How can I convert a bytes32 to a string? Does anyone has a magic function or library which does it?
- 2possible duplicate : ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/1081/…euri10– euri102016-03-31 17:13:20 +00:00Commented Mar 31, 2016 at 17:13
- This about concatenating, isn't it?anrodon– anrodon2016-03-31 17:16:07 +00:00Commented Mar 31, 2016 at 17:16
- is this a question for solidity or for outside the blockchain e.g. in javascript?Paul S– Paul S2016-03-31 20:44:08 +00:00Commented Mar 31, 2016 at 20:44
- No, just in the blockchain. I made another question with the js partanrodon– anrodon2016-03-31 20:45:18 +00:00Commented Mar 31, 2016 at 20:45
12 Answers
Based on the latest compiler version 0.4.24, I use the following.
function convertingToString()public returns(string){ bytes32 memory hw = "Hello World"; string memory converted = string(hw); return converted; } Using explicit conversion to carry it out. The reverse is also possible.
For versions 0.5.0+ please use (tested from 0.5 to 0.7.2 - it is likely that it will continue to work past 0.7.2):
function bytes32ToString(bytes32 _bytes32) public pure returns (string memory) { uint8 i = 0; while(i < 32 && _bytes32[i] != 0) { i++; } bytes memory bytesArray = new bytes(i); for (i = 0; i < 32 && _bytes32[i] != 0; i++) { bytesArray[i] = _bytes32[i]; } return string(bytesArray); } - 12This does not work in solidity version 0.5.0+Yogesh - EtherAuthority.io– Yogesh - EtherAuthority.io2019-01-04 14:38:01 +00:00Commented Jan 4, 2019 at 14:38
- 2
- 2updated for solidity version past 0.5.0Patrick Collins– Patrick Collins2020-10-08 11:37:58 +00:00Commented Oct 8, 2020 at 11:37
- 4does not work getting this error ` Failed to decode output: null: invalid codepoint at offset 2; missing continuation byte (argument="bytes", value={"0":91,"1":218,"2":113,"3":98,"4":184,"5":77,"6":255,"7":114,"8":27,"9":203,"10":143,"11":119,"12":114,"13":120,"14":180,"15":136,"16":222,"17":216,"18":209,"19":71,"20":82,"21":100,"22":212,"23":54,"24":28,"25":107,"26":10,"27":191,"28":204,"29":42,"30":153,"31":168}, code=INVALID_ARGUMENT, version=strings/5.1.0) ` was trying to convert this string
0x5bda7162b84dff721bcb8f777278b488ded8d1475264d4361c6b0abfcc2a99a8Ramesh Pareek– Ramesh Pareek2021-06-29 16:33:27 +00:00Commented Jun 29, 2021 at 16:33
As of feb 2021 you can do
bytes32 foo = "hello"; string memory bar = string(abi.encodePacked(foo)); - 1As soon as StackOverfloor gets the system vote from Medium, I'll give other 10 upvotes.Silvio Guedes– Silvio Guedes2021-05-23 02:53:55 +00:00Commented May 23, 2021 at 2:53
- 4Failed to decode output: null: invalid codepoint at offset 2; missing continuation byte (argument="bytes"....Ramesh Pareek– Ramesh Pareek2021-06-29 15:25:32 +00:00Commented Jun 29, 2021 at 15:25
- 4unfortunately it keeps zero padding which might be a problem in some cases..Ossip– Ossip2022-04-29 12:47:36 +00:00Commented Apr 29, 2022 at 12:47
- How would you remove the zero padding?Ashraile– Ashraile2024-03-21 07:44:00 +00:00Commented Mar 21, 2024 at 7:44
Here's one:
function bytes32ToString(bytes32 x) constant returns (string) { bytes memory bytesString = new bytes(32); uint charCount = 0; for (uint j = 0; j < 32; j++) { byte char = byte(bytes32(uint(x) * 2 ** (8 * j))); if (char != 0) { bytesString[charCount] = char; charCount++; } } bytes memory bytesStringTrimmed = new bytes(charCount); for (j = 0; j < charCount; j++) { bytesStringTrimmed[j] = bytesString[j]; } return string(bytesStringTrimmed); } To test, here it is combined with how to concatenate an array of bytes32. Paste the following in Remix.
contract C { function bytes32ToString(bytes32 x) constant returns (string) { bytes memory bytesString = new bytes(32); uint charCount = 0; for (uint j = 0; j < 32; j++) { byte char = byte(bytes32(uint(x) * 2 ** (8 * j))); if (char != 0) { bytesString[charCount] = char; charCount++; } } bytes memory bytesStringTrimmed = new bytes(charCount); for (j = 0; j < charCount; j++) { bytesStringTrimmed[j] = bytesString[j]; } return string(bytesStringTrimmed); } function bytes32ArrayToString(bytes32[] data) returns (string) { bytes memory bytesString = new bytes(data.length * 32); uint urlLength; for (uint i=0; i<data.length; i++) { for (uint j=0; j<32; j++) { byte char = byte(bytes32(uint(data[i]) * 2 ** (8 * j))); if (char != 0) { bytesString[urlLength] = char; urlLength += 1; } } } bytes memory bytesStringTrimmed = new bytes(urlLength); for (i=0; i<urlLength; i++) { bytesStringTrimmed[i] = bytesString[i]; } return string(bytesStringTrimmed); } } Click "Create". Then in bytes32ToString field enter "0x0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef" and click bytes32ToString.
In bytes32ArrayToString field enter ["0x0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef"] and click bytes32ArrayToString.
Both will show same result (ABI encoding): Result: "0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000200123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef"
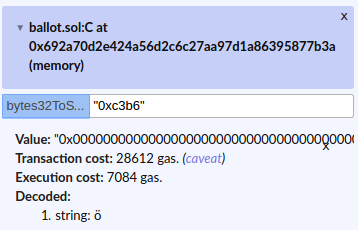
Here's another example. In bytes32ToString field enter "0xc3b6" and click bytes32ToString. You will get ö.
- I used the bytes32ToString function from above, but I obviously doesn't work with special characters such as ö ä ü etc. Is there a way to use this function with special characters?Bumblebee– Bumblebee2017-04-20 10:02:41 +00:00Commented Apr 20, 2017 at 10:02
- @Bumblebee I added an example for ö and it works. If still needed, probably ask a separate question. (The input or decoding the output might be your problem.)2017-04-21 02:31:23 +00:00Commented Apr 21, 2017 at 2:31
- I am trying your
bytes32ArrayToStringwith a fixedbytes32[10], but it seems I throw aninvalid opcodeif I use 8-10 full slots of the array. Meaning I have a test forabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdef(32 characters) 10 times in an array and pass that in, but it throws. If I have 7 or less it works. Any idea why?The Nomad– The Nomad2017-11-12 12:49:23 +00:00Commented Nov 12, 2017 at 12:49 - @TheNomad Not sure. Suggestions, try once instead of 10 times, and post a new question (a Remix or ethfiddle link might help).2017-11-19 19:37:39 +00:00Commented Nov 19, 2017 at 19:37
- 1@Russo It's not clear what you're trying to do in Python; Stackoverflow is a better fit for questions about converting from different Python types.2018-06-03 17:13:14 +00:00Commented Jun 3, 2018 at 17:13
How to convert a bytes32 to string:
pragma solidity ^0.4.15; contract Bytes32ToString { function bytes32ToStr(bytes32 _bytes32) public pure returns (string) { // string memory str = string(_bytes32); // TypeError: Explicit type conversion not allowed from "bytes32" to "string storage pointer" // thus we should fist convert bytes32 to bytes (to dynamically-sized byte array) bytes memory bytesArray = new bytes(32); for (uint256 i; i < 32; i++) { bytesArray[i] = _bytes32[i]; } return string(bytesArray); } } In version 0.5.0 and above i ended up with using Viktor answer How to convert a bytes32 to string but removing the zeros otherwise you will end up with
'ERC20\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000\u0000'
instead of
'ERC20'
This is the code:
/* bytes32 (fixed-size array) to string (dynamically-sized array) */ function bytes32ToString(bytes32 _bytes32) public pure returns (string memory) { uint8 i = 0; while(i < 32 && _bytes32[i] != 0) { i++; } bytes memory bytesArray = new bytes(i); for (i = 0; i < 32 && _bytes32[i] != 0; i++) { bytesArray[i] = _bytes32[i]; } return string(bytesArray); } It's recommended you convert a bytes32 to a string using Web3.js to avoid gas costs. To do this, you would get the value of the bytes32 from Solidity to the front end then do:
web3.utils.hexToString(bytes32);
This will convert the bytes32 to a string that you can then see and use in your frontend dApp.
Just in case, if you want to convert bytes32 to ASCII string, you can use the OpenZeppelin Strings library.
https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/openzeppelin-contracts/pull/2504
Strings.toHexString(uint256(tokenIdSeed), 32), The output should be like
0xd8df8ecd5432b247d2fc2beb0619d637e9de0df7512bd36220582deda9a1df6e (this is just covert hexadecimal value of the bytes32 to string)
- This is the simplest and most elegant solution among all the answers. Thank you!Dominik– Dominik2022-06-03 08:34:43 +00:00Commented Jun 3, 2022 at 8:34
Like @e18r already mentioned, the simplest way to do it without having to write all these crazy functions like everyone else is answering with (and would cost more gas), just do:
string(abi.encodePacked(bytes32));
- 1unfortunately it seems to keep zero padding which might be a problem in some cases.Ossip– Ossip2022-04-29 12:47:03 +00:00Commented Apr 29, 2022 at 12:47
A more gas-efficient method based on this answer (For versions 0.5.0+):
function toString(bytes32 source) internal pure returns (string memory result) { uint8 length = 0; while (source[length] != 0 && length < 32) { length++; } assembly { result := mload(0x40) // new "memory end" including padding (the string isn't larger than 32 bytes) mstore(0x40, add(result, 0x40)) // store length in memory mstore(result, length) // write actual data mstore(add(result, 0x20), source) } } This solution is using assembly to copy data to memory instead of for looping.
Here's how I'm doing it:
function char(byte b) returns (byte c) { if (b < 10) return byte(uint8(b) + 0x30); else return byte(uint8(b) + 0x57); } function bytes32string(bytes32 b32) returns (string out) { bytes memory s = new bytes(64); for (var i = 0; i < 32; i++) { byte b = byte(b32[i]); byte hi = byte(uint8(b) / 16); byte lo = byte(uint8(b) - 16 * uint8(hi)); s[i*2] = char(hi); s[i*2+1] = char(lo); } out = string(s); } // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.7; contract stringtobytes{ function set(string memory _a)public pure returns(bytes memory){ return bytes(_a); } function set1(bytes memory _a)public pure returns(string memory){ return string(_a); } } // you can convert strings to bytes(in decimal format) and vice versa with below code
//1- bytes1=8bit=2decimal
//2 bytes2=16bit=4decimal
//3 bytes3=24bit=6decimal
//4 bytes=dynamic array and reference value
- 2The question is about conversion from bytes32 to string, and your example doesn't work for that.2022-02-03 13:34:01 +00:00Commented Feb 3, 2022 at 13:34
Here's the simplest way i tried
contract ModifyString{ bytes32 public VoterName; mapping (address => VoterStruct) public voterCalls; struct VoterStruct{ address VoterAddress; string VoterID; bytes32 VoterName2; } function addVoter(string memory _VoterID, string memory _VoterName)public { // Load Voter struct trough mapping VoterStruct storage newVoter = voterCalls[msg.sender]; // If want to write to global variable VoterName = bytes32(abi.encodePacked( _VoterName)); // If want to write to struct newVoter.VoterAddress = msg.sender; newVoter.VoterID = _VoterID; newVoter.VoterName2 = bytes32(abi.encodePacked(_VoterName)); } function getVoterName() public view returns (string memory) { // To load from Global Variables bytes memory bytesData = abi.encodePacked(VoterName); return string(abi.encodePacked(VoterName)); } function getVoterName2() public view returns (string memory) { // To look Voter name in global variable bytes memory bytesData = abi.encodePacked(VoterName); return string(abi.encodePacked(bytesData)); } function getVoterName3() public view returns (string memory) { // To look Voter name in struct VoterStruct storage voterCall = voterCalls[msg.sender]; return string(abi.encodePacked(voterCall.VoterName2)); } } so to load the string, it need to be loaded in memory, as far as i know, string = bytes (without specific bytes number)
then return the output value using
string(abi.encodePacked(bytesData)) ^^^^ ^^^^^ //The converted type to //Loaded Variable into memory or storage ahh so there is to: 1.1 Write String to bytes32 to Global Variable, 1.2 Load string from bytes32 from Gobal Variable, 2.1 Write String to bytes32 to Struct, 2.2 Load String to bytes32 to struct. 😊😊😊