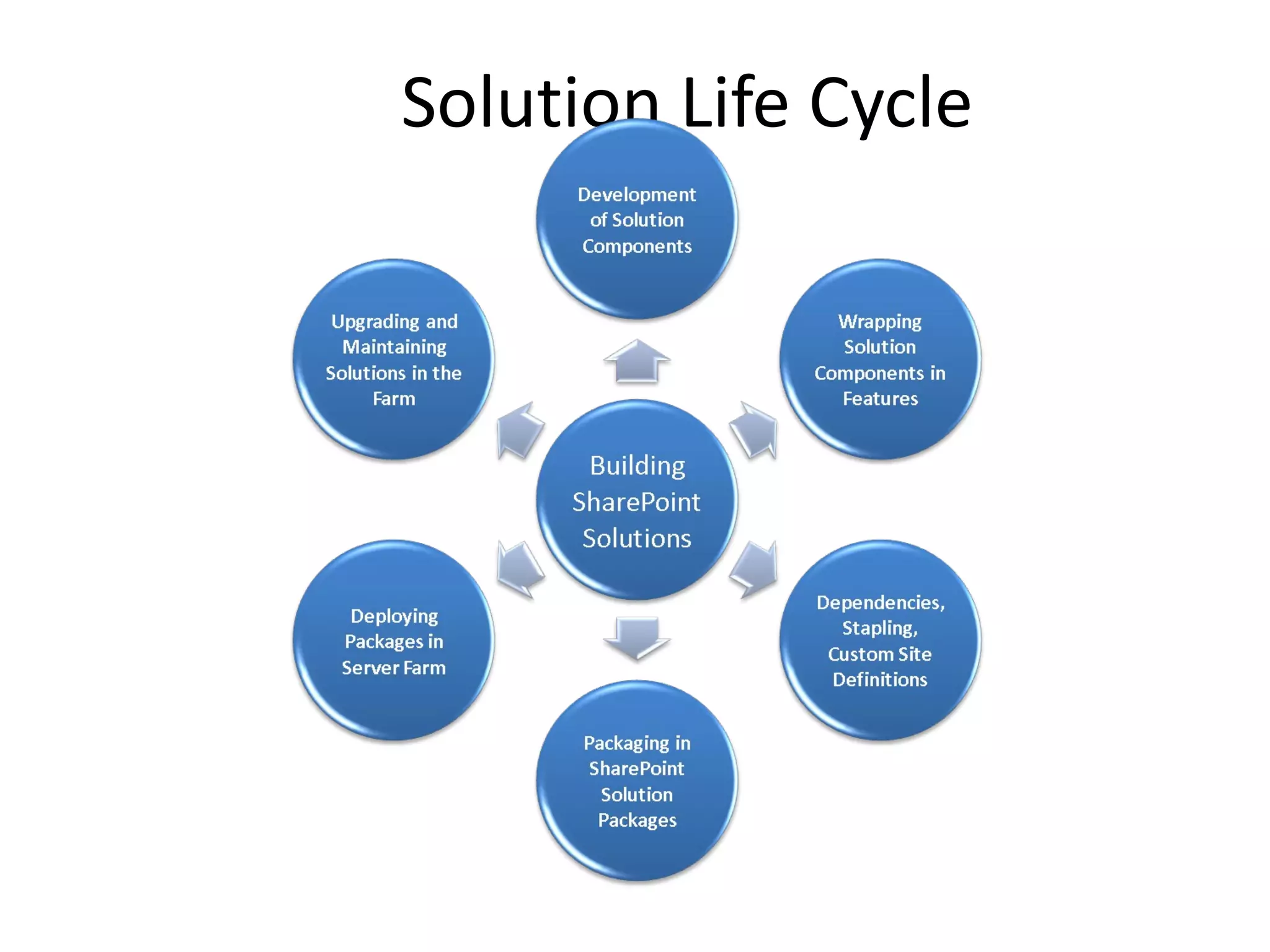
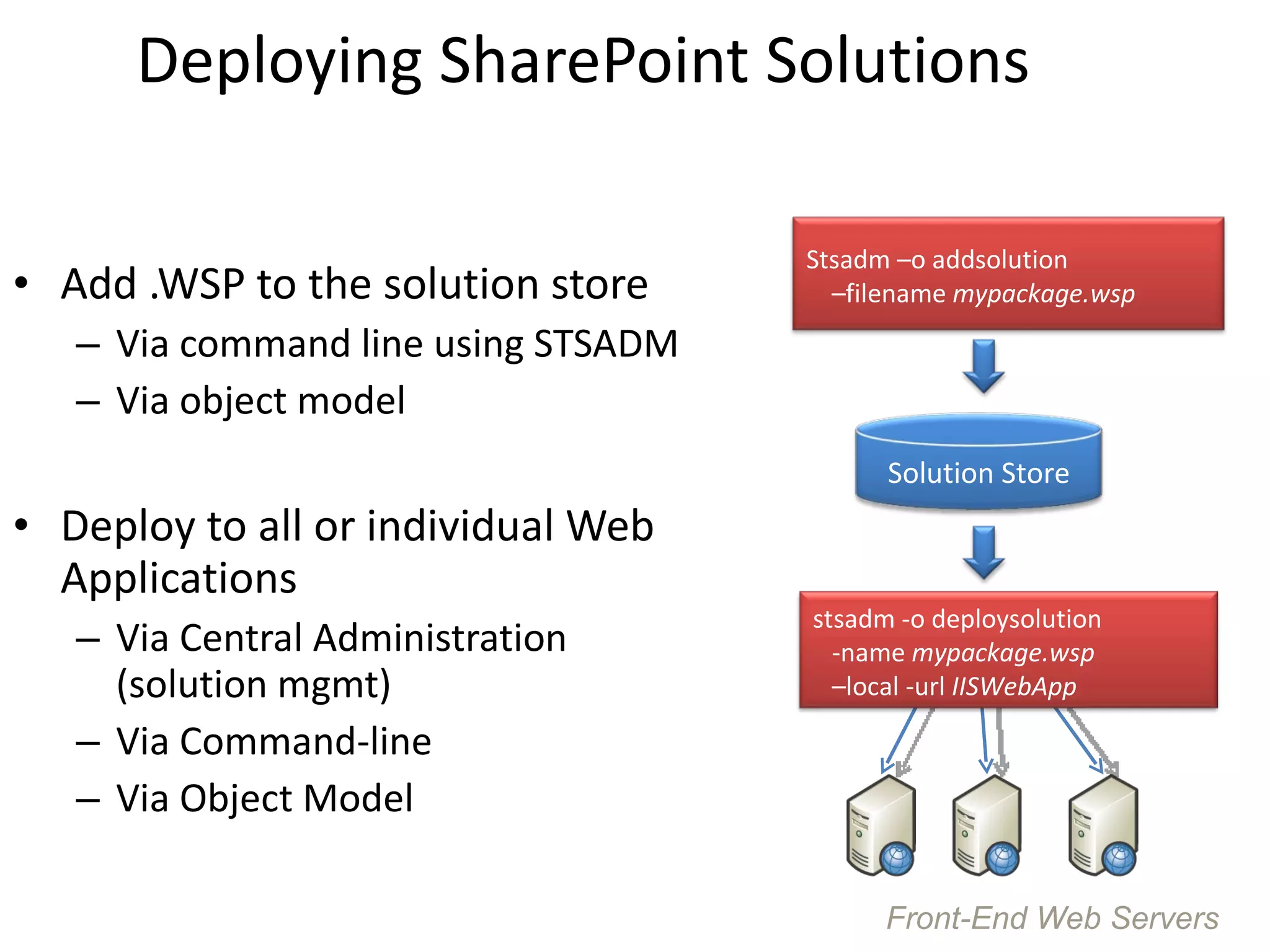
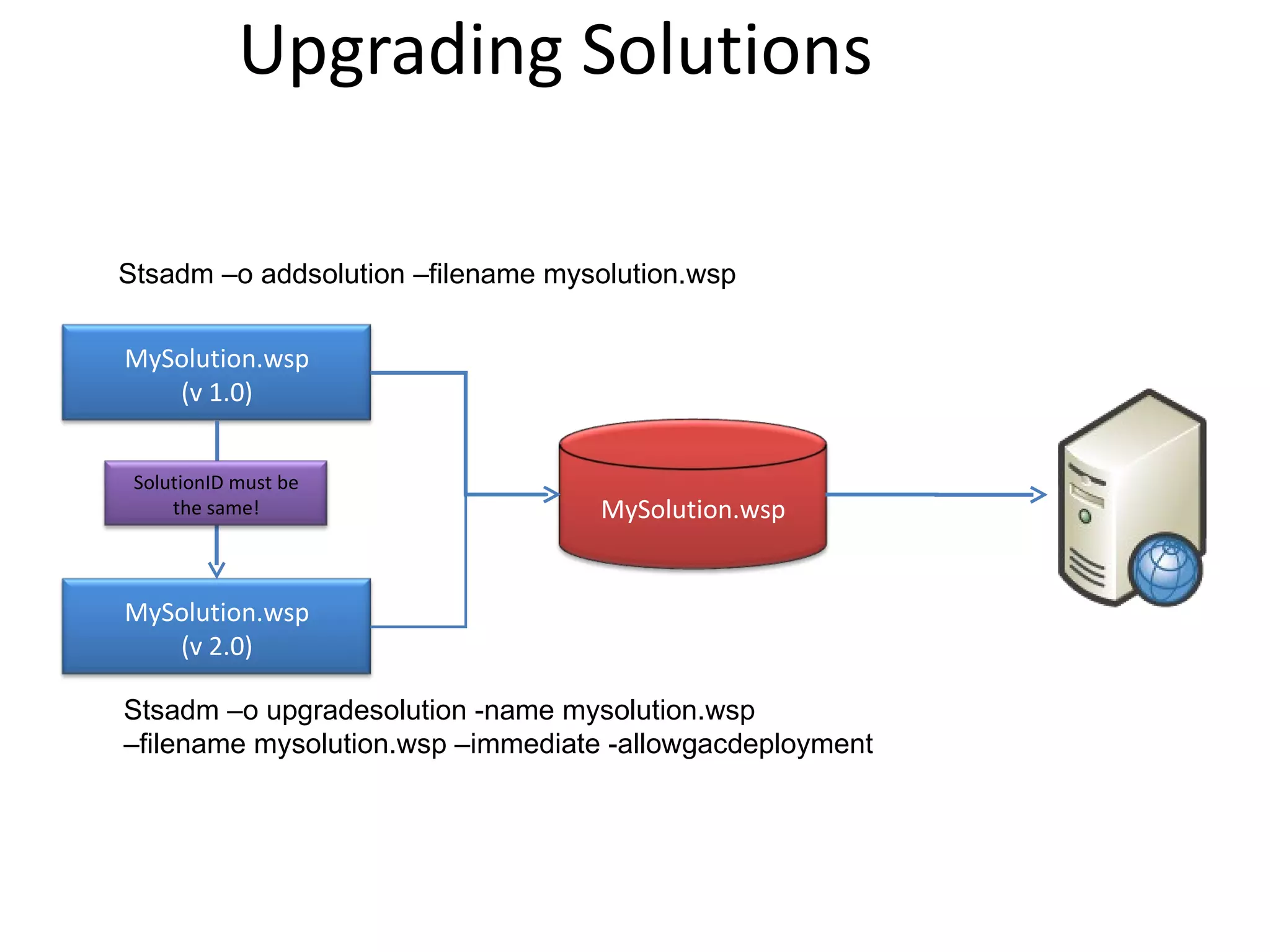
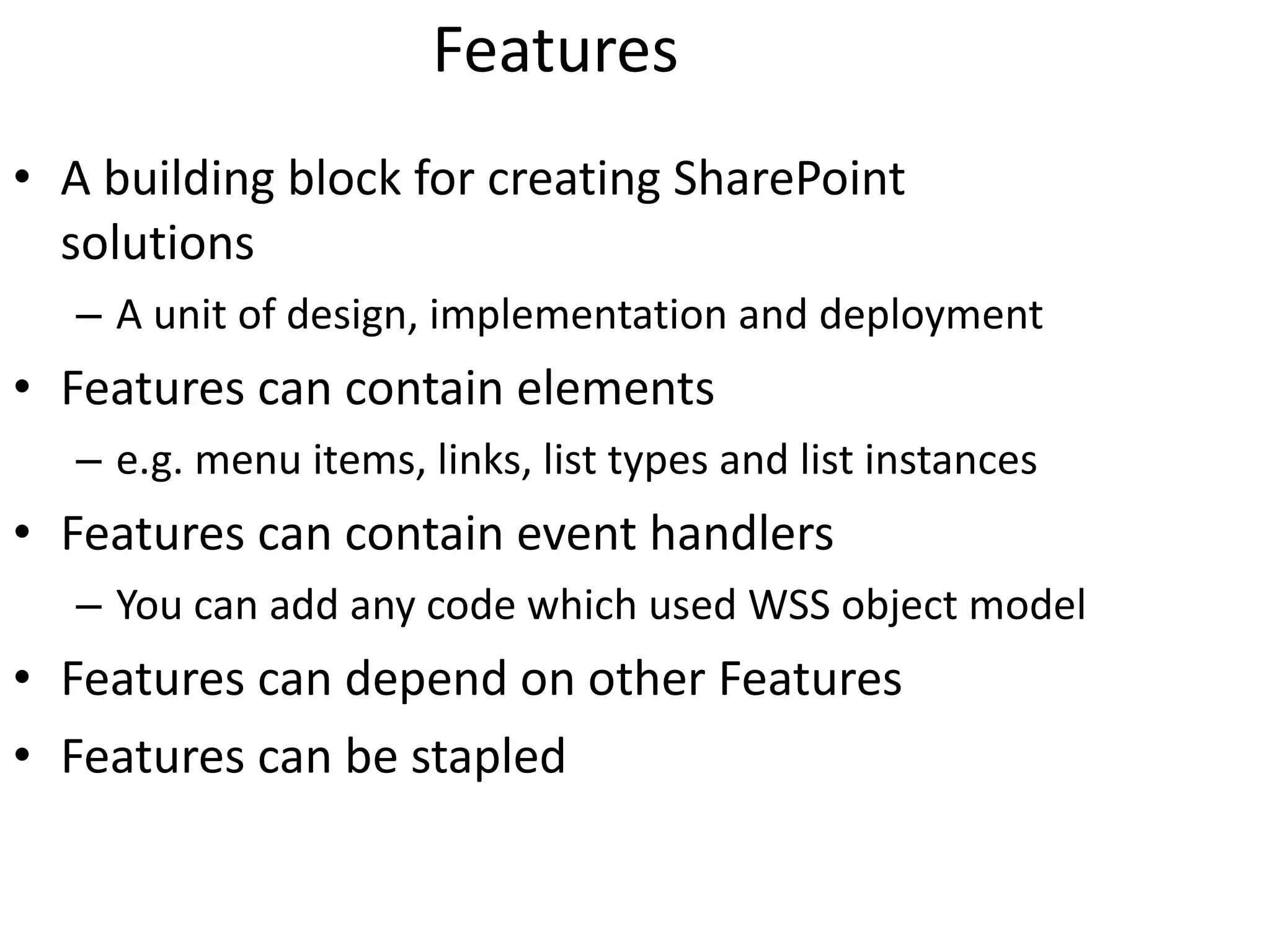
This document provides best practices for deploying SharePoint solution packages. It discusses what solution packages are and how they can be used to package and deploy custom features, site definitions, master pages and other components. It also covers the solution development lifecycle and tools for creating solutions, as well as how to deploy, retract, upgrade and manage solutions. Checklists are provided to help ensure solutions are properly tested, documented and deployed.
![Salaudeen Rajack [email_address] Best Practices for SharePoint Solution Deployment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bestpracticesforsharepointsolutiondeployment-110409081352-phpapp01/75/Best-practices-for-share-point-solution-deployment-1-2048.jpg)









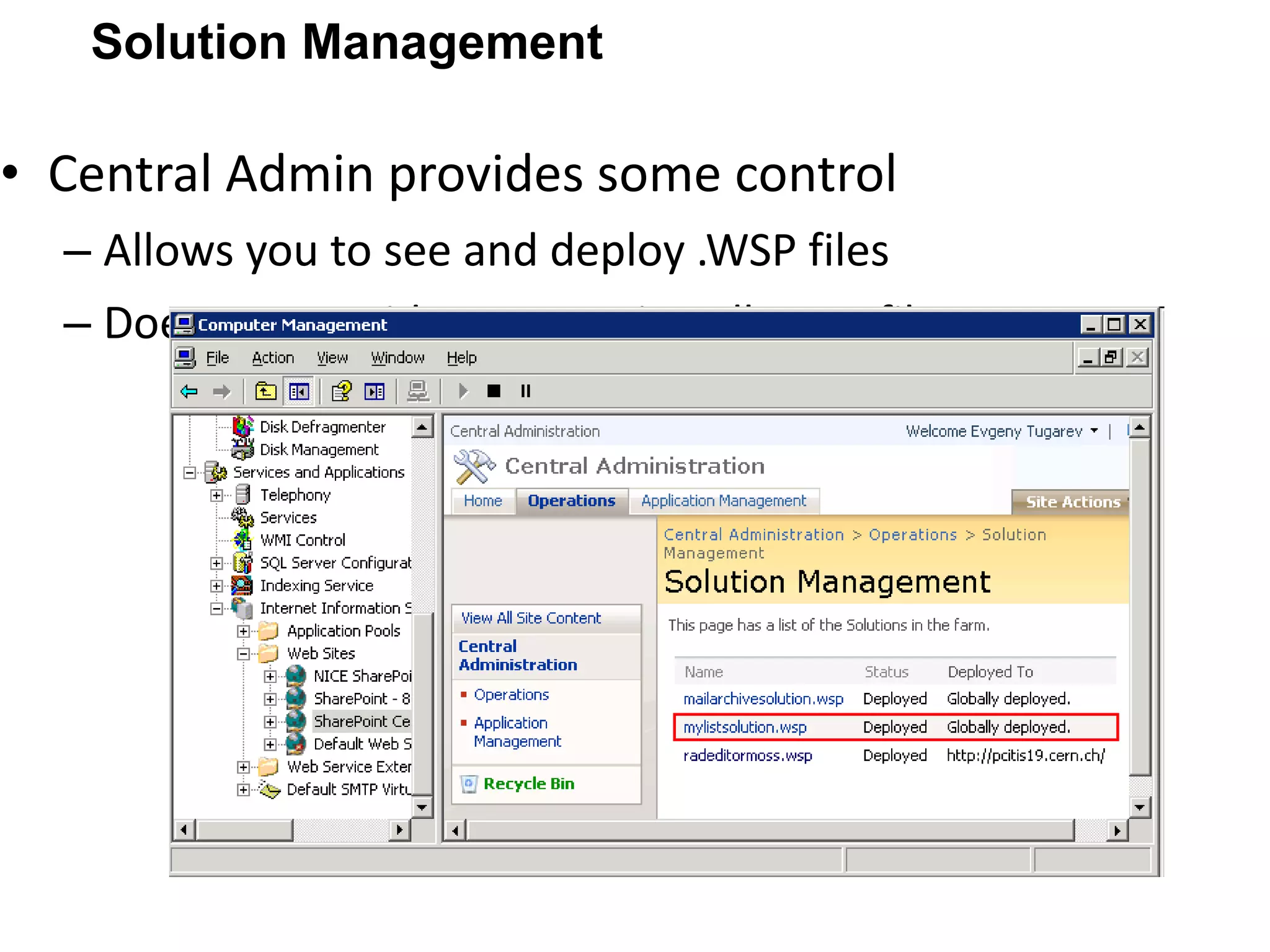
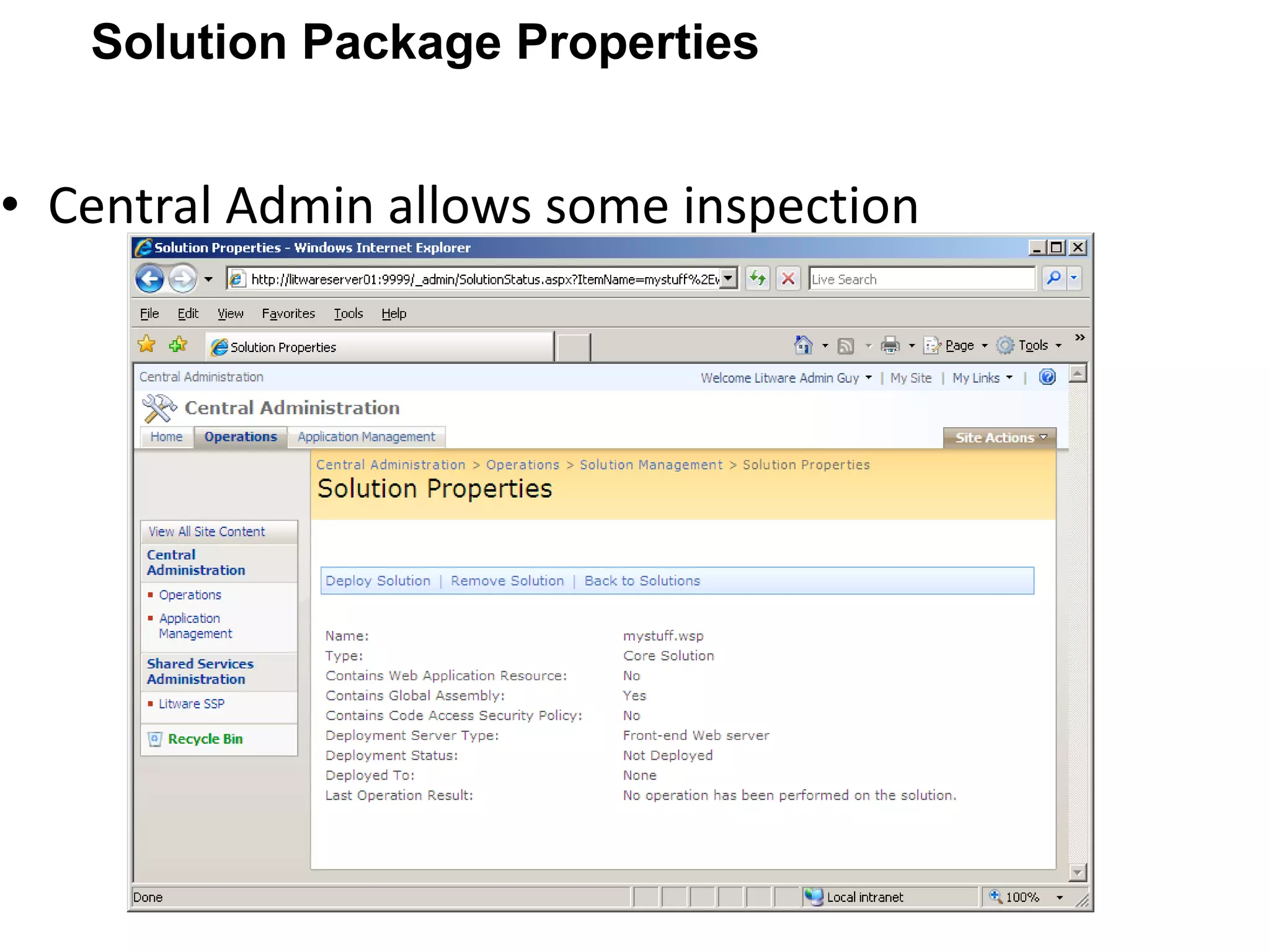
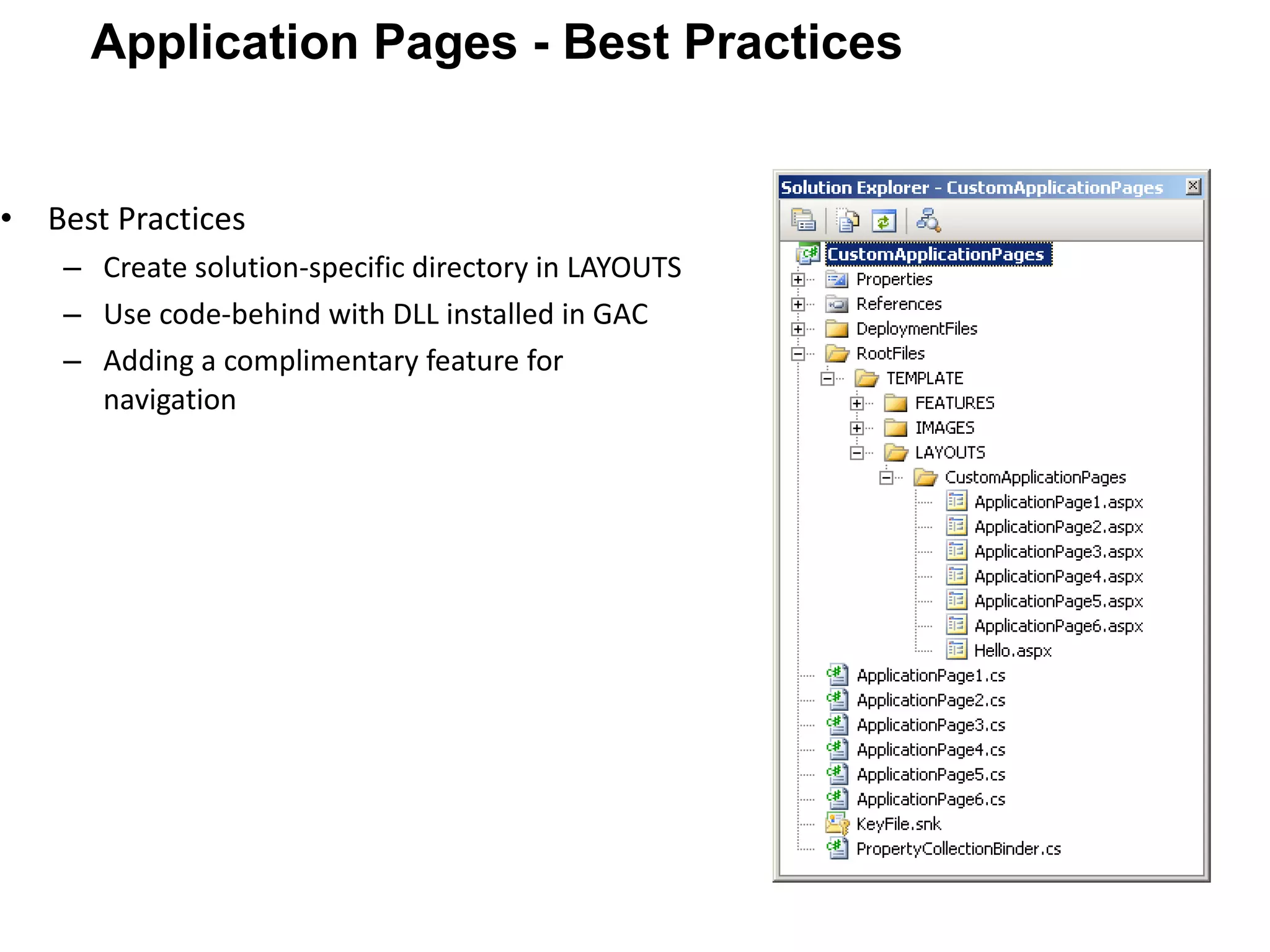

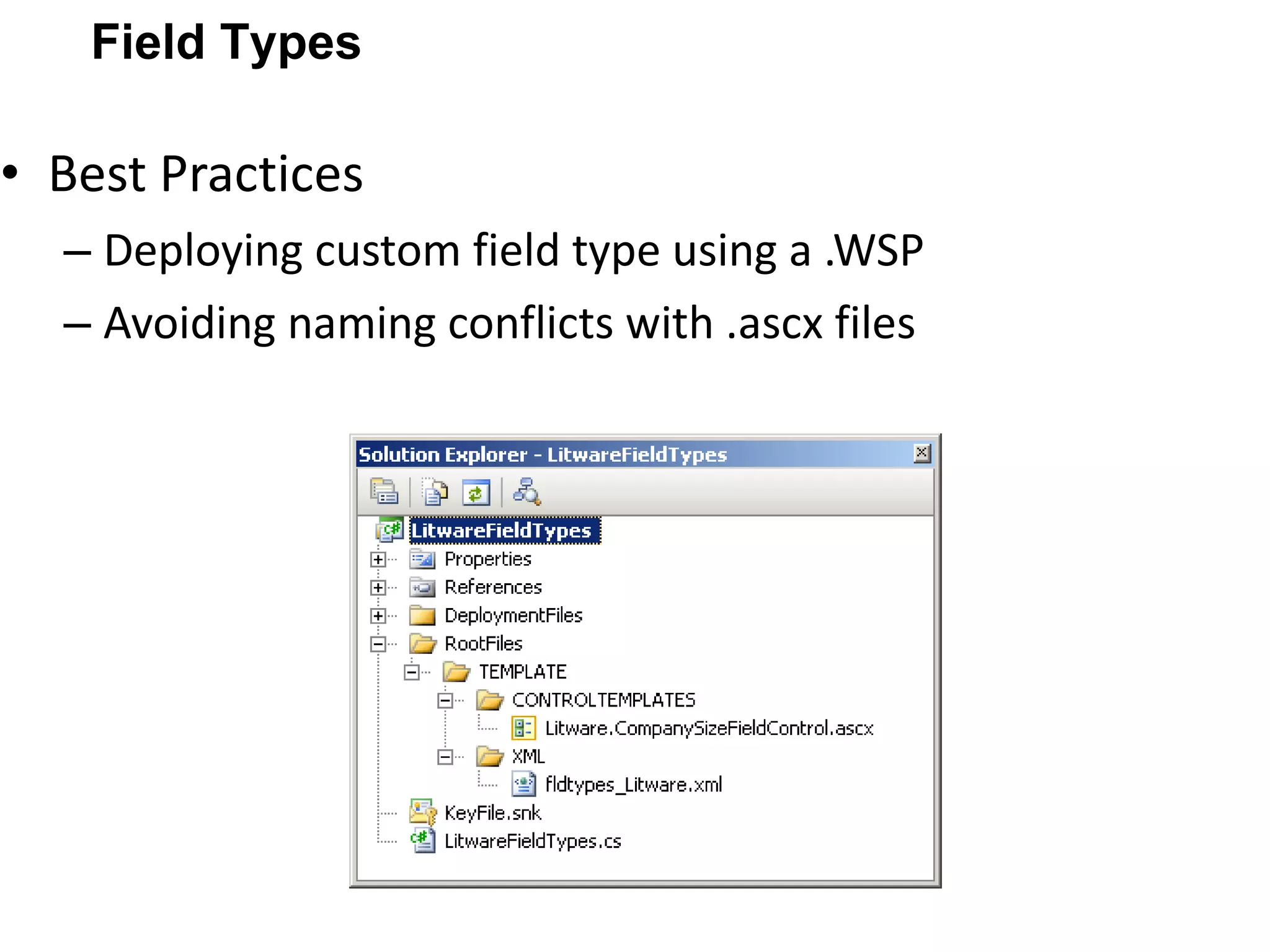







![Shoot your queries to [email_address] Thank You!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bestpracticesforsharepointsolutiondeployment-110409081352-phpapp01/75/Best-practices-for-share-point-solution-deployment-31-2048.jpg)