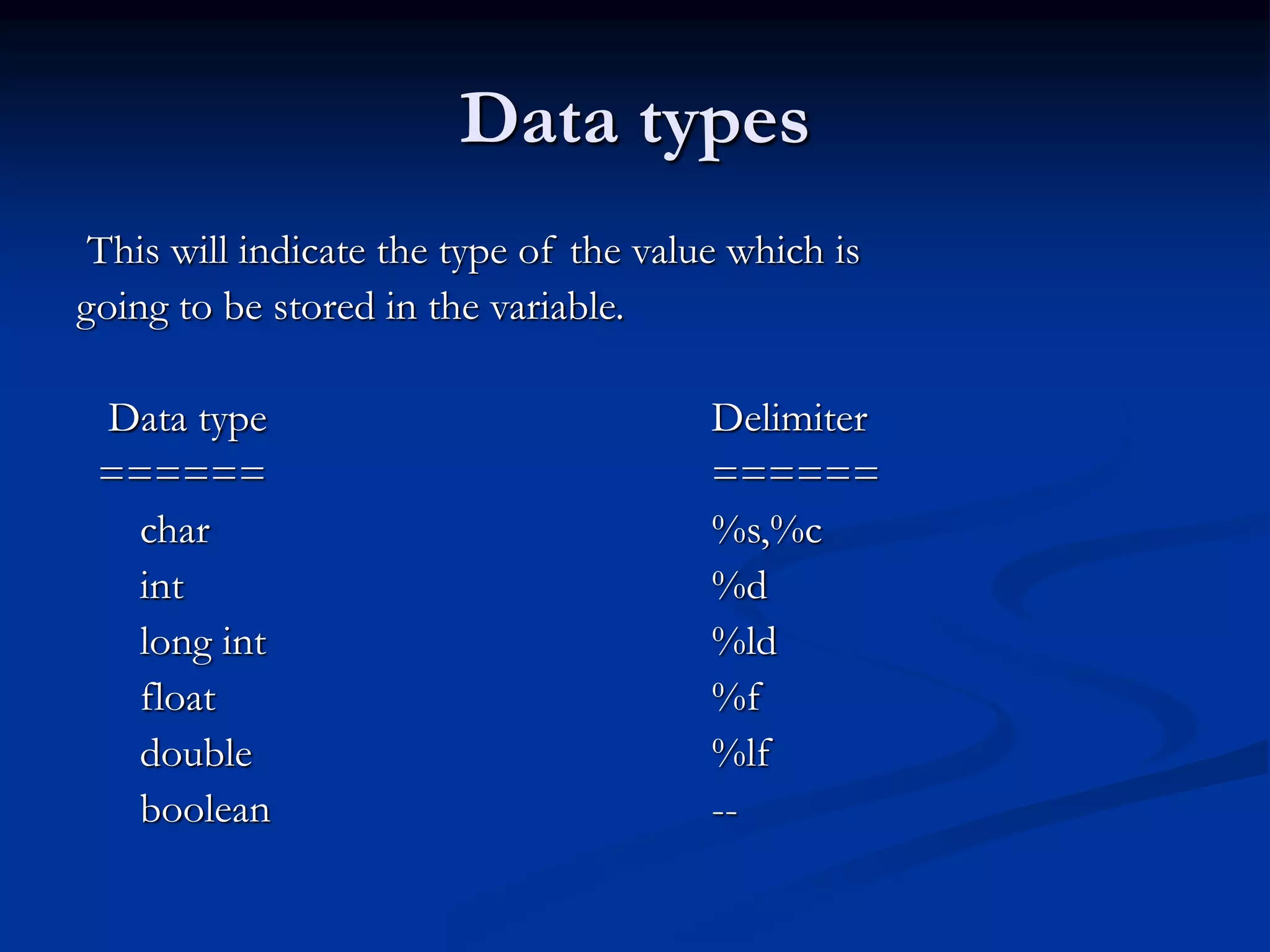
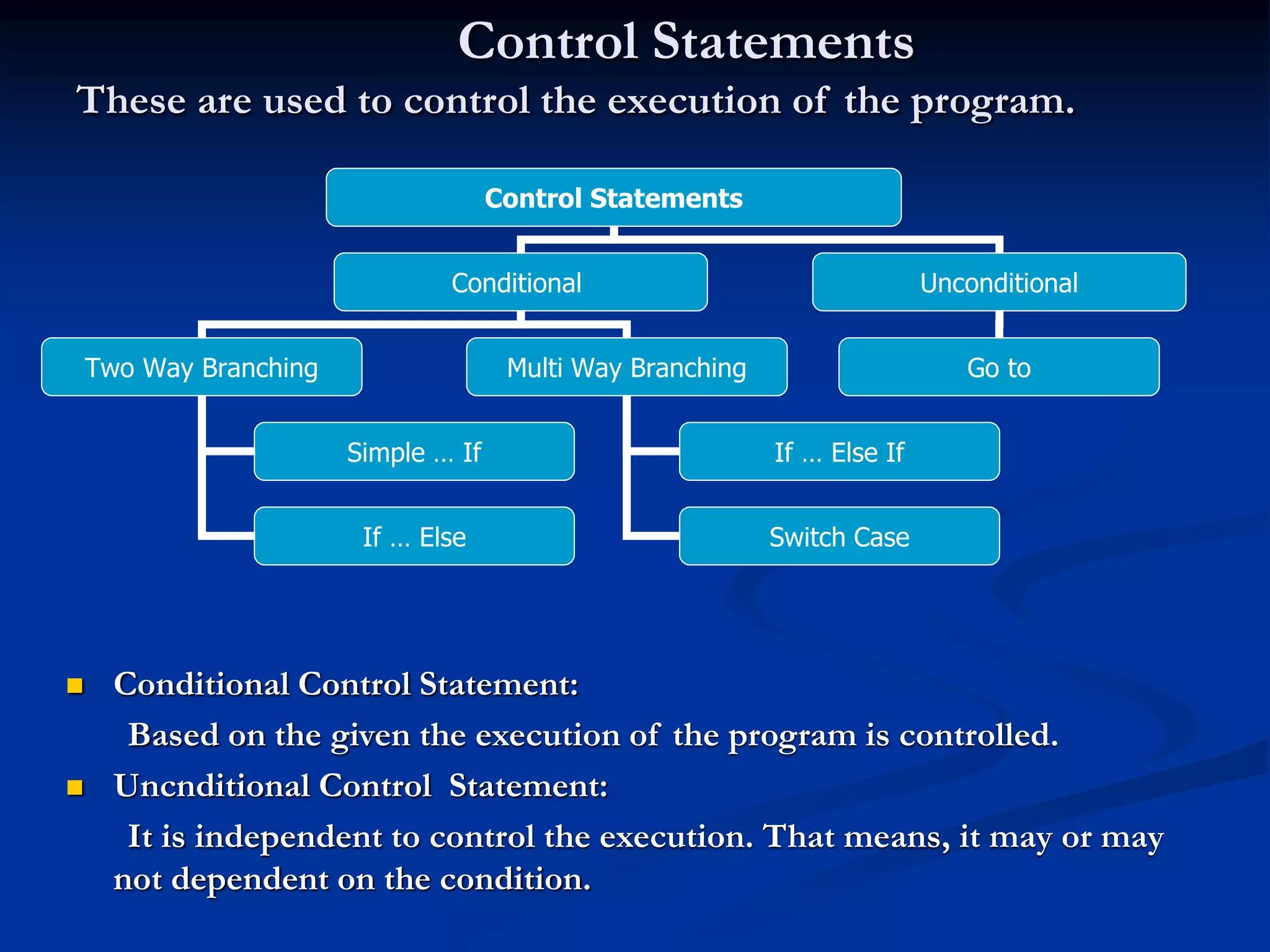
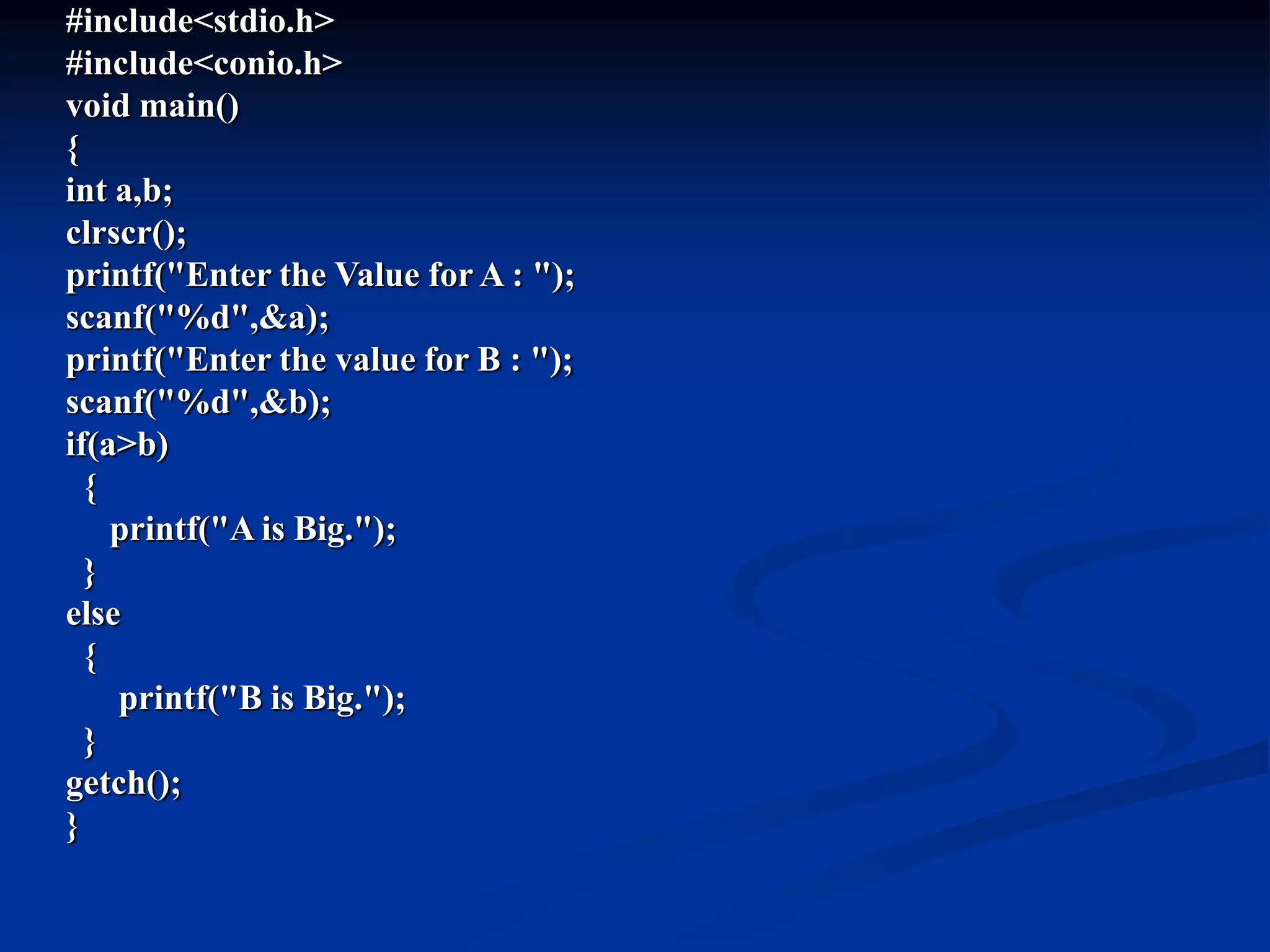
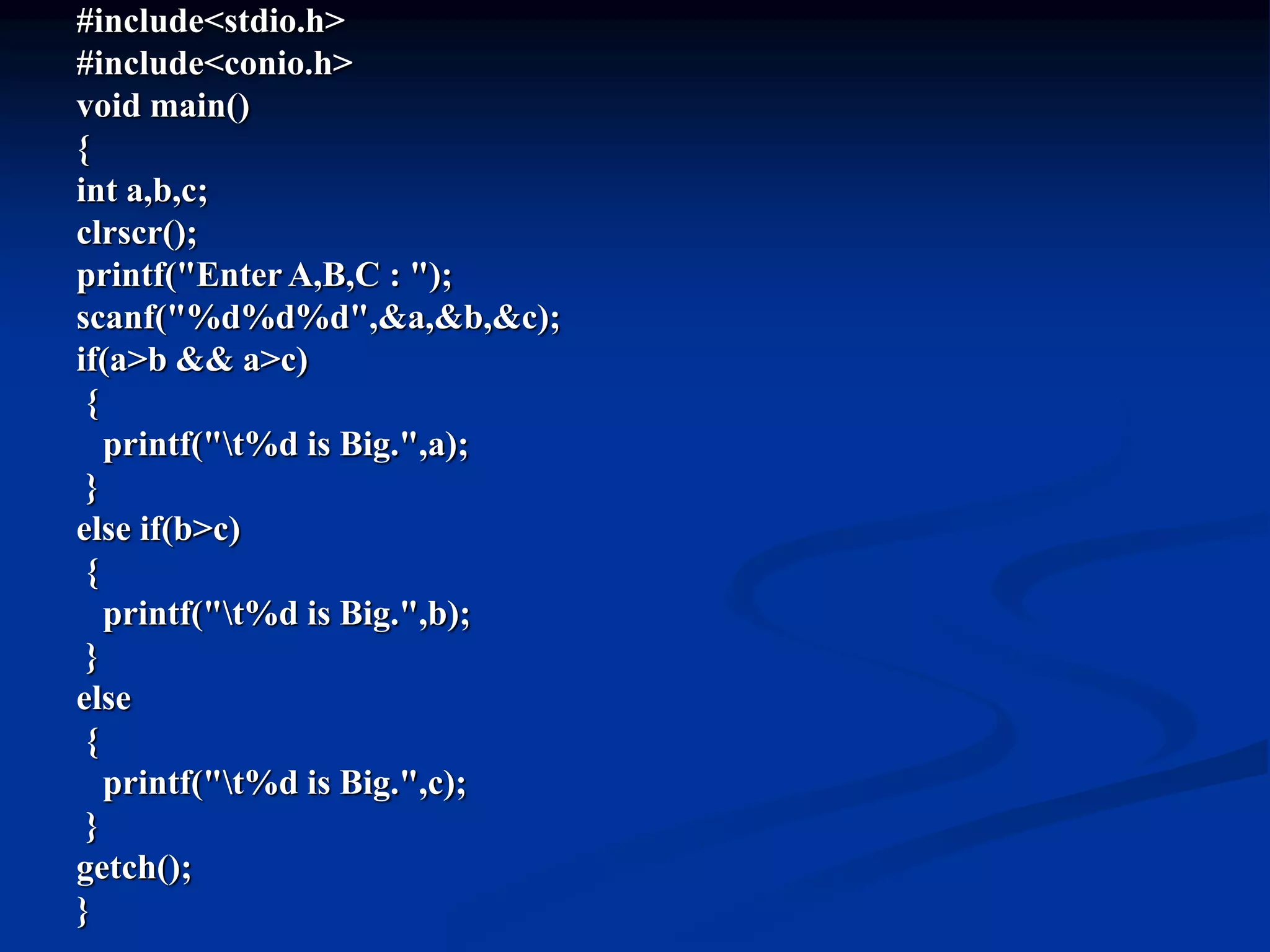
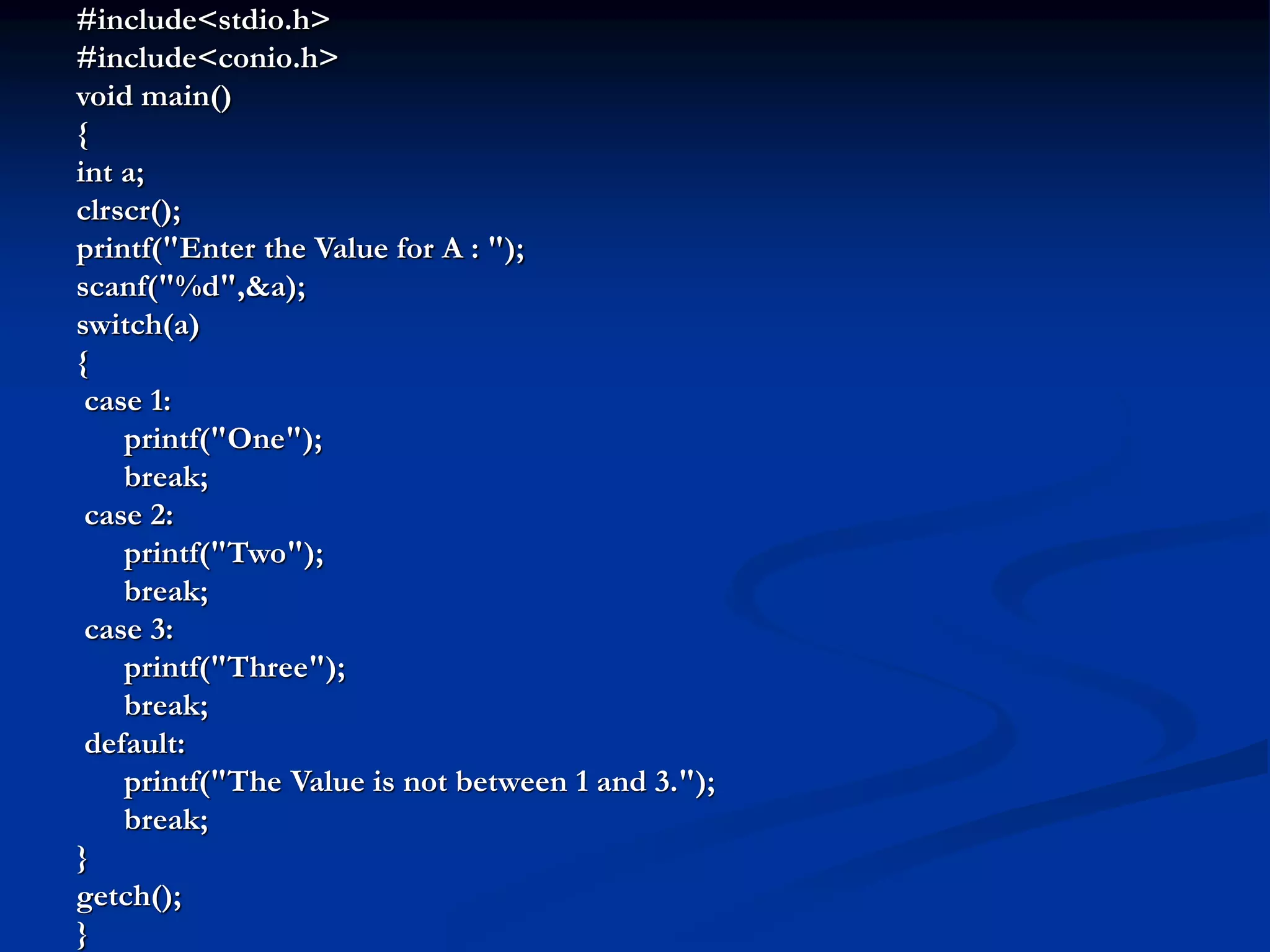
C programming language was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs. It is a middle-level language that combines elements of both high-level and low-level (assembly) languages. The key elements of a C program include documentation, header files, global declarations, main function, and other sub-functions. C programs use variables, constants, data types, operators, and control statements like if-else, switch-case, loops to perform tasks. Common data structures in C include arrays, which are used to store multiple elements of the same type under a single name.
































![Single Dimensional Array: Syntax: ====== datatype variable_Name[Size]; initialization: =============== 1) During Declaration 2)Using Assignment Operator 2) In Runtime Through Scanf using loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-38-2048.jpg)
![During Declaration datatype variable_name[size]={value}; #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> main() { int a[5]={23,43,45,34,23}; char c[5]={‘a’,’e’,’i’,’o’,’u’}; clrscr(); printf(“The value in the cell a[2]=%d",a[2]); Printf(“nThe Character in the cell c[2]=%c”,c[2]); getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-39-2048.jpg)
![Using Assignment(=) Operator variable_name[cell]=value; #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a[3]; char c[3]; a[0]=1; a[1]=2; a[2]=3; c[0]='a'; c[1]='b'; c[2]='c'; clrscr(); printf("The Value in the Cell a[2]=%d",a[2]); printf("The Character in the cell a[2]=%c",a[2]); getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-40-2048.jpg)
![In Runtime Through Scanf using loop #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> main() { int a[5],i; clrscr(); for(i=0;i<5;i++) { printf("nEnter the Value for Cell - %d :",i); scanf("%d",&a[i]); } printf("nOutputn======"); for(i=0;i<5;i++) { printf("na[%d]=%d",i,a[i]); } printf("na[2]=%d",a[2]); getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-41-2048.jpg)
![Practical Example #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> main() { int reg[10],m1[10],m2[10],n; int tot[10],i; float avg[10]; clrscr(); printf("nEnter the No of Students:"); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("nEnter the Reg.No of Student - %d : ",i+1); scanf("%d",®[i]); printf("Enter the Mark1 of Student - %d : ",i+1); scanf("%d",&m1[i]); printf("Enter the Mark2 of Student - %d : ",i+1); scanf("%d",&m2[i]); } printf("nnOutputn======"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("nnReg.No of Student - %d is : %d",i+1,reg[i]); printf("nMark 1 of Student - %d is : %d",i+1,m1[i]); printf("nMark 2 of Student - %d is : %d",i+1,m2[i]); tot[i]=m1[i]+m2[i]; avg[i]=tot[i]/2; printf("nTotal of Student - %d is : %d",i+1,tot[i]); printf("nAvverage of Student - %d is : %f",i+1,avg[i]); } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-42-2048.jpg)
![Two Dimensional Array Syntax: ====== datatype variable_name[size][size]; #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> main() { int a[25][25],b[25][25],c[25][25]; int i,j,row,clm; clrscr(); printf("ntttMatrix Addition"); printf("nttt====== ========"); printf("nEnter the Number of Rows & Columns : "); scanf("%d %d",&row,&clm); printf("nnEnter the Matrix-1 Values.n");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-43-2048.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<row;i++) { for(j=0;j<clm;j++) { printf("Enter the Value for the Cell a[%d][%d] : ",i,j); scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); } } printf("nnEnter the Matrix-2 Values.n"); for(i=0;i<row;i++) { for(j=0;j<clm;j++) { printf("Enter the Value for the Cell b[%d][%d] : ",i,j); scanf("%d",&b[i][j]); } } printf("nOutputn======"); printf("nMatrix-1n"); for(i=0;i<row;i++) { for(j=0;j<clm;j++) { printf("t%dt",a[i][j]); } printf("n"); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-44-2048.jpg)
![printf("nMatrix-2n"); for(i=0;i<row;i++) { for(j=0;j<clm;j++) { printf("t%dt",b[i][j]); } printf("n"); } printf("nMatrix Addition isn"); for(i=0;i<row;i++) { for(j=0;j<clm;j++) { c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j]; printf("t%dt",c[i][j]); } printf("n"); } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-45-2048.jpg)



![Character Pointer #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { char nam[]={"hello"}; char *ptr={"hello"}; clrscr(); printf("nName = %s",nam); printf("n*ptr =%s",*ptr); getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-49-2048.jpg)
![Pointer as Array #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a[5],*ptr[5],i; clrscr(); for(i=0;i<5;i++) { printf("nEnter the Value for the cell a[%d] : ",i); scanf("%d",&a[i]); ptr[i]=&a[i]; } printf("nOutputn======nn"); for(i=0;i<5;i++) { printf("nThe value of ptr : %u the value of *ptr : %d",ptr[i],*ptr[i]); } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-50-2048.jpg)









![String Functions #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { char s1[20],s2[20]; clrscr(); printf("Enter S1 : "); scanf("%s",&s1); printf("Enter S2 : "); scanf("%s",&s2); printf("strrev(s1) : %s",strrev(s1)); //To reverse a string printf("nStrlen(s1) : %d",strlen(s1));//to find the length of the string printf("nStrupr(s1) : %s",strupr(s1));//to convert the string to upper case printf("nStrlwr(s1) : %s",strlwr(s1));//to convert the string to lower case printf("nstrcmp(s1,s2) : %d",strcmp(s1,s2));//to compare the string s2 with s1 and retun the result printf("nstrcpmi(s1,s2) : %d",strcmpi(s1,s2));//to compare the string s2 with s1 by not taking the case and retun the result printf("nstrcat(s1,s2) : %s",strcat(s1,s2));//to join the two strings getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-60-2048.jpg)


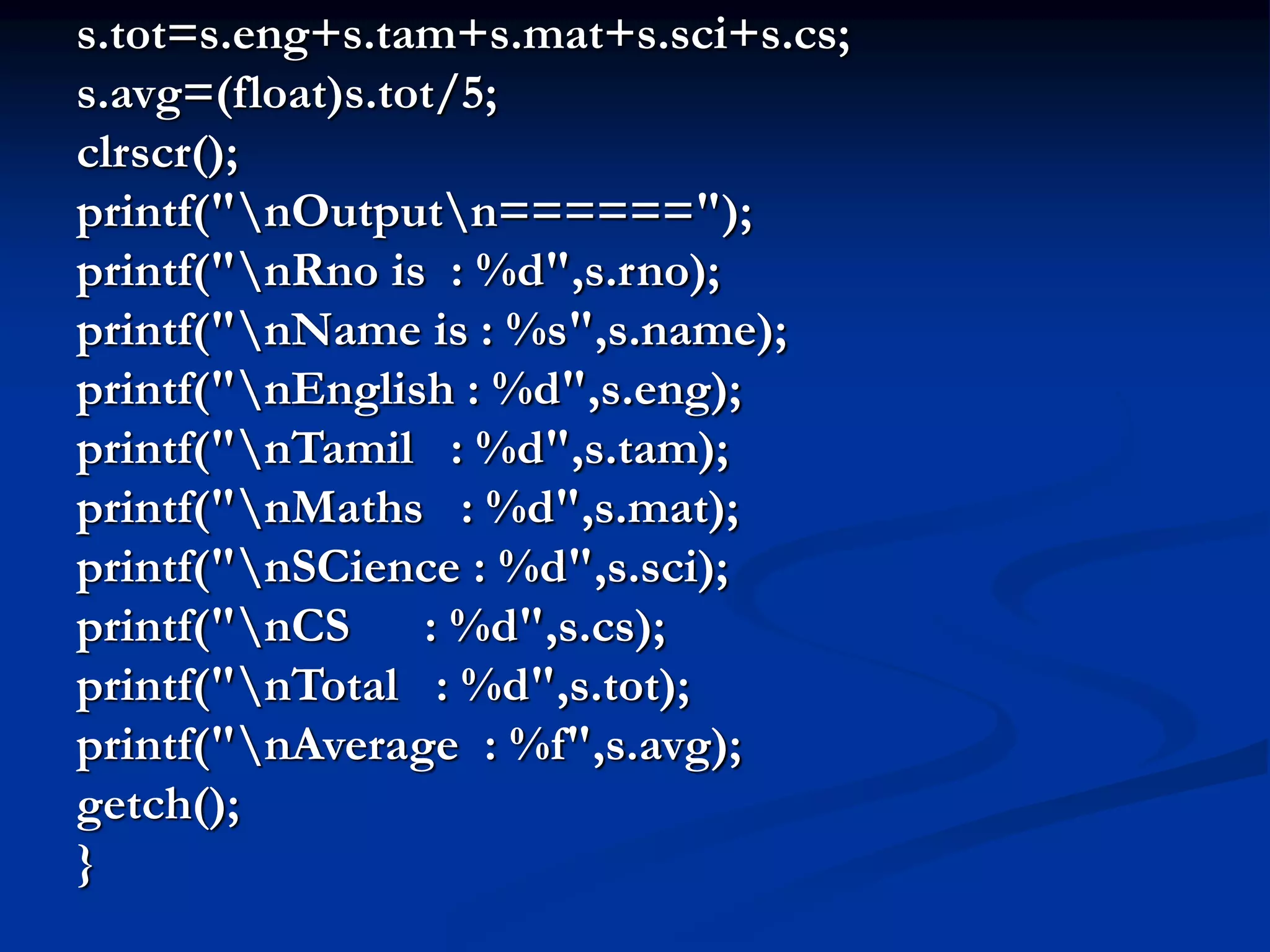
![#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> struct stu { int rno; char name[25]; int eng,tam,mat,sci,cs; int tot; float avg; }; void main() { struct stu s; clrscr(); printf("Enter the Rno :"); scanf("%d",&s.rno); printf("Enter the Name : "); scanf("%s",&s.name); printf("Enter the English Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s.eng); printf("Enter the Tamil Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s.tam); printf("Enter the maths Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s.mat); printf("Enter the Science Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s.sci); printf("Enter the CS Mark :"); scanf("%d",&s.cs);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-63-2048.jpg)
![Structure as array #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> struct stu { int rno; char name[25]; int eng,tam,mat,sci,cs; int tot; float avg; }; void main() { struct stu s[3]; int i; clrscr(); for(i=0;i<2;i++) { printf("nnEnter the Details of Student - %dn",i+1) printf("Enter the Rno :"); scanf("%d",&s[i].rno); printf("Enter the Name : "); scanf("%s",&s[i].name); printf("Enter the English Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s[i].eng); printf("Enter the Tamil Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s[i].tam); printf("Enter the maths Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s[i].mat); printf("Enter the Science Mark : "); scanf("%d",&s[i].sci); printf("Enter the CS Mark :"); scanf("%d",&s[i].cs); s[i].tot=s[i].eng+s[i].tam+s[i].mat+s[i].sci+s[i].cs; s[i].avg=(float)s[i].tot/5; } clrscr();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-65-2048.jpg)
![printf("nOutputn======"); for(i=0;i<3;i++) { printf("nnThe Details of student - %d",i+1) printf("nRno is : %d",s[i].rno); printf("nName is : %s",s[i].name); printf("nEnglish : %d",s[i].eng); printf("nTamil : %d",s[i].tam); printf("nMaths : %d",s[i].mat); printf("nSCience : %d",s[i].sci); printf("nCS : %d",s[i].cs); printf("nTotal : %d",s[i].tot); printf("nAverage : %f",s[i].avg); } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguagepspcnotes-231001044255-6863299a/75/C_Language_PS-PC_Notes-ppt-66-2048.jpg)



