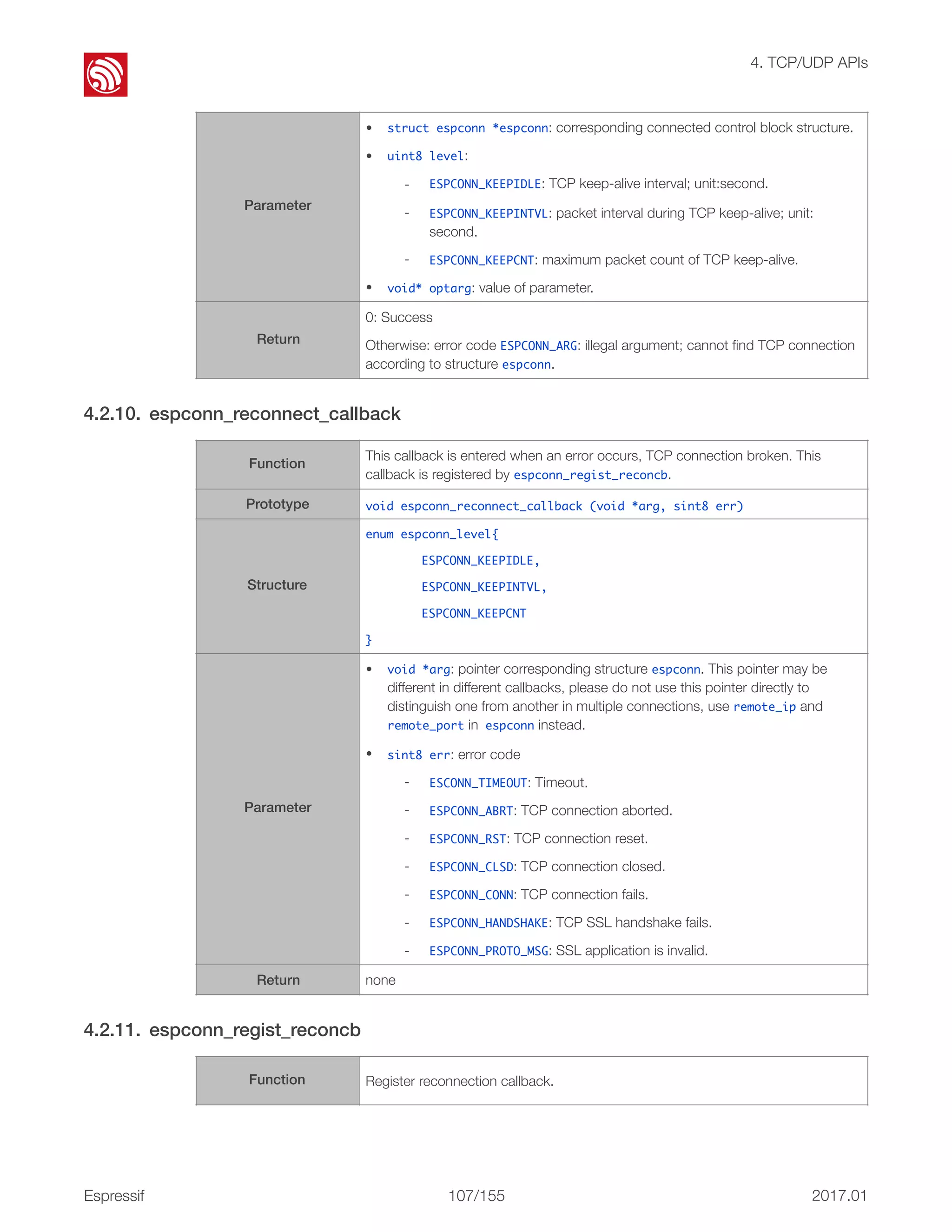
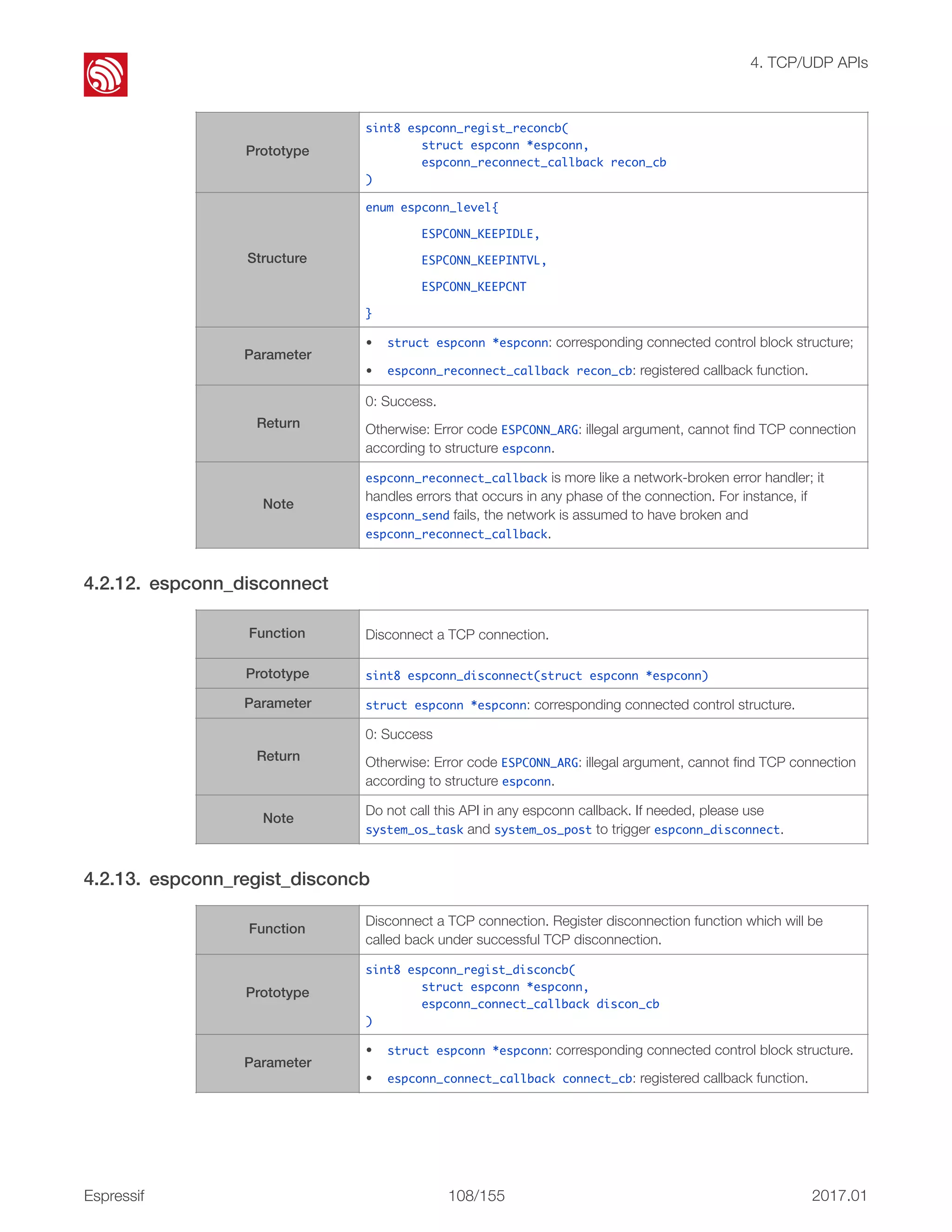
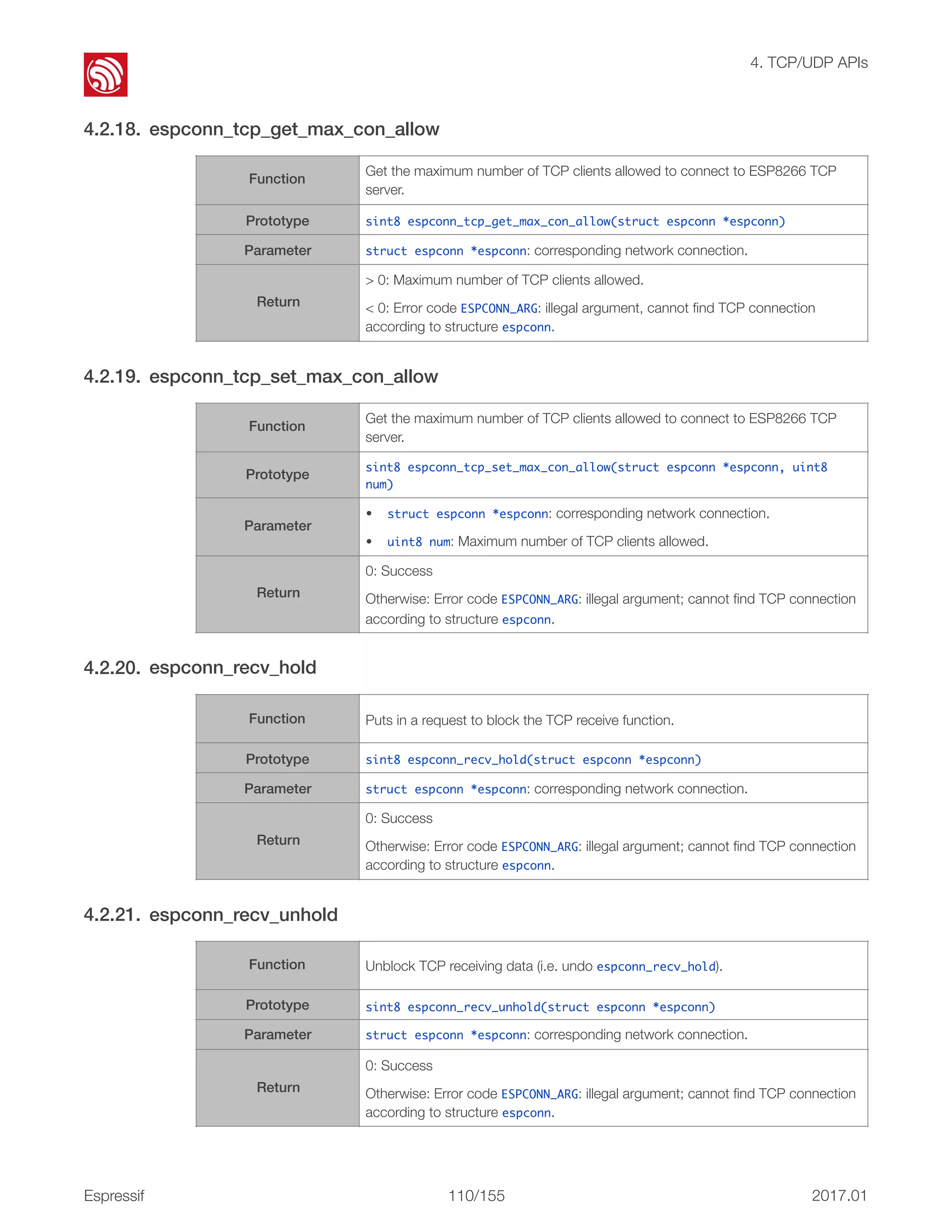
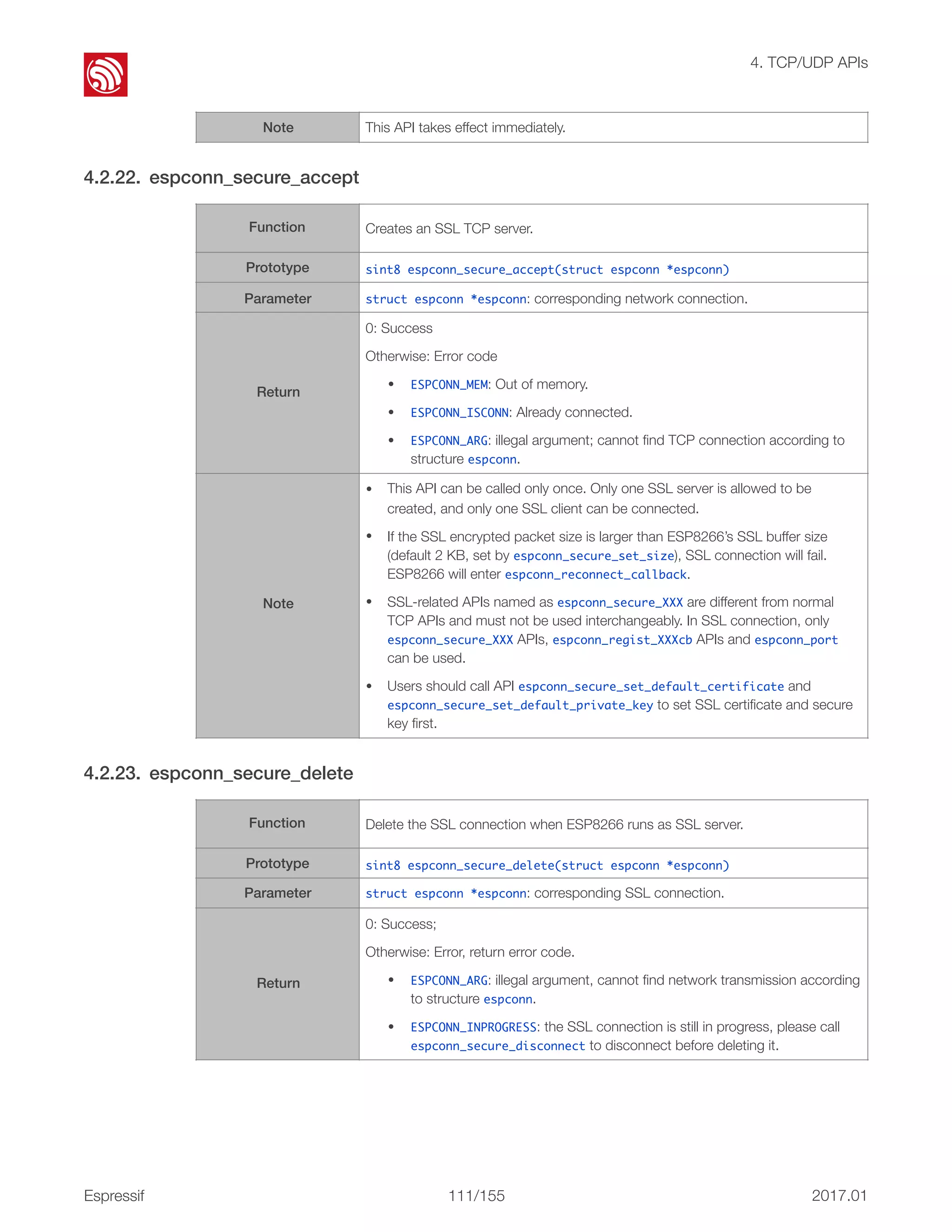
This document provides an overview and table of contents for the ESP8266 Non-OS SDK API Reference. It includes an introduction to the Non-OS SDK and code structure, describes the organization of the document into chapters covering topics like system APIs, Wi-Fi APIs, and more. The document also includes release notes listing version updates.



















![! 3. Application Programming Interface (APIs) 3.3.8. system_adc_read_fast Note • system_adc_read is only available when TOUT pin is wired to external circuitry. Input Voltage Range restricted to 0 ~ 1.0V. • The 107th byte in esp_init_data_default.bin (0 ~ 127 bytes) is named as vdd33_const, and when TOUT pin is wired to external circuitry, the vdd33_const must be set as real power voltage of VDD3P3 pin 3 and 4, and has to be less than 0xFF. • The range of operating voltage of ESP8266 is 1.8V ~ 3.6V, the unit of vdd33_const is 0.1V, so effective value range of vdd33_const is [18, 36]. If vdd33_const is an ineffective value in the range of (0, 18) or (36, 255), ESP8266 RF calibration will be 3.3V by default. • The return value of system_adc_read may be different in different Wi-Fi modes, for example, in Modem-sleep mode or in normal Wi-Fi working mode. • If high precision is needed, please use system_adc_read_fast instead. Function Fast and high-precision sampling of ADC. Prototype void system_adc_read_fast (uint16 *adc_addr, uint16 adc_num, uint8 adc_clk_div) Parameter uint16 *adc_addr: point to the address of ADC continuously fast sampling output. uint16 adc_num: sampling number of ADC continuously fast sampling; range [1, 65535]. uint8 adc_clk_div: ADC working clock = 80M/adc_clk_div; range [8, 32], the recommended value is 8. Return none Espressif ! /15511 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-25-2048.jpg)
![! 3. Application Programming Interface (APIs) 3.3.9. system_deep_sleep Example extern void system_adc_read_fast(uint16 *adc_addr, uint16 adc_num, uint8 adc_clk_div); os_timer_t timer; void ICACHE_FLASH_ATTR ADC_TEST(void *p)
{ wifi_set_opmode(NULL_MODE); ets_intr_lock( ); //close interrupt uint16 adc_addr[10]; uint16 adc_num = 10; uint8 adc_clk_div = 8; uint32 i; system_adc_read_fast(adc_addr, adc_num, adc_clk_div); for(i=0; i<adc_num; i++) os_printf("i=%d, adc_v=%dn", i, adc_addr[i]); ets_intr_unlock(); //open interrupt os_timer_disarm(&timer); os_timer_setfn(&timer, ADC_TEST, NULL); os_timer_arm(&timer,1000,1); } Note • system_adc_read_fast is only available when TOUT pin is wired to external circuitry. Input voltage range is restricted to 0 ~ 1.0V. • The 107th byte in esp_init_data_default.bin (0 ~ 127 bytes) is named as vdd33_const, and when TOUT pin is wired to external circuitry, the vdd33_const must be set as real power voltage of VDD3P3 pin 3 and 4, and has to be less than 0xFF. • The range of operating voltage of ESP8266 is 1.8V ~ 3.6V, the unit of vdd33_const is 0.1V, so effective value range of vdd33_const is [18, 36]. If vdd33_const is an ineffective value in the range of (0, 18) or (36, 255), ESP8266 RF calibration will use 3.3V by default. • To use system_adc_read_fast, Wi-Fi has to be disabled. And if ADC continuously sampling is needed, all interrupts have to be disabled, so PWM or NMI hardware timer can not be used when system_adc_read_fast is calling. Function Configures chip for Deep-sleep mode. When the device is in Deep-sleep, it automatically wakes up periodically; the period is configurable. Upon waking up, the device boots up from user_init. Prototype void system_deep_sleep(uint32 time_in_us) Parameter uint32 time_in_us: the duration of time (μs) when the device is in Deep-sleep. Return null Espressif ! /15512 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-26-2048.jpg)
![! 3. Application Programming Interface (APIs) 3.3.14. system_phy_set_tpw_via_vdd33 3.3.15. system_set_os_print 3.3.16. system_print_meminfo 3.3.17. system_get_free_heap_size Prototype void system_phy_set_max_tpw(uint8 max_tpw) Parameter uint8 max_tpw: maximum value of RF Tx Power, unit: 0.25 dBm, range [0, 82]. It can be set by referring to the 34th byte (target_power_qdb_0) of esp_init_data_default.bin (0 ~ 127 bytes). Return none Function Adjust RF Tx Power according to VDD33; unit : 1/1024 V. Prototype void system_phy_set_tpw_via_vdd33(uint16 vdd33) Parameter uint16 vdd33: VDD33, unit : 1/1024V, range [1900, 3300] Return none Note When TOUT pin is suspended, VDD33 can be got by system_get_vdd33; When TOUT pin is wired to external circuitry, system_get_vdd33 can not be used. Function Turn log printing on or off. Prototype void system_set_os_print (uint8 onoff) Parameter uint8 onoff Return none Note onoff = 0: print function off onoff = 1: print function on Default Print function on. Function Print memory information, including data/rodata/bss/heap. Prototype void system_print_meminfo (void) Parameter none Return none Function Get free heap size. Prototype uint32 system_get_free_heap_size(void) Espressif ! /15515 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-29-2048.jpg)


![! 3. System APIs 3.3.37. system_soft_wdt_feed 3.3.38. system_show_malloc 3.3.39. os_memset Prototype void system_soft_wdt_restart(void) Parameter none Return none Note This API can only be called if software watchdog is stopped (system_soft_wdt_stop). Function Feed software watchdog. Prototype void system_soft_wdt_feed(void) Parameter none Return none Note This API can only be called if software watchdog is enabled. Function For debugging memory leak issue and printing the memory usage. Prototype void system_show_malloc(void) Parameter none Return none Note • To use this API, users need to enable #define MEMLEAK_DEBUG in user_config.h, then refer to the note which is at the beginning of ESP8266_NONOS_SDKincludedmem.h. • The memory usage which cause memory leak issue may be in the logs, not ensure, just for reference. • This API is only for debugging. After calling this API, the program may go wrong, so please do not call it in normal usage. Function Set value of memory. Prototype os_memset(void *s, int ch, size_t n) Parameter void *s: pointer of memory int ch: set value size_t n: size Return none Example uint8 buffer[32]; os_memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); Espressif ! /15523 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-37-2048.jpg)
![! 3. System APIs 3.3.40. os_memcpy 3.3.41. os_strlen 3.3.42. os_printf 3.3.43. os_bzero Function Standard function for copying memory content. Prototype os_memcpy(void *des, void *src, size_t n) Parameter void *des: pointer of destination void *src: pointer of source size_t n: memory size Return none Note uint8 buffer[4] = {0}; os_memcpy(buffer, "abcd", 4); Function Get string length. Prototype os_strlen(char *s) Parameter char *s: string Return string length Example char *ssid = "ESP8266"; os_memcpy(softAP_config.ssid, ssid, os_strlen(ssid)); Function Print format. Prototype os_printf(const char *s) Parameter const char *s: string Return none Example os_printf("SDK version: %s n", system_get_sdk_version()); Note • Default to be output from UART 0. uart_init in IOT_Demo can set baud rate of UART, and os_install_putc1((void *)uart1_write_char) in it will set os_printf to be output from UART 1. • Continuously printing more than 125 bytes or repeated calls to this API may cause loss of print data. Function Set the first n bytes of string p to be 0, include ’0’. Prototype void os_bzero(void *p, size_t n) Espressif ! /15524 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-38-2048.jpg)

![! 3. System APIs 3.3.48. user_rf_cal_sector_set Example int ret = os_get_random((unsigned char *)temp, 7);
os_printf("ret %d, value 0x%08x%08xnr", ret, temp[1], temp[0]); Function Set the target flash sector to store RF_CAL parameters. Prototype uint32 user_rf_cal_sector_set(void) Parameter none Return The target flash sector to store RF_CAL parameters. Notes • The user_rf_cal_sector_set has to be added in application, but need NOT to be called. It will be called inside the SDK. • The system parameter area (4 flash sectors) has already been used, so the RF_CAL parameters will be stored in the target sector set by user_rf_cal_sector_set. Since we do not know which sector is available in user data area, users need to set an available sector in the user_rf_cal_sector_set for the SDK to store RF_CAL parameter. • If the user_rf_cal_sector_set is not added in the application, the compilation will fail in link stage. • Download blank.bin to initialize the sector stored RF_CAL parameter, and download esp_init_data.bin into flash, when the system needs to be initialized, or RF needs to be calibrated again. Example Set the 5th sector from the end of the flash to store the RF_CAL parameter. uint32 user_rf_cal_sector_set(void) { enum flash_size_map size_map = system_get_flash_size_map(); uint32 rf_cal_sec = 0; switch (size_map) { case FLASH_SIZE_4M_MAP_256_256: rf_cal_sec = 128 - 5; break; case FLASH_SIZE_8M_MAP_512_512: rf_cal_sec = 256 - 5; break; case FLASH_SIZE_16M_MAP_512_512: case FLASH_SIZE_16M_MAP_1024_1024: rf_cal_sec = 512 - 5; break; case FLASH_SIZE_32M_MAP_512_512: case FLASH_SIZE_32M_MAP_1024_1024: rf_cal_sec = 512 - 5; break; default: rf_cal_sec = 0; break; } return rf_cal_sec; } Espressif ! /15526 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-40-2048.jpg)

![! 3. System APIs 3.4.4. spi_flash_read 3.4.5. system_param_save_with_protect Function Read data to flash. Flash read/write has to be aligned to the 4-byte boundary. Prototype SpiFlashOpResult spi_flash_read(
uint32 src_addr,
uint32 * des_addr,
uint32 size
) Parameter uint32 src_addr: source address in flash. uint32 *des_addr: destination address to keep data. uint32 size: length of data; unit: byte, has to be aligned to the 4-bytes boundary. Return typedef enum {
SPI_FLASH_RESULT_OK,
SPI_FLASH_RESULT_ERR,
SPI_FLASH_RESULT_TIMEOUT
} SpiFlashOpResult; Example uint32 value; uint8 *addr = (uint8 *)&value; spi_flash_read(0x3E * SPI_FLASH_SEC_SIZE, (uint32 *)addr, 4); os_printf("0x3E sec:%02x%02x%02x%02xrn", addr[0], addr[1], addr[2], addr[3]); Function Write data into flash with protection. Flash read/write has to be aligned to the 4- byte boundary. Protection of flash read/write : 3 sectors (4 KB per sector) are used to save 4 KB data with protection; sector 0 and sector 1 are data sectors and back up each other; data is saved alternately; sector 2 is flag sector that points out which sector is keeping the latest data—sector 0 or sector 1. Prototype bool system_param_save_with_protect (
uint16 start_sec,
void *param,
uint16 len
) Parameter uint16 start_sec: start sector (sector 0) of the 3 sectors which used for flash read/write protection. For example, in IOT_Demo we could use the 3 sectors (3*4 KB) starts from flash 0x3D000 for flash read/write protection, so the parameter start_sec should be 0x3D. void *param: pointer of data need to save. uint16 len: data length, should less than a sector which is 4*1024. Return true: Success false: Failure Espressif ! /15528 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-42-2048.jpg)
![! 3. System APIs 3.4.6. system_param_load Example uint32 value; uint8 *addr = (uint8 *)&value; spi_flash_read(0x3E * SPI_FLASH_SEC_SIZE, (uint32 *)addr, 4); os_printf("0x3E sec:%02x%02x%02x%02xrn", addr[0], addr[1], addr[2], addr[3]); Note For more details about protection of flash read/write, please see ESP8266 Flash RW Operation. Function Read protected data from flash. Flash read/write has to be aligned to the 4-byte boundary. Protection of flash read/write : 3 sectors (4 KB per sector) are used to save 4 KB data with protection; sector 0 and sector 1 are data sectors and back up each other; data is saved alternately; sector 2 is flag sector that points out which sector is keeping the latest data—sector 0 or sector 1. Prototype bool system_param_load ( uint16 start_sec, uint16 offset, void *param, uint16 len
) Parameter uint16 start_sec: start sector (sector 0) of the 3 sectors which used for flash read/write protection. It cannot be sectors 1 or 2. For example, in IOT_Demo we could use the 3 sectors (3*4 KB) starts from flash 0x3D000 for flash read/write protection, so the parameter start_sec should be 0x3D. uint16 offset: offset of data saved in sector. void *param: pointer of data need to save. uint16 len: data length, should less than a sector which is 4*1024. Return true: Success false: Failure Example uint32 value; uint8 *addr = (uint8 *)&value; spi_flash_read(0x3E * SPI_FLASH_SEC_SIZE, (uint32 *)addr, 4); os_printf("0x3E sec:%02x%02x%02x%02xrn", addr[0], addr[1], addr[2], addr[3]); Note For more details about protection of flash read/write, please see ESP8266 Flash RW Operation. Espressif ! /15529 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-43-2048.jpg)

![! 3. System APIs 3.5.7. wifi_station_set_config 3.5.8. wifi_station_set_config_current Function Set Wi-Fi Station configuration, and save it to flash. Prototype bool wifi_station_set_config (struct station_config *config) Parameter struct station_config *config: Wi-Fi Station configuration pointer Return true: Success false: Failure Example void ICACHE_FLASH_ATTR user_set_station_config(void) { char ssid[32] = SSID; char password[64] = PASSWORD; struct station_config stationConf; stationConf.bssid_set = 0; //need not check MAC address of AP os_memcpy(&stationConf.ssid, ssid, 32); os_memcpy(&stationConf.password, password, 64); wifi_station_set_config(&stationConf); } void user_init(void) { wifi_set_opmode(STATIONAP_MODE); //Set softAP + station mode user_set_station_config(); } Note • This API can be called only if ESP8266 Station is enabled. • If wifi_station_set_config is called in user_init , there is no need to call wifi_station_connect after that, ESP8266 will connect to router automatically; otherwise, wifi_station_connect is needed to connect. • In general, station_config.bssid_set need to be 0, otherwise it will check BSSID which is the MAC address of AP. • This configuration will be saved in flash system parameter area if changed. Function Set Wi-Fi Station configuration; setting in flash is not updated. Prototype bool wifi_station_set_config (struct station_config *config) Parameter struct station_config *config: Wi-Fi Station configuration pointer Return true: Success false: Failure Espressif ! /15533 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-47-2048.jpg)
![! 3. System APIs 3.5.9. wifi_station_set_cert_key Example void ICACHE_FLASH_ATTR user_set_station_config(void) { char ssid[32] = SSID; char password[64] = PASSWORD; struct station_config stationConf; stationConf.bssid_set = 0; //need not check MAC address of AP os_memcpy(&stationConf.ssid, ssid, 32); os_memcpy(&stationConf.password, password, 64); wifi_station_set_config(&stationConf); } void user_init(void) { wifi_set_opmode(STATIONAP_MODE);//Set softAP + station mode user_set_station_config(); } Note • This API can be called only if ESP8266 Station is enabled. • If wifi_station_set_config is called in user_init , there is no need to call wifi_station_connect after that, ESP8266 will connect to router automatically; otherwise, wifi_station_connect is needed to connect. • In general, station_config.bssid_set need to be 0, otherwise it will check BSSID which is the MAC address of AP. Function This API is deprecated; please use wifi_station_set_enterprise_cert_key instead. Set certificate and private key for connecting to WPA2-ENTERPRISE AP. Prototype bool wifi_station_set_cert_key (
uint8 *client_cert, int client_cert_len,
uint8 *private_key, int private_key_len,
uint8 *private_key_passwd, int private_key_passwd_len,) Parameter uint8 *client_cert: certificate; HEX array. int client_cert_len: length of certificate. uint8 *private_key: private key; HEX array; can NOT be longer than 2048 bits. int private_key_len: length of private key; less than 2048 bits. uint8 *private_key_passwd: password for private key; to be supported; can only be NULL now. int private_key_passwd_len: length of password; to be supported; can only be 0 now. Return 0: Success otherwise: Failure Espressif ! /15534 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-48-2048.jpg)
![! 3. System APIs 3.5.10. wifi_station_clear_cert_key 3.5.11. wifi_station_set_username Example For example, the private key is - - - - - BEGIN PRIVATE KEY - - - - - … … … … Then the array should be uint8 key[]={0x2d, 0x2d, 0x2d, 0x2d, 0x2d, 0x42, 0x45, 0x47, … … 0x00 }; It is the ASCII of the characters, and the array needs to terminate with 0x00. Note • Connecting to WPA2-ENTERPRISE AP needs more than 26 KB of memory, please ensure enough space (system_get_free_heap_size). • So far, WPA2-ENTERPRISE can only support unencrypted certificate and private key, and only in PEM format. - Header of certificate: - - - - - BEGIN CERTIFICATE - - - - - - Header of private key: - - - - - BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY - - - - - or - - - - - BEGIN PRIVATE KEY - - - - - • Please call this API to set certificate and private key before connecting to WPA2- ENTERPRISE AP and the application needs to hold the certificate and private key. Call wifi_station_clear_cert_key to release resources and clear status after connected to the target AP, and then the application can release the certificate and private key. • If the private key is encrypted, please use OpenSSL PKey command to change it to unencrypted file to use, or use OpenSSl RSA related commands to change it (or change the start TAG). Function This API is deprecated, please use wifi_station_clear_enterprise_cert_key instead. Release certificate and private key resources and clear related status after connected to the WPA2-ENTERPRISE AP. Prototype void wifi_station_clear_cert_key (void) Parameter none Return none Function This API is deprecated, please use wifi_station_clear_enterprise_cert_key instead. Set ESP8266 Station’s user name for connecting to WPA2-ENTERPRISE AP. Prototype int wifi_station_set_username (uint8 *username, int len) Parameter uint8 *username: the user name. int len: length of user name. Return 0 : Success otherwise: Failure Espressif ! /15535 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-49-2048.jpg)
![! 3. System APIs 3.5.18. wifi_station_ap_number_set 3.5.19. wifi_station_get_ap_info 3.5.20. wifi_station_ap_change Example wifi_station_scan(&config, scan_done);
static void ICACHE_FLASH_ATTR scan_done(void *arg, STATUS status) {
if (status == OK) {
struct bss_info *bss_link = (struct bss_info *)arg;
...
}
} Function Sets the number of APs that will be cached for ESP8266 Station mode. Whenever ESP8266 Station connects to an AP, it caches a record of this AP’s SSID and password. The cached ID index starts from 0. Prototype bool wifi_station_ap_number_set (uint8 ap_number) Parameter uint8 ap_number: the number of APs that can be recorded (MAX: 5) Return true: Success false: Failure Example wifi_station_scan(&config, scan_done);
static void ICACHE_FLASH_ATTR scan_done(void *arg, STATUS status) {
if (status == OK) {
struct bss_info *bss_link = (struct bss_info *)arg;
...
}
} Note This configuration will be saved in flash system parameter area if changed. Function Get information of APs recorded by ESP8266 Station. Prototype uint8 wifi_station_get_ap_info(struct station_config config[]) Parameter struct station_config config[]: information of APs; array size has to be 5. Return The number of APs recorded. Example struct station_config config[5];
int i = wifi_station_get_ap_info(config); Function Switch ESP8266 Station connection to AP as specified. Prototype bool wifi_station_ap_change (uint8 new_ap_id) Parameter uint8 new_ap_id: AP’s record ID; start counting from 0. Return true: Success false: Failure Espressif ! /15538 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-52-2048.jpg)

![! 3. System APIs 3.5.43. wifi_softap_set_dhcps_lease_time 3.5.44. wifi_softap_get_dhcps_lease_time 3.5.45. wifi_softap_reset_dhcps_lease_time 3.5.46. wifi_softap_dhcps_status Function Set ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server lease time, 120 minutes by default. Prototype bool wifi_softap_set_dhcps_lease_time(uint32 minute) Parameter uint32 minute: lease time, uint: minute, range: [1, 2880]. Return true: Success false: Failure Note This API can only be called when ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server is enabled. Function Get ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server lease time. Prototype uint32 wifi_softap_get_dhcps_lease_time(void) Return Lease time; uint: minute. Note This API can only be called when ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server is enabled. Function Reset ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server lease time to its default value, which is 120 minutes. Prototype bool wifi_softap_reset_dhcps_lease_time(void) Return true: Success false: Failure Note This API can only be called when ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server is enabled. Function Get ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server status. Prototype enum dhcp_status wifi_softap_dhcps_status(void) Parameter none Return enum dhcp_status {
DHCP_STOPPED,
DHCP_STARTED
}; Note This API can only be called when ESP8266 SoftAP DHCP server is enabled. Espressif ! /15546 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-60-2048.jpg)

![! 3. System APIs 3.5.52. wifi_set_macaddr Example wifi_set_opmode(STATIONAP_MODE); //Set softAP + station mode struct ip_info info; wifi_station_dhcpc_stop(); wifi_softap_dhcps_stop();
IP4_ADDR(&info.ip, 192, 168, 3, 200);
IP4_ADDR(&info.gw, 192, 168, 3, 1);
IP4_ADDR(&info.netmask, 255, 255, 255, 0);
wifi_set_ip_info(STATION_IF, &info);
IP4_ADDR(&info.ip, 10, 10, 10, 1);
IP4_ADDR(&info.gw, 10, 10, 10, 1);
IP4_ADDR(&info.netmask, 255, 255, 255, 0);
wifi_set_ip_info(SOFTAP_IF, &info); wifi_softap_dhcps_start(); Note To set static IP, please disable DHCP first (wifi_station_dhcpc_stop or wifi_softap_dhcps_stop): • If static IP is enabled, DHCP will be disabled; • If DHCP is enabled, static IP will be disabled. Function Set MAC address. Prototype bool wifi_set_macaddr(
uint8 if_index,
uint8 *macaddr
) Parameter uint8 if_index: set station MAC or SoftAP MAC. #define STATION_IF 0x00
#define SOFTAP_IF 0x01 uint8 *macaddr: MAC address. Return true: Success false: Failure Example wifi_set_opmode(STATIONAP_MODE); char sofap_mac[6] = {0x16, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78, 0x90, 0xab};
char sta_mac[6] = {0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78, 0x90, 0xab};
wifi_set_macaddr(SOFTAP_IF, sofap_mac);
wifi_set_macaddr(STATION_IF, sta_mac); Note • This API can only be called in user_init. • ESP8266 SoftAP and station have different MAC addresses, please do not set them to be the same. • The bit 0 of the first byte of ESP8266 MAC address can not be 1. For example, MAC address can be “1a:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX”, but can not be “15:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX”. Espressif ! /15549 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-63-2048.jpg)


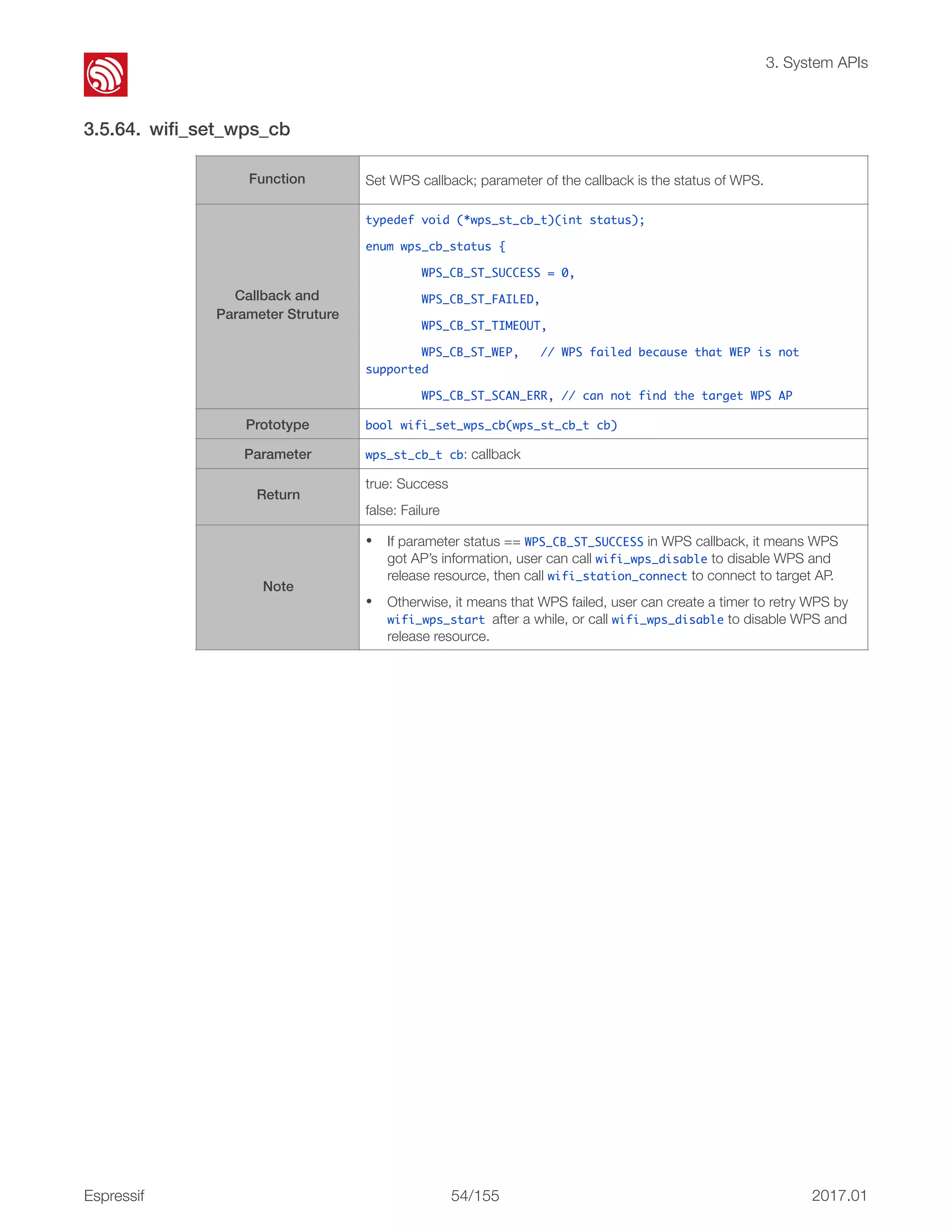
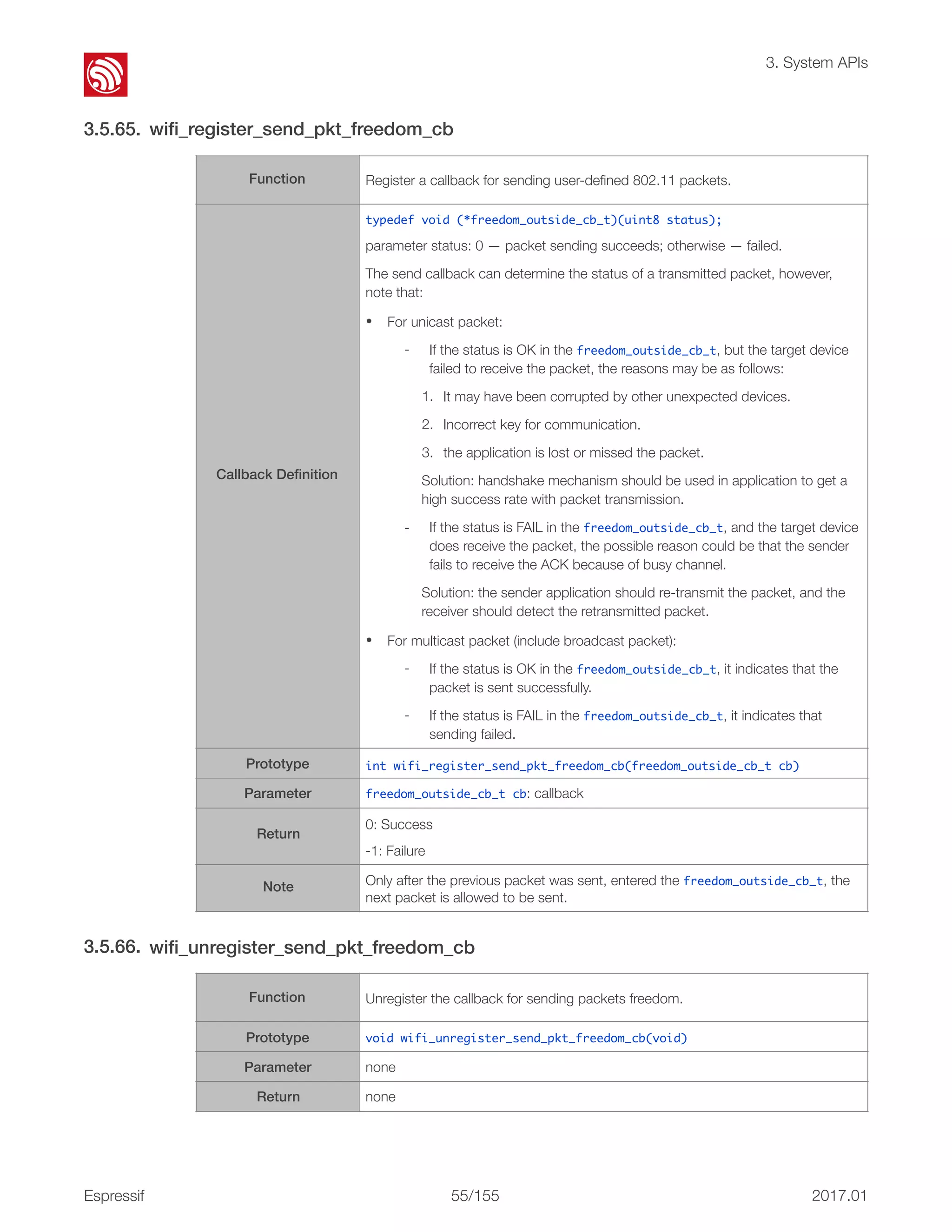
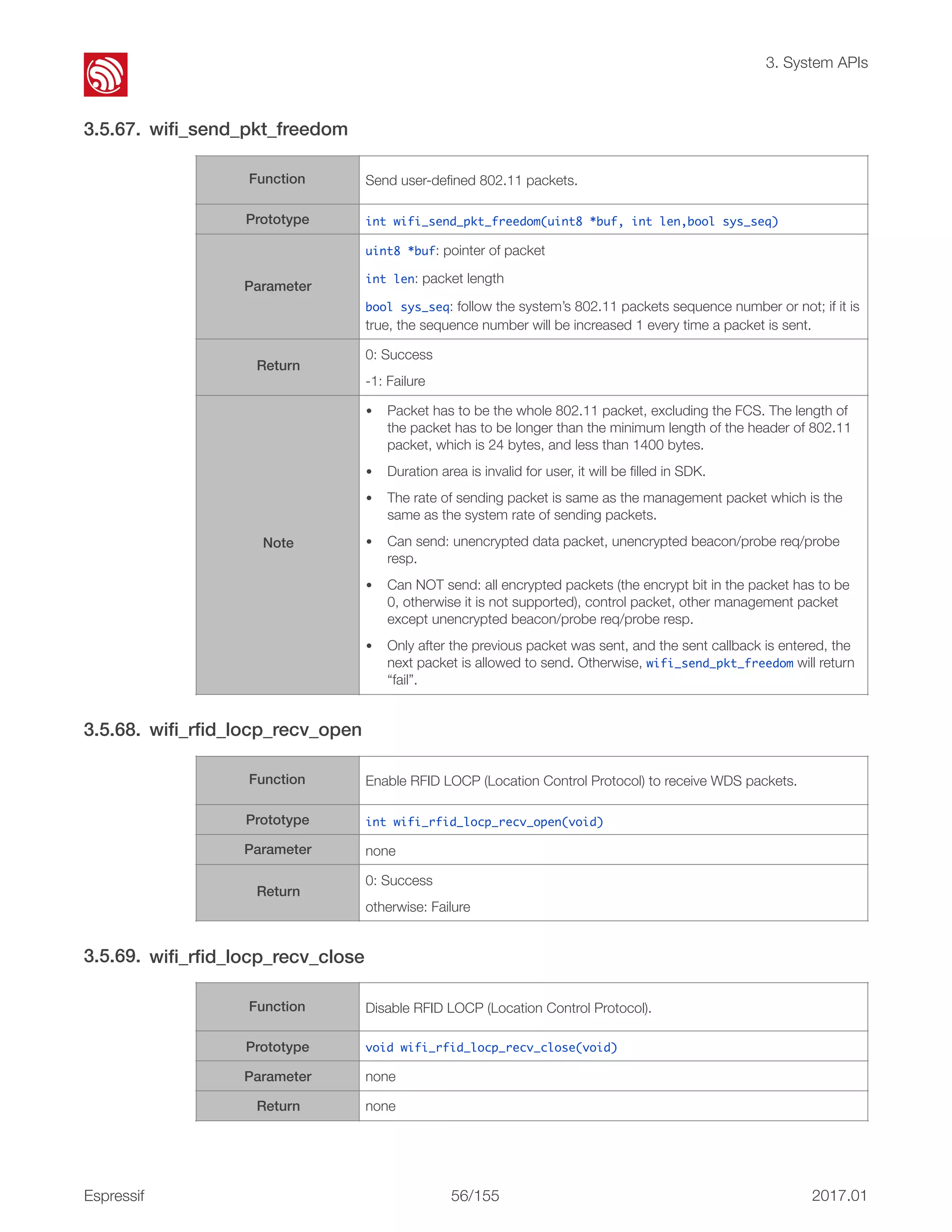
![! 3. System APIs 3.5.70. wifi_register_rfid_locp_recv_cb 3.5.71. wifi_unregister_rfid_locp_recv_cb 3.5.72. wifi_enable_gpio_wakeup Function Register a callback on receiving WDS packets, only if the first MAC address of the WDS packet is a multicast address. Callback Definition typedef void (*rfid_locp_cb_t)(uint8 *frm, int len, int rssi); Parameter uint8 *frm: point to the head of 802.11 packet. int len: packet length. int rssi: signal strength. Prototype int wifi_register_rfid_locp_recv_cb(rfid_locp_cb_t cb) Return 0: Success otherwise: Failure Function Unregister the callback of receiving WDS packets. Prototype void wifi_unregister_rfid_locp_recv_cb(void) Parameter none Return none Function Set a GPIO to wake the ESP8266 up from light-sleep mode. Prototype void wifi_enable_gpio_wakeup(uint32 i, GPIO_INT_TYPE intr_status) Parameter uint32 i: GPIO number, range: [0, 15]. GPIO_INT_TYPE intr_status: status of GPIO interrupt to trigger the wakeup process. Return none Example ESP8266 will be wakened from Light-sleep, when the GPIO12 is in low-level. GPIO_DIS_OUTPUT(12); PIN_FUNC_SELECT(PERIPHS_IO_MUX_MTDI_U, FUNC_GPIO12); wifi_enable_gpio_wakeup(12, GPIO_PIN_INTR_LOLEVEL); Note If the ESP8266 enters light-sleep automatically (wifi_set_sleep_type(LIGHT_SLEEP_T);), after being waken up by GPIO, when the chip attempts to sleep again, it will check the status of the GPIO: • If the GPIO is still in the wakeup status, the EP8266 will enter modem- sleep mode instead; • If the GPIO is NOT in the wakeup status, the ESP8266 will enter light-sleep mode. Espressif ! /15557 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-71-2048.jpg)









![! 3. System APIs 3.11. Sniffer Related APIs Sniffer APIs can be found in: /ESP8266_NONOS_SDK/include/user_interface.h. 3.11.1. wifi_promiscuous_enable 3.11.2. wifi_promiscuous_set_mac 3.11.3. wifi_set_promiscuous_rx_cb Function Enable promiscuous mode for sniffer. Prototype void wifi_promiscuous_enable(uint8 promiscuous) Parameter uint8 promiscuous: • 0: disable promiscuous; • 1: enable promiscuous Return none Note • Promiscuous mode can only be enabled in Station mode. • During promiscuous mode (sniffer), ESP8266 Station and SoftAP are disabled. • Before enable promiscuous mode, please call wifi_station_disconnect first. • Don’t call any other APIs during sniffer, please call wifi_promiscuous_enable(0) first. Function Set MAC address filter for sniffer. Prototype void wifi_promiscuous_set_mac(const uint8_t *address) Parameter const uint8_t *address: MAC address Return none Note This filter only be available in the current sniffer phase, if you disable sniffer and then enable sniffer, you need to set filter again if you need it. Example char ap_mac[6] = {0x16, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78, 0x90, 0xab}; wifi_promiscuous_set_mac(ap_mac); Function Registers an Rx callback function in promiscuous mode, which will be called when data packet is received. Prototype void wifi_set_promiscuous_rx_cb(wifi_promiscuous_cb_t cb) Parameter wifi_promiscuous_cb_t cb: callback Return none Espressif ! /15582 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-96-2048.jpg)

![! 3. System APIs Return true: Success false: Failure Example void ICACHE_FLASH_ATTR smartconfig_done(sc_status status, void *pdata) { switch(status) { case SC_STATUS_WAIT: os_printf("SC_STATUS_WAITn"); break; case SC_STATUS_FIND_CHANNEL: os_printf("SC_STATUS_FIND_CHANNELn"); break; case SC_STATUS_GETTING_SSID_PSWD: os_printf("SC_STATUS_GETTING_SSID_PSWDn"); sc_type *type = pdata; if (*type == SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCH) { os_printf("SC_TYPE:SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCHn"); } else { os_printf("SC_TYPE:SC_TYPE_AIRKISSn"); } break; case SC_STATUS_LINK: os_printf("SC_STATUS_LINKn"); struct station_config *sta_conf = pdata; wifi_station_set_config(sta_conf); wifi_station_disconnect(); wifi_station_connect(); break; case SC_STATUS_LINK_OVER: os_printf("SC_STATUS_LINK_OVERn"); if (pdata != NULL) { uint8 phone_ip[4] = {0}; memcpy(phone_ip, (uint8*)pdata, 4); os_printf("Phone ip: %d.%d.%d.%d n",phone_ip[0],phone_ip[1],phone_ip[2],phone_ip[3]); } smartconfig_stop(); break; } } smartconfig_start(smartconfig_done); Note • This API can only be called in station mode. • During smart-config, ESP8266 Station and SoftAP are disabled. • Can not call smartconfig_start twice before it finish, please call smartconfig_stop first. • Don’t call any other APIs during smart-config, please call smartconfig_stop first. Espressif ! /15585 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-99-2048.jpg)





![! 3. System APIs 3.14. WPA2_Enterprise APIs ESP8266 Station can connect to WPA2_Enterprise APs. WPA2_Enterprise APIs can be found in /ESP8266_NONOS_SDK/include/ wpa2_enterprise.h. 3.14.1. wifi_station_set_wpa2_enterprise_auth 3.14.2. wifi_station_set_enterprise_cert_key Function Set authentication of WPA2_Enterprise. To connect to WPA2_Enterprise AP, wifi_station_set_wpa2_enterprise_auth(1); should be called first. For connecting to a regular AP at a later stage, wifi_station_set_wpa2_enterprise_auth(0); should be called to clear the WPA2_Enterprise status. Prototype int wifi_station_set_wpa2_enterprise_auth(int enable) Parameter int enable: • 0, disable authentication of WPA2_Enterprise, clear the status; • otherwise, enable authentication of WPA2_Enterprise. Return 0: Success otherwise: Failure Function Set user certificate and private key for connecting to WPA2_Enterprise AP. It is used for EAP- TLS authentication. Prototype int wifi_station_set_enterprise_cert_key (
u8 *client_cert, int client_cert_len,
u8 *private_key, int private_key_len,
u8 *private_key_passwd, int private_key_passwd_len,) Parameter u8 *client_cert: user certificate, HEX array int client_cert_len: length of certificate u8 *private_key: private key, HEX array, can NOT be longer than 2048 bits int private_key_len: length of private key, less than 2048 u8 *private_key_passwd: password for private key, to be supported, can only be NULL now. int private_key_passwd_len: length of password, to be supported, can only be 0 now. Return 0: Success otherwise: Failure Example For example, the private key is - - - - - BEGIN PRIVATE KEY - - - - - … … … …, then array should be uint8 key[]={0x2d, 0x2d, 0x2d, 0x2d, 0x2d, 0x42, 0x45, 0x47, … … 0x00 }; It is the ASCII code for the characters, and the array needs to terminate with 0x00. Espressif ! /15592 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-106-2048.jpg)

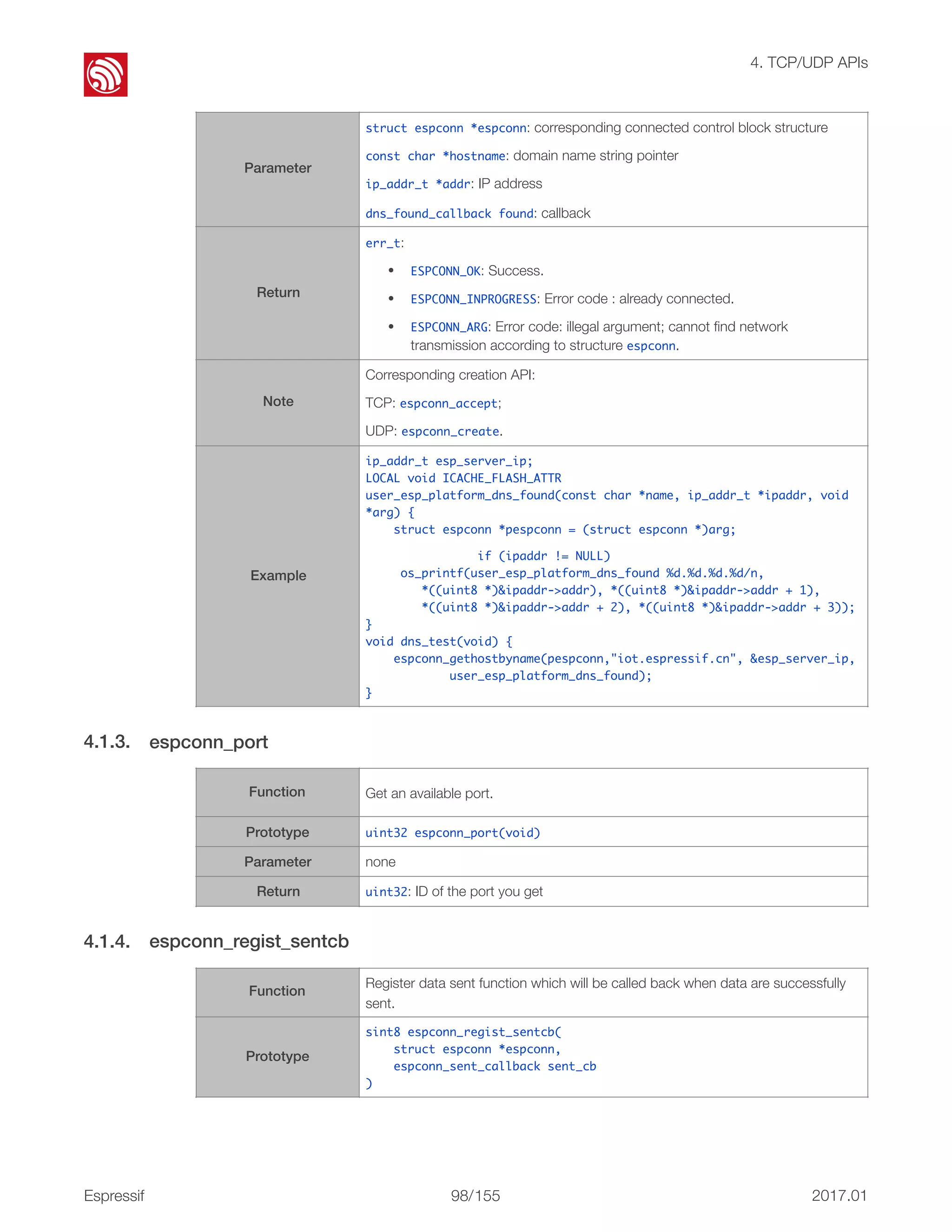


![! 4. TCP/UDP APIs 4.1.9. espconn_send Example void user_udp_recv_cb(void *arg, char *pusrdata, unsigned short length) { struct espconn *pesp_conn = arg; remot_info *premot = NULL; if (espconn_get_connection_info(pesp_conn,&premot,0) == ESPCONN_OK){ pesp_conn->proto.tcp->remote_port = premot->remote_port; pesp_conn->proto.tcp->remote_ip[0] = premot- >remote_ip[0]; pesp_conn->proto.tcp->remote_ip[1] = premot- >remote_ip[1]; pesp_conn->proto.tcp->remote_ip[2] = premot- >remote_ip[2]; pesp_conn->proto.tcp->remote_ip[3] = premot- >remote_ip[3]; espconn_sent(pesp_conn, pusrdata, os_strlen(pusrdata)); } } Function Send data through network. Prototype sint8 espconn_send(
struct espconn *espconn,
uint8 *psent,
uint16 length
) Parameter struct espconn *espconn: corresponding connected control block structure; uint8 *psent: pointer of sent data; uint16 length: data length. Return 0: Success Otherwise: Error code • ESPCONN_MEM: Out of memory; • ESPCONN_ARG: illegal argument; cannot find network transmission according to structure espconn; • ESPCONN_MAXNUM: buffer (or 8 packets at most) of sending data is full; • ESPCONN_IF: fail to send UDP data. Note • Please call espconn_send after espconn_sent_callback of the pre-packet. • If it is a UDP transmission, please set espconn->proto.udp->remote_ip and remote_port before every calling of espconn_send. Espressif ! /!101 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-115-2048.jpg)
![! 4. TCP/UDP APIs 4.1.10. espconn_sent [@deprecated] This API is deprecated, please use espconn_send instead. 4.2. TCP APIs TCP APIs act only on TCP connections and do not affect nor apply to UDP connections. 4.2.1. espconn_accept Function Send data through network. Prototype sint8 espconn_send(
struct espconn *espconn,
uint8 *psent,
uint16 length
) Parameter struct espconn *espconn: corresponding connected control block structure; uint8 *psent: pointer of sent data; uint16 length: data length. Return 0: Success Otherwise: Error code • ESPCONN_MEM: Out of memory; • ESPCONN_ARG: illegal argument; cannot find network transmission according to structure espconn; • ESPCONN_MAXNUM: buffer (or 8 packets at most) of sending data is full; • ESPCONN_IF: fail to send UDP data. Note • Please call espconn_send after espconn_sent_callback of the pre-packet. • If it is a UDP transmission, please set espconn->proto.udp->remote_ip and remote_port before every calling of espconn_send. Function Creates a TCP server (i.e. accepts connections). Prototype sint8 espconn_accept(struct espconn *espconn) Parameter struct espconn *espconn: corresponding connected control block structure. Return 0: Success Otherwise: Error code • ESPCONN_MEM: Out of memory; • ESPCONN_ISCONN: Already connected; • ESPCONN_ARG: illegal argument; cannot find TCP connection according to structure espconn. Espressif ! /!102 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-116-2048.jpg)
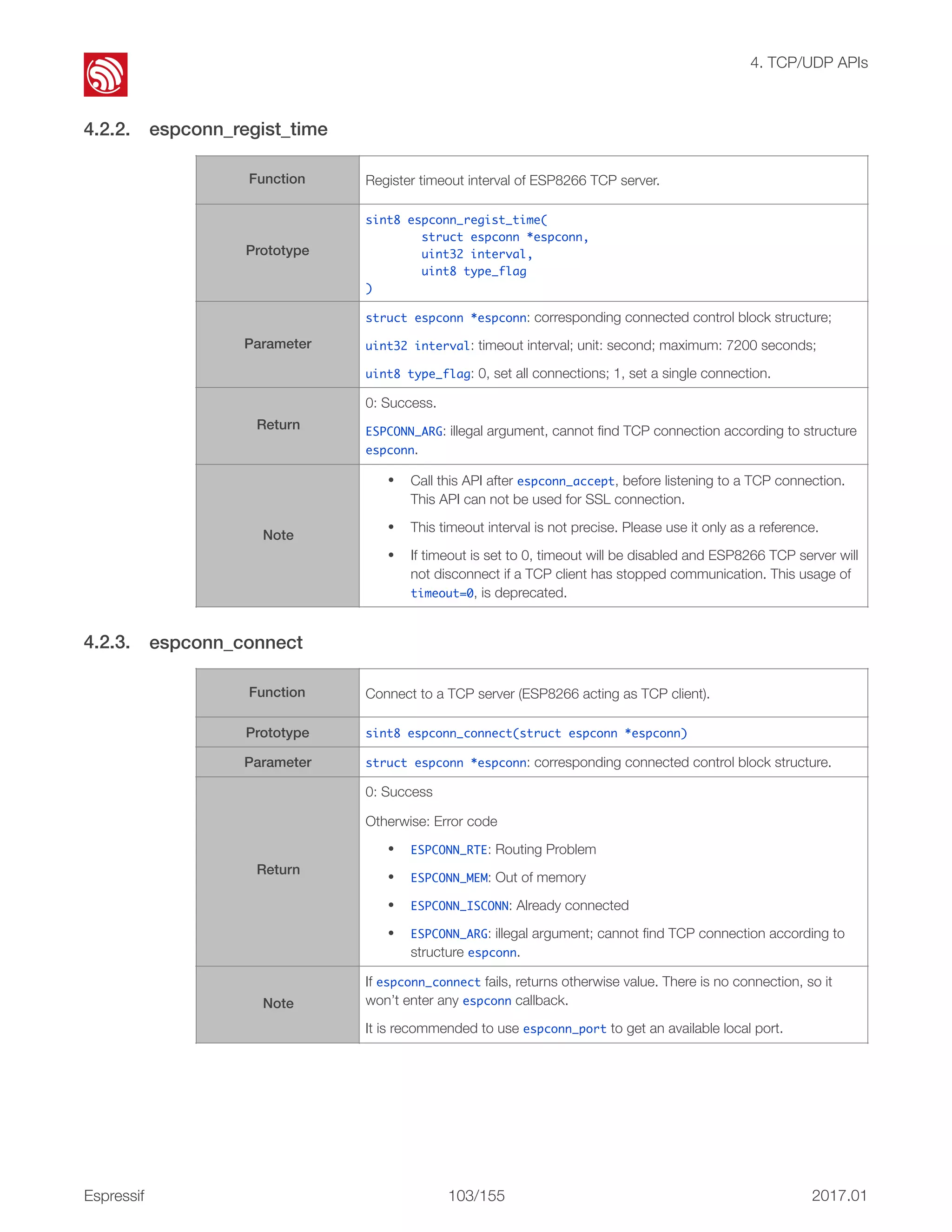
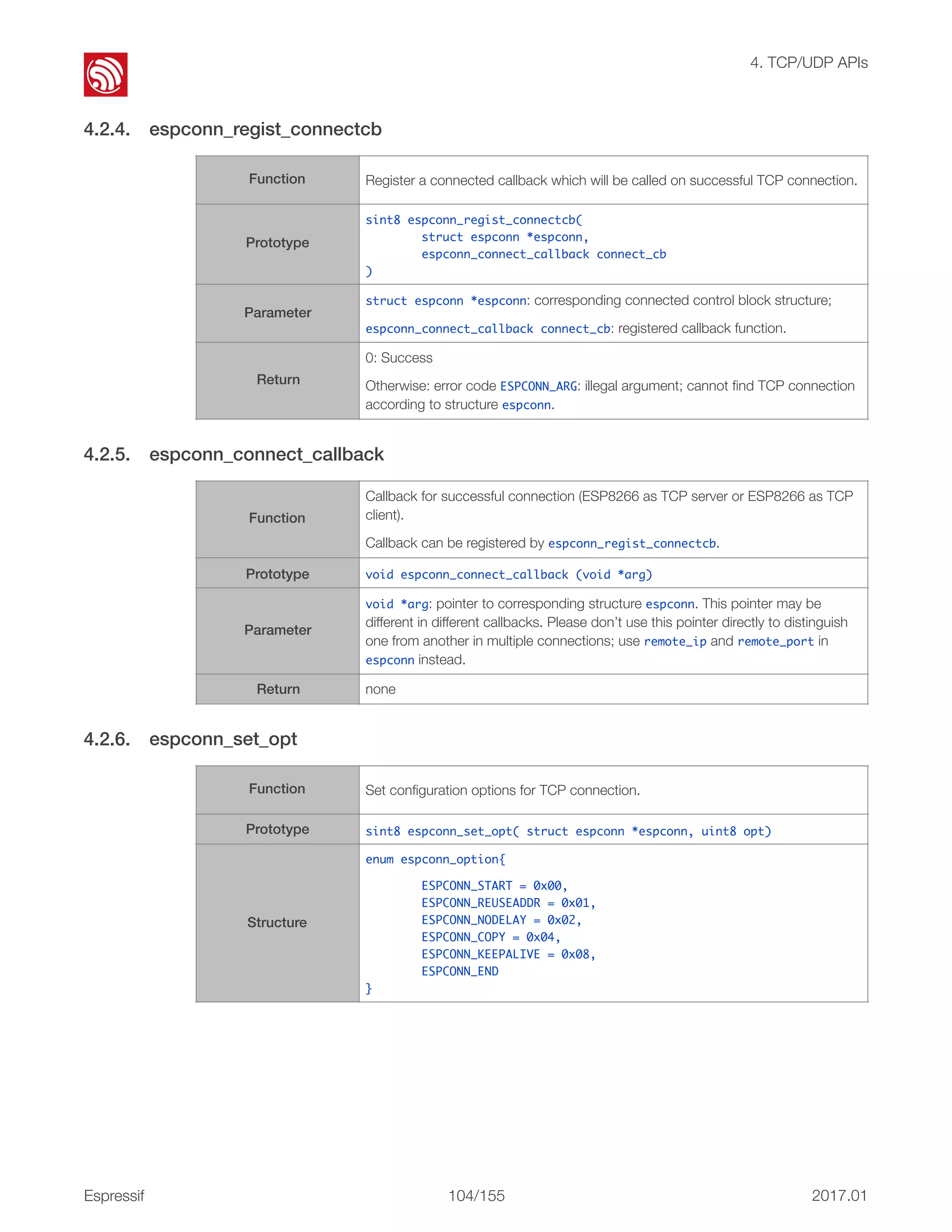

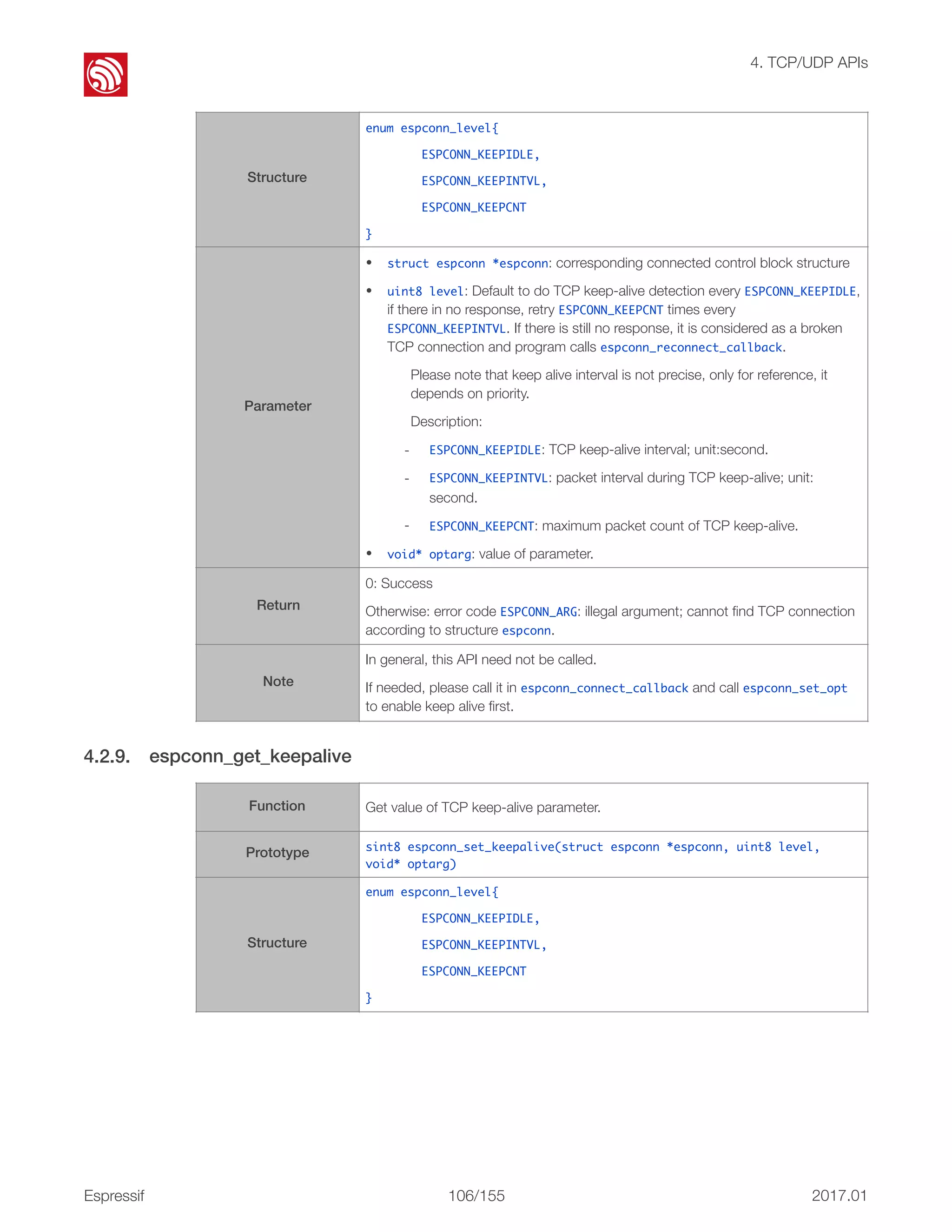

![! 4. TCP/UDP APIs 4.2.27. espconn_secure_send 4.2.28. espconn_secure_sent [@deprecated] This API is deprecated; please use espconn_secure_send instead. • If espconn_connect fails, a otherwise value will be returned. TCP connection fails and and therefore the ESP8266 will not enter any espconn callback. • Only one connection is allowed when the ESP8266 acts as a SSL client. This API can be called only once. Users can call espconn_secure_disconnect to disconnect first before calling this API to create another SSL connection. • If the SSL encrypted packet size is larger than the ESP8266 SSL buffer size (2 KB by default, set by espconn_secure_set_size), the SSL connection will fail. The ESP8266 will enter espconn_reconnect_callback • SSL-related APIs named as espconn_secure_XXX are different from normal TCP APIs and must not be used interchangeably. In SSL connection, only espconn_secure_XXX APIs, espconn_regist_XXXcb APIs and espconn_port can be used. Function Send encrypted data (SSL). Prototype sint8 espconn_secure_send (
struct espconn *espconn,
uint8 *psent,
uint16 length
) Parameter struct espconn *espconn: corresponding network connection. uint8 *psent: sent data pointer. uint16 length: sent data length. Return 0: Success Otherwise: Error code ESPCONN_ARG: illegal argument; cannot find TCP connection according to structure espconn. Note • Please call espconn_secure_send after espconn_sent_callback of the pre- packet. • The unencrypted data can be 1024 bytes at most per packet; the encrypted data can be 1460 bytes at most per packet. Function Send encrypted data (SSL). Prototype sint8 espconn_secure_send (
struct espconn *espconn,
uint8 *psent,
uint16 length
) Espressif ! /!113 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-127-2048.jpg)


![! 4. TCP/UDP APIs 4.4. mDNS APIs 4.4.1. espconn_mdns_init 4.4.2. espconn_mdns_close 4.4.3. espconn_mdns_server_register 4.4.4. espconn_mdns_server_unregister Function mDNS initialization Structure struct mdns_info{
char *host_name;
char *server_name;
uint16 server_port;
unsigned long ipAddr;
char *txt_data[10];
}; Prototype void espconn_mdns_init(struct mdns_info *info) Parameter struct mdns_info *info: mDNS information Return none Example • In SoftAP + Station mode, call wifi_set_broadcast_if (STATIONAP_MODE); first to enable broadcast for both SoftAP and Station interface. • Using Station interface, please obtain IP address of the ESP8266 Station first before calling the API to initialize mDNS; • txt_data has to be set as “key = value”. Function Close mDNS, corresponding creation API: espconn_mdns_init. Prototype void espconn_mdns_close(void) Parameter none Return none Function Register mDNS server. Prototype void espconn_mdns_server_register(void) Parameter none Return none Function Unregister mDNS server. Prototype void espconn_mdns_server_unregister(void) Espressif ! /!119 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-133-2048.jpg)

![! 4. TCP/UDP APIs 4.4.9. espconn_mdns_enable 4.4.10. espconn_mdns_disable 4.4.11. Example of mDNS Please do not use special characters (for example, “.” character), or use a protocol name (for example, “http”), when defining host_name and server_name for mDNS. struct mdns_info info; void user_mdns_config() { struct ip_info ipconfig; wifi_get_ip_info(STATION_IF, &ipconfig); info->host_name = "espressif";
info->ipAddr = ipconfig.ip.addr; //ESP8266 Station IP
info->server_name = "iot";
info->server_port = 8080;
info->txt_data[0] = "version = now";
info->txt_data[1] = "user1 = data1";
info->txt_data[2] = "user2 = data2";
espconn_mdns_init(&info); }
Function Enable mDNS. Prototype void espconn_mdns_enable(void) Parameter none Return none Function Disable mDNS, corresponding creation API: espconn_mdns_enable. Prototype void espconn_mdns_disable(void) Parameter none Return none Espressif ! /!121 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-135-2048.jpg)








![! 7. Definitions & Structures 7. Definitions & Structures 7.1. Timer typedef void ETSTimerFunc(void *timer_arg); typedef struct _ETSTIMER_ { struct _ETSTIMER_ *timer_next; uint32_t timer_expire; uint32_t timer_period; ETSTimerFunc *timer_func; void *timer_arg; } ETSTimer; 7.2. Wi-Fi-Related Structures 7.2.1. Station Parameters struct station_config {
uint8 ssid[32];
uint8 password[64];
uint8 bssid_set;
uint8 bssid[6];
}; 7.2.2. SoftAP Parameters typedef enum _auth_mode { AUTH_OPEN = 0, AUTH_WEP, AUTH_WPA_PSK, AUTH_WPA2_PSK, AUTH_WPA_WPA2_PSK } AUTH_MODE; struct softap_config { uint8 ssid[32]; uint8 password[64]; uint8 ssid_len; uint8 channel; // support 1 ~ 13 ⚠ Notice: BSSID is the MAC address of AP, which will be used when several APs have the same SSID. If station_config.bssid_set==1 , station_config.bssid has to be set; otherwise, the connection will fail. In general, station_config.bssid_set need to be 0. Espressif ! /!133 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-147-2048.jpg)
![! 7. Definitions & Structures uint8 authmode; // Don’t support AUTH_WEP in SoftAP mode uint8 ssid_hidden; // default 0 uint8 max_connection; // default 4, max 4 uint16 beacon_interval; // 100 ~ 60000 ms, default 100 }; 7.2.3. Scan Parameters struct scan_config { uint8 *ssid; uint8 *bssid; uint8 channel; uint8 show_hidden; // Scan APs which are hiding their SSID or not. }; struct bss_info { STAILQ_ENTRY(bss_info) next; uint8 bssid[6]; uint8 ssid[32]; uint8 ssid_len; uint8 channel; sint8 rssi; AUTH_MODE authmode; uint8 is_hidden; // SSID of current AP is hidden or not. sint16 freq_offset; // AP’s frequency offset sint16 freqcal_val; uint8 *esp_mesh_ie; uint8 simple_pair; }; typedef void (* scan_done_cb_t)(void *arg, STATUS status); 7.2.4. Wi-Fi Event-Related Structures enum { EVENT_STAMODE_CONNECTED = 0, EVENT_STAMODE_DISCONNECTED, EVENT_STAMODE_AUTHMODE_CHANGE, EVENT_STAMODE_GOT_IP, EVENT_STAMODE_DHCP_TIMEOUT, EVENT_SOFTAPMODE_STACONNECTED, EVENT_SOFTAPMODE_STADISCONNECTED, EVENT_SOFTAPMODE_PROBEREQRECVED, EVENT_MAX }; ⚠ Notice: If softap_config.ssid_len==0, SSID is checked till a termination character is found; otherwise, set the length of SSID according to softap_config.ssid_len. Espressif ! /!134 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-148-2048.jpg)
![! 7. Definitions & Structures enum { REASON_UNSPECIFIED = 1, REASON_AUTH_EXPIRE = 2, REASON_AUTH_LEAVE = 3, REASON_ASSOC_EXPIRE = 4, REASON_ASSOC_TOOMANY = 5, REASON_NOT_AUTHED = 6, REASON_NOT_ASSOCED = 7, REASON_ASSOC_LEAVE = 8, REASON_ASSOC_NOT_AUTHED = 9, REASON_DISASSOC_PWRCAP_BAD = 10, /* 11h */ REASON_DISASSOC_SUPCHAN_BAD = 11, /* 11h */ REASON_IE_INVALID = 13, /* 11i */ REASON_MIC_FAILURE = 14, /* 11i */ REASON_4WAY_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT = 15, /* 11i */ REASON_GROUP_KEY_UPDATE_TIMEOUT = 16, /* 11i */ REASON_IE_IN_4WAY_DIFFERS = 17, /* 11i */ REASON_GROUP_CIPHER_INVALID = 18, /* 11i */ REASON_PAIRWISE_CIPHER_INVALID = 19, /* 11i */ REASON_AKMP_INVALID = 20, /* 11i */ REASON_UNSUPP_RSN_IE_VERSION = 21, /* 11i */ REASON_INVALID_RSN_IE_CAP = 22, /* 11i */ REASON_802_1X_AUTH_FAILED = 23, /* 11i */ REASON_CIPHER_SUITE_REJECTED = 24, /* 11i */ REASON_BEACON_TIMEOUT = 200, REASON_NO_AP_FOUND = 201, REASON_AUTH_FAIL = 202, REASON_ASSOC_FAIL = 203, REASON_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT = 204, }; typedef struct { uint8 ssid[32]; uint8 ssid_len; uint8 bssid[6]; uint8 channel; } Event_StaMode_Connected_t; typedef struct { uint8 ssid[32]; uint8 ssid_len; uint8 bssid[6]; uint8 reason; } Event_StaMode_Disconnected_t; typedef struct { uint8 old_mode; uint8 new_mode; } Event_StaMode_AuthMode_Change_t; Espressif ! /!135 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-149-2048.jpg)
![! 7. Definitions & Structures typedef struct { struct ip_addr ip; struct ip_addr mask; struct ip_addr gw; } Event_StaMode_Got_IP_t; typedef struct { uint8 mac[6]; uint8 aid; } Event_SoftAPMode_StaConnected_t; typedef struct { uint8 mac[6]; uint8 aid; } Event_SoftAPMode_StaDisconnected_t; typedef struct { int rssi; uint8 mac[6]; } Event_SoftAPMode_ProbeReqRecved_t; typedef union { Event_StaMode_Connected_t connected; Event_StaMode_Disconnected_t disconnected; Event_StaMode_AuthMode_Change_t auth_change; Event_StaMode_Got_IP_t got_ip; Event_SoftAPMode_StaConnected_t sta_connected; Event_SoftAPMode_StaDisconnected_t sta_disconnected; Event_SoftAPMode_ProbeReqRecved_t ap_probereqrecved; } Event_Info_u; typedef struct _esp_event { uint32 event; Event_Info_u event_info; } System_Event_t; 7.2.5. SmartConfig Structures typedef enum { SC_STATUS_WAIT = 0, // Please don’t start connection in this phase SC_STATUS_FIND_CHANNEL, // Start connection by APP in this phase SC_STATUS_GETTING_SSID_PSWD, SC_STATUS_LINK, SC_STATUS_LINK_OVER, // Got IP, connect to AP successfully } sc_status; typedef enum { SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCH = 0, SC_TYPE_AIRKISS, SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCH_AIRKISS, Espressif ! /!136 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-150-2048.jpg)
![! 7. Definitions & Structures } sc_type; 7.3. JSON-Related Structure 7.3.1. JSON Structures struct jsontree_value { uint8_t type; }; struct jsontree_pair { const char *name; struct jsontree_value *value; }; struct jsontree_context { struct jsontree_value *values[JSONTREE_MAX_DEPTH]; uint16_t index[JSONTREE_MAX_DEPTH]; int (* putchar)(int); uint8_t depth; uint8_t path; int callback_state; }; struct jsontree_callback { uint8_t type; int (* output)(struct jsontree_context *js_ctx); int (* set)(struct jsontree_context *js_ctx,
struct jsonparse_state *parser); }; struct jsontree_object { uint8_t type; uint8_t count; struct jsontree_pair *pairs; }; struct jsontree_array { uint8_t type; uint8_t count; struct jsontree_value **values; }; struct jsonparse_state { const char *json; int pos; int len; int depth; int vstart; int vlen; Espressif ! /!137 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-151-2048.jpg)
![! 7. Definitions & Structures char vtype; char error; char stack[JSONPARSE_MAX_DEPTH]; }; JSON Macro Definitions #define JSONTREE_OBJECT(name, ...) / static struct jsontree_pair jsontree_pair_##name[] = {__VA_ARGS__}; / static struct jsontree_object name = { / JSON_TYPE_OBJECT, / sizeof(jsontree_pair_##name)/sizeof(struct jsontree_pair), / jsontree_pair_##name } #define JSONTREE_PAIR_ARRAY(value) (struct jsontree_value *)(value) #define JSONTREE_ARRAY(name, ...) / static struct jsontree_value* jsontree_value_##name[] = {__VA_ARGS__}; / static struct jsontree_array name = { / JSON_TYPE_ARRAY, / sizeof(jsontree_value_##name)/sizeof(struct jsontree_value*), / jsontree_value_##name } 7.4. espconn Parameters 7.4.1. Callback Functions /** callback prototype to inform about events for a espconn */ typedef void (* espconn_recv_callback)(void *arg, char *pdata, unsigned short len); typedef void (* espconn_callback)(void *arg, char *pdata, unsigned short len); typedef void (* espconn_connect_callback)(void *arg); 7.4.2. espconn Structures typedef void* espconn_handle; typedef struct _esp_tcp { int remote_port; int local_port; uint8 local_ip[4]; uint8 remote_ip[4]; espconn_connect_callback connect_callback; espconn_reconnect_callback reconnect_callback; espconn_connect_callback disconnect_callback; espconn_connect_callback write_finish_fn; } esp_tcp; typedef struct _esp_udp { int remote_port; int local_port; uint8 local_ip[4]; uint8 remote_ip[4]; Espressif ! /!138 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-152-2048.jpg)






![! 8. Peripheral-Related Drivers 8.4. PWM-Related APIs The document will introduce PWM-related APIs from pwm.h. For more information on PWM-related APIs please see ESP8266 Technical Reference. PWM APIs can not be called when APIs in hw_timer.c are in use, because they use the same hardware timer. Do not set the system to be Light-sleep mode (wifi_set_sleep_type(LIGT_SLEEP);), because CPU is halted and will not be interrupted by NMI during Light-sleep. To enter Deep- sleep mode, PWM needs to be stopped first. 8.4.1. pwm_init 8.4.2. pwm_start Function Initialize PWM function, including GPIO selection, period and duty cycle. Prototype void pwm_init(
uint32 period,
uint8 *duty,
uint32 pwm_channel_num,
uint32 (*pin_info_list)[3]) Parameter uint32 period: PWM period uint8 *duty: duty cycle of each output uint32 pwm_channel_num: PWM channel number uint32 (*pin_info_list)[3]: GPIO parameter of PWM channel.It is a pointer of n * 3 array which defines GPIO register, IO reuse of corresponding PIN and GPIO number. Return none Example uint32 io_info[][3] =
{{PWM_0_OUT_IO_MUX,PWM_0_OUT_IO_FUNC,PWM_0_OUT_IO_NUM},
{PWM_1_OUT_IO_MUX,PWM_1_OUT_IO_FUNC,PWM_1_OUT_IO_NUM},
{PWM_2_OUT_IO_MUX,PWM_2_OUT_IO_FUNC,PWM_2_OUT_IO_NUM}}; pwm_init(light_param.pwm_period, light_param.pwm_duty, 3, io_info); Note This API can be called only once. Function Starts PWM. This function needs to be called after PWM configuration is changed. Prototype void pwm_start (void) Parameter none Return none Espressif ! /!147 155 2017.01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2c-esp8266nonossdkapireferenceen-170318054546/75/2c-esp8266-non-os_sdk_api_reference_en-161-2048.jpg)