objects for boolean operations. That inlcudes Text objects, as they are considered curves as well. Those objects would need to converted to mesh by pressing ⎇ AltC.