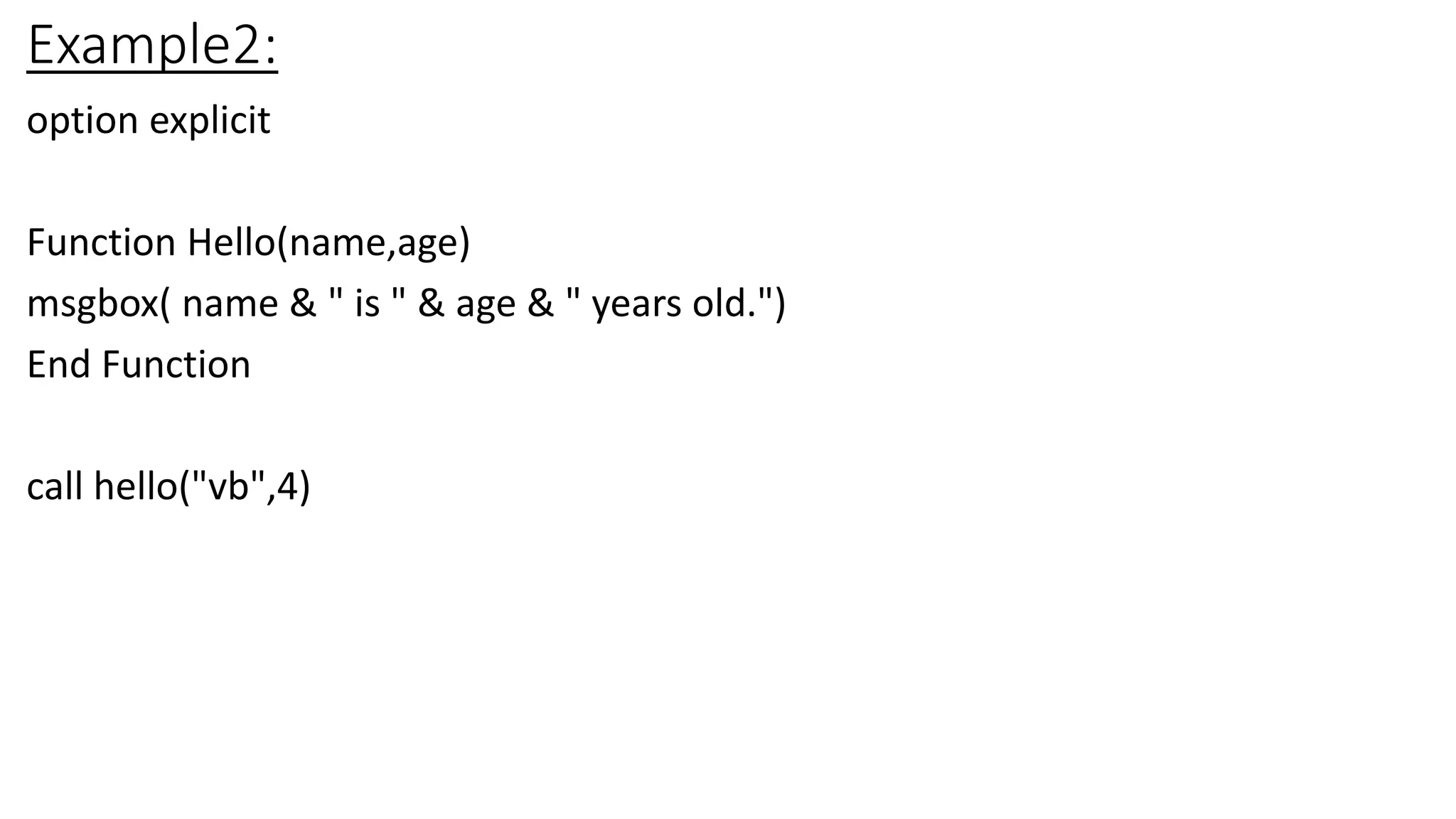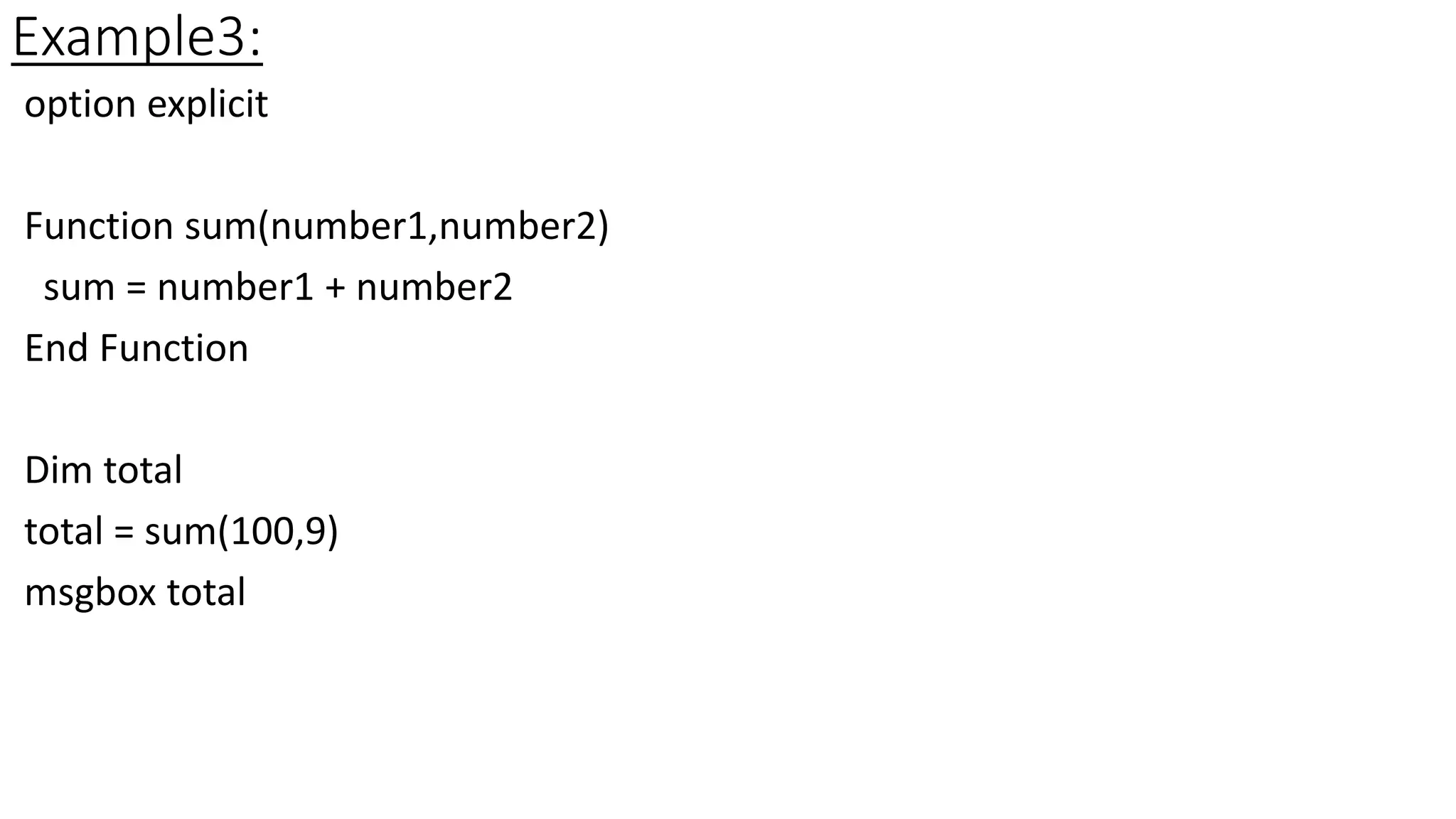Arrays allow developers to store multiple values in a single variable. They can be static or dynamic. Static arrays have a fixed size while dynamic arrays can change size. Arrays are declared with Dim and values assigned using indexes. Functions are reusable blocks of code that can take parameters and return values. They are defined using the Function keyword and called using Call or without for Sub procedures. Parameters can be passed ByVal or ByRef.