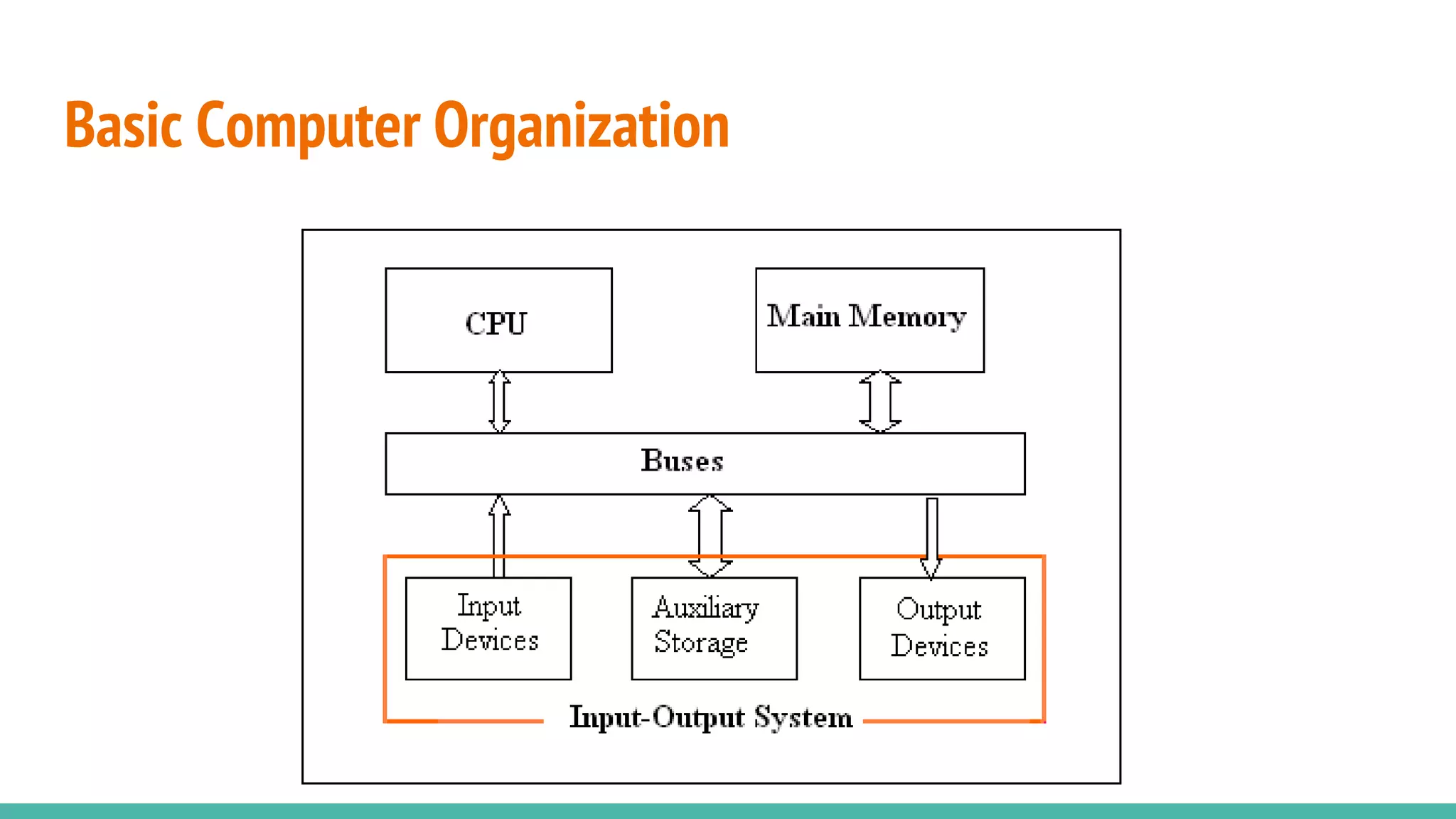
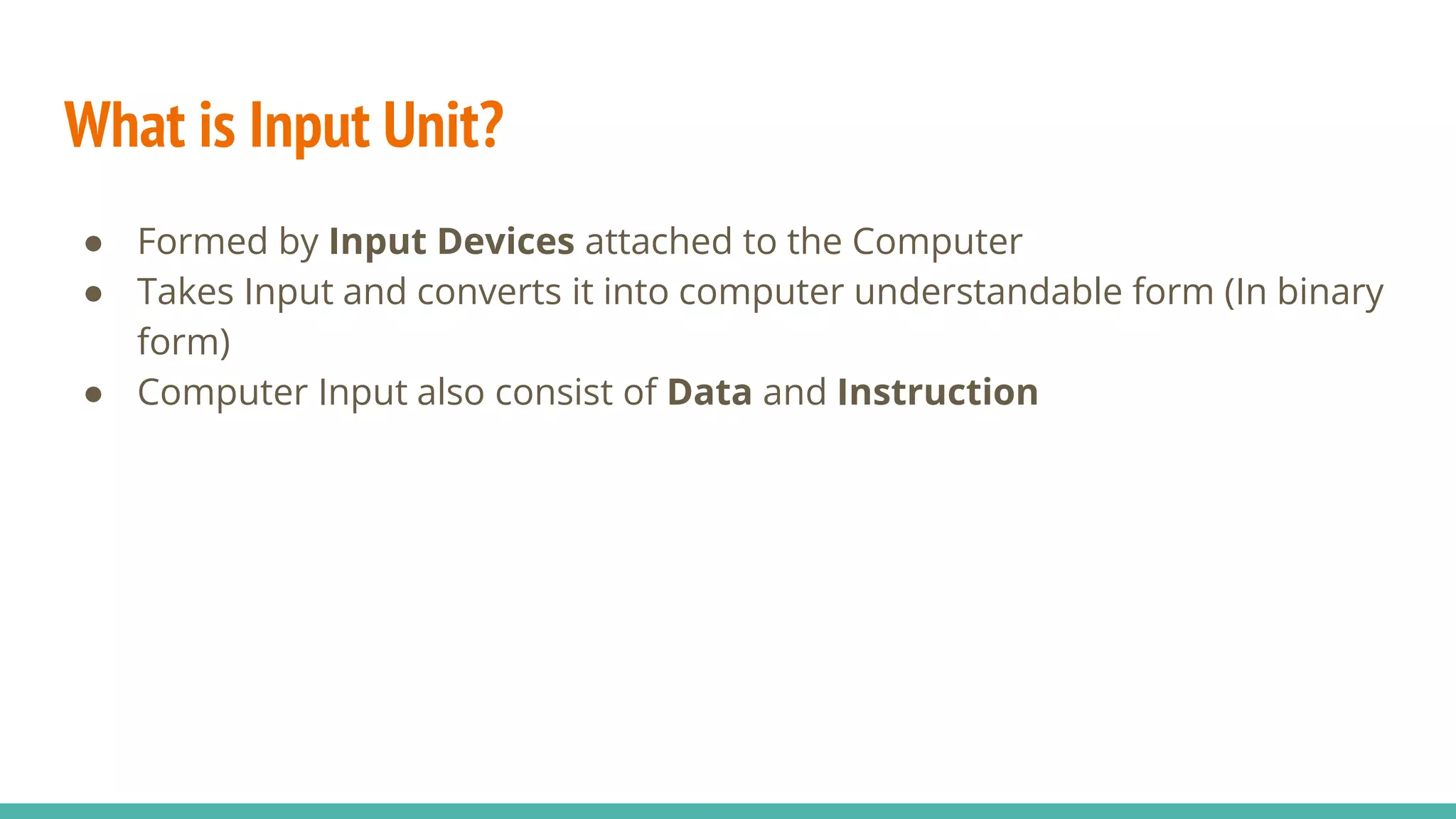
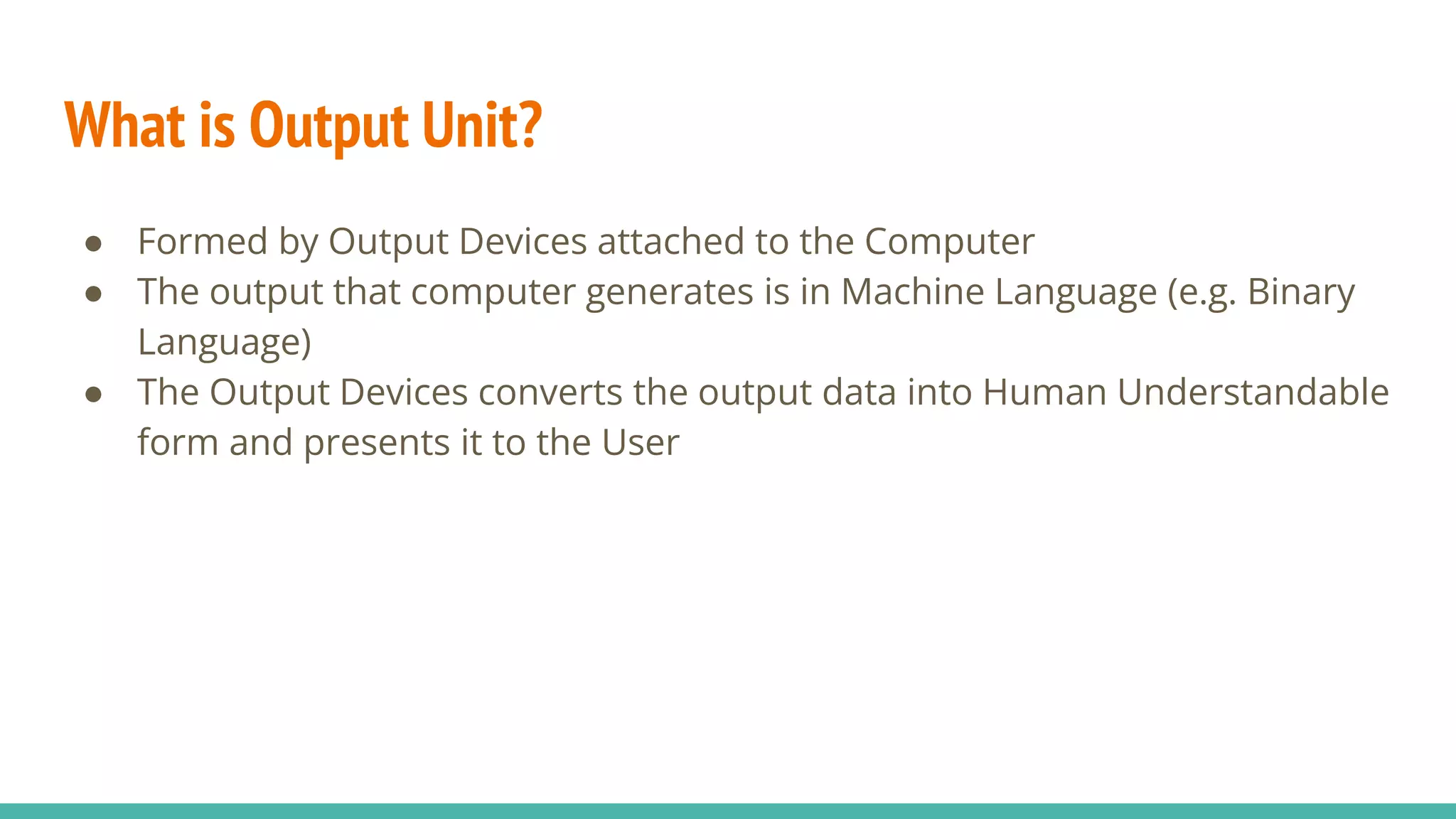
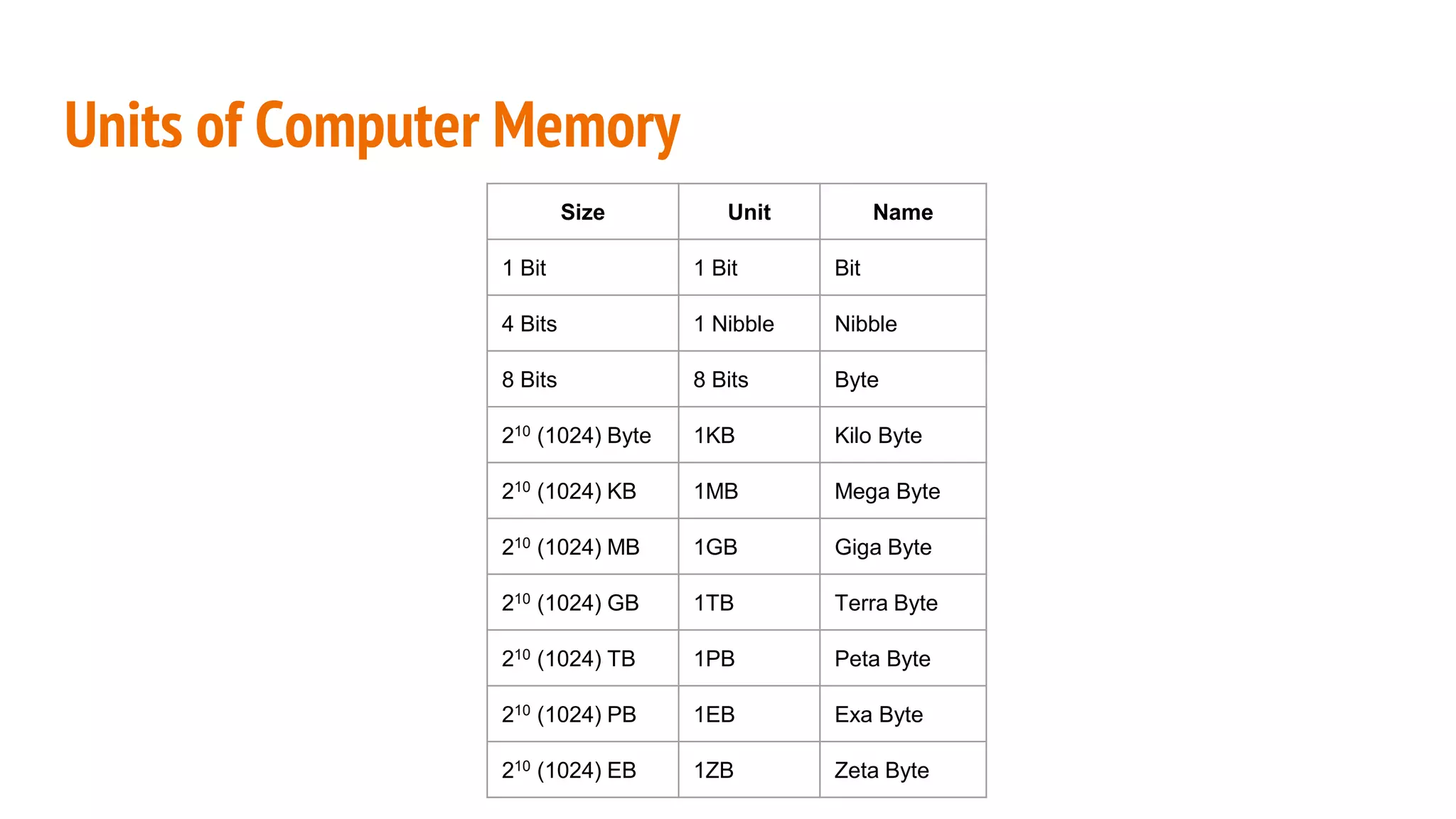
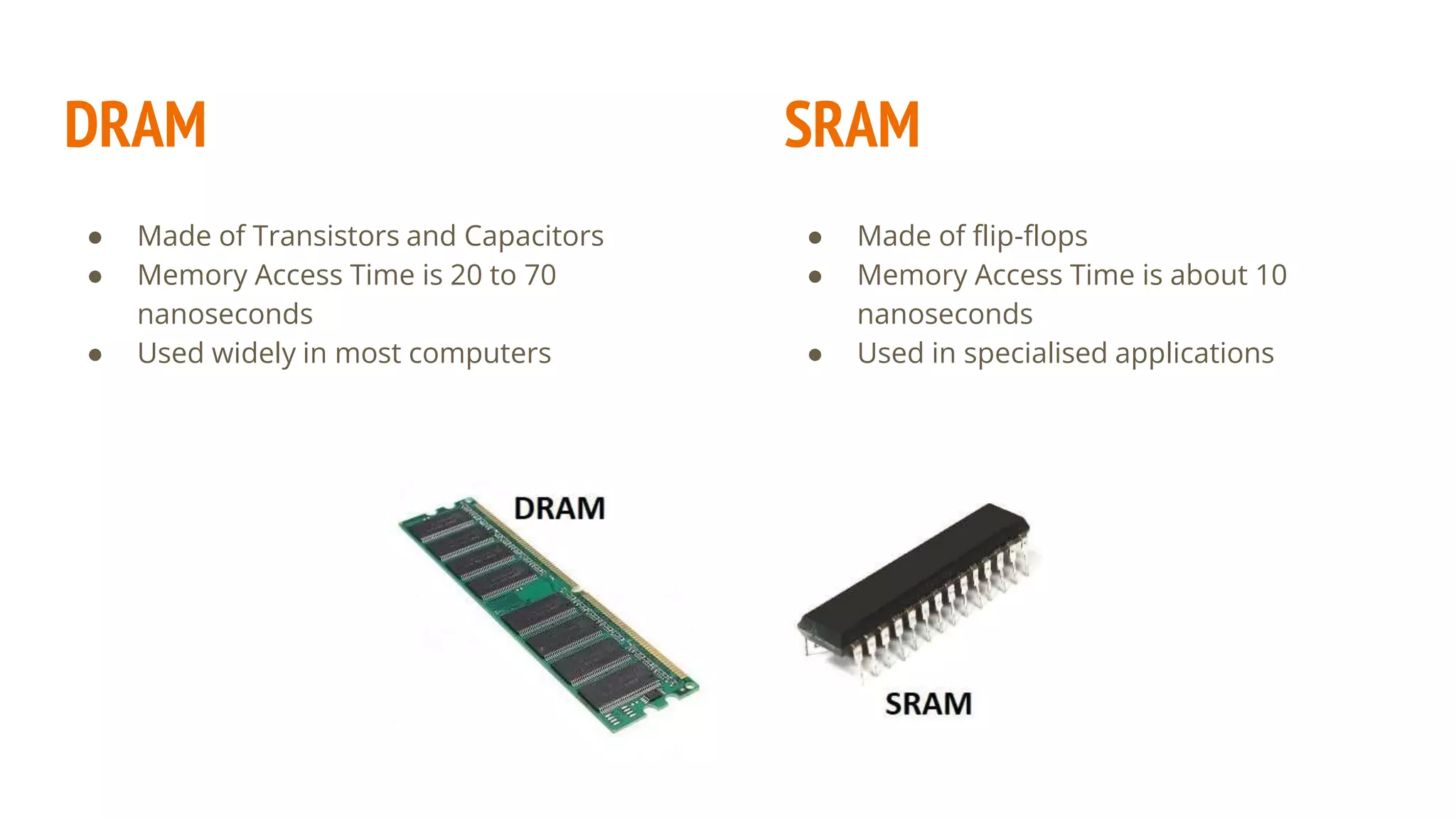
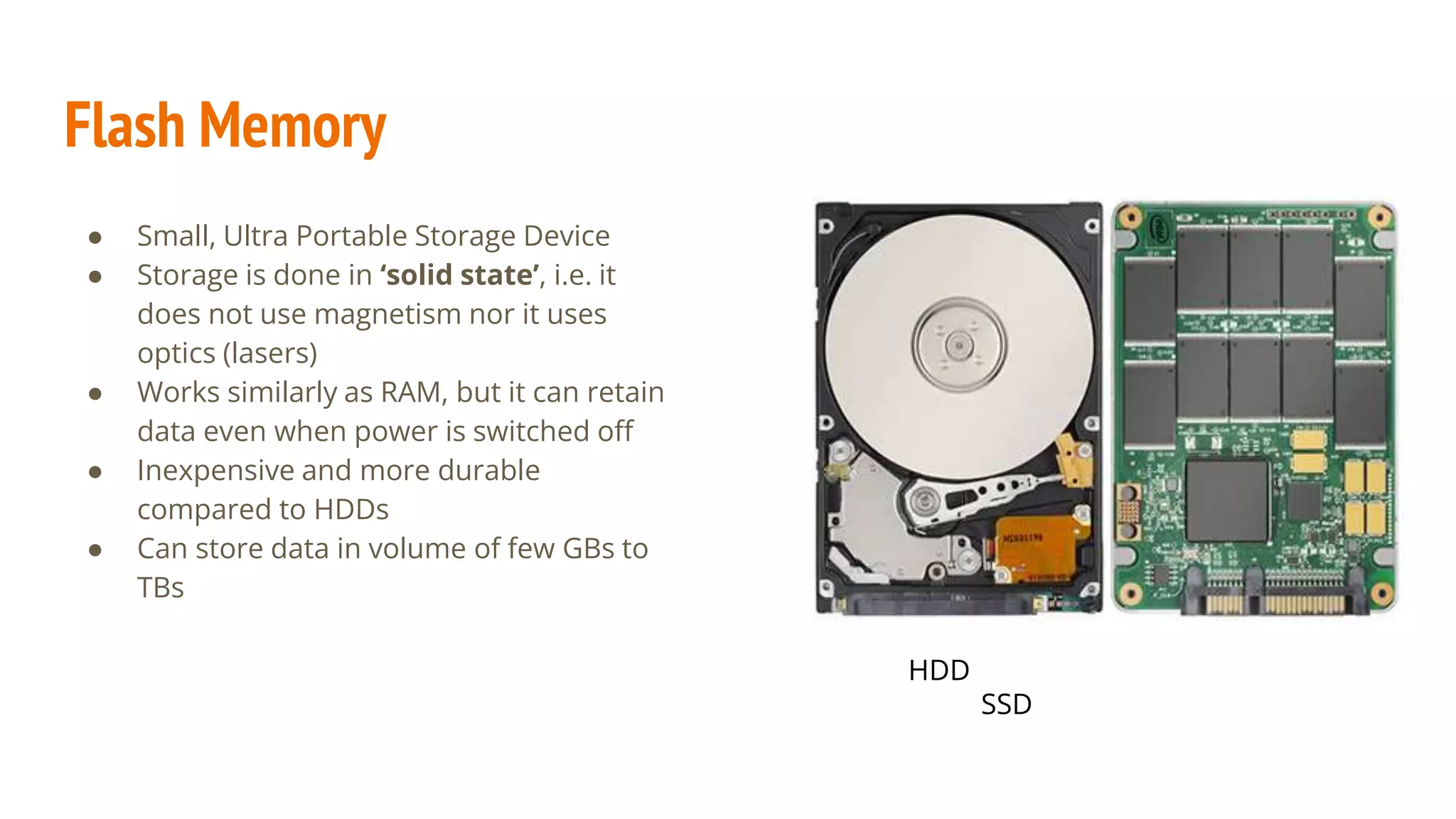
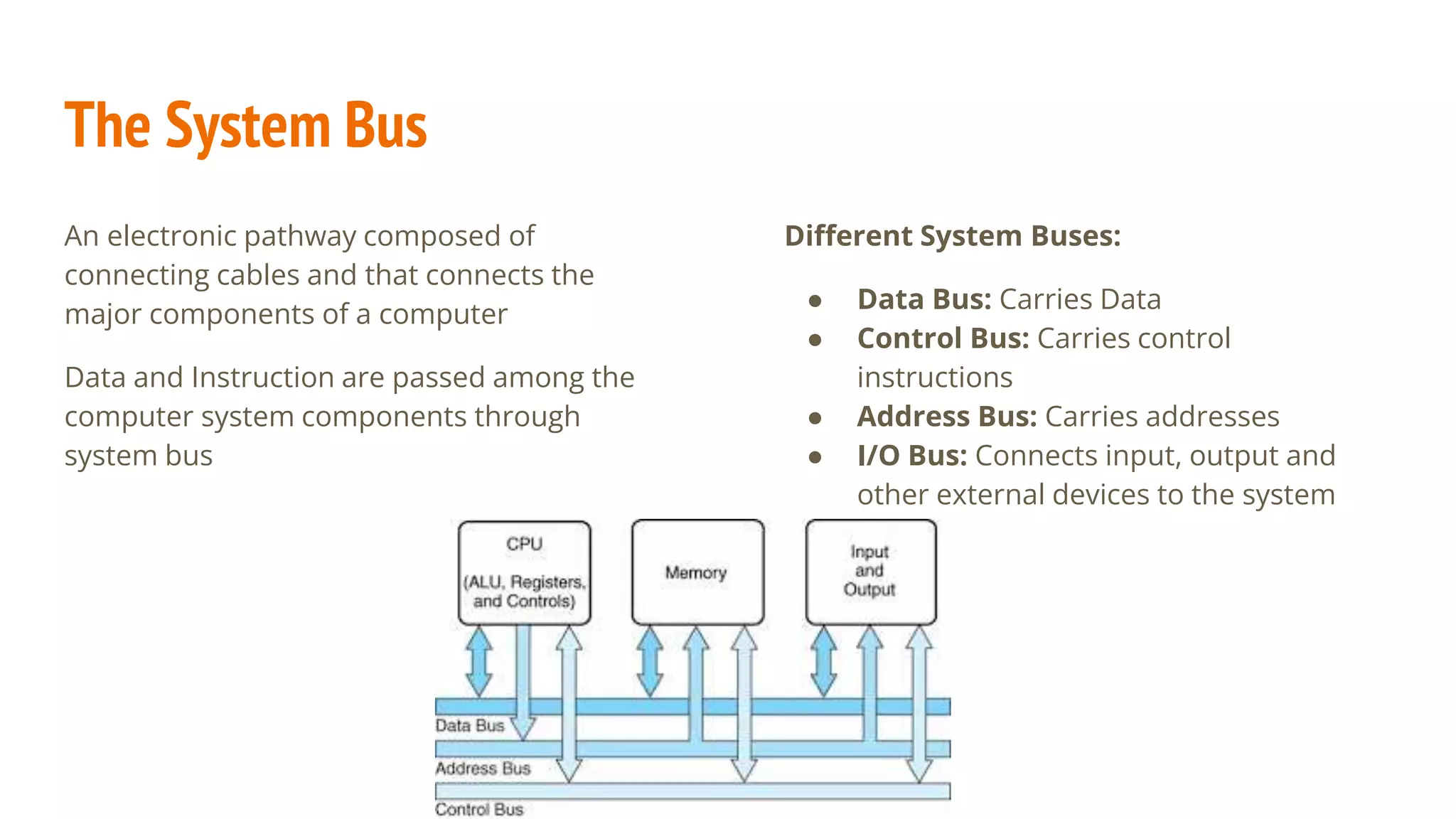
This document provides an overview of basic computer system organization. It discusses that a computer accepts raw data as input and processes it using a program to produce output. The main components are the hardware, which are the physical parts, and software, which are the recorded instructions. It then describes the basic units of a computer system including the input and output units, central processing unit (CPU), memory, and storage. The CPU contains the arithmetic logic unit, control unit, and registers. The document also discusses the different types of memory, including RAM, ROM, and their characteristics. Finally, it covers the different types of software including system software like operating systems and language processors, as well as application software.