The document outlines the content of a Java threading module which includes processes, threads, creating threads using the Thread class and Runnable interface, thread priority, and network server thread programming. It provides code examples of defining and starting threads using both Thread and Runnable, setting thread priority, and creating a multi-threaded network server using threads to handle client connections and requests.


![Java main method as a starting thread class TypicalClass { public void aMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); } public static void main(String[] args) { // main() is run in a single thread System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); TypicalClass hWorld = new TypicalClass(); hWorld.aMethod(); } } Thread[main,5,main] Thread[main,5,main]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08javathreadingv1-151031160808-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-08-java-threading-6-2048.jpg)
![Defining and Starting a Thread 1.) Runnable Interface. The Runnable interface defines a single method, run, meant to contain the code executed in the thread. The Runnable object is passed to the Thread constructor, public class HelloRunnable implements Runnable { public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); System.out.println("Hello from a thread!"); } public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); (new Thread(new HelloRunnable())).start(); } } Thread[main,5,main] Thread[Thread-0,5,main] Hello from a thread!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08javathreadingv1-151031160808-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-08-java-threading-7-2048.jpg)
![Defining and Starting a Thread 2.) Subclass Thread. The Thread class itself implements Runnable, though its run method does nothing. An application can subclass Thread, providing its own implementation of run, public class HelloThread extends Thread { public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); System.out.println("Hello from a thread!"); } public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); (new HelloThread()).start(); } } Thread[main,5,main] Thread[Thread-0,5,main] Hello from a thread!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08javathreadingv1-151031160808-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-08-java-threading-8-2048.jpg)
![Thread Priority package BasicThread; public class ThreadPriorityDemo extends Thread{ ThreadPriorityDemo(String name) { super(name); } public void run() { for (int i = 0; i<100; i++) System.out.print(getName()); } public static void main(String args[]) { ThreadPriorityDemo t01 = new ThreadPriorityDemo("T01"); ThreadPriorityDemo t02 = new ThreadPriorityDemo("T02"); t01.start(); t02.start(); t02.setPriority(10); // 1 min, 5 default, 10 max } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08javathreadingv1-151031160808-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-08-java-threading-9-2048.jpg)
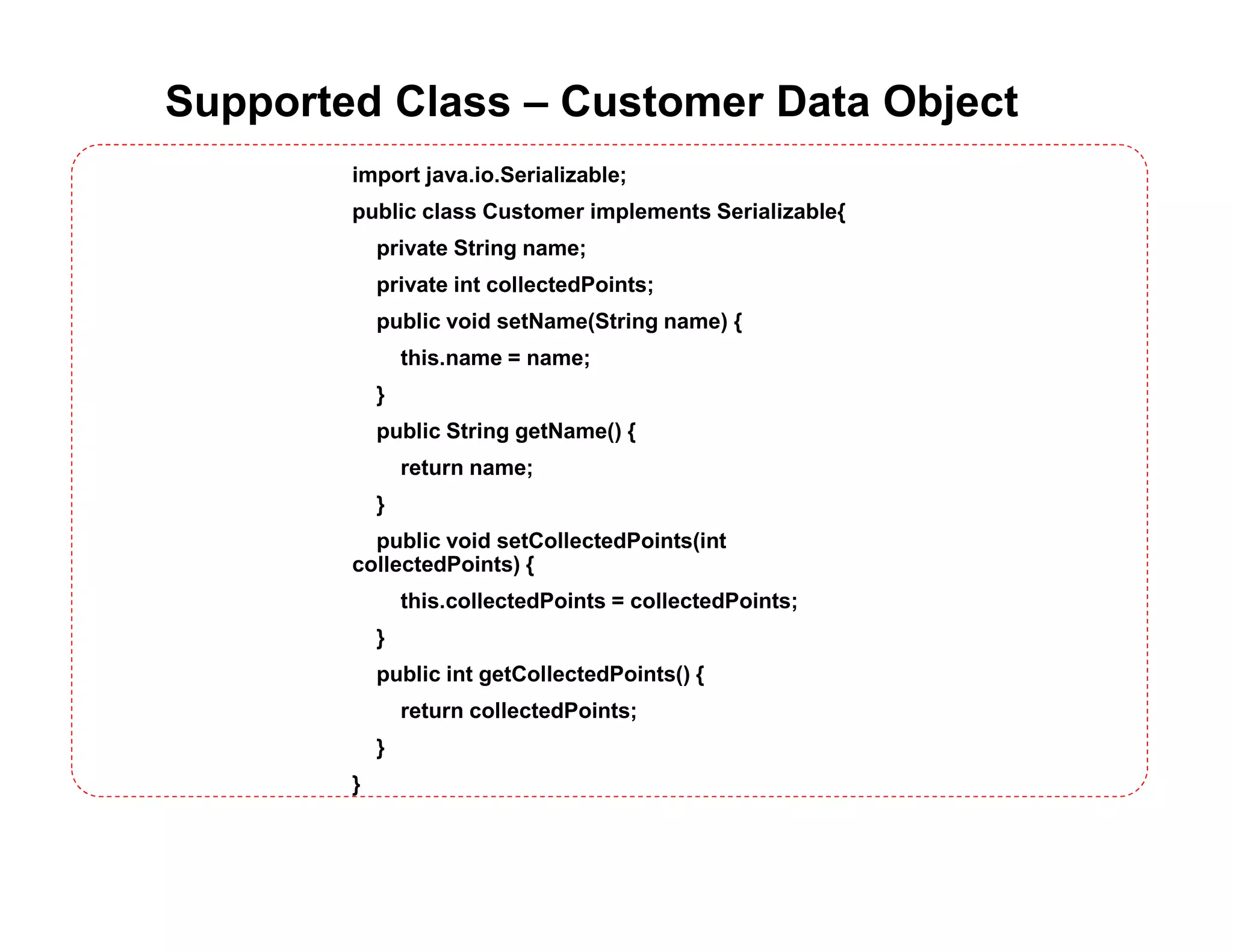
![Network Server Thread Programming import java.io.*; import java.net.*; public class MyServerThread extends Thread { ServerSocket s; public MyServerThread() throws Exception { super(); // Register service on port 1234 s = new ServerSocket(1234); } public void run() { try { while (true) { Socket s1 = s.accept(); // Wait and accept a connection // Read input from client ObjectInputStream objInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(s1.getInputStream()); Customer cust1 = (Customer)objInputStream.readObject(); cust1.setCollectedPoints(3000); // Dummy result // Write result to client OutputStream s1out = s1.getOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream objOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(s1out); objOutputStream.writeObject(cust1); // Close the connection, but not the server socket objOutputStream.close(); s1out.close(); objInputStream.close(); s1.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { MyServerThread myServerThread = new MyServerThread(); myServerThread.start(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08javathreadingv1-151031160808-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-08-java-threading-10-2048.jpg)
![Client Test import java.net.*; import java.io.*; public class MyClient2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // Open your connection to a server, at port 1234 Socket s1 = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 1234); // Write object to the socket server Customer cust1 = new Customer(); cust1.setName("Somchai"); ObjectOutputStream objOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(s1.getOutputStream()); objOutputStream.writeObject(cust1); // Get result from server InputStream s1In = s1.getInputStream(); ObjectInputStream objInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(s1In); Customer custResult = (Customer)objInputStream.readObject(); System.out.println(custResult.getName() + " has " + custResult.getCollectedPoints() + " points"); // When done, just close the connection and exit objInputStream.close(); s1In.close(); objOutputStream.close(); s1.close(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08javathreadingv1-151031160808-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-08-java-threading-11-2048.jpg)