Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
















This document discusses browser caching and techniques to improve website performance through caching. Browser caching involves temporarily storing recently visited web pages on a user's hard disk to load them faster during the same browsing session. Making fewer HTTP requests, adding expires headers, using content delivery networks, and leveraging browser caching directives like Cache-Control can help optimize caching. Common file types like CSS, JavaScript, images that should be cached are also mentioned. The document provides details on various caching strategies and their benefits like reducing bandwidth usage and loading websites faster.



















Presentation by Jaiswal Siddharth on Browser Caching.
Topics covered include Virtual Memory, Process Execution, and Demand Paging.
Caching optimizes performance and scalability. Types include Client-Side, Browser, Server-Side, and Object Caching.
Browser caching stores webpages for speed. Benefits include faster delivery and reduced bandwidth costs.
Techniques such as fewer HTTP requests, using CDN, and creating image sprites to reduce load times.
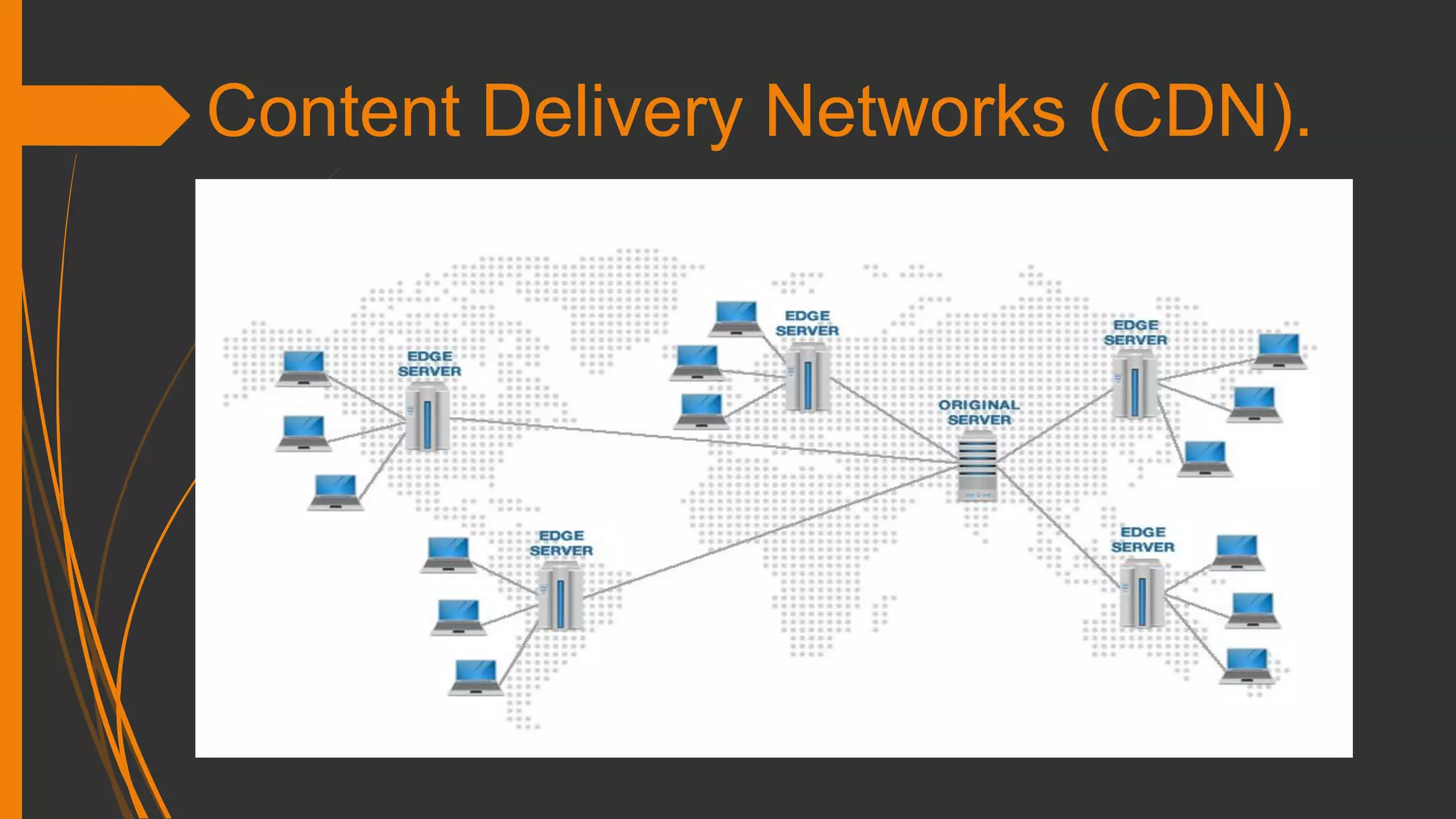
CDNs are distributed servers that deliver content based on geographic location for faster service.
Using Expires Headers to reduce HTTP requests and improve cache efficiency.
Cache-Control directives manage caching behavior, including max-age settings and public/private responses.
Caching directives help manage DNS lookups for better performance.
Advantages on memory allocation like easy handling, reduced fragmentation, and efficient swapping.
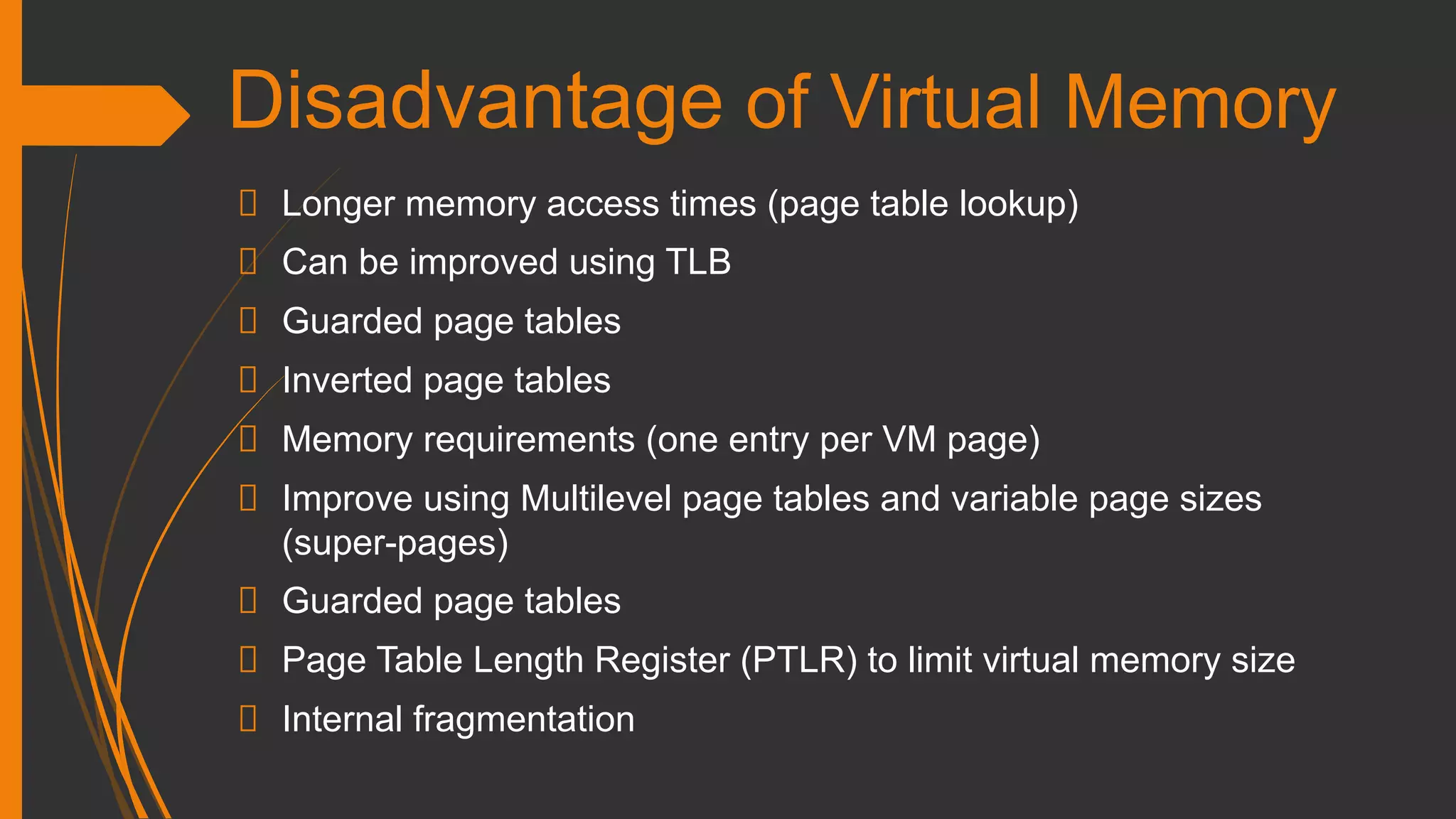
Challenges include longer access times and memory requirements, addressed by advanced tables.
Questions from the audience directed to Jaiswal Siddharth.
Ending remarks and thanks from Jaiswal Siddharth.