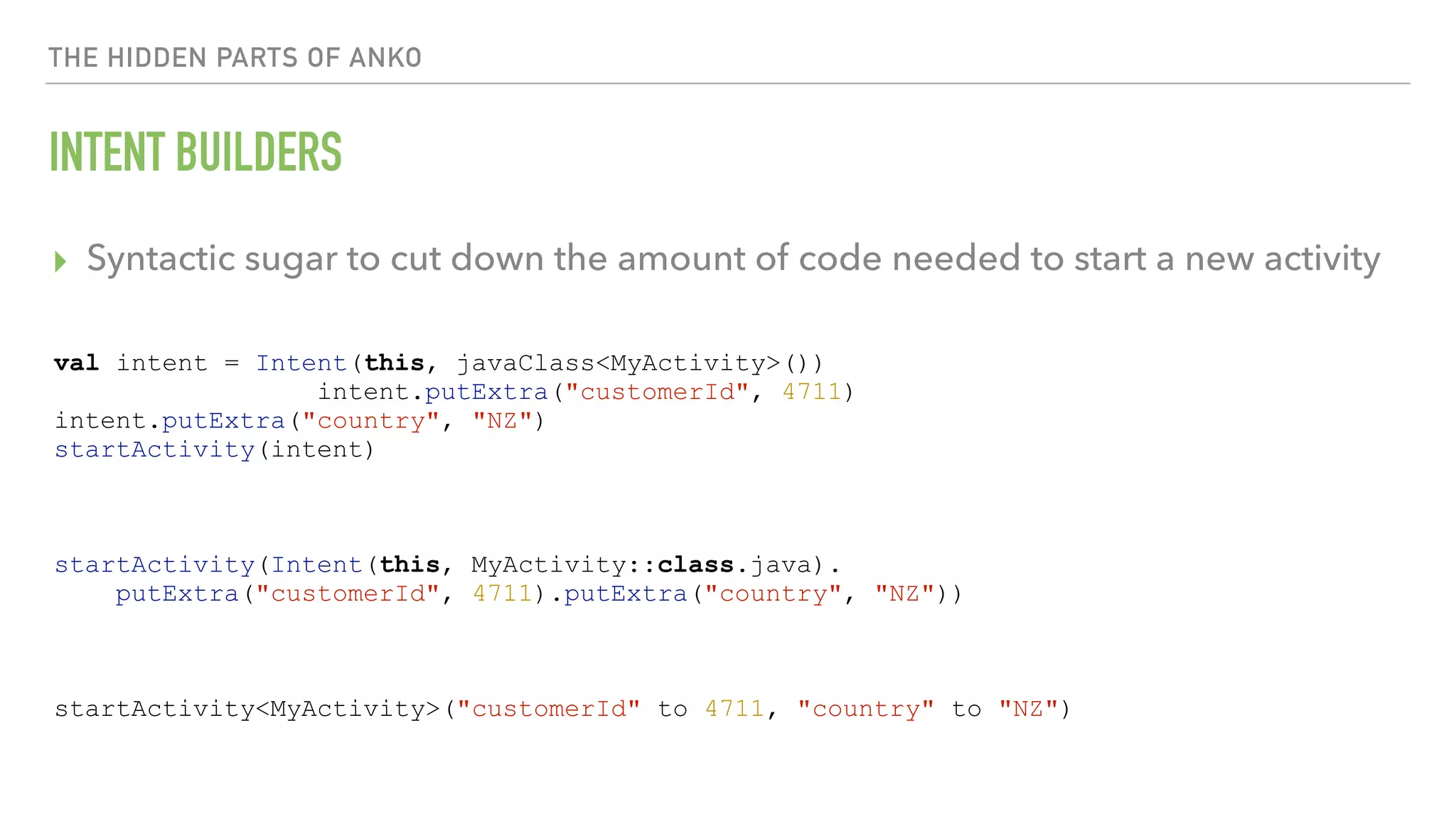
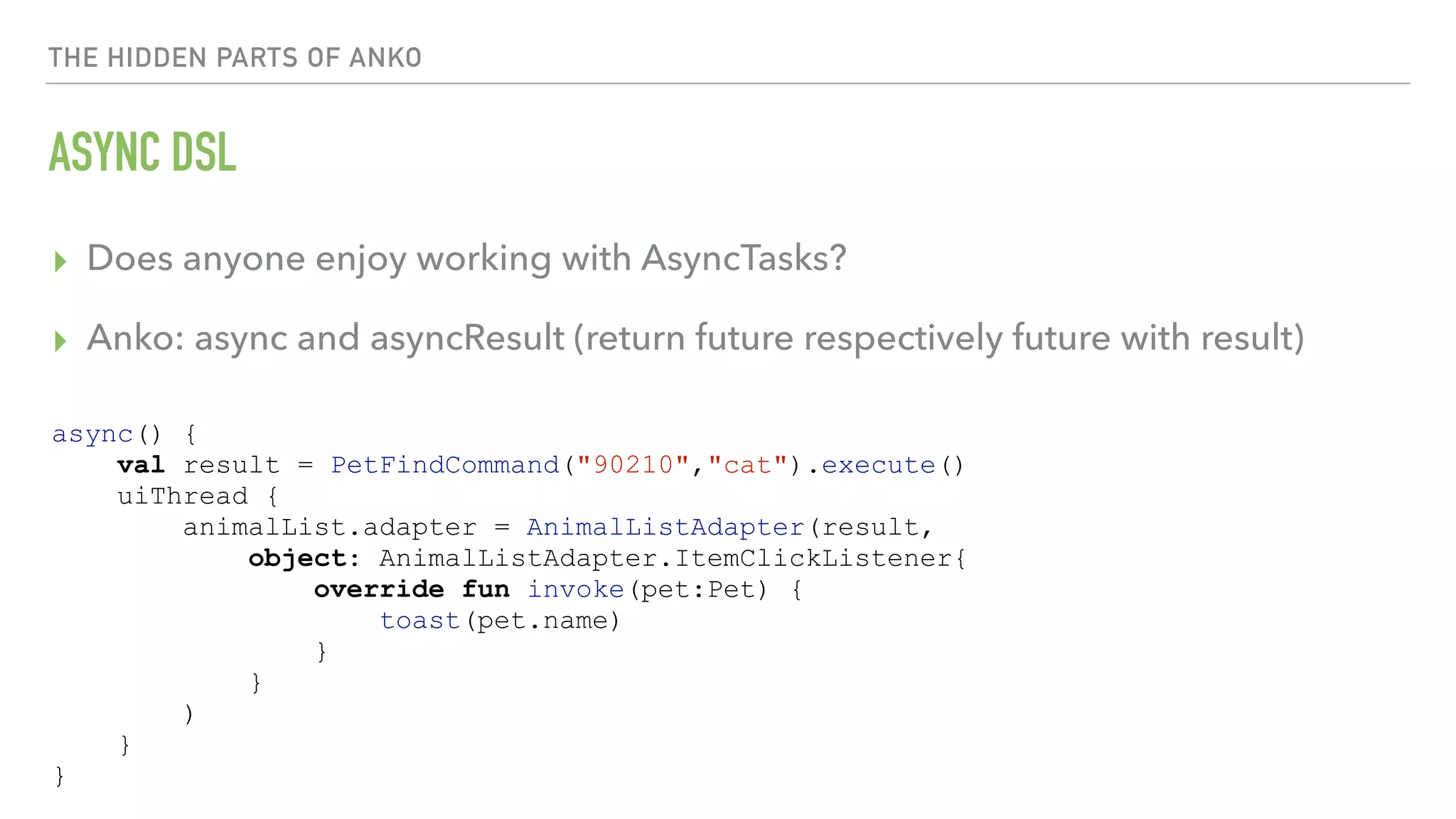
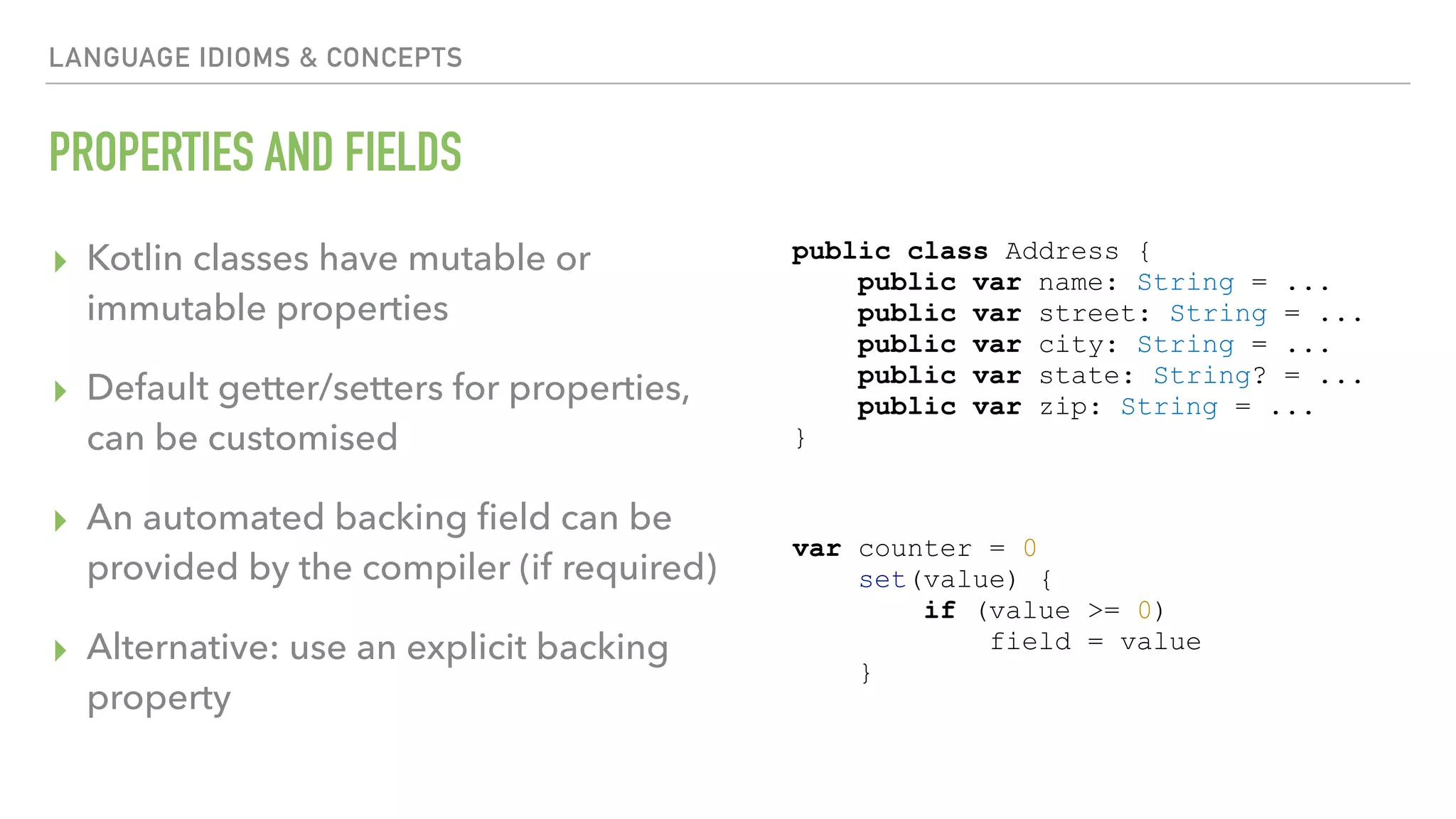
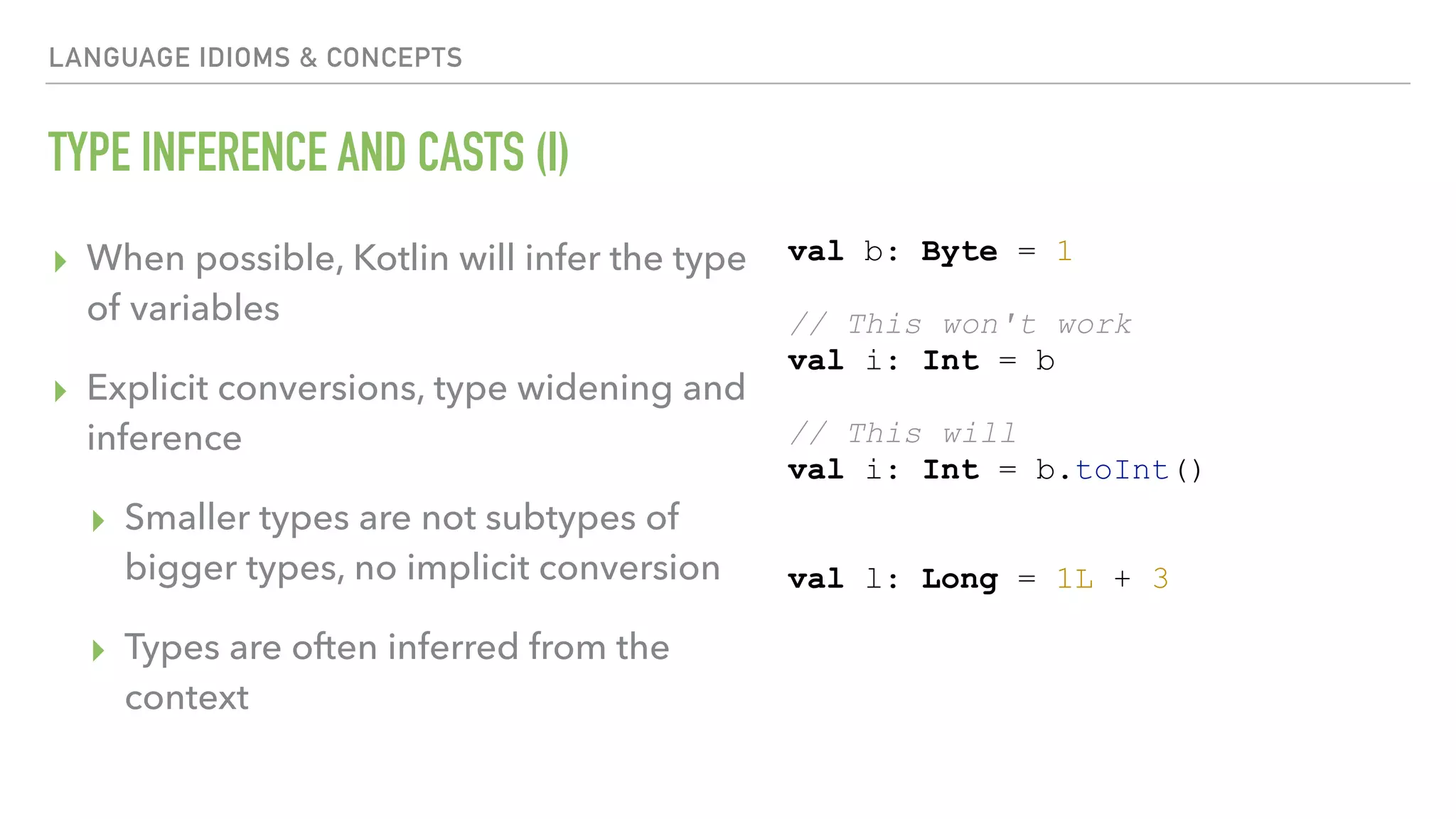
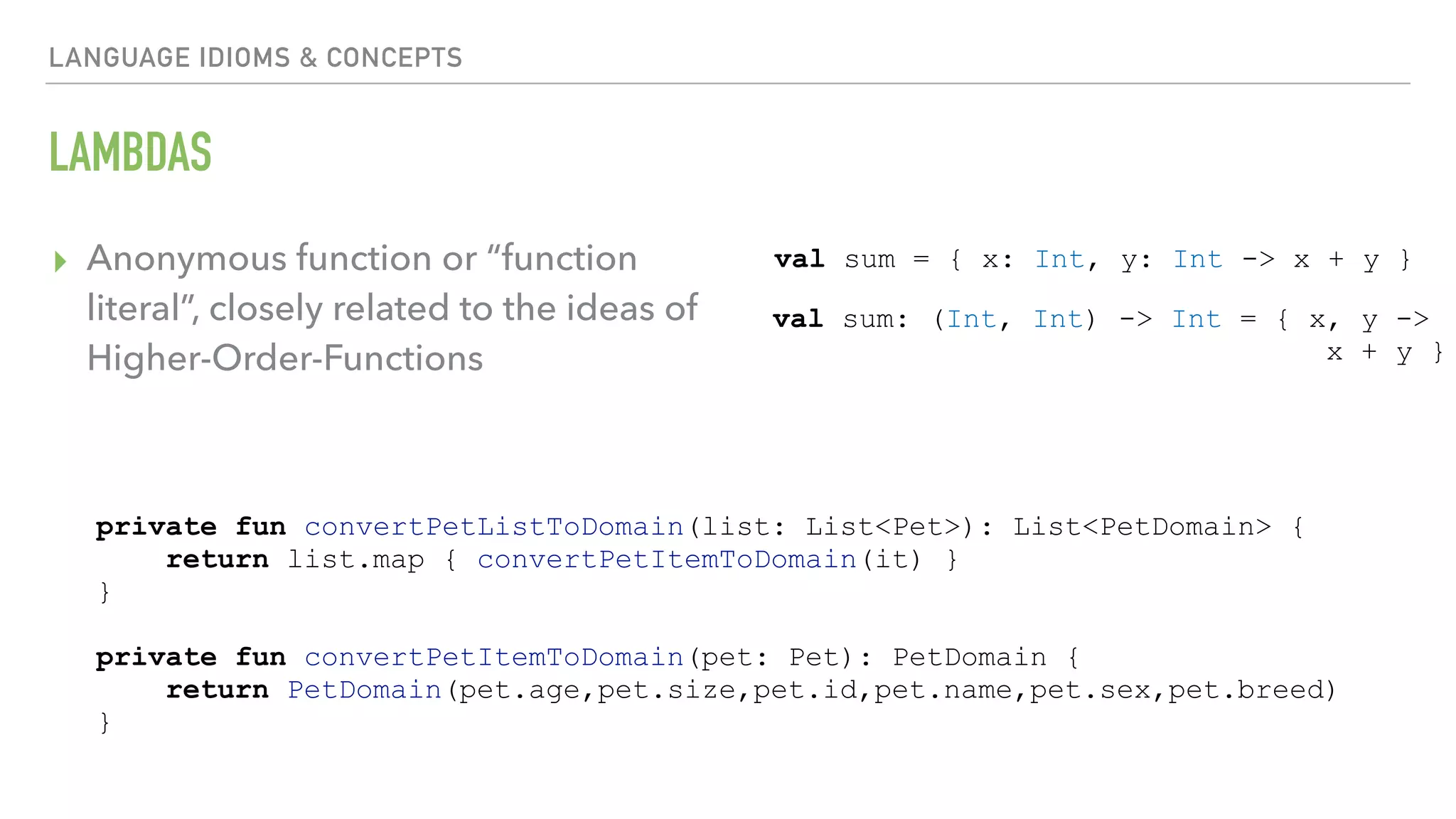
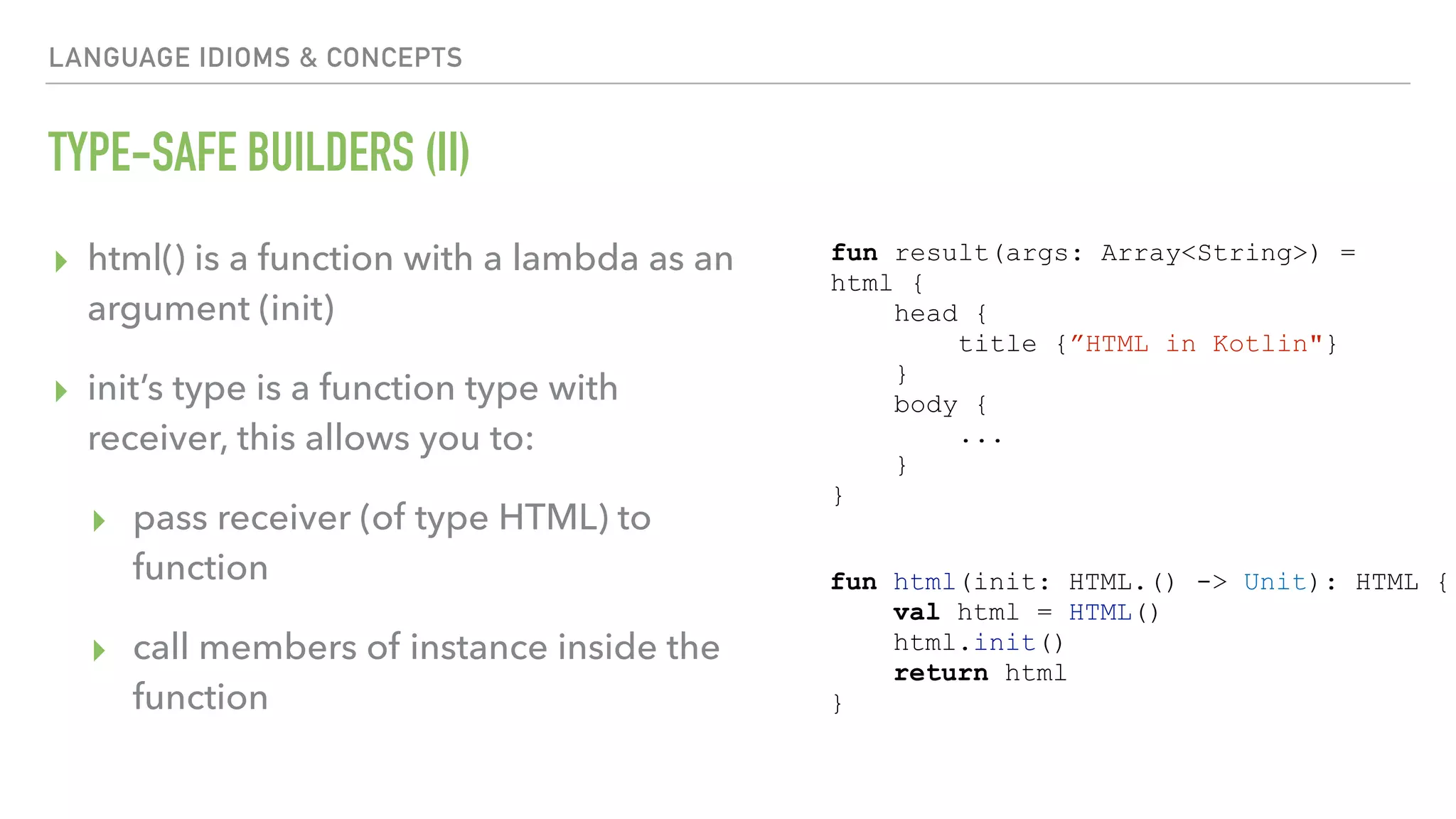
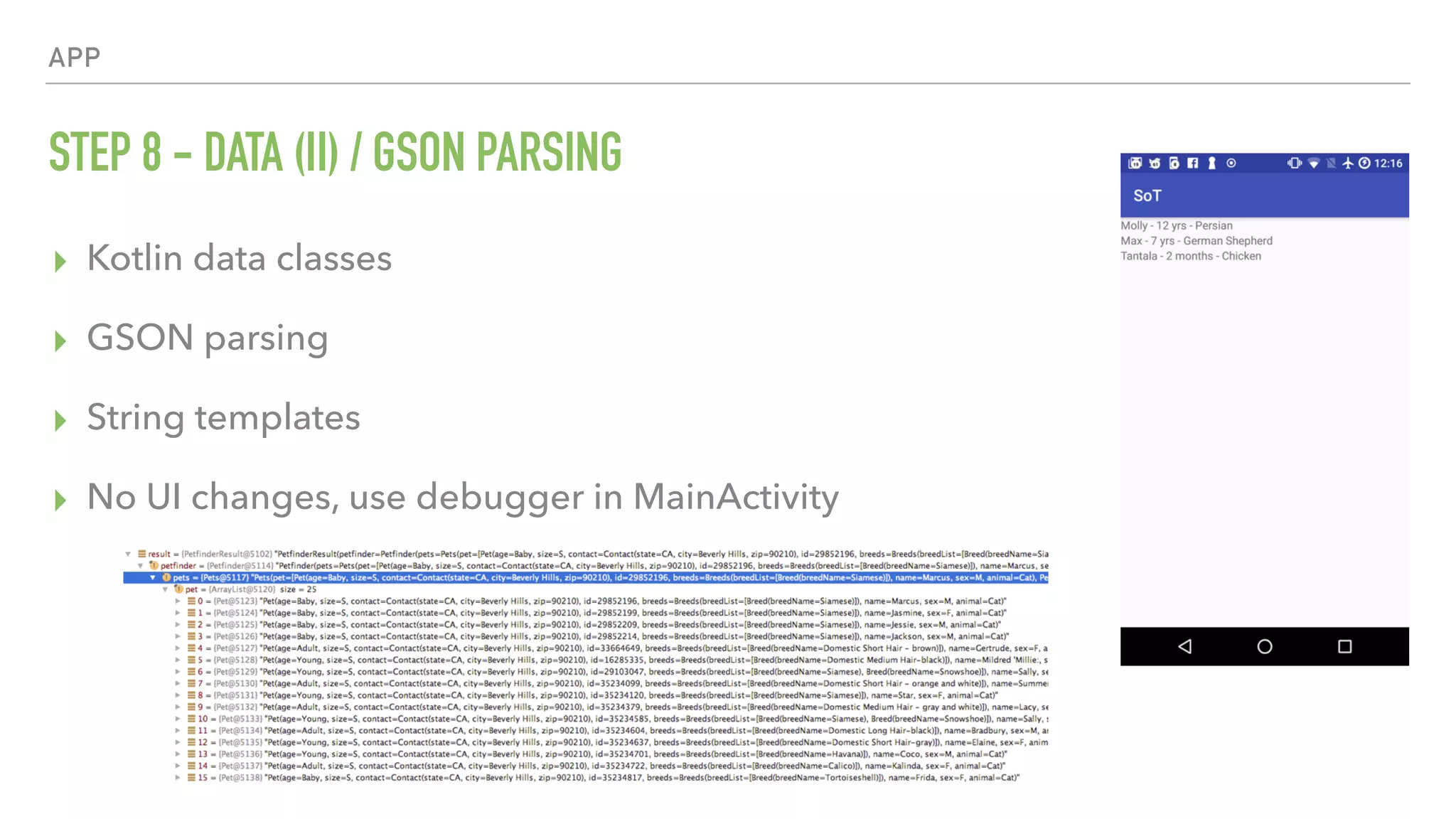
The document provides an overview of a 90-minute workshop on building a simple Android app with Kotlin. It introduces Kotlin and the Anko DSL, discusses Kotlin language concepts and idioms, and outlines the steps to build an app that loads and displays sample JSON data using Kotlin and Anko. The workshop covers Kotlin setup, refactoring existing Java code to Kotlin, using Kotlin Android extensions and Butterknife for view binding, adding a RecyclerView with sample data, loading and parsing JSON data with Gson, and introducing the Anko DSL and command pattern for asynchronous operations.














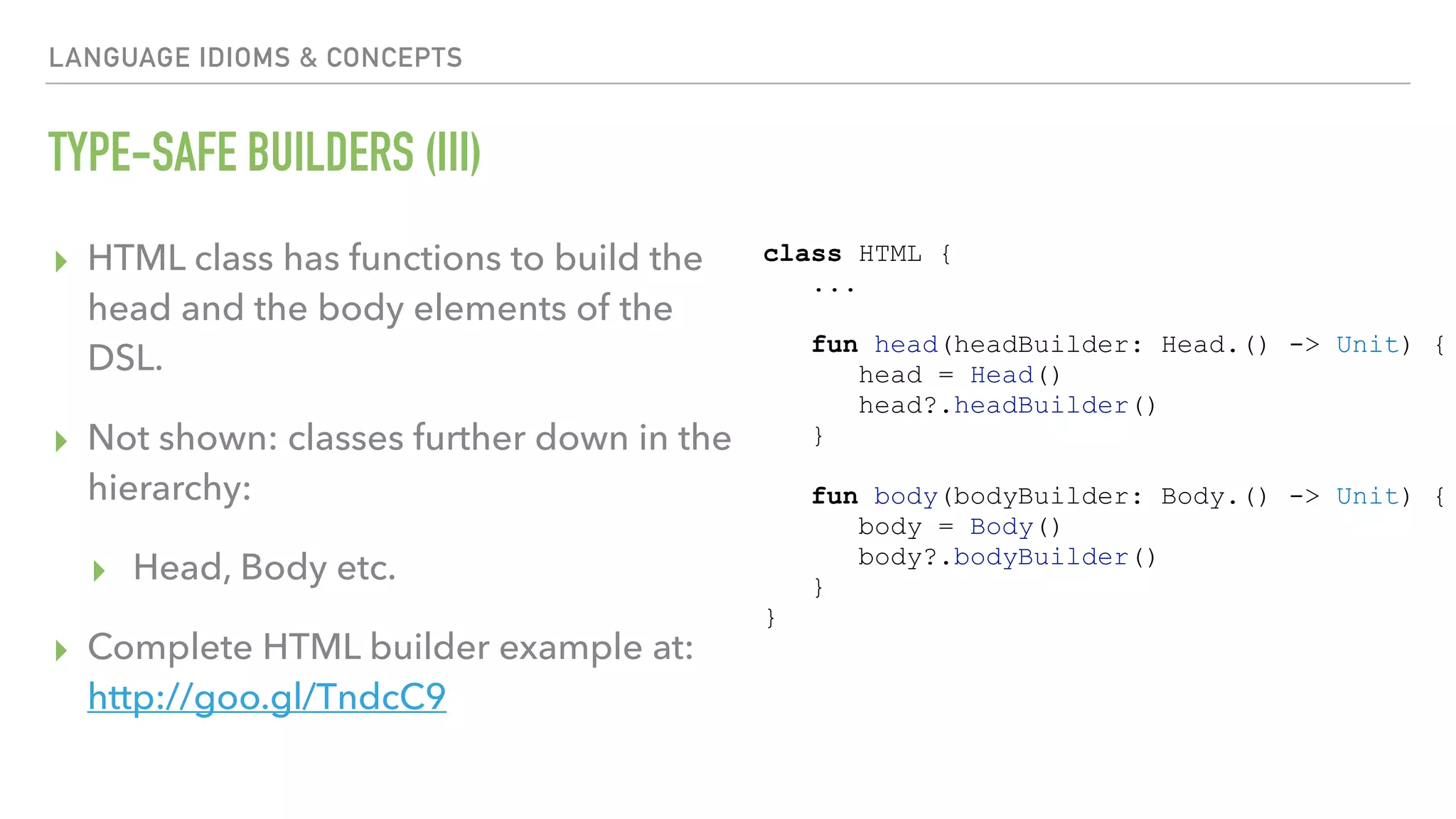


















![THE HIDDEN PARTS OF ANKO BUT THERE’S MORE ▸ Intent wrappers for various purposes: e.g. sendSMS(number, [text]) ▸ Intent builders ▸ Service shortcuts ▸ Configuration qualifiers: configuration(screenSize = ScreenSize.LARGE, orientation = Orientation.LANDSCAPE) { … } ▸ Asynchronous tasks ▸ SQLLite](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sot2018-180416060524/75/Android-101-Building-a-simple-app-with-Kotlin-in-90-minutes-53-2048.jpg)