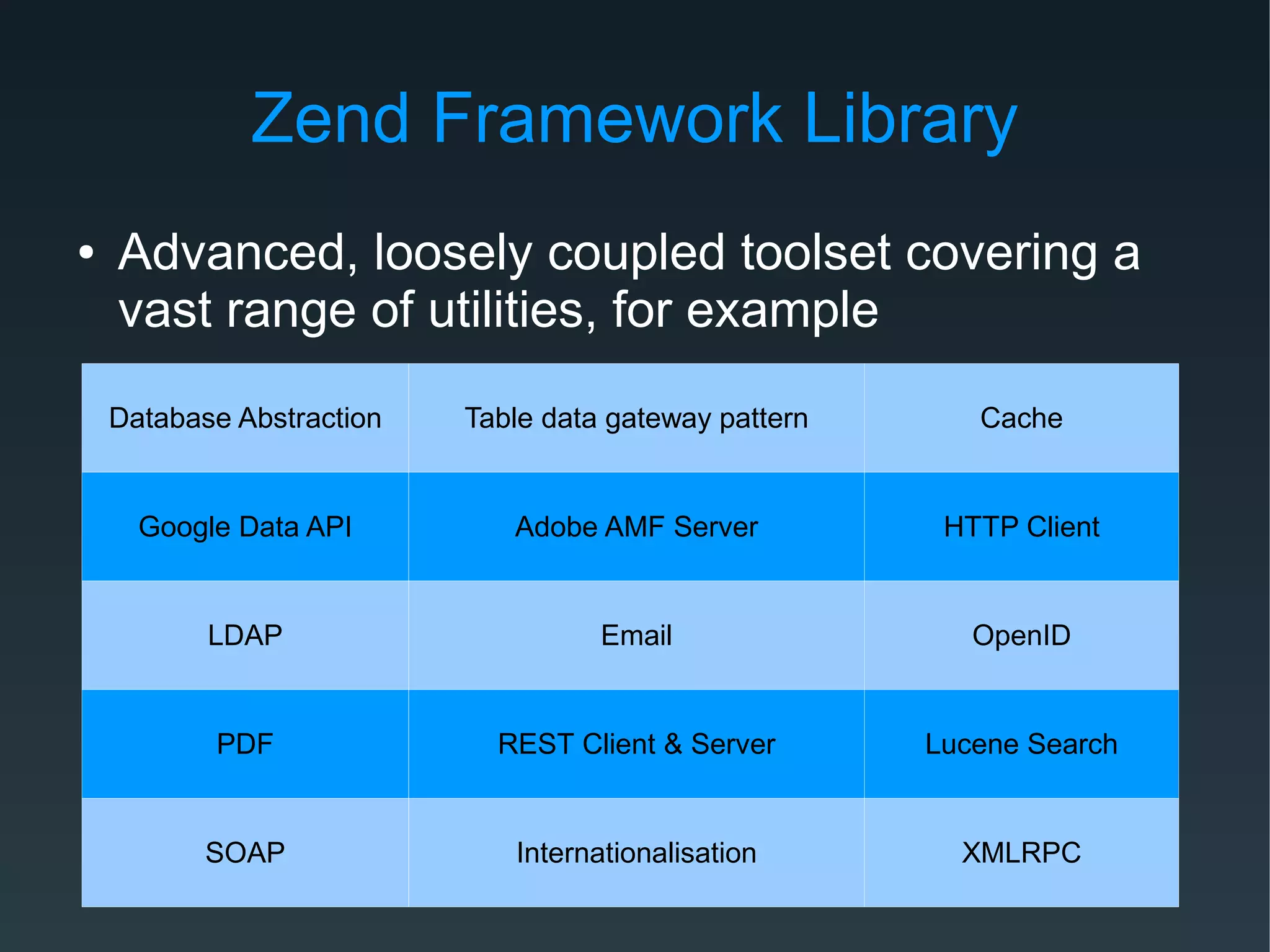
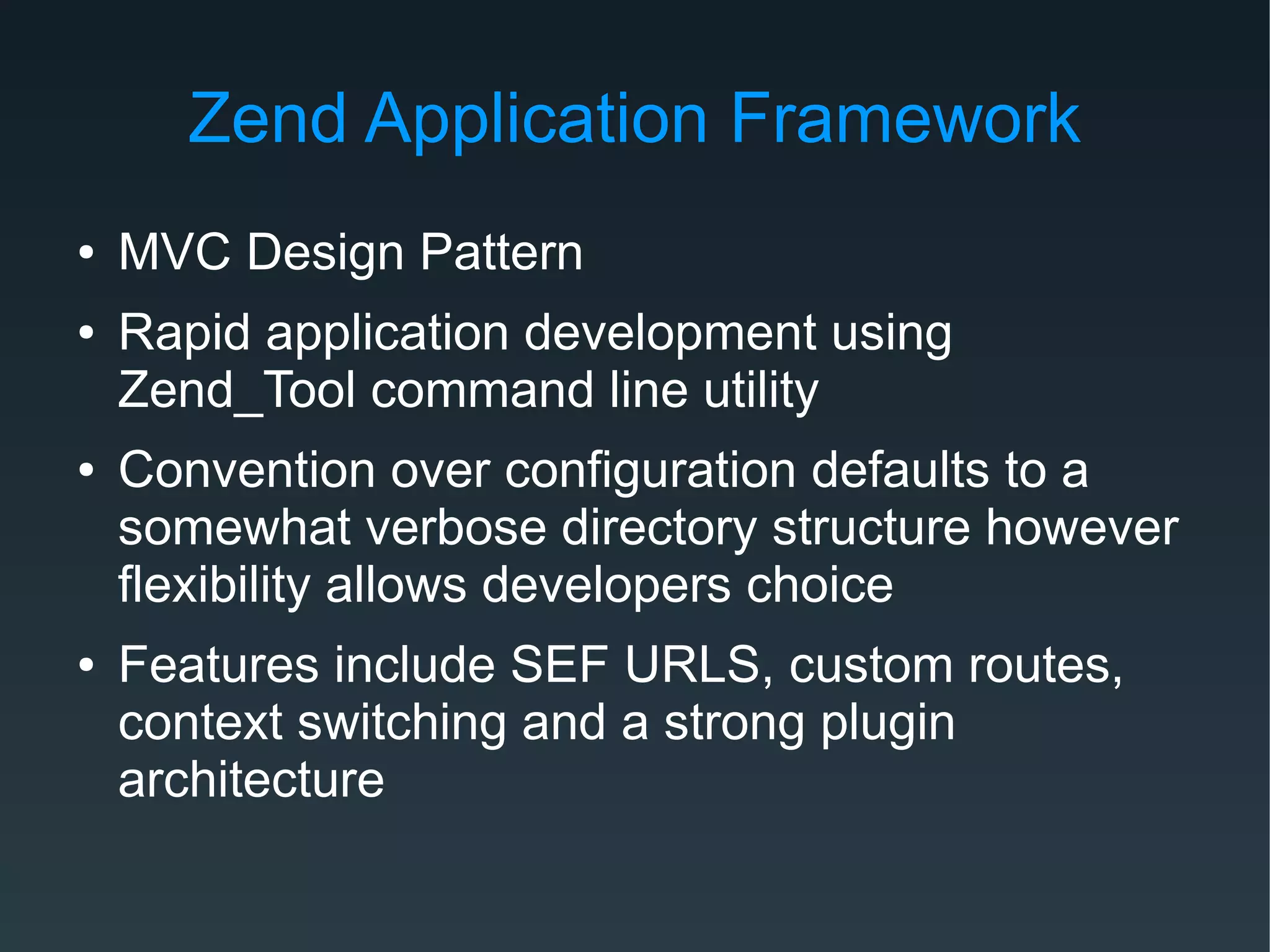
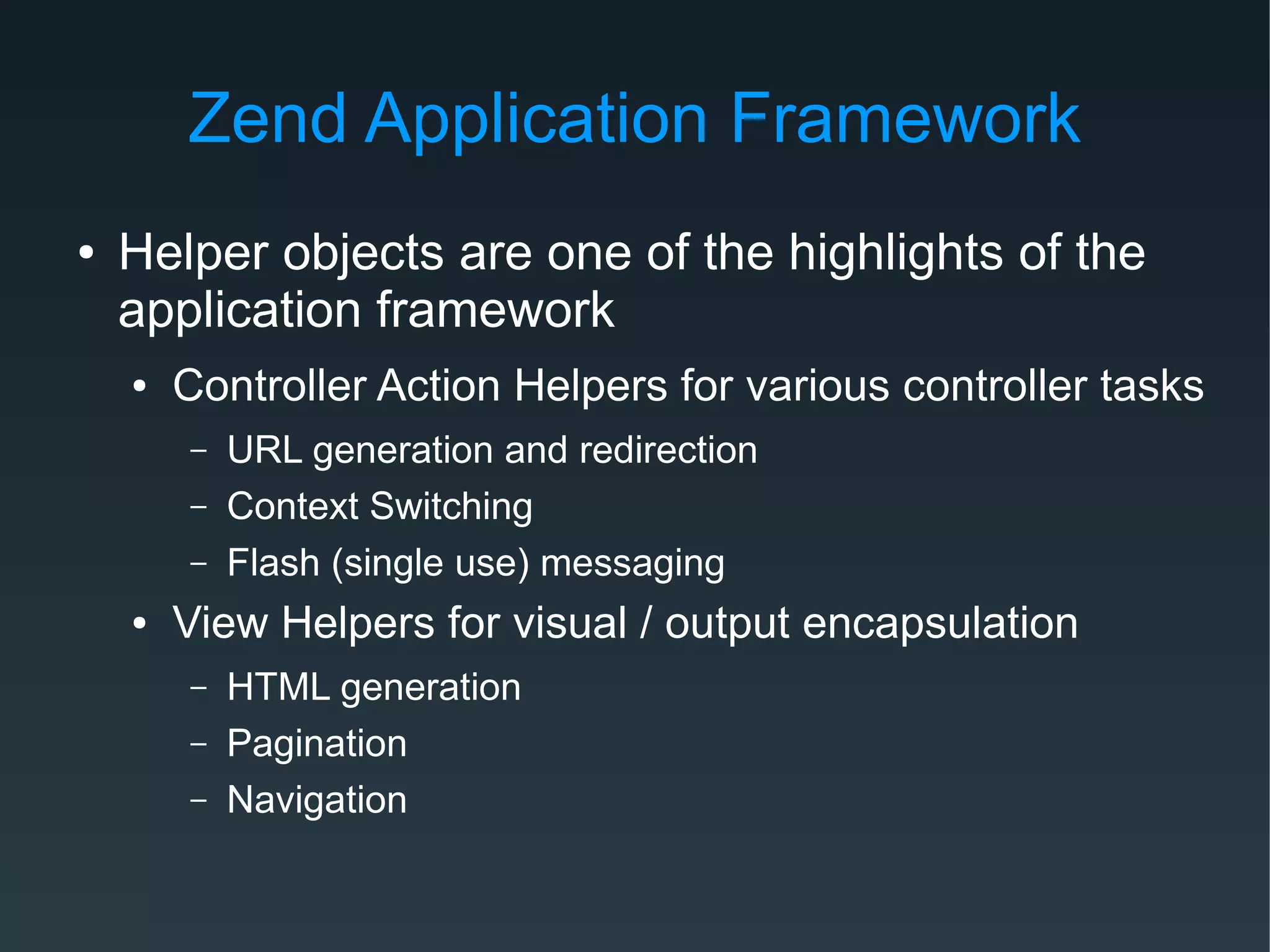
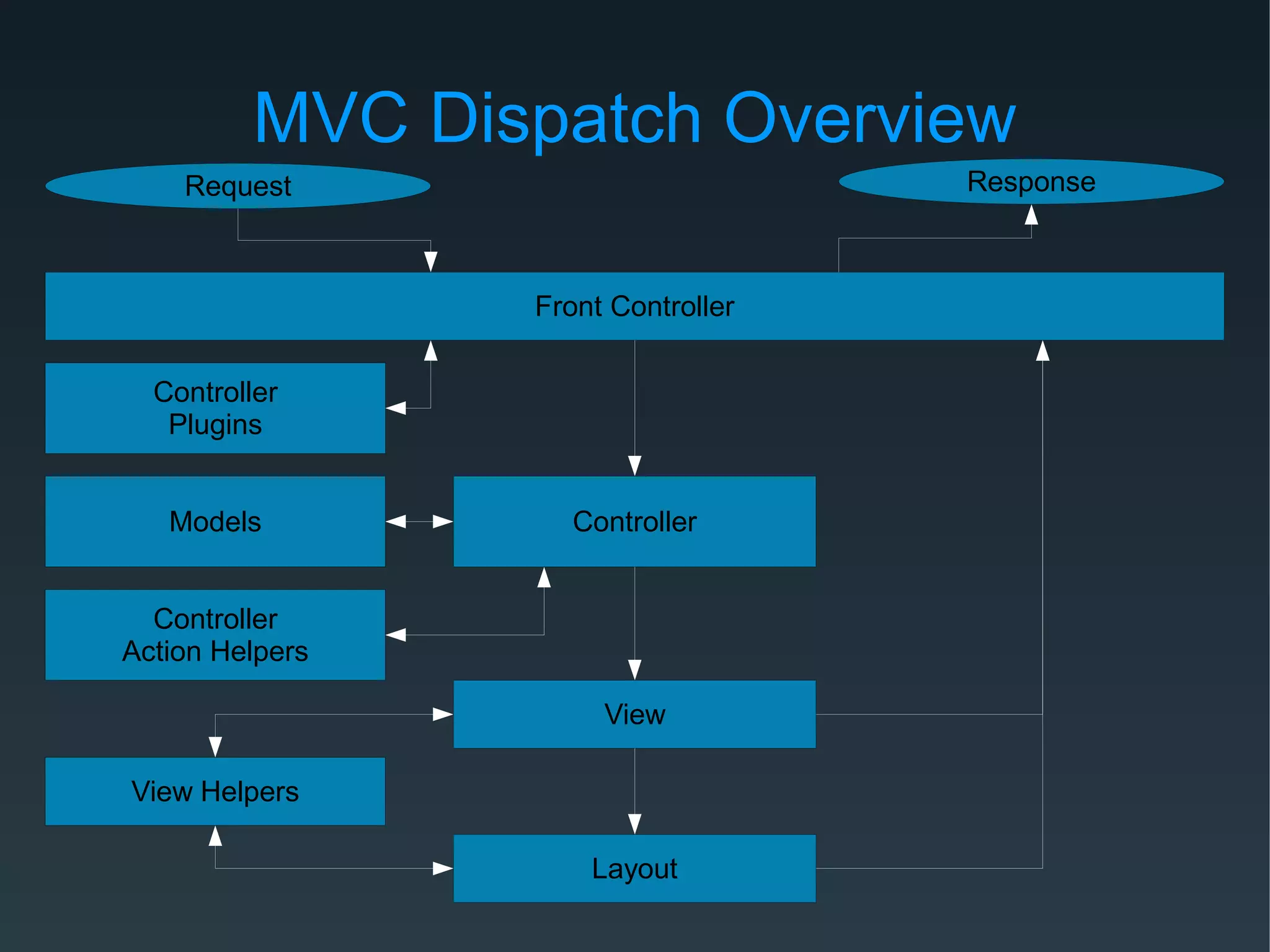
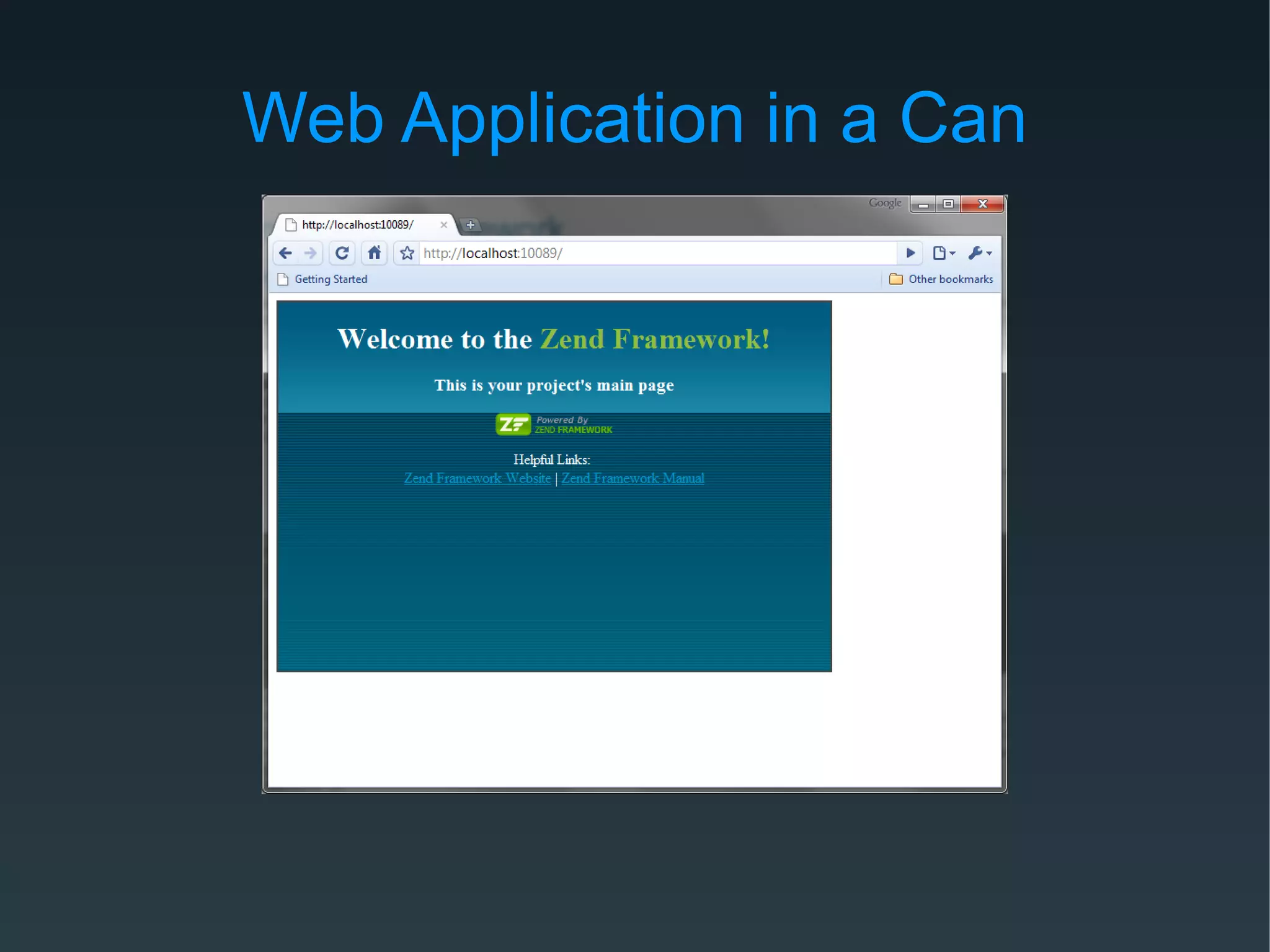
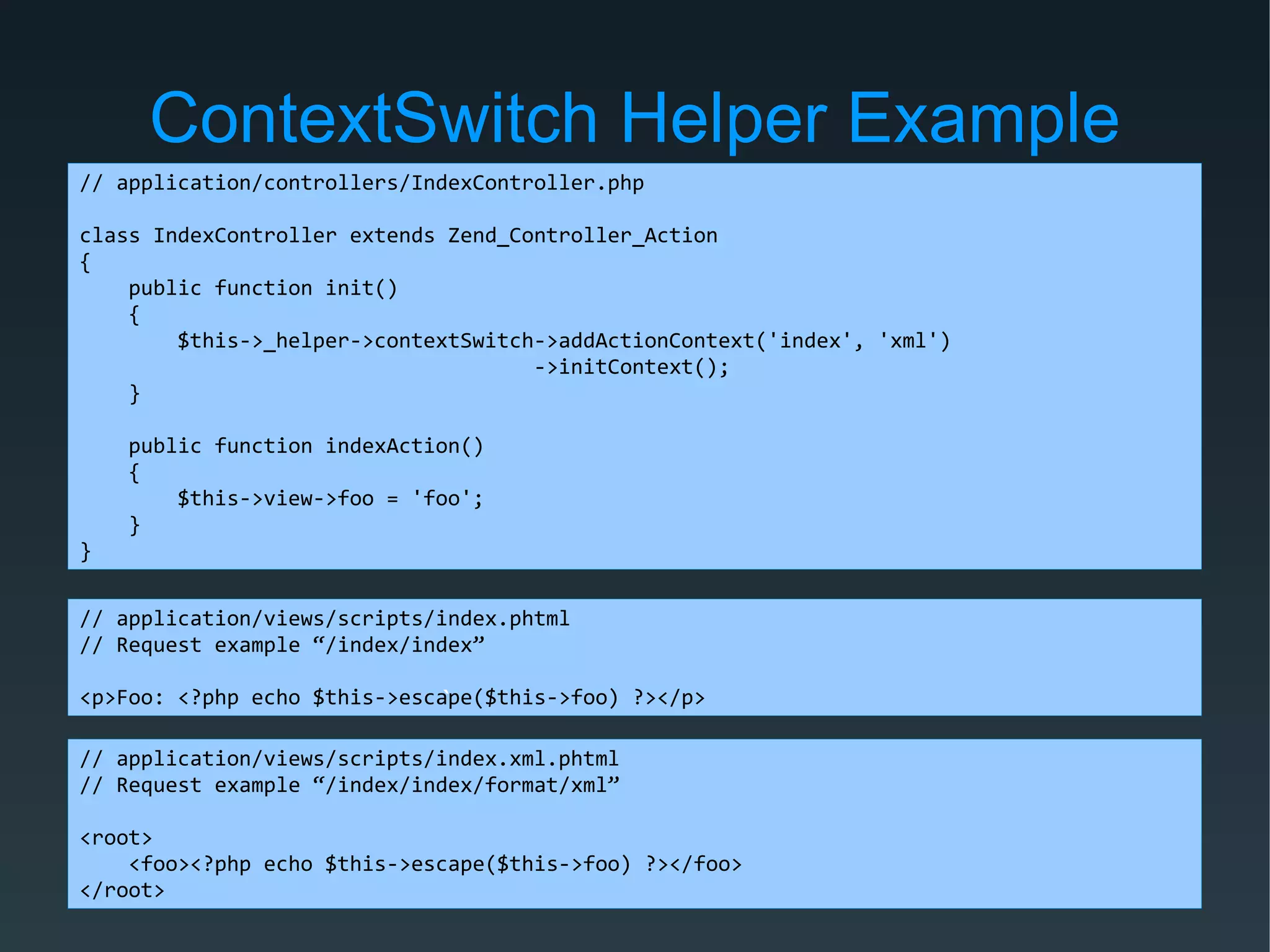
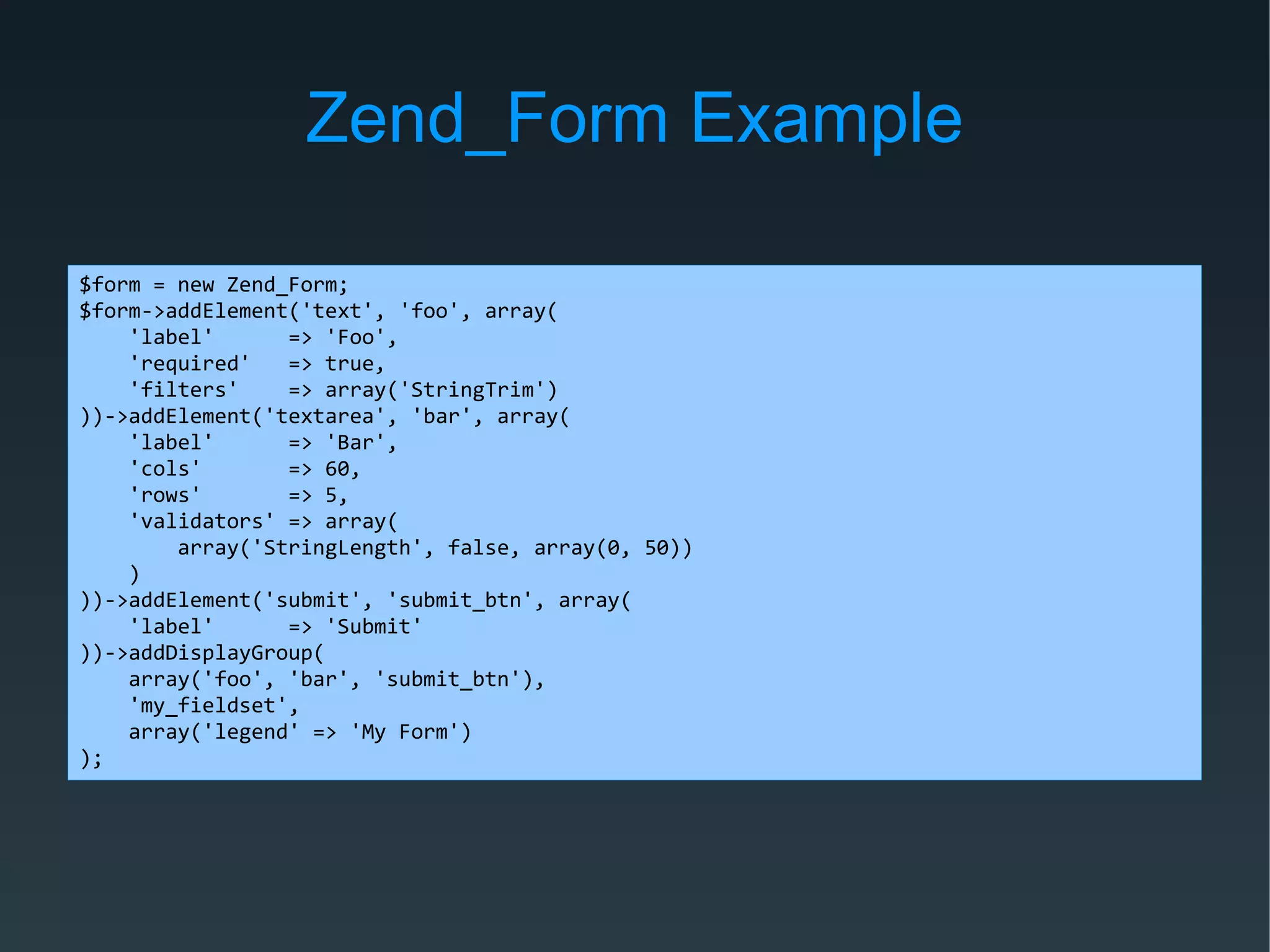
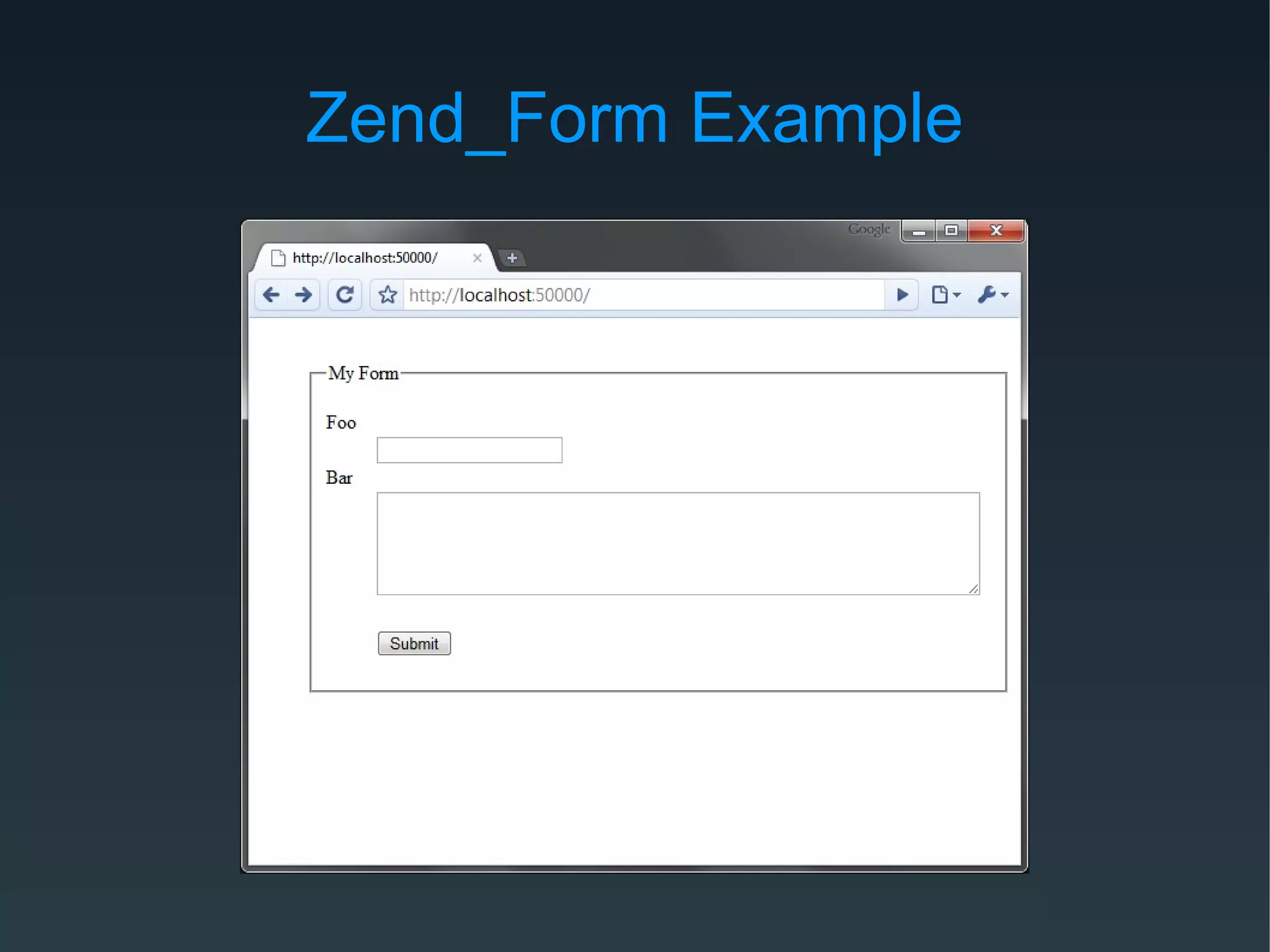
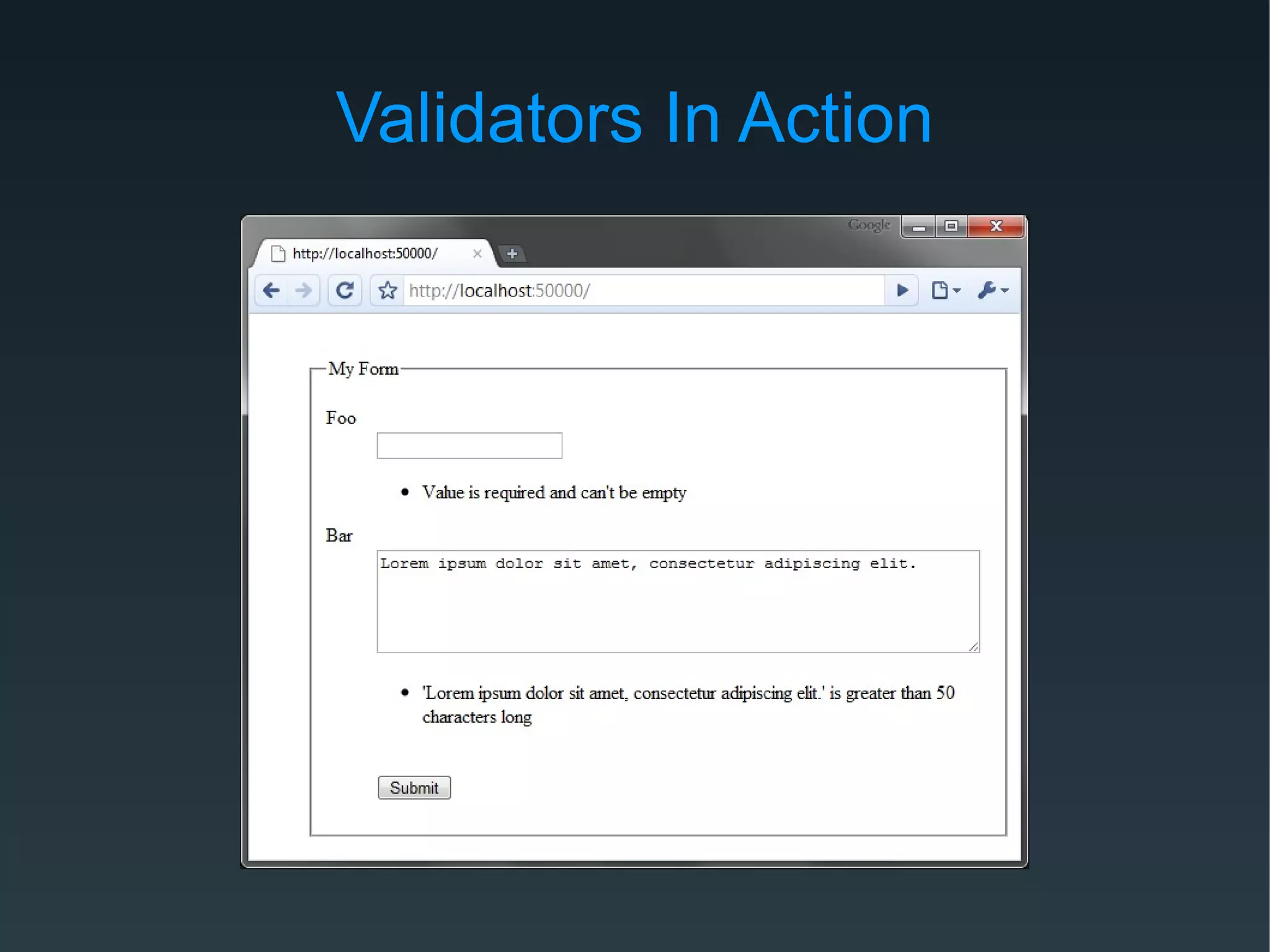
Zend Framework is both a library of PHP classes and an MVC application framework. It includes tools for database access, caching, internationalization, and more. As an MVC framework, it uses conventions like controllers and views. Controller action helpers and view helpers provide reusable functionality. The framework supports plugins, custom routing, and context switching to determine the response format. Forms can be built from code or configuration and include validation, filtering, and internationalization.