The small(er) things before we tackle the elephant in the room:
Naming
Your names aren't terrible, but could be a lot better. However, whatever you name things, you should comply with standard naming conventions. To wit:
Local Variables: Written in camelCase.
Dim localVariable As String
includes method arguments.
Module / Global Variables: Written in PascalCase.
Private ModuleVariable As String
Global PublicVariable As Long
Method Names: Verbs. Written in PascalCase
Private Function ReturnThisValue() As Long
Public Sub DoThisThing()
Constants: Written in SHOUTY_SNAKE_CASE
Public Const CONSTANT_VALUE As String = "This Value Never Changes"
Also, Block is declared and set but never used. It should be removed.
Don't use :
Just don't. Keep your instructions on separate lines. They're too easy to miss and violate too many conventions.
Put things in Variables
Range("C" & i)
You see this? This is telling Excel to go and find that range. Every time you write it. What if you want to check a different column? Right now, you'll have to rewrite the declaration on 20 different lines.
Instead, put it in a variable then just reference the Variable. Now, if the variables need to change, you only have to change them in 1 place, and the rest takes care of itself.
Dim cCell As Range, dCell As Range, eCell As Range Set cCell = Range("C" & i) Set dCell = Range("D" & i) Set eCell = Range("E" & i) Dim countryName As String countryName = "Canada" If Instr(1, cCell, countryName) Or Instr(1, dCell, countryName) Or Instr(1, eCell, countryName) Then ... ...
Don't Repeat Yourself
Also known as DRY. Take your i = i + 1 statement. That is always going to happen. So why write it 20 times when you can just put it at the start or end of your loop?
While i <= lastRow Code Code Code ... i = i + 1 Wend
Boom. 12 lines of code gone
And now the big stuff:
Refactoring
Refactoring is the process of splitting one big thing into many little things. Any time you find yourself copy-pasting code, you should be thinking "Hmm, this can probably be turned into a method of some kind".
1st Refactoring
This check:
If Instr(1, cCell, countryName) Or Instr(1, dCell, countryName) Or Instr(1, eCell, countryName) Then
Can be a Separate Method Like so:
Public Function NameIsInRange(ByVal searchName As String, ByRef range1 As Range, range2 As Range, range3 As Range) As Boolean Dim result As Boolean result = InStr(1, range1, searchName) Or InStr(1, range2, searchName) Or InStr(1, range3, searchName) NameIsInRange = result End Function
And now we're down to:
Sub PullCountries() Dim i As Long i = 1 Dim LastRow As Long LastRow = Range("B1").End(xlDown).Row While i <= LastRow Dim resultRange As Range Set resultRange = Range("A" & i) Dim cCell As Range, dCell As Range, eCell As Range Set cCell = Range("C" & i) Set dCell = Range("D" & i) Set eCell = Range("E" & i) If NameIsInRange("Canada", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "Canada" ElseIf NameIsInRange("United States", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "United States" ElseIf NameIsInRange("Britian", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "UK" ElseIf NameIsInRange("UK", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "UK" ElseIf NameIsInRange("Spain", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "Spain" ElseIf NameIsInRange("Portugal", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "Portugal" ElseIf NameIsInRange("Ireland", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "Ireland" ElseIf NameIsInRange("Japan", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "Japan" ElseIf NameIsInRange("Greece", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "Greece" ElseIf NameIsInRange("Italy", cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = "Italy" End If i = i + 1 Wend End Sub Public Function NameIsInRange(ByVal searchName As String, ByRef range1 As Range, range2 As Range, range3 As Range) As Boolean Dim result As Boolean result = InStr(1, range1, searchName) Or InStr(1, range2, searchName) Or InStr(1, range3, searchName) NameIsInRange = result End Function
2nd Refactoring
The only things that actually change in the loop are the name to check and the name to output. So, why don't we make those a list? For an iterable list with more than 1 element per line, I'd use an Array.
Let's make a new sheet and give it the codename wsCountryNames. Then a function to get the table and pass it to an Array:
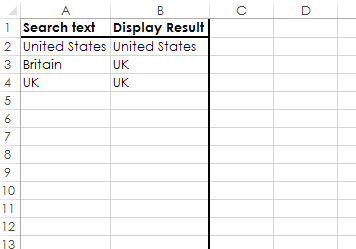
Public Function GetCountryNamesTable() As Variant With wsCountryNames Dim topLeftCell As Range Set topLeftCell = .Cells(1, 1) '/ "A1" Dim finalRow As Long finalRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, topLeftCell.Column).End(xlUp).Row Dim tableWidth As Long tableWidth = 2 Dim tableRange As Range Set tableRange = .Range(topLeftCell, Cells(finalRow, topLeftCell.Column + tableWidth - 1)) End With GetCountryNamesTable = tableRange End Function
The value in Cell A1 is now in GetCountryNamesTable(1, 1), A2, (2, 1), B1, (1, 2) etc.
Now, we can just iterate through your list:
Sub PullCountries() Dim i As Long, j As Long i = 1 Dim LastRow As Long LastRow = Range("B1").End(xlDown).Row Dim namesList As Variant namesList = GetCountryNamesTable Dim searchName As String, displayName As String While i <= LastRow Dim resultRange As Range Set resultRange = Range("A" & i) Dim cCell As Range, dCell As Range, eCell As Range Set cCell = Range("C" & i) Set dCell = Range("D" & i) Set eCell = Range("E" & i) For j = LBound(namesList, 1) + 1 To UBound(namesList, 1) '/ +1 for header row searchName = namesList(j, 1) displayName = namesList(j, 2) If NameIsInRange(searchName, cCell, dCell, eCell) Then resultRange = displayName Exit For '/ We found our result so we can terminate the loop early End If Next j i = i + 1 Wend End Sub Public Function NameIsInRange(ByVal searchName As String, ByRef range1 As Range, range2 As Range, range3 As Range) As Boolean Dim result As Boolean result = InStr(1, range1, searchName) Or InStr(1, range2, searchName) Or InStr(1, range3, searchName) NameIsInRange = result End Function Public Function GetCountryNamesTable() As Variant With wsCountryNames Dim topLeftCell As Range Set topLeftCell = .Cells(1, 1) '/ "A1" Dim finalRow As Long finalRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, topLeftCell.Column).End(xlUp).Row Dim tableWidth As Long tableWidth = 2 Dim tableRange As Range Set tableRange = .Range(topLeftCell, Cells(finalRow, topLeftCell.Column + tableWidth - 1)) End With GetCountryNamesTable = tableRange End Function
3rd Refactoring
I'm going to put your search range in an Array:
Public Function GetSearchRange() As Variant With (codename of your sheet here, call it wsSearchSheet for now) Dim topLeftCell As Range Set topLeftCell = .Cells(1, 1) '/ "A1" Dim finalRow As Long finalRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).Row '/ "2" for "B" column Dim finalCol As Long finalCol = 5 '/ "E" column Dim tableRange As Range Set tableRange = .Range(topLeftCell, Cells(finalRow, finalCol)) End With GetCountryNamesTable = tableRange End Function
And Re-Jig the IsInRange function to deal with an array value instead:
Public Function ValueContainsString(ByVal valueToSearch As Variant, ByVal searchString As String) As Boolean ValueContainsString = InStr(1, CStr(valueToSearch), searchString) End Function
And implement these changes to the main sub:
Option Explicit Sub PullCountries() Dim i As Long, j As Long, k As Long Dim namesList As Variant namesList = GetCountryNamesTable Dim searchNameCol As Long, displayNameCol As Long searchNameCol = 1 displayNameCol = 2 Dim searchArray As Variant searchArray = GetSearchValues Dim searchStartCol As Long, searchEndCol As Long searchStartCol = 3 searchEndCol = 5 Dim outputCol As Long outputCol = 1 Dim foundMatch As Boolean Dim valueToSearch As Variant Dim searchName As String, displayName As String For i = LBound(searchArray, 1) To UBound(searchArray, 1) foundMatch = False For j = searchStartCol To searchEndCol valueToSearch = searchArray(i, j) For k = LBound(namesList, 1) + 1 To UBound(namesList, 1) '/ +1 for header row searchName = namesList(k, searchNameCol) If ValueContainsString(valueToSearch, searchName) Then displayName = namesList(k, displayNameCol) searchArray(i, outputCol) = displayName foundMatch = True Exit For '/ We found our result so we can terminate the loop early End If Next k If foundMatch Then Exit For Next j Next i '/ Read output back to sheet. For i = LBound(searchArray, 1) To UBound(searchArray, 1) Range("A" & i) = searchArray(i, outputCol) Next i End Sub Public Function ValueContainsString(ByVal valueToSearch As Variant, ByVal searchString As String) As Boolean ValueContainsString = InStr(1, CStr(valueToSearch), searchString) End Function Public Function GetCountryNamesTable() As Variant With wsCountryNames Dim topLeftCell As Range Set topLeftCell = .Cells(1, 1) '/ "A1" Dim finalRow As Long finalRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, topLeftCell.Column).End(xlUp).Row Dim tableWidth As Long tableWidth = 2 Dim tableRange As Range Set tableRange = .Range(topLeftCell, Cells(finalRow, topLeftCell.Column + tableWidth - 1)) End With GetCountryNamesTable = tableRange End Function Public Function GetSearchValues() As Variant With (codename of your sheet here, call it wsSearchSheet for now) Dim topLeftCell As Range Set topLeftCell = .Cells(1, 1) '/ "A1" Dim finalRow As Long finalRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).Row '/ "2" for "B" column Dim finalCol As Long finalCol = 5 '/ "E" column Dim tableRange As Range Set tableRange = .Range(topLeftCell, Cells(finalRow, finalCol)) End With GetSearchValues = tableRange End Function
Want to change your country names? Just change the values in your table. Your data moves about? Just change the GetSearchValues targets. You can extend either as far as you like.
Total number of values you now have to change in your code: Maybe 10. And then only if your sheet data moves around positions.
Codenames Addendum
Codenames are big and clever. Every worksheet and workbook has a "name" that the user can see and change.
MyCurrentWB.Worksheets("Country Names")
is referencing a sheet name.
A Codename on the other hand is a secret name that can only be set/changed in the IDE.
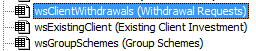
the name in brackets is the "name". The name not in brackets is the "codename". It is set in the properties window.
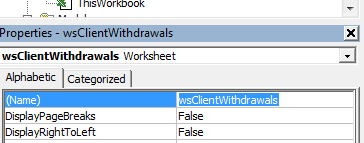
If you give a sheet a codename then the user can change the name as much as they like, all you have to do is use
wsCountryNames.Cells()
in your code and it will keep running.



