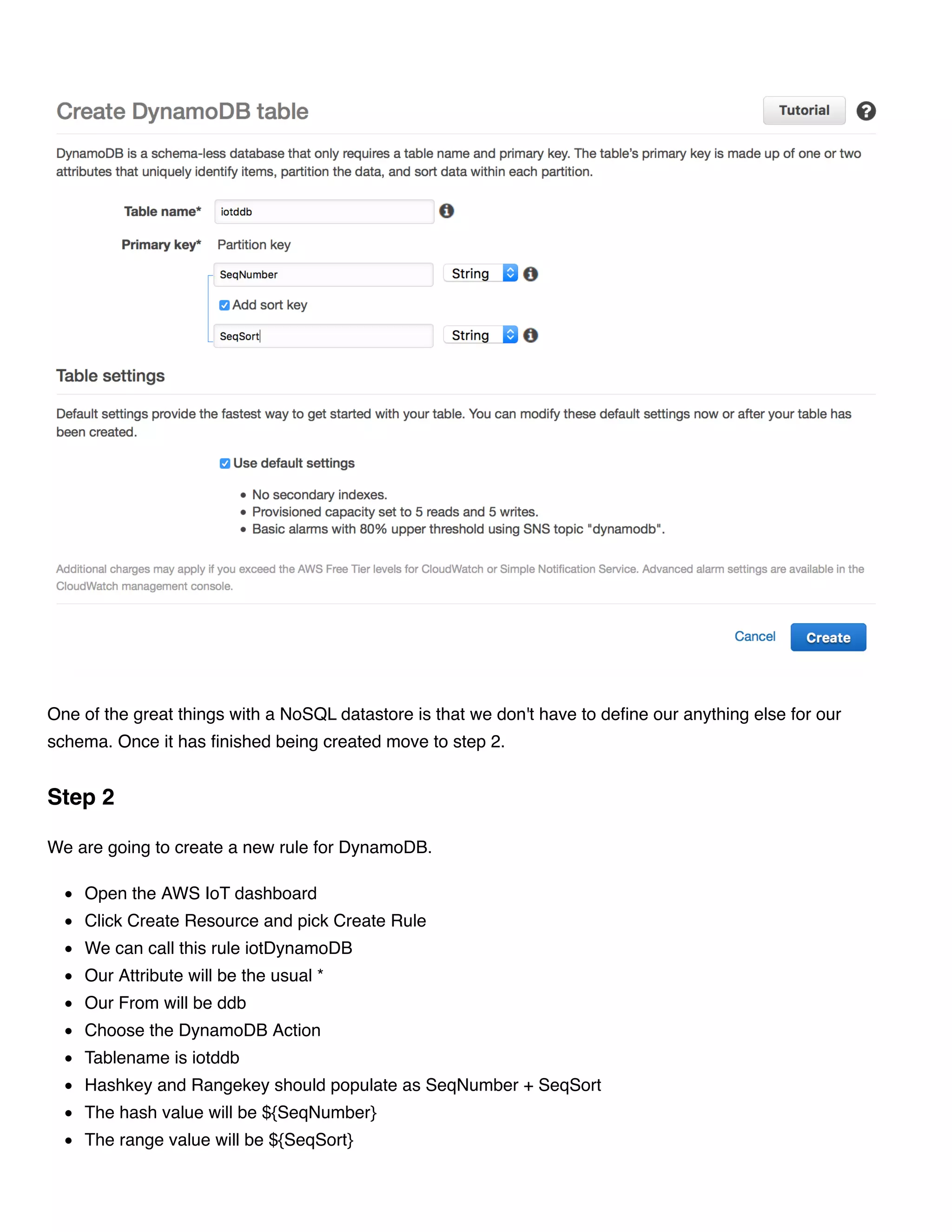
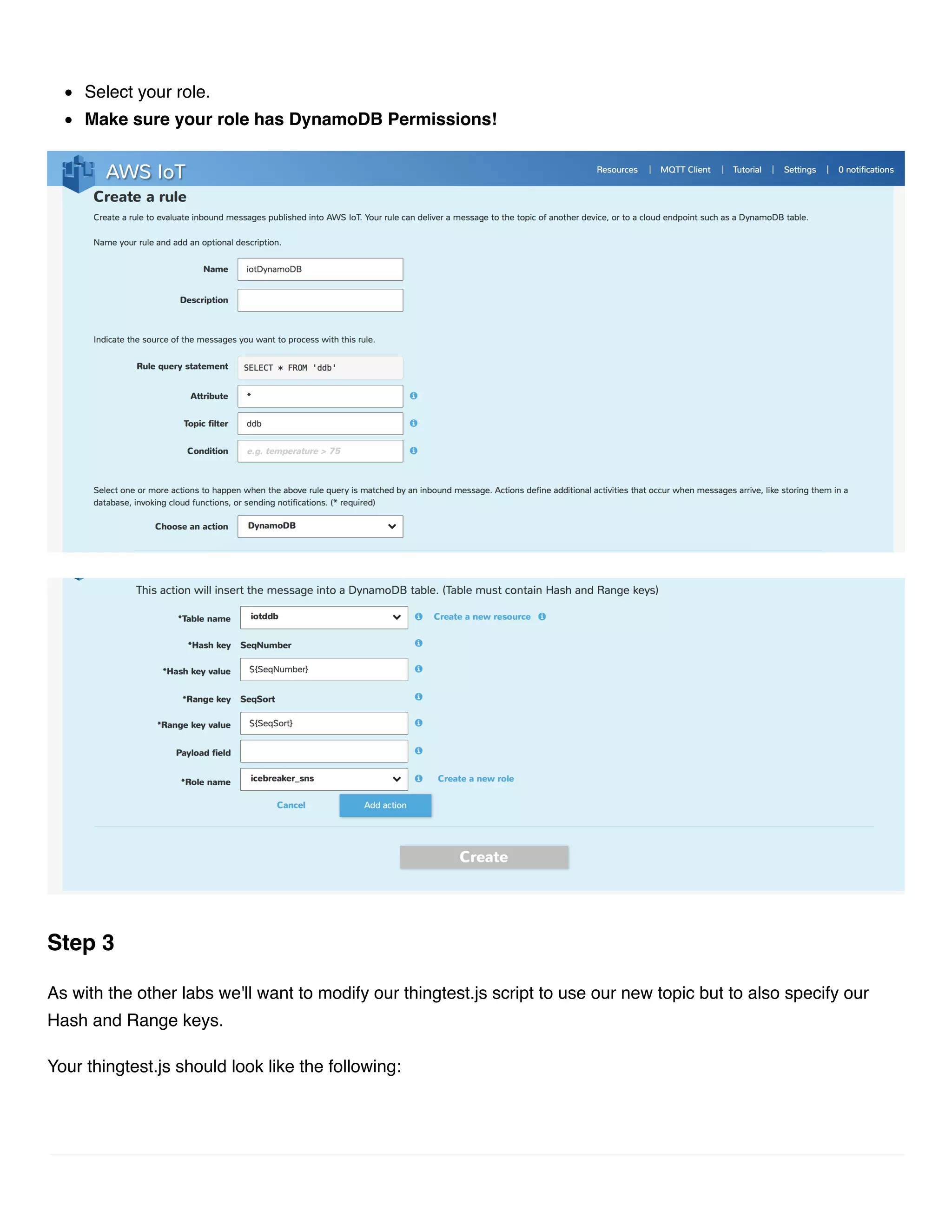
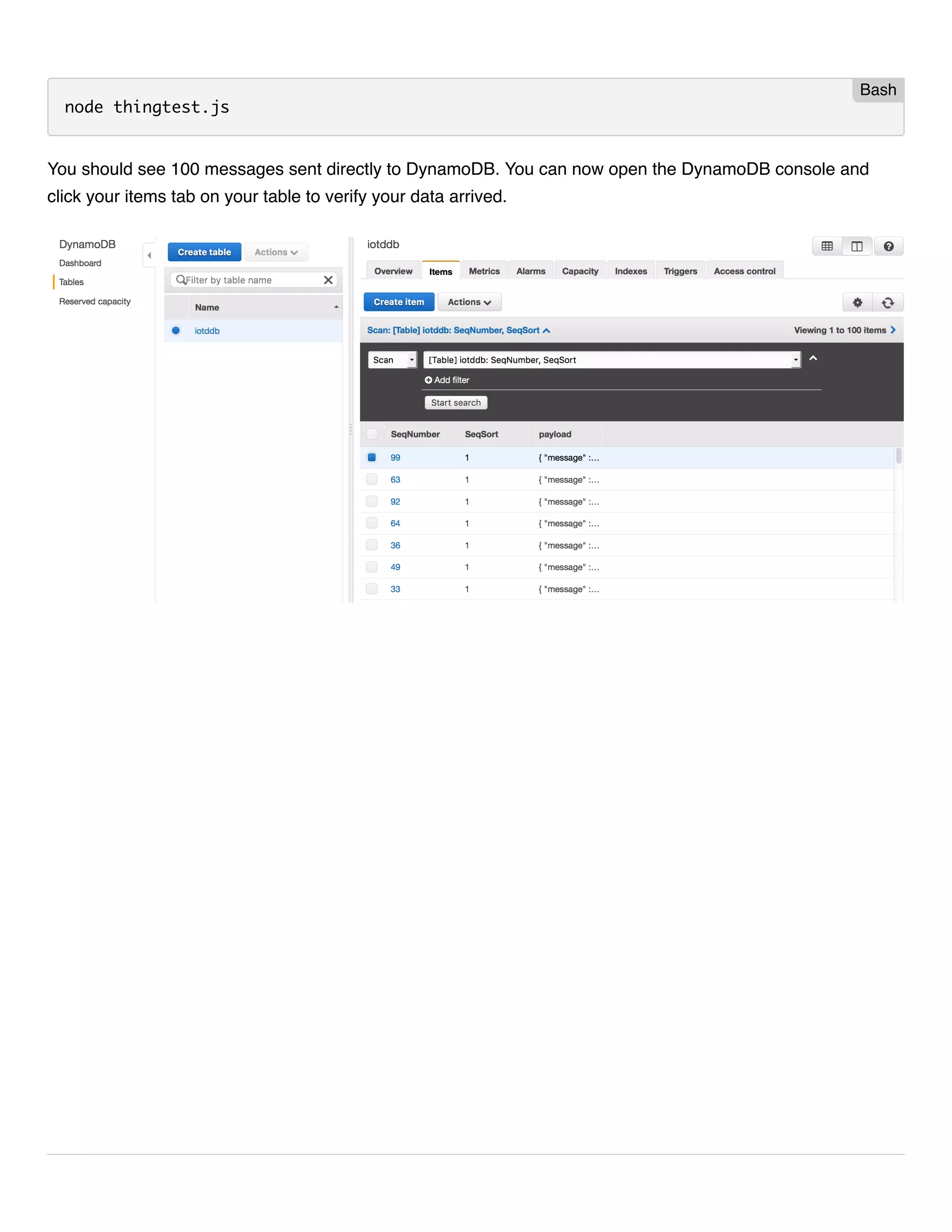
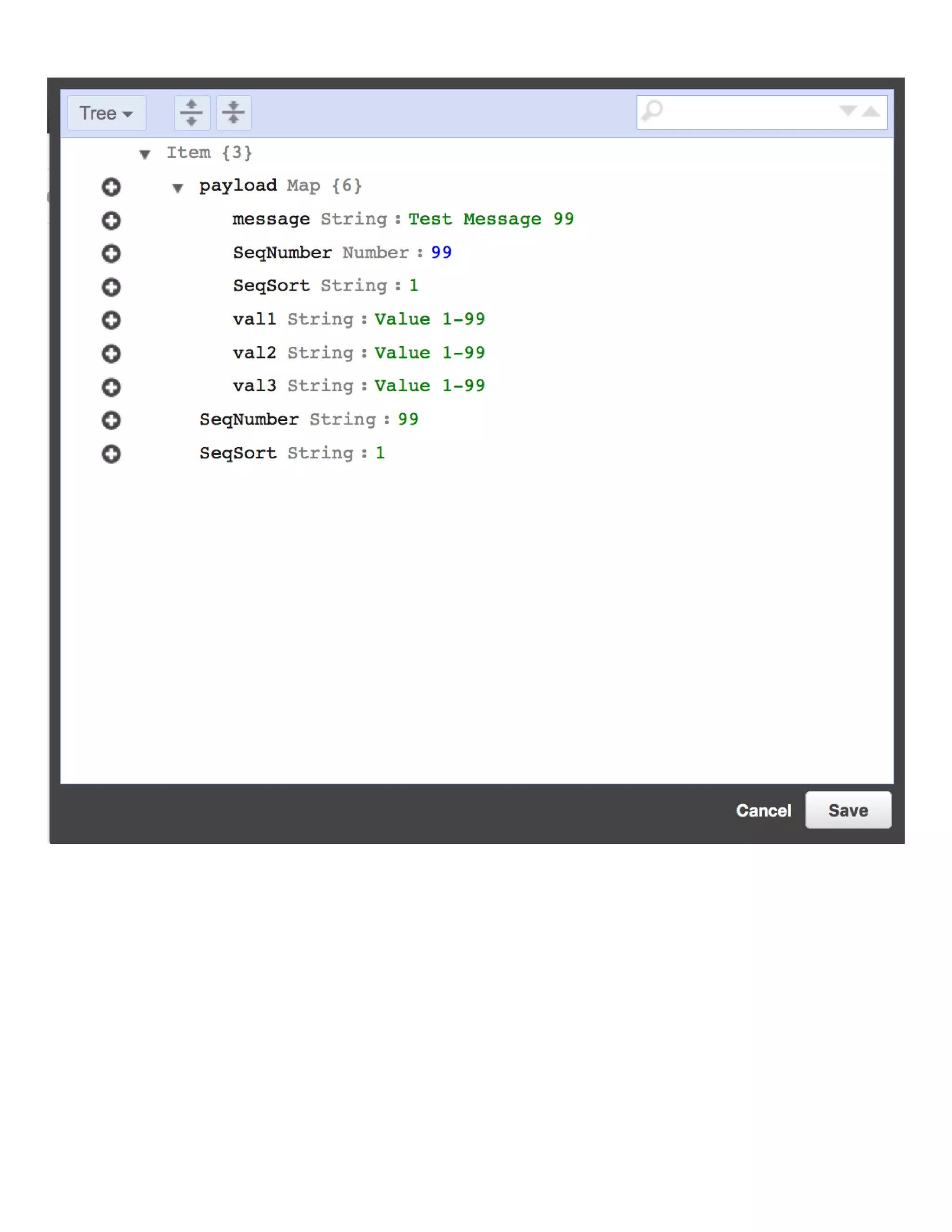
This document provides instructions for streaming IoT device data directly to an AWS DynamoDB table using AWS IoT rules. It outlines the steps to create a DynamoDB table with the required partition and sort keys, create an AWS IoT rule to stream data to the DynamoDB table, and modify a device script to publish messages to the new topic with the partition and sort keys.