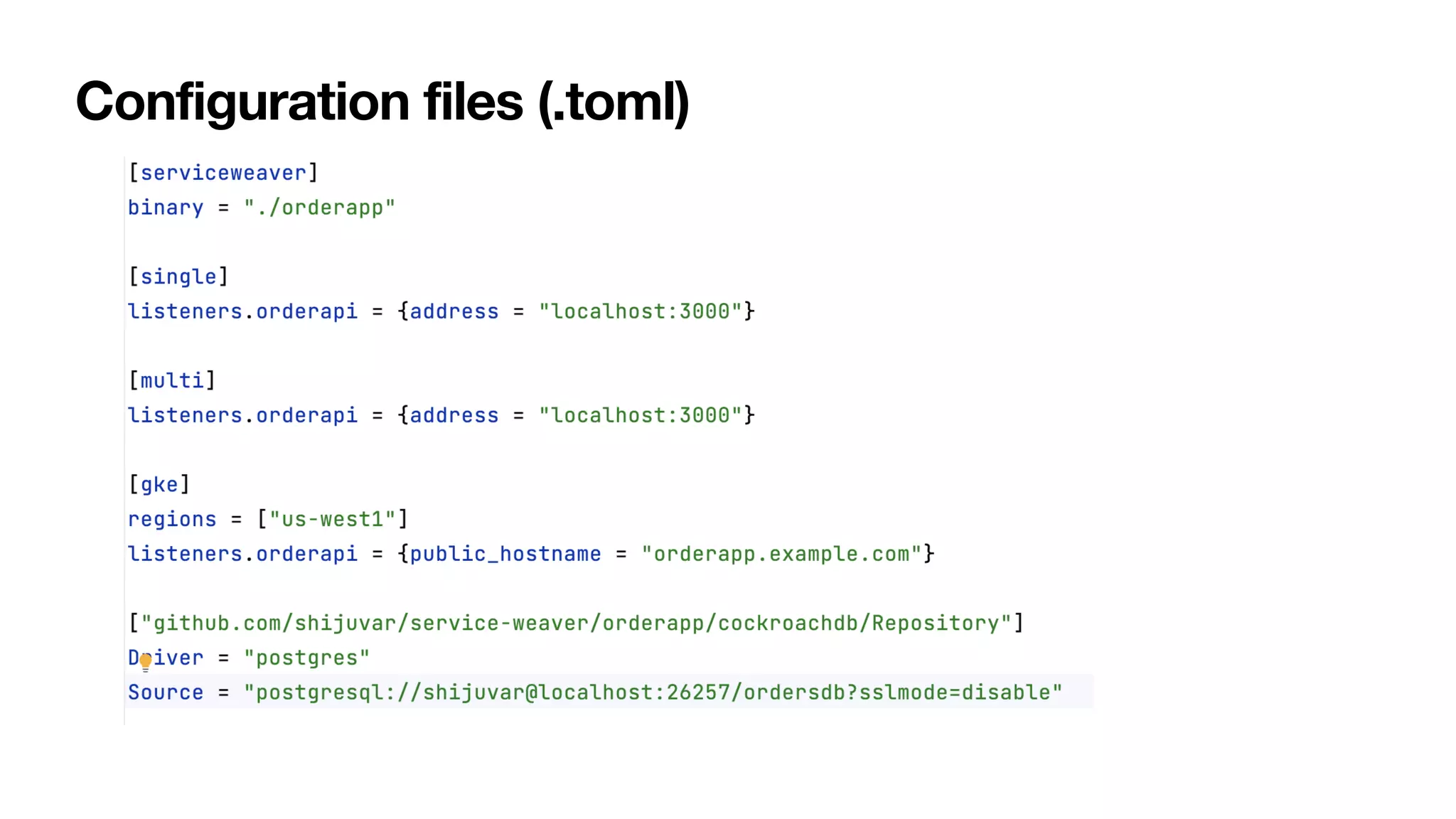
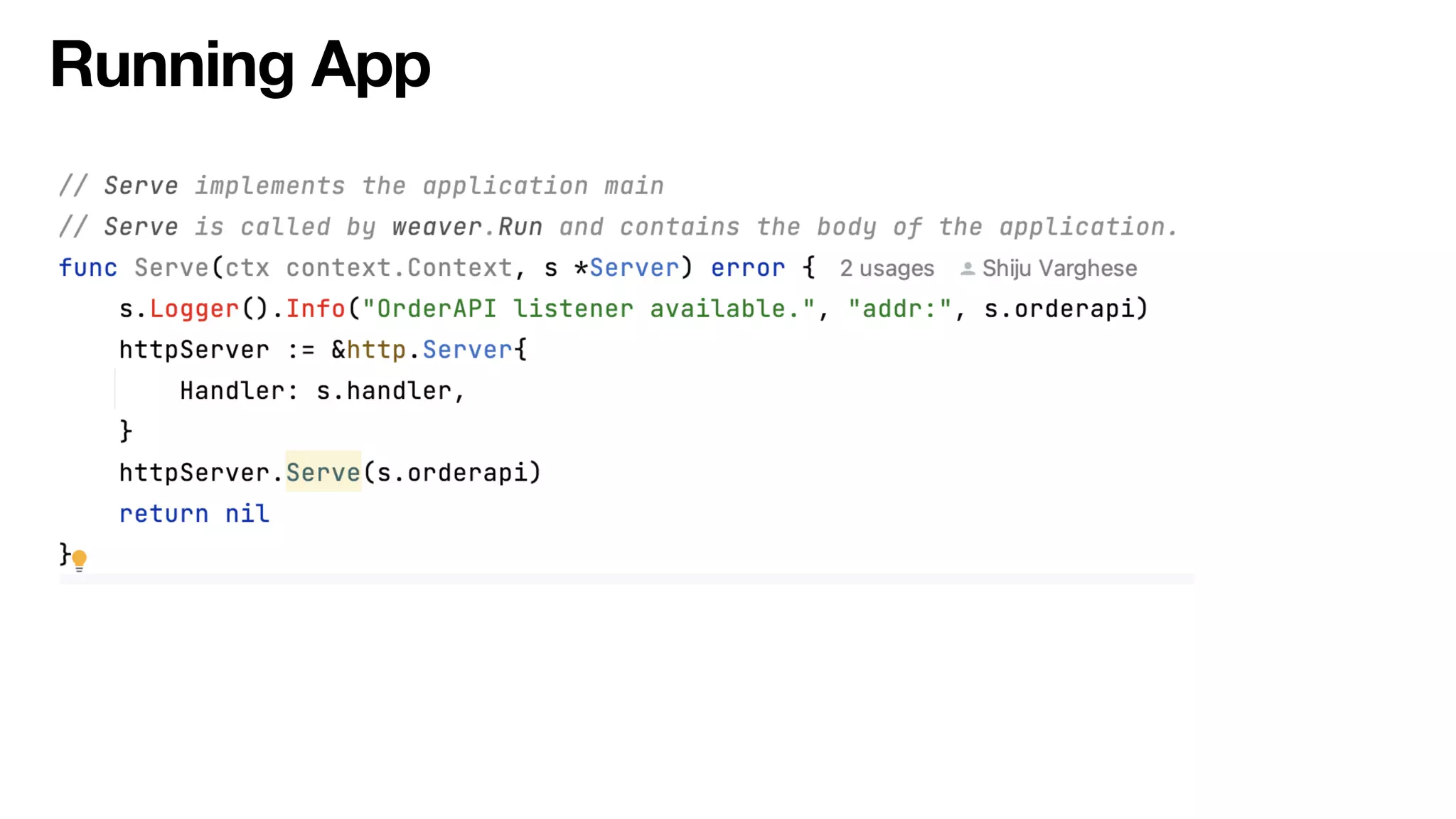
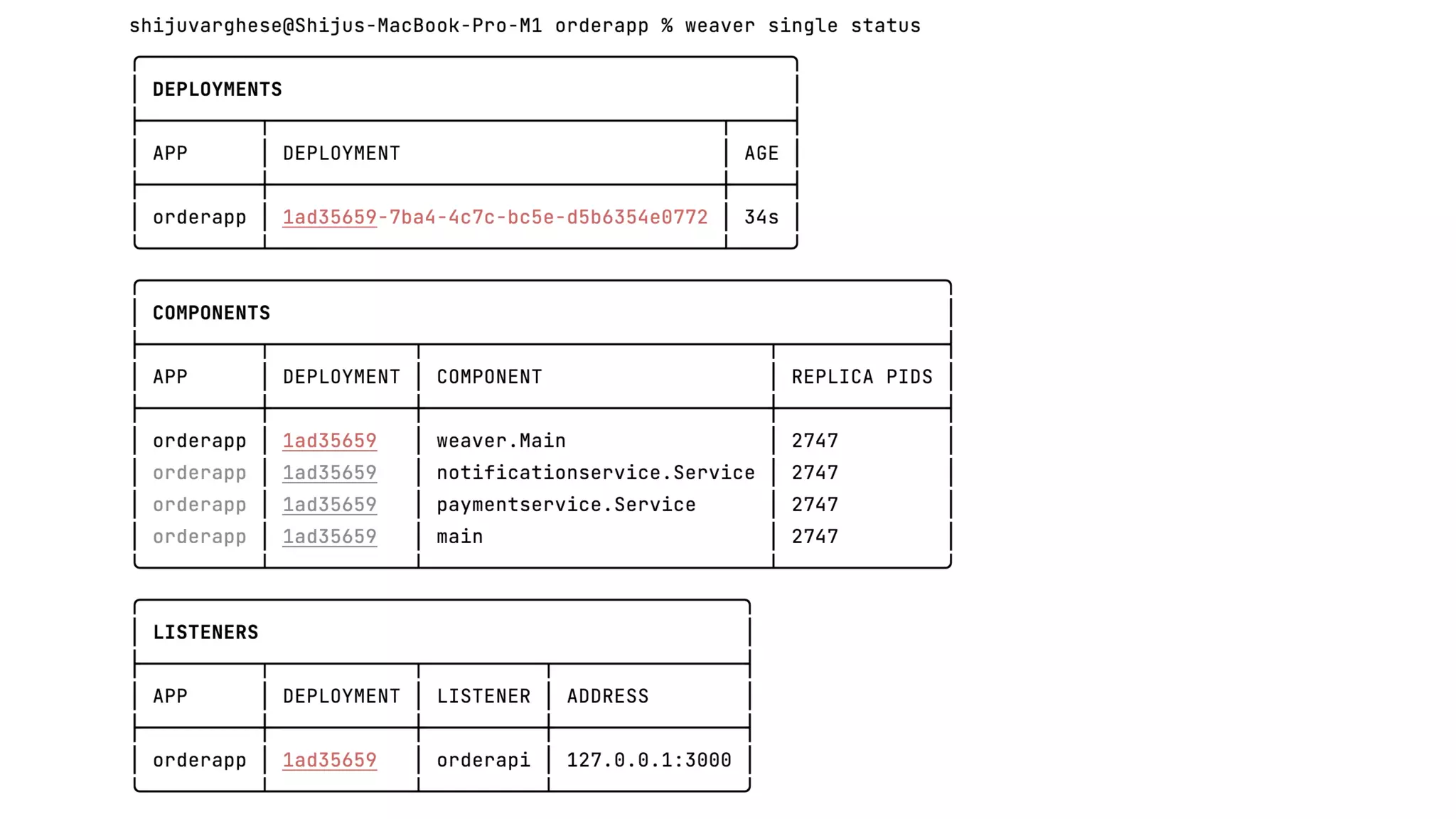
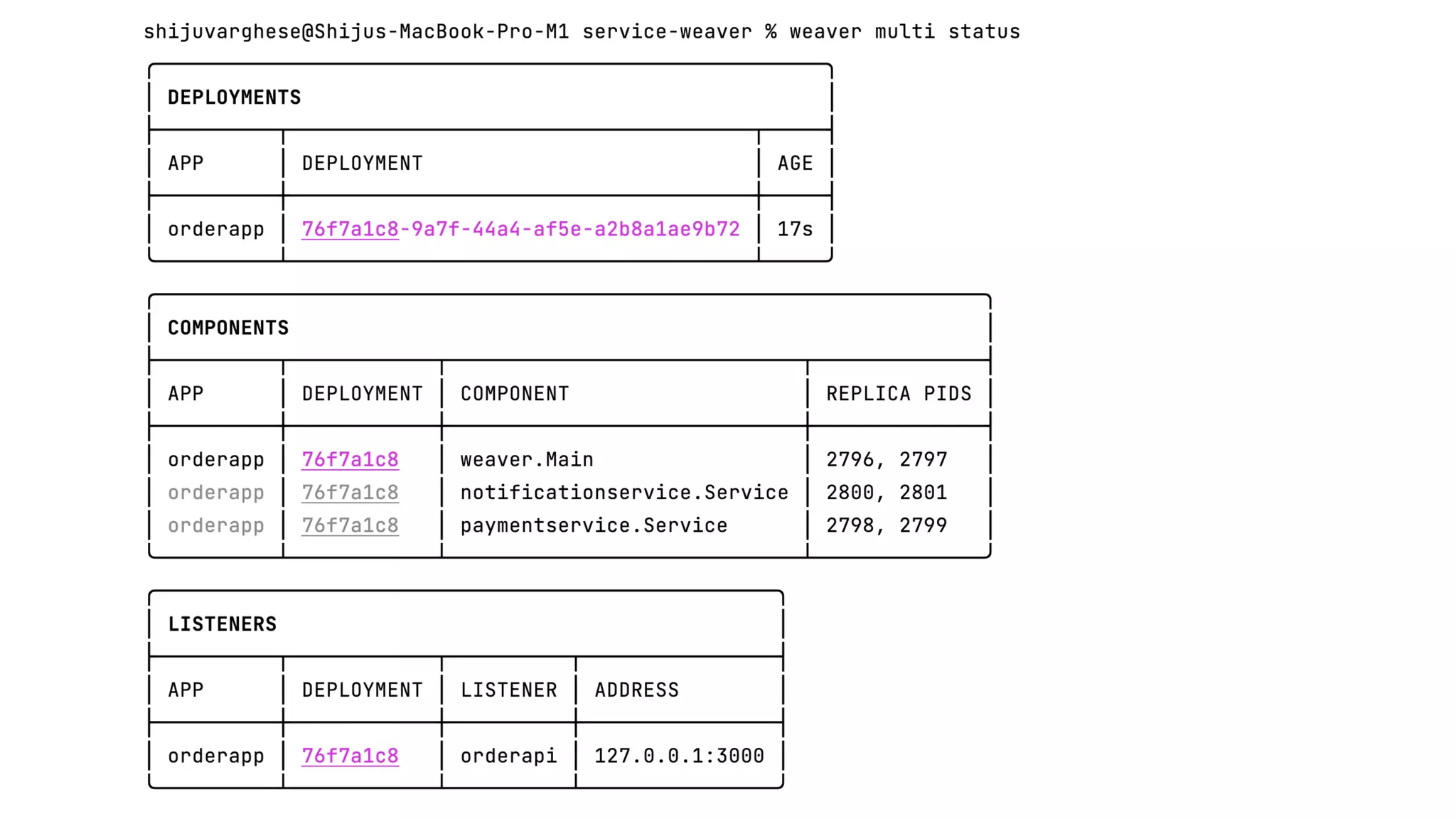
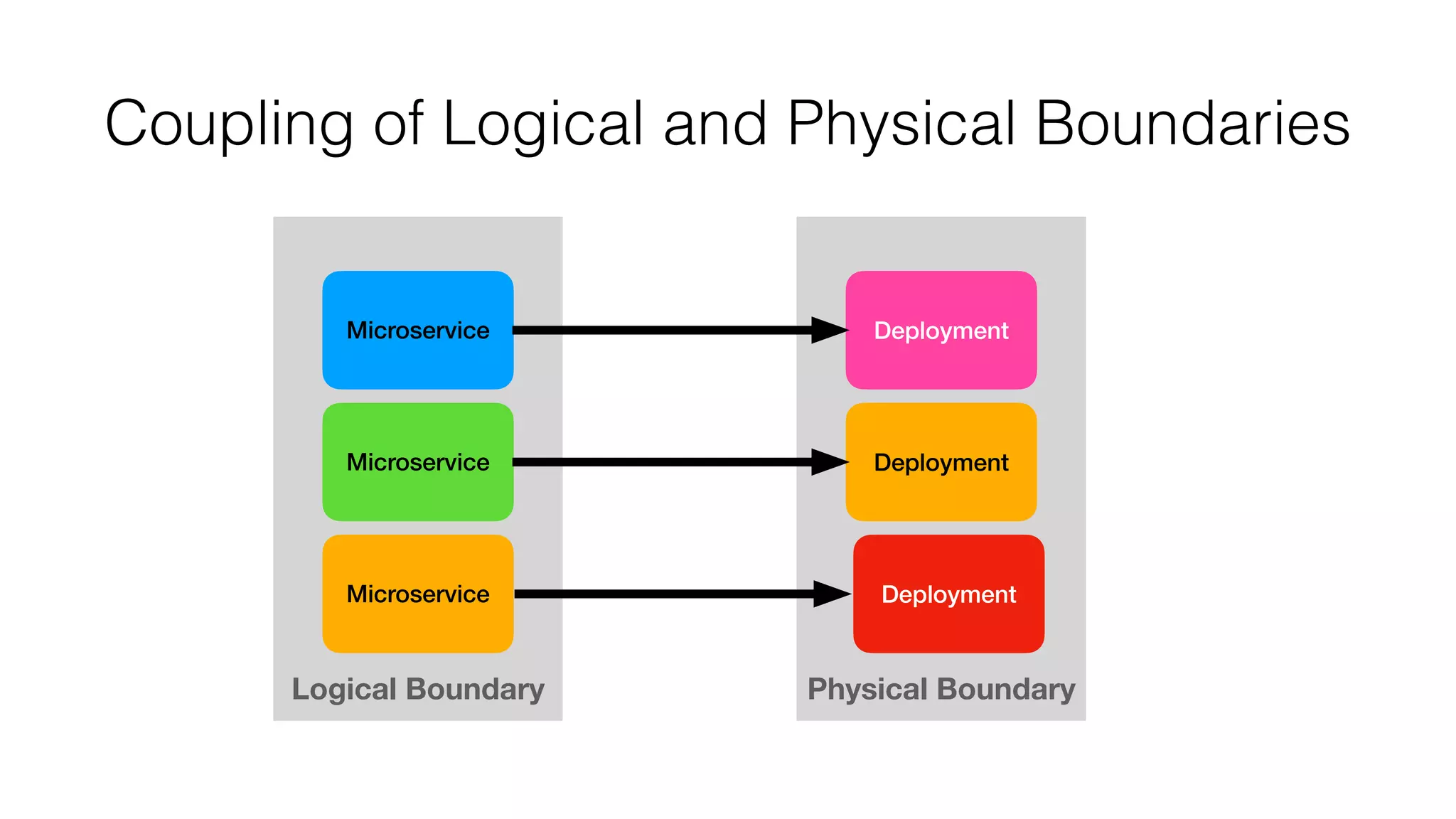
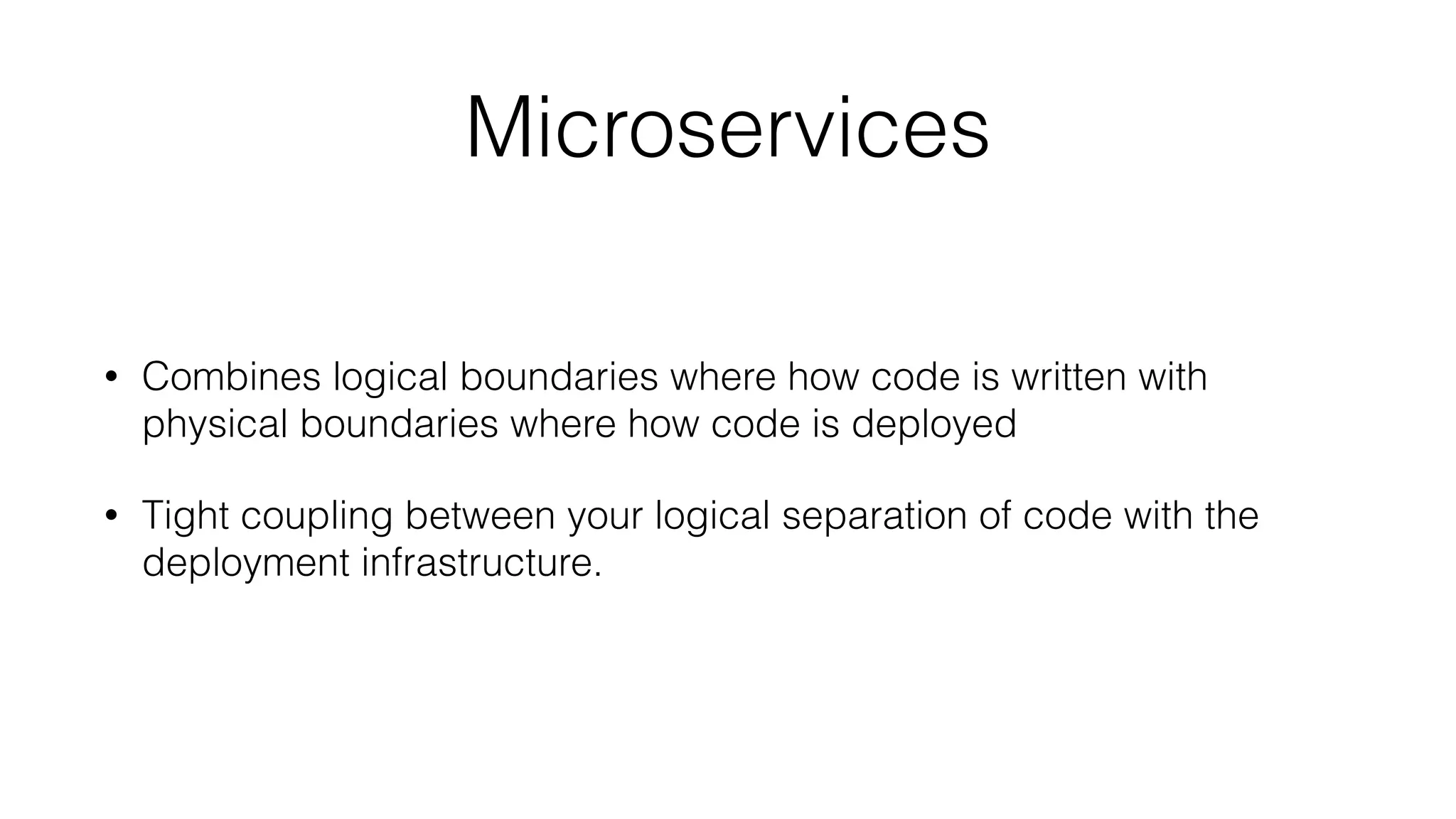
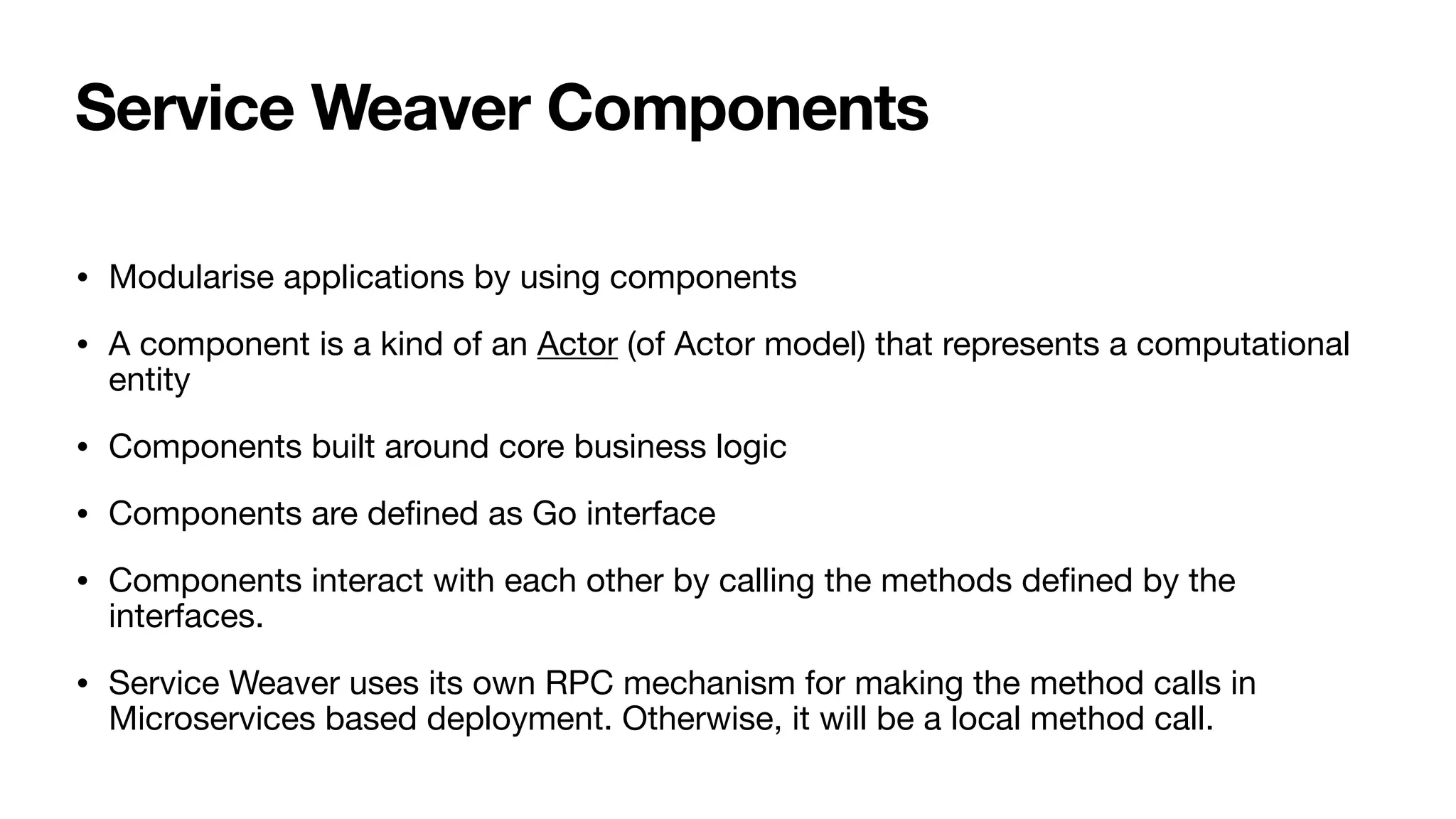
Service Weaver is a framework that allows building distributed applications in Go by decoupling logical and physical boundaries. It allows writing code as a modular monolith but deploying it as microservices. Components define interfaces and reference each other. The framework handles communication between components when deployed as microservices. It provides tools for running locally as a monolith or distributed, and deploying to Kubernetes. The presentation demonstrated its use through an example application.








![type OrderPayment struct { weaver.AutoMarshal OrderID string CustomerID string Amount float64 } type Notification struct { weaver.AutoMarshal OrderID string CustomerID string Event string Modes []string } Serializable Types Embedding weaver.AutoMarshal to make types as serialisable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-weaver-shijuvar-230806030057-04da580a/75/Building-Modern-Distributed-Applications-in-Go-with-Service-Weaver-15-2048.jpg)
![type Service interface { MakePayment(ctx context.Context, orderPayment model.OrderPayment) error } type implementation struct { weaver.Implements[Service] } func (s *implementation) MakePayment(ctx context.Context, orderPayment model.OrderPayment) error { } Component de fi ned as an interface Provides an implementation by embedding the generic type weaver.Implements[T]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-weaver-shijuvar-230806030057-04da580a/75/Building-Modern-Distributed-Applications-in-Go-with-Service-Weaver-16-2048.jpg)
![type Server struct { weaver.Implements[weaver.Main] handler http.Handler // http handler instance paymentService weaver.Ref[paymentservice.Service] notificationService weaver.Ref[notificationservice.Service] orderRepository weaver.Ref[cockroachdb.Repository] orderapi weaver.Listener //`weaver:"orderapi"` } Component references other components using weaver.Ref[T] • Embedded weaver.Implements[weaver.Main] into main component • A component implementation may use network listeners using weaver.Listener](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-weaver-shijuvar-230806030057-04da580a/75/Building-Modern-Distributed-Applications-in-Go-with-Service-Weaver-17-2048.jpg)