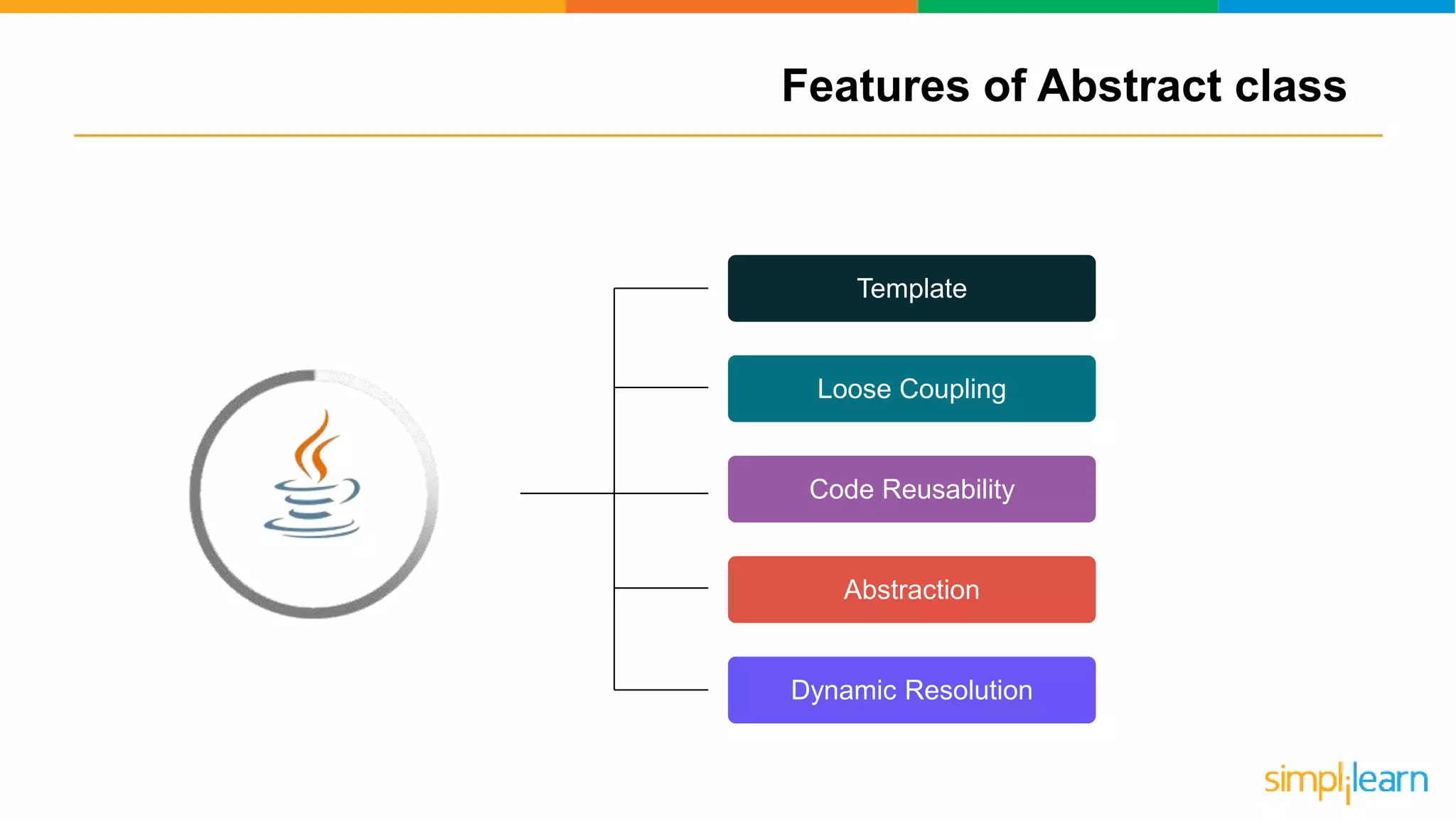
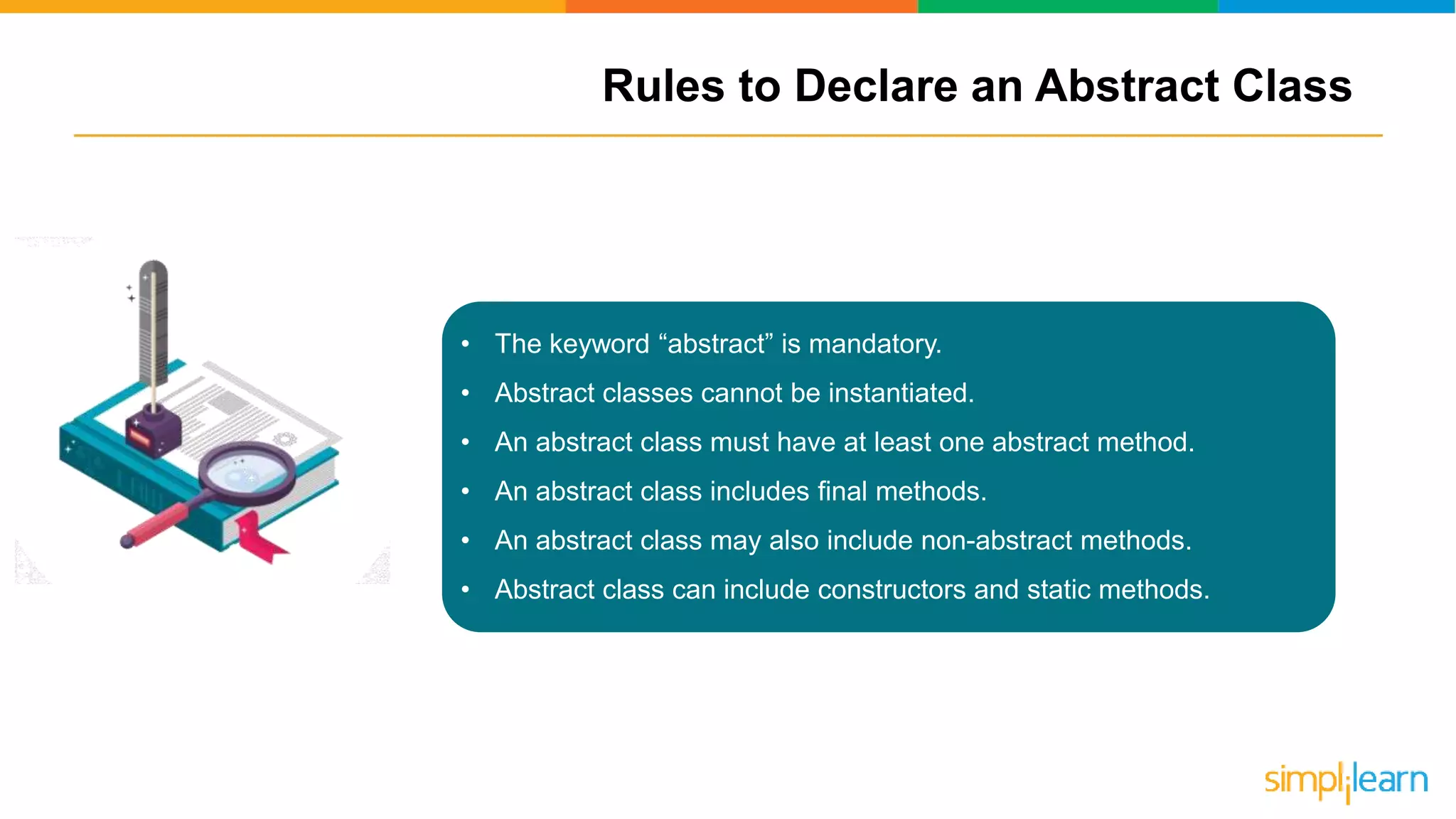
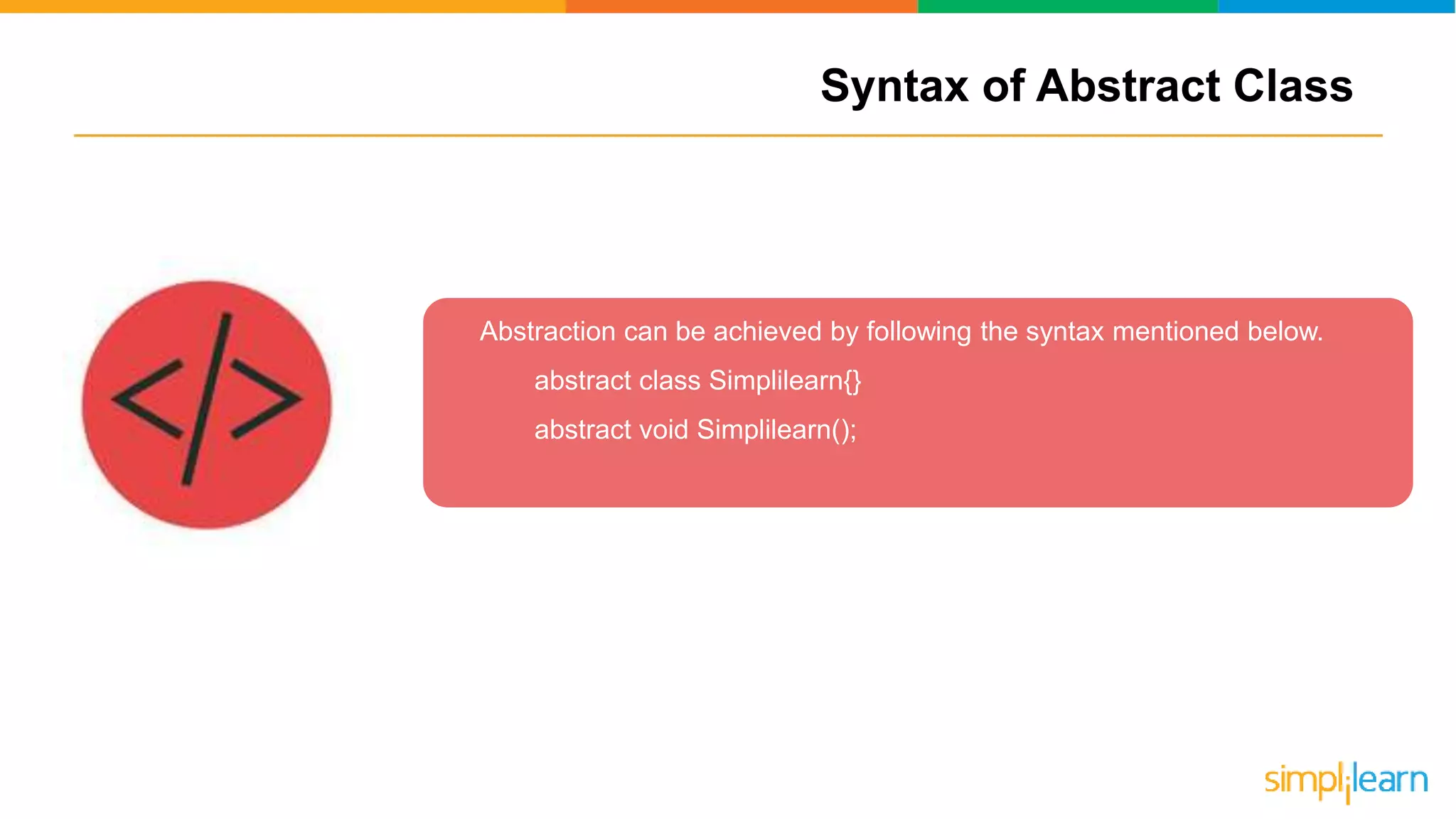
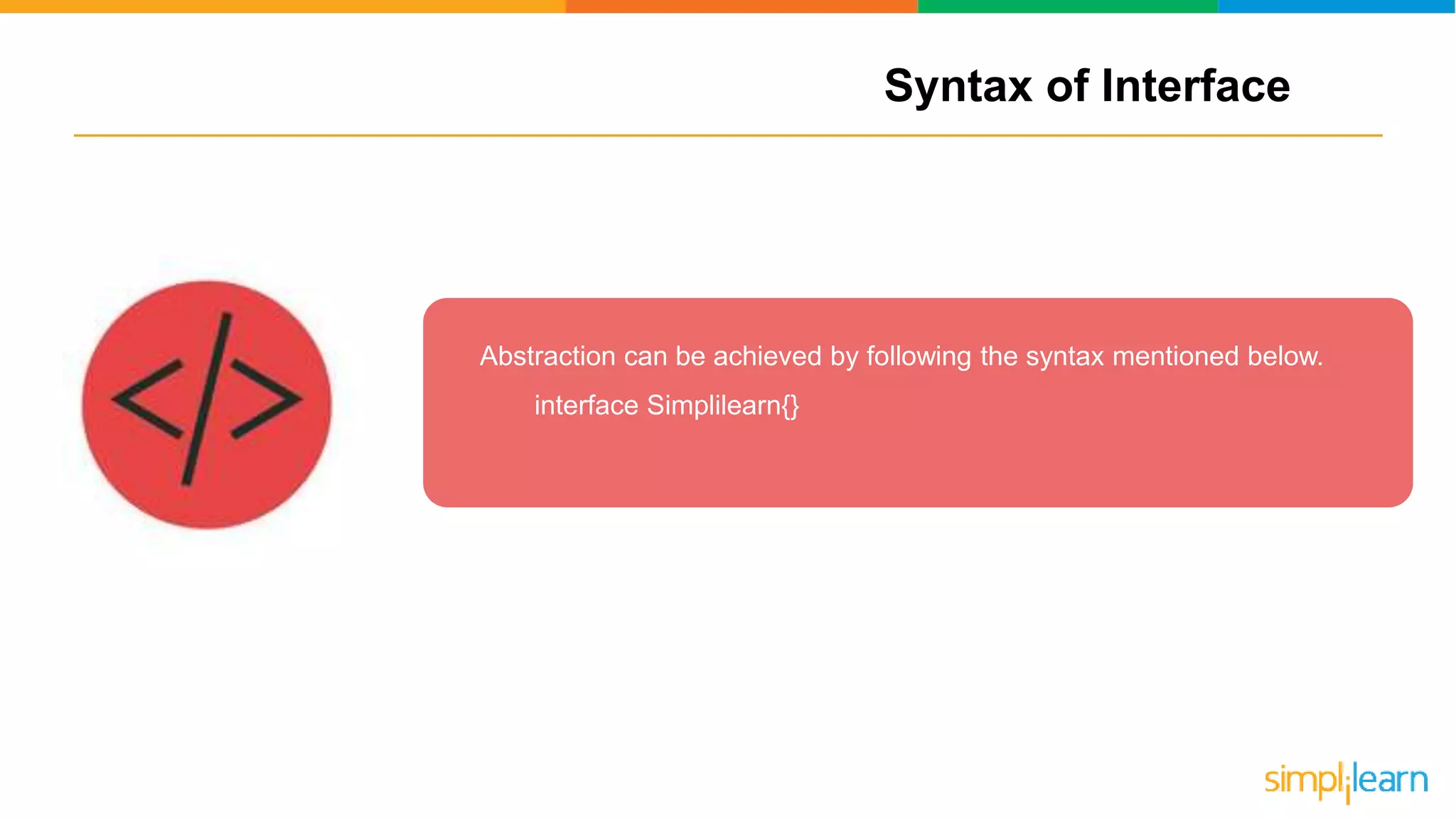
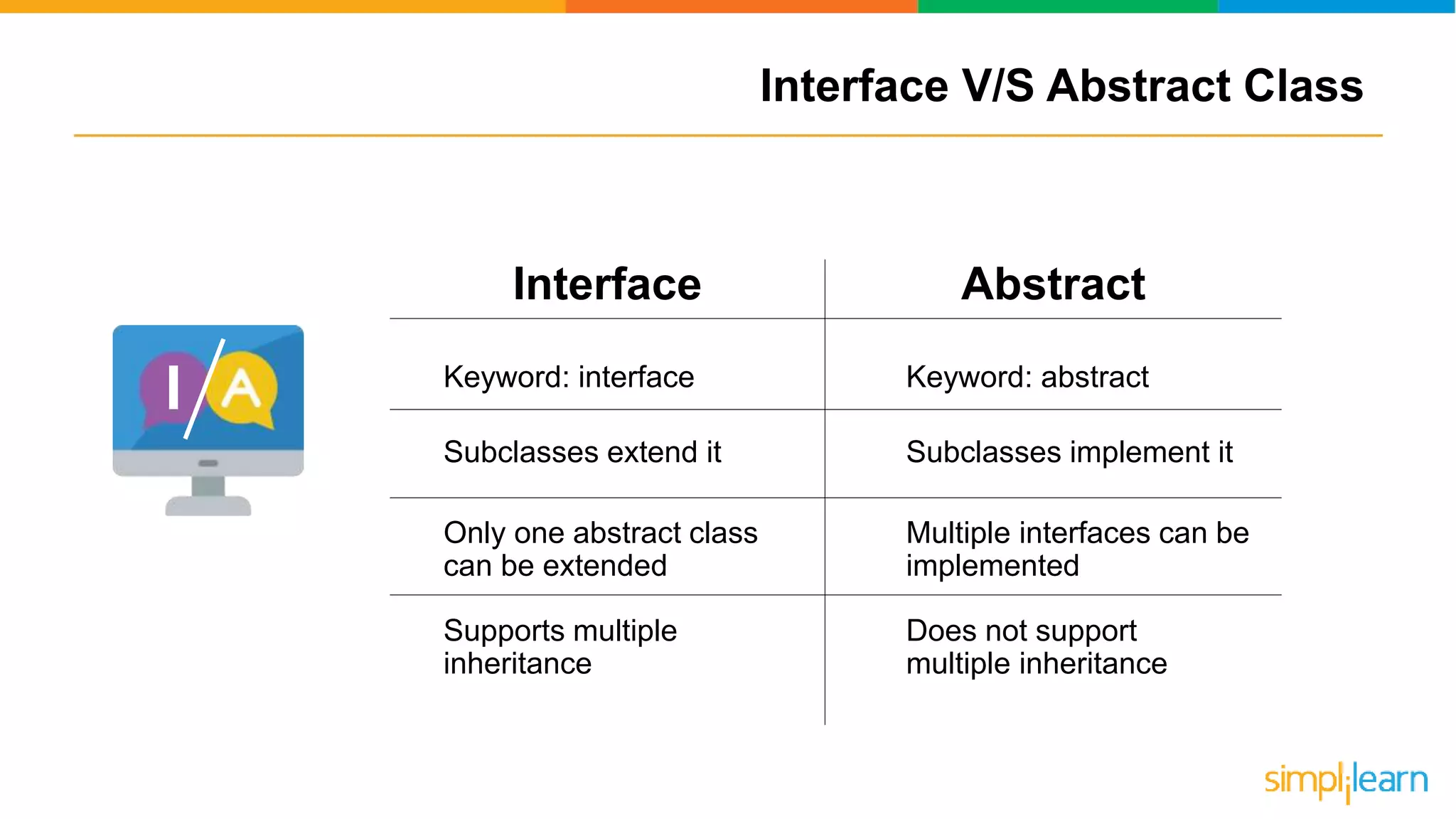
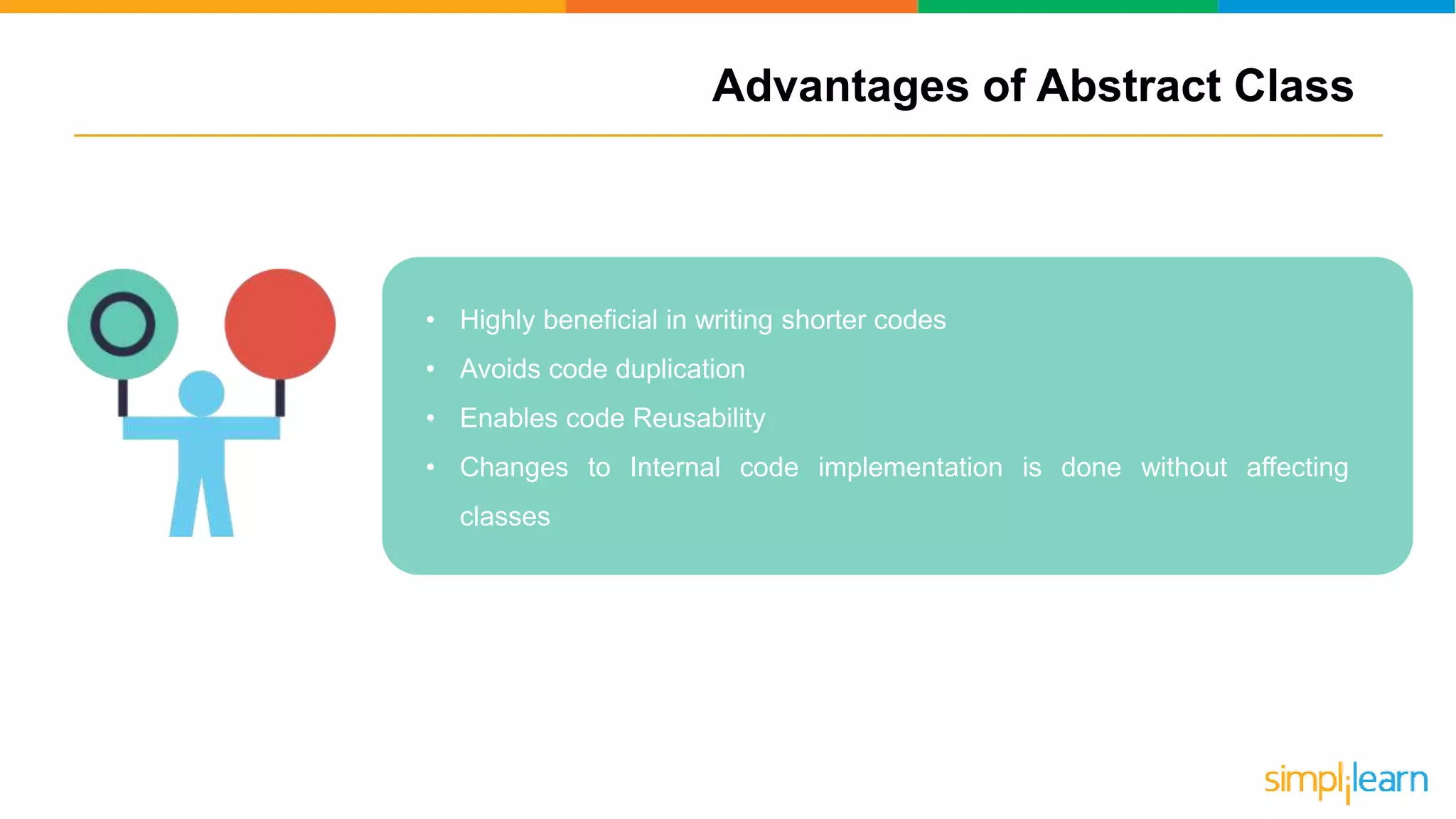
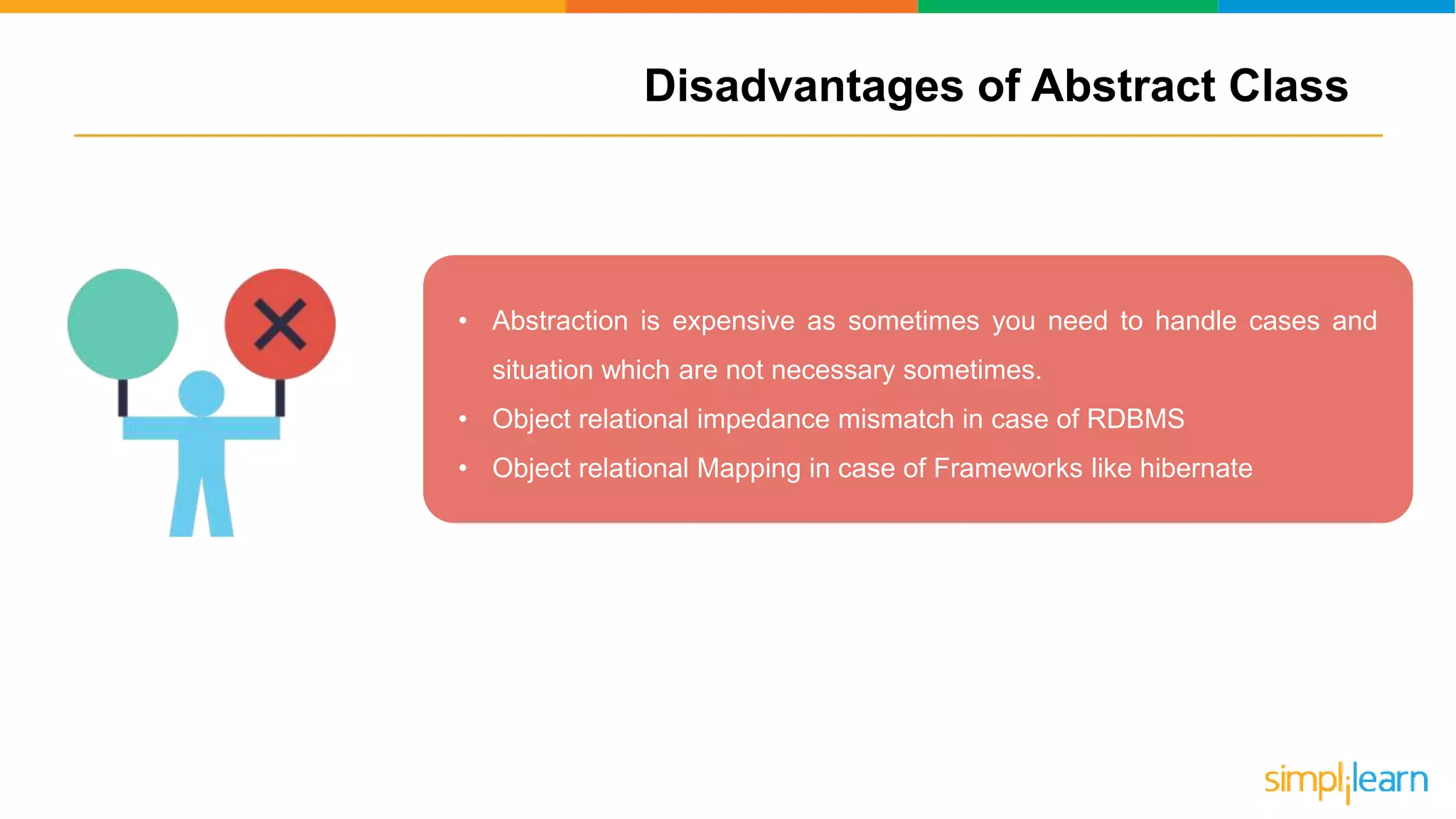
The document discusses abstract classes in Java, defining them as templates for methods and variables that cannot be instantiated directly. It outlines features, rules for declaration, procedures to achieve abstraction, and contrasts abstract classes with interfaces, highlighting their advantages such as code reusability and disadvantages like potential complexity. Overall, it serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the concept and implementation of abstract classes in object-oriented programming.