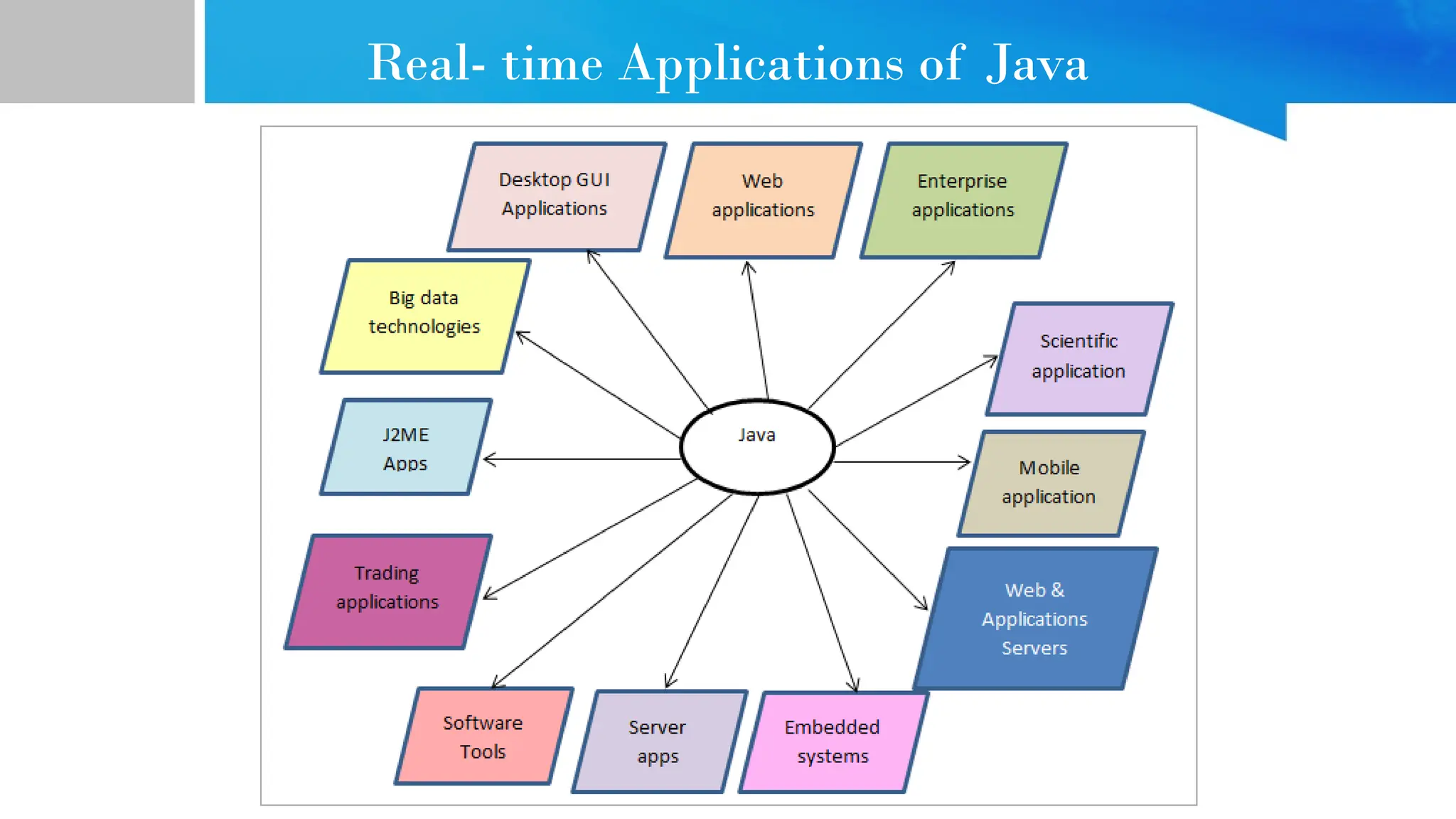
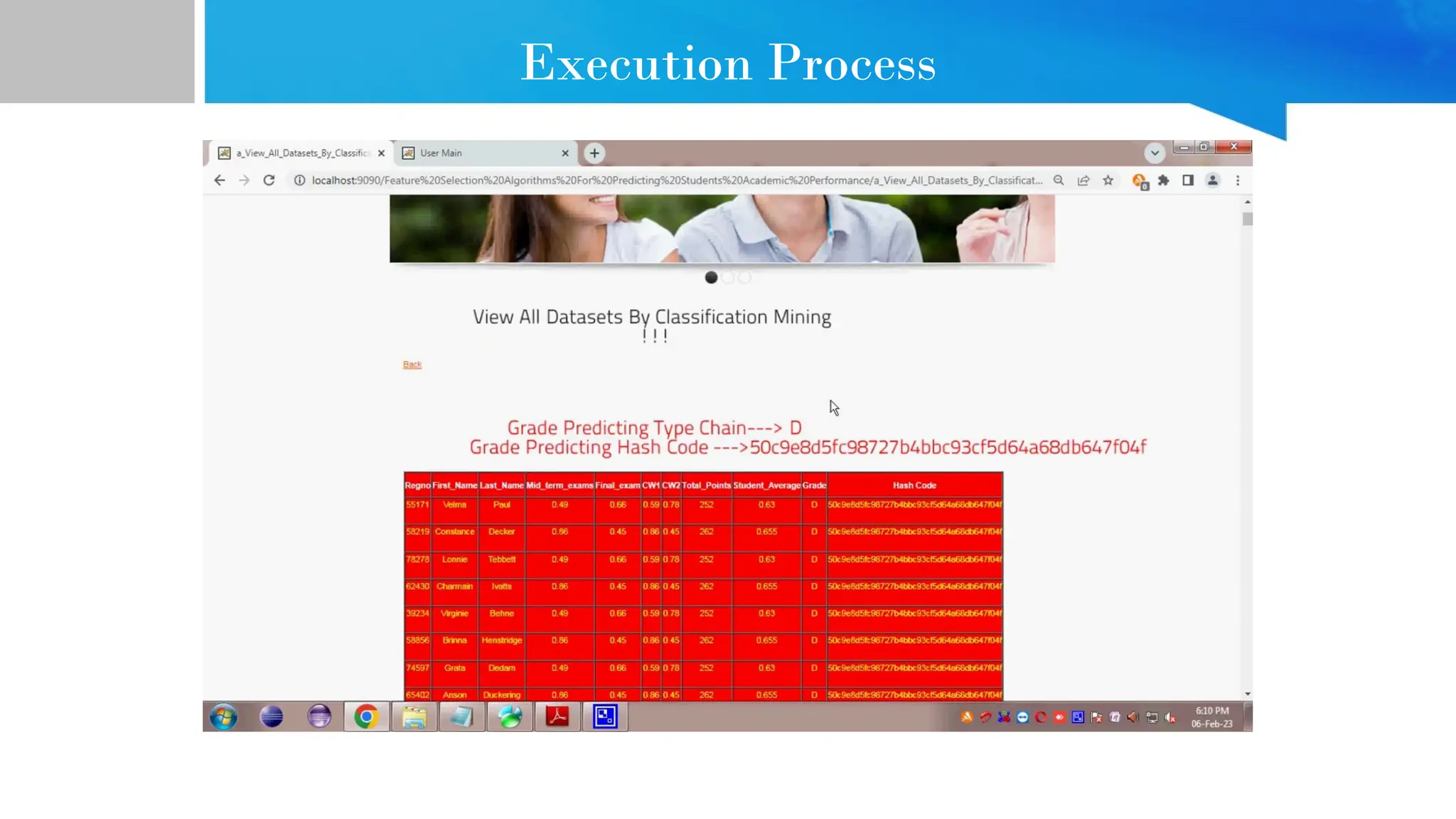
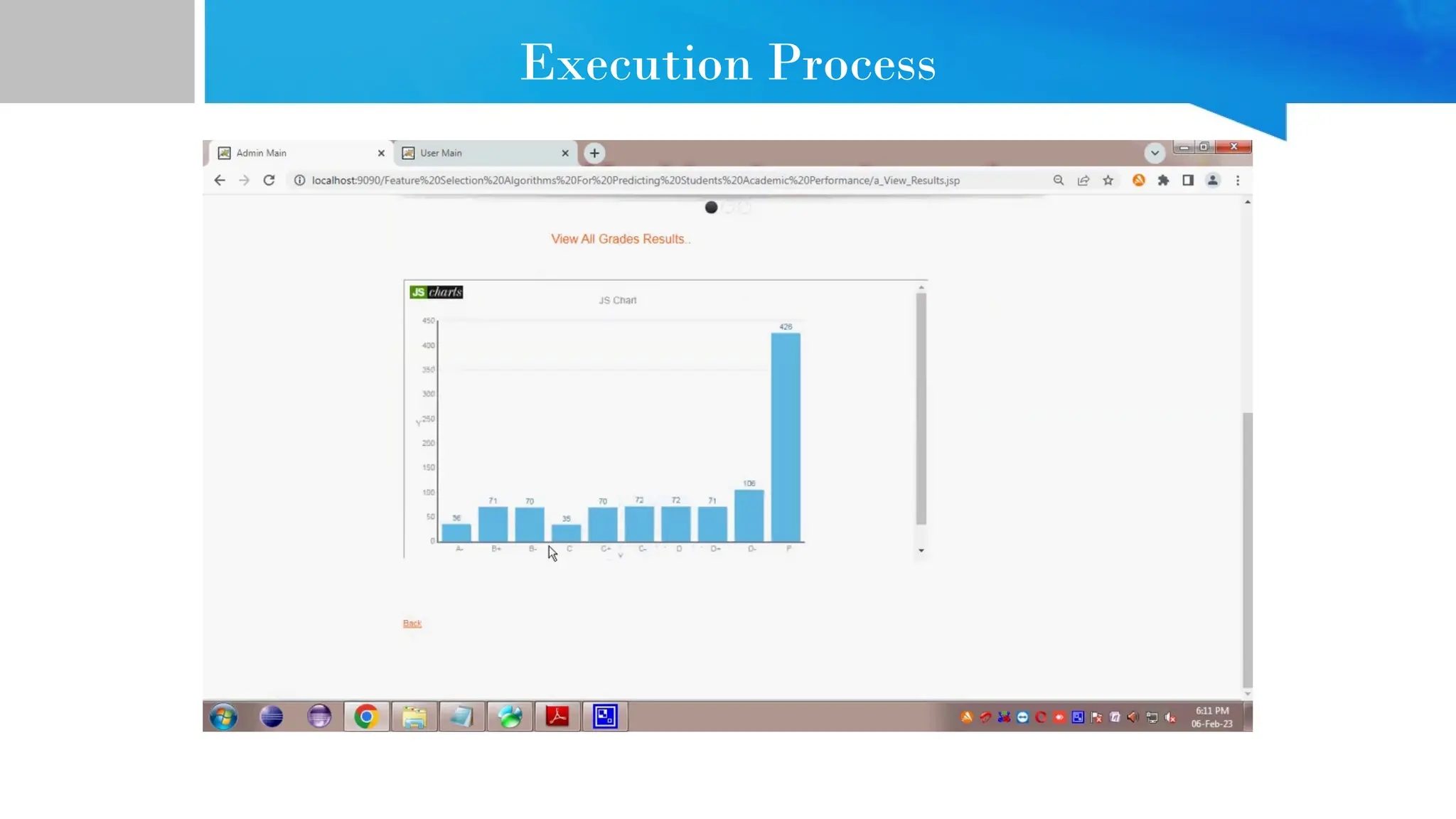
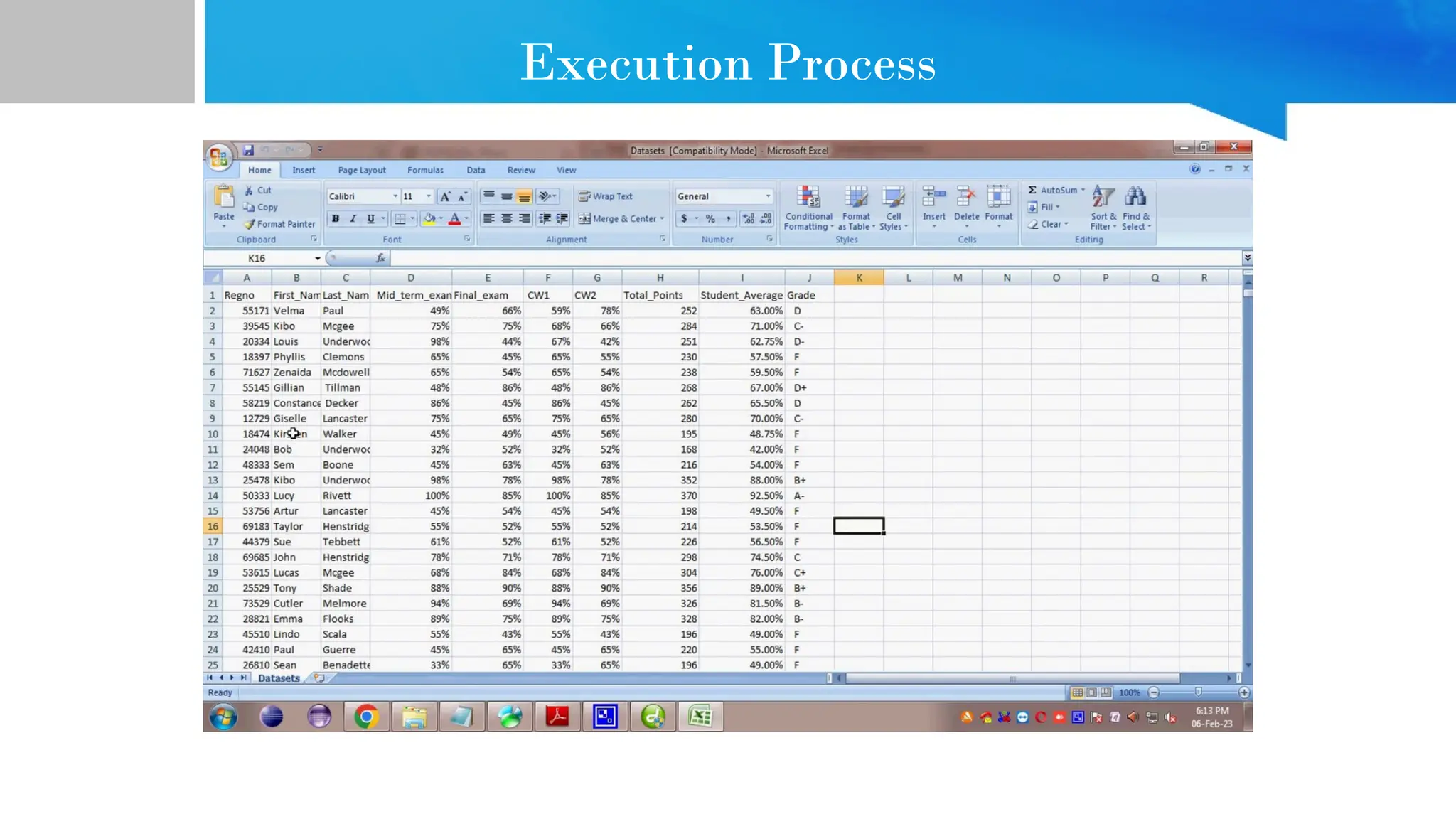
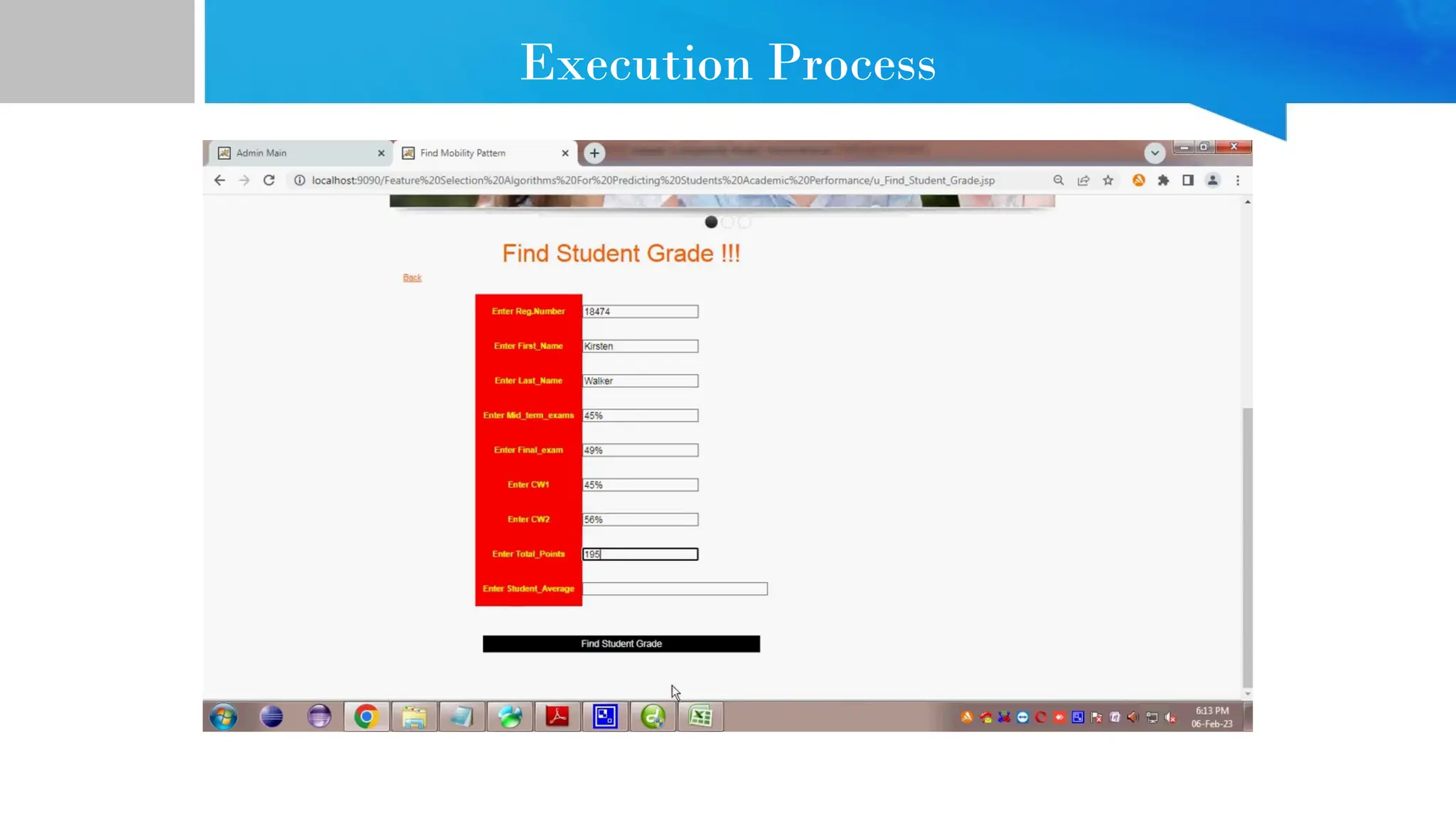
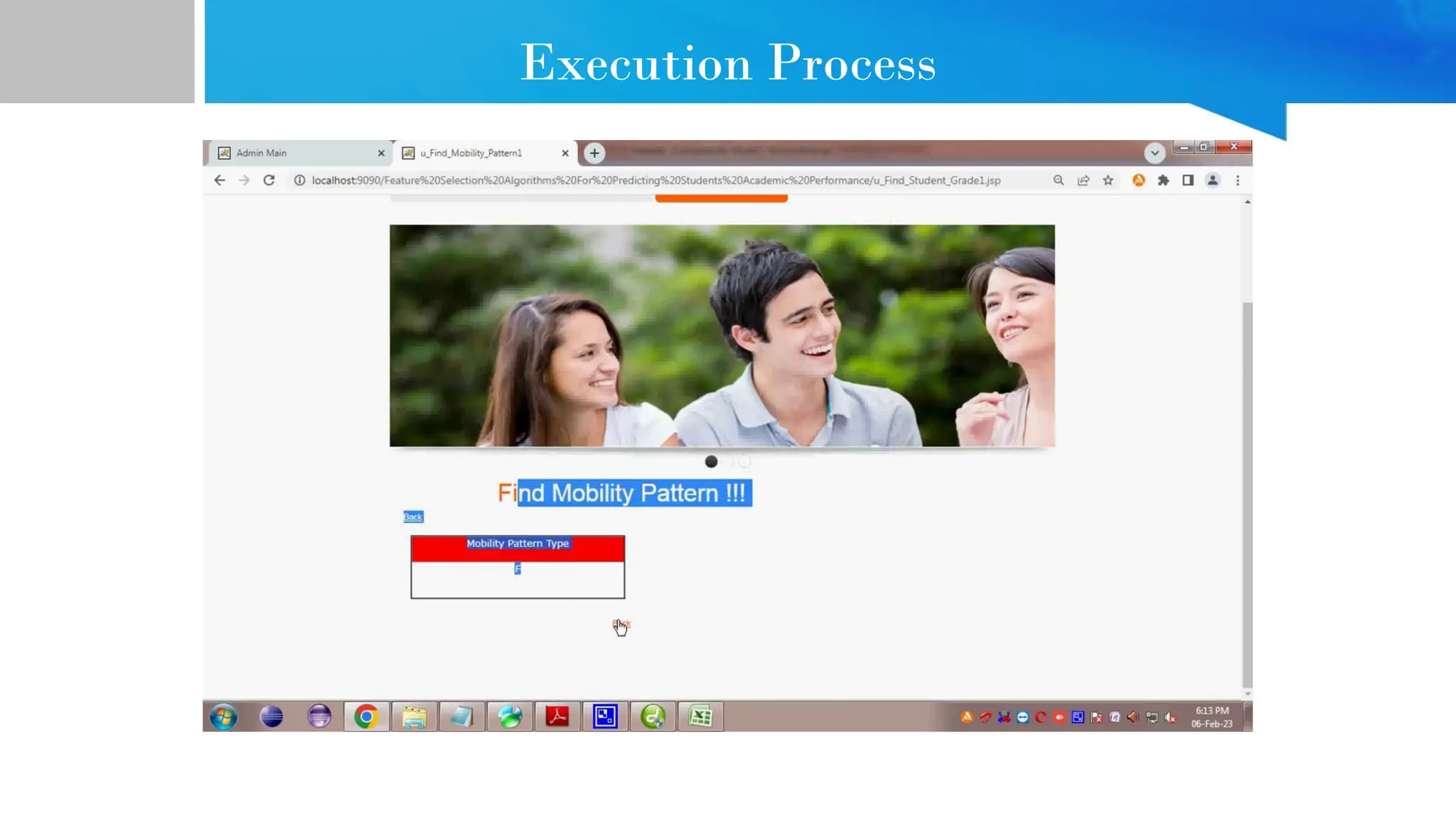
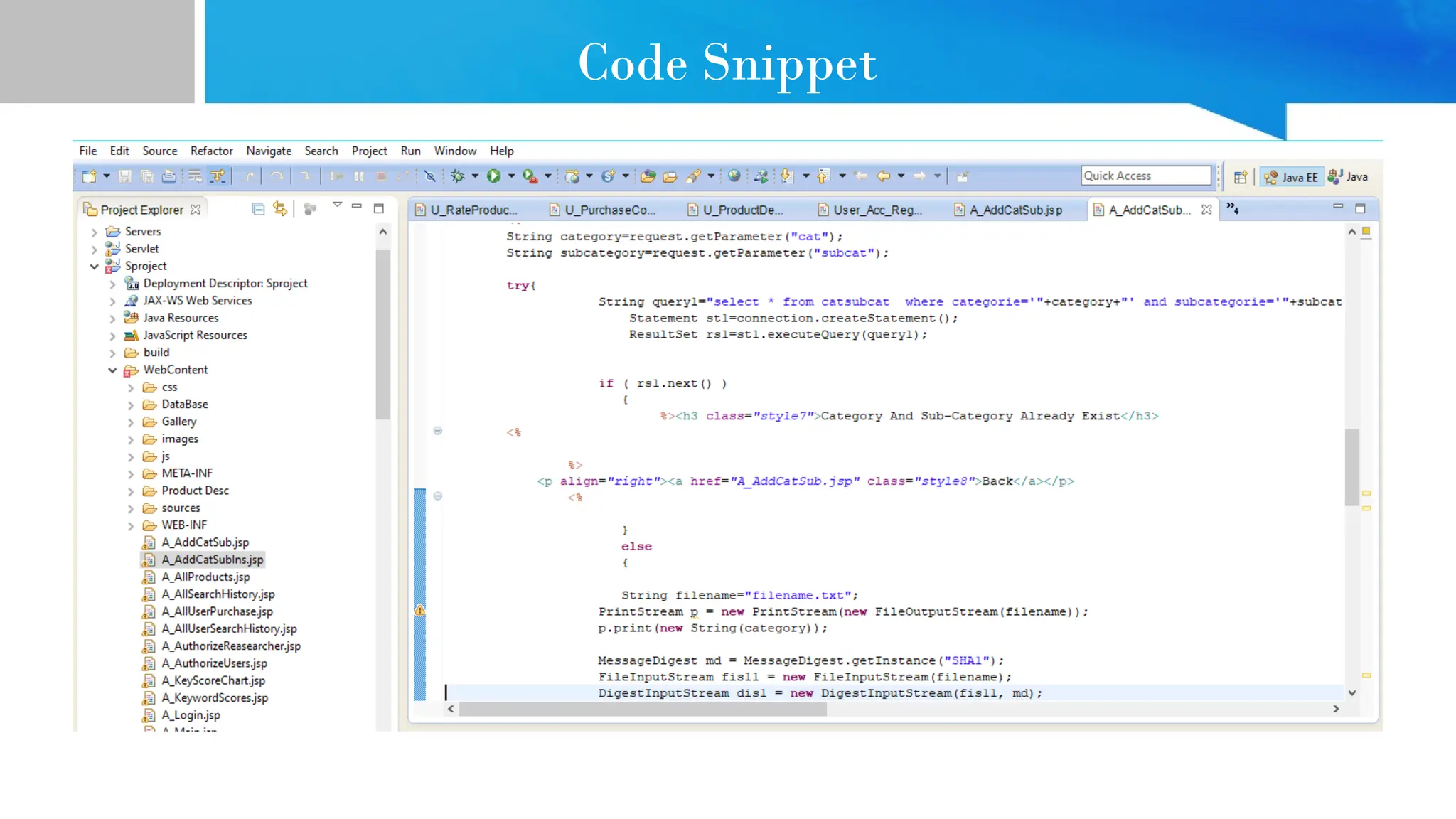
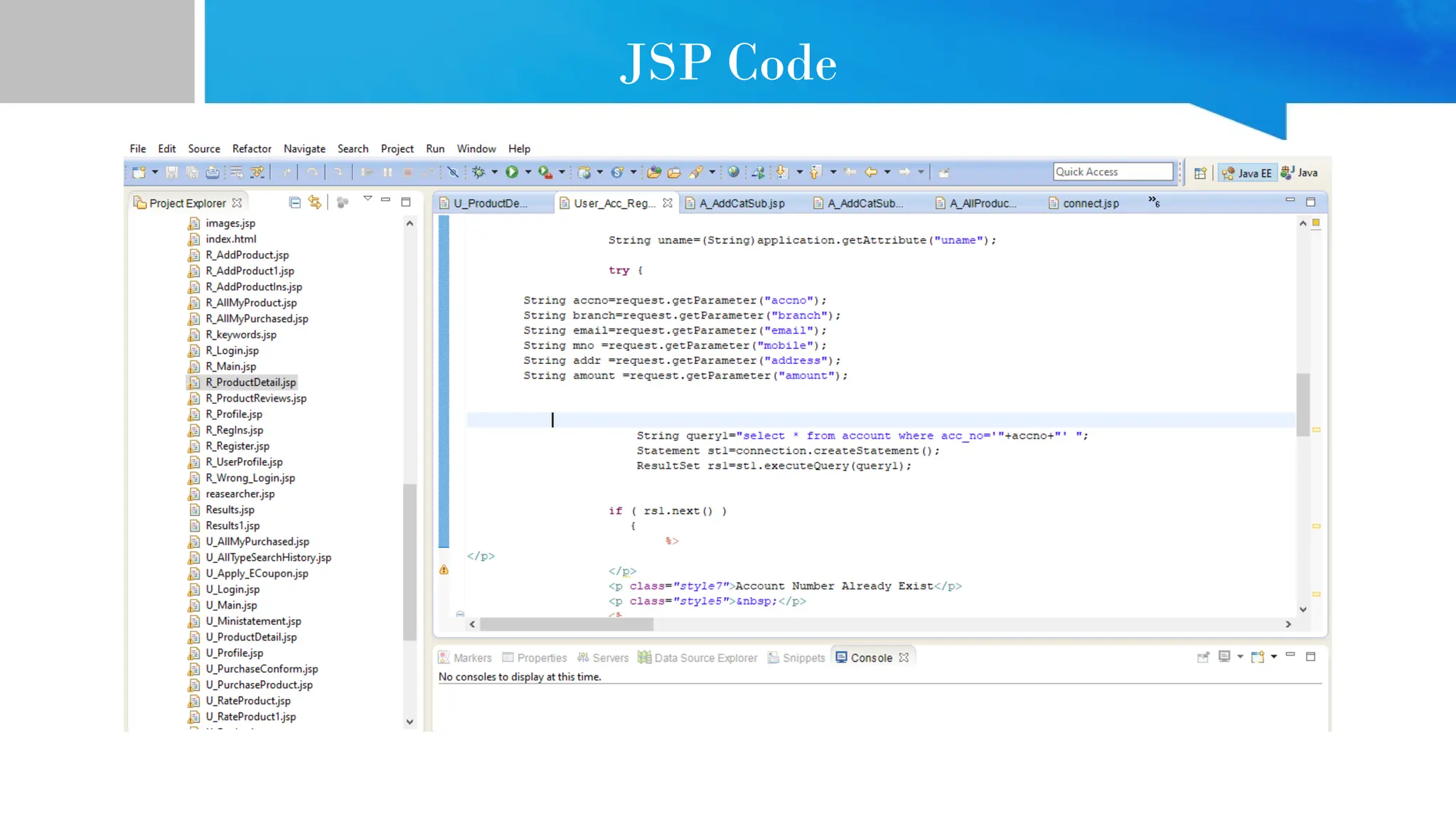
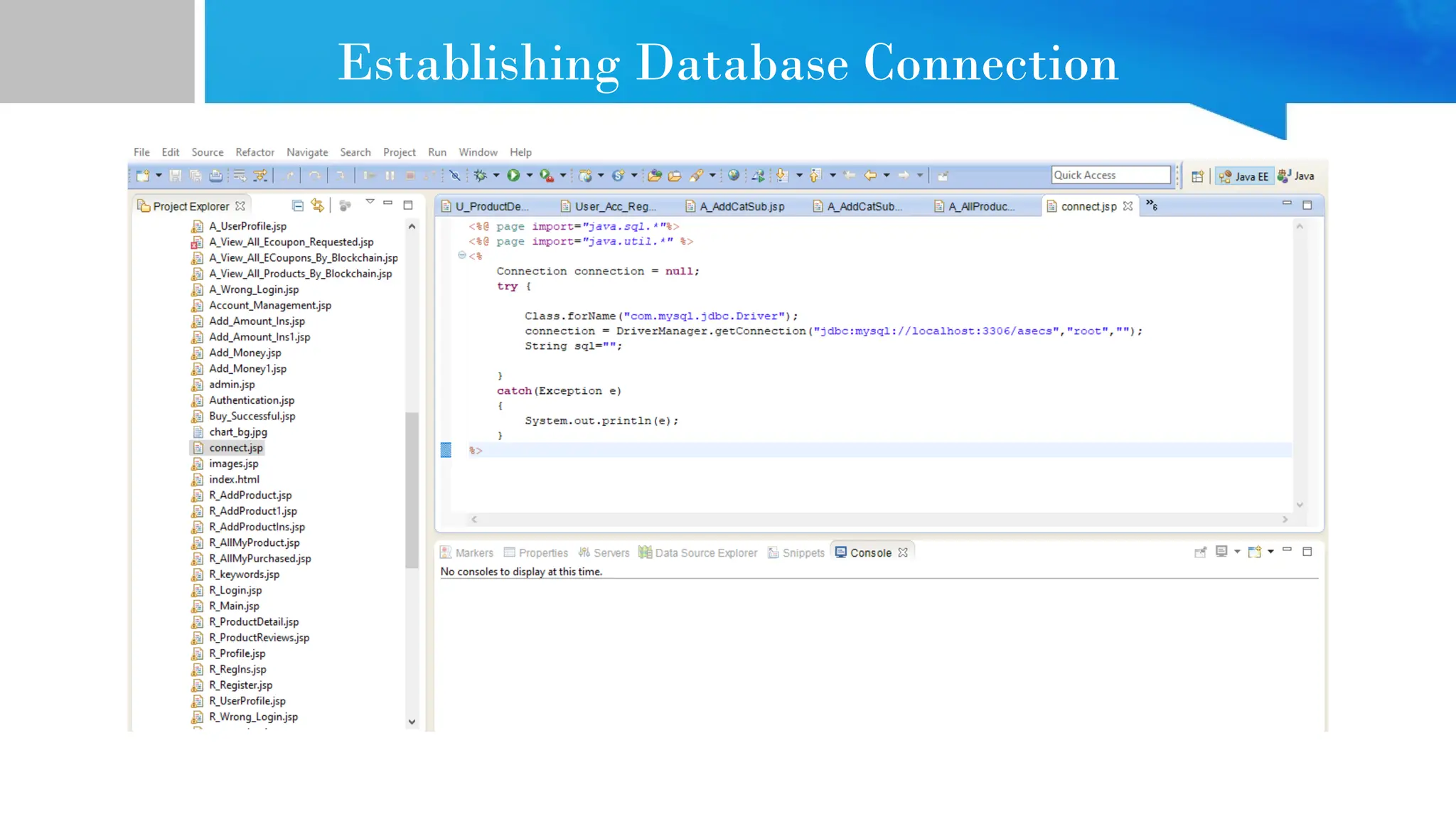
The document provides comprehensive guidance on Java programming, including its basics, real-time applications across various domains such as web, mobile, and enterprise systems, and advanced features like JDK, JRE, and JVM. It also covers the development process of educational data mining (EDM) systems, highlighting feature selection techniques to improve student performance prediction. The document emphasizes Java's robustness, security, and platform independence, detailing several case studies and practical applications of Java technology.