Documentation: https://array-api.readthedocs.io
Source Code: https://github.com/34j/types-array-api
Typing for array API and array-api-compat
Install this via pip (or your favourite package manager):
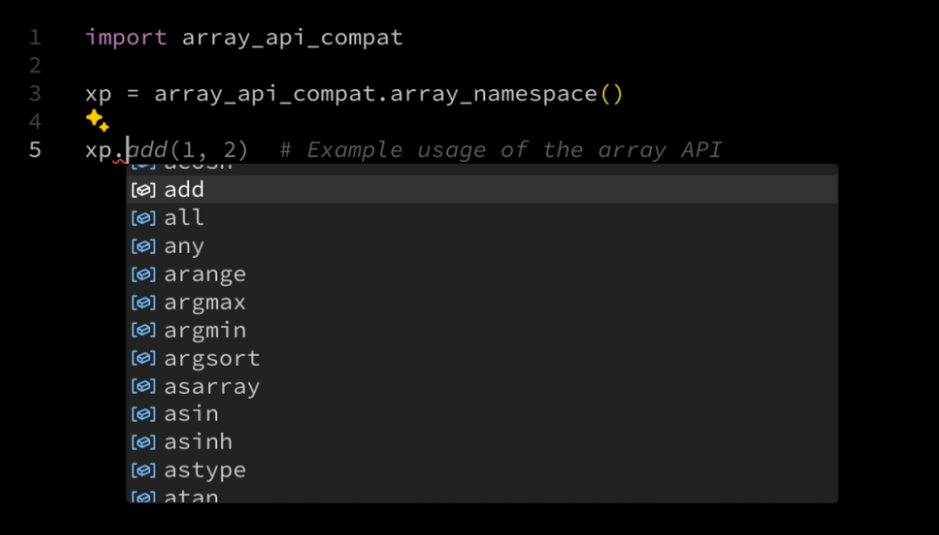
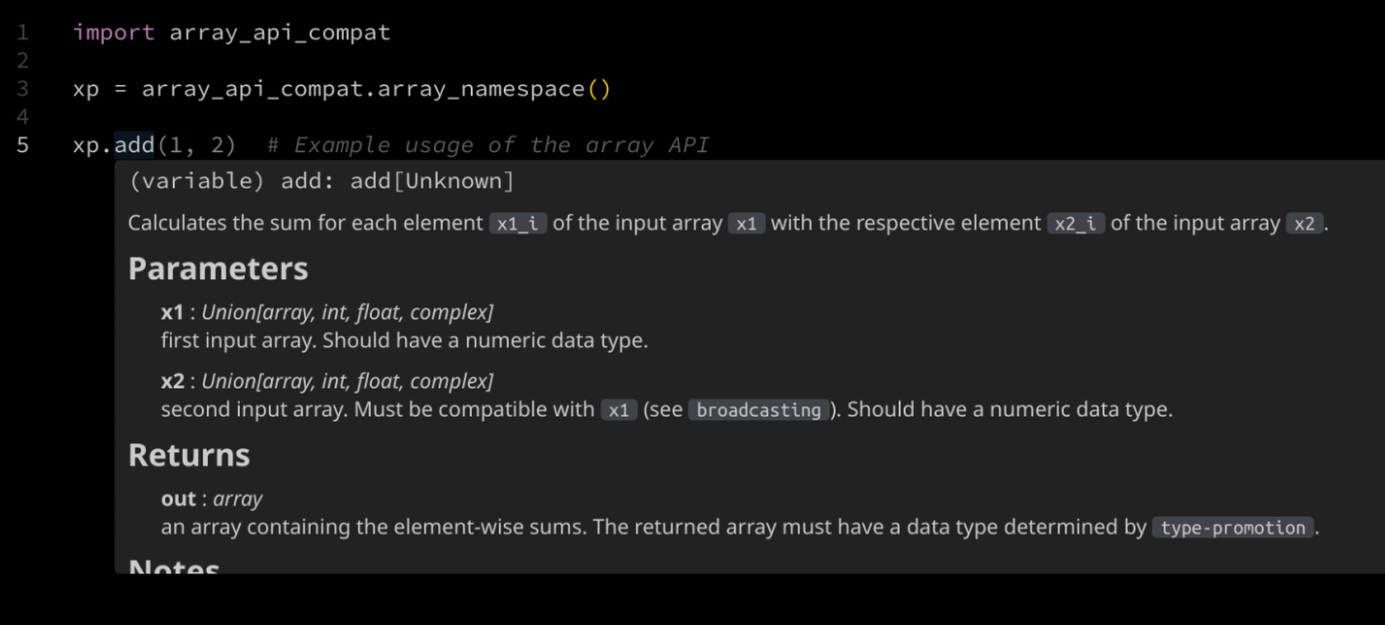
pip install types-array-apiAutocompletion for array-api-compat is available in your IDE just by installing this package.
import array_api_compat xp = array_api_compat.array_namespace(x)There are multiple ways to type functions:
-
from array_api._2024_12 import Array def simple(x: Array) -> Array: return x + 1
The simplest way to enjoy autocompletion for
Array. This should be enough for most use cases. -
To make sure that the same type of array is returned (
ndarray→ndarray,Tensor→Tensor), aTypeVarbound toArraycan be used:def generic[TArray: Array](x: TArray) -> TArray: return x + 1
You can test if an object matches the Protocol as they are runtime-checkable:
import array_api_strict from array_api._2024_12 import ArrayNamespace, ArrayNamespaceFull assert isinstance(array_api_strict, ArrayNamespace) # Full version contains fft and linalg # fft and linalg are not included by default in array_api_strict assert not isinstance(array_api_strict, ArrayNamespaceFull)-
To clarify the input and output shapes,
ShapedArrayandShapedAnyArraycan be used:from array_api._2024_12 import ShapedAnyArray as Array def sum_last_axis[*TShape](x: Array[*TShape, Any]) -> Array[*TShape]: return xp.sum(x, axis=-1)
More complex example using NewType or type aliases:
RTheta = NewType("RTheta", int) XY = NewType("XY", int) def polar_coordinates[*TShape](randtheta: Array[*TShape, RTheta]) -> Array[*TShape, XY]: """Convert polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates.""" r = randtheta[..., 0] theta = randtheta[..., 1] x = r * xp.cos(theta) y = r * xp.sin(theta) return xp.stack((x, y), axis=-1)
Note that
ShapedAnyArrayexists only for documentation purposes and internally it is treated asArray. Using both generic and shaped are impossible due to python/typing#548. -
Note that the below example is ideal but impossible due to Python specification.
def impossible[ TDtype, TDevice, *TShapeFormer: int, *TShapeLatter: int, TArray: Array ](x: TArray[*TShapeFormer, *TShapeLatter | Literal[1], TDtype, TDevice], y: TArray[*TShapeLatter | Literal[1], TDtype, TDevice]) -> TArray[*TShapeFormer, *TShapeLatter, TDtype, TDevice]: return x + y # broadcasting
Thanks goes to these wonderful people (emoji key):
This project follows the all-contributors specification. Contributions of any kind welcome!
This package was created with Copier and the browniebroke/pypackage-template project template.