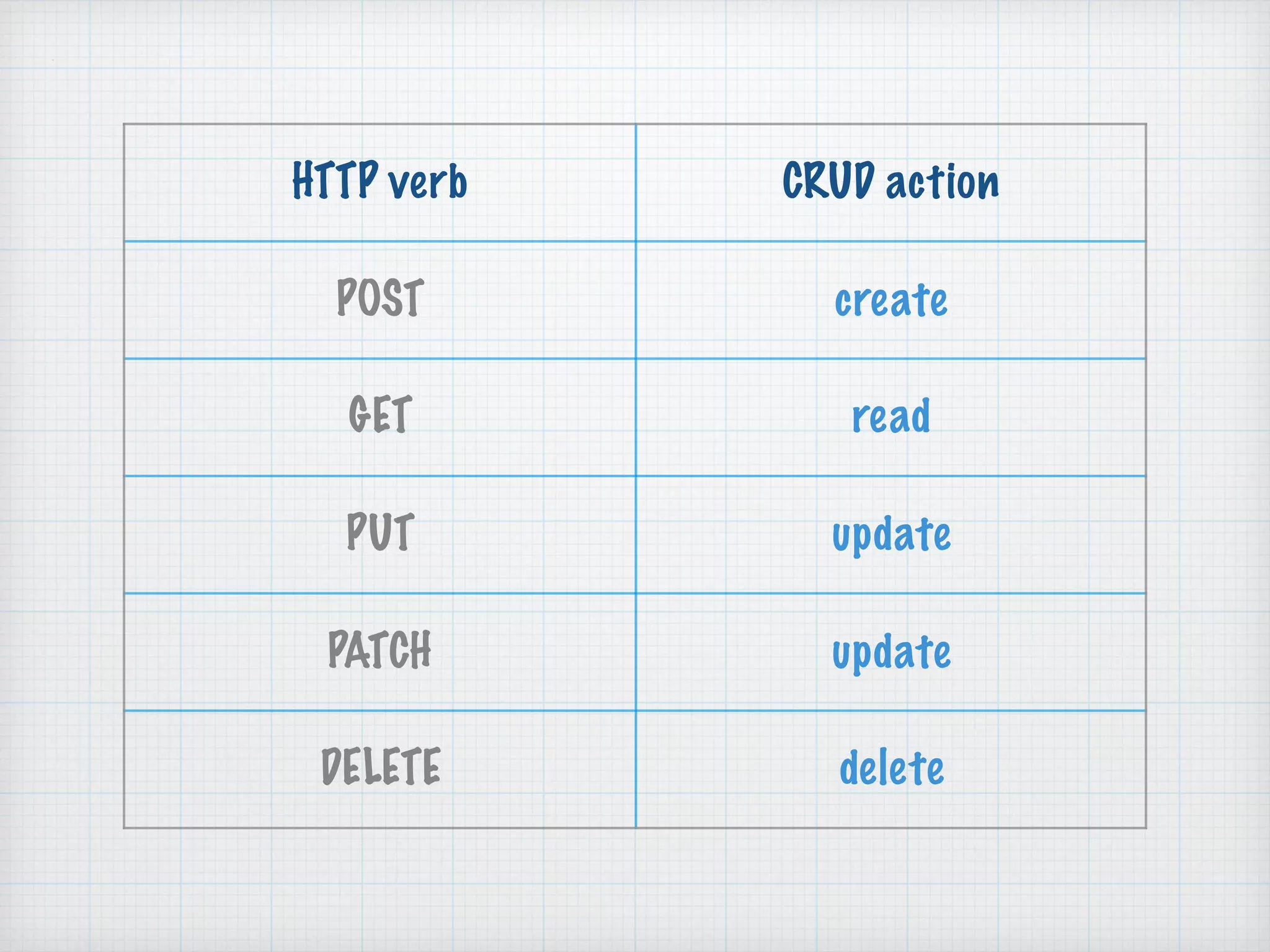
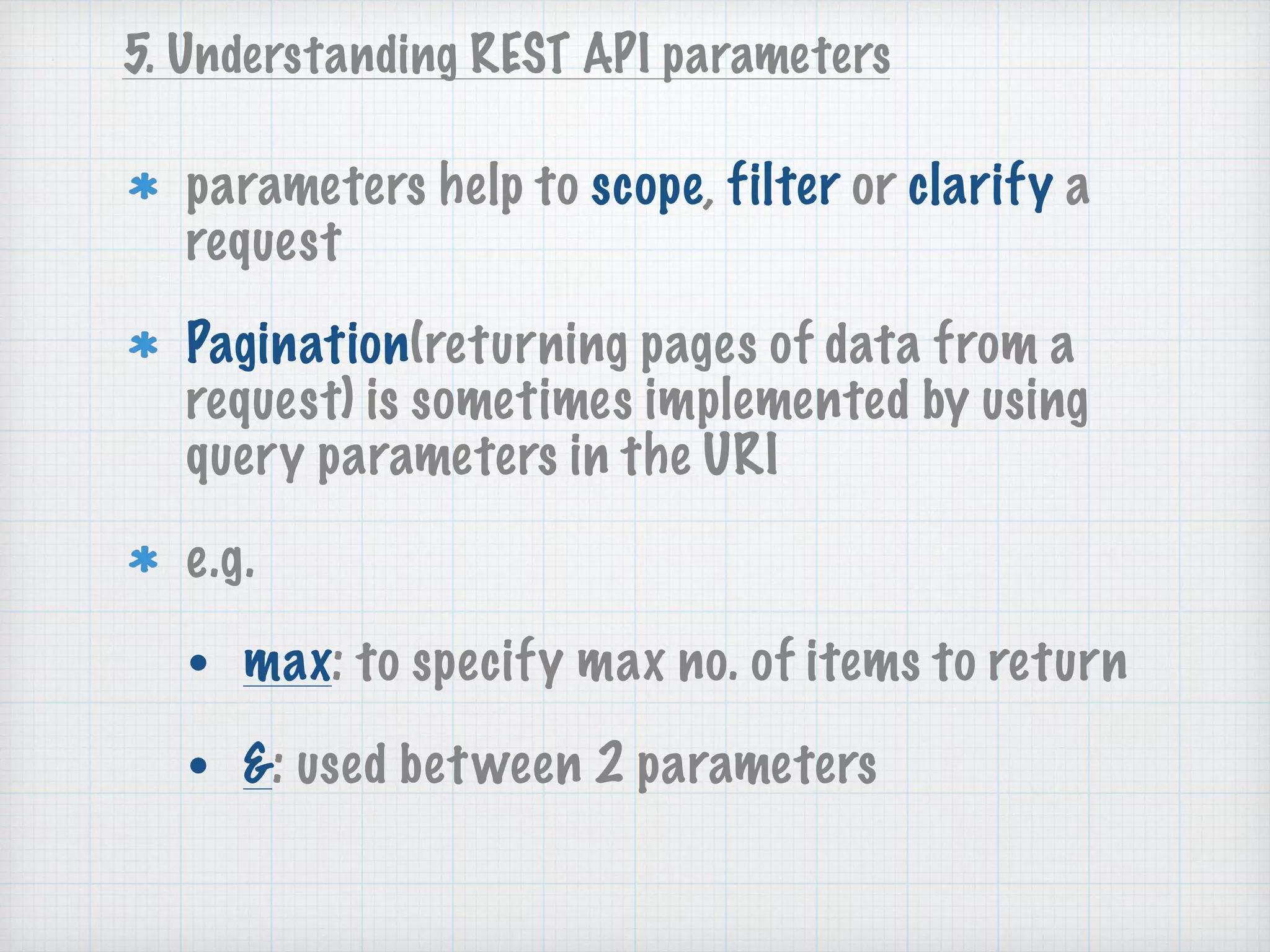
API Basics discusses software defined networking (SDN) and REST APIs. SDN separates the control plane and data plane in network devices to allow remote configuration. REST APIs use HTTP to enable communication between applications through requests and responses that include resources, parameters, headers and payloads in JSON or XML format. The document provides examples of REST API components like endpoints, verbs, parameters and data formats to help understand how to work with REST APIs.