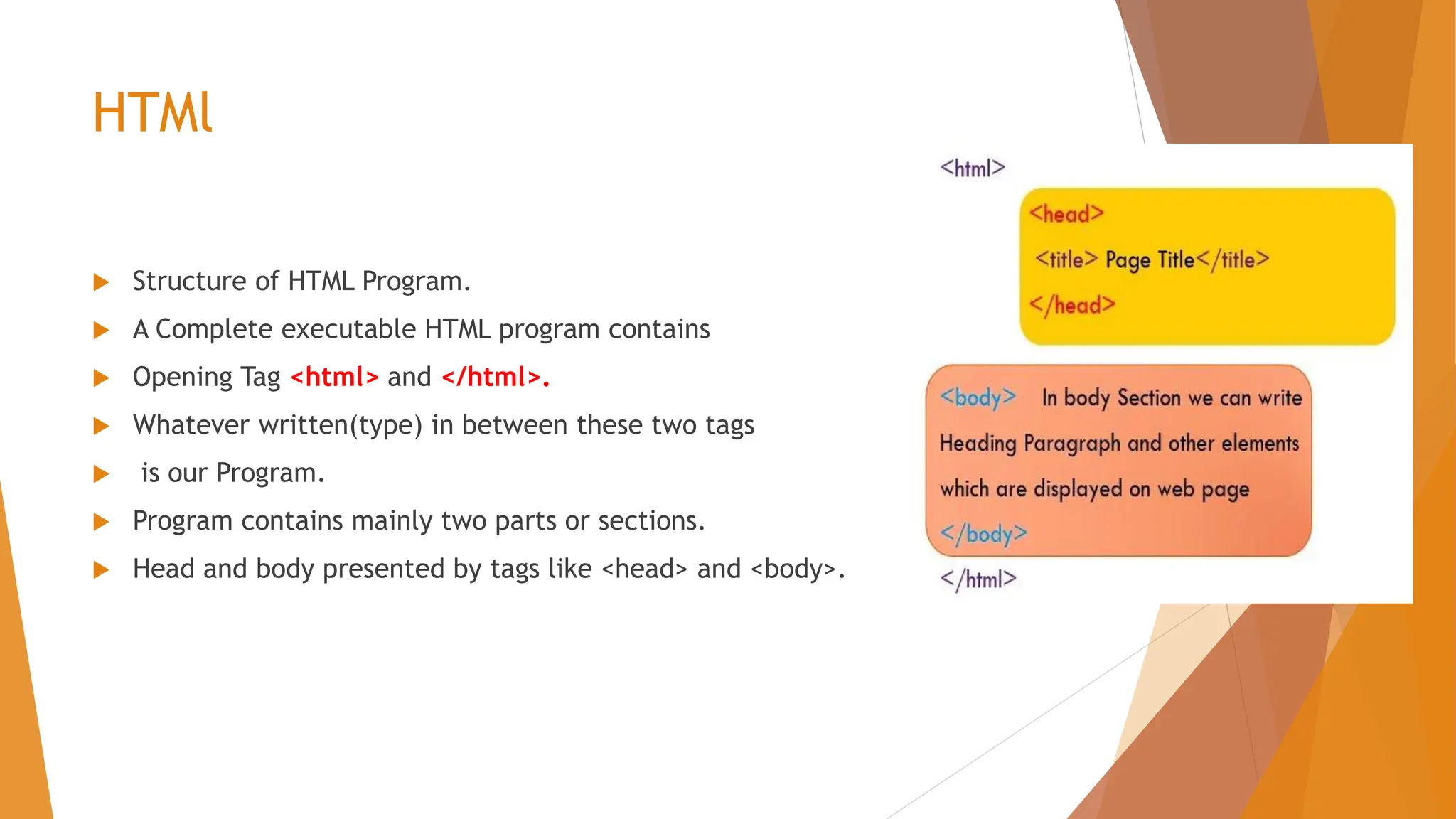
The document provides an overview of web technology, including its definitions, examples, and the functions of HTML, XML, CSS, and programming languages. It explains the roles of web servers and databases in facilitating communication and data management over the internet. The text emphasizes the importance of various markup and programming languages in web development and data representation.